9-10 PPTX FLASHCARDS
1/203
Earn XP
Description and Tags
9.Brain & cranial nerves + 10. Spine & Spinal Nerves
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
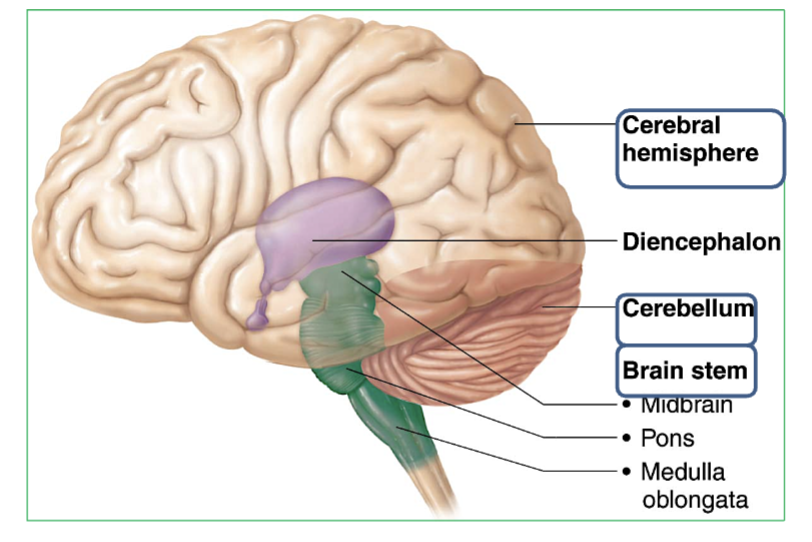
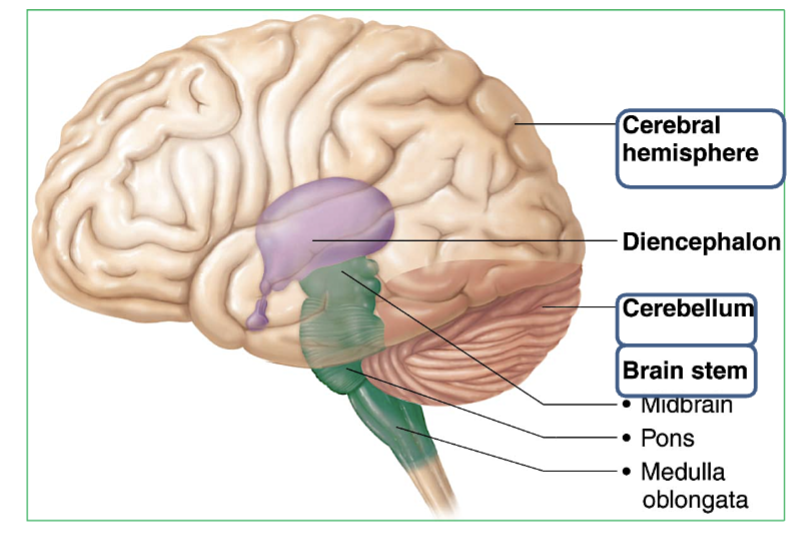
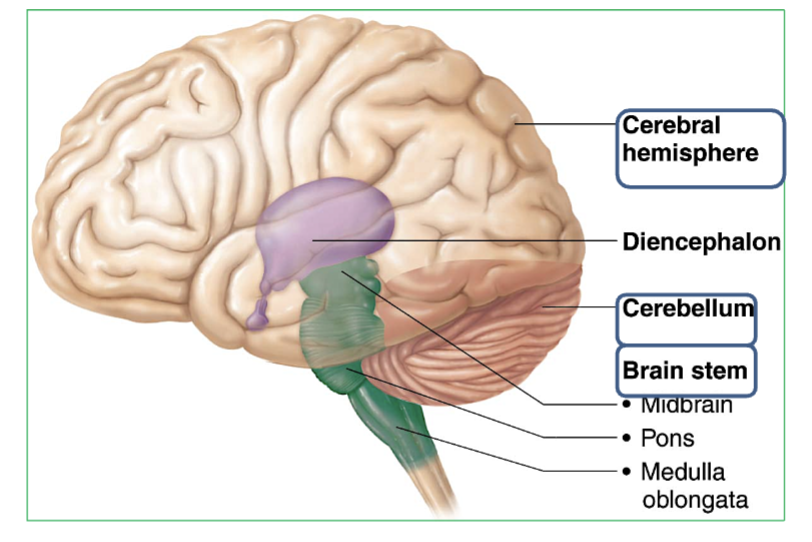
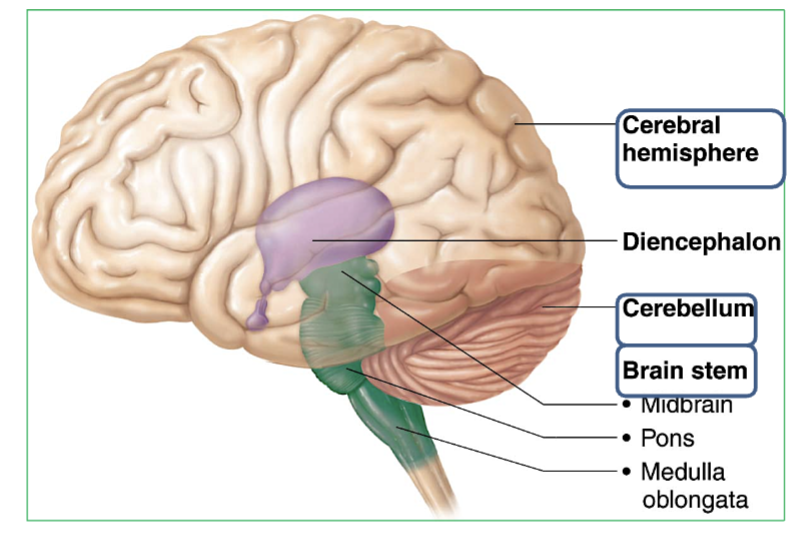
The 3 Major regions of the brain?
Cerebrum : Thinking, memory, voluntary movement. Two halves connected by corpus callosum.
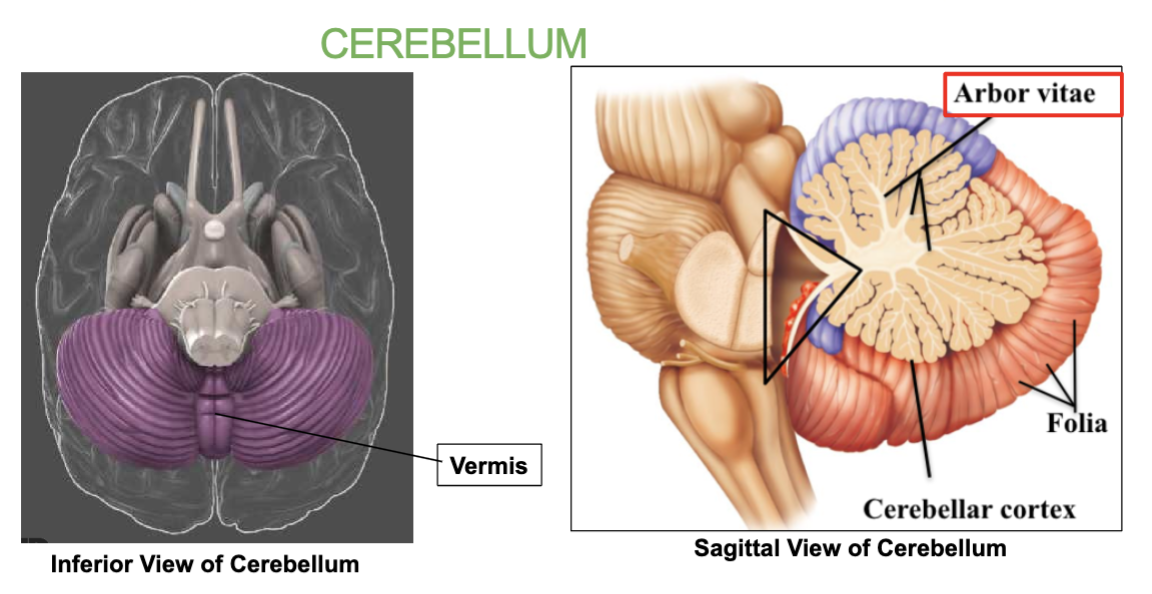
Cerebellum : Balance, coordination & Equilibrium. Has two halves joined by the vermis, with tree-like arbor vitae pattern.
Brainstem : Contains the Midbrain, Pons, & Medulla
Where is the Cerebrum & whats it’s job?
The cerebrum is in the whole top part of the brain. sits above the brainstem and cerebellum, and is divided into left and right hemispheres.
→ It’s responsible for sensation, communication, memory, understanding, and voluntary movement
Where is the Cerebellum & what it’s job?
At the back and bottom of the brain, under the cerebrum and behind the brainstem.
→It’s responsible for Equilibrium , balance, & Coordination of movement:
it communicates with the motor areas of the cerebrum to smooth and coordinate movement
Cerebrum Vs Cerebellum , key differences
Cerebrum = thinking and doing
Cerebellum = balancing and smoothing movements
Where is the brainstem and it’s 3 parts?
The brainstem is located at the base of the brain, connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord.
→ It includes three parts (from top to bottom): Midbrain, Pons, Medulla
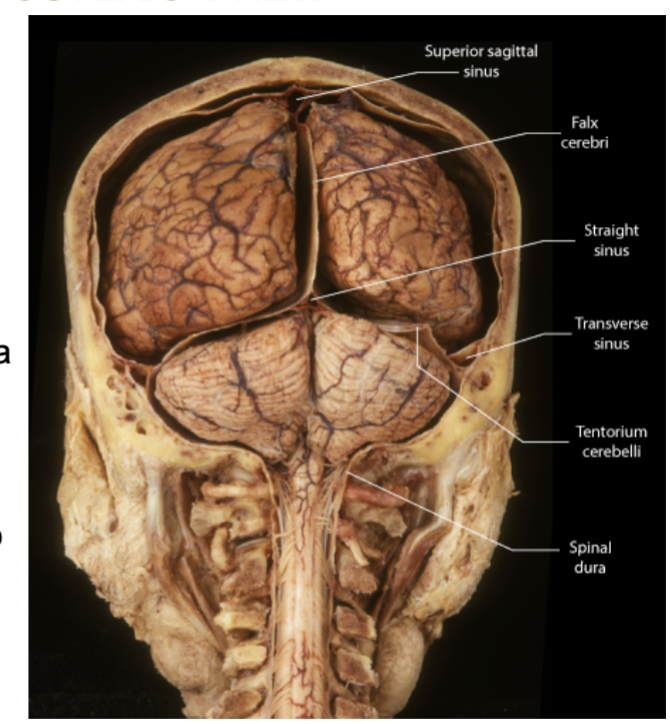
the 3 layers of meninges of the brain (outer to inner)?
Dura mater: Tough outer layer. Forms 3 protective folds - falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli , & Falx cerebelli
Arachnoid mater: Middle layer; contains
CSF in subarachnoid space between arachnoid and pia
Pia mater: Last thin layer stuck to brain surface.
(this is from surface to deepest)
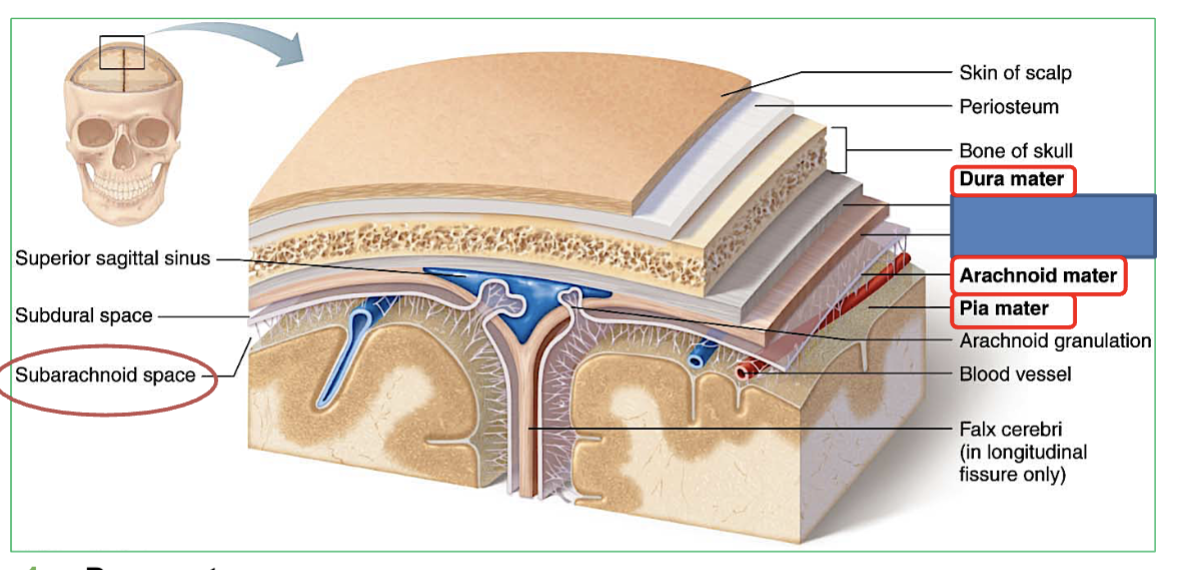
Which layer is the Dura mater a meninges of the brain?
(outer (1st,) middle (2nd), inner (3rd)?
Tough outer layer. Forms 3 protective folds - falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli & falx cerebelli
Which layer is the Arachnoid Mater a meninges of the brain?
(outer (1st,) middle (2nd), inner (3rd)?
Middle layer
contains CSF in subarachnoid space between arachnoid mater and pia mater
Which layer is the Pia Mater a meninges of the brain?
(outer (1st,) middle (2nd), inner (3rd)?
Last/inner thin layer stuck to brain surface.
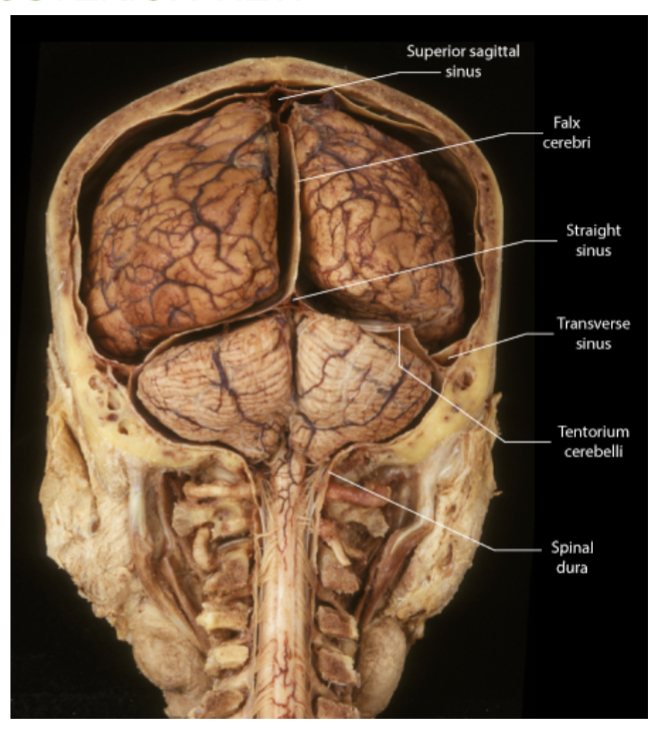
The 3 folds of the Dura Mater?
The dura mater extends inward to form 3 folds!
1.Falx cerebri - between two cerebral hemispheres
2. Falx cerebelli - between two cerebellum hemispheres.
3. Tentorium cerebelli - like a tent over the cerebellum. Between cerebrum and cerebellum
Which Meninges layer contains CSF?
The Arachnoid Mater contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the subarachnoid space, providing cushioning for the brain.
Where is the falx cerebri located?
Between the 2 Cerebrum hemispheres, in the longitudinal fissure. (vertically)
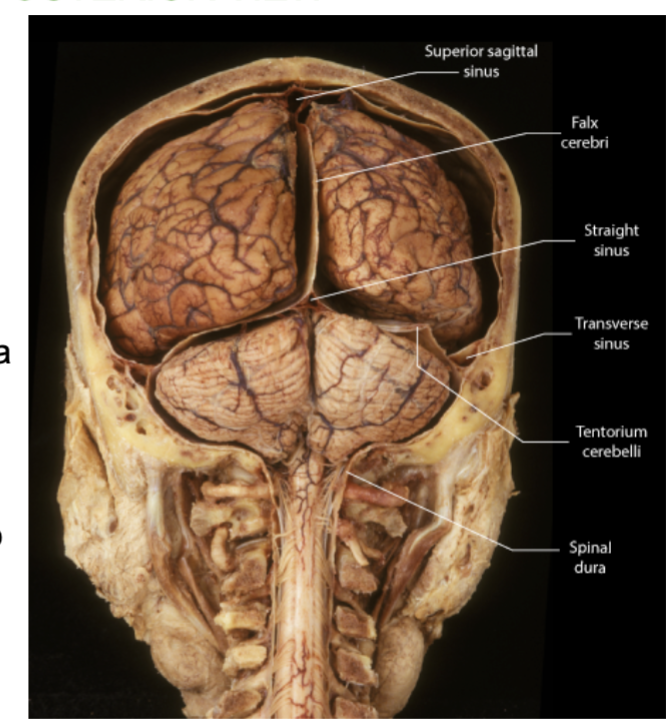
Where is the tentorium cerebelli located?
Between the cerebrum and the cerebellum, forming a horizontal tent.
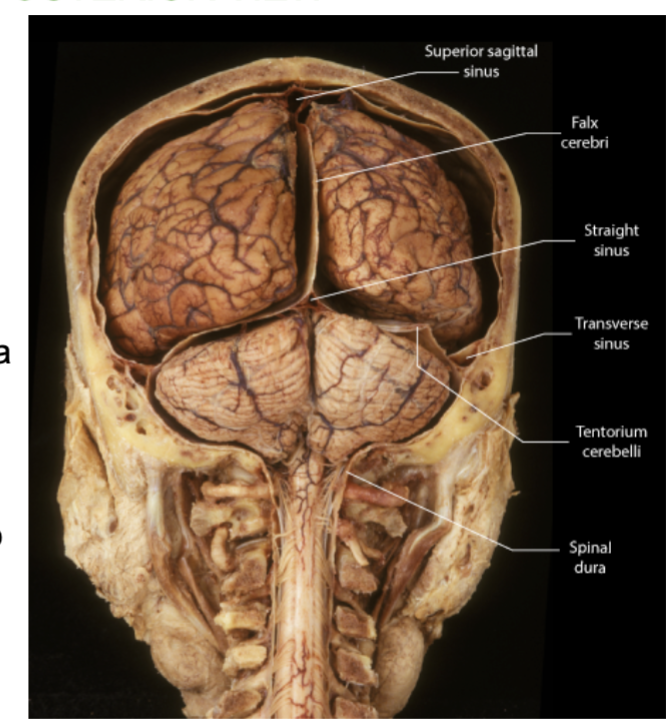
Where is the falx cerebelli located?
Between the two hemispheres of the cerebellum. (vertically)
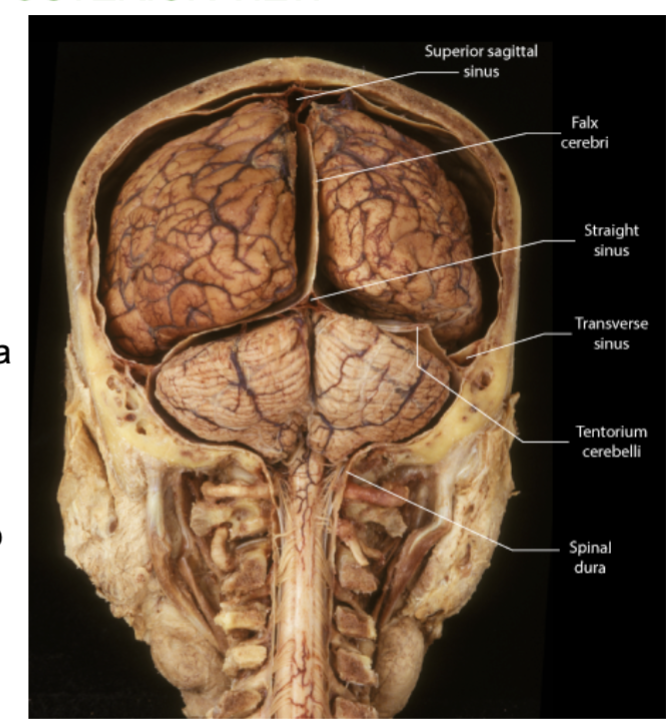
Which fold of the Dura creates a “tent” over a part of the brain?
the tentorium cerebelli , which is between the cerebrum and the cerebellum.
What does the cerebrum control & what is it made up of?
It controls our sensation, communication, memory, understanding and voluntary movement.
Made of two cerebral hemispheres which are connected by white matter called the corpus callosum.
