A Level Biology, 3.5 - Energy Transfers in and Between Organisms
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Life depends on continuous transfers of energy. In photosynthesis, light is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is linked to the production of ATP. In respiration, various substances are used as respiratory substrates. The hydrolysis of these respiratory substrates is linked to the production of ATP. In both respiration and photosynthesis, ATP production occurs when protons diffuse down an electrochemical gradient through molecules of the enzyme ATP synthase, embedded in the membranes of cellular organelles. The process of photosynthesis is common in all photoautotrophic organisms and the process of respiration is common in all organisms, providing indirect evidence for evolution. In communities, the biological molecules produced by photosynthesis are consumed by other organisms, including animals, bacteria and fungi. Some of these are used as respiratory substrates by these consumers. Photosynthesis and respiration are not 100% efficient. The transfer of biomass and its stored chemical energy in a community from one organism to a consumer is also not 100% efficient. [AQA] :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
ATP Properties
Stores or releases only a small, manageable amount of energy at a time, so no energy is ___________________.
Small, ___________ molecule so it can be easily transported around the cell.
Easily broken down, so energy can be easily released ______________________.
Can be quickly remade.
Can make other molecules more reactive by transferring one of its phosphate groups to them (_________________).
Can’t pass out of the cell, so the cell always has an _________________ of energy.
wasted as heat / soluble / instantaneously / phosphorylation / immediate supply
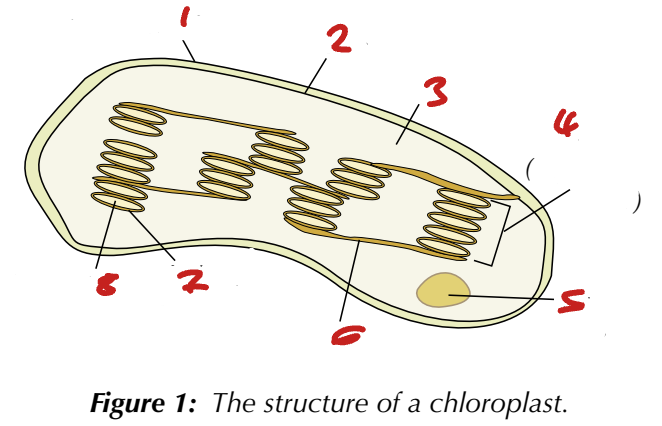
Name the Organelles of the Chloroplast (1→8)
outer membrane / inner membrane / stroma / granum (thylakoid stack) / starch grain / lamella / thylakoid membrane / thylakoid
What are the coloured substances that absorb light for photosynthesis? Where are they found? What are they called when attached to proteins?
photosynthetic pigments / thylakoid membranes / photosystem
What wavelength of light does PSI absorb the best?
700nm
What wavelength of light does PSII absorb the best?
680nm
Stroma
__________ substance contained within ___________________ & surrounding the _____________.
Contains ________________________________.
Carbohydrates that are produced by photosynthesis but not used straight away are stored as _____________ in the stroma.
gel-like / chloroplast inner membrane / thylakoids / enzymes, sugars & organic acids / starch grains
How does a coenzyme work? What is a coenzyme used in photosynthesis? What does this do in photosynthesis?
transfers chemical groups between molecules / NADP / REDOX by H transfer
What can reduced NADP be written as?
NADPH
Photosynthesis: The Light-Dependent Reaction
_______________________ (the process of adding phosphate to a molecule using light): making ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
______________________.
___________: the splitting of water into protons (H+), electrons + oxygen.
photophosphorylation / NADP reduction / photolysis
What is photophosphorylation, a process driven by energy in photosynthesis?
ADP + pi produce ATP
What is reduction, a process driven by energy in photosynthesis?
NADP produces NADPH
What is photolysis, a process driven by energy in photosynthesis?
splitting of water into protons, electrons + oxygen
Which two molecules are produced by the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis?
