3.9 not finished
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Cost centre
These are departments of a business that incur costs but are not involved in generating any profit.
Profit centre
These are departments of a business that incur both costs and revenues.
Adv and dis
Adv :
Accountability of managers
Identifies areas of weakness
Promotes team spirit
Eliminates cost classifications into fixed/variable and direct/indirect costs
Allows for benefits from benchmarking
Improves motivation from delegation of responsibility
Dis :
Subjective allocation of indirect costs
Departmental profits can be misleading due to apportionment of fixed costs across centres
Time consuming data collection for accurate cost and profit allocations
Added pressure on staff to manage centres
ignores social and ethical responsibilities
Tension and conflict arising from unnecessary internal competition
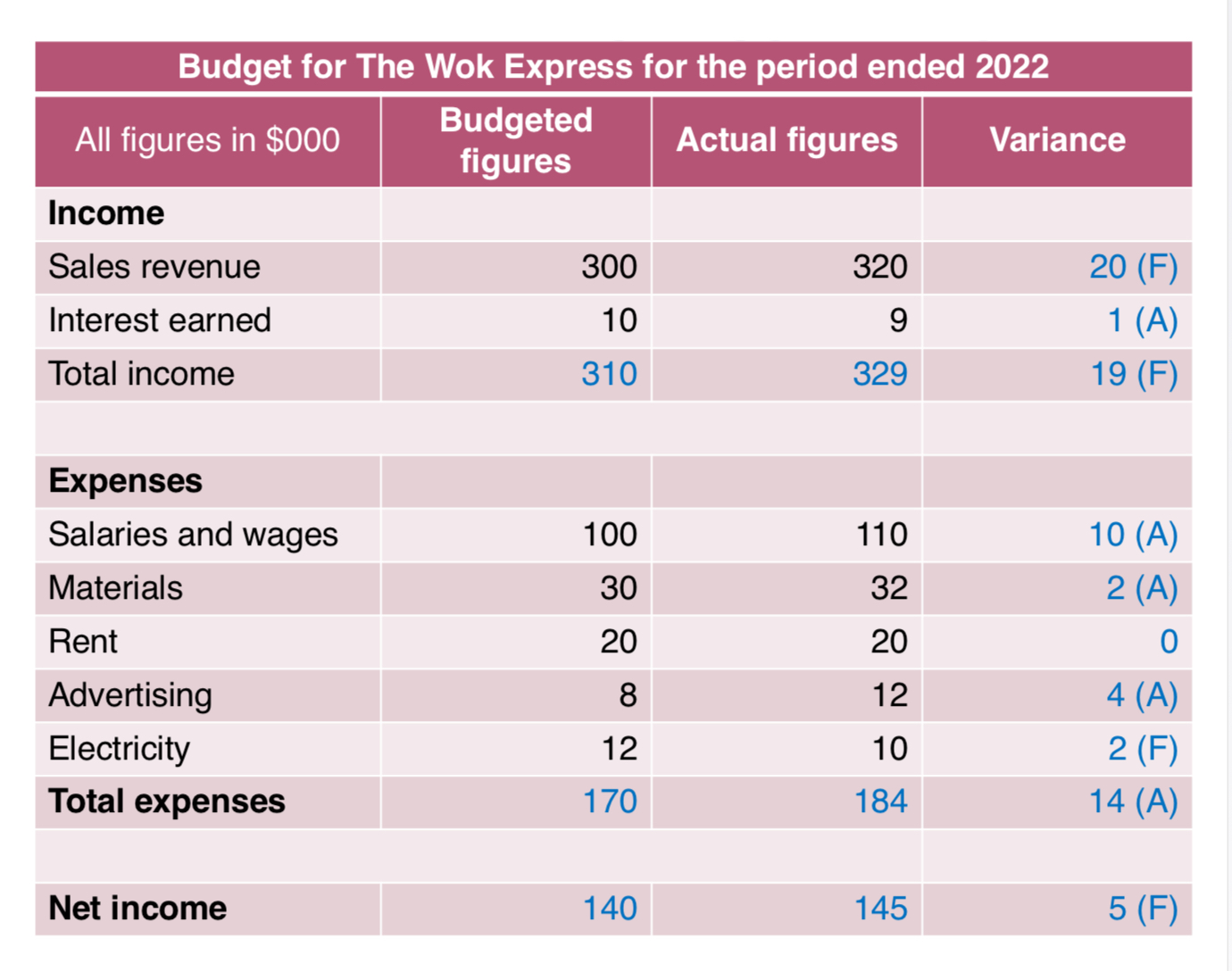
Budgets
•A budget is a financial plan of expected revenue and expenditure for an organization, or a department within an organization, for a given time period.
