working memory model (WMM)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
summarise the case study of KF - Shallice and Wallington (1970)
motorcycle accident, resulting in brain damage to his left occipital lobe
STM damaged (digit span of 1) but LTM normal
remembered words better if presented visually rather than auditorily
how is the case study of KF evidence to support the WMM?
remembered words better if presented visually rather than auditorily
highlights that there are separate STM components for visual information: visuo-spatial sketchpad and verbal information: phonological loop
who proposed the WMM?
Baddeley and Hitch (1974)
describe/draw the structure of WMM:
central executive transfers information between 3 subsystems: phonological loop, episodic buffer and visuo-spatial sketchpad
phonological loop can be /ed into articulatory control system and phonological store
visuo-spatial sketchpad can be /ed into inner scribe and visual cache
subsystems transfer information to long term storage memory
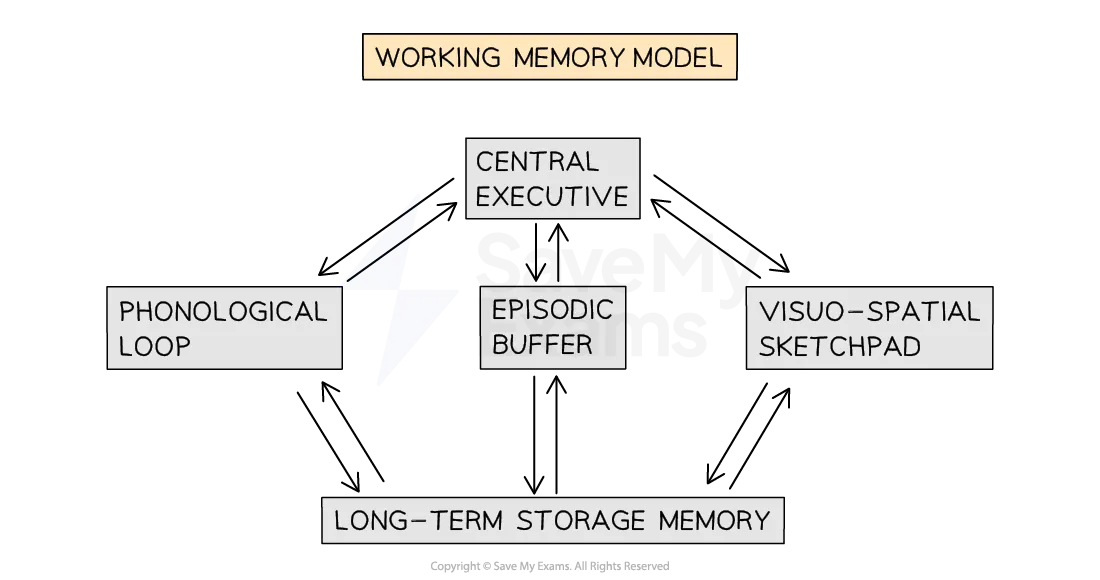
what is the function of the central executive?
directs attention to other tasks
controls other systems by determining how resources will be allocated
what is the function of the visuo-spatial sketchpad?
processes visual and spatial info (how things look and where they are)
further sub/ed into a visual cache and inner scribe
what is the function of the episodic buffer?
general store - added later to the model (2000) to account for things that use both visual and acoustic info
what is the function of the phonological loop?
controls auditory info
further sub/ed into phonological store (inner ear) and articulatory process (inner voice)
summarise Baddeley et al. (1975) - what does it suggest about WMM?
ppts carried out a visual and verbal task simultaneously
performance on each similar to when carried out separately
but when both tasks visual/verbal, performance on both declined
→ reinforces existence of phonological loop and visuo-spatial sketchpad
give 3 strengths of WMM:
research support - Baddeley et al. (1975)
not a unitary store
explains STM as an active process (compared to MSM - passive)
give a limitation of WMM:
we know very little about CE and EB - very difficult to test