ATP + NADPH
Which 3 reactions in photosynthesis does energy from photoionisation drive?
photophosphorylation / NADP reduction / photolysis
What is the electron transport chain?
protein chain where excited electrons flow
What are the stages of non-cyclic photophosphorylation (in the light-dependent reaction)?
light energy excites electrons in chlorophyll / water photolysis / energy from excited electrons makes ATP then generates NADPH
Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reaction: Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation - Stage 1
________________ is absorbed by ______ which _____________ in chlorophyll.
The electrons move to a ______________.
These high-energy electrons are released from the chlorophyll and move down the ____________________ to the ____.
light energy / PSII / excites electrons / higher energy level / electron transport chain / PSI
Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reaction: Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation - Stage 2
As the _______________ from chlorophyll leave ____ to move down the electron transport chain, they must be replaced.
____________: light energy splits water into protons (H+), electrons & oxygen.
The reaction is: H2O →2H⁺ + ½ O2
excited electrons / PSII / photolysis
Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reaction: Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation - Stage 3
The excited electrons _________ as they move down the electron transport chain.
This energy is used to __________ (H+ ions) into the thylakoid so that the thylakoid has a higher concentration of protons than the stroma.
This forms a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
Protons move down their concentration gradient, into the stroma, via the enzyme __________, which is embedded in the thylakoid membrane.
The energy from this movement combines ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) to form ATP.
lose energy / transport protons / ATP synthase
What is the proton gradient between the thylakoid and stroma?
thylakoid has higher proton conc than stroma
Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reaction: Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation - Stage 4
_______________ is absorbed by _____, which excites the electrons again to an even higher energy level.
Finally, the electrons are transferred to NADP, along with a proton (H+ ion) from the stroma, to form ___________.
light energy / PSI / NADPH
What is process of chemiosmosis?
electrons flowing down ETC, creating proton gradient across membrane to drive ATP synthesis
Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reaction
Cyclic Photophosphorylation produces ___ and only uses _____.
It’s called ‘cyclic’ because the electrons from the chlorophyll molecule aren’t passed onto NADP, but are passed back to PSI via electron carriers.
ATP / PSI
What are the 3 stages of the Calvin cycle (light-independent reaction)?
glycerate 3-phosphate formation / triose phosphate formation / ribulose bisphosphate regeneration
Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reaction - Cyclic Photophosphorylation vs Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
Reaction produces…
__________ in cyclic.
__________ in non-cyclic.
Electrons….
______________ in cyclic (____________ doesn’t take place).
__________________ in non-cyclic.
ATP / ATP + NADPH / continuously recycled / photolysis / in PSII replaced by photolysis
Photosynthesis Light-Independent Reaction (The Calvin Cycle) - Stage 1: Formation of Glycerate 3-Phosphate
CO2 enters the leaf through the stomata and diffuses into the stroma of the chloroplast. Here, it’s combined with _______________.
Reaction is catalysed by the enzyme ________.
This gives an unstable ___________ compound, which quickly breaks down into two molecules of a __________ compound called glycerate 3-phosphate (GP).
ribulose bisphosphate / rubisco / 6-carbon / 3-carbon
What is carbon fixation?
CO2 + RuBP
Photosynthesis Light-Independent Reaction (The Calvin Cycle) - Stage 2: Formation of Triose Phosphate
_________________ (from the light-dependent reaction) provides energy to reduce the 3-carbon compound (GP) to a different 3-carbon compound _________________.
This reaction also requires ___, which come from ______ (also from the light-dependent reaction).
Reduced NADP is recycled to NADP.
Some triose phosphate is then converted into useful organic compounds (e.g. glucose) and some continues in the Calvin cycle to ______________________.
ATP hydrolysis / triose phosphate / H+ / NADPH / regenerate RuBP
Photosynthesis Light-Independent Reaction (The Calvin Cycle) - Stage 3: Regeneration of Ribulose Bisphosphate
____ molecules of TP produced in the cycle aren’t used to make useful organic compounds, but to regenerate RuBP.
Regenerating RuBP uses the rest of the ATP produced by the light-dependent reaction.
5/6
What is glucose made by the joining of?
2 triose phosphate molecules
How & what are lipids synthesised from in the Calvin cycle?
fatty acids - glycerate 3-phosphate / glycerol - triose phosphate
What are some of the coenzymes used in respiration & which chemical group do they transfer?
