Visual Fields II
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Key step before starting a visual field test
Explain the test clearly to the patient
How is it going to work?
What they need to do?
Why you are doing the test?
What are the room lighting requirement for visual field testing?
Room lighting needs to be dimmed
consider dark adaptation
Refractive correction during visual field testing
Contact lens wearers can wear lenses while performing test
otherwise full aperture lenses can be used for other ametropes → full to prevent artefact scotoma
ensure lens close enough to eye (prevent artefact scotoma)
How is trial lens power determined?
Patients Rx can be entered
field analyser will calculate a trial lens
how can we ensure patient comfort during visual field testing?
ensure machine at correct height for px
px shouldn’t be hunched over
test takes a while so ensure px comfortable → increases reliability as if not comfortable may loose focus
What is the Purpose of gaze monitoring?
Ensures the patient maintains fixation throughout the test
Why is encouragement important during testing?
test will take a number of mins
usually more if there is a defect
What does WANDER stand for ?
W – What was used
A – Accuracy
N – Normal or not
D – Defect + (what type)
E – Evaluate
R – Review/Repeat
W in WANDER example
What test and parameters were used
Name of test, what target used , stimulus , background illumination, which eye tested
patient demographics (age, pupil size , refractive correction
pupil size, date + time of test)
A in WANDER
Accuracy and reliability of the test
> Need to consider:
Fixation losses
False positives
False negatives
Fixation losses definition
used to check if eye looking at target
flagged at 20%
30% considered more accurate cut-off
monitor yourself + make a decision
What does gaze tracking measure?
eye movements using purkinje images
upward detection = eye movements
downward deflection = loss of signal → blinking etc
relies on subjective assessment of whether you think fixation was good enough

What are False positives?
“trigger happy” patient
px respond when NO stimulus presented
high false positives → happy clicker, randomly press button in hopes of passing test
poor understanding of test → instruct them properly
should be <20%
What are False negatives?
failure to respond to supra threshold target
associated with fatigue or inattention
should be <20%
may be better to repeat on another day if not improved with repeat
N in WANDER
is field Normal or not
look at:
threshold values
Greyscale plot
Total deviation
Pattern deviation
Glaucomal hemifield Analysis
Global indices
mean deviation (MD)
Pattern Standard deviation
What do Threshold values show?
exact threshold value for every point tested
higher numbers = higher sensitivity, px can detect very dim lights
low numbers → lights need to be very bright for patient to see them = poor sensitivity
triangle indicates position of blind spot
look for clusters of points with reduced sensitivity
What is the Purpose of the greyscale plot?
Visual representation of raw threshold values, where darker spots indicate poor sensitivity → problem areas
doesn’t consider age of px , or change in threshold with retinal eccentricity
main purpose to demonstrate problem areas to your patient → why you referred them
What is the Total deviation plot ?
compared with age-matched normal value → difference shown on plot
positive numbers → px performed above average
negative values → worse than average
p- value shows statistical significance of any abnormal value → also takes into account retinal eccentricity
What is the purpose of Pattern deviation?
takes all values from total deviation plot , orders them numerically + selects the 7th highest value
value subtracted from each of numbers on total deviation plot
reduces effects of diffuse loss → sensitivity depressed due to cataract or refractive blur
→ defects which show up on this plot more suggestive of pathological change in visual pathway
Mean deviation (MD)
mean difference in decibels between expected hill of vision (normal) and patients hill of vision
monitor overall change in patients visual field
What is Pattern standard deviation (PSD)?
amount by which shape of hill of vision differs from expected
low value → little difference
High value → irregular shape
What is the Purpose of the Glaucoma Hemifield Test (GHT)
Detect glaucomatous field loss
compares symmetry of superior field against inferior field in 5 predetermined zones
(glaucoma tends to produce arcuate defects that respond to horizontal midline)
values from PD plot in each zone scored + compared in the 2 hem fields
Possible GHT outcomes
Within normal limits
borderline
outside normal limits
general reduction in sensitivity
abnormally high sensitivity
GHT outside normal limits definition
At least one zone pair differs at <1% of normal subjects
GHT borderline definition
At least one zone differs between 1–3% of normal subjects.
D in WANDER
Describe the defect
Altitudinal
Arcuate
Constriction
Nasal step
Heminopia
Quadrantanopia
Scotoma → central , paracentral Caecocentral
What is an Altitudinal defect?
