P3.2.2 Refraction of light
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
What is refraction?
The change in direction of a light ray passing from one medium to another with a different optical density
Optically denser medium: light rays bend towards the normal, light travels slower
Optically less dense medium: light rays bend away from the normal, light travels faster
What is the refractive index?
How much a medium can refract light
Higher refractive index slows down light more
State the three equations you can use to calculate refractive index
Using speed of light: speed of light in a vacuum (3×108) / speed of light in a medium
Snell’s Law: n = sin (i) / sin (r) → you must know how to rearrange this
Using critical angle: n = 1/sinC → you must know how to rearrange this
What are the conditions needed for total internal reflection to occur?
Angle of incidence must be greater than critical angle
Light must travel from a more dense medium into a less dense medium
Light is always totally internally reflected in the denser medium
What is a critical angle?
When the angle of refraction equals 90° (only 90 not more), the incident angle is called critical angle
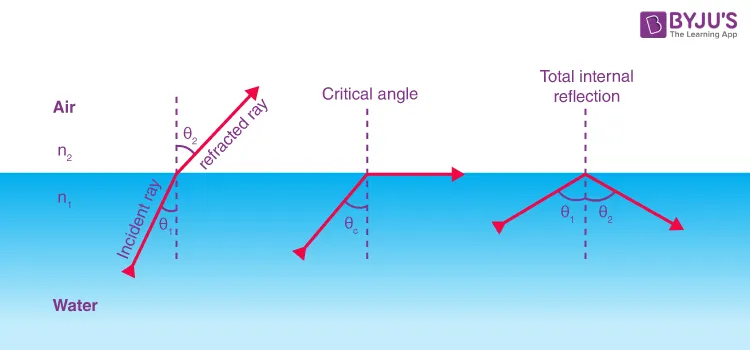
Describe applications for total internal reflection
Optical fibres: used in endoscopes and communication systems
Periscopes