IB Biology Year 1 - Epigenetics, Mutations, and Viruses
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Epigenetics
Study of how environmental conditions alter gene expression → does not change DNA sequence
There is mounting evidence that the chemical modifications that occur to the DNA in gametes could in certain circumstances be passed on to the next generation both at the cellular level as well as whole organism level
Quorum Sensing
a form of cell-to-cell communication in bacteria where they release chemical signals to coordinate their behavior and gene expression in response to population density. Creates biofilm. These signals, called autoinducers, accumulate in the environment and trigger changes in gene expression once they reach a certain concentration.
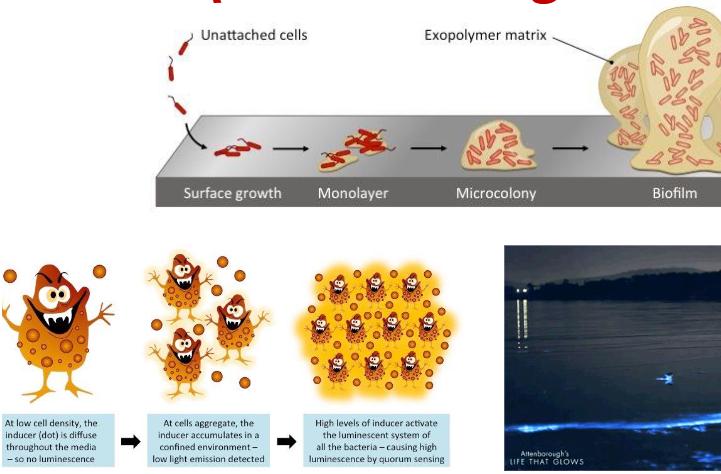
Regulation of Gene Expression by the Environment → Epigenesis
differentiation of cell structures/functions from undifferentiated state (stem cells!) to acquire specific functions and structures. This process is influenced by epigenetic mechanisms
Epigenetic mechanisms
Biological processes that control gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence.
Examples:
DNA methylation
Histone modification
Chromatin remodeling
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs)
List some environmental factors/conditions that can affect the epigenetic status
Methionine, folic acid, vitamin B, nicotinic (produces effects of nicotine), reservatrol, high-fat diet, metal ions, nickel, etc.
Give an example of Phenotypic Plasticity based on Environment and an Example of regulating gene expression.
UV exposure increases expression of the gene that codes for the melanin protein.
Give another example of regulating gene expression:
There is substantial evidence that smoking increases the rate of DNA methylation. Mothers who smoke while pregnant have been shown to influence the methylation patterns of their unborn children too, potentially influencing gene expression and increasing the risk of certain diseases later in life in offspring.
What does DNA methylation do?
Alters gene expression without changing the DNA sequence itself
Regulates gene expression by recruiting proteins involved in gene repression or by inhibiting the binding of transcription factor(s) to DNA.
What if a tumor suppressor gene is methylated?
It can be silenced, leading to unchecked cell growth and potentially contributing to cancer development
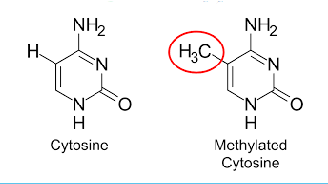
Methylation Recap
H-group replaced by H3C in the nitrogen bases of DNA (usually Cytosine! In promoter region)
This methyl group is now considered an “epigenetic tag” = chemical modification that changes the expression of a gene (protein + or -)
Most methylations repress gene expression…usually
Methylation of Histones
DNA wraps around histones to condense
Nucleosome is a unit of histones bound together (8)
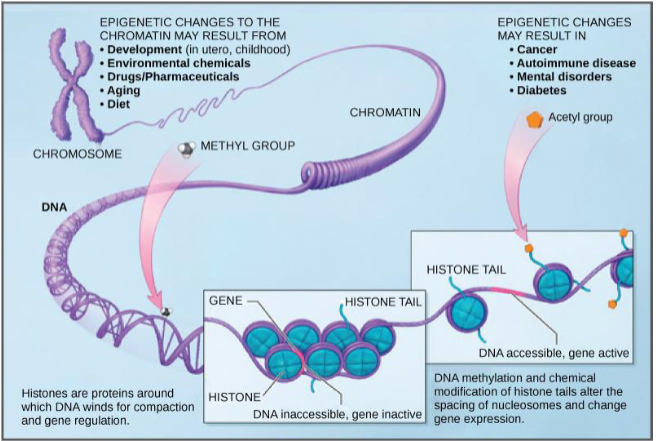
How are air pollutants epigenetic tags?
