Lecture 13: Comparative Anatomy and Physiology of the Female Reproductive System (Exam 2)
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
How did the vertebrates millions of years ago adapted for life on land?
Amnion
Amnion
A thin membrane forming a closed sac about the embryo or fetus of a reptile, bird, or mammal and containing a watery fluid in which the embryo or fetus is immersed for eater retention.
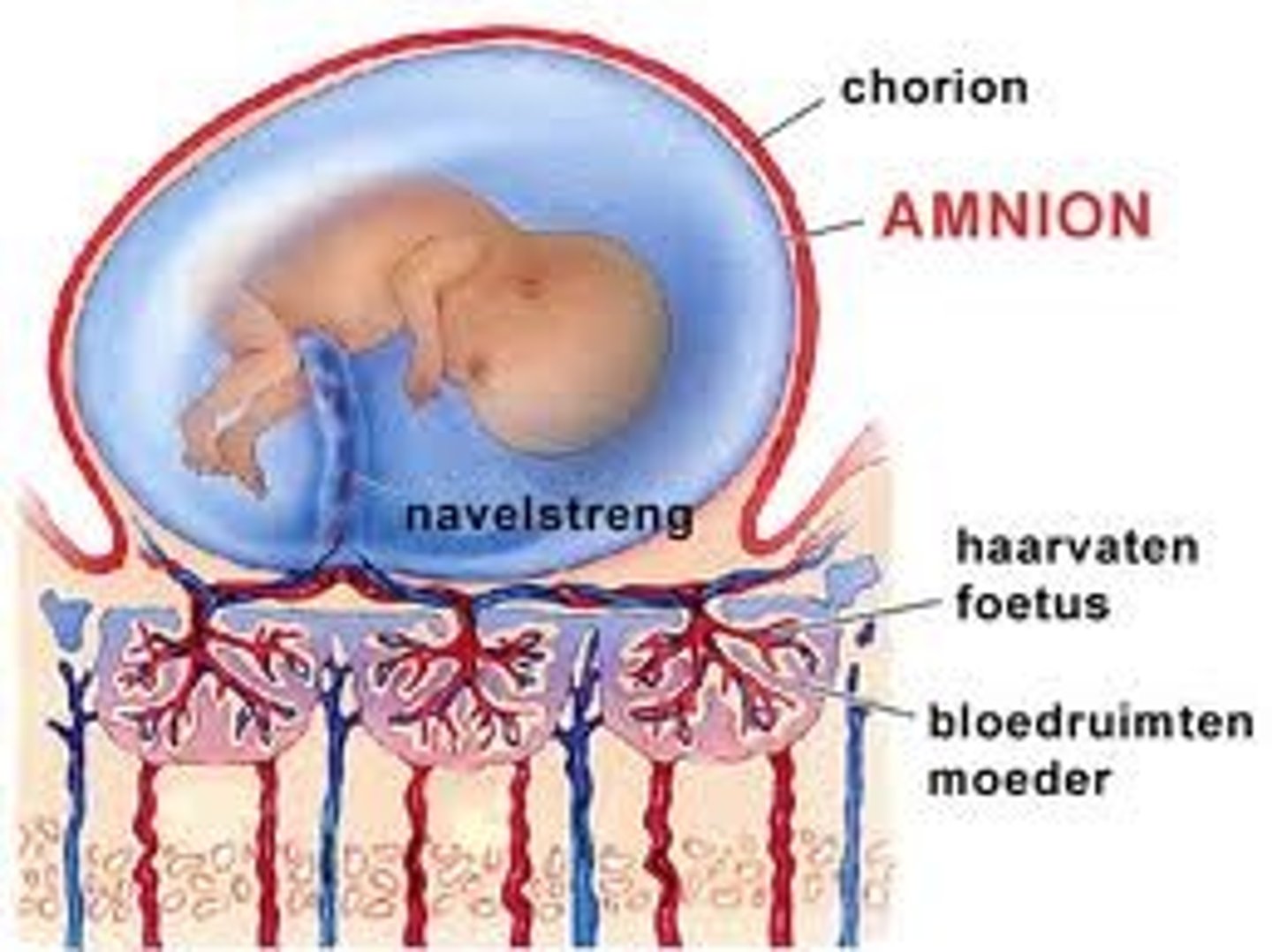
Amniota
An animal whose embryo develops in an amnion and chorion and has an allantois; a mammal, bird, or reptile.
- Mammals, birds
- Adapted for life on land
- Retains water (water tight skin and egg)
- Embryo produces amnionic membrane
- Shell types: None, hard, soft
What produces the amnionic membrane?
Embryo
Eutheria
- Placental
- Rodents, carnivores, primates
(most orders, n=21)

Metatheria
- No placenta
- Marsupials (opossum, kangaroo)

Prototheria
- Egg laying mammals
- Monotremes: platypus

How is animal reproduction classified?
By birth
Viviparous
Live births = mammals
- Egg fertilized inside
- Embryos hatch inside
- Females gestate (develop young in uterus)
• Placental (Eutharian) - nutrients from mother
• Non-Placental (Metatherian)- no placenta, marsupials

Gestate
Carrying a fetus in the womb from conception to birth.
What are the two types of gestation?
• Placental (Eutharian) - nutrients from mother
• Non-Placental (Metatherian)- no placenta, marsupials
Oviparous
- Egg layers; mostly birds and reptiles
- Eggs fertilized internally
- Fertilized eggs laid and hatch in external environment
- No placenta or gestation
- Exceptions: egg laying mammals
ex. platypus (monotremeta) & spiny anteater (echidna)

What are the exceptions to classifying oviparous in animal reproduction?
Egg laying mammals
• Platypus (monotremeta)
• spiny anteater (Echidna)
Induced ovulators (another way to classify reproduction)
An animal that ovulates only after mating with a male
Ex. Cats, rabbits, llamas, Alpacas

Spontaneous ovulators (another way to classify reproduction)
Mammals that release eggs without needing to mate. This happens at regular intervals, and is controlled by a cycle of hormones.
Ex. Humans, dogs, sheep
Seasonal breeders (another way to classify reproduction)
Animals that only mate during specific times of the year. These times are chosen to help young survive by optimizing food, water, and temperature.
Ex. sheep, deer, foxes

Number of offspring (another way to classify reproduction)
Mono or polytocous
Monotocous
One offspring per birth

Polytocous
Litter bearing

Uterus structure (another way to classify reproduction)
Placental structure (another way to classify reproduction)
What are some methods to diagnose female reproductive status?
- Reproductive behaviors (observations and records)
- Ultrasound
- Palpation
- Surgical laparoscopy
- Post-mortem reproductive tract assessment
- Hormone assay of milk feces, urine, saliva, blood
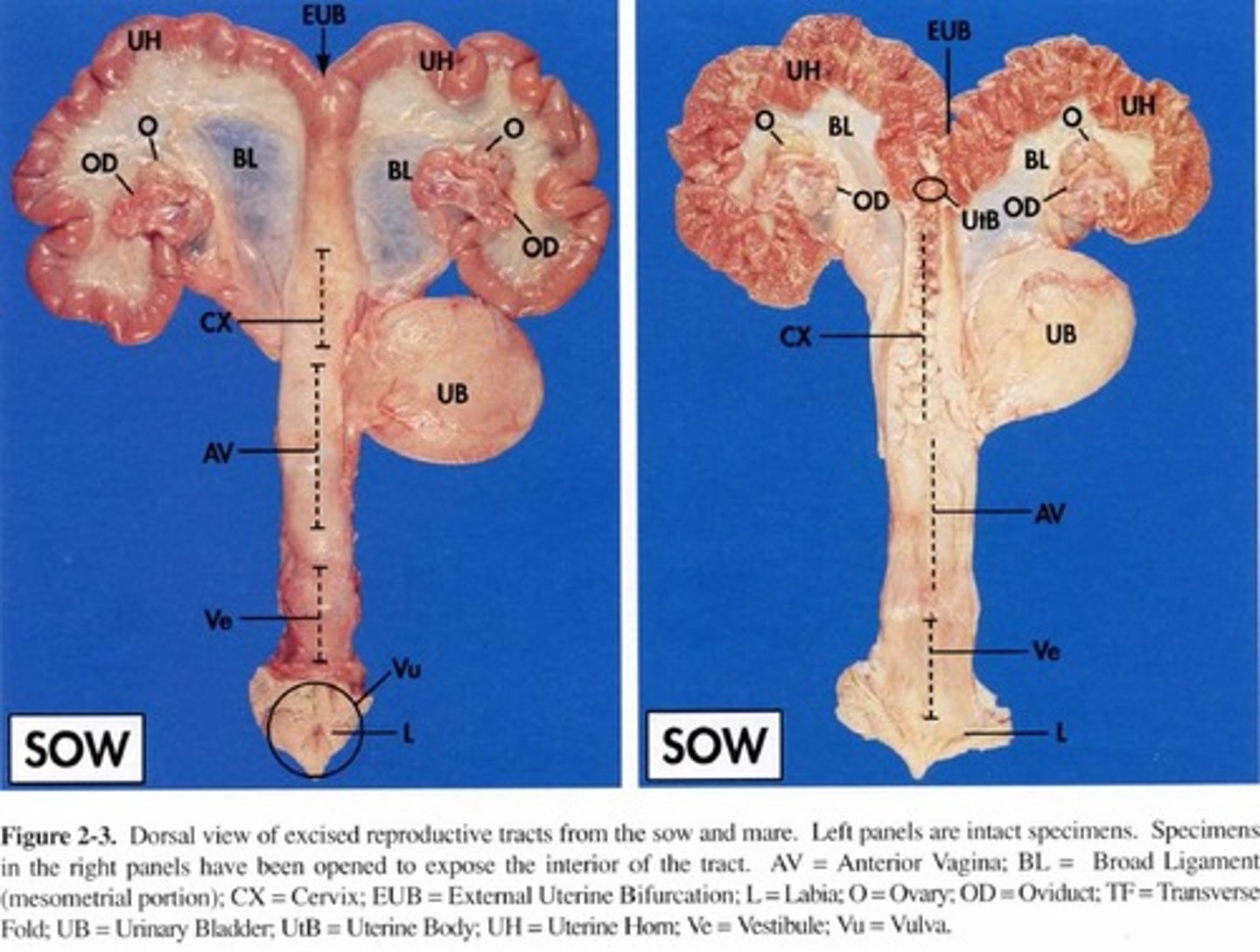
Sow reproductive tract
- Has very large uterine horns
- 18 inches long
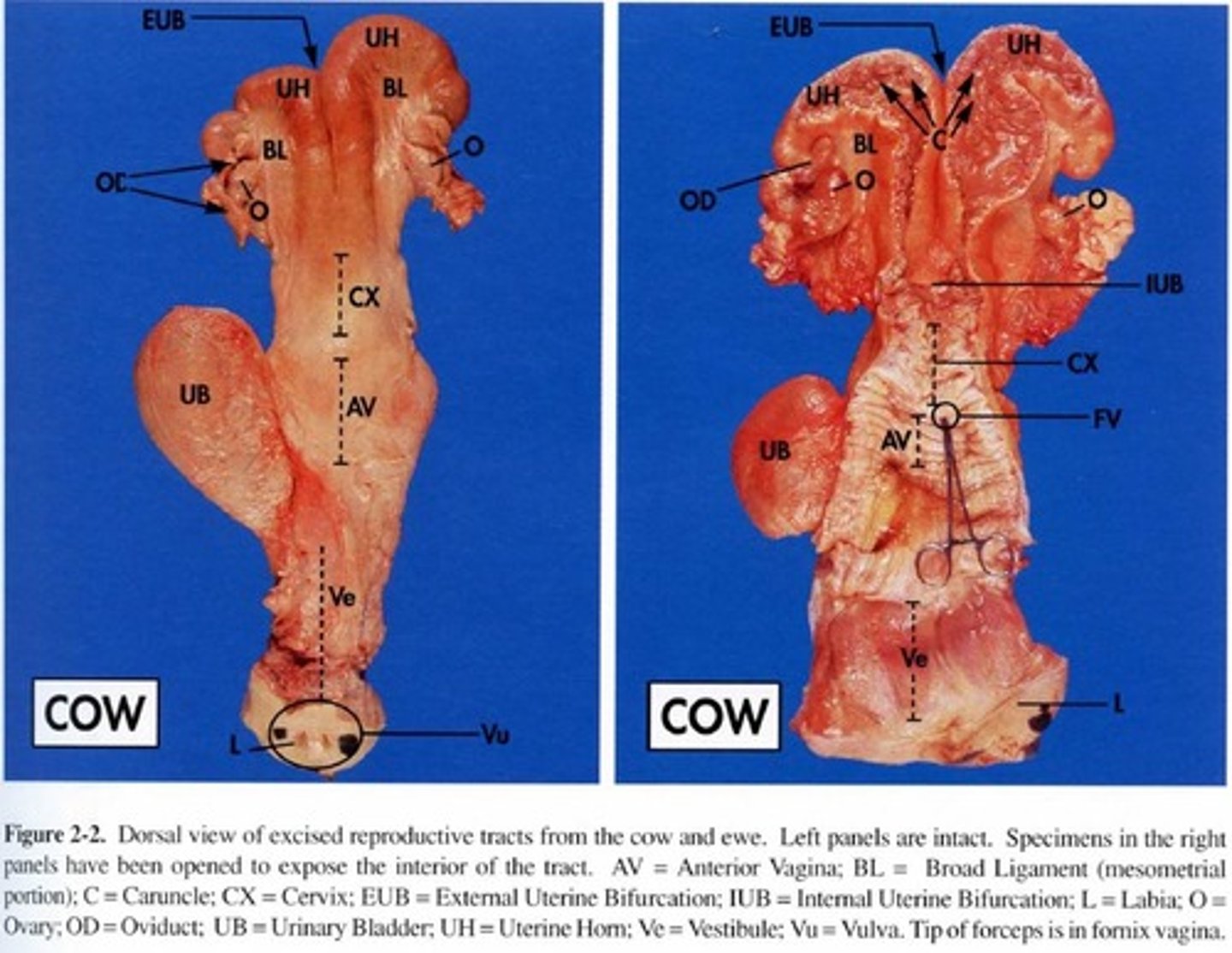
Cow reproductive tract
- Has short uterine horns
- Long tract (16 inches)
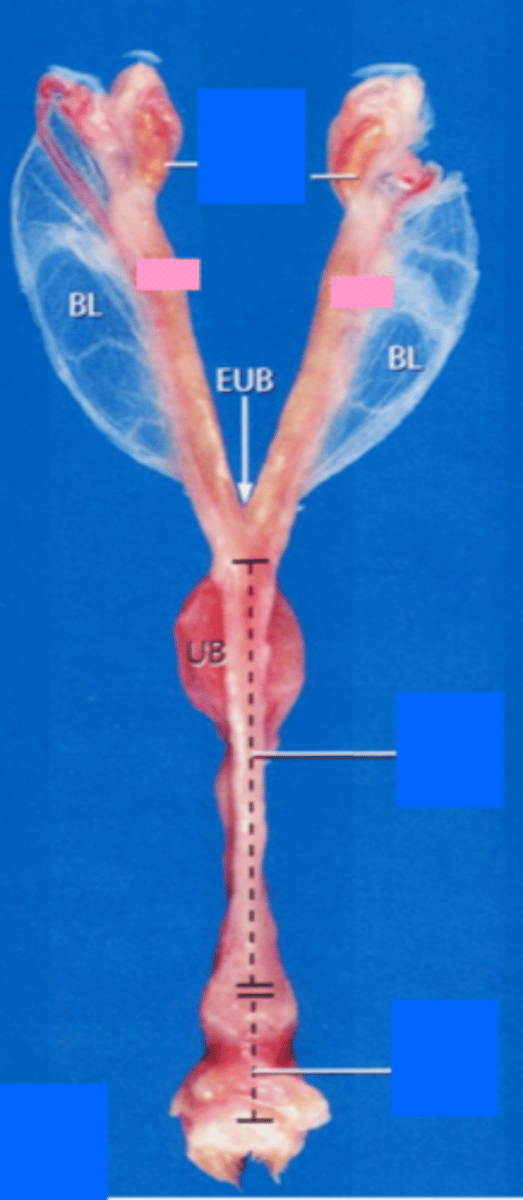
Cat reproductive tract
- 2 distinct horns
- Very small uterine body
- 4 inches
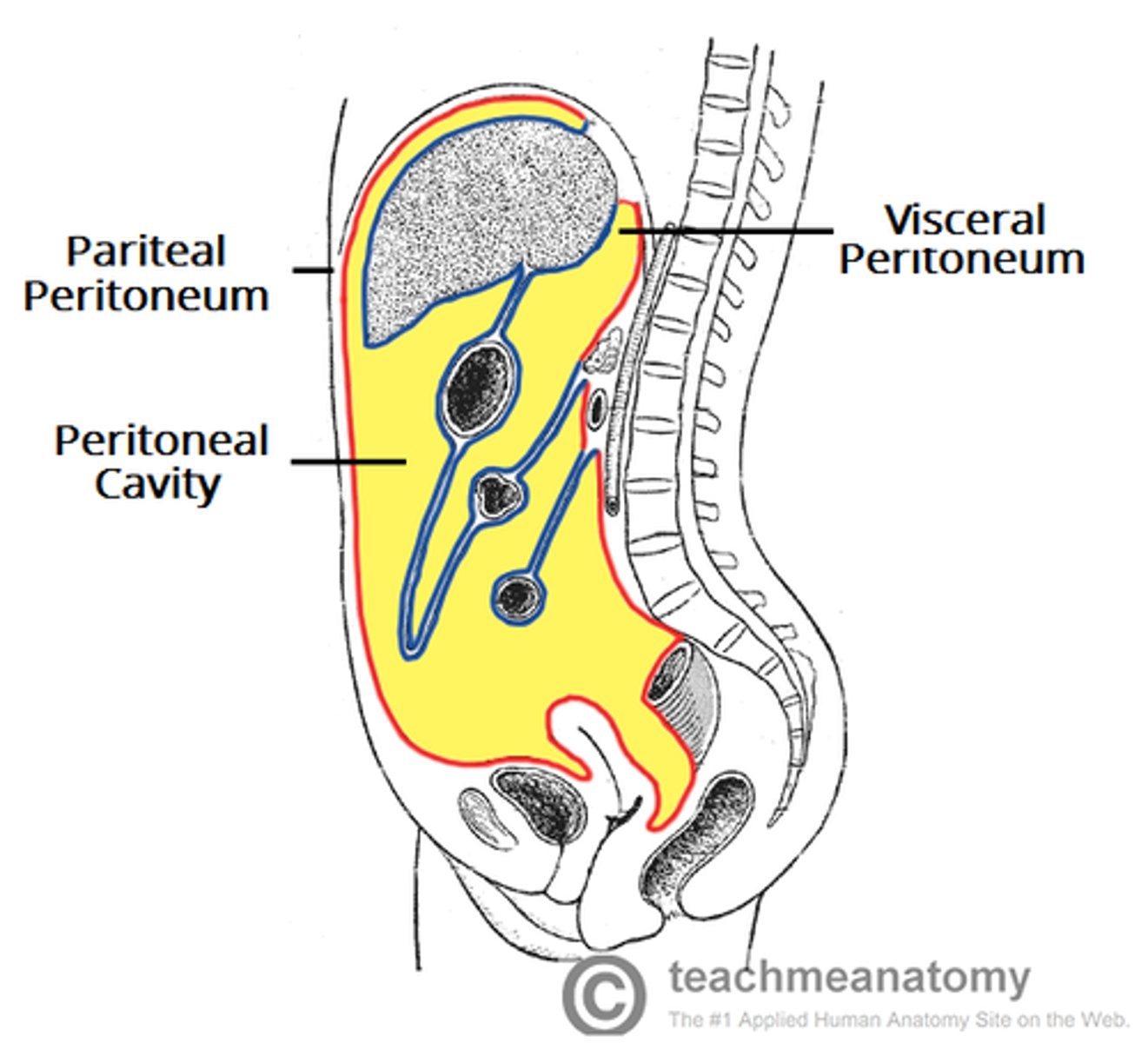
Peritoneum
A thin, serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers most of the abdominal organs.
