evolution test 1: intro
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
evolution
Change in the properties of groups of organisms over generations
define groups of organisms in terms of evolution
evolution is a property of populations, not individuals
what does “over generations” mean in terms of evolution
does not occur within a single organism in its lifetime – change is heritable
early evolutionary thought (specifically Aristotle)
How did they rank it?
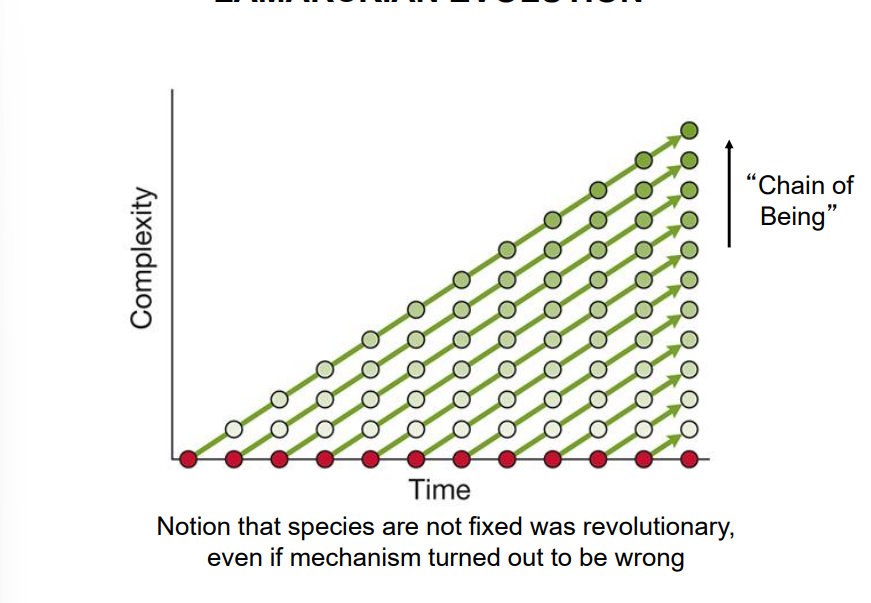
that life’s diversity was arranged in a “scale of nature” or Great Chain of Being.
-– Ranking; gradation from minerals through plants, “lower” animals, humans & other spiritual beings
Linnaeus established
– Established modern taxonomy to describe diversity of life
– Groupings based on similarity
– Nested hierarchy describing relationships of organisms
e Enlightenment led to
modern science
from the enlightenment, geologists found…
• The earth was very old
• It had undergone dramatic (but gradual) changes
• Many creatures have gone extinct
• Different rock layers contain distinct fossils
• Rock layers can be aged
Chevalier de Lamarck
who was he and what did he create?
– Philosophie Zoologique (1809)
– 1 st coherent theory of organic evolution
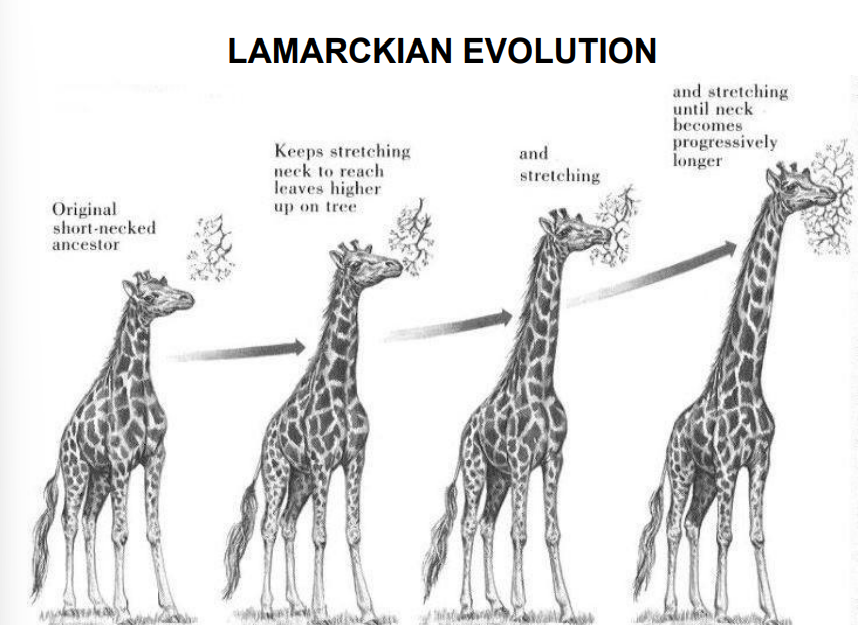
what was the Lamarckian evolution
Organisms continually arise by spontaneous generation.