Budgets have to be continuously monitored to ensure a company is spending its finances wisely.
Variance
•Variance analysis is looking at the difference between the budgeted figure and the actual expenditure figure.
•There are two types of variance:
•Favourable: a difference that is of benefit to the business.
Adverse: a difference that is harmful to the business.
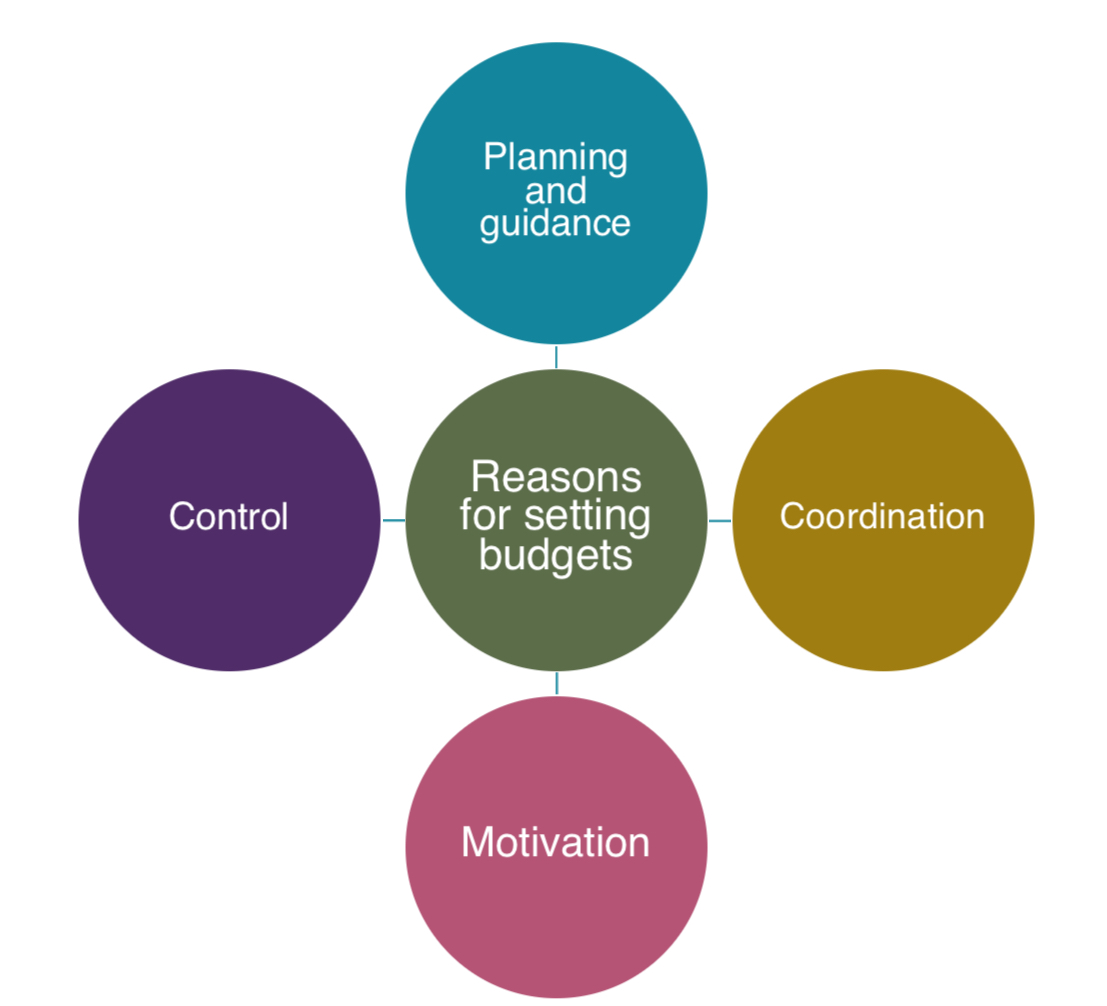
Reasons for setting budget
Financial planning
monitoring
Planning
Controlling
Setting
Planning and guidance