- Contains 2 layers:
• Parietal peritoneum: Lines the abdominal wall
• Visceral peritoneum: Covers the abdominal organs
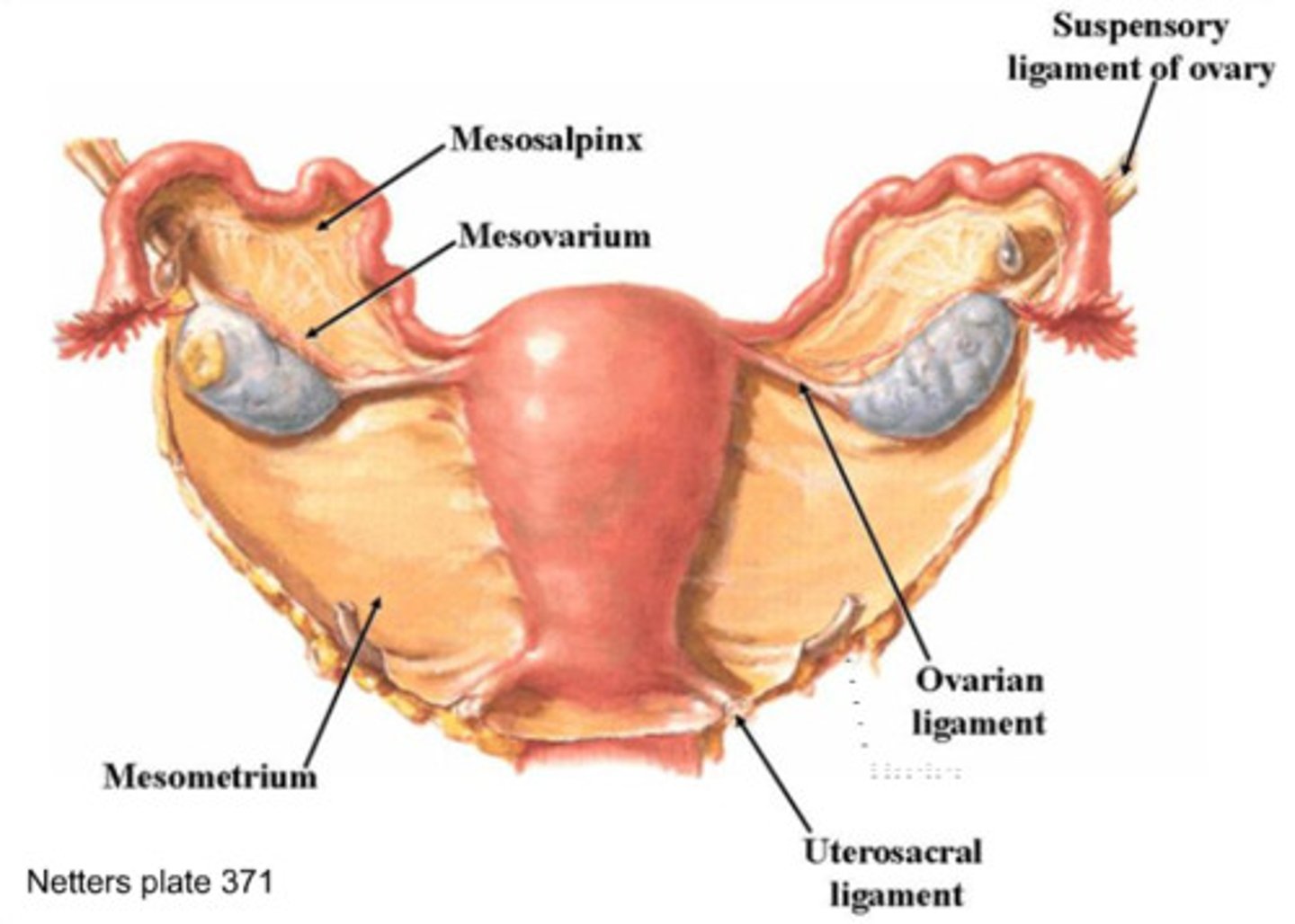
Broad ligaments (reproductive tract support)
- Continuous with peritoneum of abdominal cavity
- Contains through connective tissues to support the tract
- Has blood vessels/nerves
Mesometrium
A tissue that supports the uterus and is part of the broad ligament (Uterus)
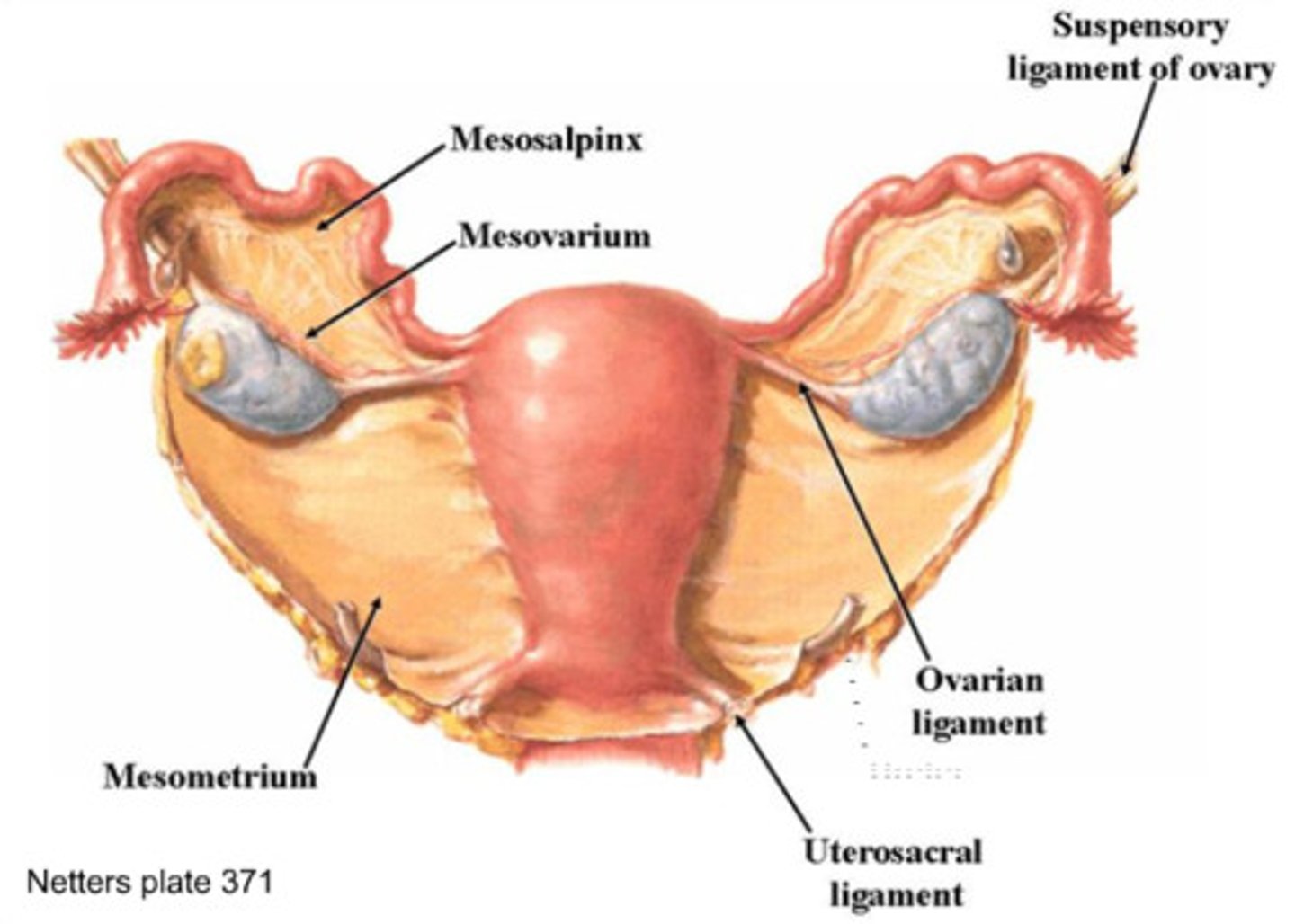
Mesosalpinx
A fold of peritoneum that extends from the uterus to the fallopian tube. (Oviduct/fallopian tube)
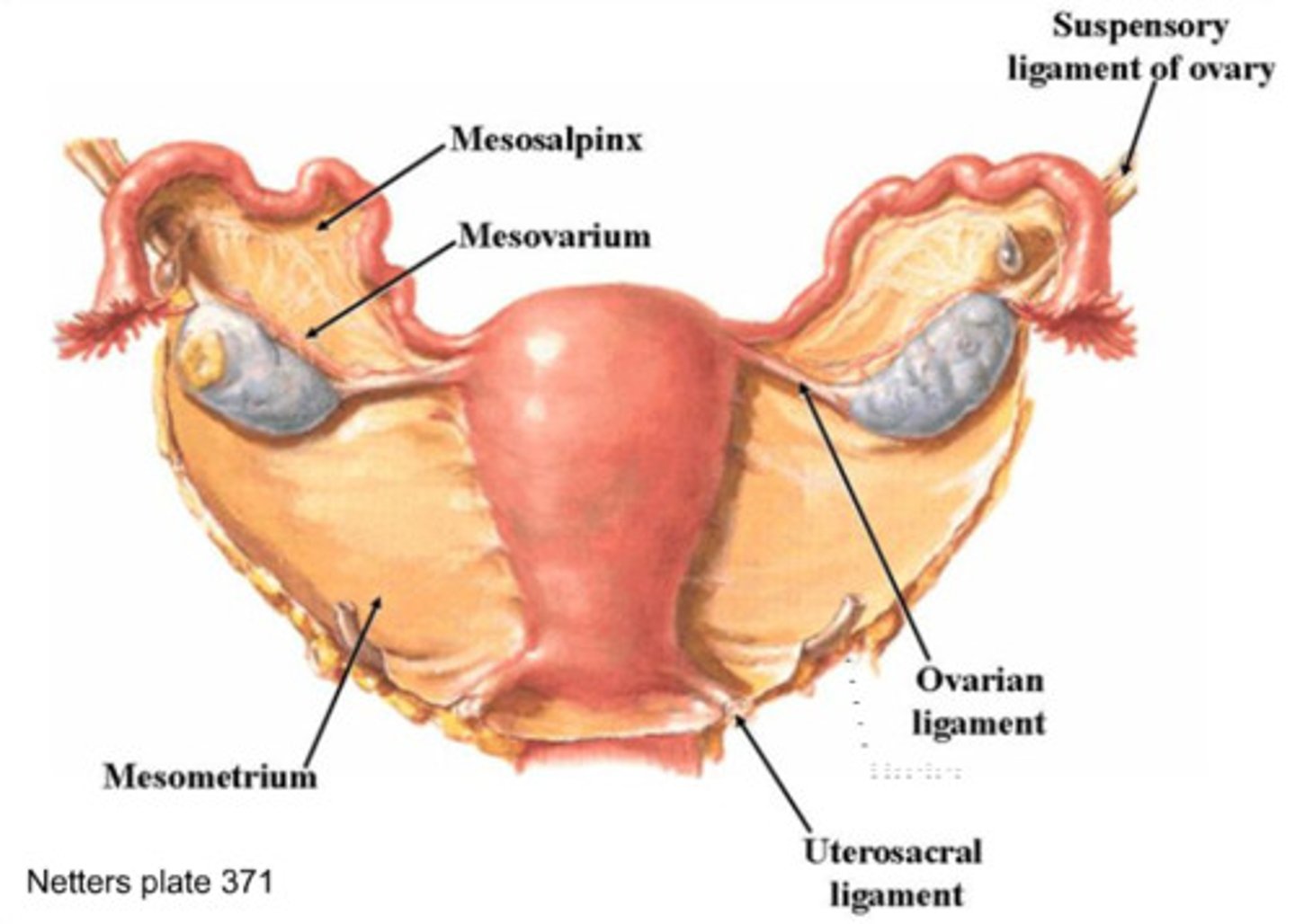
Mesovarium (hilus)
A part of the broad ligament that connects the ovaries to the broad ligament, and the ovarian hilus is a depression in the ovary where blood vessels and nerves enter. Ovarian hilus cells are found in the ovarian hilum and mesovarium. (Ovary)
Ovarian artery (blood supply to reproductive tract)
Has direct branch off abdominal aorta
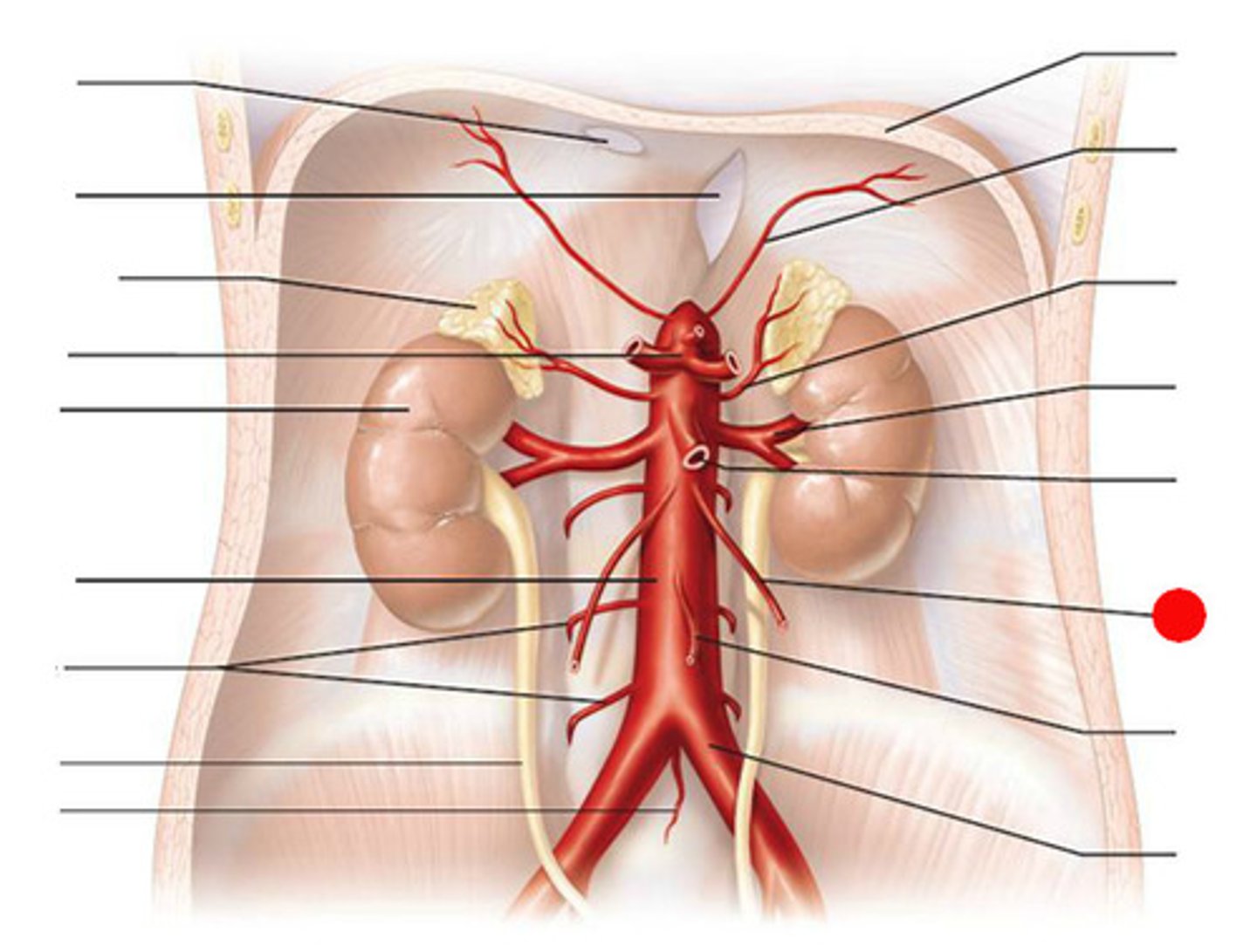
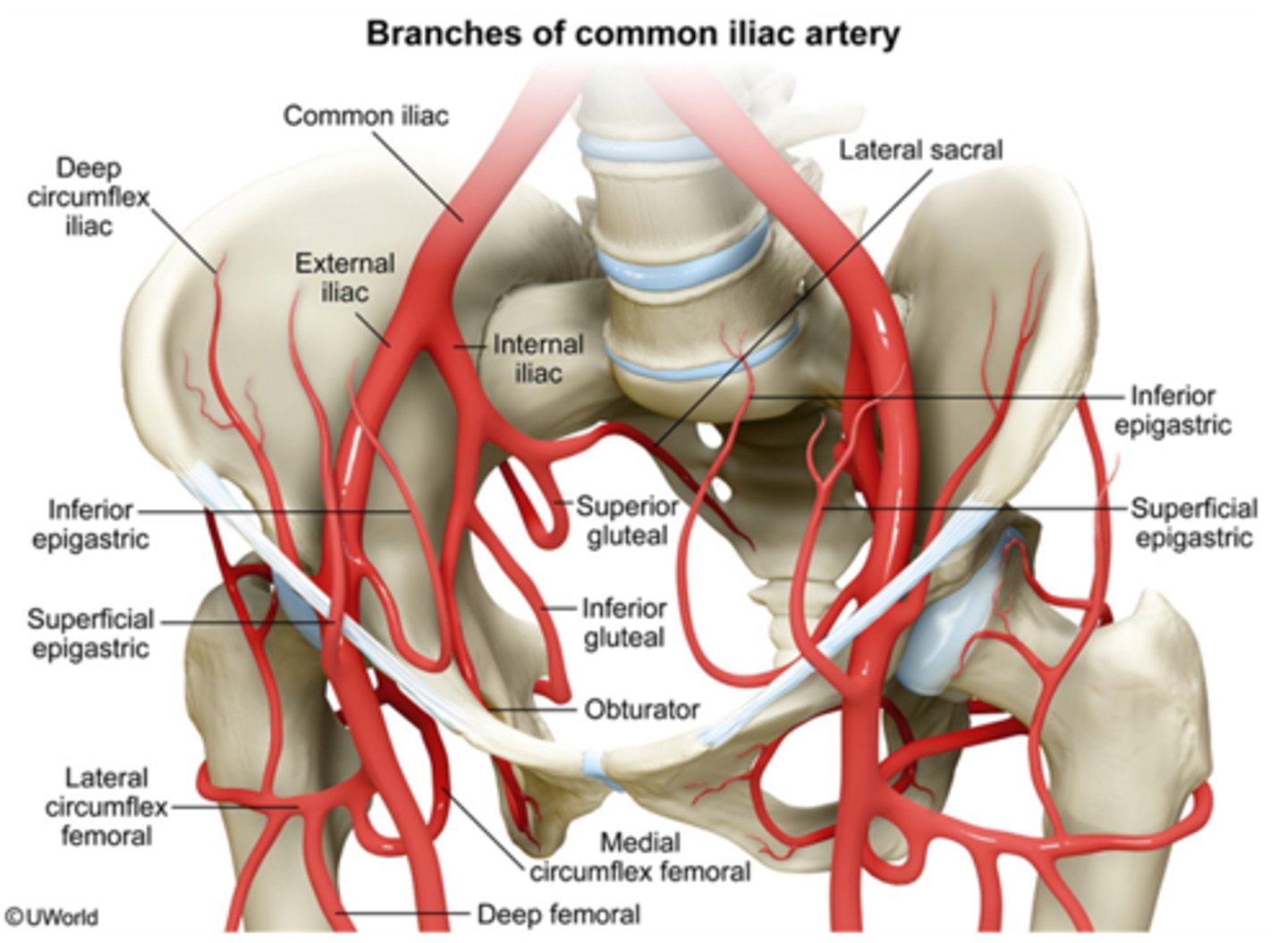
What does the aorta split into?
