Lec 1: Colour Vision
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Wavelength ranges for violet, red, ultraviolet and infrared
Violet is around 400nm
Red is around 700nm
Infrared is abv 700 and we normally don’t see it
Ultraviolet is below 400 and we normally don’t see it
Trichromatic vision
The ability of humans to sense color using three types of cones: red, green, and blue.
Human eyes wavelength range
We see 400-700nm of visible light, which includes all colours from violet to red
Human eyes evolved in water, where seawater is most transparent to light <500nm (blue-green) shaping our visual system to detect these wavelengths.
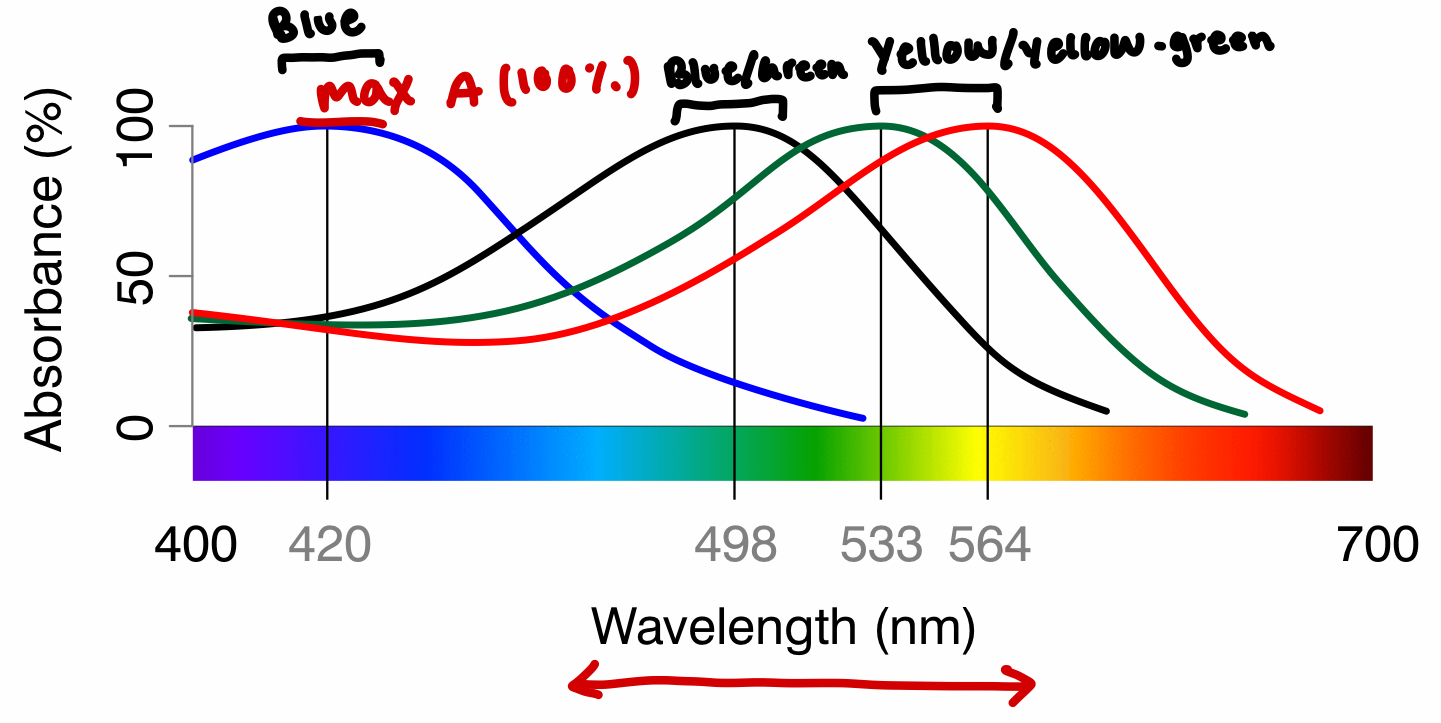
3 types of cone and %
We are trichromats b/c we sense 3 types of cones; RBG
63% Red
31% Green
6% Blue
Visual pigments and what light colour they prefer:
Prefer = When they are most sensitive to light (most absorbance)
Red + Green cone: Yellow and Yellow green light (533-564)
Blue cone: Blue (420~)
Rhodopsin (black curve): Blue-Green (498~)
Melanopsin (5th visual pigment): Blue (420~)
Spectral vs Extraspectral
Spectral: “in spectrum”/”in rainbow”
Can be evoked by the light of a single wavelength (same)
Ex; violet through blue
Ex; green, yellow and orange to red
Extraspectral:
Prod. by mixing wavelengths, such as purple, which cannot be prod. by a single wavelength
Ex; Purple needs 2+ wavelengths; red and blue
Ex; White
Ganglion cell color signals + channels
Ganglion cells process colour signals by combining inputs from cone signals:
R+G cells → Yellow channel
Red + Green = Yellow
Red-Green Opponent Channel:
R-G cells → Red excites, green inhibits
G-R cells → Green excites, red inhibits
Blue-Yellow Opponent Channel:
B-(R+G) cells → Blue excites, red + green inhibits
Y-B cells → Yellow excites, blue inhibits
Daltonism
Red-Green colour blindness is a genetic condition affecting the perception of red and green colours.
Inheritance pattern
X-linked: Colour-blind fathers have normal daughters who have colour-blind sons
women are saved by their 2nd X-chromosme
btw if a woman has 2 different functional “red” cones, shes a tetrachromat
Tetrachromat
Tetrachromacy:
An individual with 4 types of cone cells for colour vision, allowing them to perceive a broader spectrum of colours than typical trichromats.
Example: A woman with 2 different functional red cones can be classified as a tetrachromat, enabling her to distinguish colours that others cannot.
Very rare
Reflectance
The intrinsic colour of a surface based on its tendency to reflect certain wavelengths of light and absorb others. Reflectance of an object carries information about it.
Ex; yellow banana reflects yellow light more than others. Colour would reflect ripeness.
Our brain usually infers reflectance so even in green light, we see a yellow banana. This is Colour Constancy.
Color Constancy
The ability of the brain to perceive colors of objects consistently under different lighting conditions.
Opsin
The non-chromophore part of a chromoprotein, sometimes used to refer to the whole chromoprotein.
Photopigments
The non-protein, chromophore parts of chromoproteins that undergo chemical changes when they absorb light.
Wavelength
The distance from one wave peak to the next; different wavelengths correspond to different colors.
Retinal
The chromophore that is bound to opsins in human photoreceptors.
Visual pigments
Light-sensitive molecules in photoreceptors that absorb specific wavelengths of light.
Illumination
The amount and type of light that affects how objects are perceived in terms of color.
Chromophores
The part of a molecule responsible for its color, often bound to opsin proteins in photoreceptors.
Cone cells
Photoreceptor cells in the retina that are responsible for color vision and operate under bright light conditions.
Chevreul Illusions
Visual phenomena where colors appear to change based on surrounding colors, demonstrating the effects of contrast and color perception.
