ansc 108
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
castrated male pig
barrow
where is fat evaluated on swine
jowls
behind shoulder
over top
rear and front flanks
underline
predominant swine production states are located in?
Midwest; it produces most corn and soybean meal
swine diet
corn: energy source
soybean: primary protein source
spraying
gets rid of external parasites
pork producing countries
china
european union
brazil
vietnam
top 5 swine ? states (midwest oriented)
iowa
minnesota
north carolina (not midwest + corporate)
illinois
indiana
where is most of the swine production in texas based in?
texas panhandle
why is the panhandle preffered?
away from large cities (environmental soundness)
water availability
feedstruffs
remote locations
trainable workforce
what percentage of hogs in the market are crossbred?
95%
rotational system
most popular
market hogs are produced as well as replacement gilts
sire breeds are rotated each generation
replacement females are kept and mated to the sire breed that is least related
lower heterosis than terminal
terminal system
all of the offspring is marketed
no replacement gilts are kept
consistent genetics
better performance
rotaterminal system
combination of rotational and terminal
maximum heterosis
20% focused on maternal genetics
80% is terminal
sow gestation length
3 months, 3 weeks, 3 days = 114 days
sow farrowing crates
5×7
sows are moved around a week before birth
sow side: water and feed, cooler temp (60-65 deg)
piglet side: escape underneath to nurse, warmer temp (85-90)
all in, all out
everyone enters and leaves at once for sow to give birth
clean and disinfect farrowing house before next sow comes in
farrowing houses
high biosecurity
__ pounds of feed per __ of gain
3 pounds; 1 pound
baby pig processing steps
clip needle teeth
cut navel cord
iron injection to prevent anemia
dock tail for safety
crastrating males
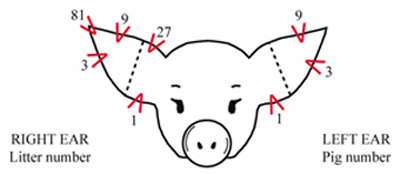
ear notching
right ear notch
litter number
left ear notch
individual number
ear notching chart (usually)
pigs right, our left
pigs left, our right
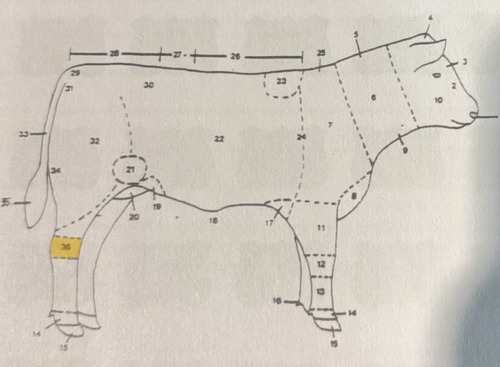
sow underline
6 teats on each side preffered = 12 in total
sow underline issues
inverted teats
blunted teats
extremely small
poor spacing
piglets are?
creatures of habits
sows produce __ milk in the front of their udder and __ in the back part of their udder
more; less
runt piglet
suck on the back of the udders (less milk)
bigger piglets
suck on the front of the udders (more milk)
ewe
female sheep
wether
castrated male sheep or goat
mutton
meat from sheep over one year of age
edward’s plateu
where majority of sheep are located
main type of ewes used are?
rambouillet and rambouillet crosses
top states for lamb feedlot industry
colorado
texas
hair production breed
angora goat for mohair
meat production goat
boer goat: brown face & neck
milk production goat
saanen
butterfat production goat
nubian
top state for dairy production
wisconsin
california
lamb are __ breeders. they breed in the __ and lamb in the __.
seasonal; fall; spring
sheep and goat gestation length
150 days
estrous cycle for sheep
17 days
estrous cycle for goats
21 days
reasons for tail docking?
sanitation reasons
elastrator
can be used for docking and castration
crutching
removing wool around reproductive tract for hygienic reasons
usually during lambing season (around udder)
facing
trimming wool around face to prevent wool blindness
way to remove internal parasites or deworm
drenching
predator control for sheep
great pyraneese
donkeys
llamas
where is the dental pad?
top of mouth with teeth at the bottom
when do they get a full mouth of teeth?