It splits into common iliac artery
- Internal iliac branch
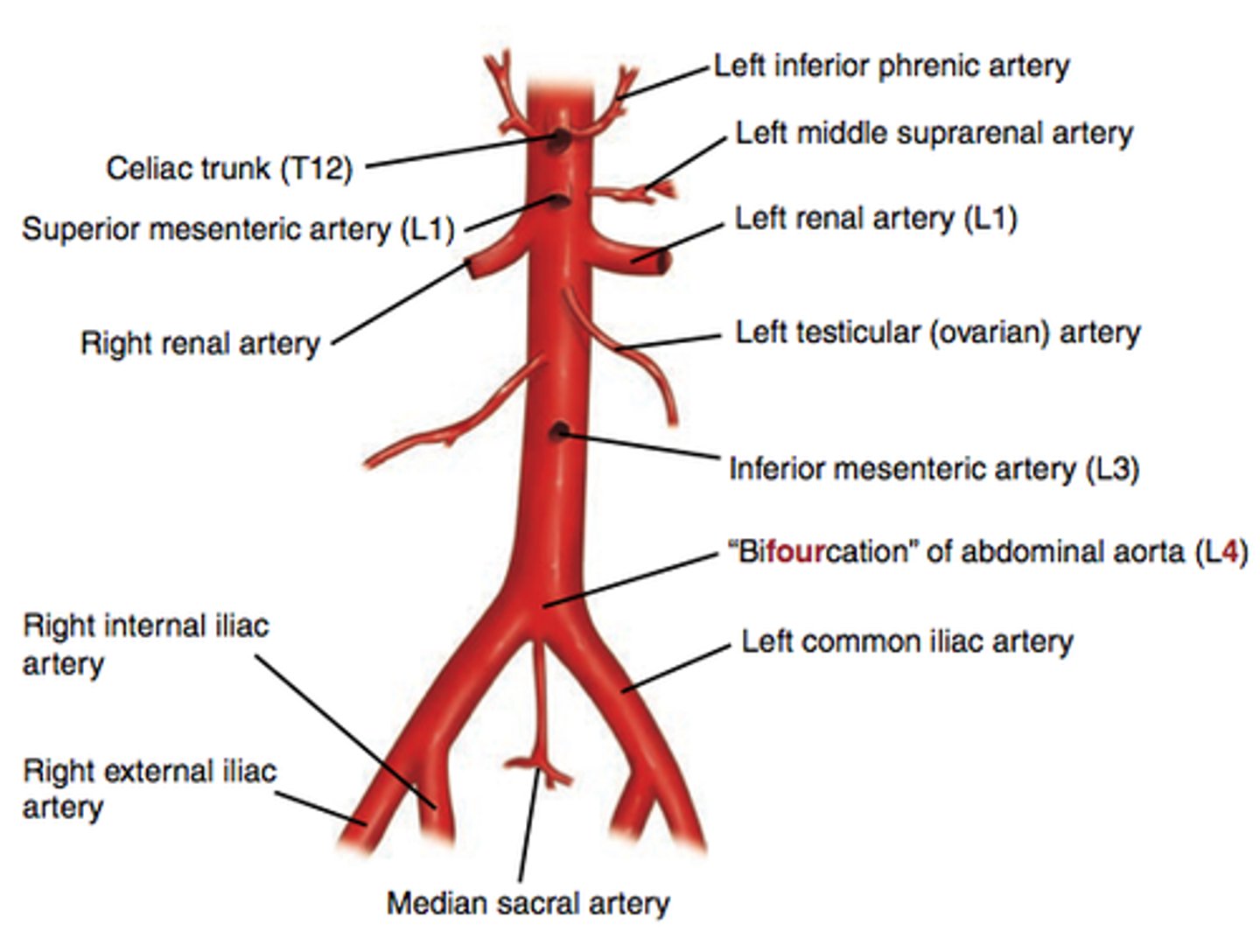
Internal iliac branch
Supplies the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall
The lumbar branch supplies the quadratus lumborum and psoas major muscles
- Uterine artery branch
- Vaginal artery branch
When does blood supply in the reproductive tract increases in volume?
During the cycle and in pregnancy caused by estrous which increases blood flow
How does blood supply change in the reproductive tract?
It responds to hormones
How can reproductive tissues swell?
- Increased flow (vasodilation)
- Fluid retention (vasoconstriction)
Vasodilation
Increases flow
Vasoconstriction
Fluid retention
The close arrangement (coiling) of the uterine vein (drain) around the ovarian artery (supply) allows counter current hormone ___________across vessels
Transfer
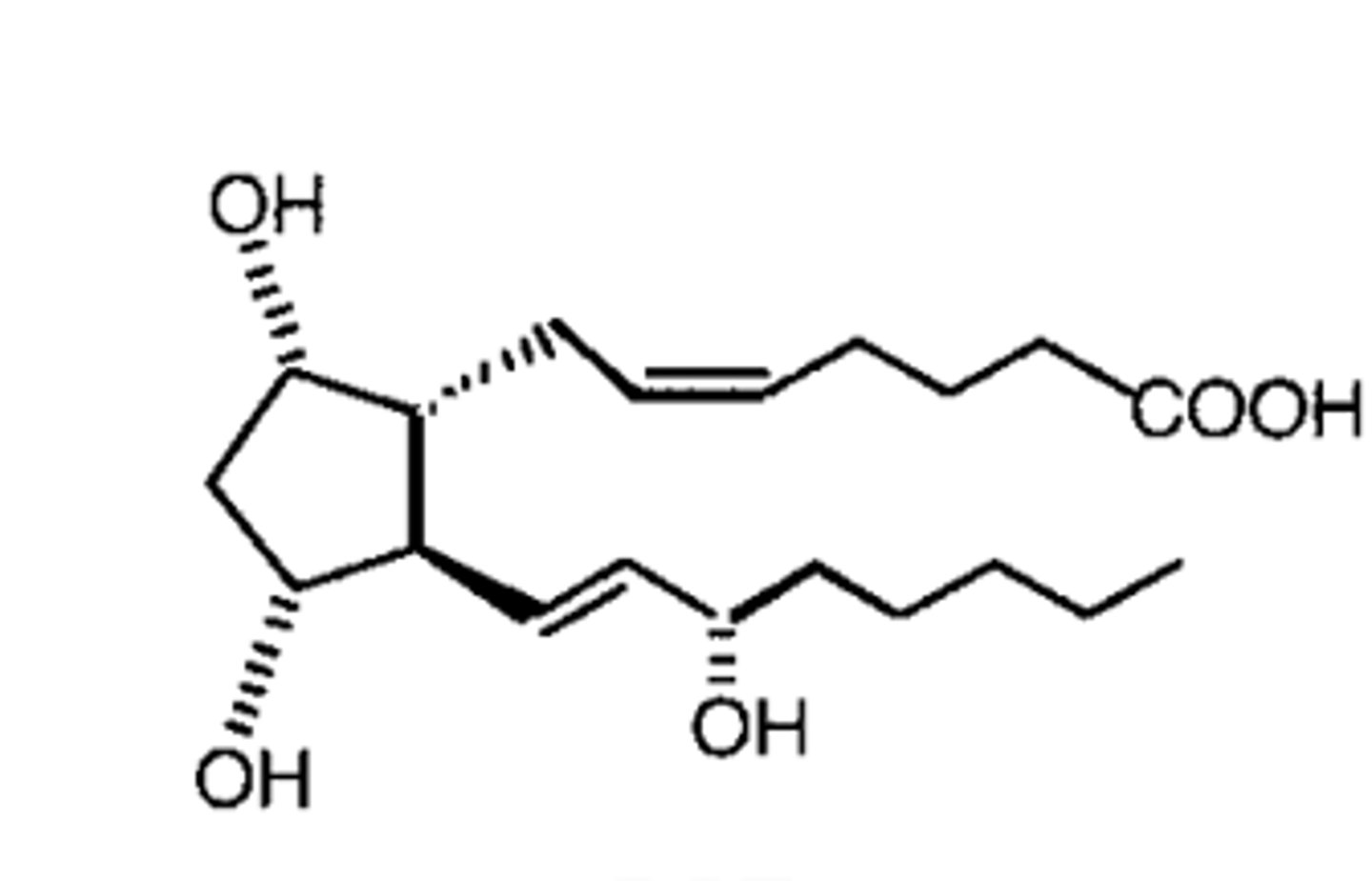
Prostaglandin (PGF2)
Hormone-like lipids that regulate many bodily processes, including inflammation, blood flow, and pain
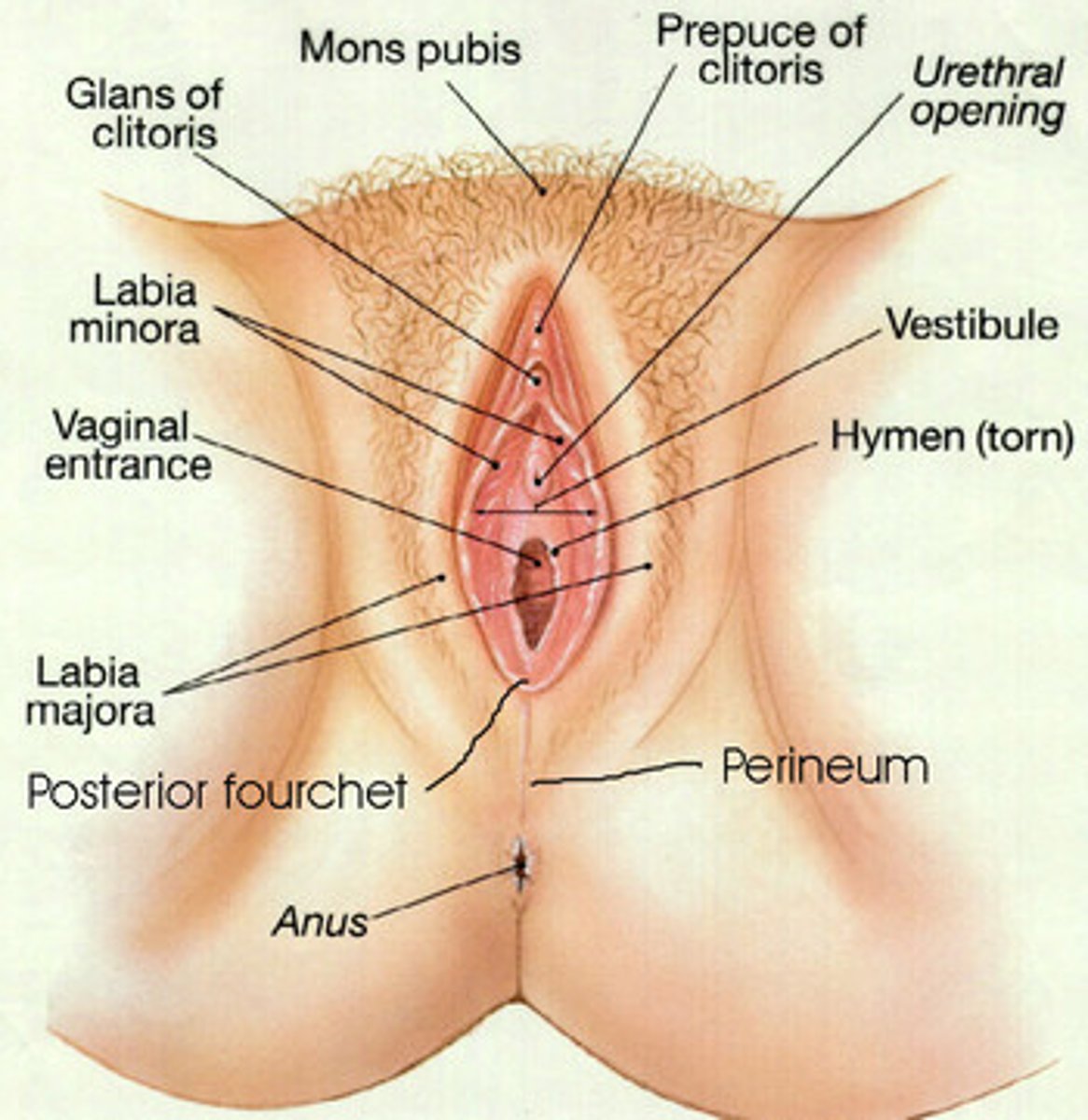
Perineum
The area of skin between vulva and anus
- This can tear
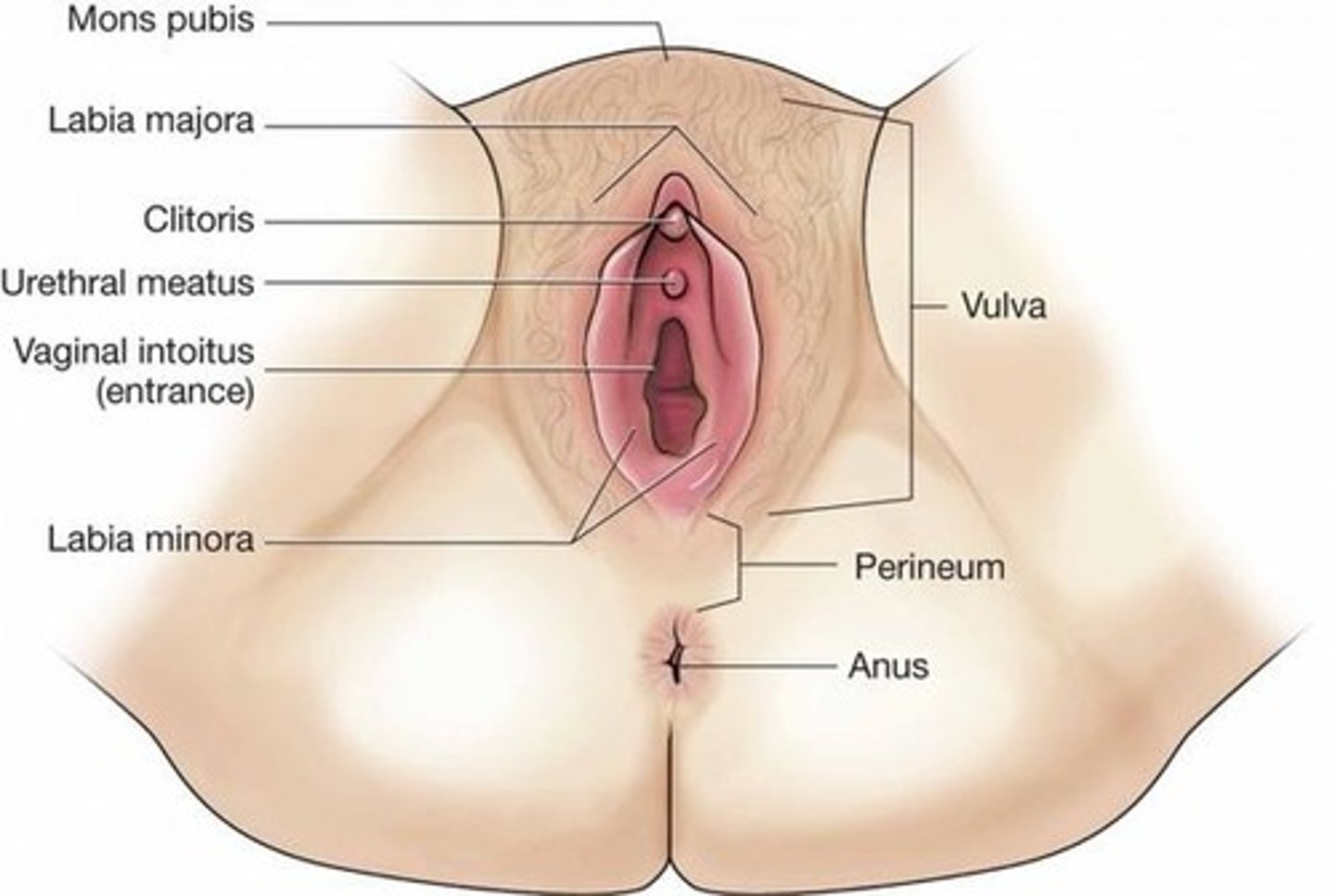
Vulva
- Labia (Right and Left)
- External opening to the reproductive tract
- Serves to protects sensitive mucus membranes
- Swells in response to hormones
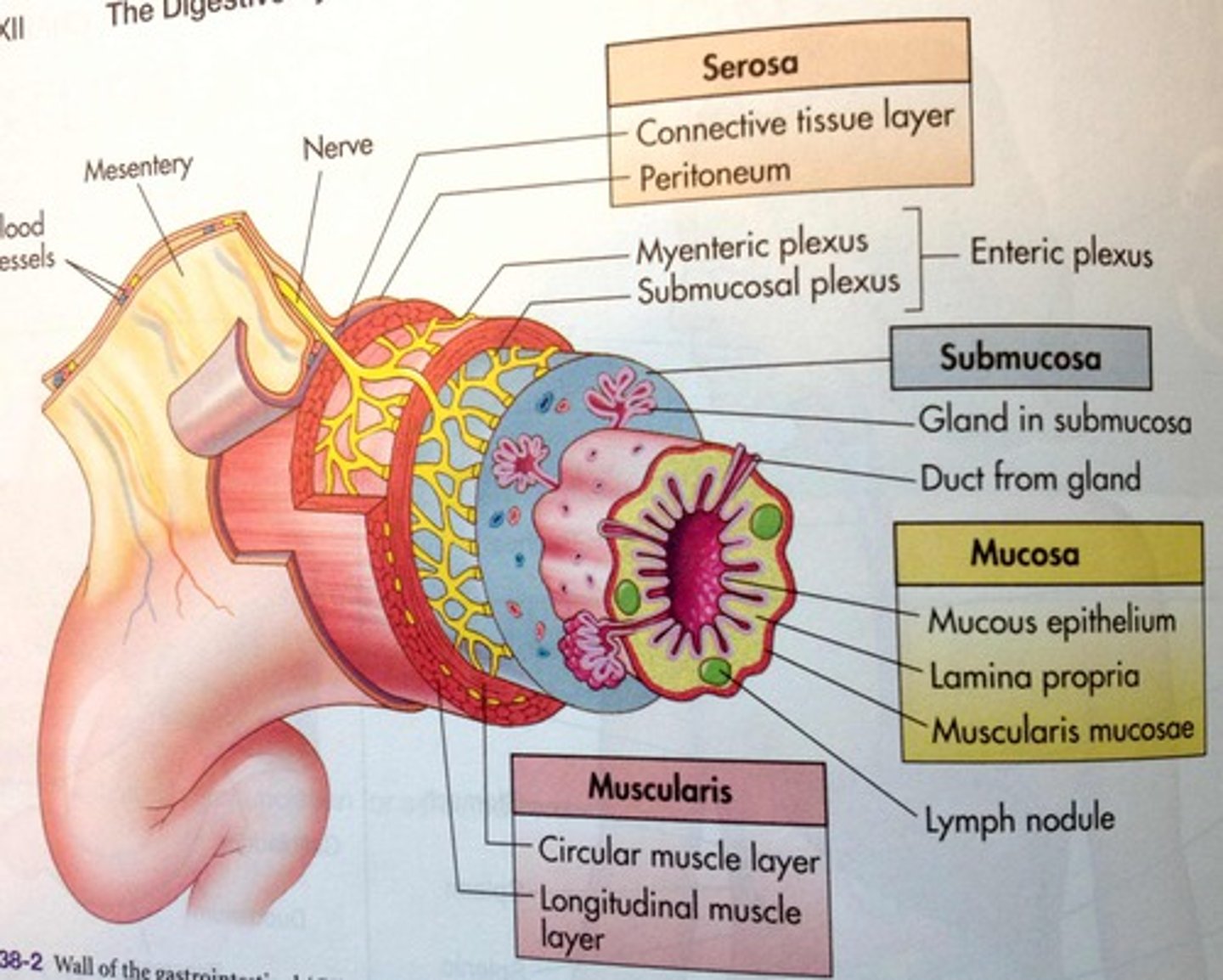
What do the vagina, cervix, uterus, & oviduct all have in common?
