STRUCTURAL EFFECTS ON ACIDITY
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
strength of an acid
The _ is determined by the stability of the conjugate base that forms when the acid loses its proton: the more stable the base, the stronger its conjugate acid.
base; conjugate acid
The strength of an acid is determined by the stability of the conjugate base that forms when the acid loses its proton: the more stable the _, the stronger its -.
base
The weaker the _, the stronger its conjugate acid or the more stable the base, the stronger its conjugate acid .
conjugate acid
The weaker the base, the stronger its _ or the more stable the base, the stronger its conjugate acid .
base
The weaker the base, the stronger its conjugate acid or the more stable the _, the stronger its conjugate acid .
conjugate acid
The weaker the base, the stronger its conjugate acid or the more stable the base, the stronger its _
HA (aq) ←→ H+ (aq) + A- (aq)
acid c. base
strong acid
high tendency to lose their proton; they’d rather done or lose their proton and exist without it. they want to lose proton (H+), it prepares to be in the conjugate base form. it exists without the proton; if it prefers to exist without the proton, it means A- is very small; it prefers to be left alone by the proton. high tendency to donate its proton and is very stable in cb form bcs it prefers to be without the proton.
High
The preference of a strong acid to exist without H⁺
Strong acid
The tendency of an acid to lose its proton easily
Conjugate base
The form an acid prefers after donating its proton
Proton (H⁺)
The particle lost by an acid during dissociation
A⁻
A stable form of a strong acid after losing H⁺
High
The strength of an acid when its conjugate base is weak
Stability
The reason why A⁻ does not accept back the proton
Complete
The extent to which HA dissociates in water
unstable
A conjugate base that prefers to reunite with a proton is _.
A-
After dissociation, strong acids mostly exist in the form of
donate
A strong acid has a high tendency to _ its proton.
A⁻
In strong acids, the conjugate base _ is more stable than HA.
HA
At equilibrium, weak acids mostly exist as _.
HA
In weak acids, _ is more stable than A-
stability
Weak acids mostly exist in the HA form because of _.
unionized (HA)
When the conjugate base is unstable, the acid prefers to stay in its _ form.
conjugate base
we usually determine the strength of an acid by determining the strength of its _
conjugate base (A-)
a strong acid (HA) has a weak
conjugate base
a weak acid has a strong_
STRONG ACID (HA)
Unstable
STRONG ACID (HA)
High tendency to lose proton
STRONG ACID (HA)
High tendency to accept electron pair
(negative charge)
WEAK CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
Stable
STRONG ACID (HA) OR WEAK CONJUGATE BASE (A-)?
WEAK CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
Low tendency to gain proton
STRONG ACID (HA) OR WEAK CONJUGATE BASE (A-)?
WEAK CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
Low tendency to donate electron pair
(negative charge)
STRONG ACID (HA) OR WEAK CONJUGATE BASE (A-)?
WEAK ACID (HA)
Stable
WEAK ACID (HA) OR STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
WEAK ACID (HA)
Low tendency to lose proton
WEAK ACID (HA) OR STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
WEAK ACID (HA)
Low tendency to accept electron pair
(negative charge)
WEAK ACID (HA) OR STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
Unstable
WEAK ACID (HA) OR STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
High tendency to gain proton
WEAK ACID (HA) OR STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
High tendency to donate electron pair (negative charge)
WEAK ACID (HA) OR STRONG CONJUGATE BASE (A-)
Electronegativity
Hybridization
Size
Inductive Effect
Steric Effect
Pi Electron Delocalizaton/Resonance
Interaction of Structural Effects
STRUCTURAL EFFECTS ON
ACIDITY (7)
electronegative
The more _ an element is, the more it helps to stabilize the negative charge of the conjugate base.
conjugate base
The more electronegative an element is, the more it helps to stabilize the negative charge of the _.
strongest acid
When atoms are similar in size, the _ has its hydrogen attached to the most electronegative atom.
electronegative
hen atoms are similar in size, the strongest acid has its hydrogen attached to the most _ atom.
relative electronegativities
C < N < O < F
F
relative electronegativities
C < N < O < F
most electronegative
relative acidities
CH4 < NH3 < H2O < HF
HF
relative acidities
CH4 < NH3 < H2O < HF
strongest acid
relative stabilities
-CH3 < -NH2 < HO- < F-
F-
relative stabilities
-CH3 < -NH2 < HO- < F-
most stable
anion
_ is stabilized by having negative charge om a highly electronegative atom
HYBRIDIZATION
formation of hybrid orbitals from the combination of individual orbitals
HYBRIDIZATION
affects electronegativity.
