Space Physics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
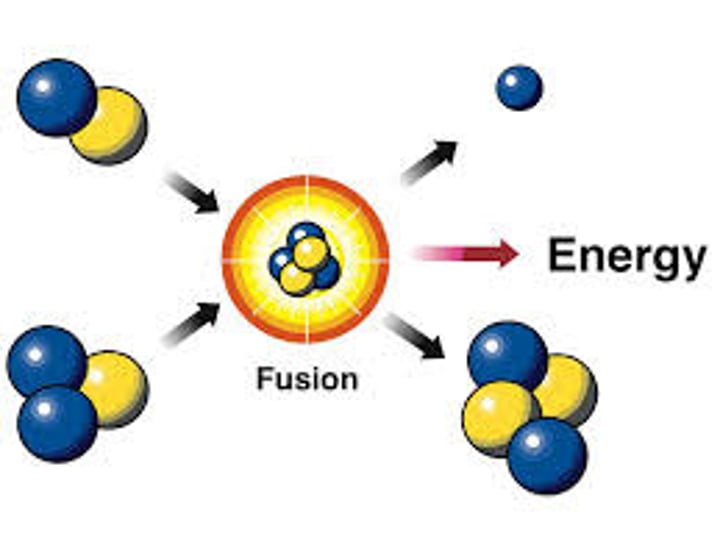
How does nuclear fusion occur in stars?
- particles collapse due to gravity
- temperature rises
- nuclear fusion occurs
- hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium nuclei
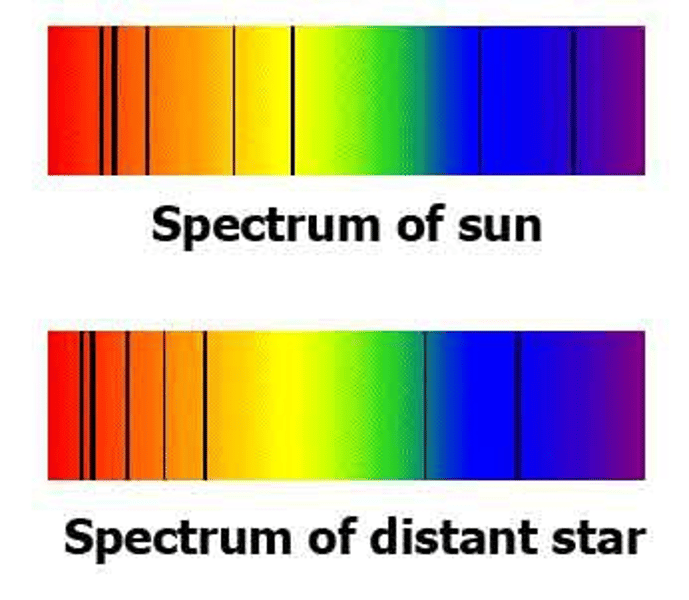
What is red shift?
An increase in the wavelength of light from distant galaxies
Why is is thought that the universe was once very small?
- the furthest galaxies from us are moving the fastest
- suggesting the universe is expanding from a small region
What is red-shift evidence for?
- that space is expanding
- the Big Bang theory
What is a moon?
a natural satellite that orbits a planet

What galaxy is our solar system in?
Milky Way galaxy

How was the sun formed?
The Sun was formed from a nebula (cloud of dust and gas) pulled together by gravitational attraction