They all have three distinct cell layers that have this tubal structure
- Serosa
- Muscle layers (muscularis)
• Longitudinal smooth muscle
• Circular smooth muscle
- Submucosa
- Mucosa
Serosa
Outer single layer of flat cells
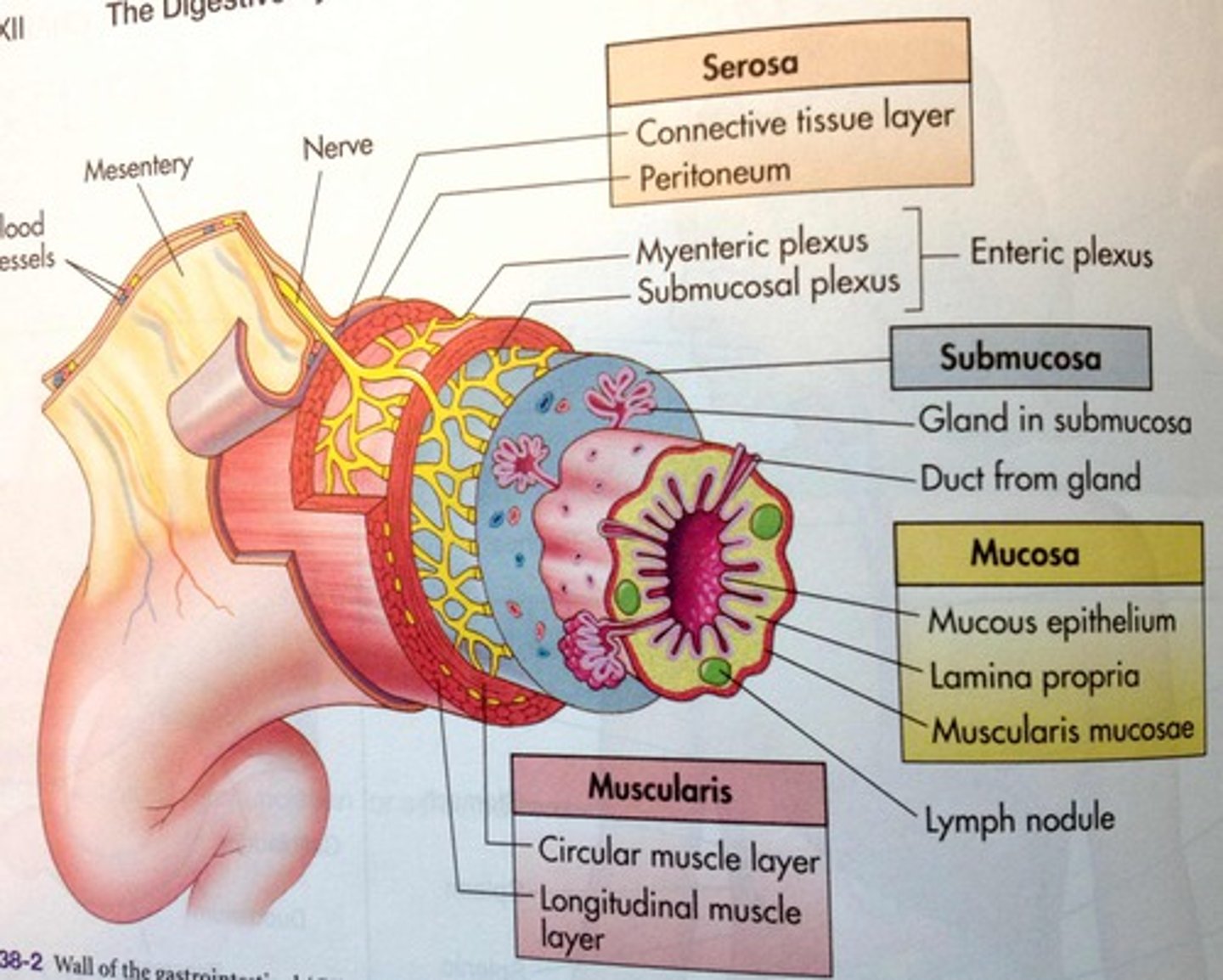
Muscle layers (Muscularis)
Moves things
- Inner circular and outer longitudinal
- Well developed in oviduct and uterus
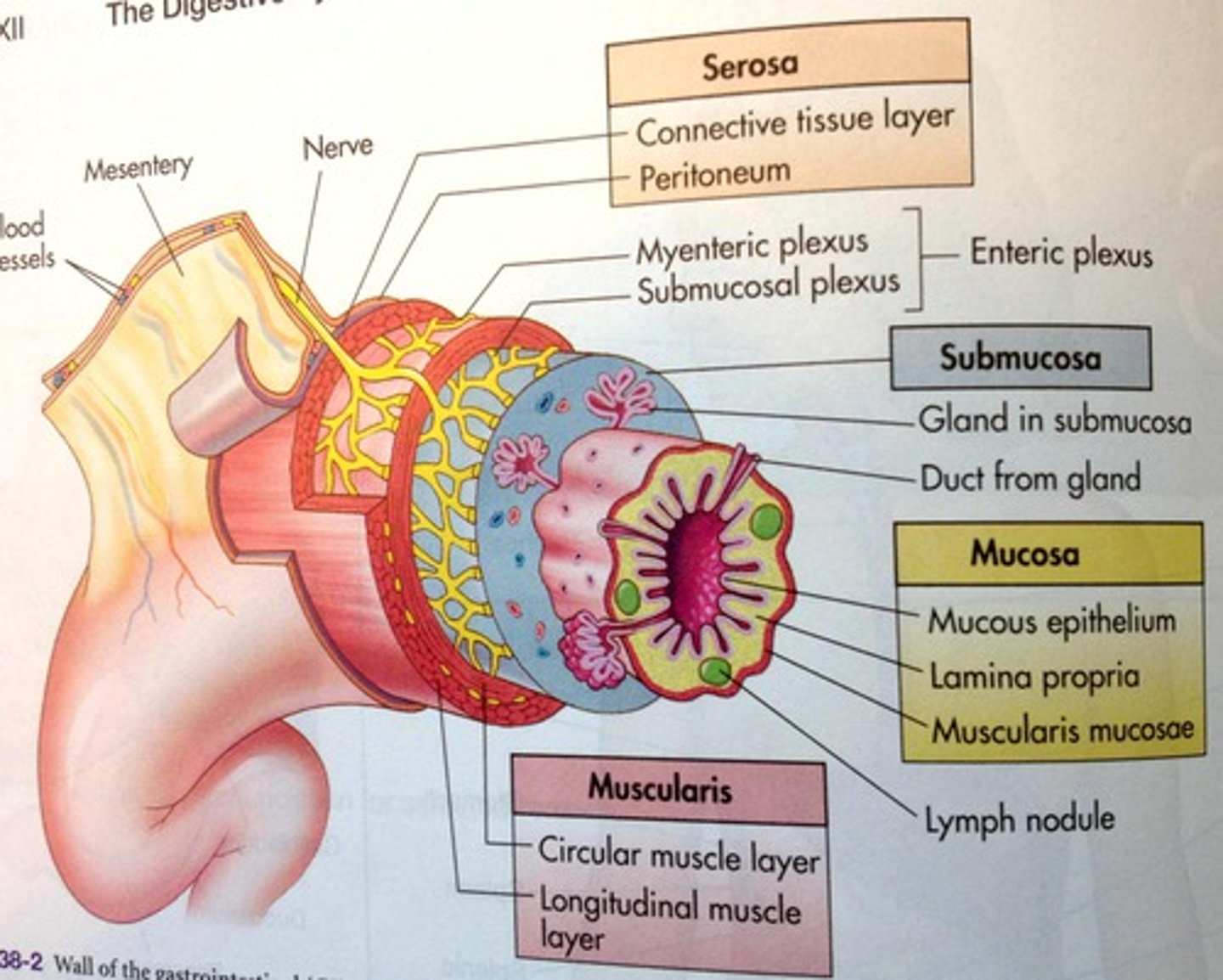
What are the two parts that make up the muscle layers (Muscularis)?
- Longitudinal smooth muscle (outer)
- Circular smooth muscle (inner)
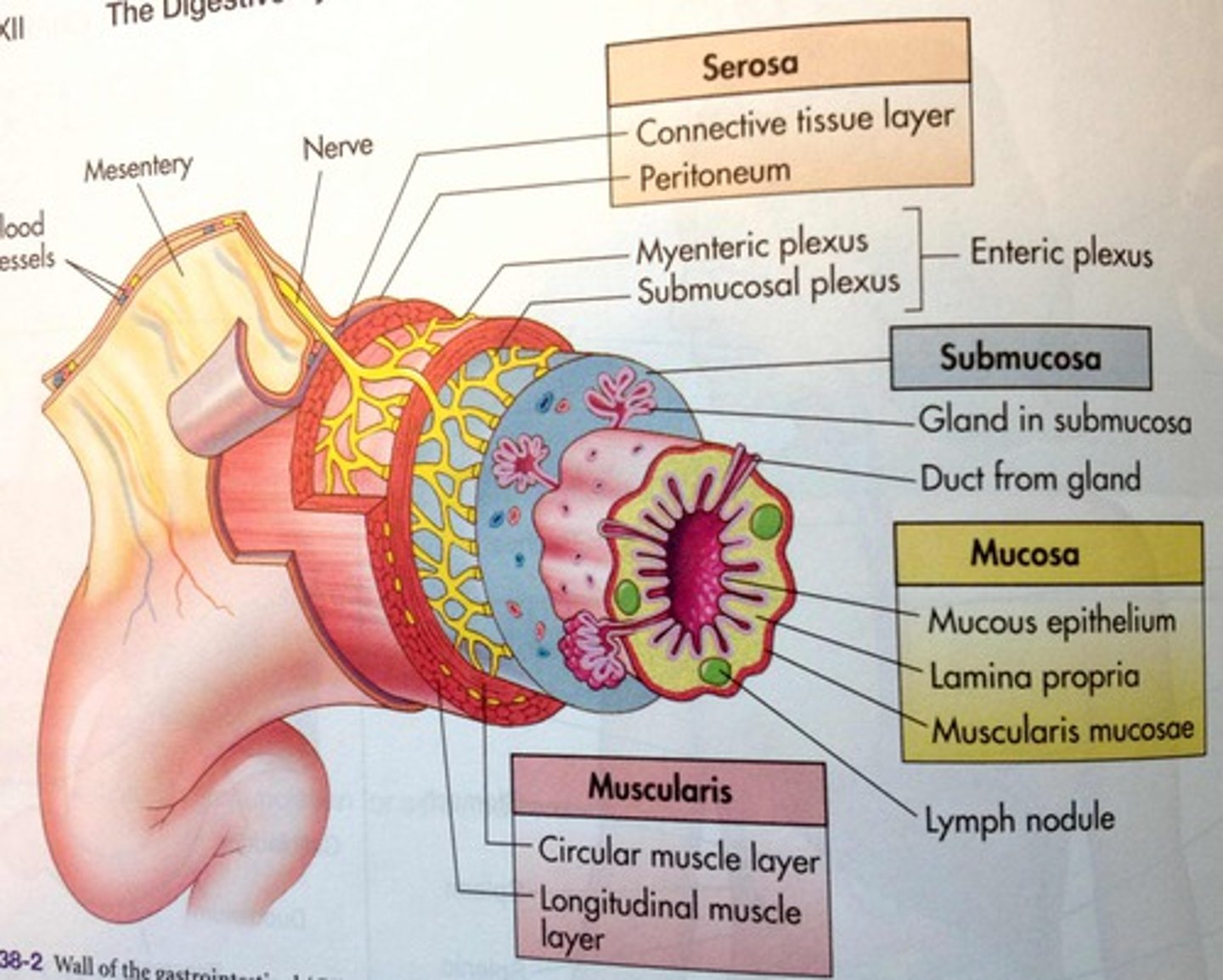
Submucosa
- Changes thickness and secretions by stage of cycle
- Vessels, nerves, interstitial connective tissue
- Produces hormones, nutrients, fluids
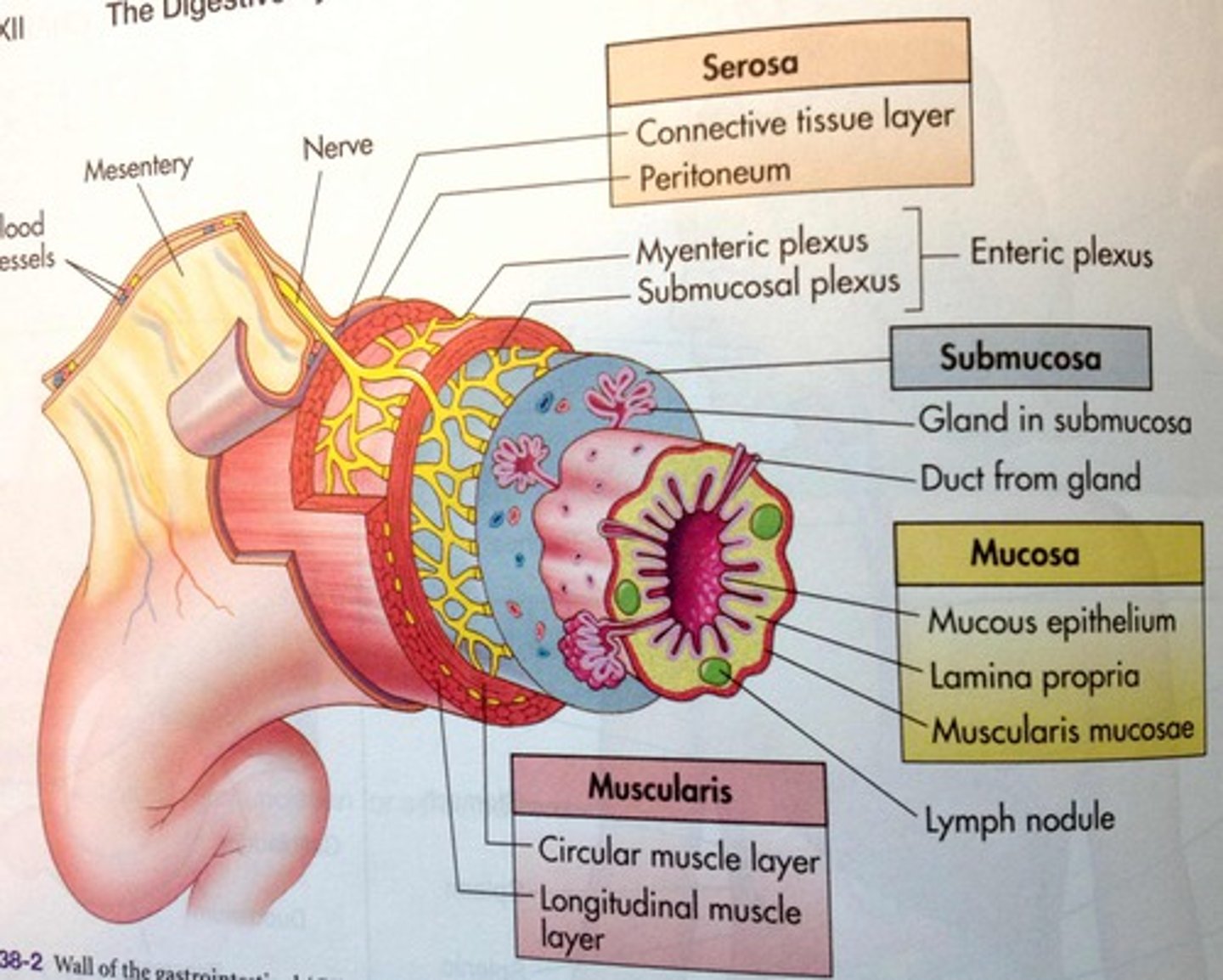
Mucosa
- Single layer of columnar epithelial cells lining tubes
- Produces hormones, nutrients, fluids
• Oviduct: columnar epithelium + mix of Ciliated
• Vagina: stratified squamous
- Thickens at estrus to protect
- Immunoglobulins (IgA and G)
- Low pH
- Secretions have odors associated with ESTRUS
Vagina/vestibule functions
- Birth canal, urine passage, copulatory organ
- Site for semen deposition in many species
- Mucosa
Vestibule
- Caudal section of vagina
- From external urethral opening to Labia
- Common Passageway for urine and reproduction
Vagina
- From Cervix to urethral opening (bladder)
- Some mucus cells near cervix
Clitoris
- On ventral surface
- Erectile tissue
Erectile tissue
A specialized type of tissue that contains blood vessels, nerves, and smooth muscle cells
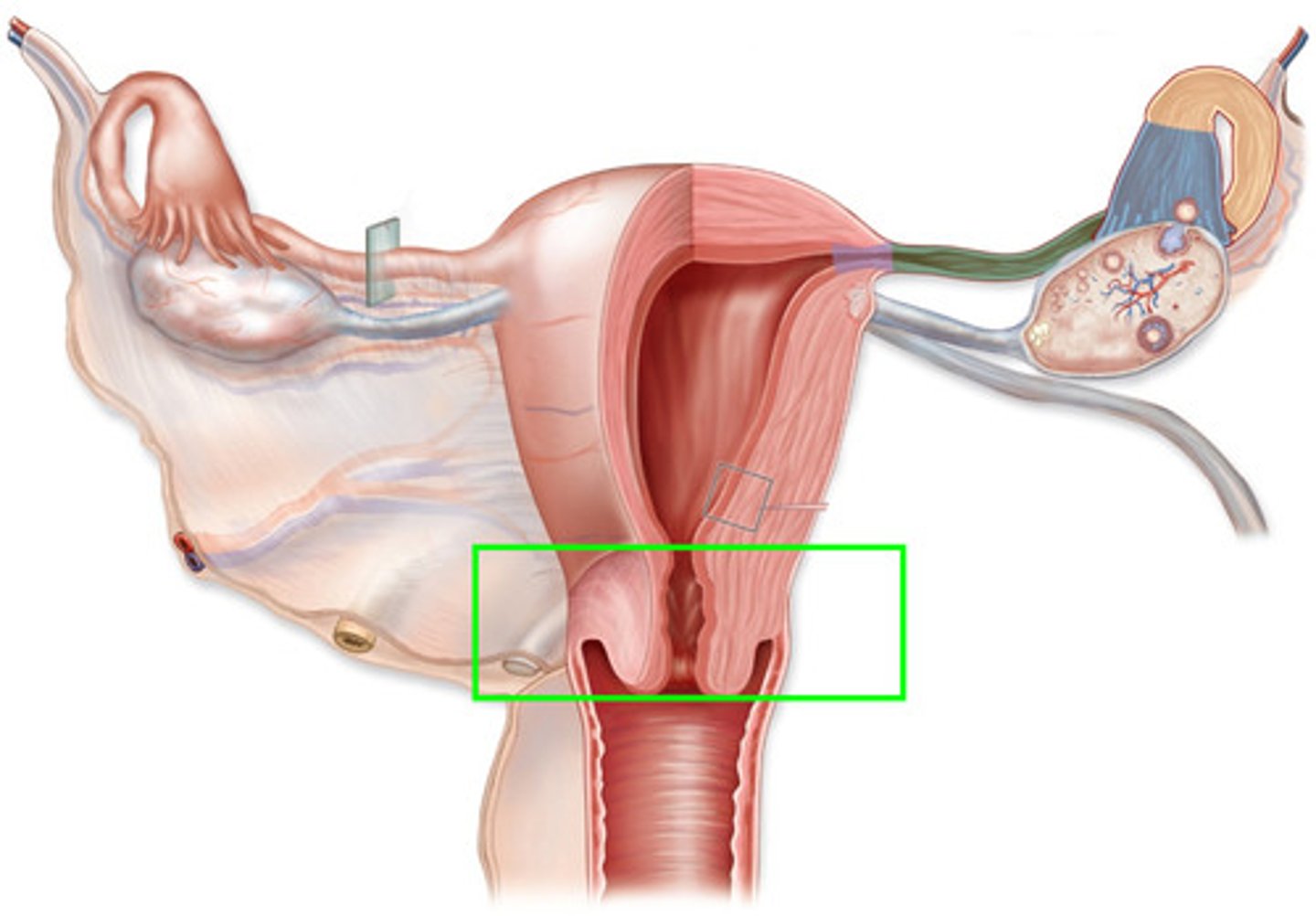
Cervix
- Neck of the uterus
- Serves as a barrier for the uterus
Neck of the Uterus (Cervix)
- Thick walled canal
- Cervical Os (opening)
- Lumen is a passageway
- Can be smooth, folded or with rings
- Has 4 cell layers
- Mucus: major source for vagina
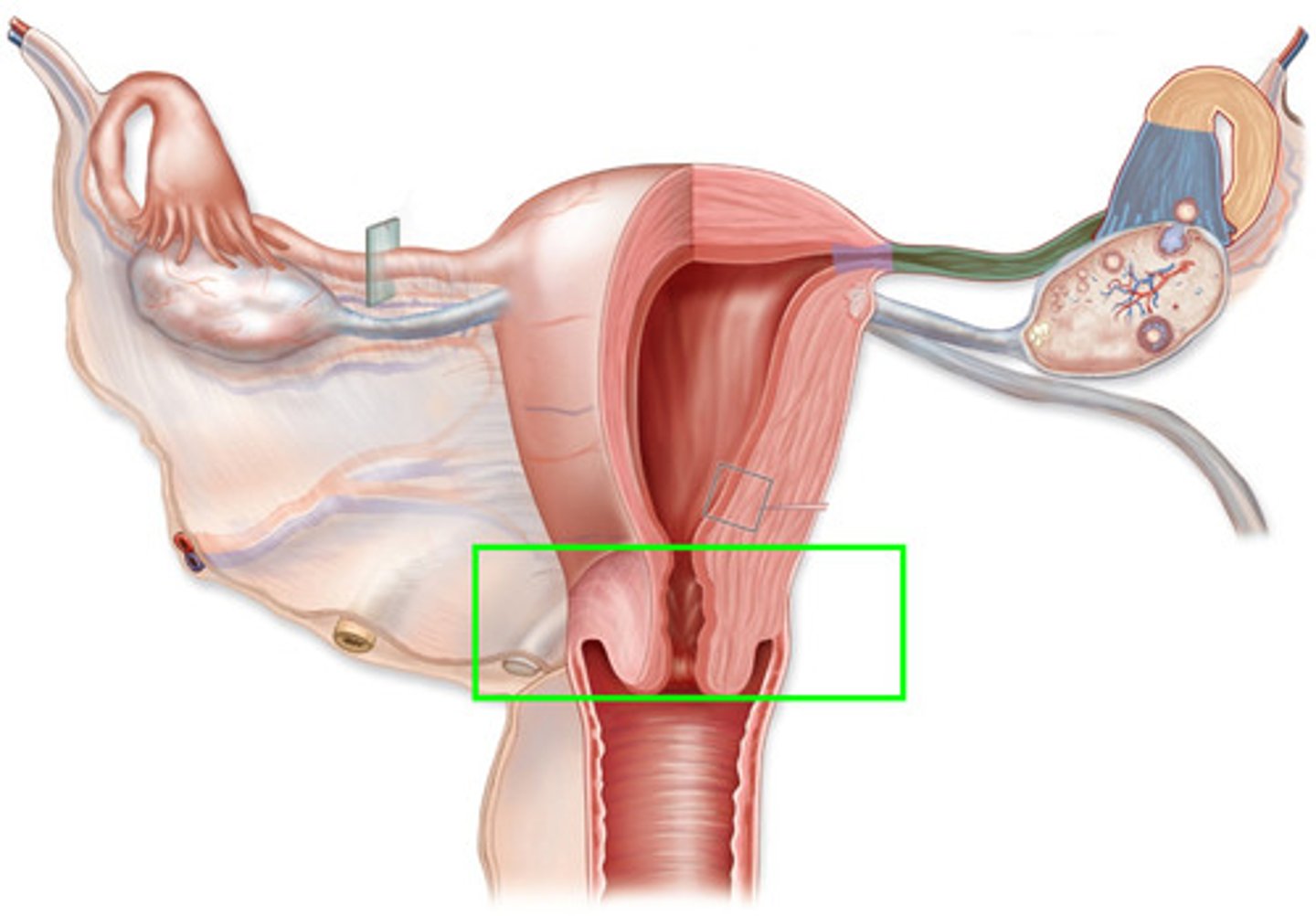
Serves as a barrier for the uterus (Cervix)
- Limits entry of bacteria
- Passageway for sperm
- Contains fetus through pregnancy (keeps the fetus in place)
- Can change shape & dilate at estrus and birth
- Can be rigid and closed during pregnancy
- Can serve as a sperm reservoir (for some species)
When does the cervix dilate?