4 years
sore mouth
scabs around mouth
zoonotic
overshot
overbite
“parrot mouth”
more common than under
undershot
underbite
“monkey mouth”
mohair production is __ in Texas?
#1
heifer
female that has not produced calf
steer
castrated male cattle
feedlots
higher concentrate diet
starts with roughage then gets more concentrated
leading cattle countries
brazil
india
USA
texas is #1 in the nation for total __
cattle, ranches, # of beef cattle, and feed lot cattle
cow calf
calf is born and is sold right after weaning
what do commercial producers prefer?
crossbed genetics
big seed stock operations
#3 44 farms, Cameron, TX
#6 R.A Brown Ranch, TX
#1 cow calf operation in the US
Deseret Cattle & Citrus, FL
cattle estrous cycle
21 days
cattle gestation length
283 days, 9 months
stocker operation
after weaning, grass or forage based diet is introduced
fall / winter months
minimum 100 days in feedlot
methods of identification
tattoos
ear tag
hot branding
freeze branding
electronic ear tags
why do we castrate?
aggresive bulls become docile
fatten faster
prevents poor genetics
easiest way to dehorn
polled genetics
higher $$ value
ear implants
more efficiency and rate of gain
10-15%
does not affect quality grades
where are injections usually given?
shoulder and neck (preferably neck) (triangular region)
frame size
height of animal
depends on age and sex
large frame = 9
avg cows today = 3-5
scrotum circumference
minimum of 30-32 cm
larger scrotum = heifers that mature quicker and breed faster
too large 40 cm maximum (30 > x < 40)
what affects weaning weight
age and sex
when do cows produce the best quantity of milk?
5-10 years of age
dystocia
difficult birth
cimmon in younger
affected by:
birth weight of calf
sex of calf
pelvic size
EPD
expected progency difference
genetic estimate of offspring performance
what does milking ability reflect?
weaning weight of calf
fastest growing in feedlot?
highest yearling weight
which would you keep away from first calf heifers
higherst birth weight
which should give birth to more maternal daughters?
maternal milk EPD
EPD difference
+1
-3
difference between both is 4
fat
deposited from front to back
fatter = softer, smoother over ribs
fatter on brisket, belly and flank
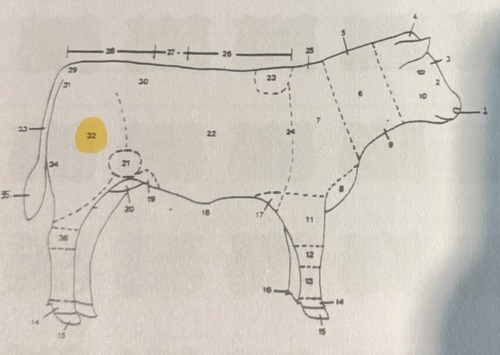
hock
what affects yield grade?
cutability
what impacts quality grade?
marbling and maturity
beef quality grades
prime, choice, select, standard
average dressing percent for beef
62%
yield grades for lamb
predict % of boneless closely trimmed retail cuts
round, loin, rib, chuck
4 factors that impact yield grade
external fat thickness over ribeye at 12th rib
kPH
REA
carcass weight
lamb quality grades
prime, choice, good, utiliity
lamb yield grade based on
12th rib fat
lamb yield grade equation
0.4 + (10 x adjusted fat thickness)
where is muscle evaluated on swine
forearm
shoulder
top
loin
rump
ham
swine dressing percent
72%
simple stomach & skin stays on
swine loin eye area
(2 * live weight / 100)+ 0.5
swine muscle score
thin
moderate
thick (avg for show pigs)
pork cuts
ham
loin
picnic shoulder: lower shoulder
boston: upper shoulder
quarter or round