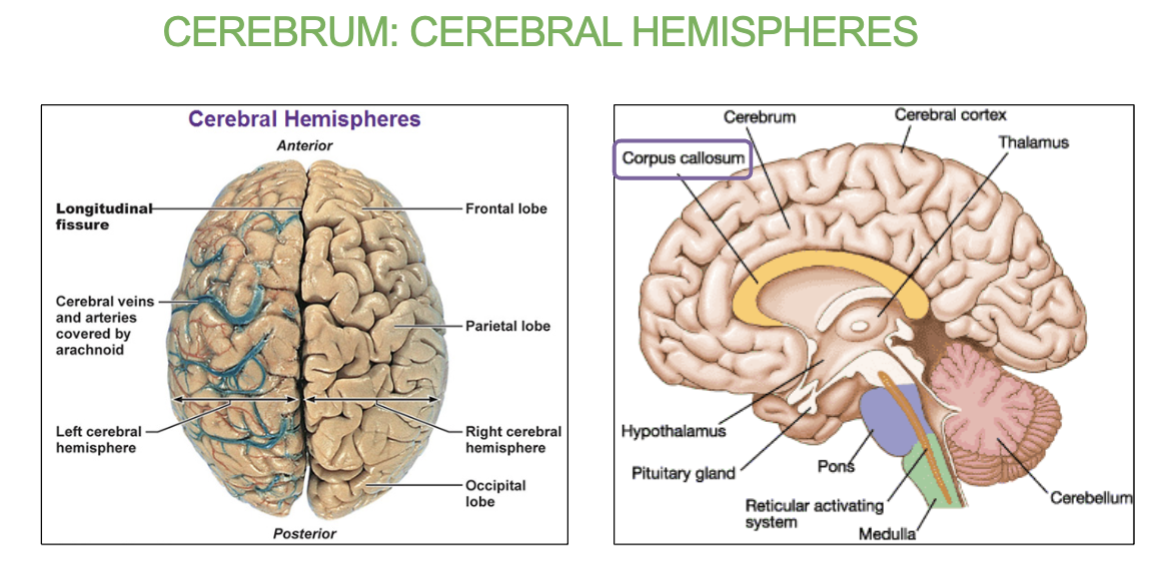
What is made up of two cerebral hemispheres which are connected by white matter called the corpus callosum?
the Cerebrum
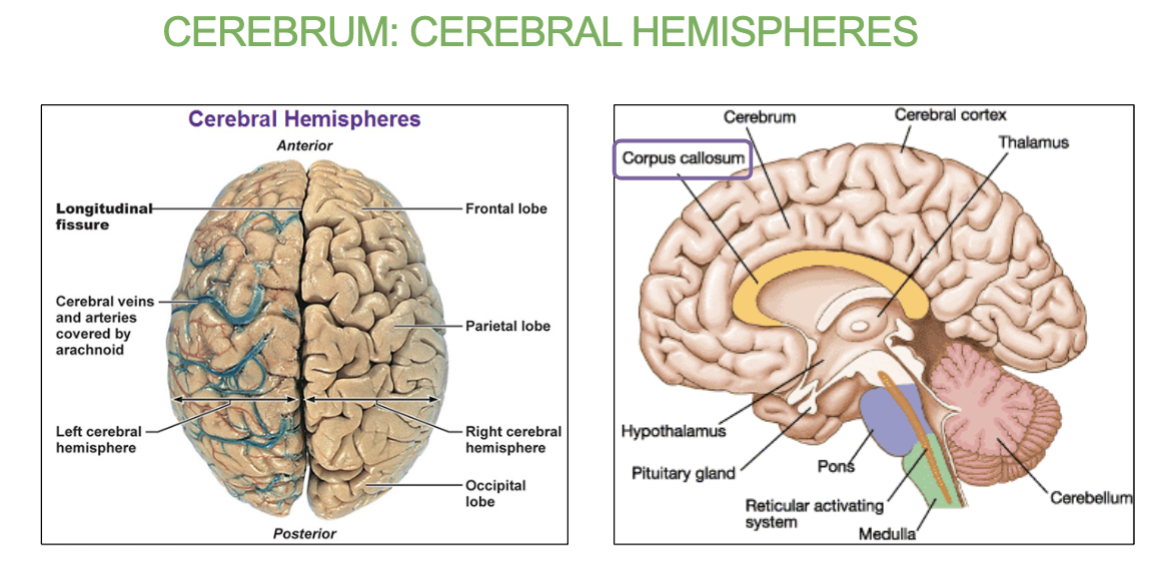
What connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum?
Corpus callosum (white matter structure).
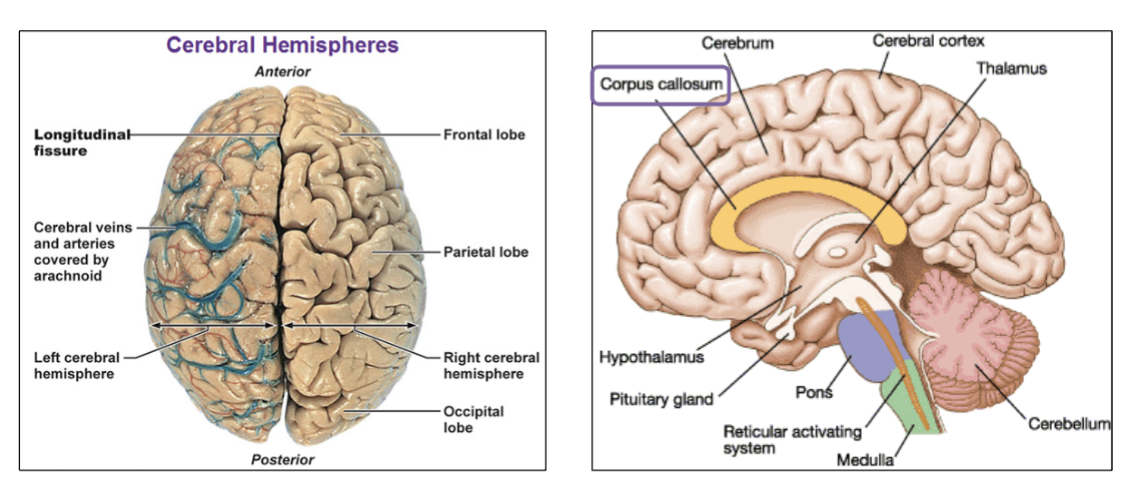
2 types of Cerebrum FIssures?
Longitudinal Fissure: between right and left hemispheres
Transverse Fissure: between cerebrum and cerebellum
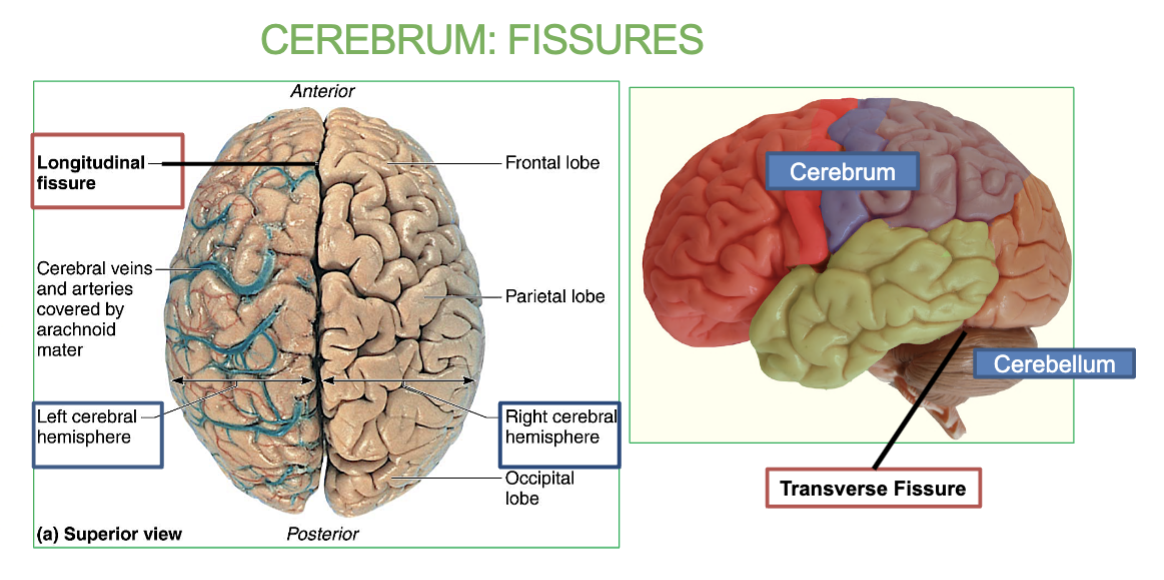
What are fissures & the 2 types of fissures in the Cerebrum?
Fissure are Deep grooves & longitudinal/Transverse fissures.
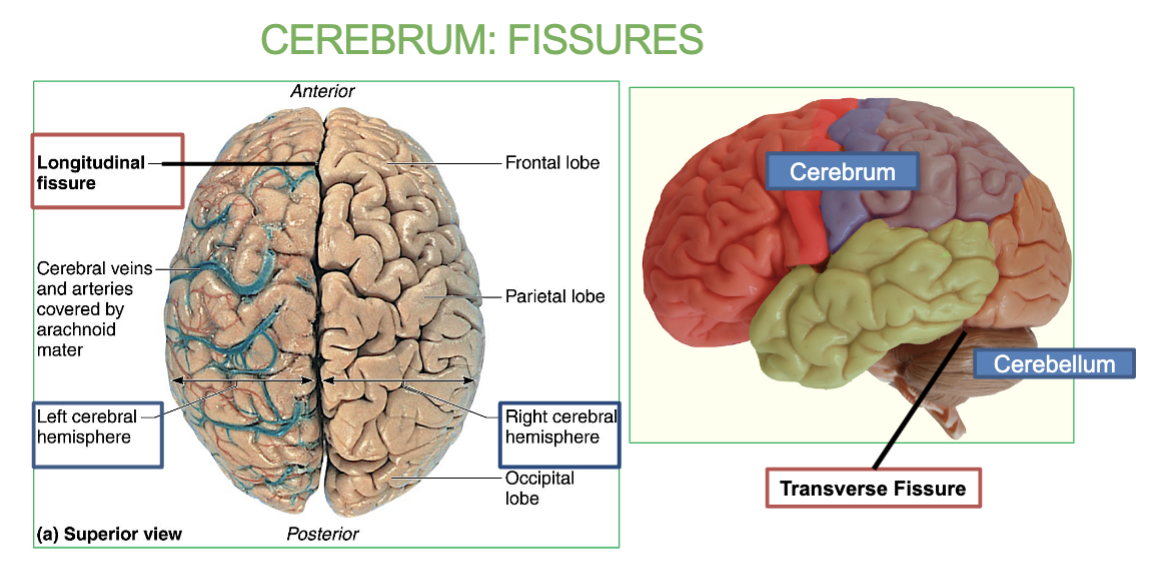
What are Sulci & Gyri?
“wrinkles” of the brain
Sulci are the grooves or folds in the brain’s surface.
Gyri are the ridges or raised areas between the sulci.
In the Cerebrum
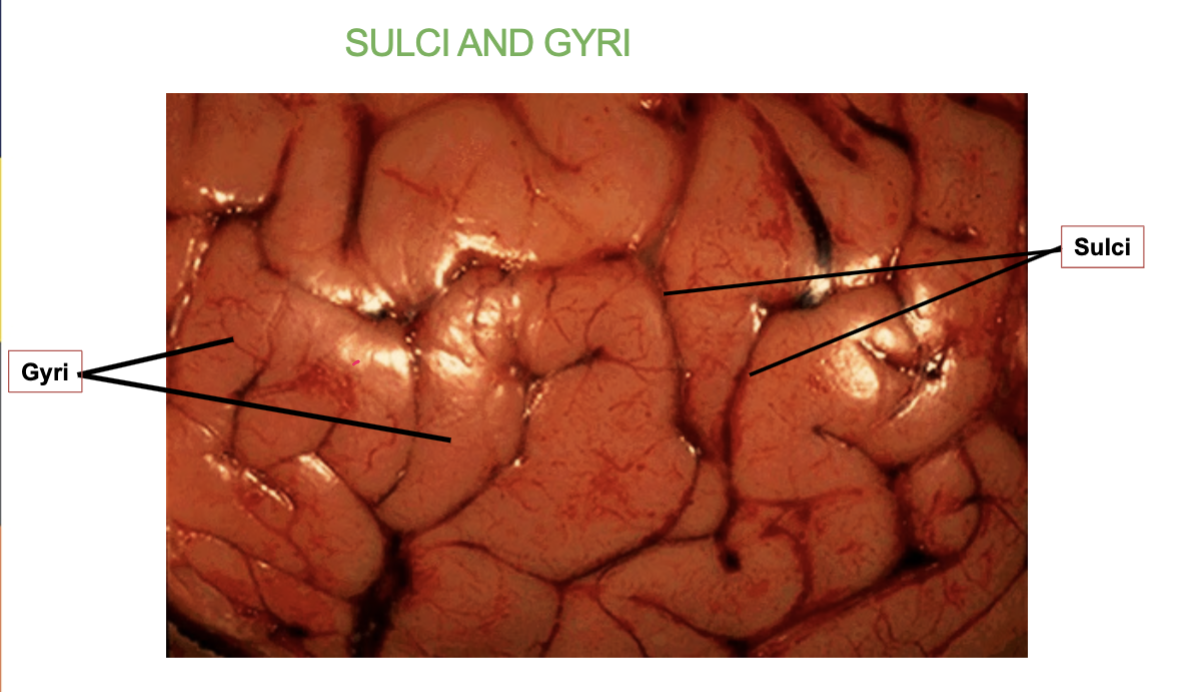
What are the 3 Major Sulci’s in the Cerebrum
Three major sulci demarcate lobes of the brain
1. Central Sulcus: between frontal and parietal lobes
2. Parieto-occipital Sulcus: between parietal and occipital lobes
3. Lateral Sulcus: between frontal and temporal lobes
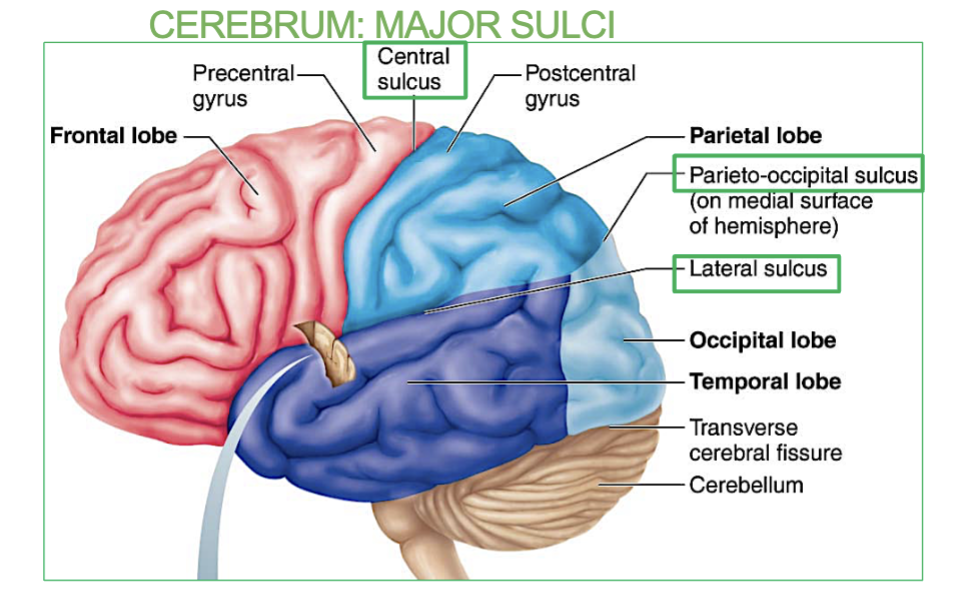
What do the 3 major Sulci of the brain do?
Seperate the 4 lobes of the Cerebrum.
Where is the Central Sulci?
between frontal and parietal lobes
(a major sulci in the Cerebrum)
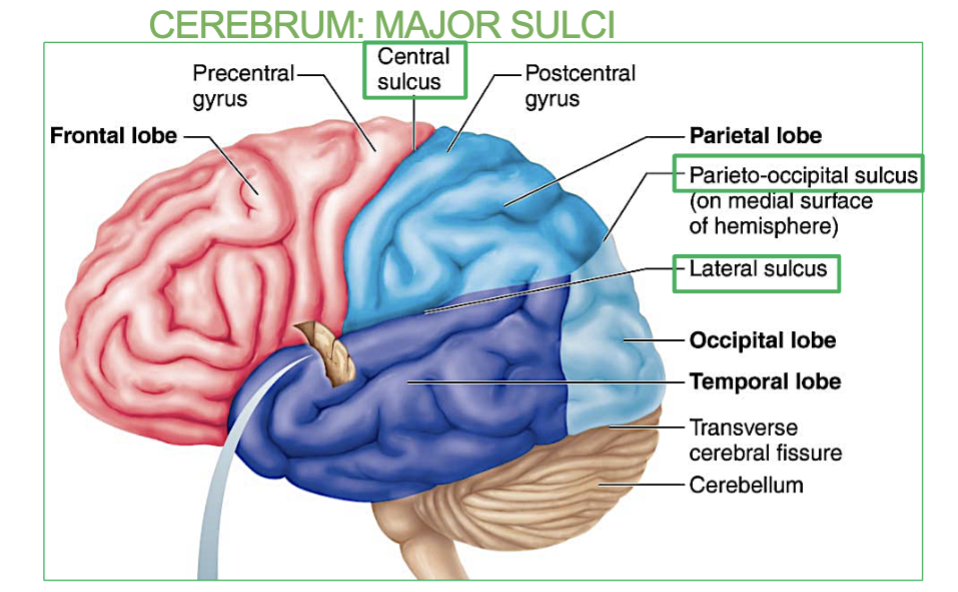
Where is the Parieto-occipital Sulcus?
between parietal and occipital lobes
(a major sulci in the Cerebrum)
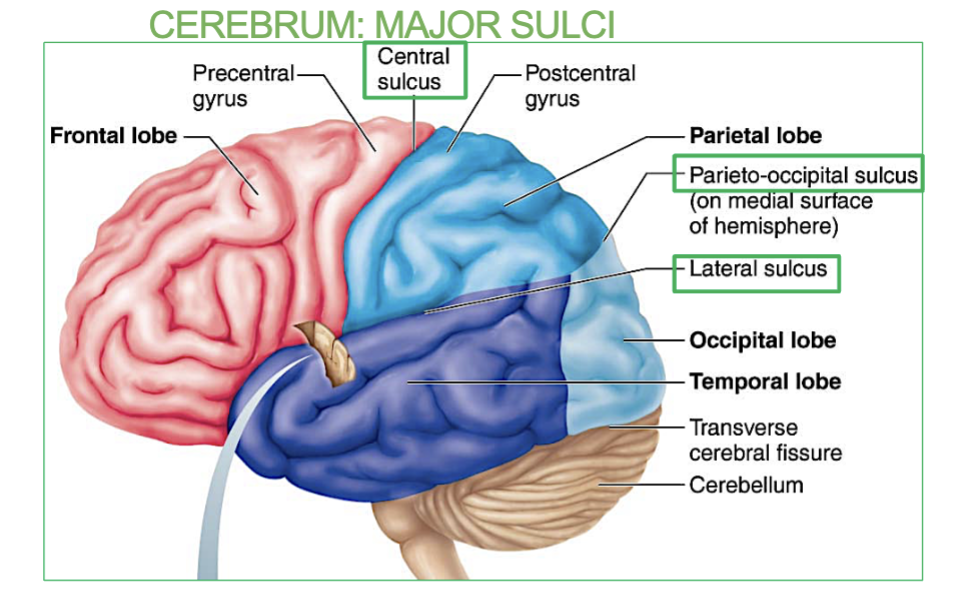
Where is the Lateral Sulcus?
between frontal and temporal lobes (transversely)
(a major sulci in the Cerebrum)
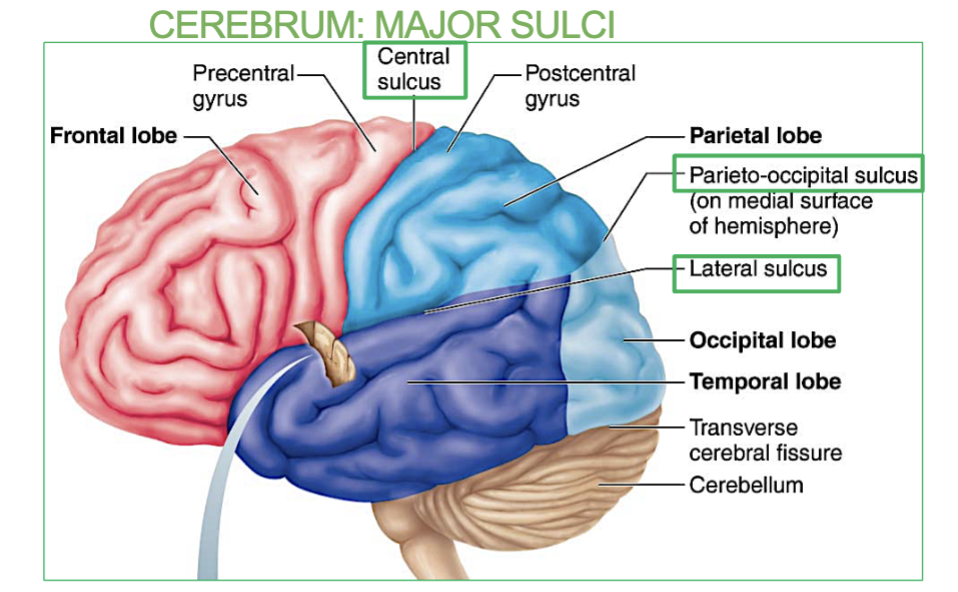
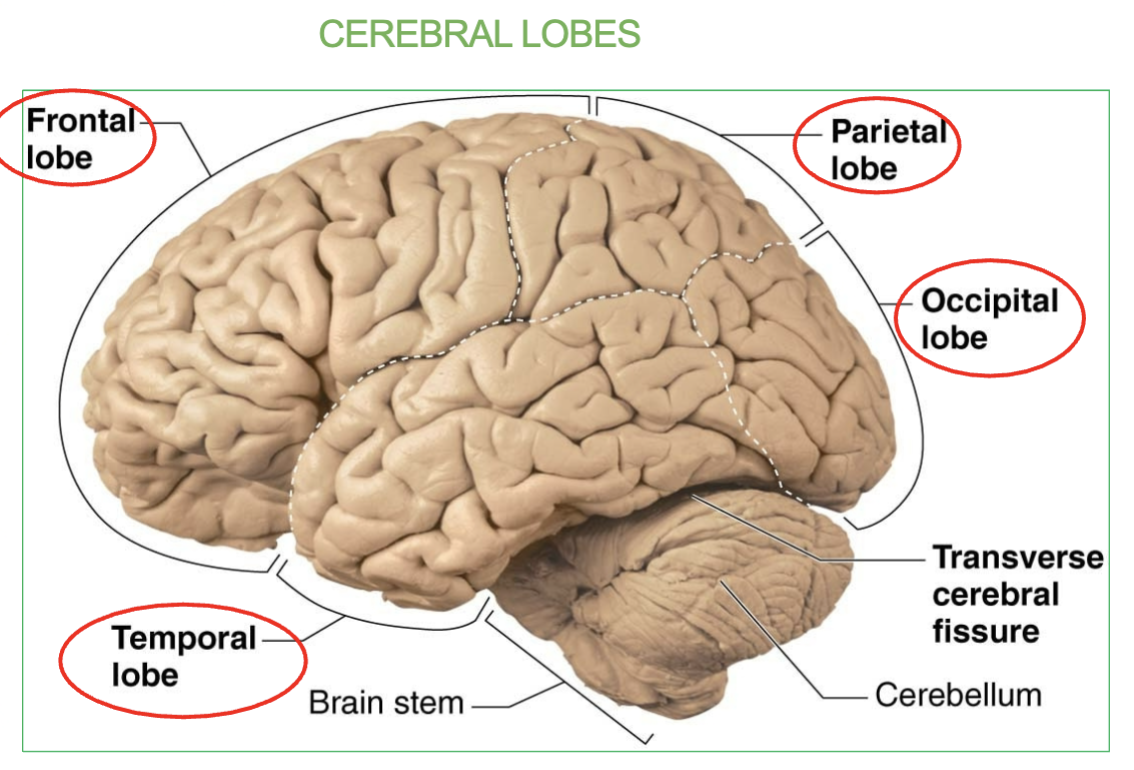
What are the 4 Cerebral lobes of the brain?
