Campbell Biology Chapter 8
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
metabolic pathway
A series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler compounds.
catabolic pathway
A metabolic pathway that releases energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds.
anabolic pathway
A metabolic pathway that consumes energy to synthesize a complex molecule from simpler compounds.
bioenergetic
The study of energy flow or energy transformations into and within living systems.
energy
The ability to cause change.
kinetic energy
The energy an object has due to its motion.
thermal energy
Kinetic energy associated with the random movement of molecules or atoms.
potential energy
The energy that an object has because it's position, shape, structure, location, or condition.
chemical energy
A form of potential energy that is stored in chemical bonds between atoms.
thermodynamics
The study of energy transformations that occur in a collection of matter.
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness.
second law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
spontaneous process
A process that can occur without an input of energy.
free energy
Measures the portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system, as in a living cell.
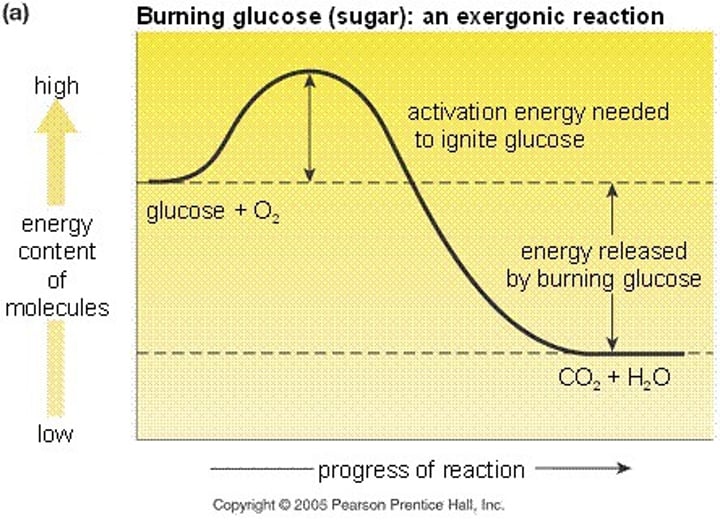
exergonic reaction
Reaction that proceeds with a net release of free energy.
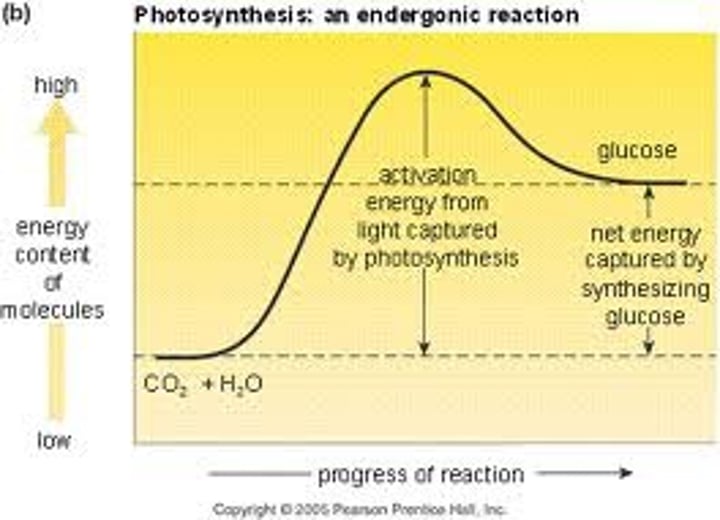
endergonic reaction
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings.
energy coupling
The use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one.
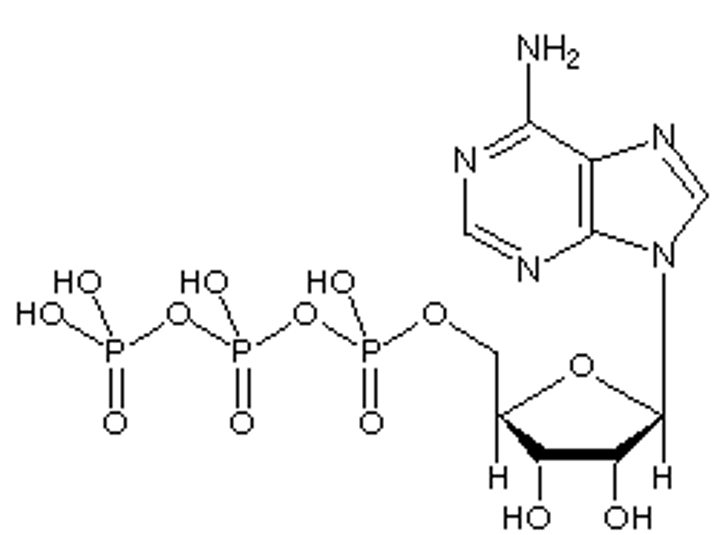
ATP
A molecule used to store energy temporarily in organisms. The molecule is broken down to release energy to drive metabolic processes. Contains the sugar ribose, with the nitrogenous base adenine and a chain of three phosphate groups bonded to it.
phosphorylated intermediate
A molecule (often a reactant) with a phosphate group covalently bound to it, making it more reactive (less stable) than the unphosphorylated molecule.
enzyme
A protein that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction.
catalyst
A substance that initiates or accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being affected
activation energy
The amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur.
substrate
The reactant on which an enzyme works.
enzyme-substrate complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
active site
The part of an enzyme molecule where a substrate molecule attaches (by means of weak chemical bonds); typically, a pocket or groove on the enzyme's surface.
induced fit
The change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate, induced by entry of the substrate.
cofactor
Any nonprotein molecule or ion that is required for the proper functioning of an enzyme. They can be permanently bound to the active site or may bind loosely with the substrate during catalysis.
coenzyme
If the cofactor is an organic molecule.
competitive inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor that competes with substrate for binding at the active site of teh enzyme. When the it is bound, no product can be made.