Helps plan for future
Anticipating financial problems before they actually happen
Consider:
How much money to spend
Workforce planning and costs
How cut to set aside for contingency fund (plan B)
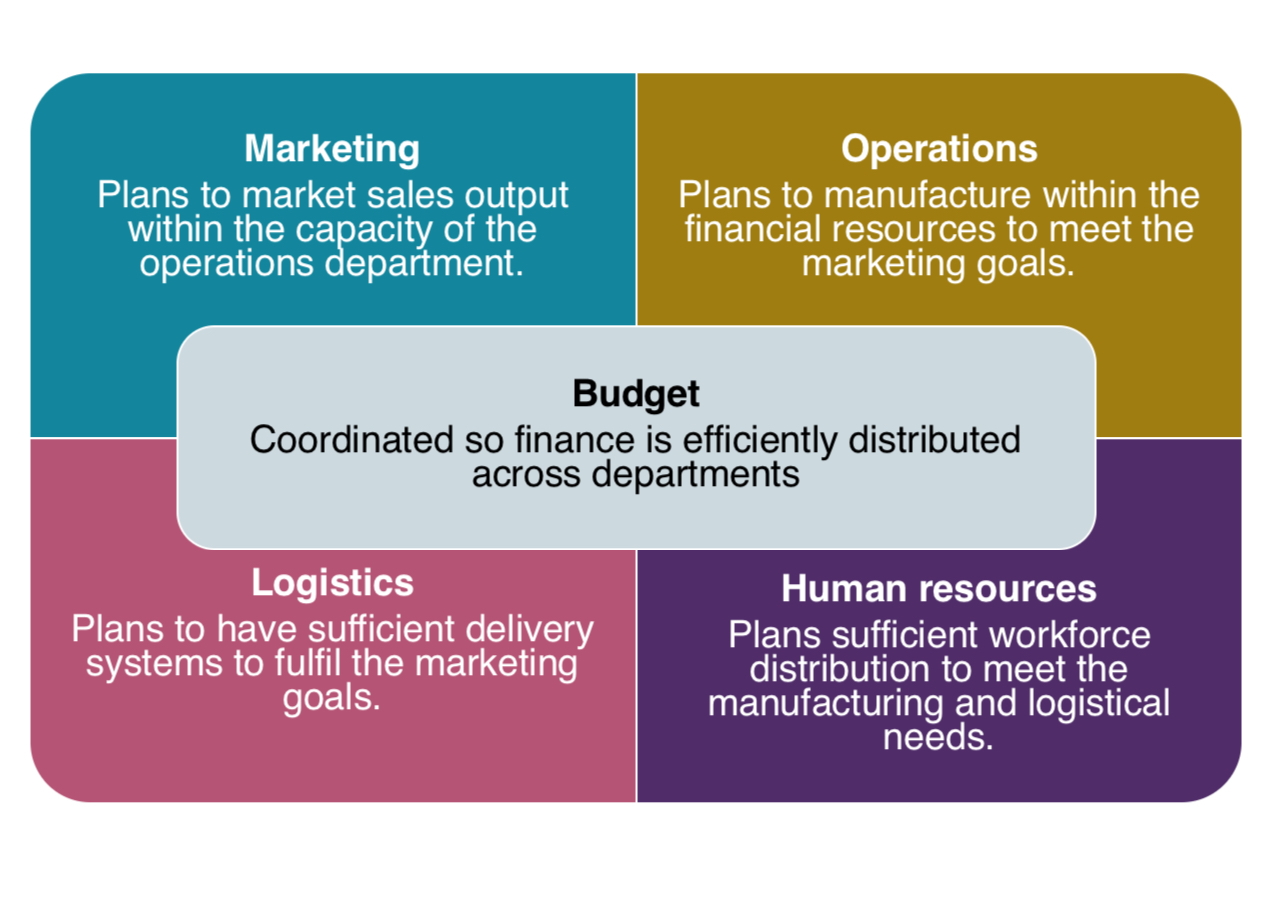
Coordination
•Budgets help different departments to coordinate objectives and expenditures with each other.
Control
Budgets offer financial control to prevent overspending.
Budget holders are held accountable for variances between planned and actual expenditure.