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Occipital
Cerebrum = Cerebral
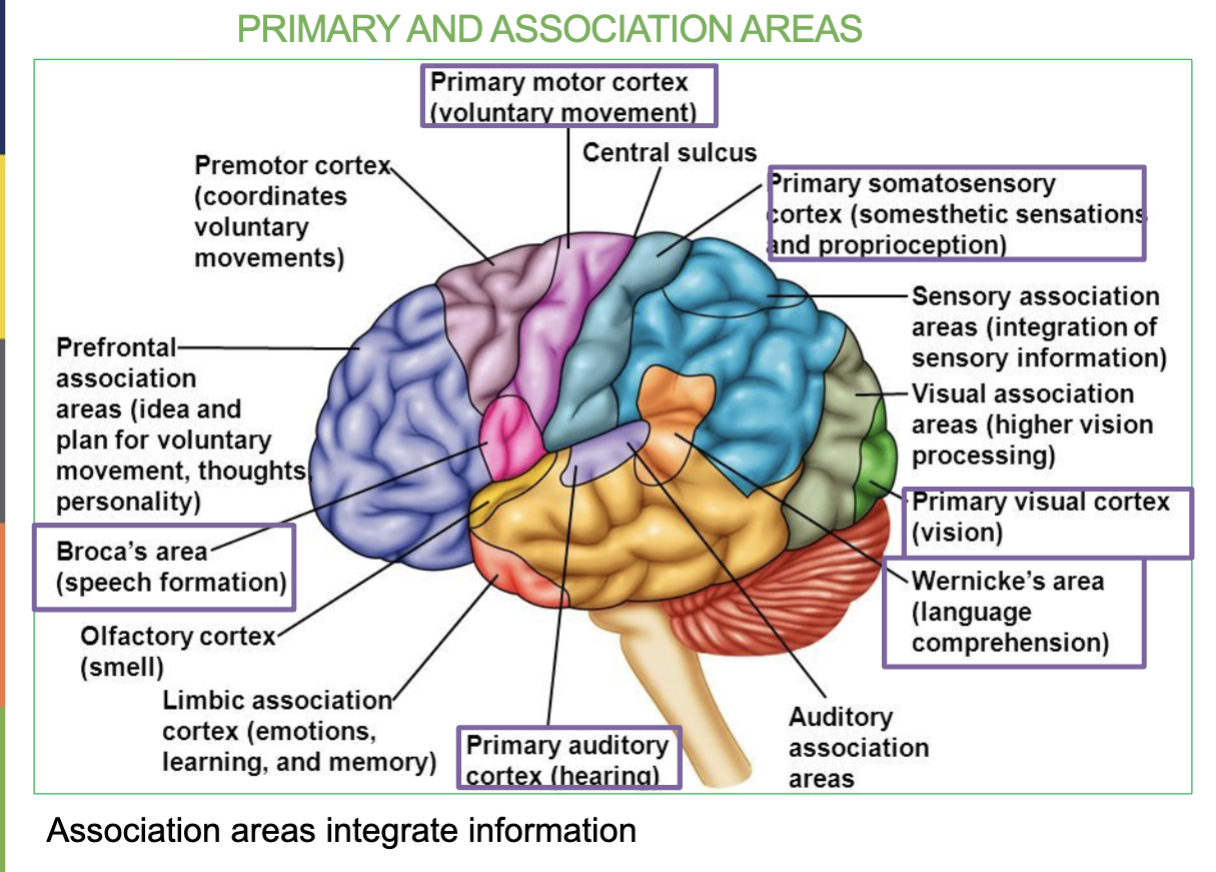
Areas & Function of the Frontal lobe?
The frontal lobe is the Primary Motor Area & the Broca’s Area.
Function → Controls voluntary movement, Language organization & speech
formation (broca’s area)
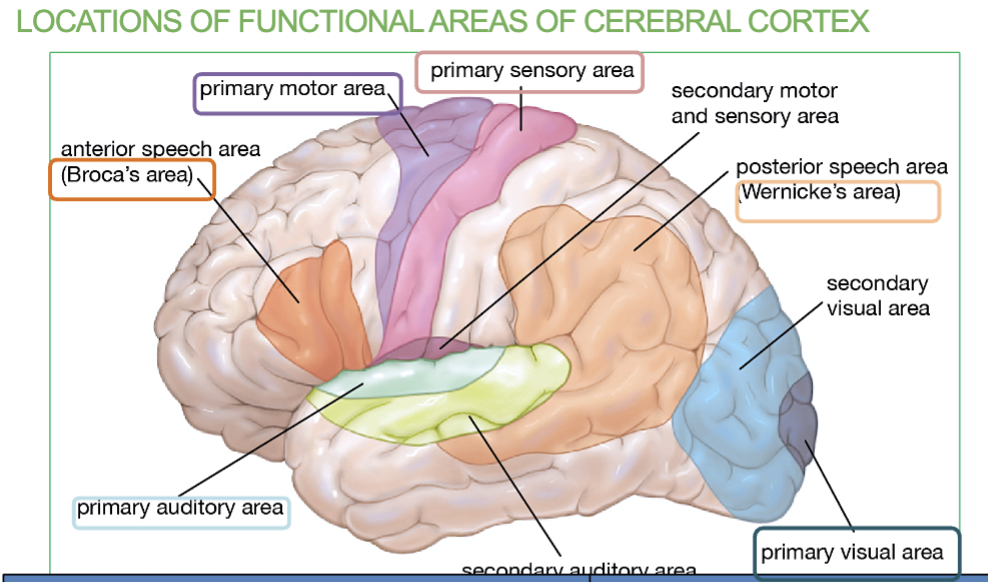
Area & Function of the Parietal lobe?
Primary somatosensory area (allows you to feel)
Function → Receives sensory information
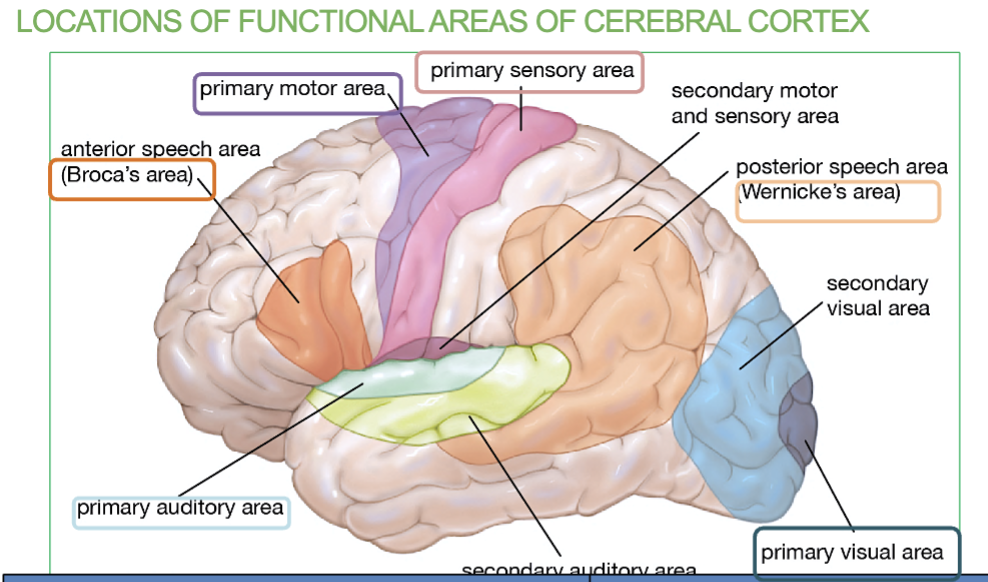
Areas & Function of the Temporal lobe?
Primary Auditory Area & Wernicke’s Area.
function → Receives sound information from ear & Speech interpretation
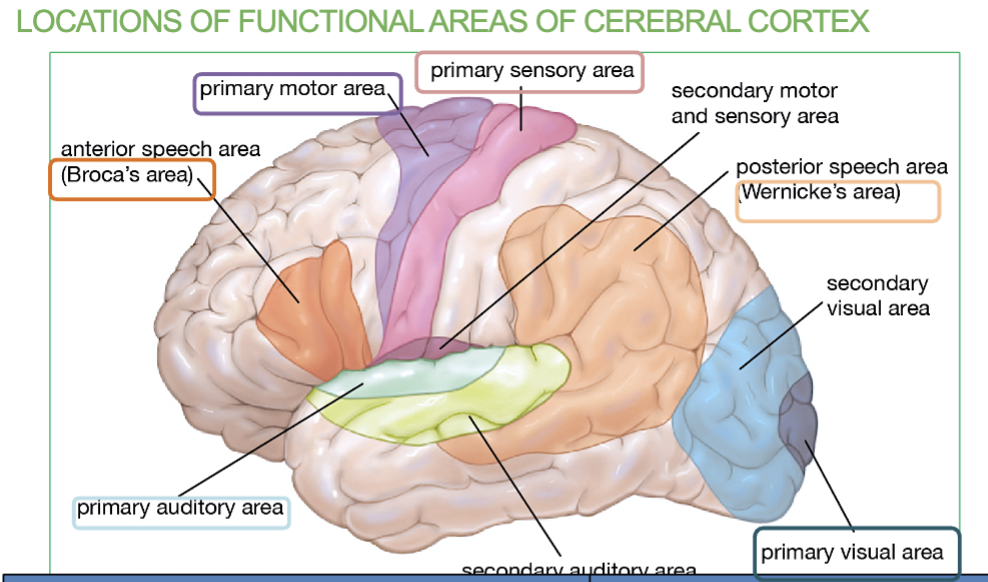
Area & Function of the Occipital lobe?
Primary Visual Area
Function → Recieves visual information from eye
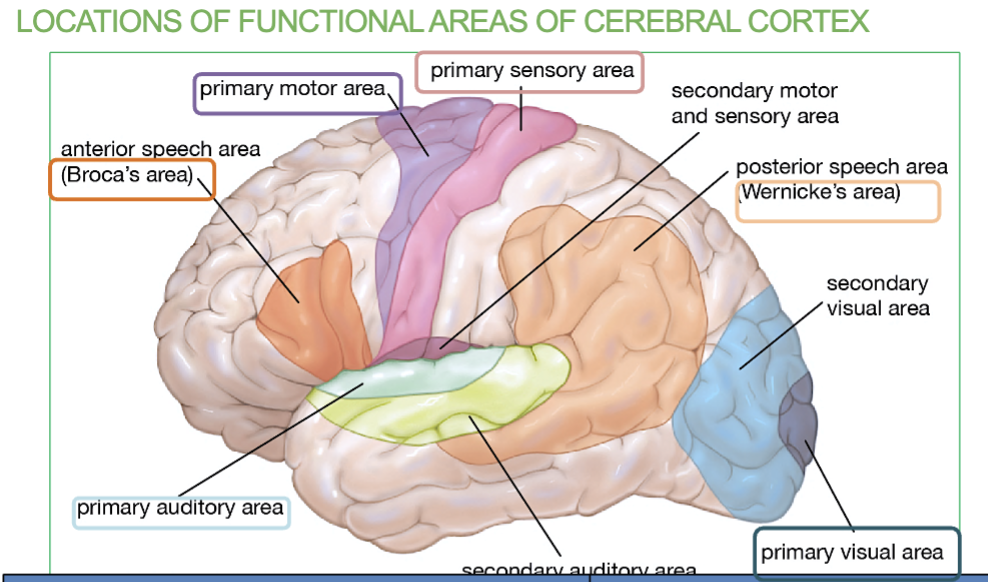
What are the 6 Primary Association Areas & their job/locations?
Primary Motor Cortex - Controls voluntary movements (Frontal lobe)
Broca’s Area- Speech Formation (Frontal lobe)
Primary Somatosensory Area - receives sensory information (Parietal lobe)
Primary Auditory Area - receives sound information from ears (temporal lobe)
Wernicke’s Area - Speech interpretation (temporal lobe)
Primary Visual Area - receives visual information from eyes (occipital lobe)
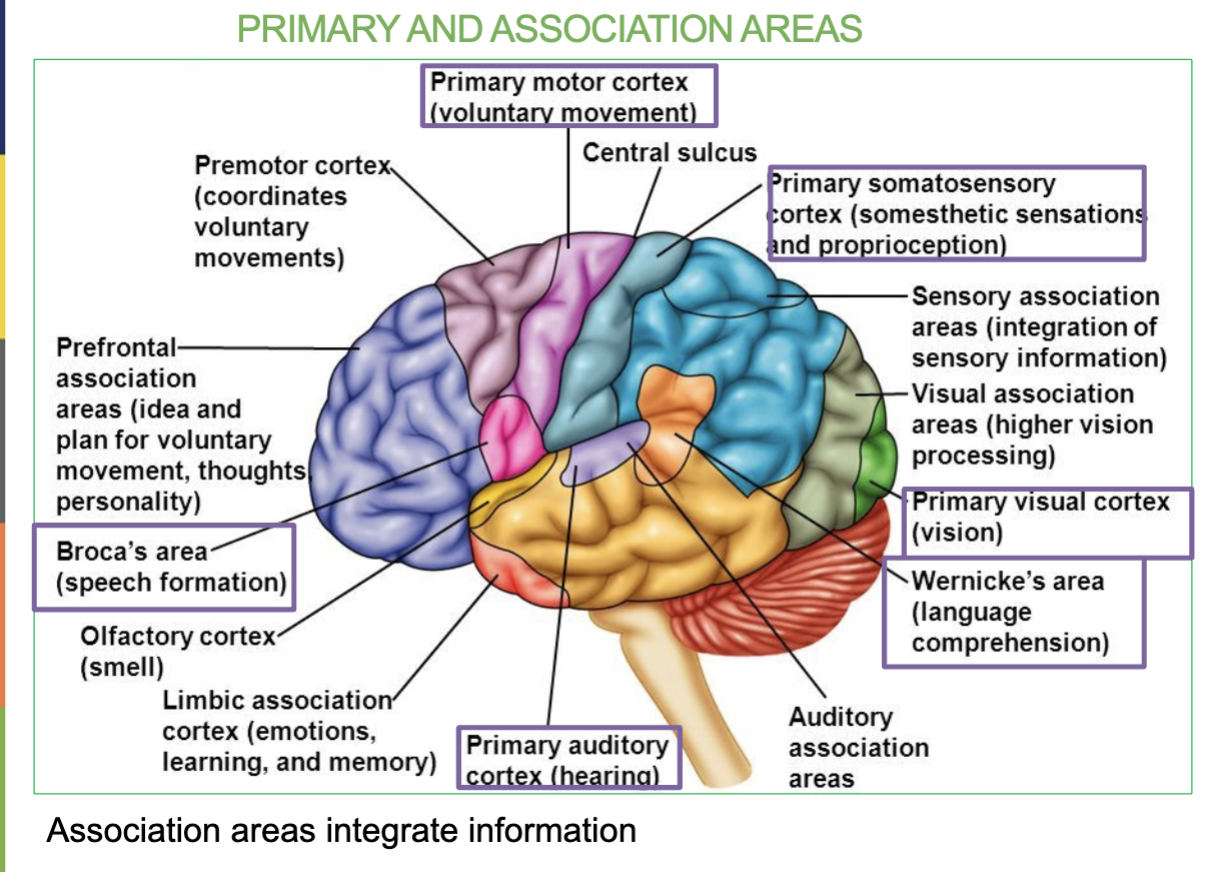
Where is the Primary Motor Cortex/Area & what is it responsible for?
Area located in the frontal lobe & Controls Voluntary movement
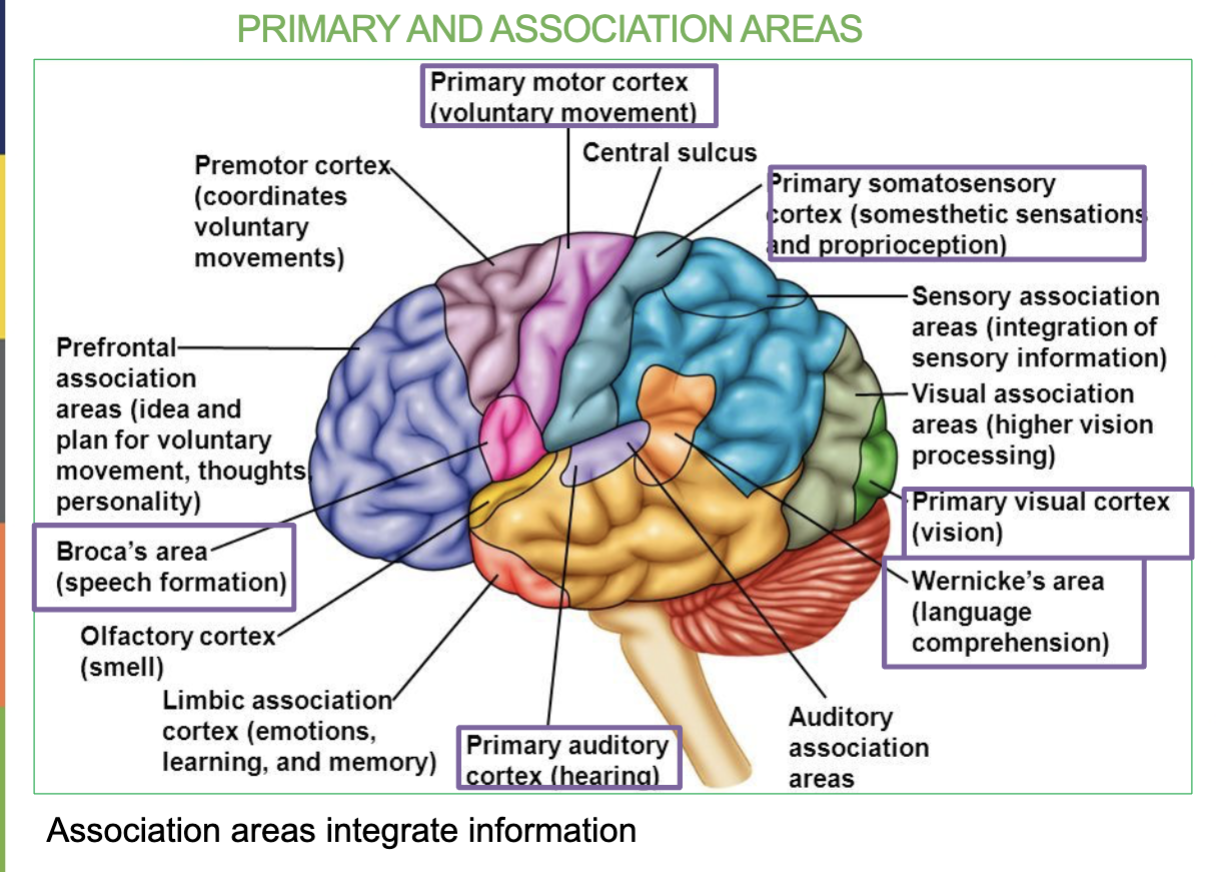
Where is the Broca’s Area & what is it responsible for?
Small are located in the Frontal lobe & Speech formation
(under the primary motor cortex)
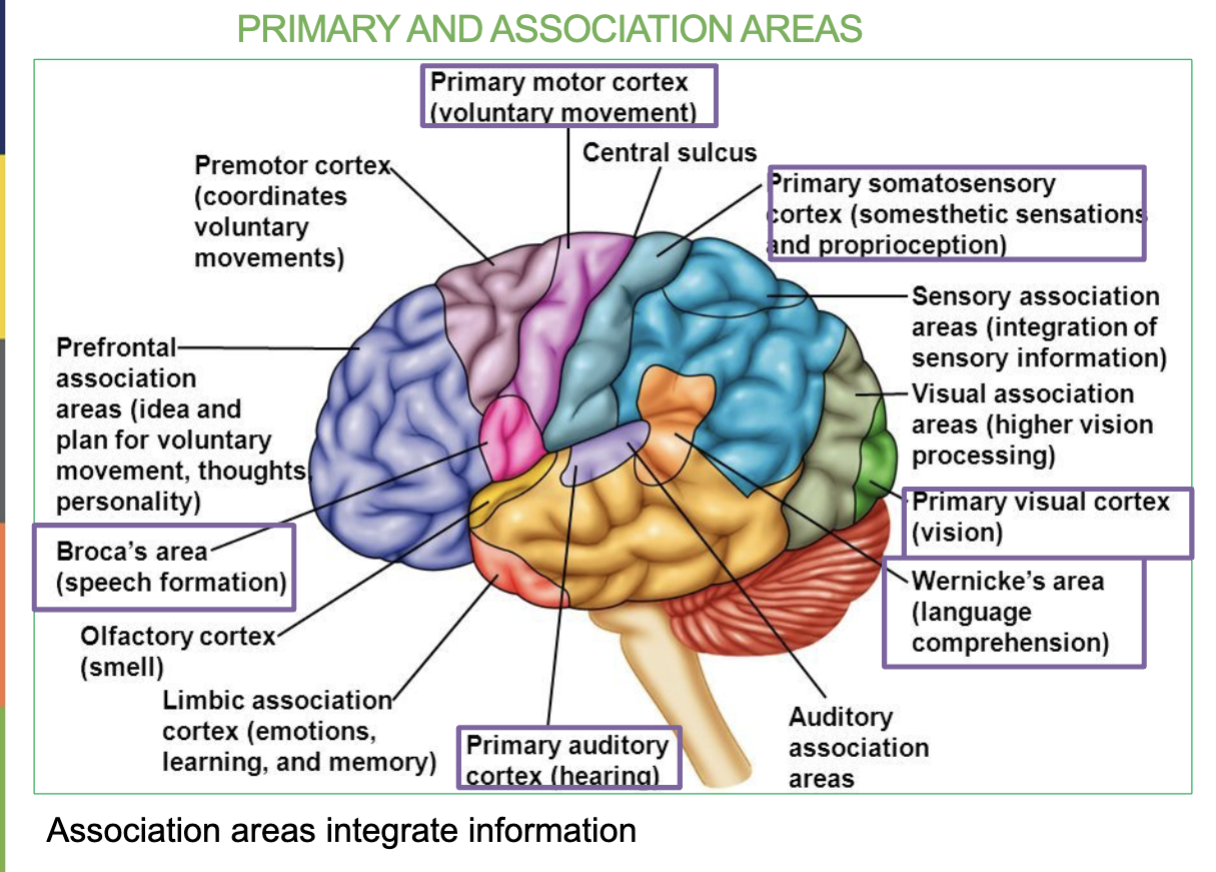
Where is the Primary Somatosensory Area & what is it responsible for?