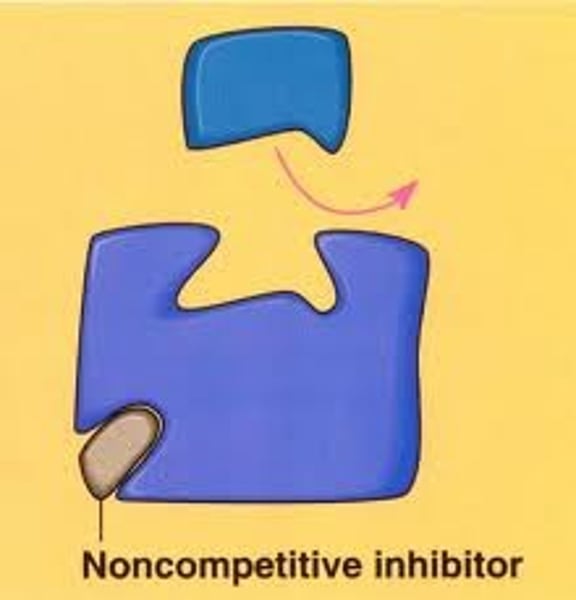
noncompetitive inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate.
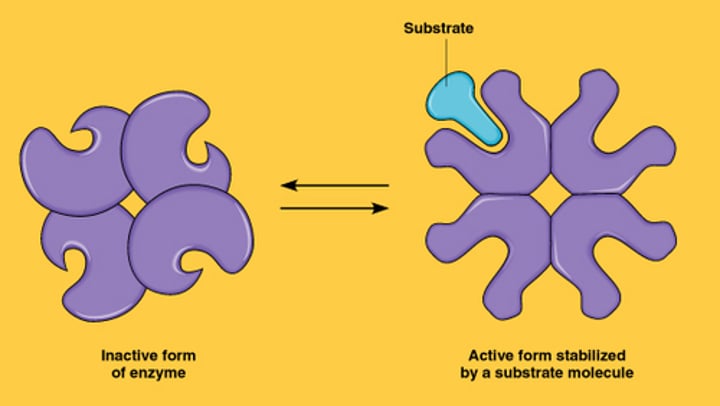
allosteric regulation
The binding of a regulatory molecule to a protein at one site that affects the function of the protein at a different site.
cooperativity
A kind of allosteric regulation whereby a shape change in one subunit of a protein caused by substrate binding is transmitted to all the others, facilitating binding of subsequent substrate molecules.
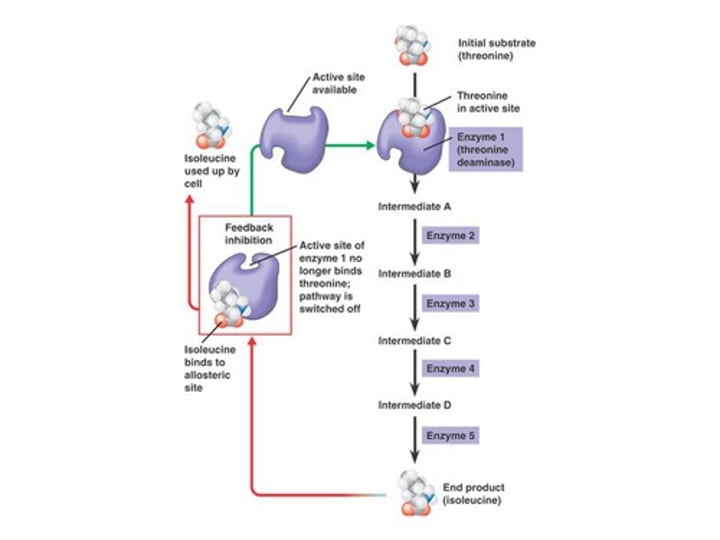
feedback inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
Exergonic reaction
Endergonic reaction
ATP
Normal binding
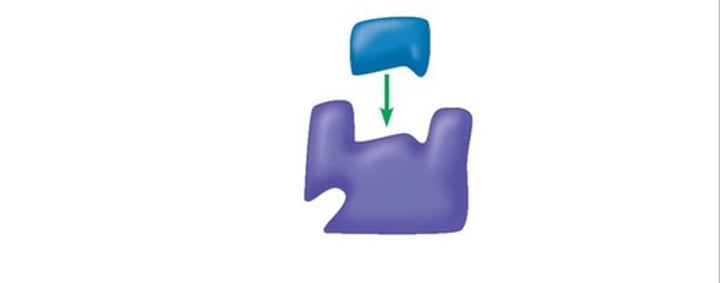
Competitive inhibition

Noncompetative inhibition
Feedback inhibition
Allosteric regulation
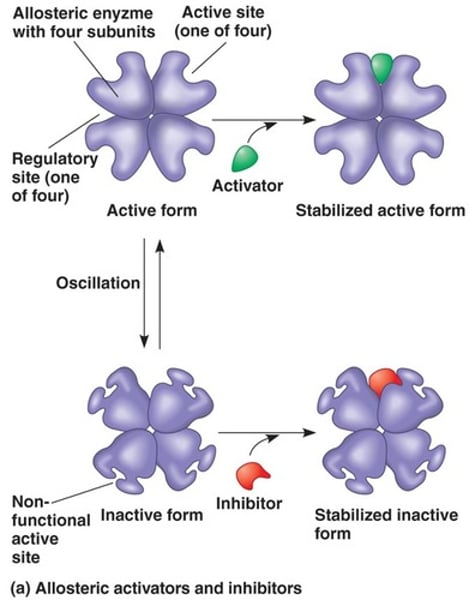
Cooperativity