NAD - hydrogen / coenzyme A - acetate / FAD - hydrogen
What are the stages in aerobic respiration?
glycolysis / link reaction / Krebs cycle / oxidative phosphorylation
Anaerobic Respiration
Which type takes place in plants & yeast?
Which type takes place in animals?
ethanol fermentation / lactate fermentation
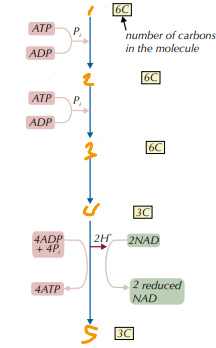
Label the Products in the Process of Glycolysis (1→5)
glucose / glucose phosphate / hexose bisphosphate / 2 triose phosphate / 2 pyruvate
Respiration - Stage 1: Glycolysis
Glucose is ________________ using a phosphate from a molecule of ATP. This creates 1 molecule of ________________________ and 1 molecule of ______.
ATP is then used to add another phosphate, forming _____________________.
This is then split into ________________________.
This is _______________ (loses hydrogen), forming ___________________.
________ collects the H+, forming ________________.
4 ATP are produced, but 2 were used up during phosphorylation, so there’s a net gain of ________.
phosphorylated / glucose phosphate / ADP / hexose bisphosphate / 2 triose phosphate / oxidised / 2 pyruvate / NAD / 2 NADH / 2 ATP
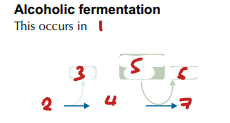
Label the Process of Alcoholic Fermentation Post-Glycolysis (1→7)
plants & yeast / pyruvate / CO2 / ethanal / NADH / NAD / ethanol
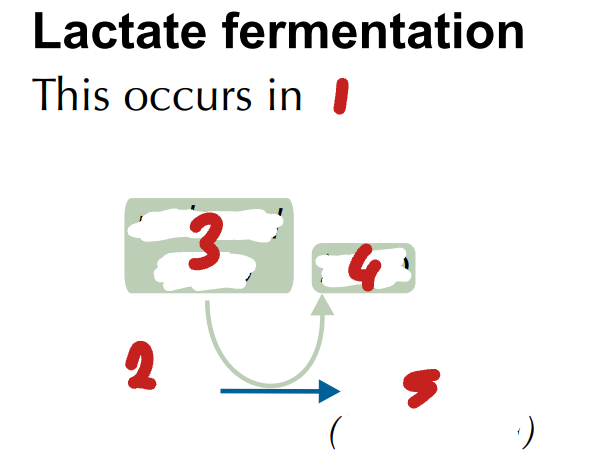
Label the Process of Lactate Fermentation Post-Glycolysis (1→5)
animals & some bacteria / pyruvate / NADH / NAD / lactate (lactic acid)
In aerobic respiration, where do the ___ ______ from glycolysis go?
2 NADH / oxidative phosphorylation
In aerobic respiration, where do the ___ __________ from glycolysis go?
2 pyruvate / actively transported into mitochondrial matrix for link reaction
In aerobic respiration, where does ___ ______ (net gain) from glycolysis go?
2 ATP / used for energy
In order, what are the products of glycolysis’s reactions?
ADP / 6C / ADP / 6C / 2 3C / 4 ATP / 2 NADH / 2 3C
Aerobic Respiration - Stage 2: The Link Reaction
_________________ (from glycolysis) is __________________, so one carbon atom is removed in the form of CO2.
At the same time, the starting molecule is oxidised to form ____________ & _____________________.
This is then combined with ____________________ to form _____________________.
No ______ is produced in this reaction.
Two pyruvate molecules are made for every glucose molecule that enters glycolysis.
This means the link reaction and the Krebs cycle happen _________ for every glucose molecule.
pyruvate / decarboxylated / acetate / NAD reduced / coenzyme A / acetyl coenzyme A / ATP / twice
In aerobic respiration, where do the ___ ________ ______________ ___ from the link reaction go?