In the Parietal Lobe & it receives sensory information (allows you to feel)
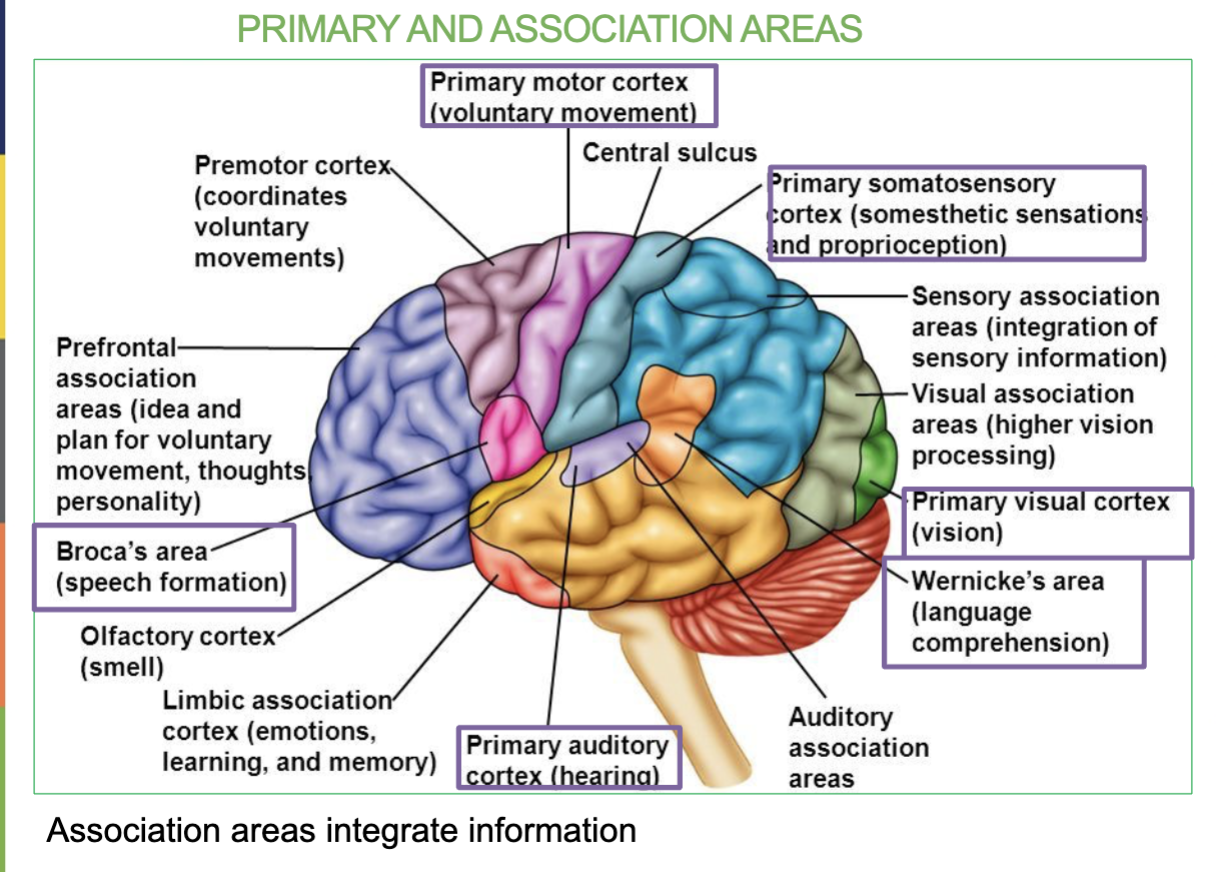
Where is the Primary Auditory Area & what is it responsible for?
In the Temporal Lobe & it receives sound information from ears
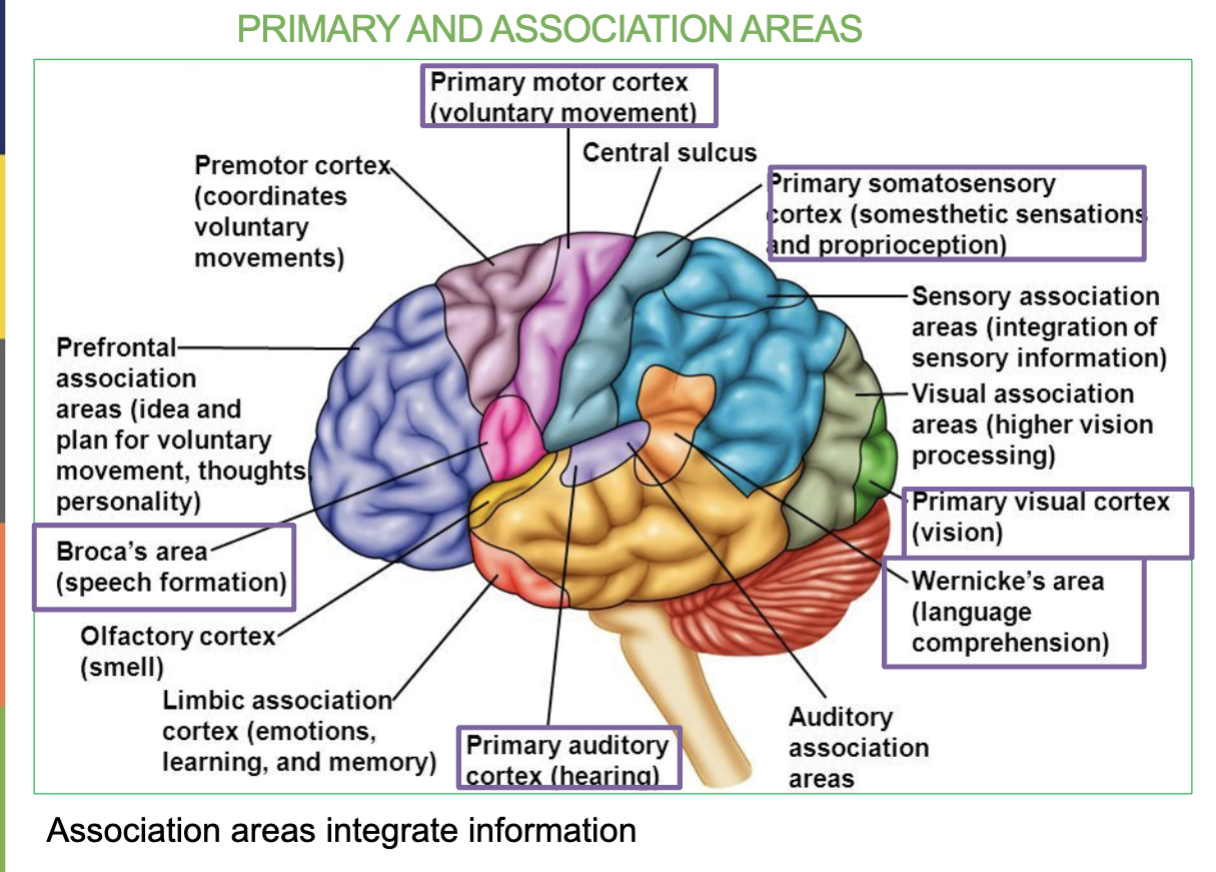
Where is the Wernicke’s Area & what is it responsible for?
In the Temporal Lobe & it’s responsible for speech interpretation (allows you to understand what youre hearing)

Where is the Primary Visual Area & what is it responsible for?
In the Occipital Lobe & it receives visual information from eyes
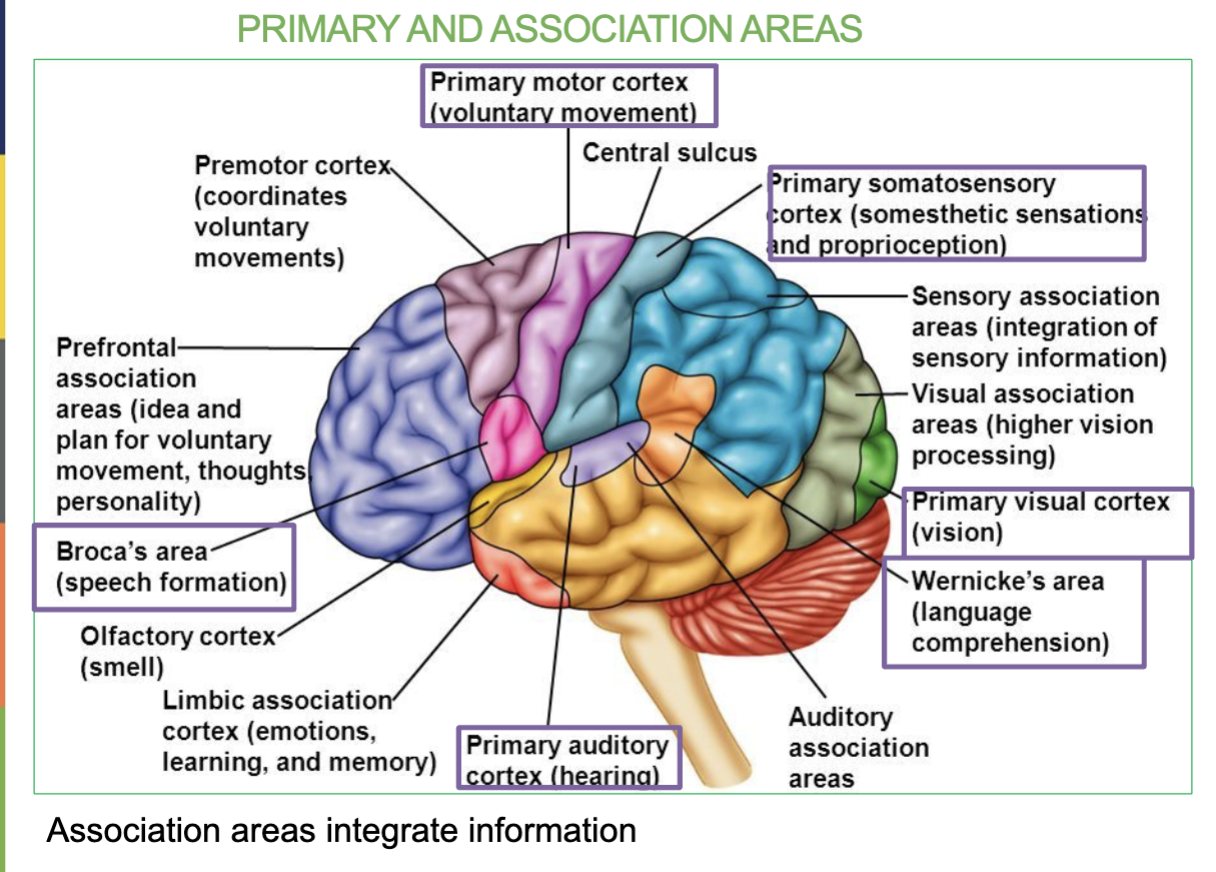
Difference between Broca’s Area & Wernicke’s Area
Broca’s Area → In frontal lobe , Speech formation (talking)
Wernicke’s Area →in temporal lobe, Speech interpretation & understanding
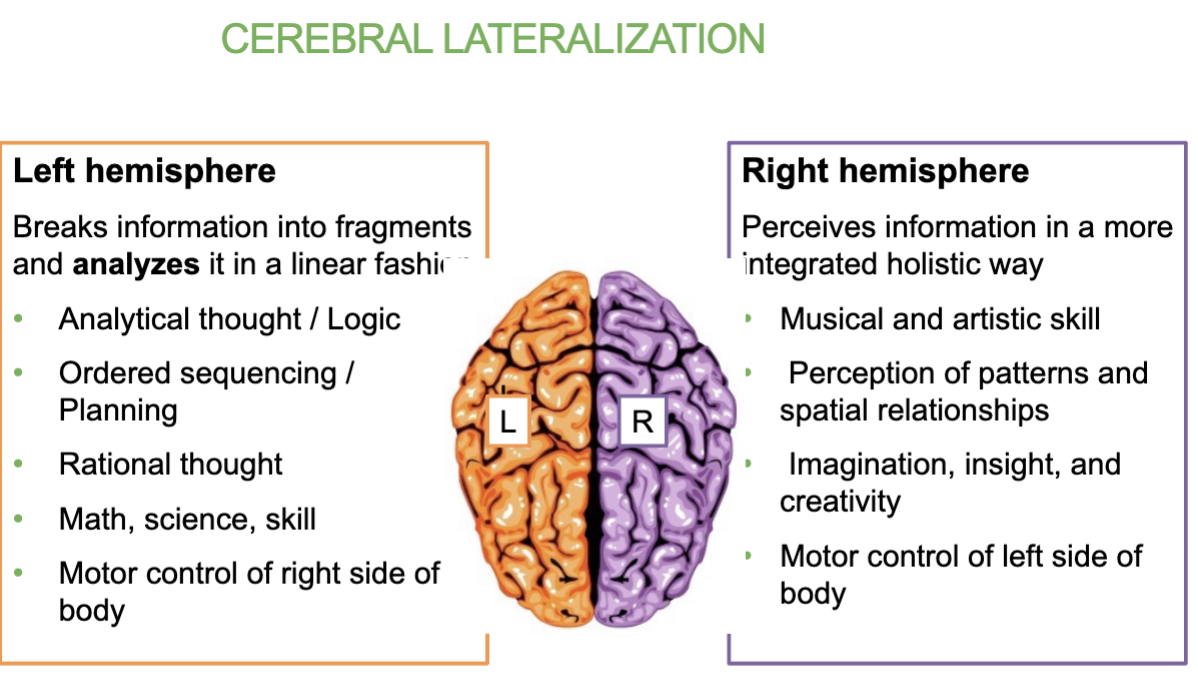
What does Cerebral Lateralization mean?
Means that each hemisphere of the brain specializes in different functions & Both sides control their opposite side.
Left hemisphere: Analytical thought logic, math, rational thoughts, controls right side of body
Right hemisphere: creativity, musical & artistic skill, imagination, insight, creativity & spatial awareness, controls left side of body
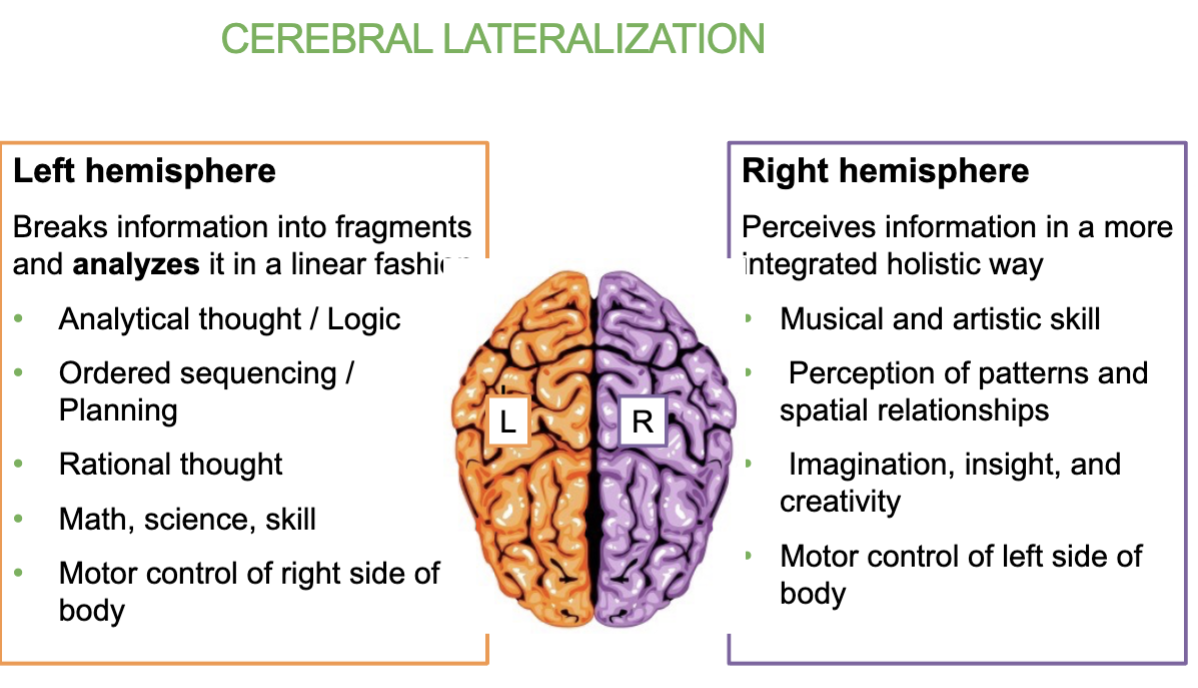
Job of the left hemisphere of the brain?
Breaks information into fragments and analyzes it in a linear fashion.
Analytical thought/logic, math, ordered sequencing/planning ,rational thoughts
→ controls right side of body
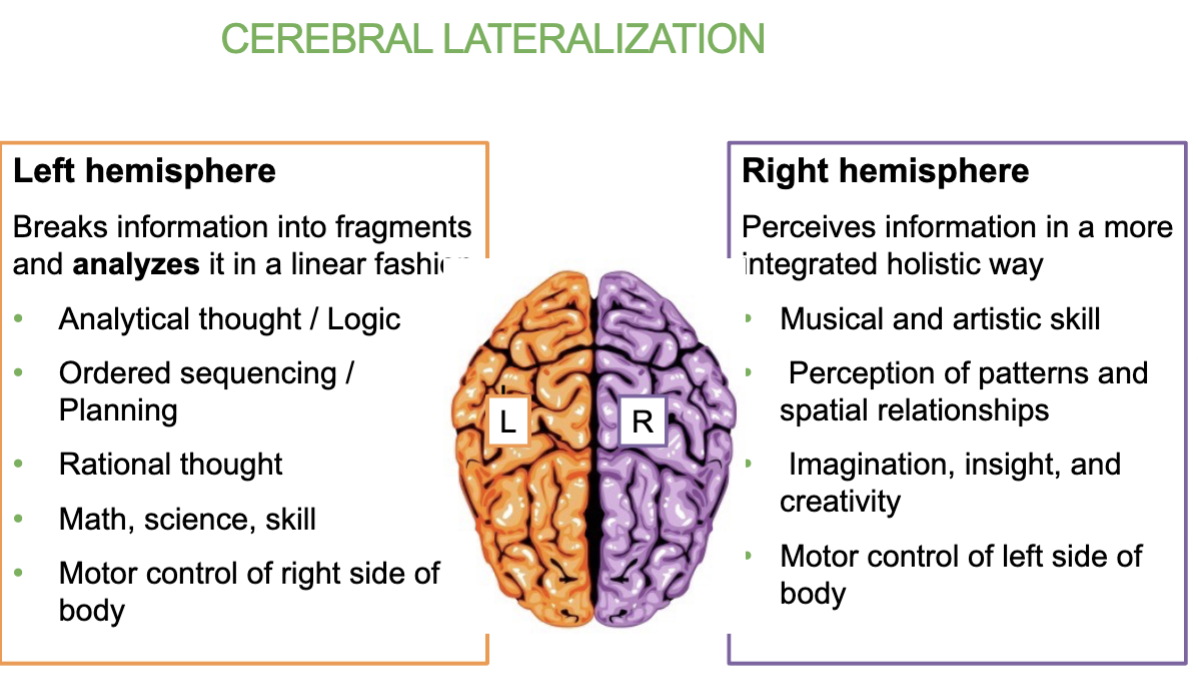
Job of the Right hemisphere of the brain?