HYBRIDIZATION
The most electronegative atom will be the one with its bonding electrons closest to the
nucleus.
nucleus
The most electronegative atom will be the one with its bonding electrons closest to the
_.
s
The strongest acid has its hydrogen attached to the atom with most _ character.
sp
sp > sp2 > sp3
most en
sp3
sp > sp2 > sp3
least en
sp
sp > sp2 > sp3
closer to nucleus
strongest acid (most en)
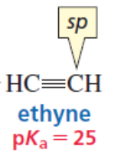
middle (acid)
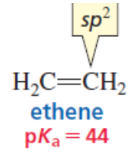
weakest acid (not that en)
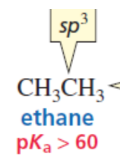
The size of the atom is more important than its electronegativity in determining acid strength.
size
acidity affects _ of cb
size
The _ of the atom is more important than its electronegativity in determining acid strength.
SIZE
As we go down a column in the periodic table, the atoms get larger, the electrons are more dispersed, and the stability of the atoms increases even though the electronegativity of the atoms decreases.
decreases
As we go down a column in the periodic table, the atoms get larger, the electrons are more dispersed, and the stability of the atoms increases even though the electronegativity of the atoms _.
hydrogen
The strongest acid has its _ attached to the largest atom.
I-
F- < Cl- < Br- < I-
largest
HI
HF < HCl < HBr < HI
strongest acid
60
CH4 pKa
36
NH3 pKa
15.7
H2O pKa
7.0
H2S pKa
3.2
HF pKa
-7
HCl pKa
-9
HBr pKa
-10
HI pKa
50%
sp %
33%
sp2 %
25%
sp3 %
electronegativity
when u belong to the same period, what matters is the _ than the size (sizes r somewhat similar)
HC≡C- + CH3CH3 (more favorable)
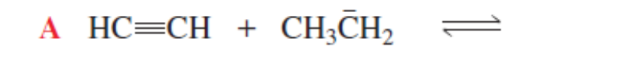
H2C=CH- + HC≡CH (backward rxn more favorable)
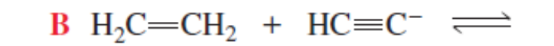
CH3CH2- + H2C=CH2 (backward rxn more favorable)
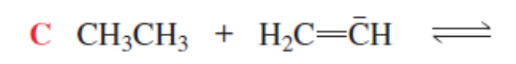
WEAKER
RXN IS MORE FAVORABLE WHEN THE STRONGER ACID PROTONATES THE _ ONE
oxygen
Which is more electronegative, oxygen or sulfur?
H2S
Which is a stronger acid, H2O or H2S?
CH3SH
Which is a stronger acid, CH3OH or CH3SH?
HBr (size is bigger, more stable)
Which is a stronger acid?
HCl or HBr
CH3CH2CH2O+H2
Which is a stronger acid?
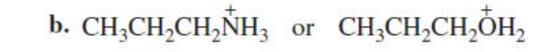
oxygen
Which is a stronger acid?
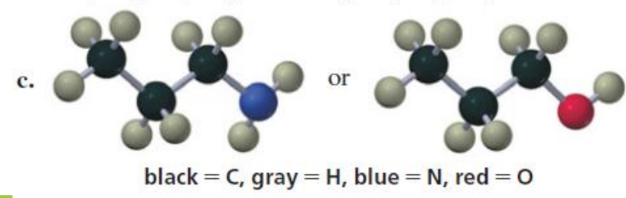
Which is a stronger acid?
size
same grp diff period