2 acetyl coenzyme A / Krebs cycle
In aerobic respiration, where do the ___ ________ ______________ from the link reaction go?
2 carbon dioxide / released as waste product
In aerobic respiration, where do the ___ ______ from the link reaction go?
2 NADH / oxidative phosphorylation
In order, what are the products of the link stage’s reactions?
CO2 + NADH + 2C / acetyl CoA
Aerobic Respiration - Stage 3: The Krebs Cycle
__________________________ (from link reaction) combines with __________________ to form 6C citrate.
Coenzyme A goes back to the link reaction to be used again.
6C citrate converted to 5C molecule. _______________ (H used to ___________________) & __________________ (CO2 removed) occur.
5C molecule is then converted to 4C oxaloacetate.
Decarboxylation and dehydrogenation occur, producing __________________.
_______________________: ATP produced by the direct transfer of a phosphate group from an intermediate compound to ADP.
acetyl coenzyme A / 4C oxaloacetate / dehydrogenation / reduce NAD / decarboxylation / FADH2 + 2NADH / substrate-level phosphorylation
In aerobic respiration, where does the ___ ________________ ____ from the Krebs cycle go?
1 coenzyme A / reused in next link reaction
In aerobic respiration, where do the _______________ from the Krebs cycle go?
oxaloacetate / regenerated for next Krebs cycle
In aerobic respiration, where do the ____ C____ from the Krebs cycle go?
2 CO2 / released as waste
In aerobic respiration, where does the ____ A____ from the Krebs cycle go?
1 ATP / energy
In aerobic respiration, where do the ____ ______ from the Krebs cycle go?
3 NADH / oxidative phosphorylation
In aerobic respiration, where does the ____ ______ from the Krebs cycle go?
1 FADH2 / oxidative phosphorylation
In order, what are the products of the Krebs cycle’s reactions?
CoA + 6C / CO2 + NADH + 5C / CO2 + 2NADH + ATP + FADH2 + 4C
Aerobic Respiration - Stage 4: Oxidative Phosphorylation
H released from NADH + FADH2 as they’re oxidised. H split into protons (H+) & electrons.
Electrons move down the ___________________, losing energy at each carrier.
Energy used by the ________________ to pump protons from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space.
_______________________ formation: proton concentration is now higher in the ______________________ than in the mitochondrial matrix.
Protons then move down this, back across the inner mitochondrial membrane and into the mitochondrial matrix, via _______________ ( embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane). This movement drives the synthesis of ATP from ADP and pi.
_____________________: ATP production driven by the movement of H+ across a membrane (due to electrons moving down an electron transport chain).
In the mitochondrial matrix, at the end of the transport chain, the protons, electrons and oxygen (from the blood) combine to form water. Oxygen is said to be the _____________________.
electron transport chain / electron carriers / electrochemical gradient / intermembrane space / ATP synthase / chemiosmosis / final electron acceptor
Aerobic Respiration - ATP
How many ATP molecules can be made from 1 molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration?
How many are made from each NADH?
How many are made from each FADH2?
For each molecule of glucose, how many molecules of ATP are produced by oxidative phosphorylation?
32 / 2.5 / 1.5 / 28
How are organic molecules produced by the plant used?
respiratory substrates / making other biological molecules
What does calorimetry do?
burns biomass / determines chemical energy released per gram
What is gross primary production?
total amount of chemical energy converted from light energy by plants in given area
What is productivity?
biomass generation rate in ecosystem
What is the equation for net secondary production?
energy in ingested food - energy lost in faeces, urine & production
Approximately how many trophic levels can food chains support? Why is this?
4-5 / very low net production at top of food chain
What are the 4 stages of the nitrogen cycle?
nitrogen fixation / ammonification / nitrification / denitrification
Nitrogen Cycle - Saprobiont Nutrition
_______________________: secrete enzymes onto the __________________.
The enzymes break down large, insoluble molecules into smaller, soluble molecules.
These smaller molecules can then be _______________ by the saprobiont.
The saprobiont will then either store the molecules or use them in ______________.
extracellular digestion / dead organic matter / absorbed / respiration
What briefly happens in nitrogen fixation?