Shown to decrease methylation → which means things that should be turned off (like inflammation) will turn on (causing asthma)
Indoor cooking can cause decreased methylation (increase risk of inflammation)
Regulation of Gene Expression by the Environment (think of twins)
For some traits it can be hard to tell how much influence the environment has over gene expression
Comparing identical and fraternal twins can be helpful in determining that
There is an increased percentage of identical twins sharing a trait that suggest that a genetic component contributes to the onset of the trait
However, when the twins are younger, there are less differences in epigenetics → this can drift apart when they are older due to differing lifestyle choices or environmental exposures
What is an Epigenome?
Sum of all epigenetic tags in cell/organism
Tags can be passed on via mitosis
Reprograming (wiping of tags) occurs (twice!) in formation of gametes = meiosis
Some epigenetic marks can persist and be inherited. Therefore, even with meiosis, children can still inherit some epigenetic effects from their parents.
Epigenetics and the environment emerging patterns and implications
Different environment cues (such as nutrition, chemical compounds, temperature changes and other stresses) can affect phenotypes and epigenetic gene regulation in experimental model systems
A growing number of human studies have demonstrated long-term effects as a consequence of diet, exposure to chemical components and other external factors; the effects are particularly apparent when exposure to the environmental factors occurs during gestation
Impacts of Fetal Programming?
Early life nutritional insults (under-/over-nutrition) can lead to metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes by causing epigenetic changes in hypothalamic appetite regulatory genes in the fetus.
Hypothalamus is a key brain region involved in regulating appetite and energy balance
Famine in pregnancy is shown to impact an offspring’s mental health in adulthood
Albinism
Caused by genetic mutations that disrupt melanin production. Methylation, a chemical modification to DNA, can influence gene expression but is not the direct cause of albinism.
Formation of Alleles
New alleles are formed by mutations, which are changes to the base pair sequence of the organism’s genetic code
Insertions and Deletions
Known as “frameshifts” b/c they shift the reading frame of DNA, usually leave proteins non-functional
Adding a nucleotide/letter → Insertion
Removing a nucleotide/letter → Deletion
Substitution mutations
One base is replaced by a different base. “Point” mutations!
3 types:
silent mutations
missense mutations
nonsense mutations
Location of Mutations: Gamete/Somatic
If a mutation occurs in germ-line cell (one that will give rise to gametes i.e. egg or sperm cells), then this mutation can be passed to an organism’s offspring
This means that every cell in developing embryo will carry the mutation
As opposed to germ-line mutation, somatic mutations occur in cells found elsewhere in an organism’s body
Such mutations are passed to daughter cells during the process of mitosis, but they are NOT passed to offspring conceived via sexual reproduction
Causes of Mutation (4 main types)
Spontaneous: Mutation that arises spontaneous
Physical: exposure to radiation that damages the DNA
Chemical: exposure to chemicals (ex: heavy metal ions) that damage the DNA
Biological: viruses that insert themselves into host DNA
Wild Type
refers to the standard “normal” allele; the non-mutated version of the gene that codes for a functional protein
Silent type
Base substitution that results in no change of the amino acid when the altered messenger RNA (mRNA) is translated
Missense
Base substitution that results in the replacement of one amino acid for another in the protein made by the gene. This change in amino acid can alter the protein's structure and function.
Nonsense substition
Based substitution that results in a shortened polypeptide that may function improperly or not at all
Frameshift - Insertion
A frameshift mutation shifts the grouping of the 3 bases that code for 1 amino acid; the resulting protein is usually nonfunctional
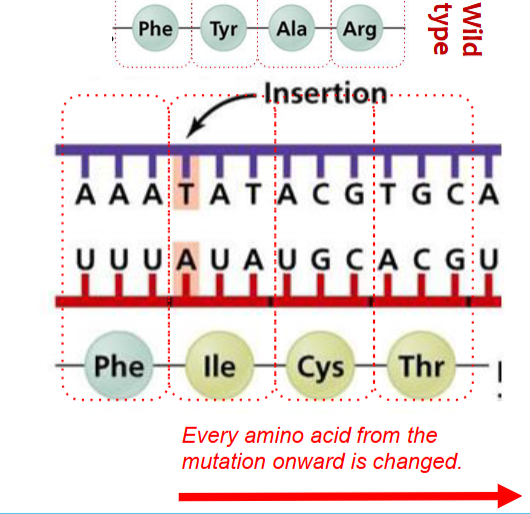
Frameshift - Deletion
A frameshift mutation shifts the grouping of the 3 bases the code for 1 amino avoid; the resulting protein is usually nonfunctional
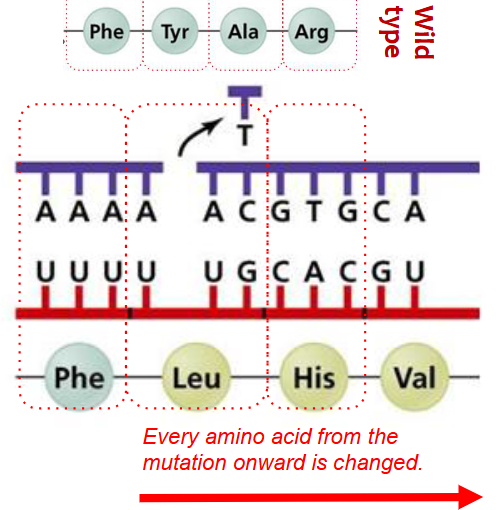
Effect of a Mutation
Analyzing the specific change in DNA and its impact on the resulting protein, gene expression, or organismal phenotype
Mutations are more likely to be deleterious rather than beneficial when..