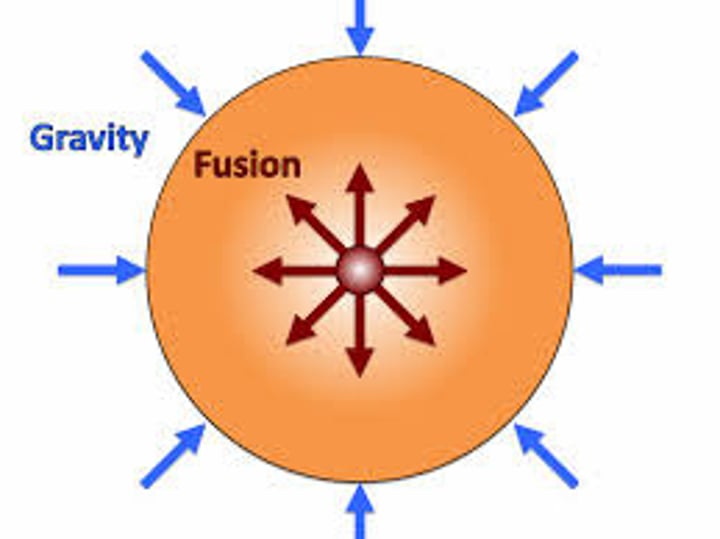
What does it mean if a star is in equilibrium (stable)?
outward expansion due to nuclear fusion is in equilibrium with the inward force due to gravitational attraction
Life cycle of a star (size of sun)
- nebula
- protostar
- main sequence star
- (expands) red giant
- (collapses) white dwarf
- (cools) black dwarf
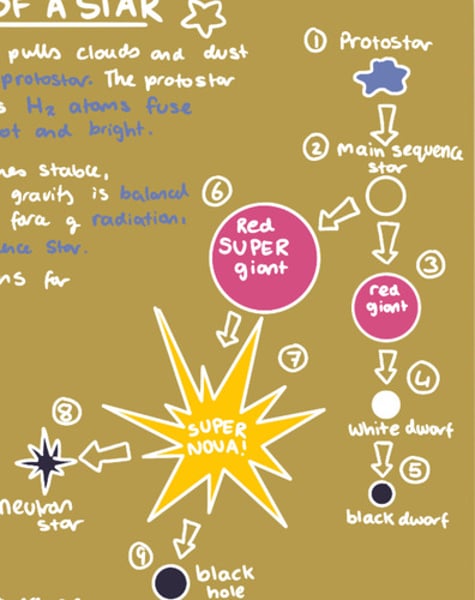
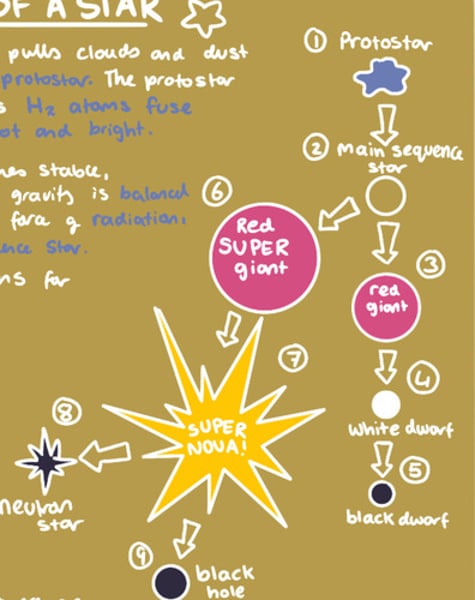
Life cycle of a star bigger than the sun
- nebula
- protostar
- main sequence star
- red super giant
- supernova
- black hole/ neutron star
How are naturally occurring elements produced?
in fusion processes in stars

How are elements heavier than iron produced?
in a supernova
How are elements distributed throughout the universe?
in a supernova explosion
What maintains circular orbits?
gravity
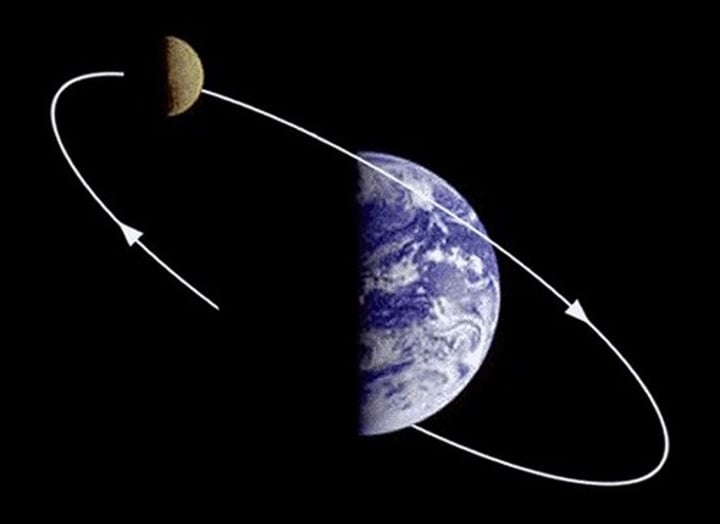
In circular orbits, why can velocity change, but speed remain constant?
gravity causes the planet to change direction constantly meaning velocity is always changing (velocity = direction and speed)
For a stable orbit, why must the radius change if speed changes?
- if a planet moves closer to the sun (orbital radius decreases)
- gravitational attraction to the sun increases
(so does acceleration due to changing velocity)
- so speed of planet increases
What does the Big Bang theory suggest?
The universe began from a very small, hot, dense region

In 1988 what did observations of supernovae suggest?
distant galaxies are receding faster than ever
What do we call matter that isn't understood and can't be detected?
dark energy/matter