Motivation
Employee motivation
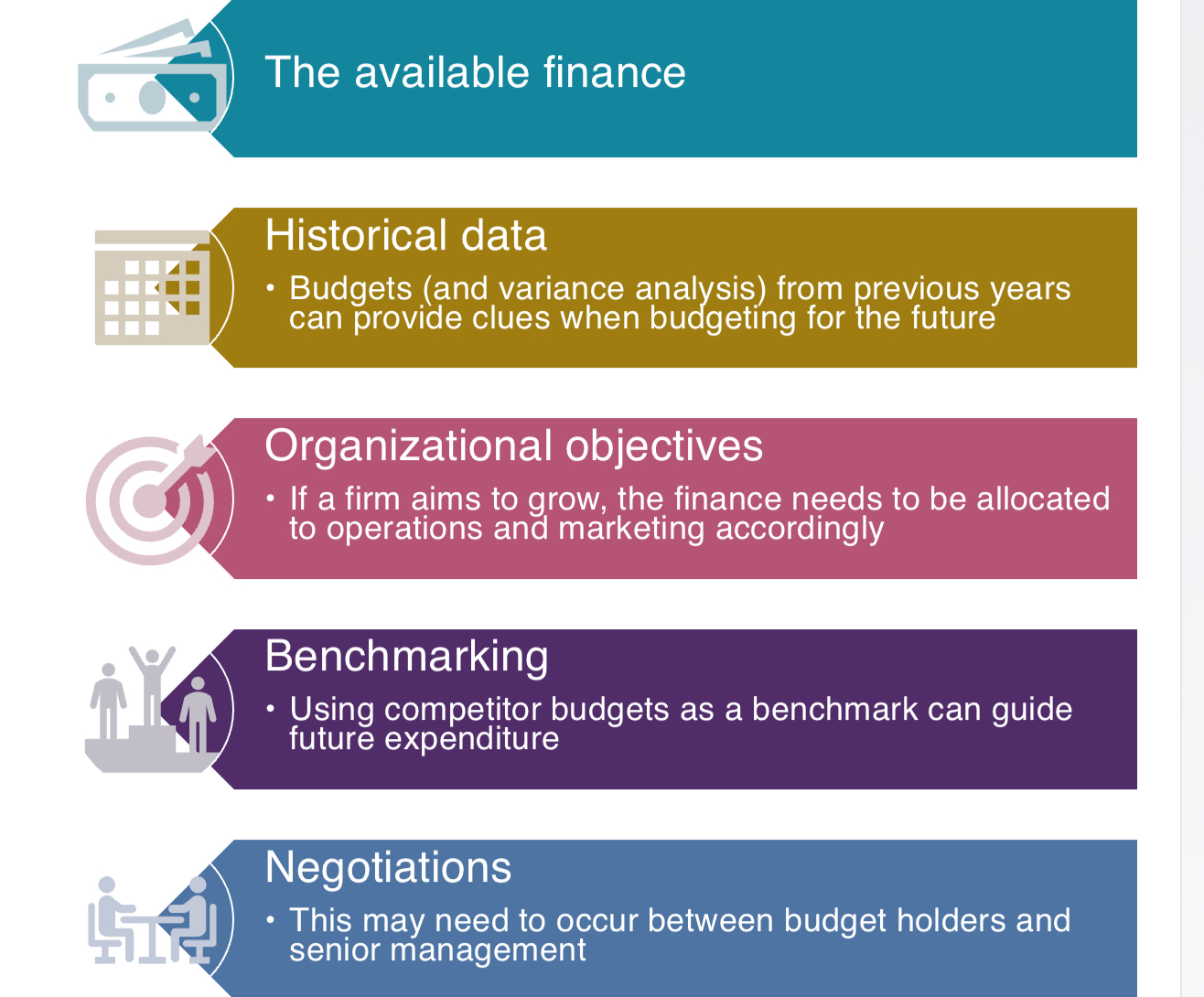
Considering when setting budgets
Available finance
Historical data
Organisational objectives
Bench marking
Negotiations
Limitations of budgeting
•Unrealistic/ unachievable budgets can occur.
•Wasteful use of resources due to overbudgeting and/or no carrying over budget surpluses to following year.
•Less useful for businesses with fluctuating sales revenues.
Quality may be harmed if budgets are excessively limited and rigid.
Budget sheet