Perceives information in a more integrated and holistic way.
creativity, musical & artistic skill, imagination, insight, creativity & spatial awareness
→ Controls left side of body
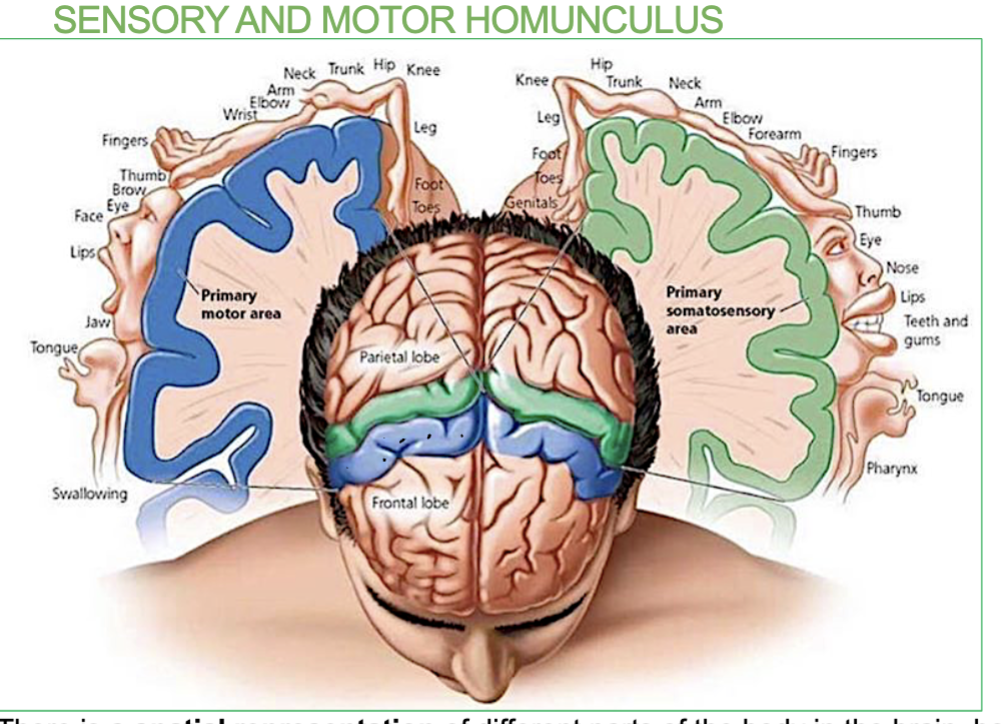
What is the Sensory and Motor Homunculus?
It’s a map of the body on the brain.
→ There is a spatial representation of different parts of the body in the brain, both for receiving sensation and initiating movement.
(It shows which brain areas are responsible for sensing and moving specific body parts)
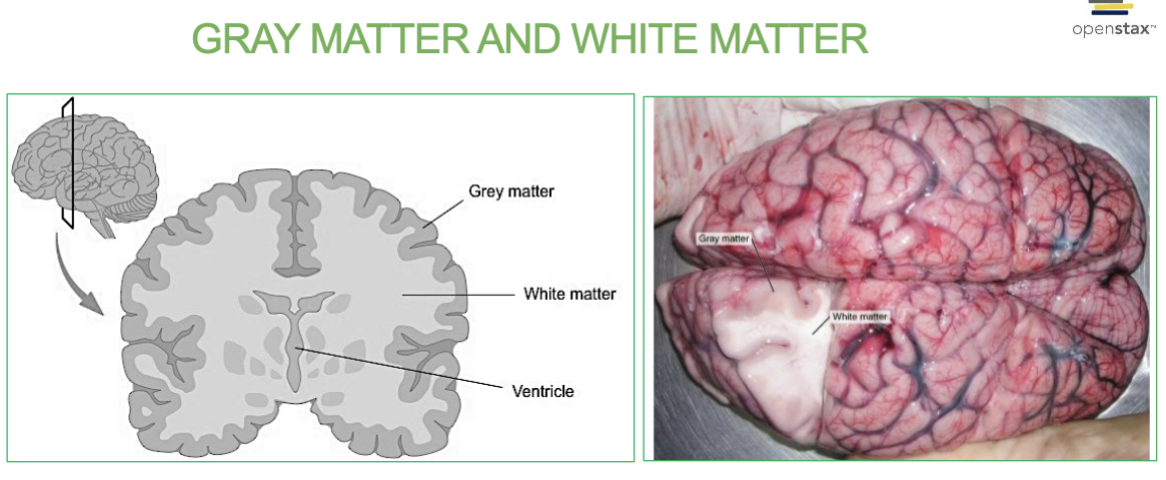
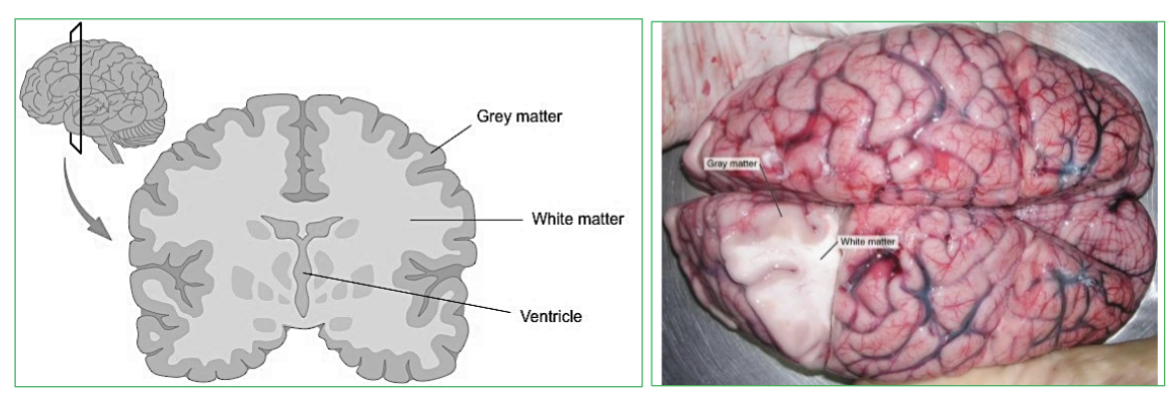
What is Gray Matter?
Area with NO myelin.
→ filled with neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and neuroglia
Forms the outer surface layer (cortex)
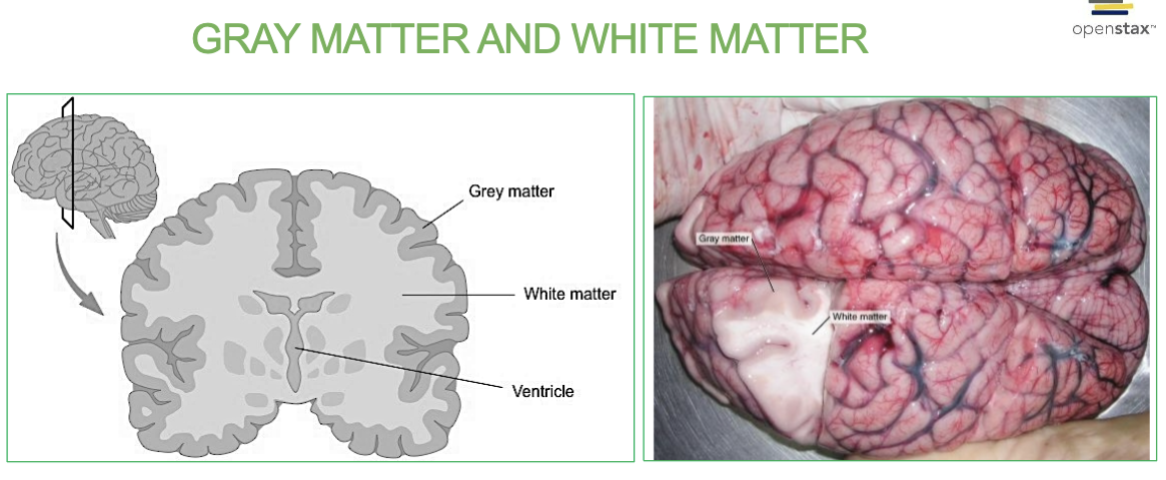
What is White Matter?
Area with myelin!
→ Bundles of axons and tracts . (Lies deep to gray matter in brain, but outside of gray matter in spinal cord)
Pearly white color from myelin around nerve fibers
Which matter forms the outer surface layer (cortex) of the brain? White or gray matter?
Gray Matter.
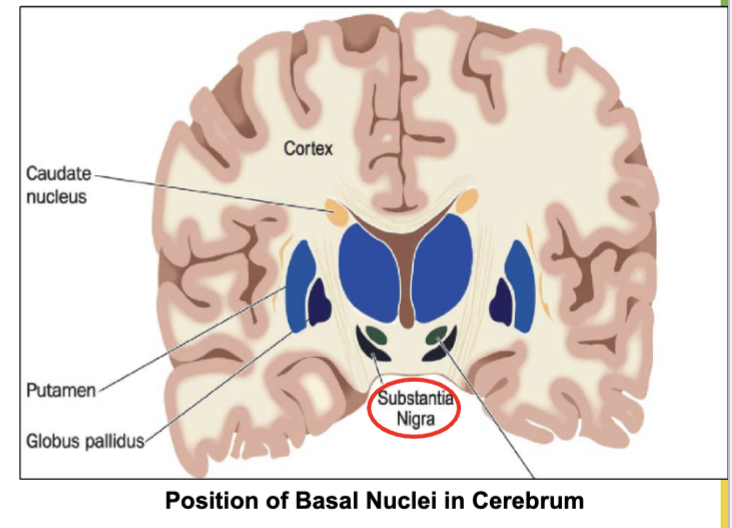
What is Basal ganglia (nuclei) & it’s job?
Group of neuronal cell bodies (gray matter) located deep in brain.
Job- Receive input from an area in midbrain called Substantia nigra to control unwanted movement.
(located in the cerebrum)
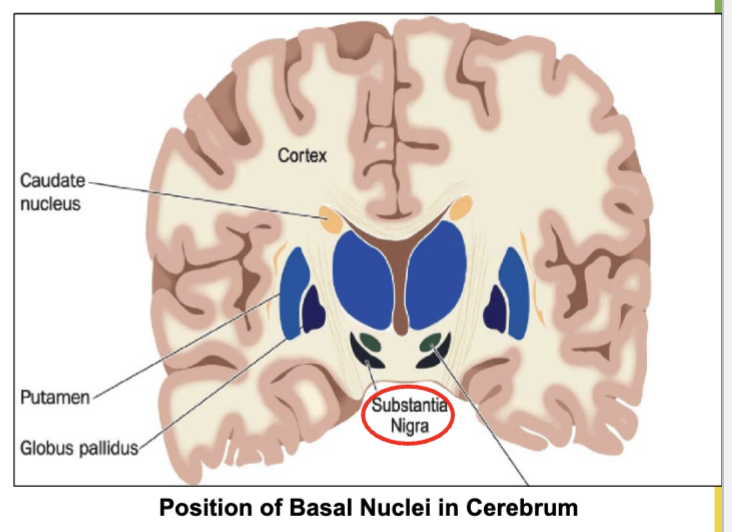
Why is it good to have healthy & good substantia ganglia?
Prevents Parkinson’s Disease
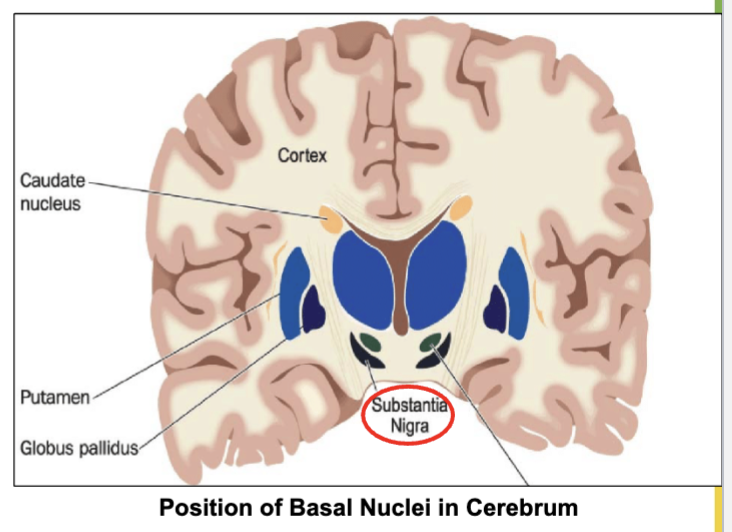
Degeneration of neurons in __________ leads to Parkinson’s disease
substantia nigra. located in the midbrain
What type of matter is the Basal Ganglia (nuclei) made up of? White or gray matter?
Made up of groups of neuronal cell bodies (gray matter) located deep in brain.
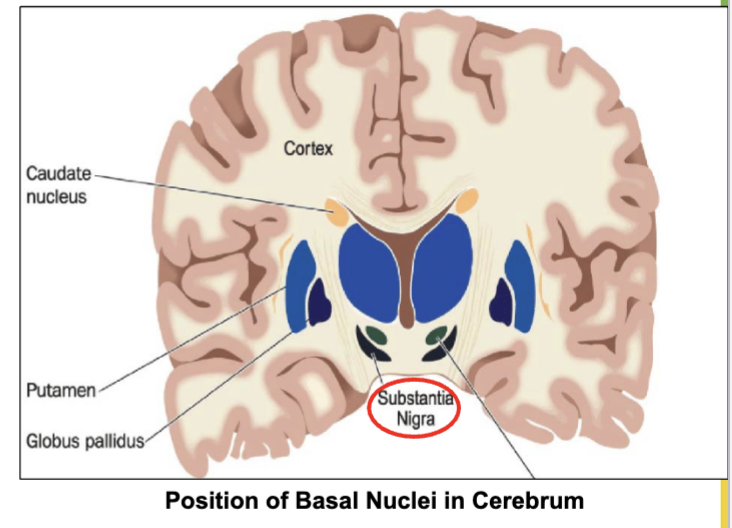
Where does the Basal Ganglia recieve input from to control unwanted movement?
From an area in the midbrain called Substantia Nigra.
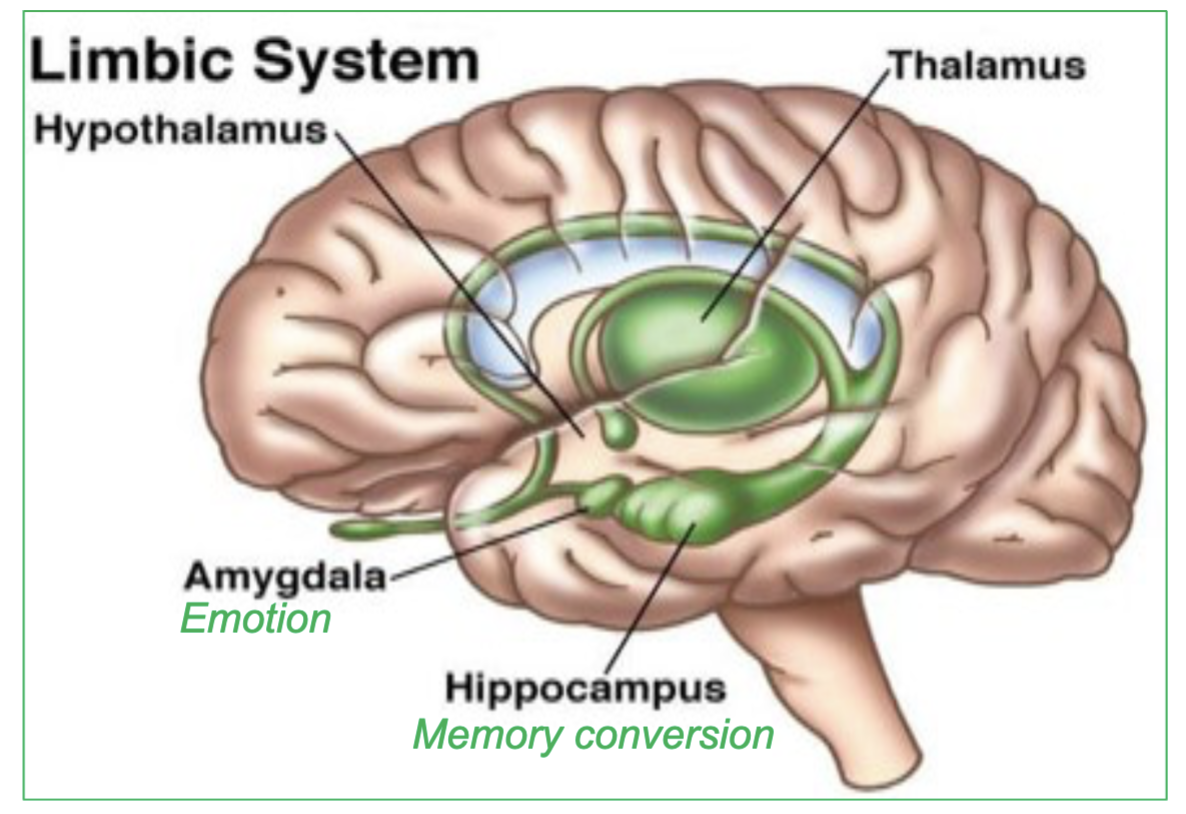
What is the Limbic System ?
a group of brain structures involved in controling …
emotions & memory
Gratification : sensations of pleasure or reward
Aversion: sensations of fear or sorrow emotion
(includes the hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, and thalamus)
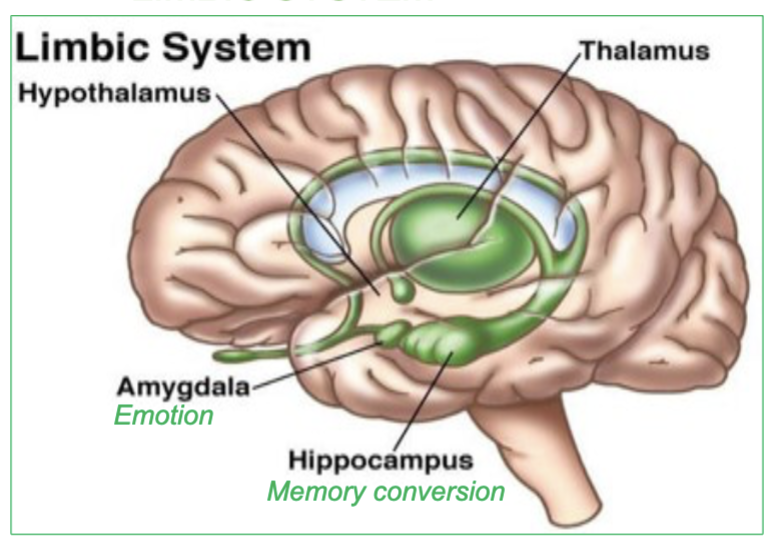
Which 4 parts of the brain are involved in the limbic System?
the hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, and thalamus
These structures are critical for emotional regulation, memory processing, and the experience of pleasure and fear.
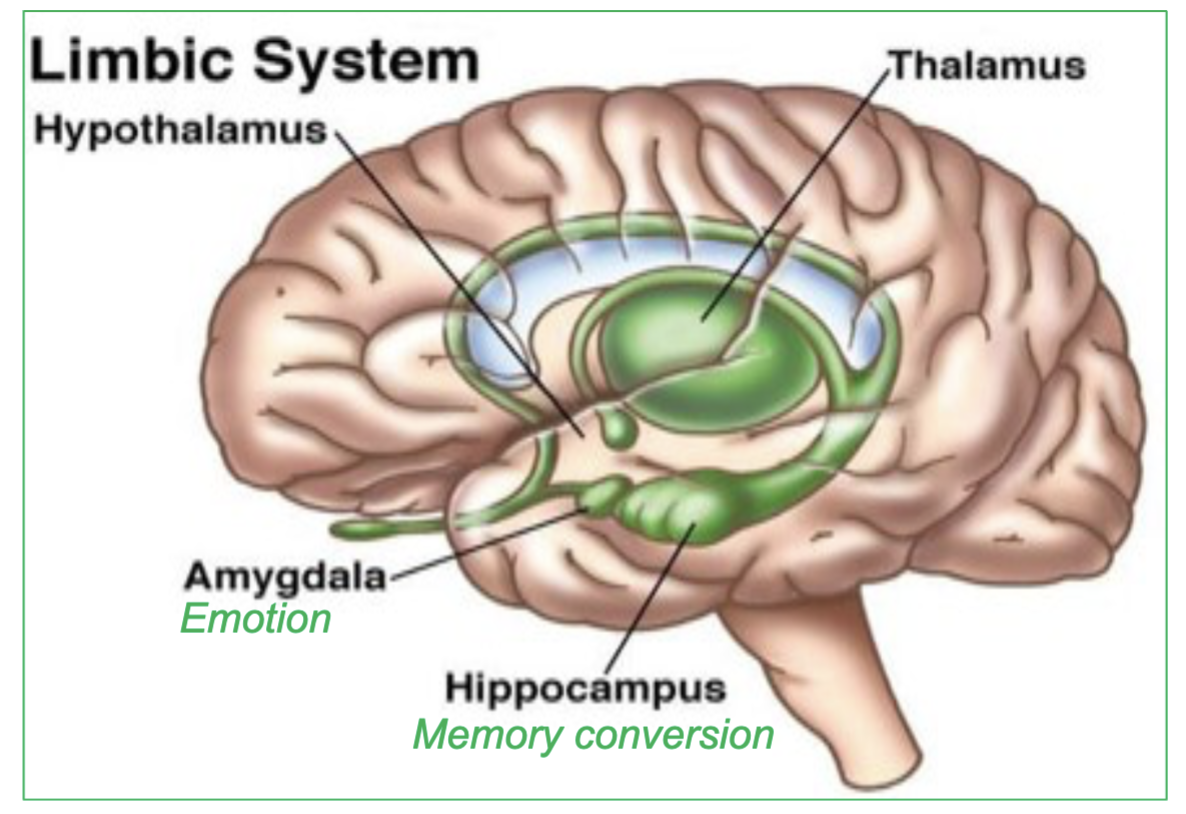
what does the Amygdala specifically control?