They occur in essential genes or coding regions, or when they affect a large number of base pairs
Beneficial mutations affect the gene pool by increasing…
the frequency of specific beneficial alleles within a population's gene pool, ultimately leading to changes in the overall genetic makeup over time
If mutations are in a non-coding region…
Can disrupt regulatory mechanisms, influencing gene expression and potentially leading to disease, including cancer
Sickle cell anemia
Is caused by…?
It is a _____ _____ disorder.
Which is/are the worst for malaria? Which is/are the best?
Why the best?
Missense mutation
Autosomal recessive
Homozygous sickle cell anemia or homozygous normal blood cells is not great for malaria, but heterozygous sickle cell anemia is the perfect combination
Protist from mosquitos can’t really attach to a sickle cells → they can still do so, but it is difficult, which is why people with heterozygous sickle cell anemia get less infections than others in the population, and those with homozygous sickle cell affect theit body's ability to deliver oxygen much greater, and not to an advantageous point
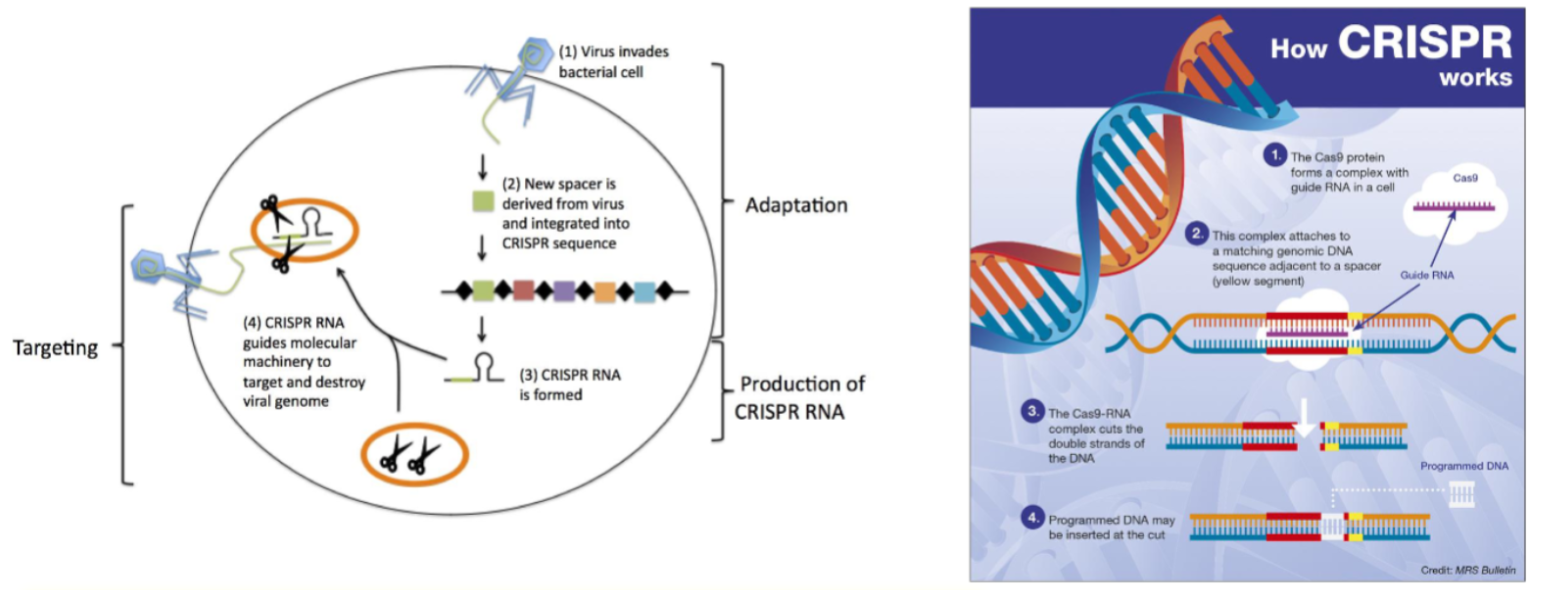
CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats)
Mutation rate for humans?