N2 reduced by adding H2 to form ammonia, catalysed by nitrogenase enzyme
Nitrogen Cycle - Nitrogen Fixation (Stage 1)
Atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted to ammonia (NH3) by _______________ in the soil.
Bacteria (e.g. Rhizobia) form a _______________ relationship with leguminous plants by inhabiting their _______________.
Leguminous plants (e.g. alfalfa, peas, beans) are a family of plants.
The bacteria provide a source of ammonium ions for the plants and the plant provides sugars.
nitrogen-fixing bacteria / mutualistic / root nodules
What briefly happens in ammonification?
amino acid breakdown into ammonium compounds that form ions in soil
Nitrogen Cycle - Ammonification (Stage 2)
When an organism dies or produces waste (e.g. faeces), it is _________________ by saprobionts.
This releases the nutrients contained inside.
Saprobionts decompose the organisms' biomass by ________________________ and _________________________ are released into the soil.
Ammonification is a by-product of saprobiont nutrition.
decomposed / extracellular digestion / inorganic ammonium ions
What briefly happens in nitrification?
ammonium compounds oxidised to nitrates in 2 stages
Nitrogen Cycle - Nitrification (Stage 3)
Nitrifying bacteria (e.g. Nitrosomonas) firstly convert ammonium ions (from ______________________) to _____________ by ________________.
Another bacteria (e.g. Nitrobacter) then convert these to ___________.
ammonification / nitrites / oxidation / nitrates
What briefly happens in denitrification?
nitrates converted into N2 by anaerobic bacteria
Nitrogen Cycle - Denitrification (Stage 4)
Denitrifying ____________ convert ______________ in soil back into atmospheric nitrogen (N2).
This takes place in ________________ conditions (e.g waterlogged soils).
bacteria / nitrates / anaerobic
Phosphorus Cycle - Mycorrhizae
Fungi that form ____________________ with the roots of plants. Help plants absorb inorganic ions and water from the soil.
The fungi associate with the roots using ___________, long strands that extend from the _______________. These increase the _______________ of the _______________ to help plants take up ions that are in short supply (e.g. phosphorus) and water at a faster rate.
symbiotic relationships / hyphae / cell body / surface area / plant root system
Phosphorus Cycle
Phosphate ions are ______________ by plants because of the symbiotic relationship between the plant roots and mycorrhizae.
Mycorrhizae help to increase the rate of phosphate ion uptake.
As phosphate ions are transferred through the food chain, they are lost as waste products or when an organism dies.
_________________ decompose waste and dead organisms through ___________________.
Phosphate ions are released into the soil and can be ___________ for reuse in the cycle.
assimilated / saprobiants / extracellular digestion / recycled
What is guano?
waste produced by sea birds which contains high K+ proportion
What are hyphae?
long strands that extend from mycorrhizae that increase surface area
Using Fertilisers
Adding fertiliser replaces the lost minerals, so more energy from the ecosystem can be used for growth, increasing the efficiency of energy transfer.
Fertilisers can be artificial or natural.
Artificial fertilisers are _____________ - contain pure chemicals (e.g. ammonium nitrate) as powders or pellets.
Natural fertilisers are ________________ - include manure, composted vegetables, crop residues (the parts left over after the harvest) and sewage sludge.
inorganic / organic
What is leaching?
mineral salts being removed from soil by rain or ground water
What is eutrophication?
excess mineral buildup in lakes which causes algal blooms, killing larger aquatic organisms
Eutrophication
Mineral ions leached from fertilised fields stimulate the rapid growth of algae in ponds and rivers (_________________).
Large amounts of algae block ________ from reaching the plants below which leads to death because they’re unable to _________________ enough.
Bacteria feed on the _________________. The increased numbers of bacteria reduce the _________________ in the water by carrying out _________________.
Fish and other aquatic organisms die because there isn’t enough dissolved oxygen.
algal bloom / light / photosynthesise / dead plant matter / oxygen conc / aerobic respiration
Is eutrophication more likely to be caused by phosphorus or nitrates? Why?
nitrates / more soluble in water