“Nervous fluid” acts to move each species up the “great chain of being”. Organisms develop adaptations to changing environment through the use and disuse of organs.
Acquired characteristics are inherited.
what is the chain of being?
Darwin believed
Descent with modification
• Natural selection
Darwins evidence?
• High levels of variability within a species
. • Variants can pass these characteristics to offspring.
• Artificial selection can rapidly alter the characteristics of a breed.
what did darwin and malthus believe about population growth?
Populations reproduce exponentially.
Natural populations have a large capacity to reproduce. If left unchecked they will increase at a rapid rate.
MANY MORE ORGANISMS ARE BORN THAN CAN POSSIBLY SURVIVE
malthus vs darwin
Malthus applied his observations about population growth and resource limitations to human societies, while Darwin extended these principles to the natural world to develop his theory of natural selection, proposing that traits for survival and reproduction become more common over generations
descent with modification
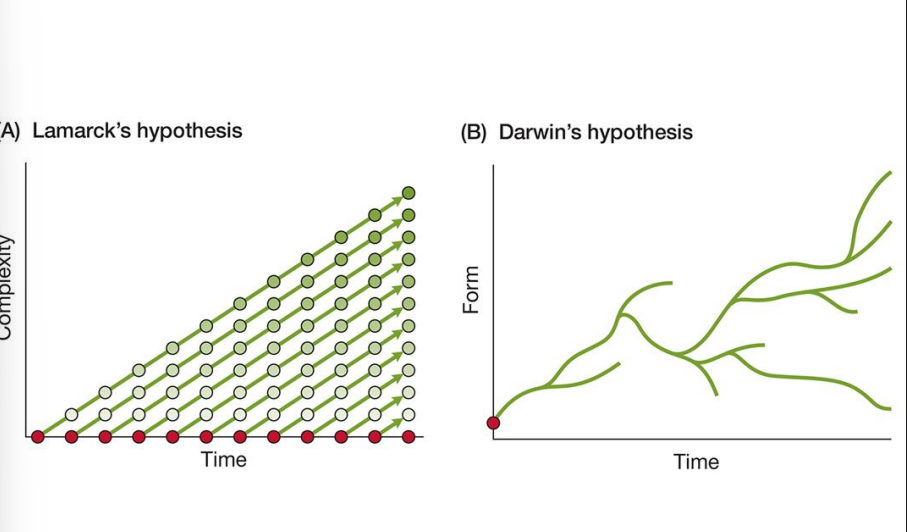
lamarcks hypothesis of descent with modification vs darwin
Darwin’s (& Wallace’s) logical argument that evolution must take place IF
– Individuals vary in their phenotypes
– Variations are at least partially inherited
– Individual survival and reproduction are non-random; instead depending on the phenotype. Individuals with some phenotypes do better than others
natural selection
a mechanism for change over time: if it takes place, then the composition of a population will change from one generation to the next.
is on individuals
evolution is the …
composition of the population changes from one generation to the next.
occurs across generations
adaption is the
changing of sp to better survive
answers to darwin’s unanswered questions of
But how is variation generated?
But how is variation transmitted to offspring
Mutation (+recombination, sexual reproduction) as the source of heritable variation
2. Mendelian genetics as the mechanism of inheritance
3. Gradual evolution results from small genetic changes that rise and fall in frequency under natural selection