- At estrus
- Birth
When is the cervix rigid and closed?
During pregnancy
Uterus
- 4 cell layers
- Uterine horns: sections separated by septum
- Uterine body: common section
What is the function of the Uterus?
- Sperm TRANSPORT and CAPACITATION (modify)
- Site of Embryo and fetal attachment /placenta
- Luteal REGRESSION
- Birth process
What two layers are linked (endometrium) in the uterus?
- Mucosa
- Sub-mucosa
Two inner layers are liked (endometrium) in the Uterus
- Interact with sperm, embryo
- Mucosa
- Sub-mucosa
- Smooth, folds or caruncles (ruminants)
• Caruncles raised elevations for attachment and blood supply but without glands
Myometrium
- This tissue layer has two distinct cell layers (inner and outer muscle) - Functions in tone and contractions
- Under neural and endocrine control
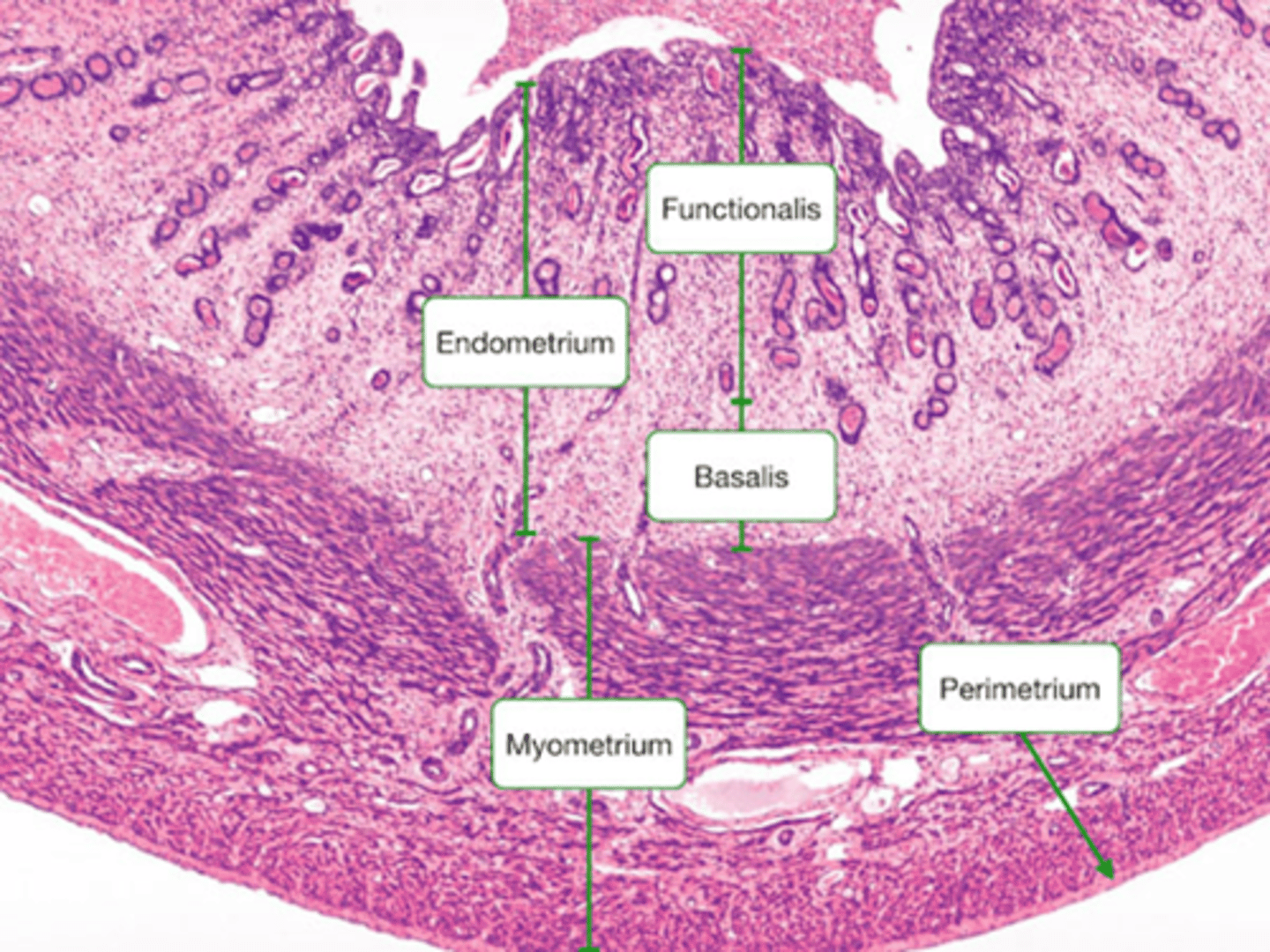
Uterine cell layers
- Glands
- Submucosa
- Mucosa (epithelial layer)
- Lumen
( changes in blood flow and thickness during cycle)
Uterine smooth muscle layers
- Outer longitudinal
- inner circular
- Muscle function: movement of sperm, embryo, fetus
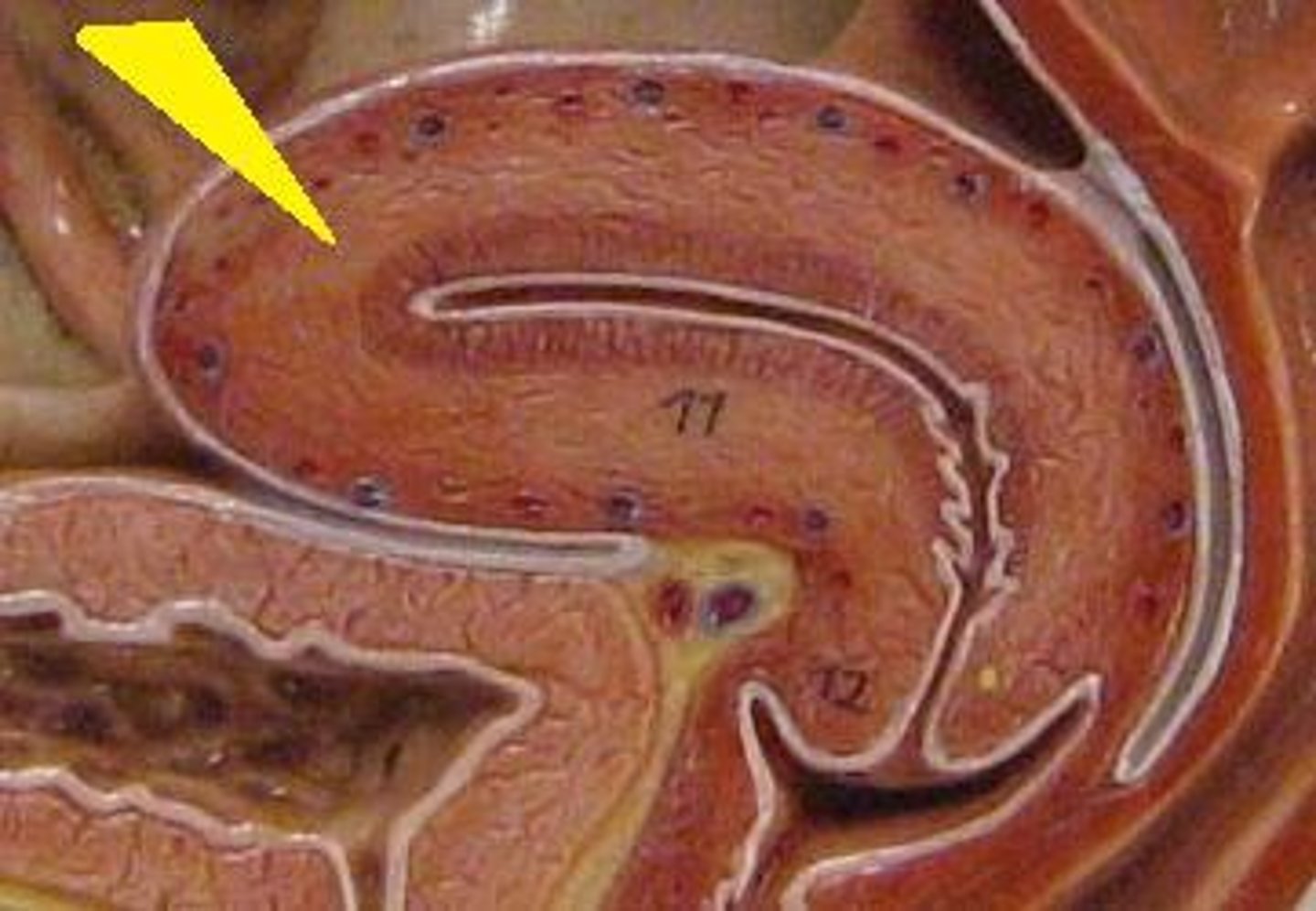
What is the muscle function of the uterine smooth muscle layers?
Movement of:
- sperm
- embryo
- fetus
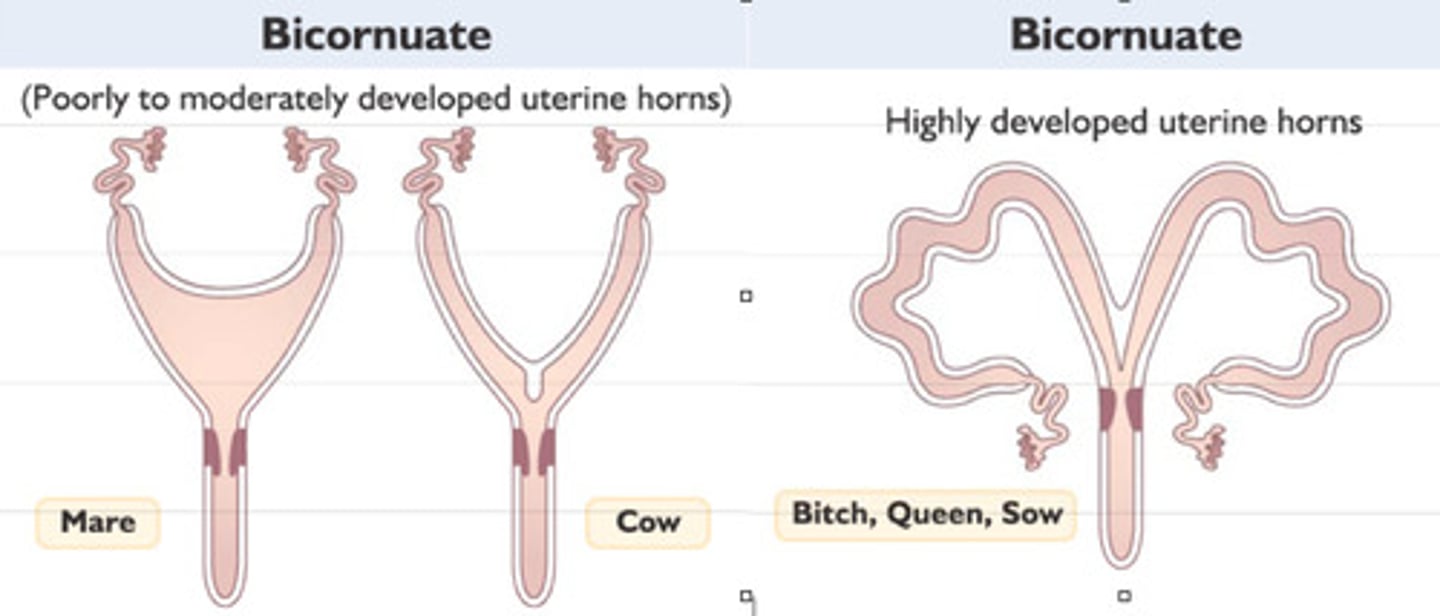
Bicornuate
- Swine, cattle, sheep, horses, cats, dogs, most lab rodents
- 2 horns + 1 body, 1 cervix; 1 vagina
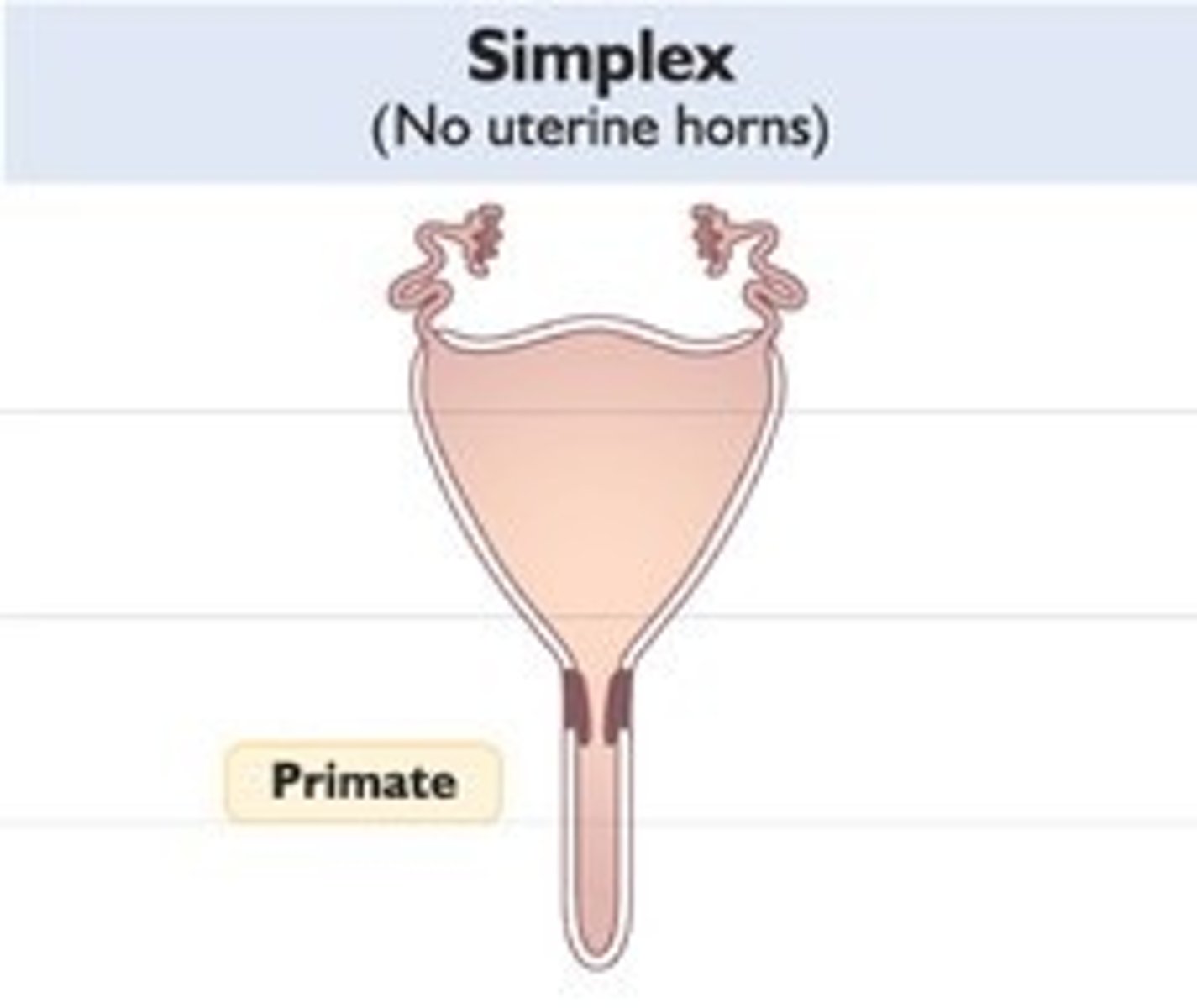
Simplex
- humans, primates
- no formed horns, 1 Large body, 1 cervix; 1 vagina
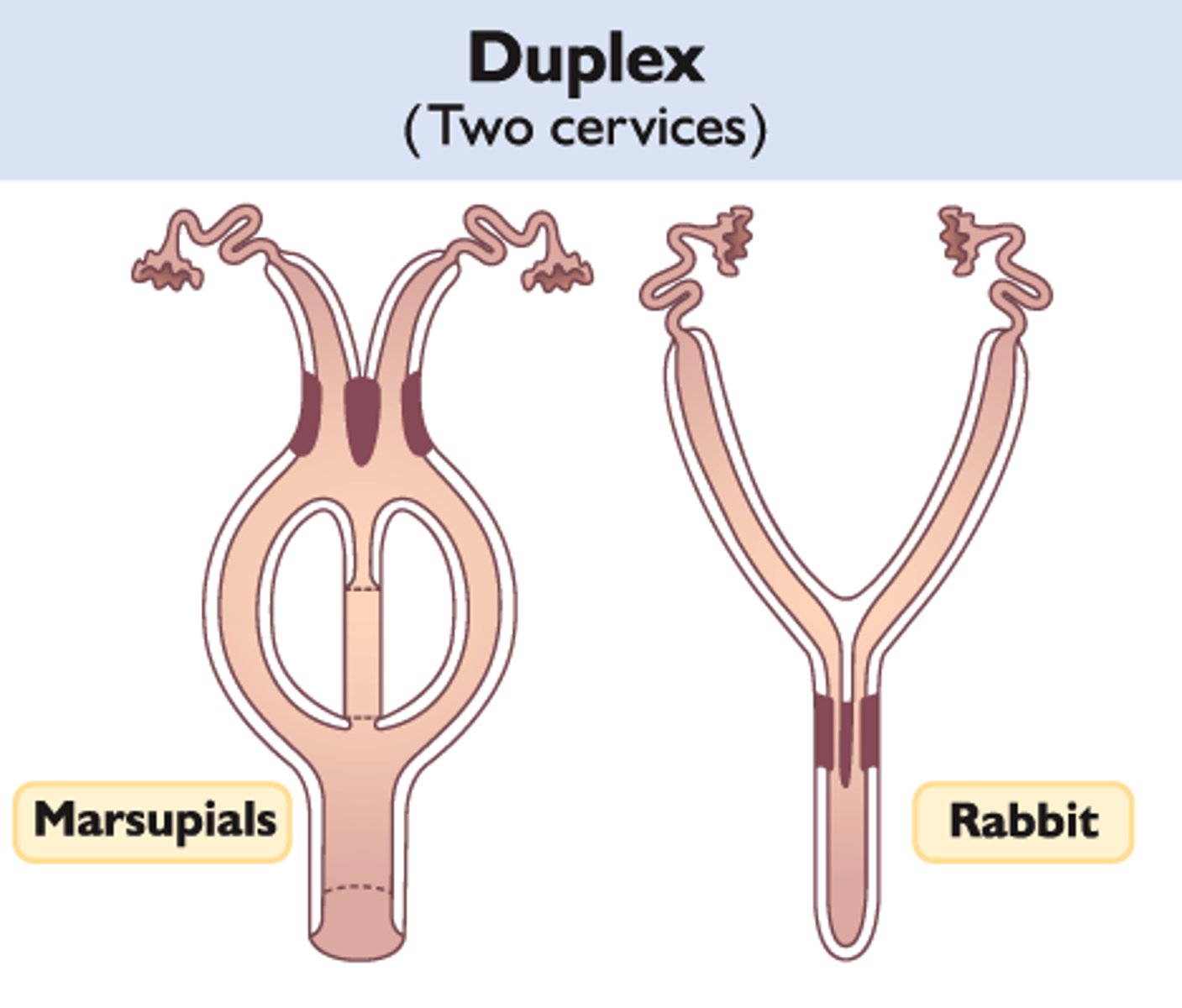
Duplex
- Rabbits, some rodents (squirrel)
- 2 horns (no body), 2 cervices; 1 vagina
- 2 horns (no body), 2 cervices; 2 Vaginas + Urogenital sinus
- Marsupials; how far septum penetrates cervix matches penis bifurcation
- Kangaroo - no bifurcation ; Opposum -bifurcated penis
- 2 horns (no body), no cervix; + Cloaca (no Vagina)
- Monotremes (egg laying mammal):platypus
Oviduct (fallopian tube)
- Site of fertilization
- Sperm reservoir
- Transports sperm and eggs
- Early embryo development
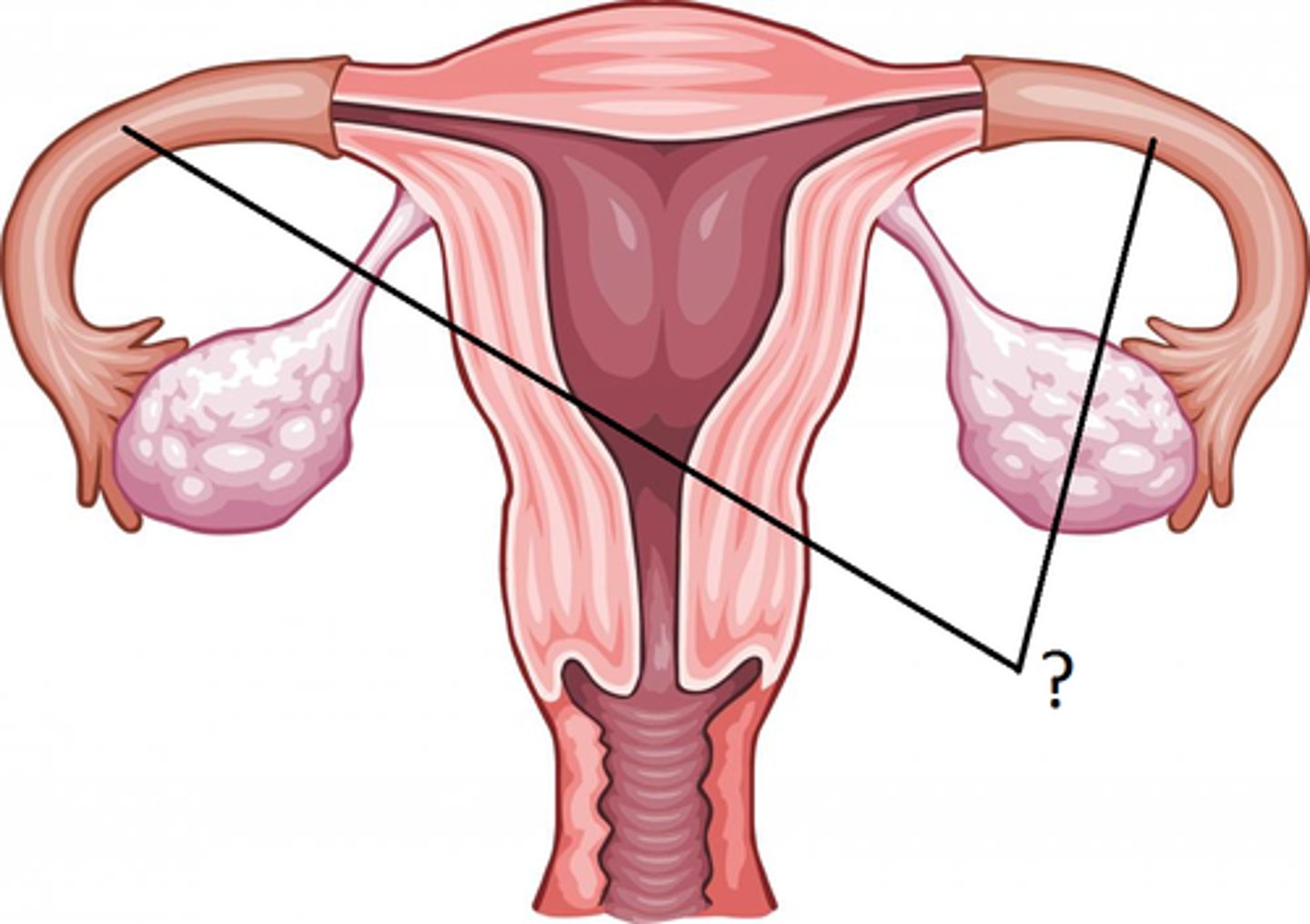
What proximately positions the ovary/oviducts?