> involves both quadrants of either the superior or inferior field
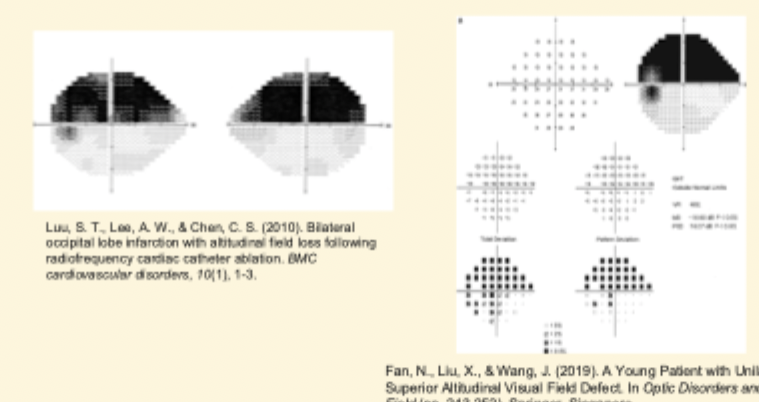
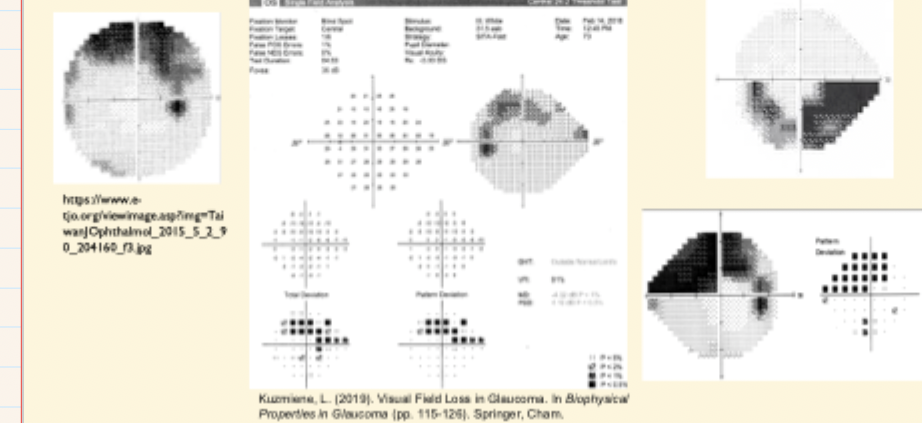
What is an Arcuate defect?
follows pattern of retinal nerve fibres (in an arc, radiating from disc)
Typical in glaucoma → obeys horizontal midline
What is a Constriction defect?
Shrinking of entire visual field (in towards the centre)
e.g Retinitis pigmentosa
What is Nasal step?
characteristic of early glaucoma → obeys horizontal midline
affecting nasal retina
What is a Hemianopia ?
Affects one half of Visual Field → 2 quadrants
respects vertical midline
Highly congrues
affects back of head → stroke, tumour
e.g pituitary tumour
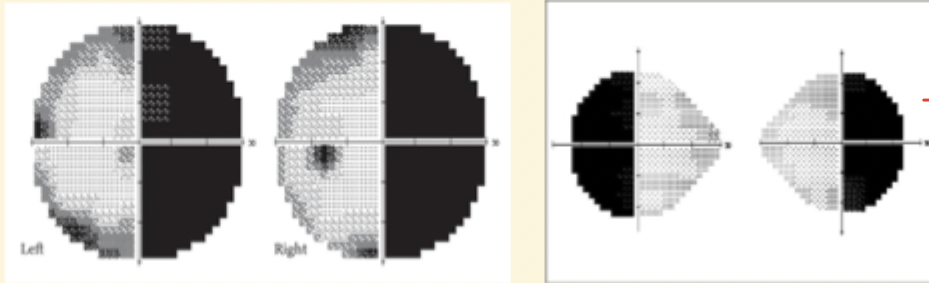
What is Quadrantanopia ?
affects one quadrant of Visual field
if temporal →tumour, aneurysm, stroke
What is a Scotoma ?
localised defect
may be absolute (no vision at all) or relative (reduced visual function)
3 types:
Central , paracentral and Caecocentral
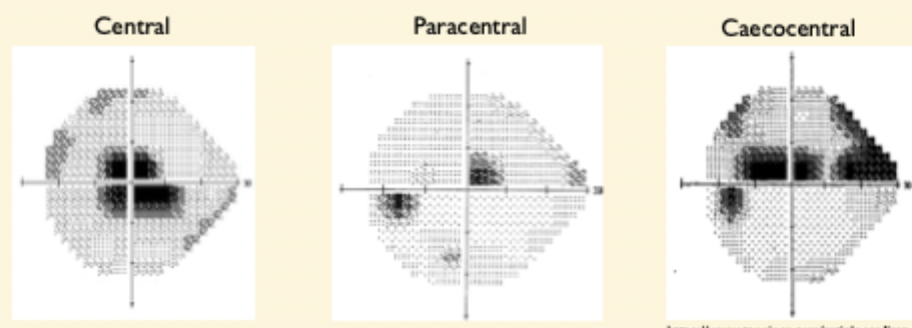
What other terminology can be used to describe defects?
Homonymous → same side of space
Heteronymous → affects opposite sides of space
Unilateral → one eye
Bilateral → both eyes
Congruity → level of similarity between 2 eyes
E in WANDER
Evaluate what disease is suggested
progression
R in WANDER
Review or repeat to confirm findings
new defect is NOT a defect until repeated
need to consider effects of learning + fatigue