emotion
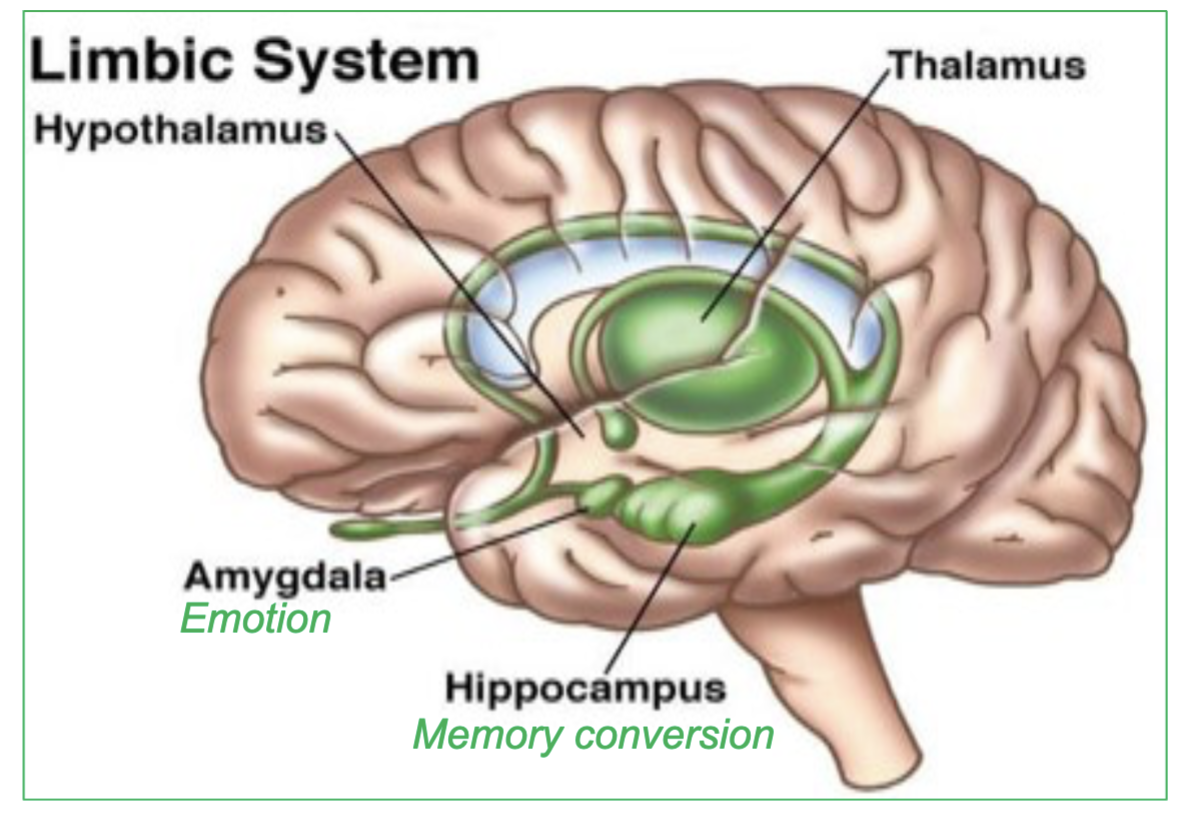
What does the Hippocampus specifically control/do?
memory conversion
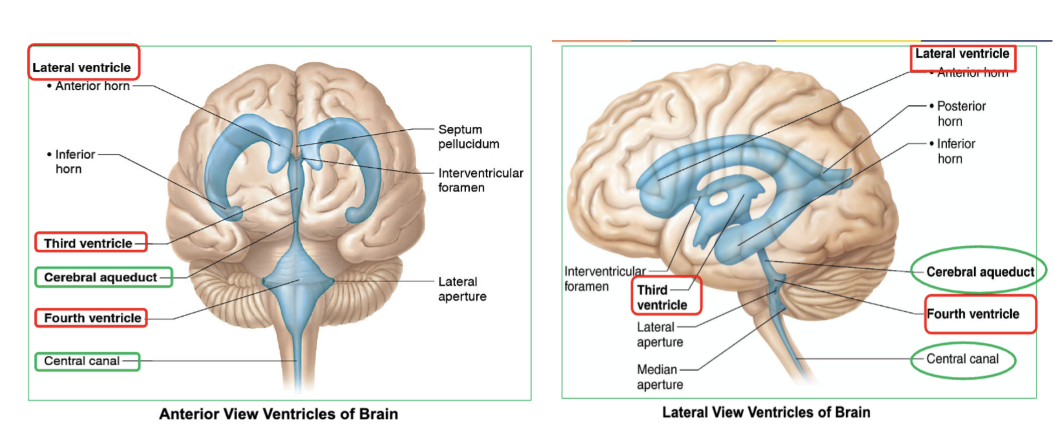
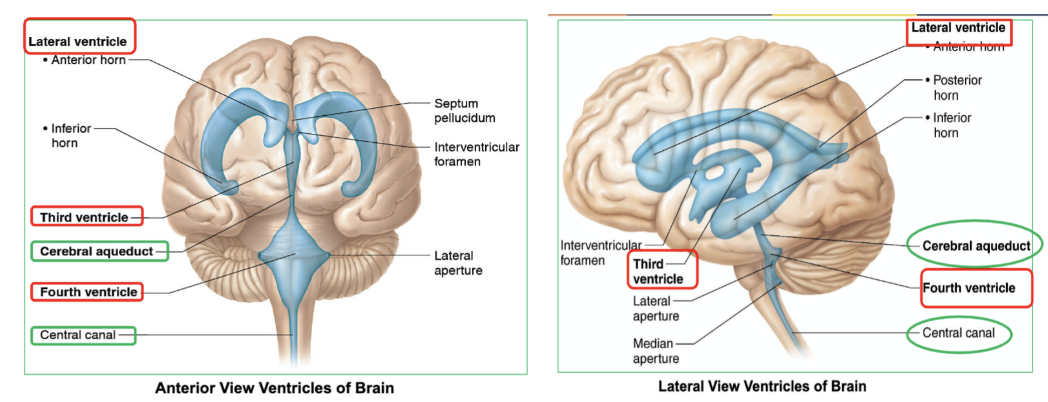
Which are the 4 Ventricles of the brain that contain CSF?
2 lateral ventricles
third ventricle : cerebral aqueduct connects the 3rd ventricle to fourth ventricle, allowing CSF to flow between them.
fourth ventricle : continuous with central canal of spinal cord
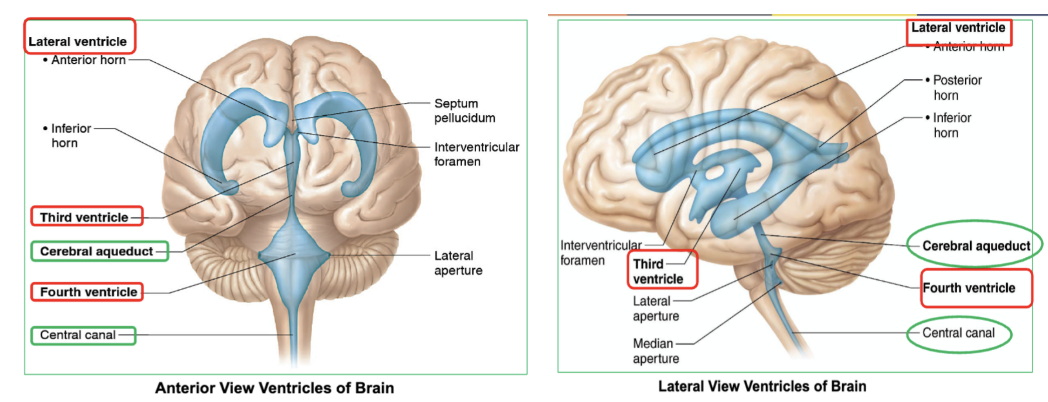
Which ventricle of the brain connects to fourth ventricle, allowing CSF to flow between them?
the third ventricle
which ventricle of the brain is continuous with central canal of spinal cord?
fourth ventricle
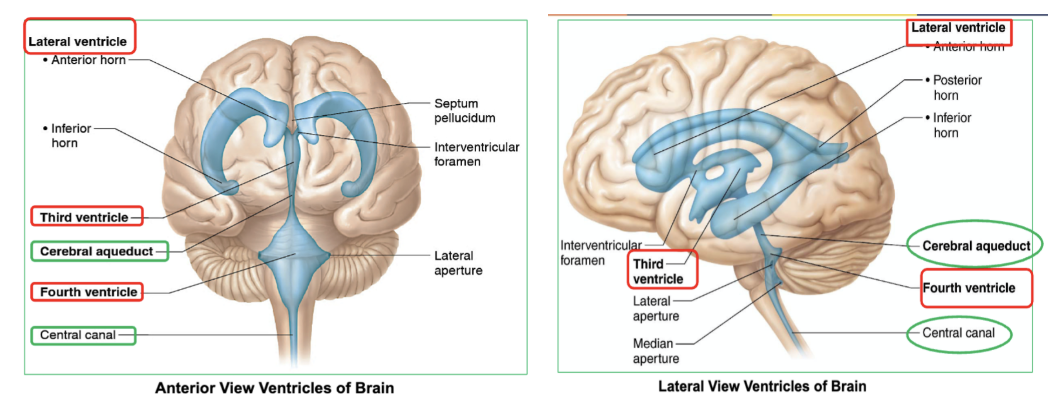
what do the 4 ventricles of the brain contain?
CSF
What are the 2 sources of CSF in the brain?
Choroid plexus : Network of capillaries located in roof of each ventricle
Ependymal cells : Cells lining the ventricles
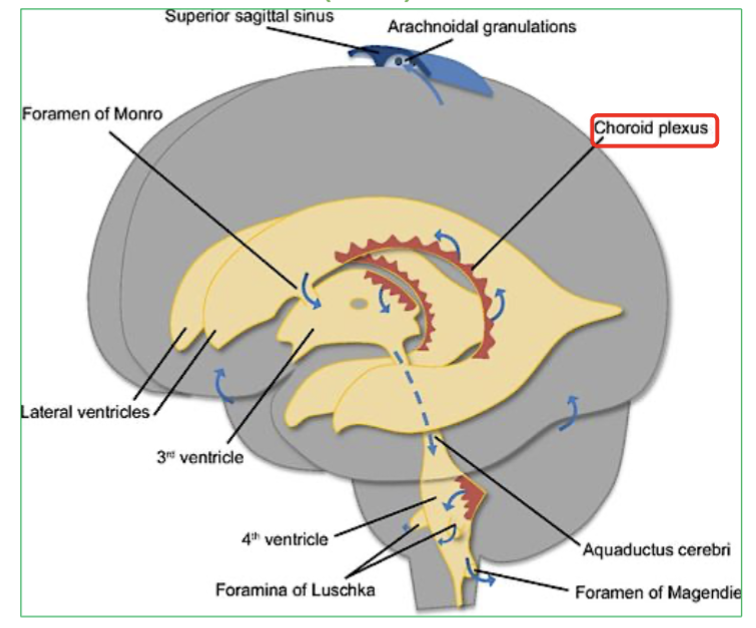
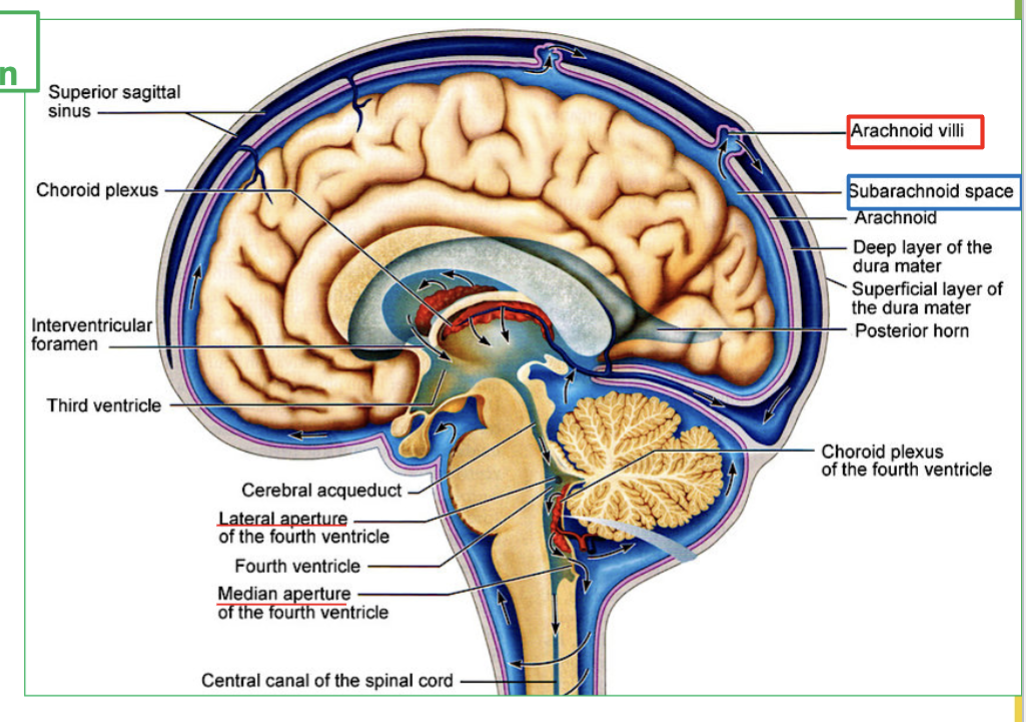
Explain the process of CSF Circulation in the brain (4 steps)
CSF flows out of the fourth ventricle to subarachnoid space, through the median and lateral apertures.
It will surround the brain and spinal cord.
Then CSF is then reabsorbed via the arachnoid villi into the blood.
Finally It ends up in large veins in the brain called the dural sinuses
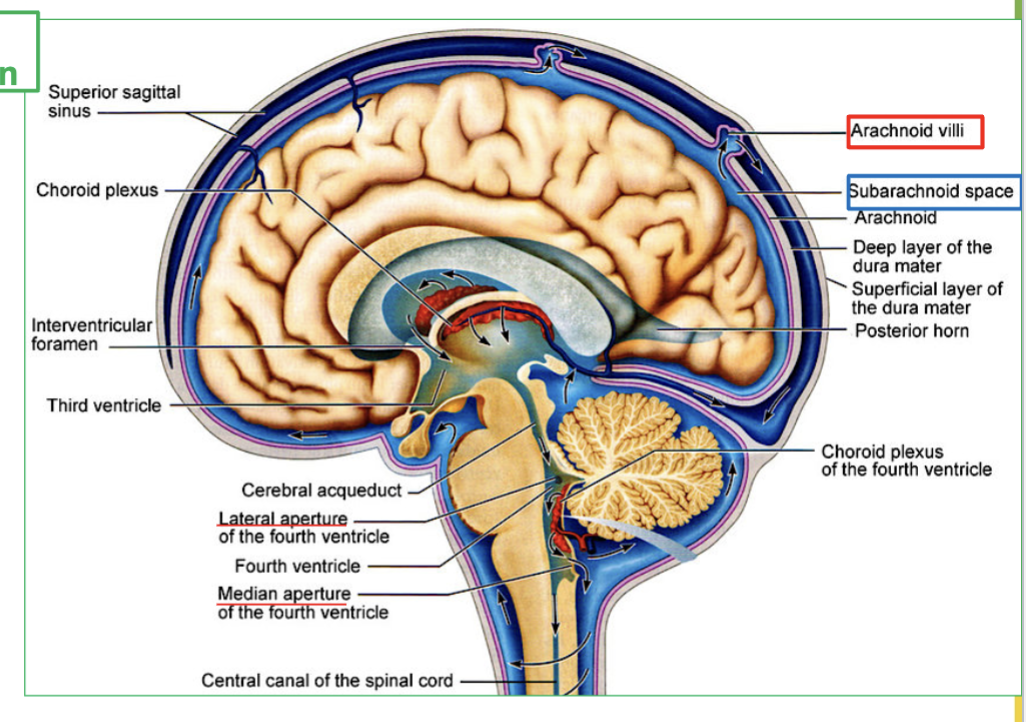
Where does CSF flow out of the fourth ventricle?
CSF flows out of the fourth ventricle through the median and lateral apertures to the subarachnoid space.
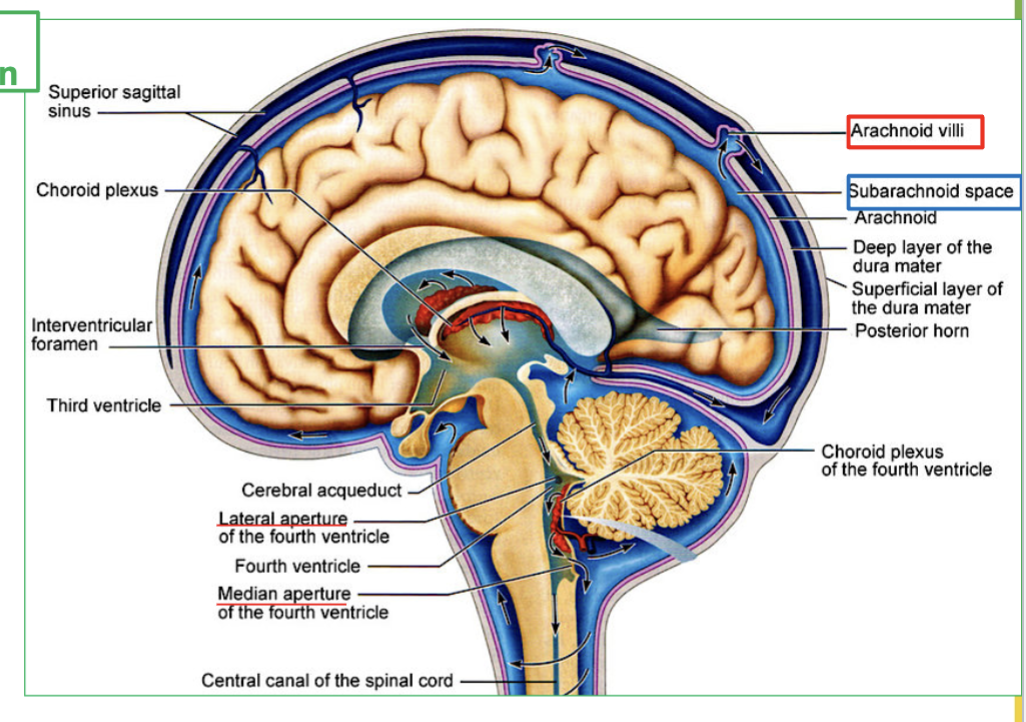
What area does CSF surround after leaving the fourth ventricle?
CSF surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
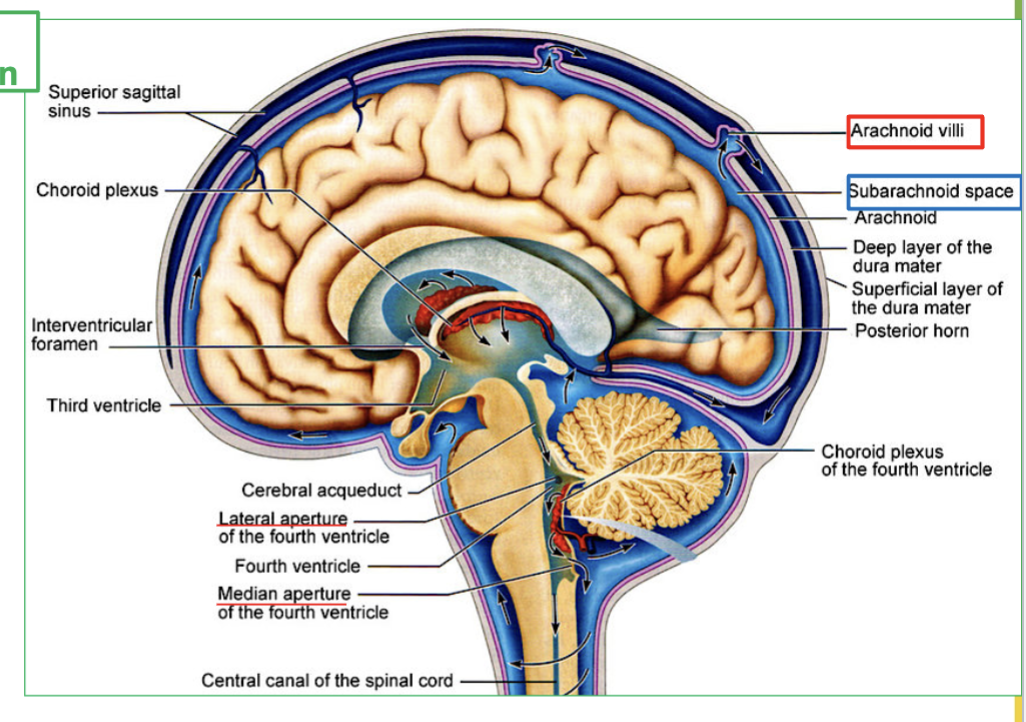
How is CSF reabsorbed into the blood?
CSF is reabsorbed via the arachnoid villi into the blood.
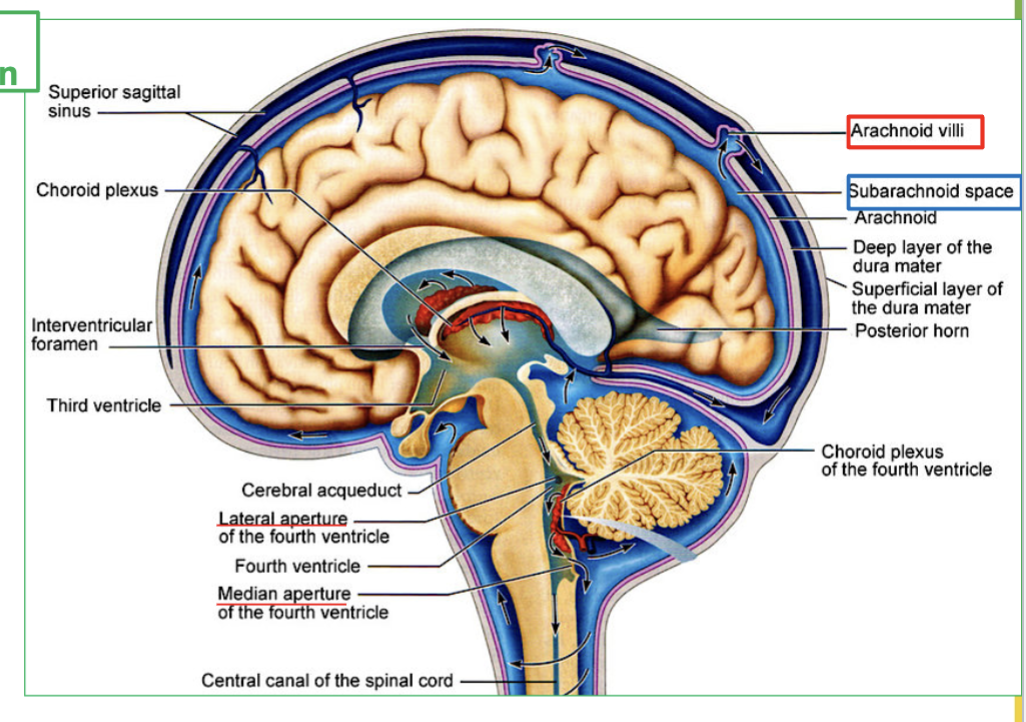
Where does CSF end up after being reabsorbed?
CSF ends up in large veins in the brain called the dural sinuses.