Mesosalpinx
Mesosalpinx
A fold of tissue that covers and supports the fallopian tube
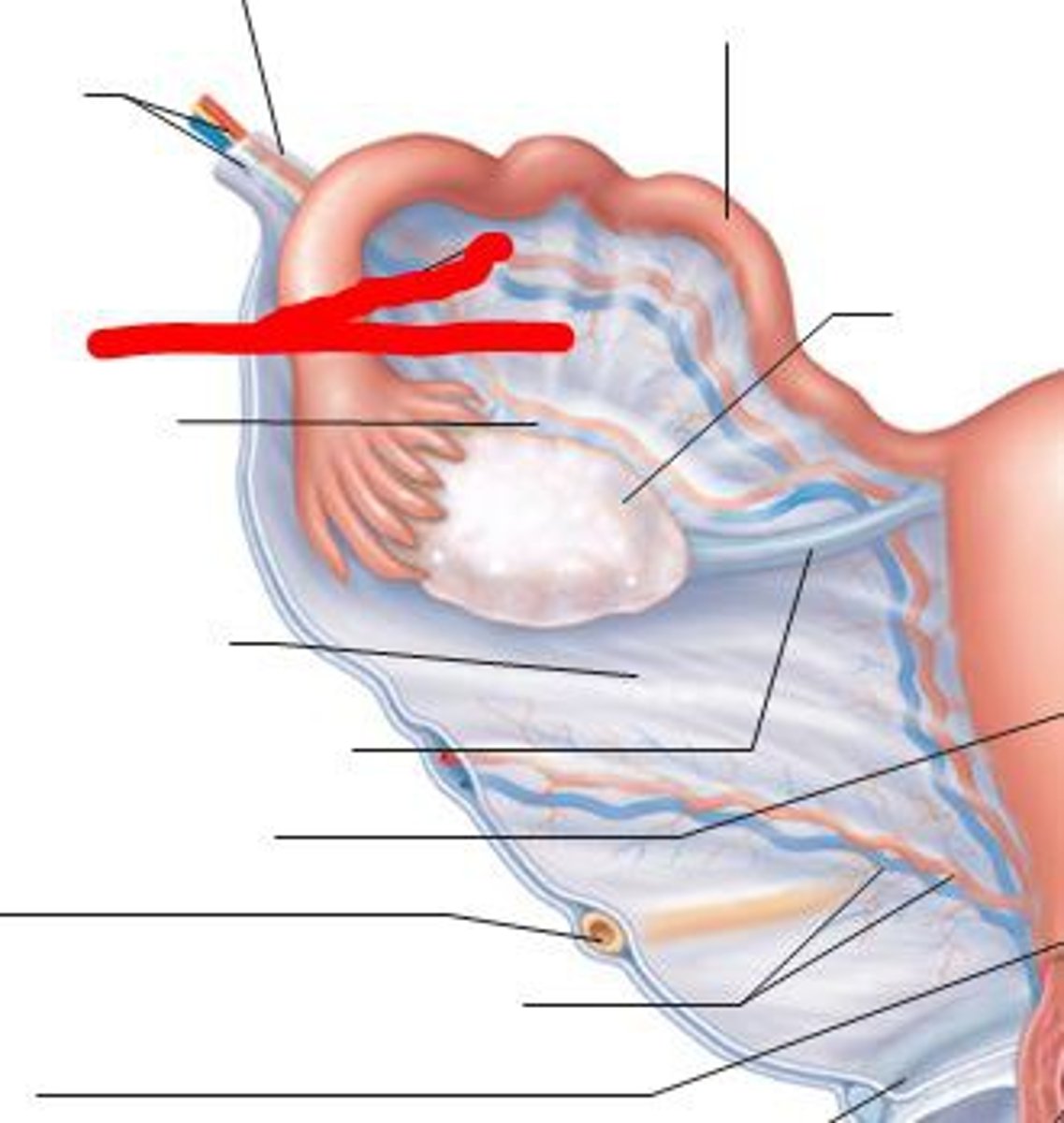
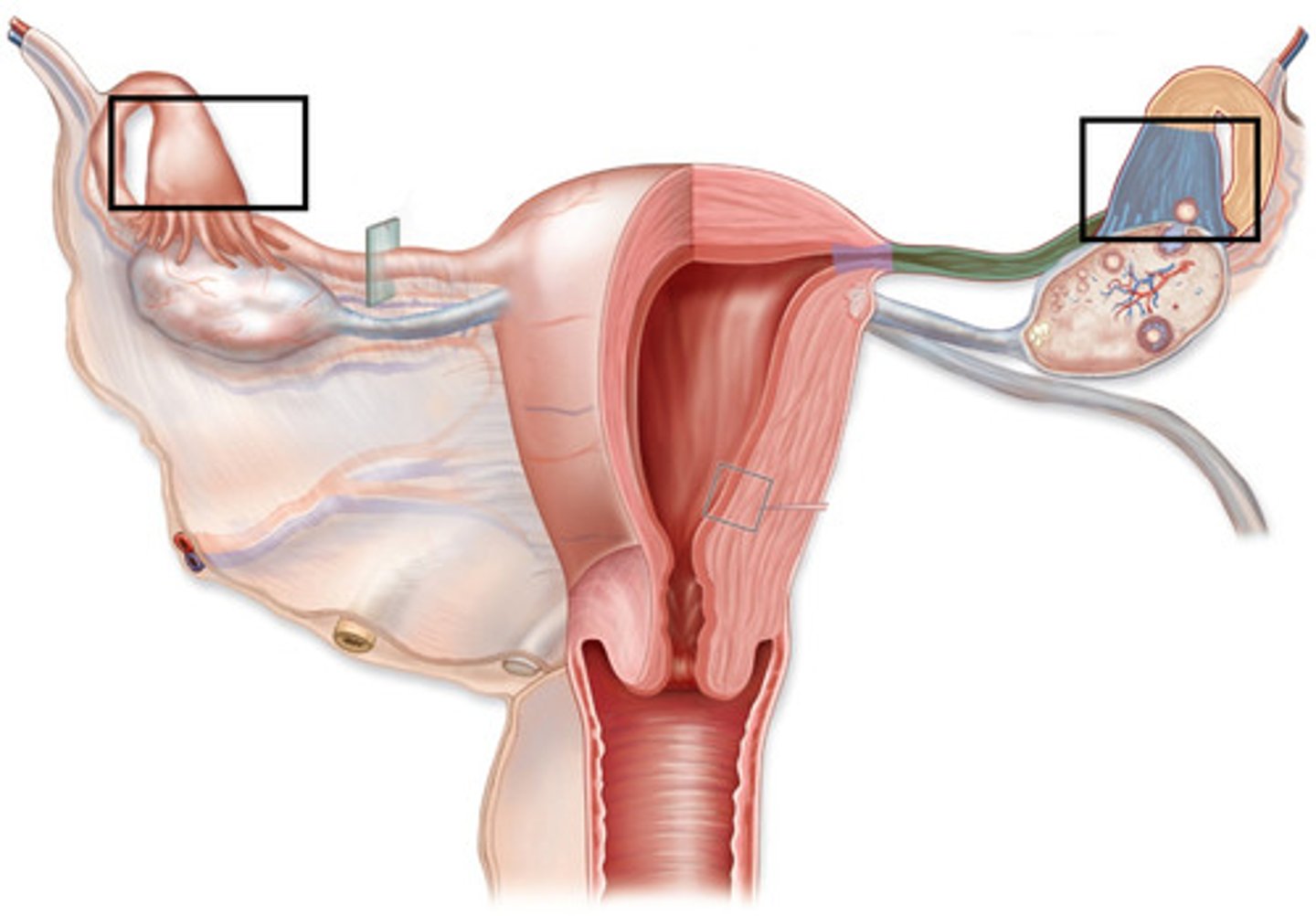
Tissue structures along oviduct
1. Infundibulum
2. Ampulla
3. Isthmus
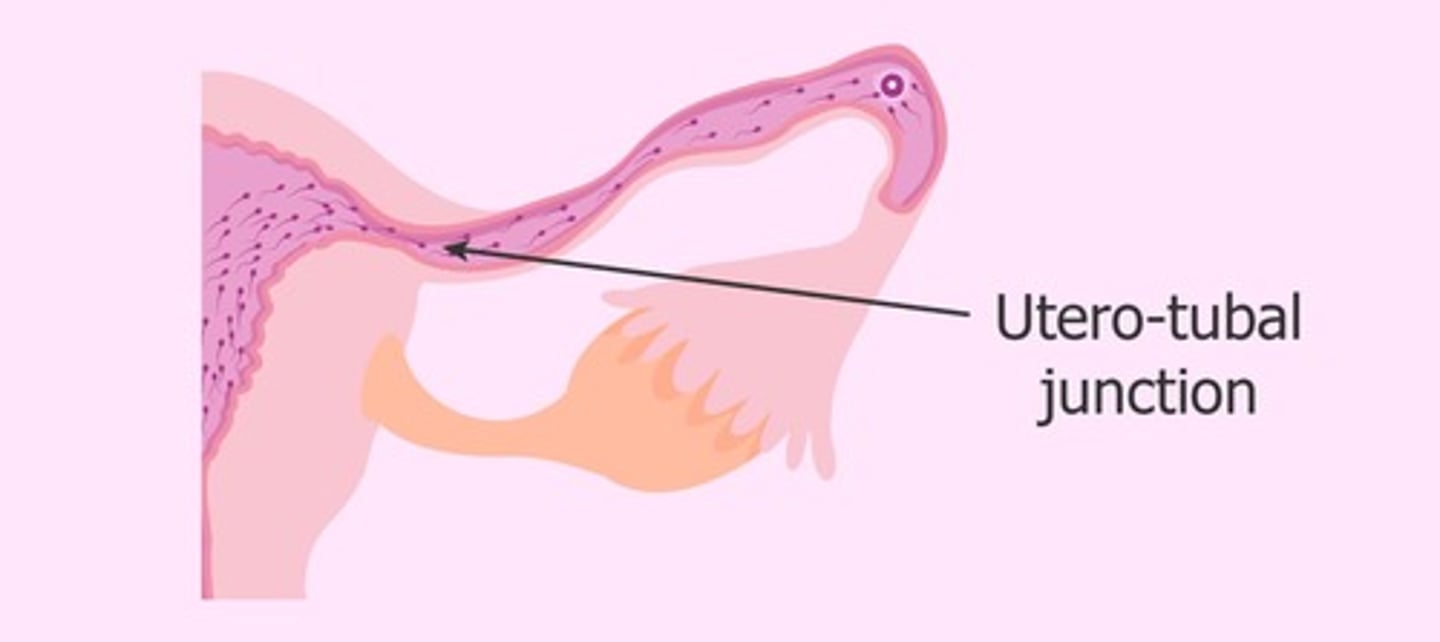
4. Uterotubal junction
Infundibulum
Funnel shape, with fimbria in lumen to cat ova
Ampulla
Site of fertilization (1/2 of the duct)
Isthmus
Thick walled and sperm reservoir
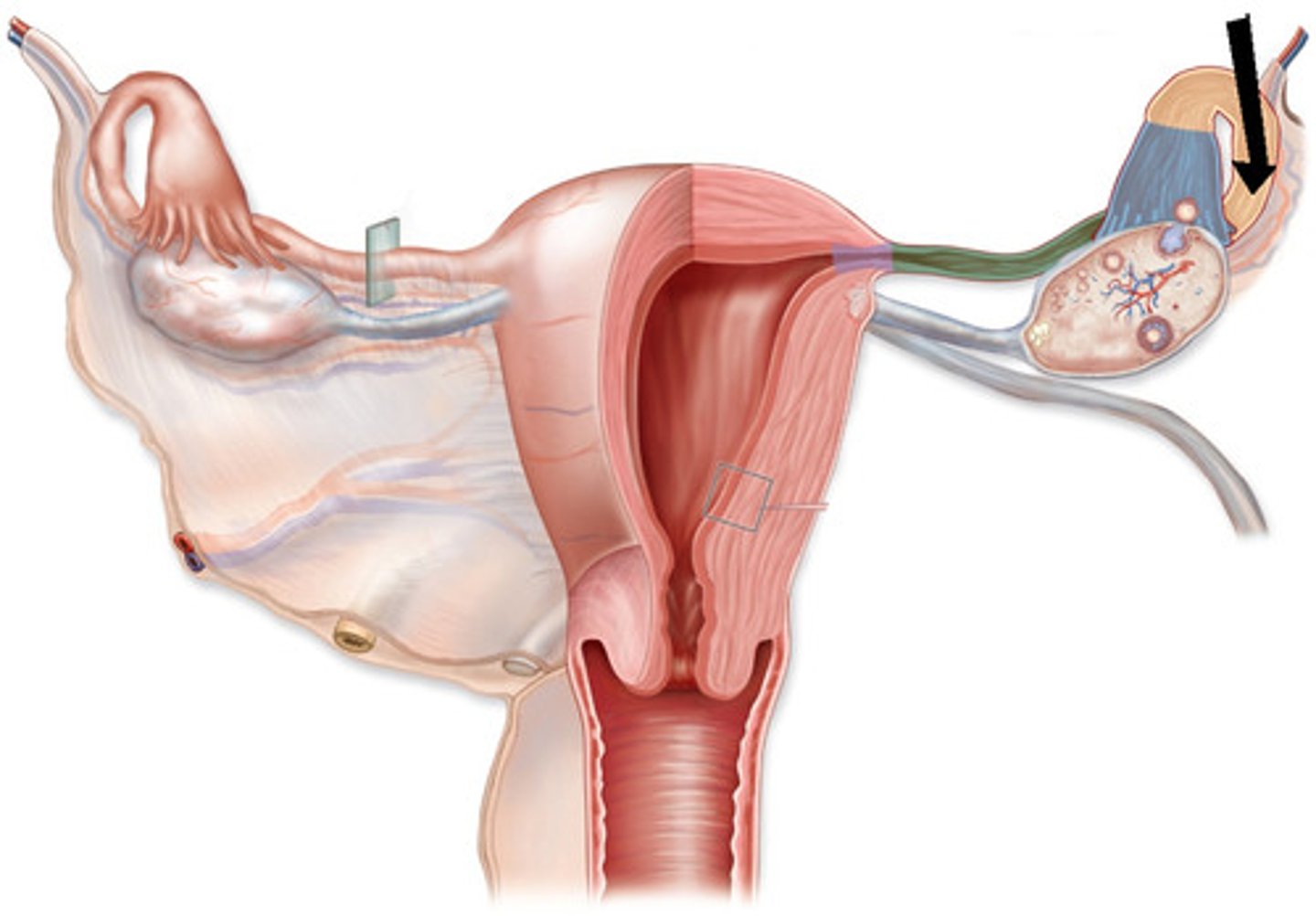
Uterotubal junction (restriction to entry)
Kinks in ruminants and constrict in other
Ovary
- Most species paired and functional
• Random ovulation
• Birds only left side is function
- Produces eggs and hormones
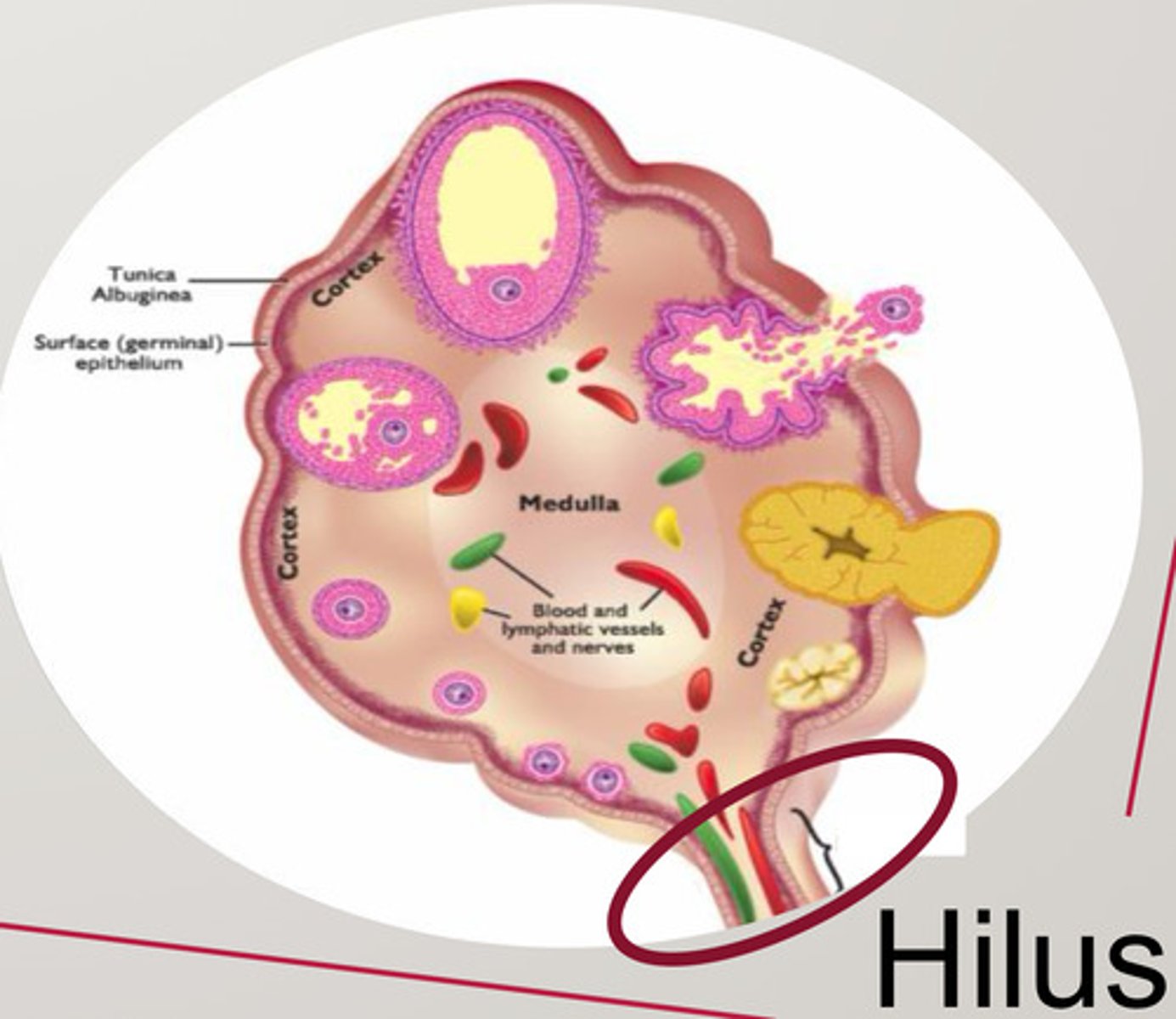
What are the ovary tissue layer
- Germinal epithelium
- Tunica albuginea
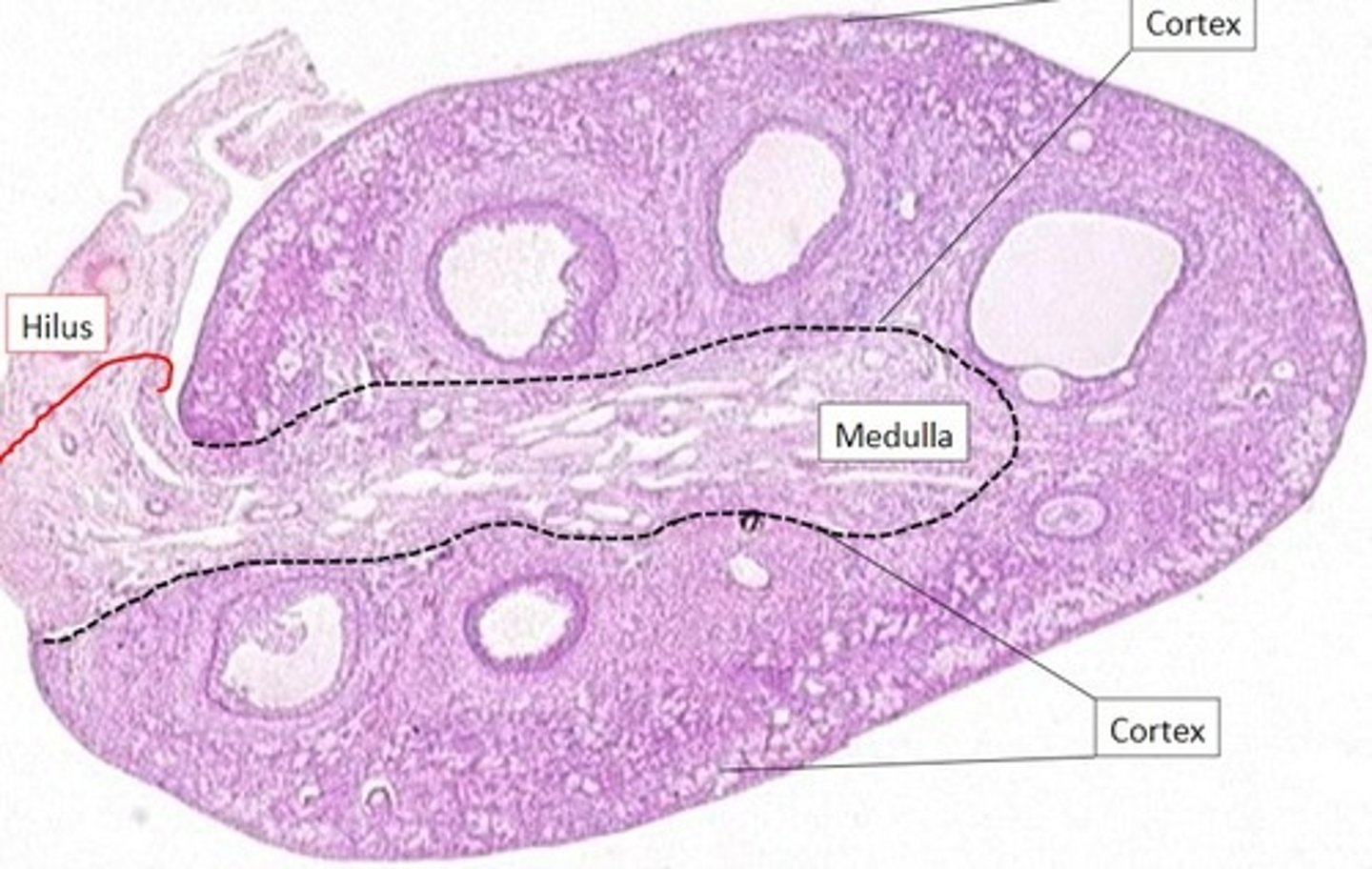
- Cortex-outer layer
- Medulla
- Hilus
Germinal epithelium
Single outer layer
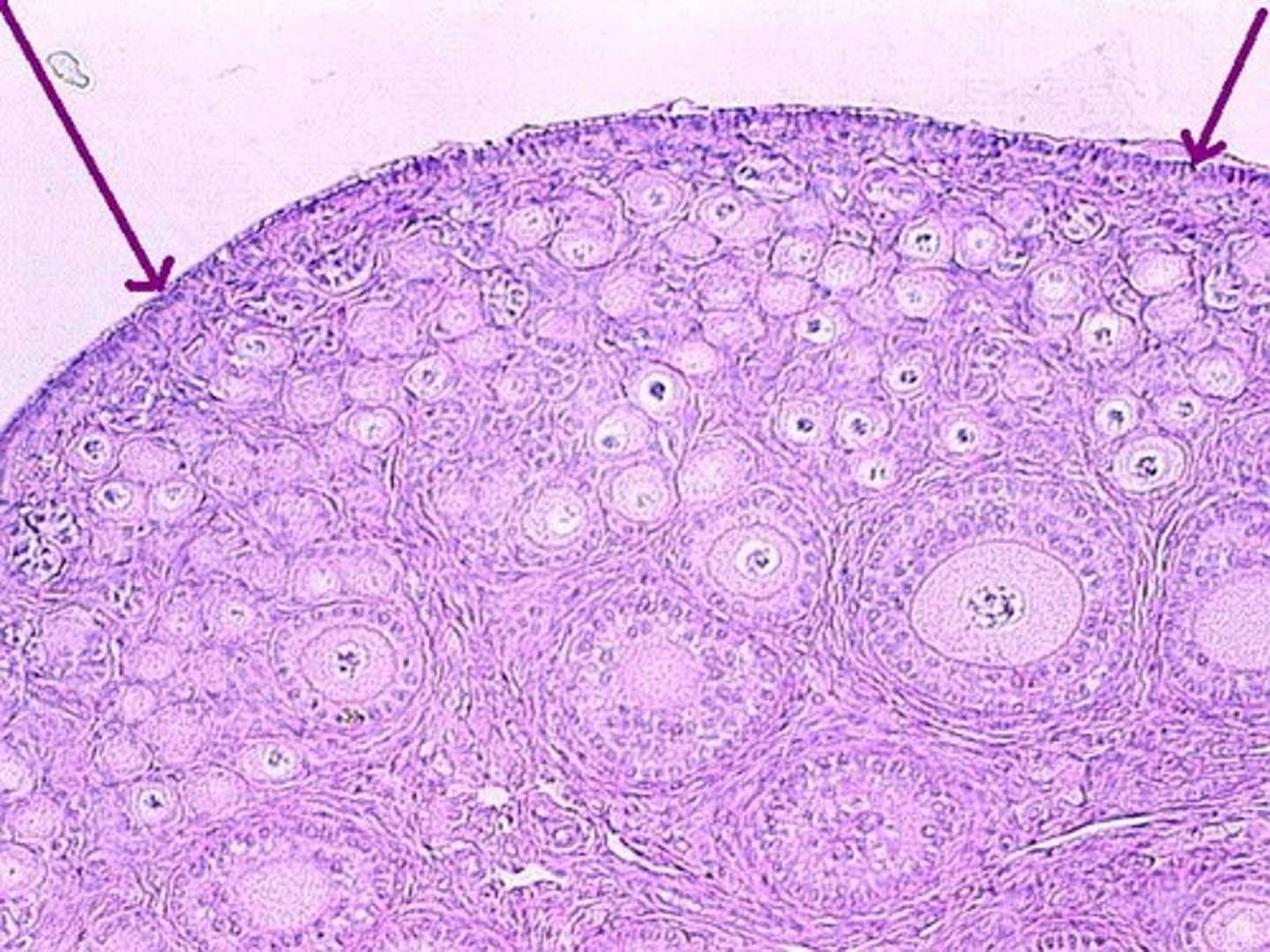
Tunica albuginea
Connective tissue layer
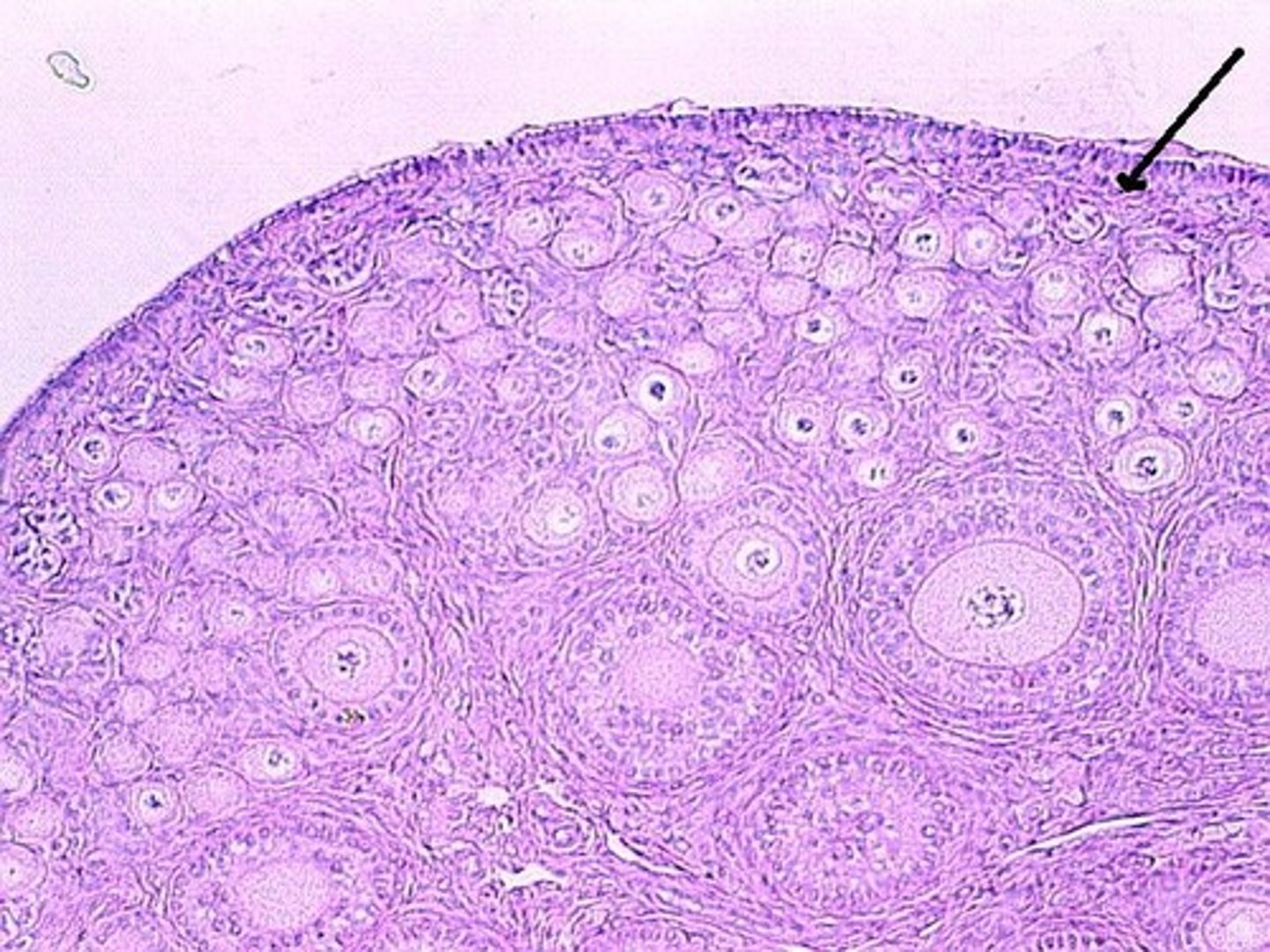
Cortex-outer layer