What keeps it low?
How could you increase it?
1 in 1 billion
It is kept low b/c of DNA Polymerase III
You could increase it by smoking, radiation, extreme heat
What term best describes viruses?
Obligate molecular parasites
Viruses are strict molecular parasites of cells
They must infect cells and reproduce inside them
Describe the:
lytic cycle
lysogenic cycle
The infective cycle begins when a virion injects or releases its nucleic acid in a cell. Once in the cell, the viral genome is transcribed and translated by the cell using the cellular machinery and energetic resources. The viral genome gets replicated using cell resources. If the infection results in a high number of virions rapidly synthesized, the cell lyses OR the virus reproduces and bursts out of the host cell, kill it.
Sometimes, the viral genomes can be incorporated in the host genome and remain there silently, being reproduced with the host cell for generations OR the virus assimilates its genome within the host cell’s genome to achieve replication without killing the host
Cells share a _____ ____ (____)
Viruses share ___ ___, suggesting they have ____ ____ origins
common ancestor (LUCA)
few features; multiple evolutionary
Viruses vary in: (list 5 things)
Size
Shape
Genetic material type
Genes present
Enveloping
Structures common to viruses:
Use nucleic acid as their genetic material; some viruses use DNA, some use RNA.
Have an outer coating (“capsid”) made of protein.
Fill in the blank:
Viruses are ___ than bacteria. Viruses ___ in size. Viruses ___ grow.
smaller
vary
do not
Most viruses are in the range of ______ micrometers
They are small so they can ________
0.02-0.2
infect cells and because they have few (or no) enzymes and do not have cytoplasm or other organelles!!!
Viruses are not considered living because…
They are not made out of cells
They can not keep themselves in a stable
state
They do not grow
They can not replicate themselves
They can not perform independent metabolism
True or false:
Positive sense viral RNA is already 'ready' for translation as it would be equivalent to our human mRNA.
True!
Retroviruses…
are RNA that must be switched to DNA before viral protein synthesis can occur
or
have RNA that is first “reverse transcribed” to make DNA. The DNA is then transcribed and translated to make virus proteins
Enveloped viruses can more easily infect…
…animal hosts/cells.
The lipid envelope of animal cells, which allows for efficient entry and exit from cells, is a key factor in this preference.
The ___ phase is the hidden, dormant part of viral reproduction, while the ___ phase is the active stage of viral reproduction, and the deadlier one, initiated by stressors.
lysogenic, lytic
Generation time…
Generation time for humans?
Generation time for viruses?
What does generation time mean for species?
is the average time between two consecutive generations in the lineages of a population.
In human populations, generation time typically ranges from 20 to 30 years.
Viruses can be less than an hour!
Natural selection changes a population from generation to generation.
So, in the same amount of time: A species with a shorter generation time will have undergone more rounds of selection (more opportunity for evolutionary change)
A species with a longer generation time will have undergone fewer rounds of selection (less opportunity for evolutionary change)
Origin of Viruses
Three main hypotheses have been suggested for the origin of viruses
Which are/aren’t supported by current hypothesis?
The progressive hypothesis states that viruses arose by taking and modifying cell components.
✔ This hypothesis is supported by current evidence.
The regressive hypothesis asserts that viruses arose by loss of cellular components.
✔ This hypothesis is supported by current evidence.
The virus-first hypothesis states that viruses predate or co-evolved with their current cellular hosts.
❌This hypothesis is not supported by current evidence.
❌All viruses are intracellular parasites, requiring a cell to replicate. Because the virus-first hypothesis proposes that virus could replicate without a cell, it is disregarded by many scientists.
❌Viruses use the same genetic code as all cells (A1.2.10). The virus-first hypothesis would require that a single ancestral virus used this code and then evolved to become the first cell or that there was independent evolution of cells using the same genetic code. There is no evidence for either scenario.
Lytic Cycle
There are seven steps to the lytic cycle:
1) Phage attachment to host cell
2) Phage DNA entry into host cell
3) Phage DNA replication
4) Phage protein synthesis
5) Assembly of new phage viruses
6) Lysis
7) Spread
Lysogenic Cycle
There are 5 steps to the Lysogenic cycle:
Phage attachment to host cell
Phage DNA entry into host cell
Phage DNA is integrated into host genome
DNA replication
Cell division