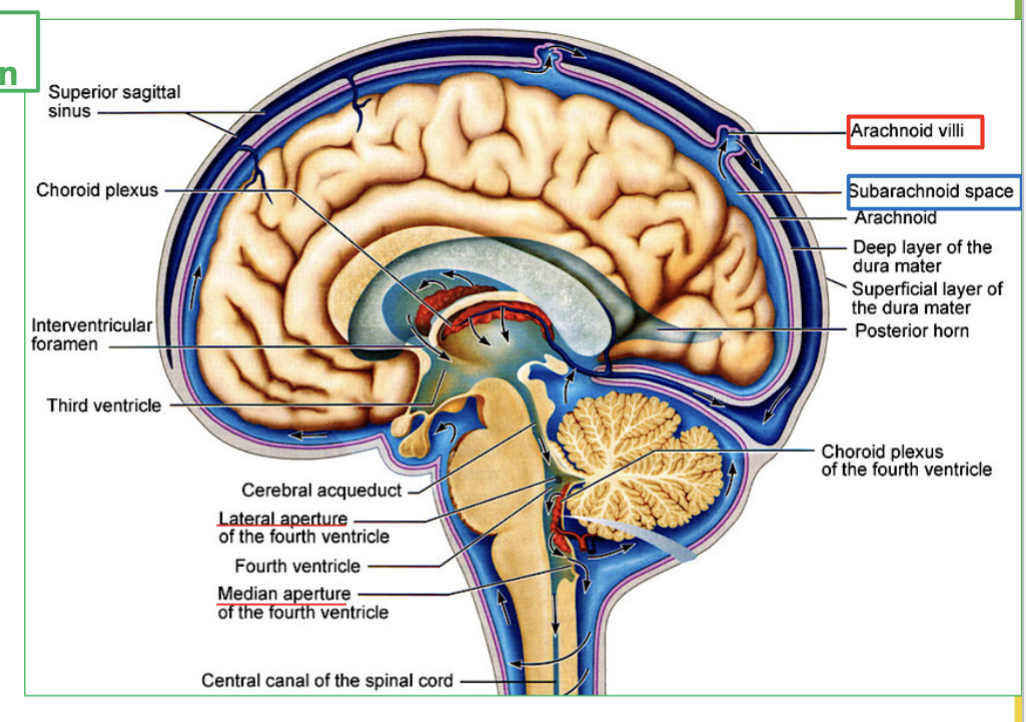
What is Dural Sinuses?
the large veins the brain that collects CSF.
What is the Diencephalon?
part of the brain located between the Brainstem and the Cerebrum.
Contains 3 major parts → Thalamus, Hypothalamus, & Epithalamus
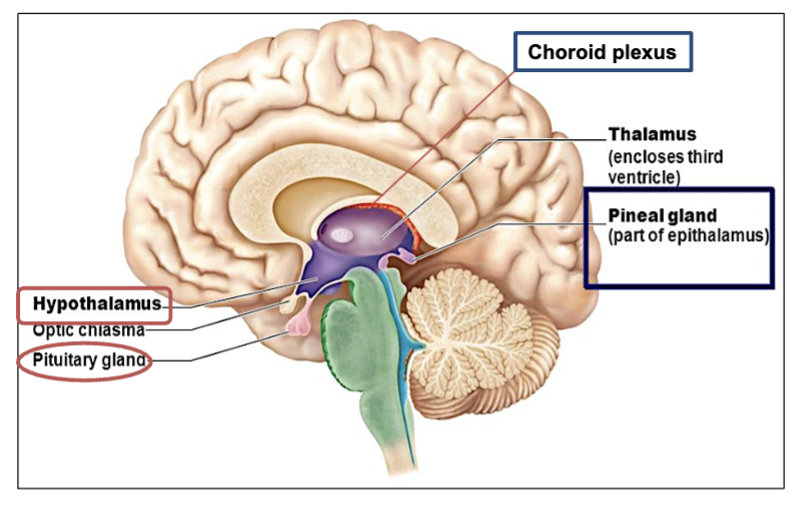
What are the 3 Major Parts of the Diencephalon?
Thalamus: relay station to the cerebrum. All input to the cerebrum synapses at the thalamus.
→ (in charge of designating & deciding where info goes to which area of the brain)
Hypothalamus: Connected to pituitary gland. Control of endocrine functions and heat regulation.
Epithalamus: contains the choroid plexus of 3rd ventricle and pineal gland.
( on top & behind of thalamus ! )
What is the job/function of the Diencephalon?
The diencephalon with it its 3 major parts, it acts as a relay center & Maintains homeostasis.
processes sensory information
regulates autonomic functions
controls hormonal balance.
It plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis and connecting different brain regions.
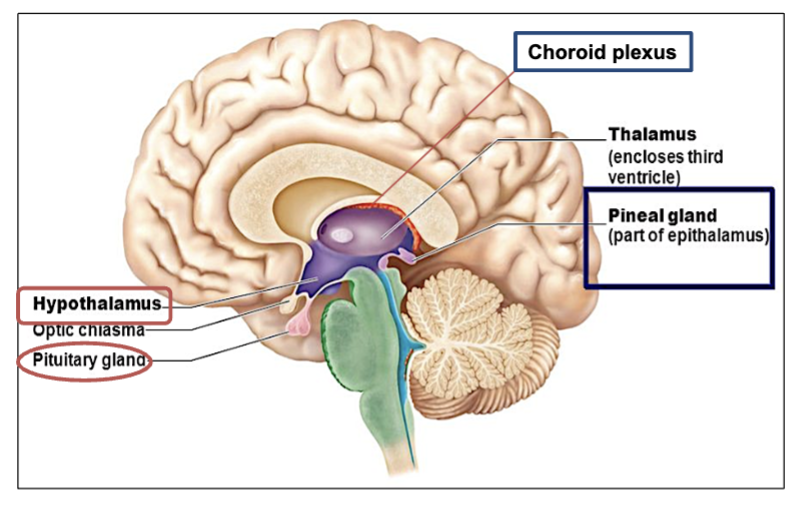
What is the function of the thalamus?
acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals to the Cerebrum.
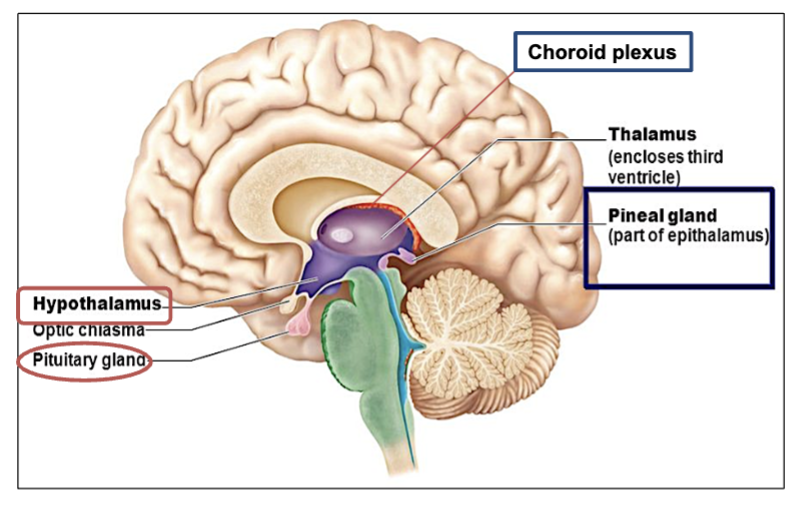
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
Connected to pituitary gland it, Controls endocrine functions and heat regulation ( under the thalamus, controls hormones & temp )
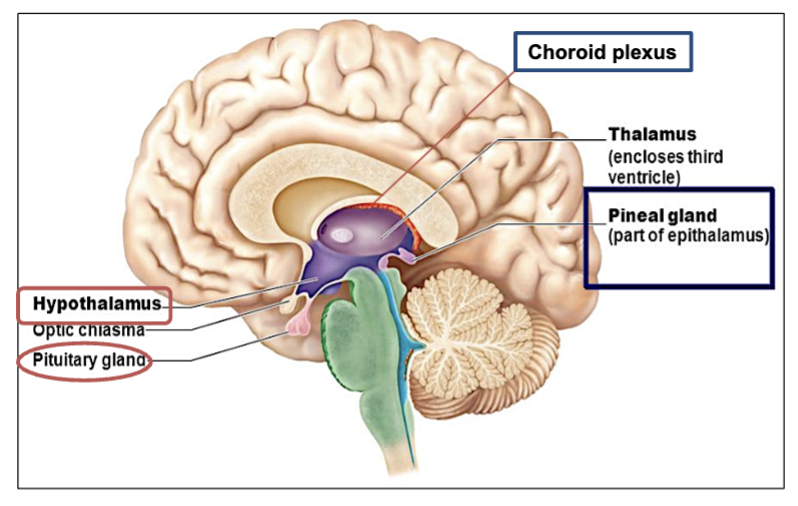
What is the role of the Epithalamus?
The epithalamus contains the pineal gland & the choroid plexus of 3rd ventricle
→ the Epithalamus regulates sleep-wake cycles through the production of melatonin.
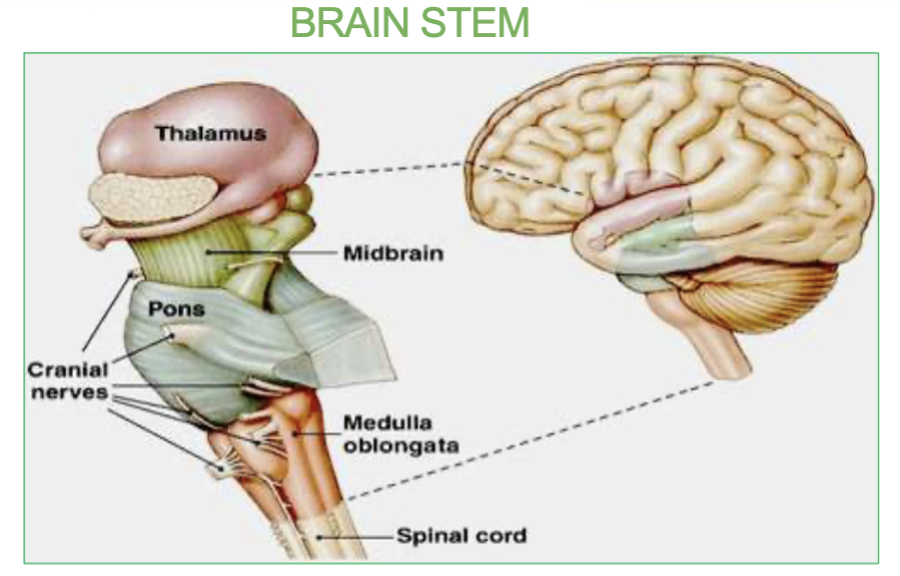
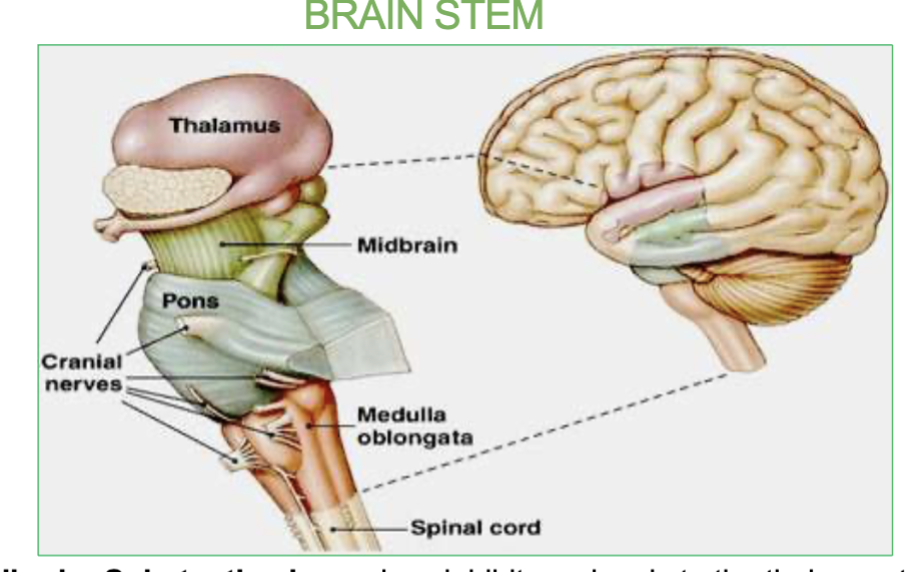
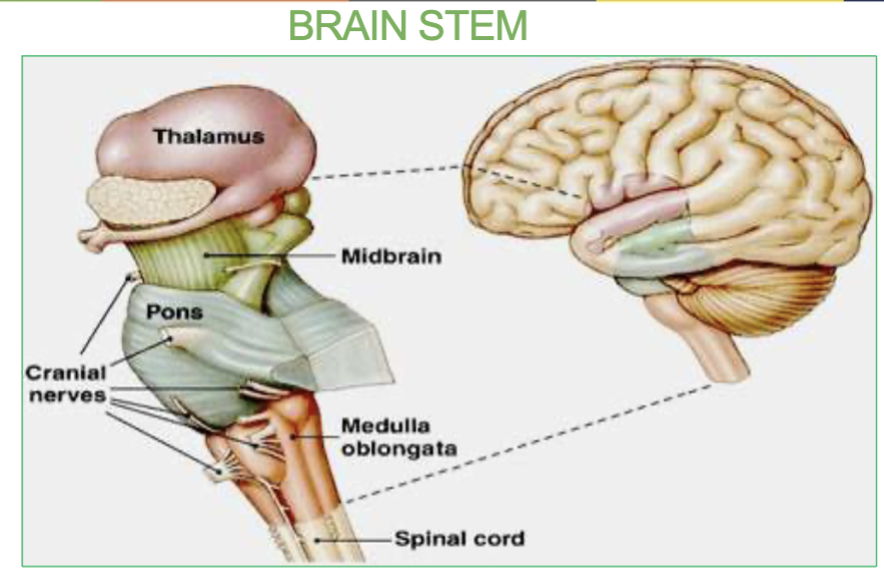
What are the 3 parts of the brainstem & their functions?
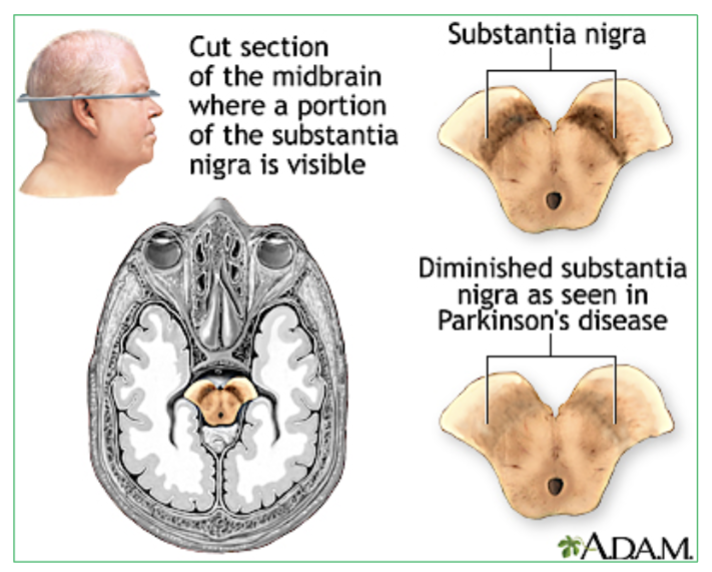
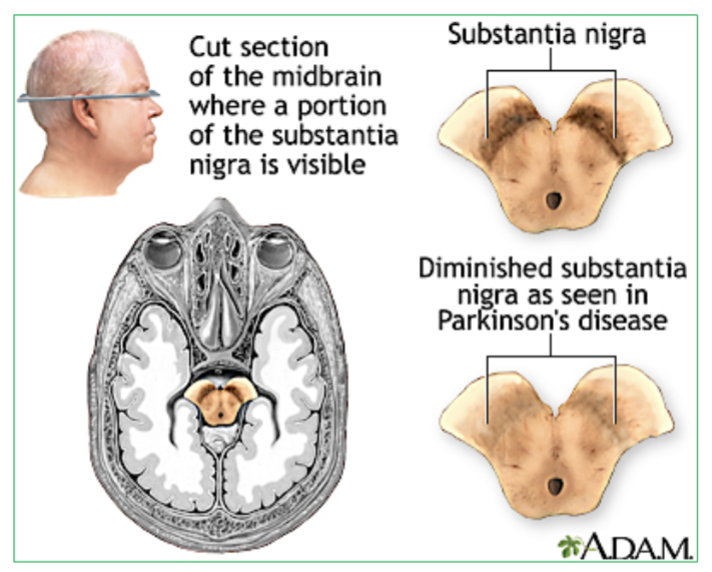
Midbrain : Contains the Substantia Nigra. it relays inhibitory signals to the thalamus to prevent unwanted movements.
(Degeneration of neurons in substantia nigra leads to Parkinson’s disease)
Pons: origin of cranial nerves
Medulla - Under the pons, it contains the cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory vital centers.
What is the function of the Substantia Nigra? (what does it produce & its job)
involved in producing dopamine, which helps regulate movement, coordination, and motor control. If damaged it can lead to parkinson’s disease.
Which structure in our brain is in charge of producing dopamine?
The Substantia Nigra
What happens if the Substantia Nigra is damaged?
Degeneration of neurons that secrete neurotransmitter Dopamine will result in Parkinson’s disease.
→ This leads to motor control issues such as tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
to which parts of the brain does the substantia nigra relay inhibitory signals to, to prevent unwanted movements?
the thalamus & also Basal ganlia
What 3 vital centers are located in the medulla?
the cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory vital centers.
What functions are regulated by the brainstem?
Autonomic functions
Breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure (vital centers) BUT specifically by the Medulla
(keeps you alive while you sleep)
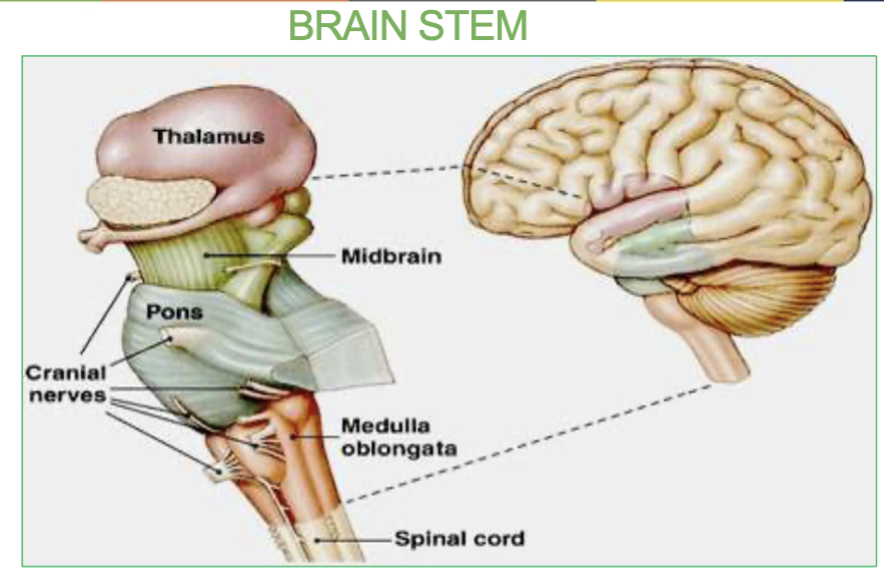
Which brain structure is in charge of designating & deciding where info goes to which area of the brain?
the thalamus.
What is the role of the Cerebellum?
Controls balance, posture, and coordination of movements.
What is the Pyramidal Decussation in the medulla?
Area where most of the motor fibers cross to the other side. occurs in the medulla.
→ Explains how lesions on one side of the brain may result in motor deficit on the
contralateral (opposite) side of the body
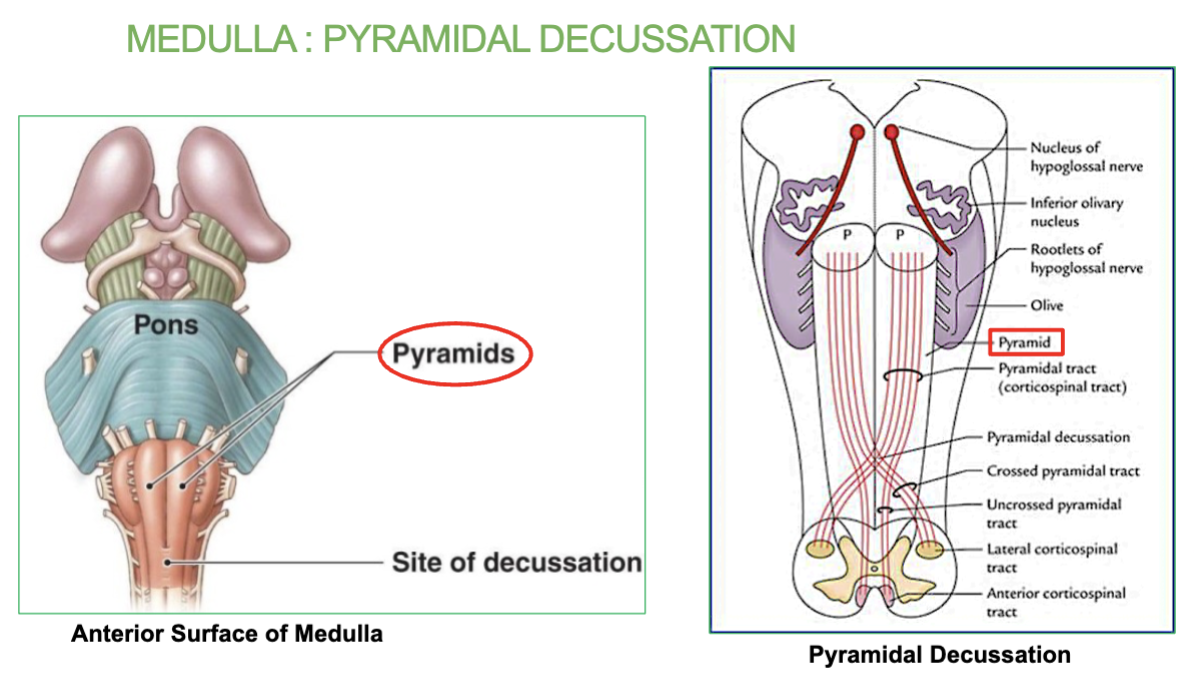
Where does the Pyramidal Decussation occur?
occurs in the lower part of the medulla, near the spinal cord.