Follicles
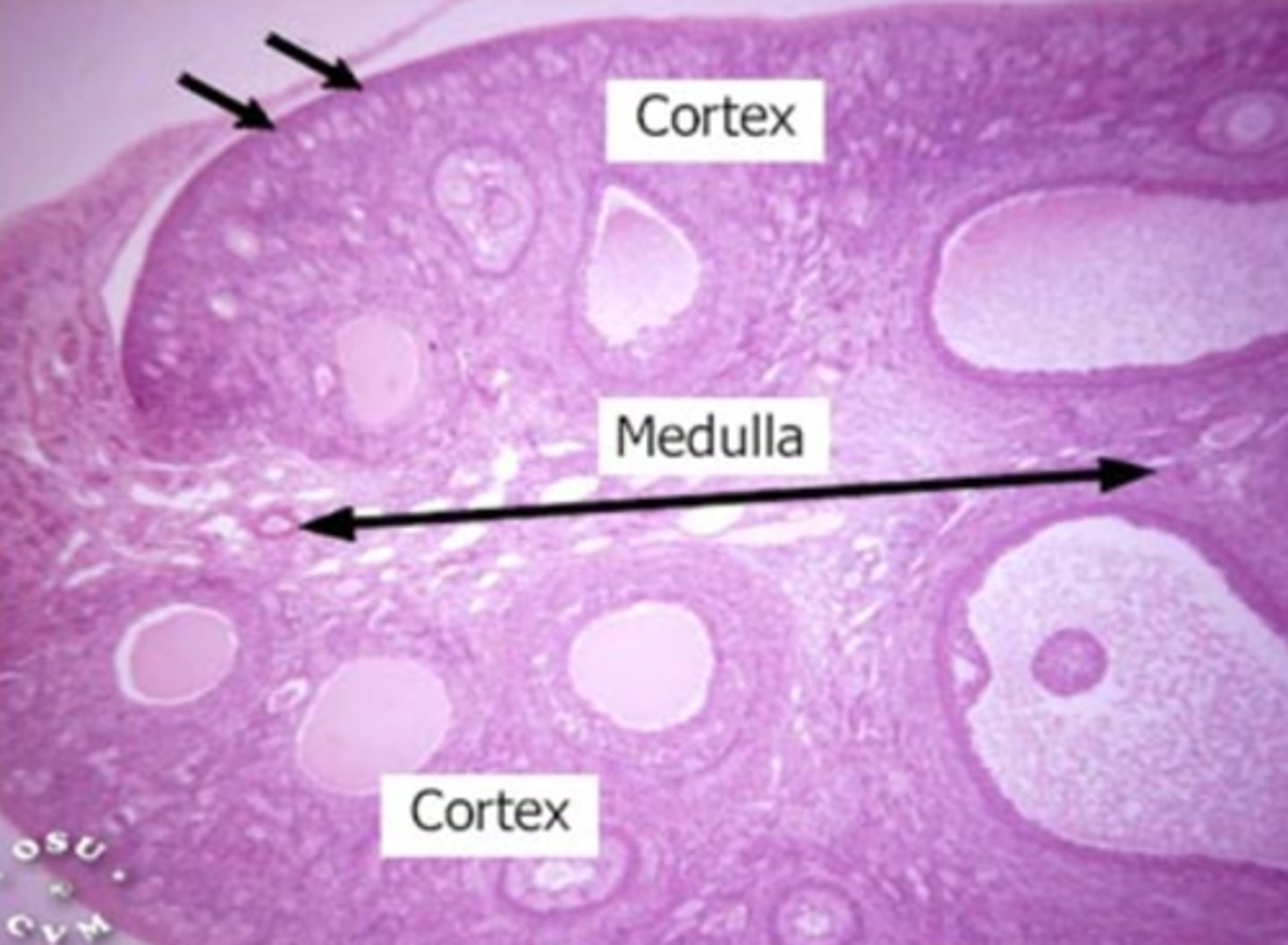
Medulla
Connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves
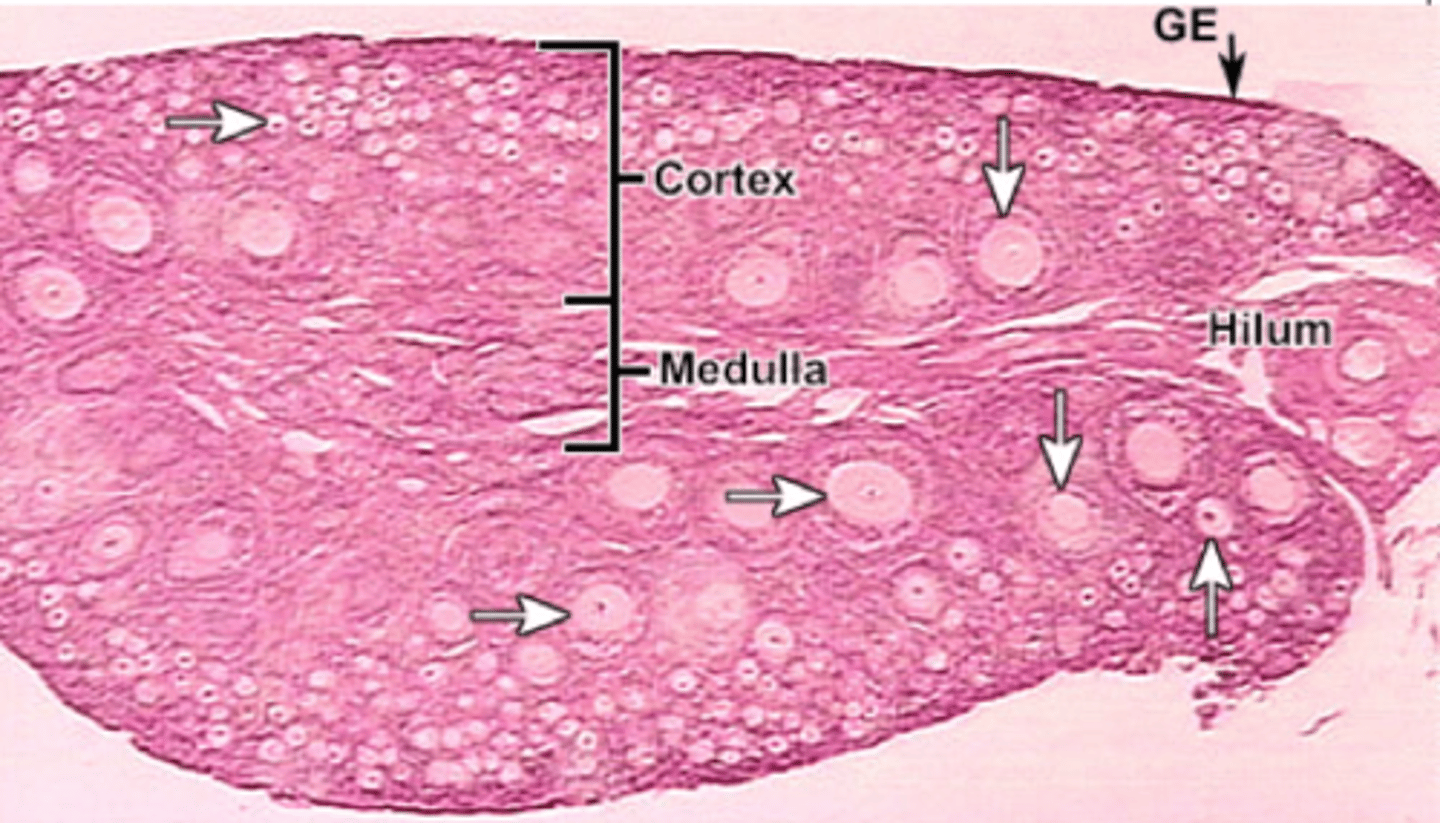
Hilus (ovary)
The opening on medial side of the ovary which leads into the renal sinus and through which the ovarian blood vessels and nerves enter/leave the ovary
Development of a follicle
- Most grow microscopically below tunica
- Primordial
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary/antral/graafian
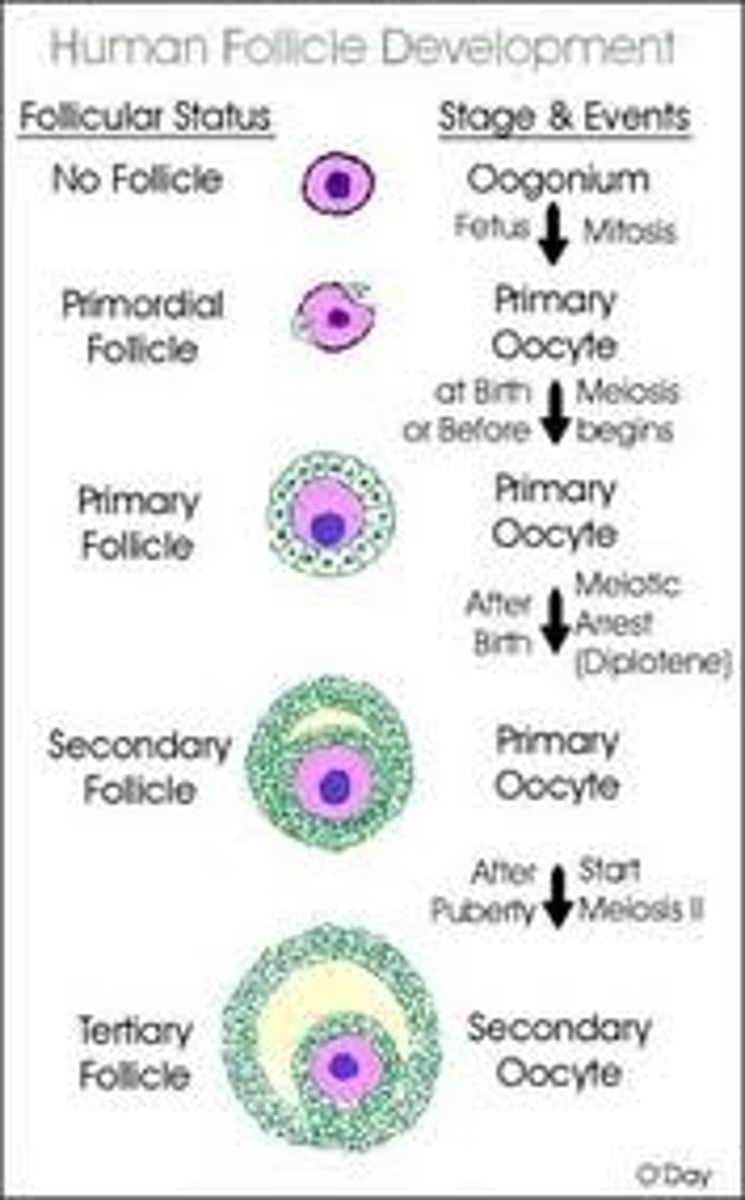
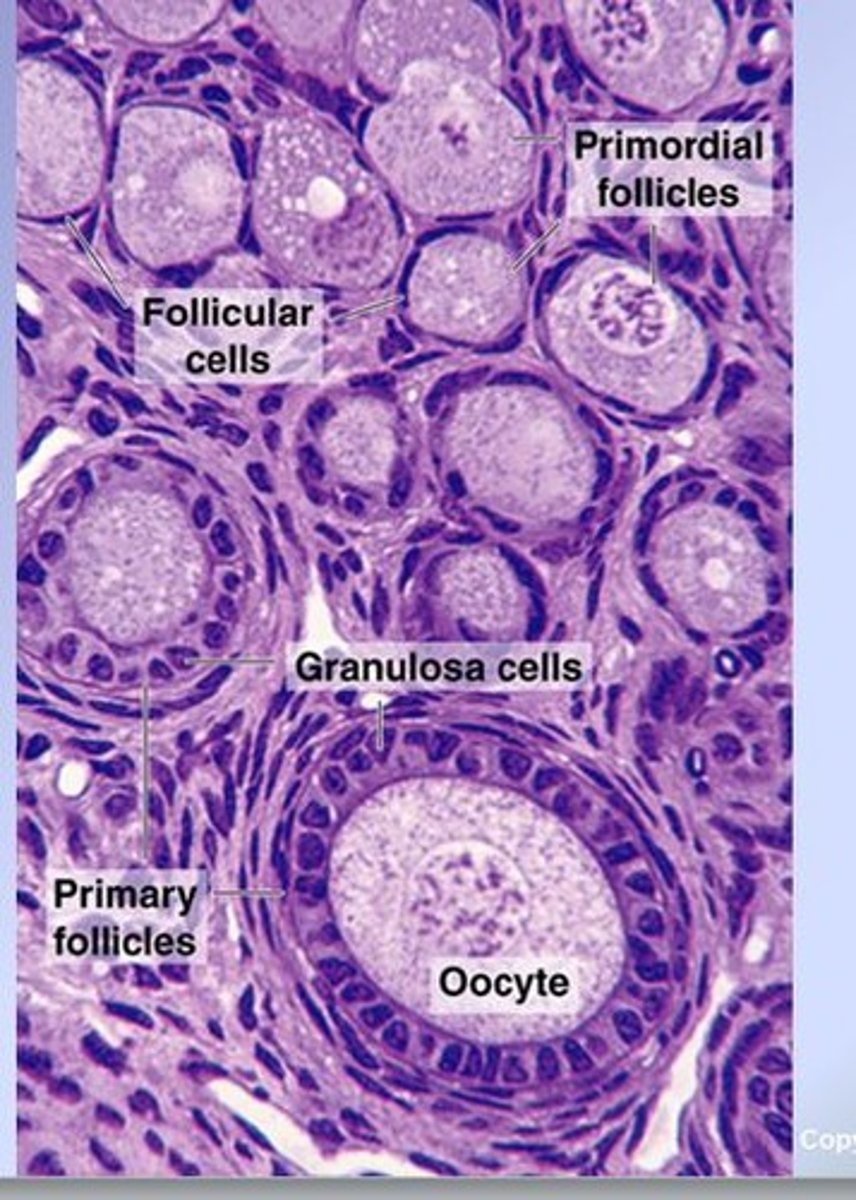
Primordial follicle
1-flat layer of cells/small oocyte
Primary follicle
1 expanded layer + small oocytes
Secondary follicle
- 2 layers
- No antrum
- Large oocyte
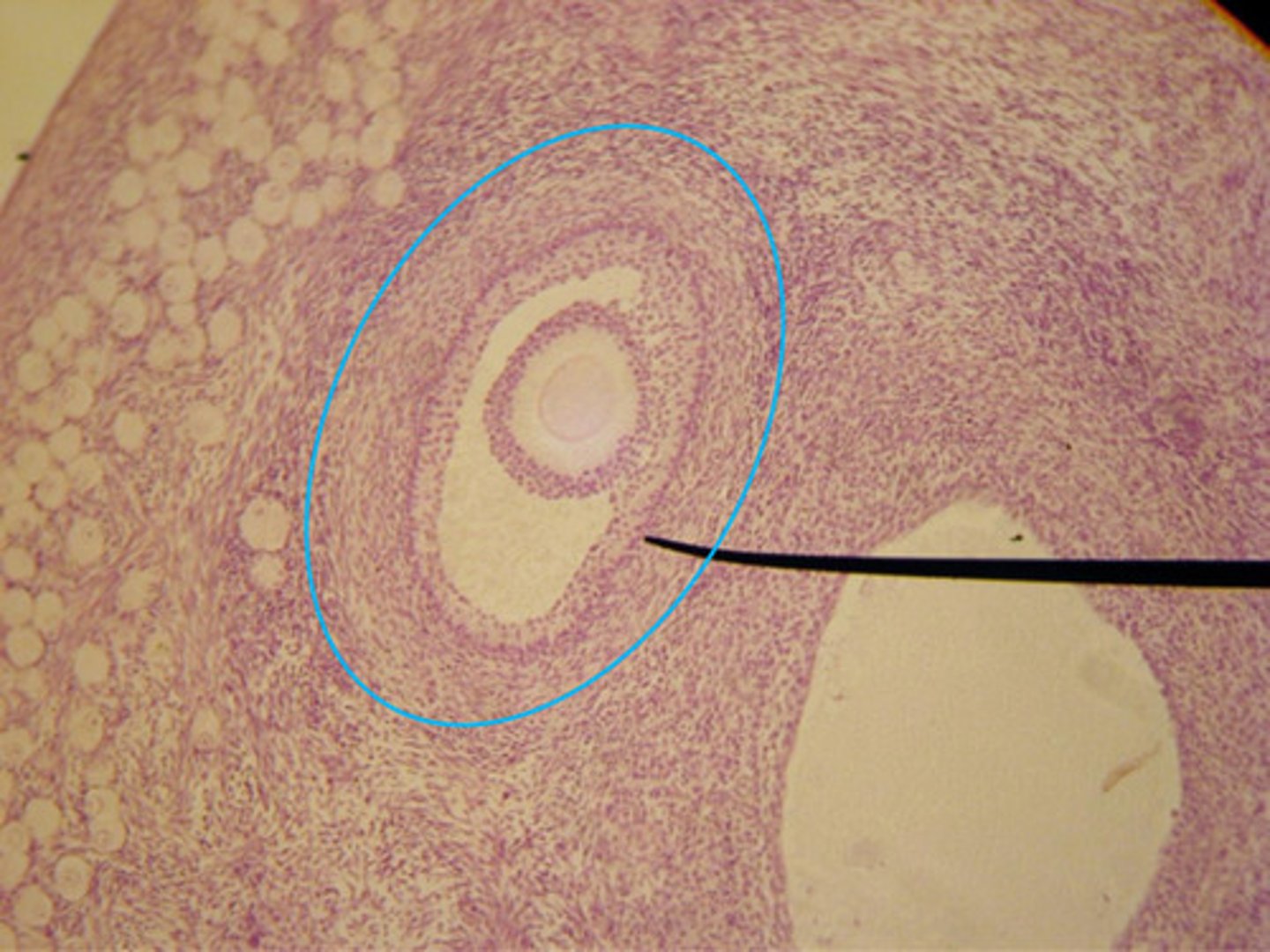
Tertiary/antral/graafian
- 3 or more layers + antrum
- Larger oocyte
- Depends upon hormones to grow
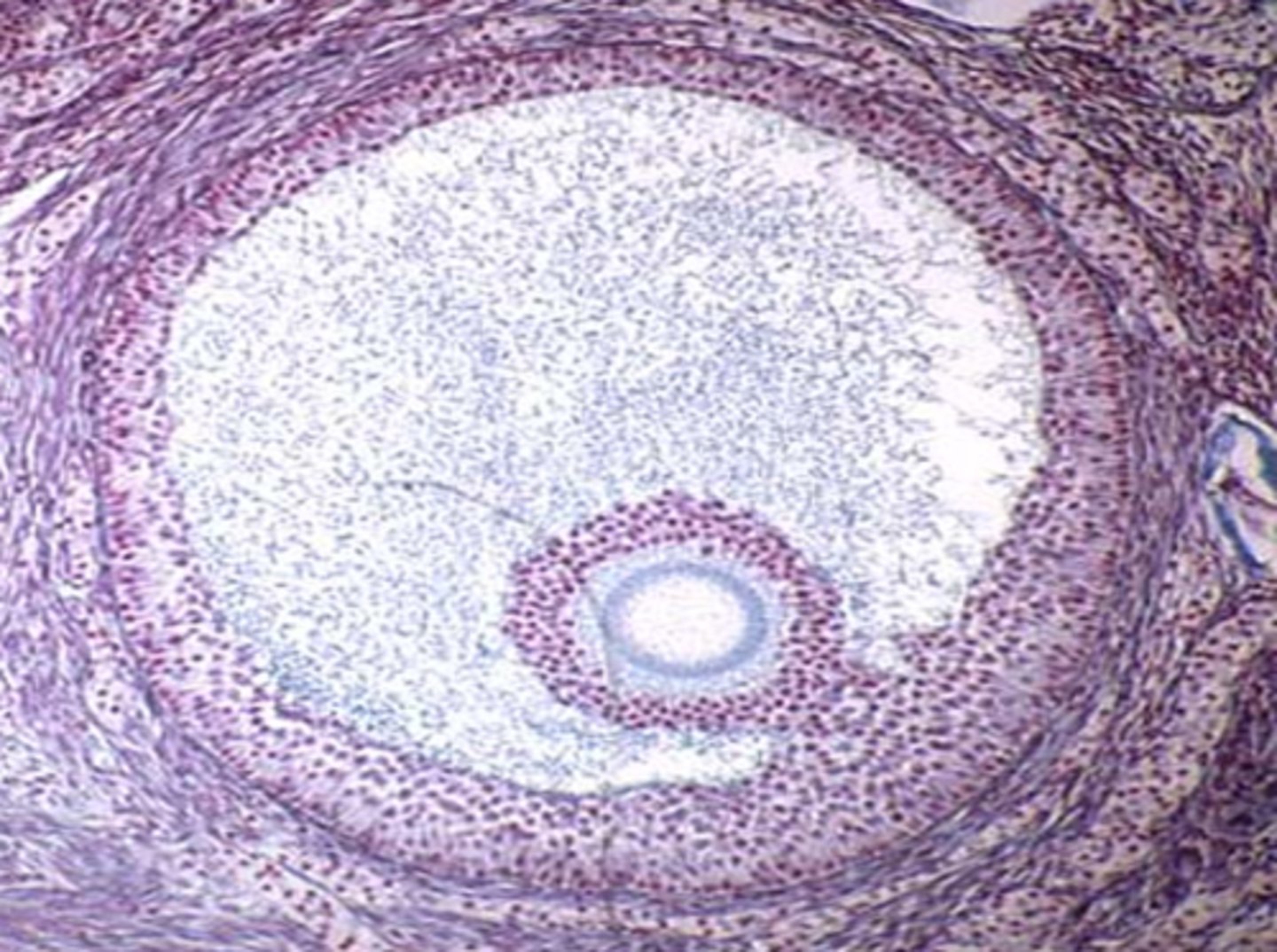
How is the life cycle of a follicle classified?
Size
- Small
- Medium
- Large: dominant: ovulatory
What size follicle would be most likely to ovulate?
