Topic 6 - The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is the Rate of Reaction?
It is the rate of how fast the reactants are changed into products.
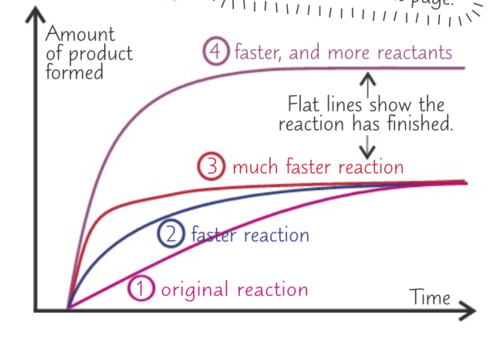
Describe a graph of rate of reaction?
See Image:
Explain Collision Theory?
Surface Area Increased (Smaller Pieces) = Greater SA : Volume = Greater area for collisions
Higher Concentration/Pressure = More Particles / cm³
Greater Temp = Particle Kinetic Energy Increase
Greater number of particles/cm³ or Kinetic Energy or Area for collisions, therefore increases number of successful collisions
How does a Catalyst affect Rate/Collisions?
A catalyst increases the rate of reaction by providing a pathway to particles with a lower activation energy.
What is the formula for Rate of Reaction?
Rate = Amount of Reactant used or Amount of Product formed / Time
What are three ways to measure rate?
Precipitation and Colour Change - Visual change for solution to cloud and block cross experiment. (Sodium Thiosulfate and HCL)
Change in Mass - Mass leaving from experiment measured regularly. (Magnesium and HCL)
Volume of Gas given off - Gas syringe measure gas given off.
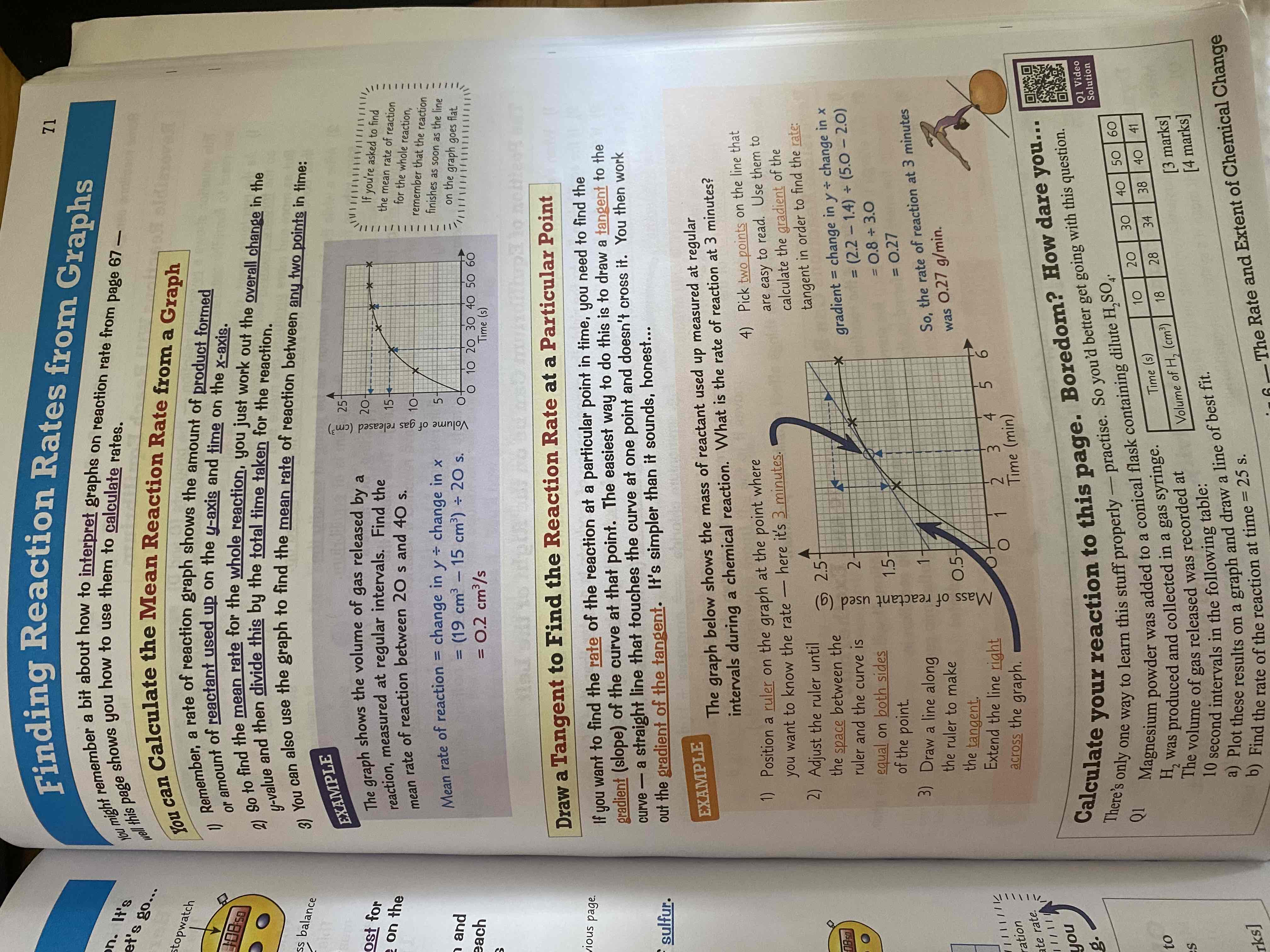
How to calculate the mean rate of reaction?
Graph Given
Change in Y / Change in X
Finding Rate of Reaction at a point using a tangent?
See Image:
What is a Reversible Reaction?
A reaction where the products can react again to make the reactants.
What is Equilibrium?
The point at which the rates of the forward and backward reactions in a reversible reaction are the same, and so the amounts of reactants and products in the reaction container don’t change. Only in a closed system.
What is Le Chatelier’s Principle?
It is the idea that if you change the conditions of a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the system will try to counteract the change.
What are 3 changes that can be counteracted?
Temperature - Equilibrium will move to decrease/increase it.
Pressure - Equilibrium will move to decrease(move to more molecules)/increase(move to less molecules) it.
Concentration - Equilibrium will move to increase reactants/products it.