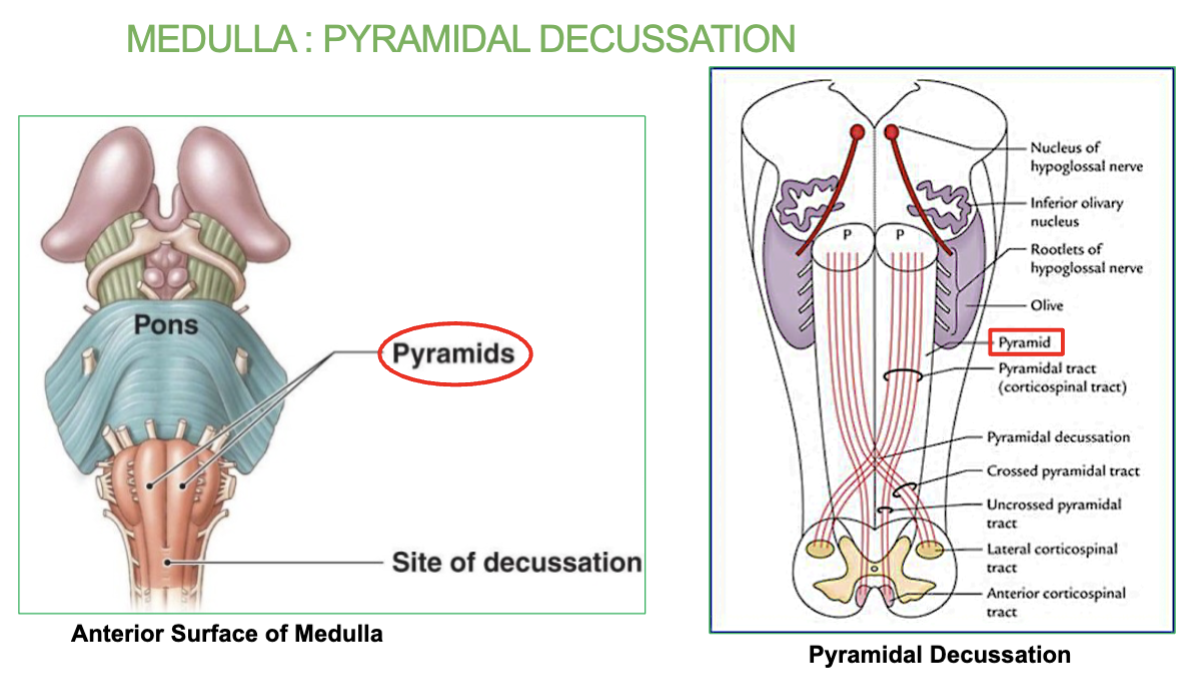
What does the Pyramidal Decussation explain?
Explains how lesions on one side of the brain may result in motor deficit on the
opposite side of the body
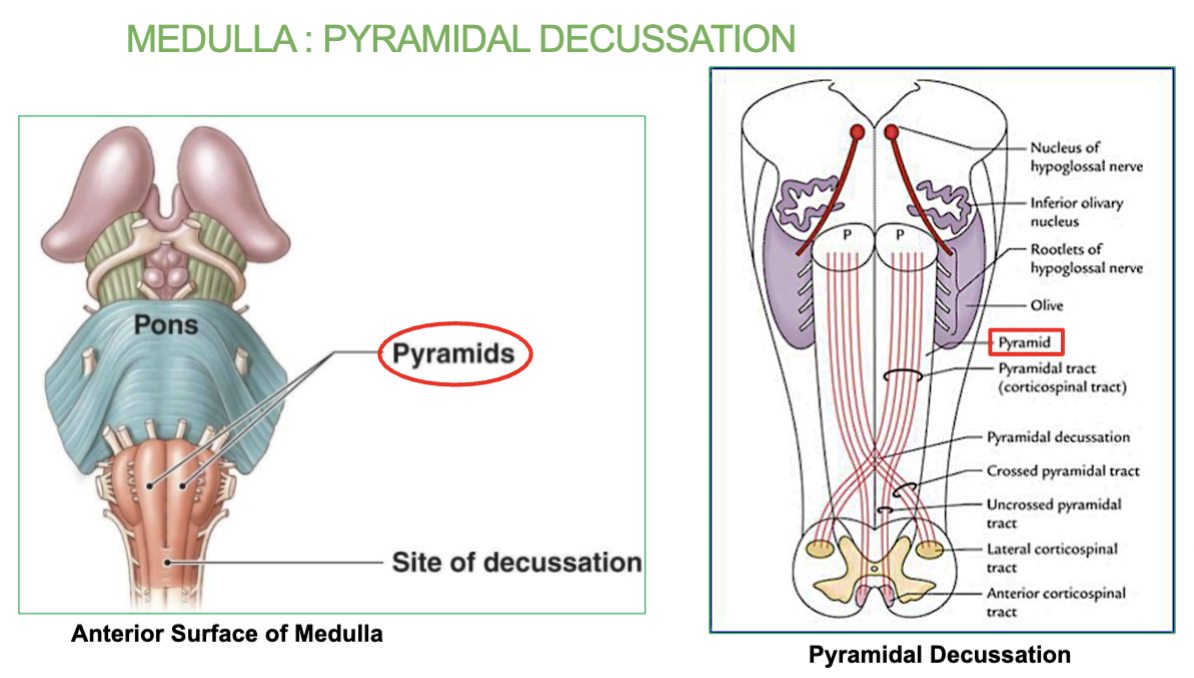
What structure connects the two Cerebellum hemispheres?
The vermis, which helps coordinate motor activity between the hemispheres.
(Arbor vitae are the distinctive tree-like pattern of its white matter in the cerebellum)
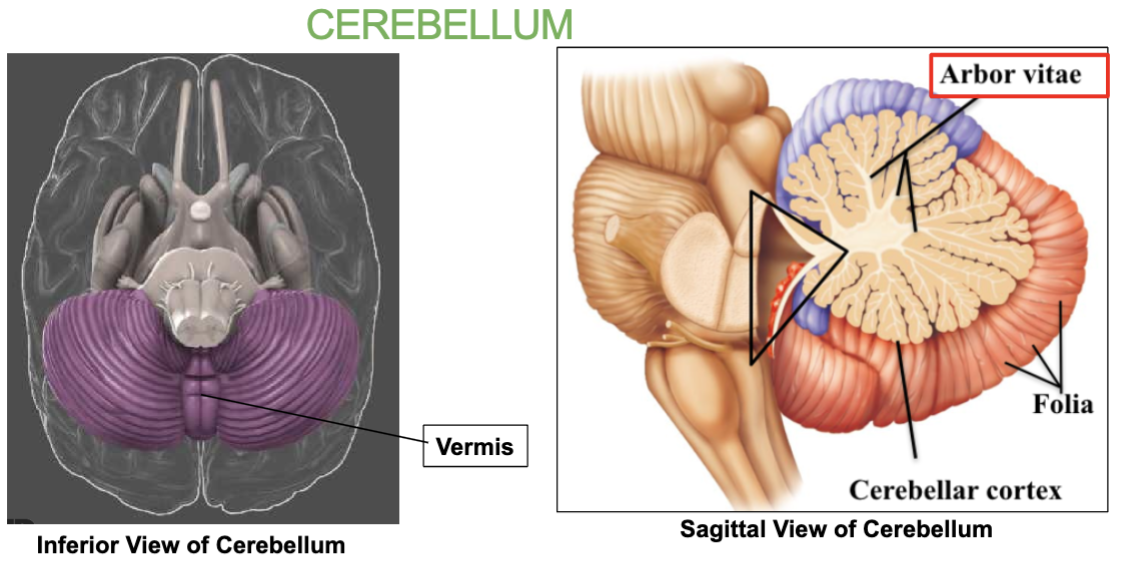
What is the tree-like pattern inside the Cerebellum called?
Arbor vitae
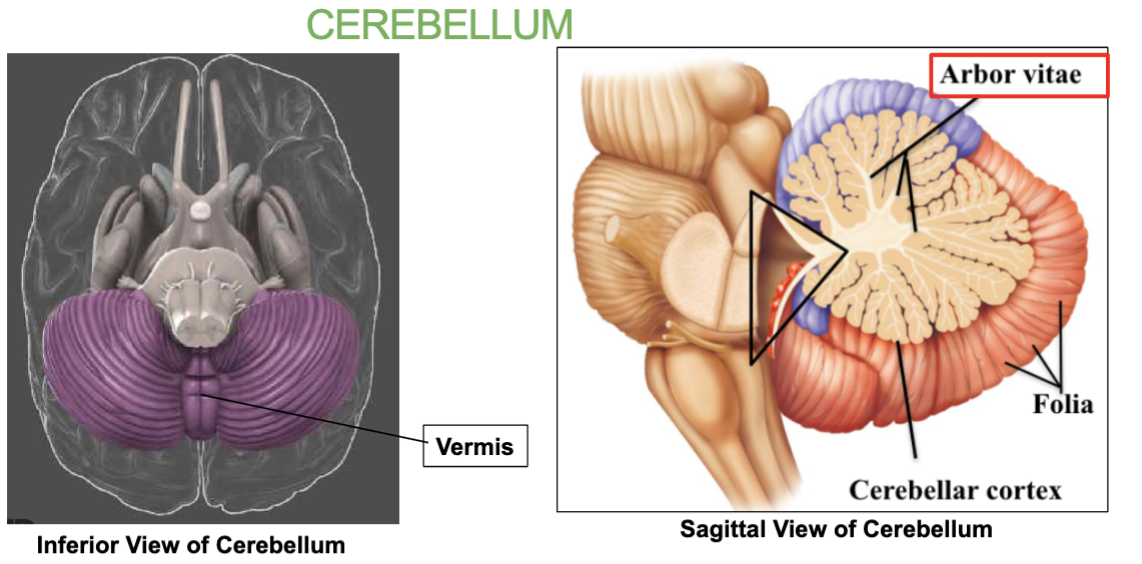
What type of matter is the arbor vitae made up of?
White matter.
What are the 3 main functions of the Cerebellum?
Equilibrium
Balance
Coordination of movement - it communicates with the motor areas of the cerebrum to smooth and coordinate movement
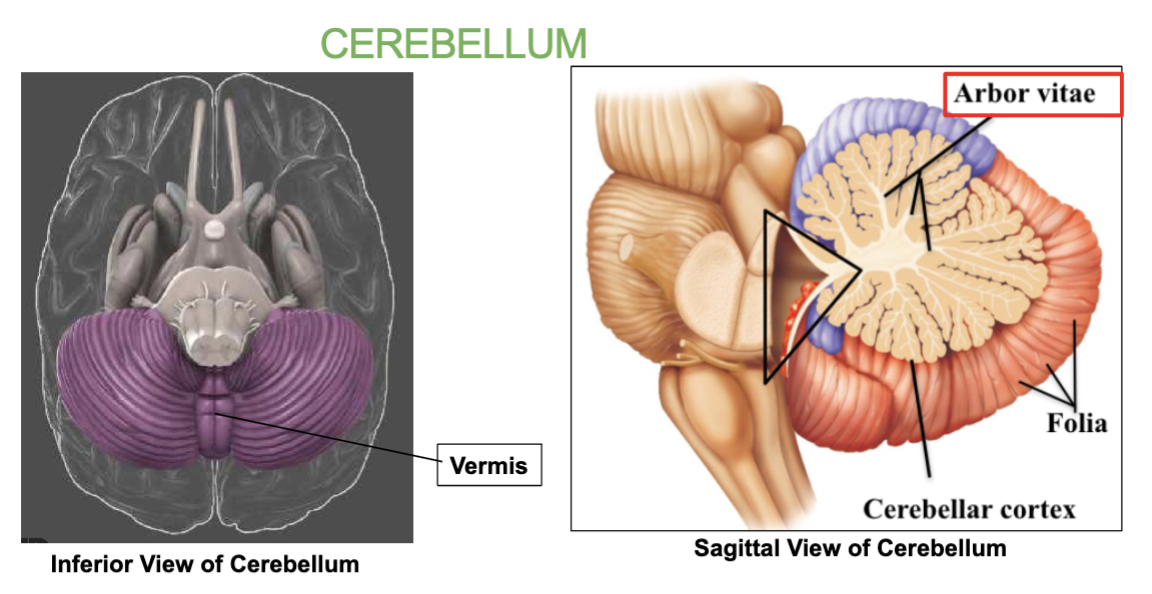
What is the Arbor Vitae?
the tree-like pattern inside the Cerebellum.
What connects the the 2 Cerebral hemispheres?
The Corpus callosum.
(made up of white matter)
What connects the 2 Cerebellar hemispheres?
the Vermis
Job of the midbrain & where is it?
Made up of the substantia nigra. Located above the pons, the midbrain relays inhibitory signals to the thalamus to prevent unwanted movements.
Degeneration of neurons in substantia nigra leads to Parkinson’s disease
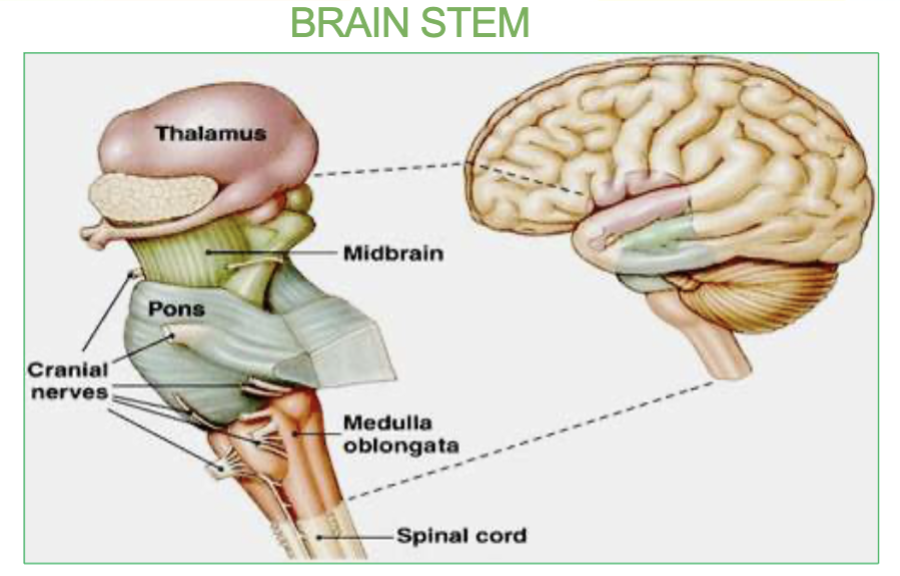
where is the substantia nigra located?
The substantia nigra is located in the midbrain, situated above the pons.
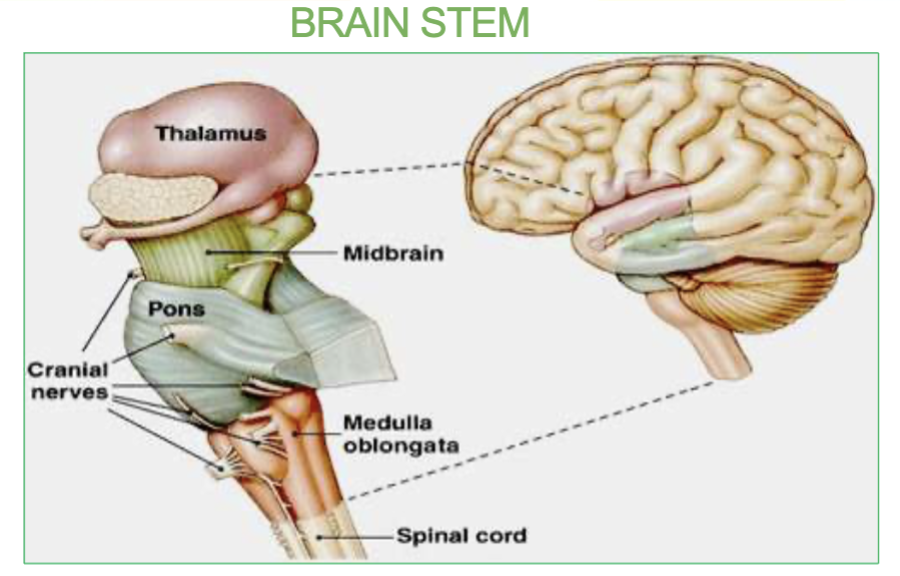
What is the Pons & where is it located?
it is the origin of cranial nerves and located in the brainstem.
In the middle of the midbrain and the medulla.
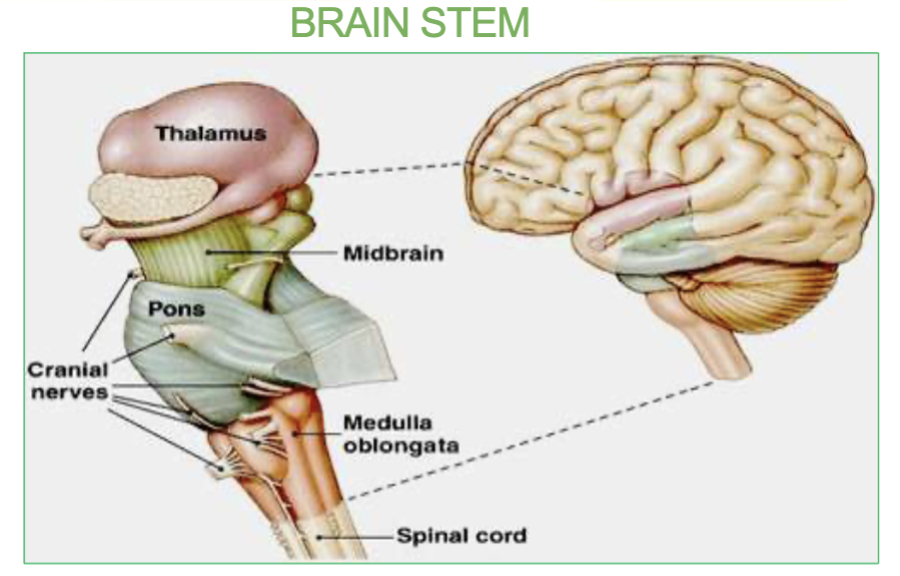
Job of the medulla & where is it?
located under the pons, controls our vital center like cardiac (heart rate), vasomotor(blood pressure) & respiratory center(breathing).
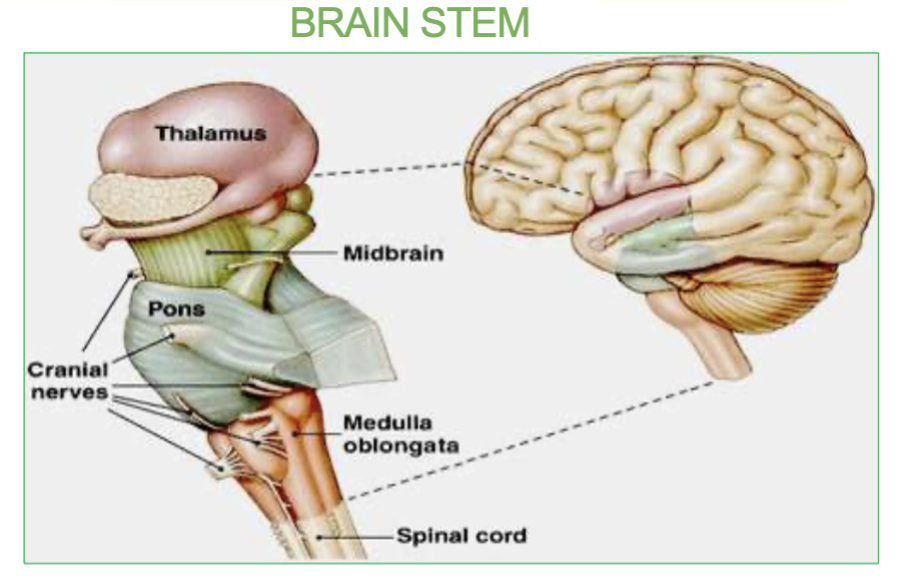
What are the 3 Sensory Cranial Nerves?
l Olfactory
ll Optic
Vlll Vestibulocochlear
How many Sensory Nerves do we have & what are they?
3
l (1) Olfactory
ll (2) Optic
Vlll (8) Vestibulocochlear
How many Motor Nerves do we have & what are they?
5
III (3) Oculomotor → Eye movements
IV (4) Trochlear → Eye movements
VI (6)Abducens → Eye movements
XI (11)Accessory → Neck muscles Motor
XII(12) Hypoglossal → Muscles of pharynx and larynx Motor
How many Mixed Nerves do we have & what are they?
4
V Trigeminal → Sensory/motor face
VII Facial → Motor face muscles, taste
IX Glossopharyngeal → Taste and pharyngeal movement Mixed
X Vagus → Viscera thoracic and upper abdominal organs (heart , stomach, and small intestines)
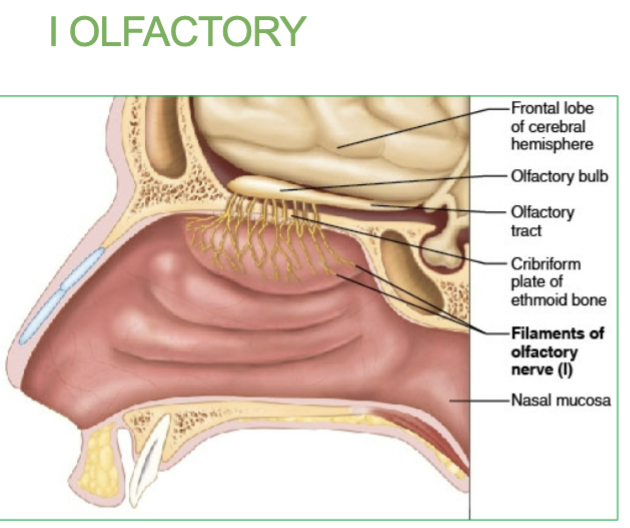
Job of the l Olfactory Cranial Nerve
Smell