Large or dominant follicle
What would form if a follicle is ovulated?
- Corpus Hemorrhagicum (LH)
- Corpus Luteum (CL)
- Corpus Albicans (CA)
What happens near the end of the trimester
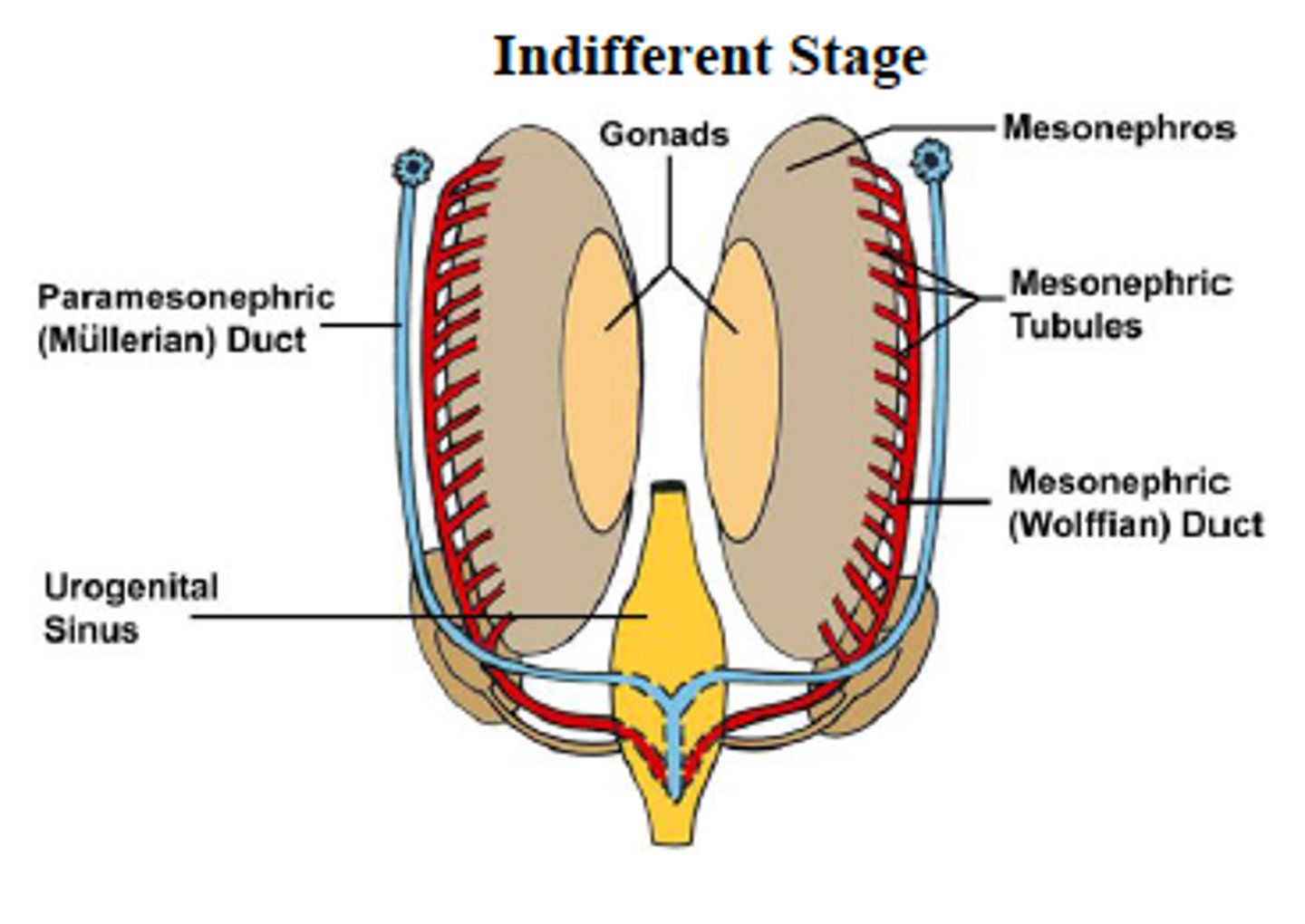
1. Germ cells migrate toward kidney, divide, & differentiate
2. In females mammals (XX) Mullerian ducts (ParaM) and ovaries begin to develop.
3. Degree/location of mullerian duct fusion during development determine uterine structure
What happens if there is a Y chromosome present?
The genes expressed and proteins produce will cause TESTES to form (TDF) and Mullerian ducts to regress (MIF)
Mullerian ducts
Paired tubes that develop into female reproductive organs.
TDF
Testes determining factor
MIF
Mullerian inhibiting factor
What different uterine structures that are created by degree/location of Mullerian duct fusion?
- Fusion high: simplex
- Fusion moderate: bicornuate
- Fusion low: duplex
What is the mullerian duct was fusion high?
Simplex uterine structure
What is the mullerian duct was fusion moderate?
Bicornuate uterine structure