APCalculus
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
IVT
Intermediate Value Theorem
If f is a continuous function on interval [a,b] then for every value M between f(a) & f(b) there’s a value C contained in (a, b) such that f© = M
Corrolary
If f is continuous on [a, b] and if f(a) & f(b) are nonzero w/ opposite signs, then f has a zero in (a, b) w/ a c in [a, b]
Continuity + Rules
Continuous is on an open interval if the graph of f(x) has no breaks, gaps & interruptions
f© is defined
lim x to c f(x) exists
f© and lim x to c f(x) are the same
types of discontinuities
removable discontinuity
infinite discontinuity
jump discontinuity
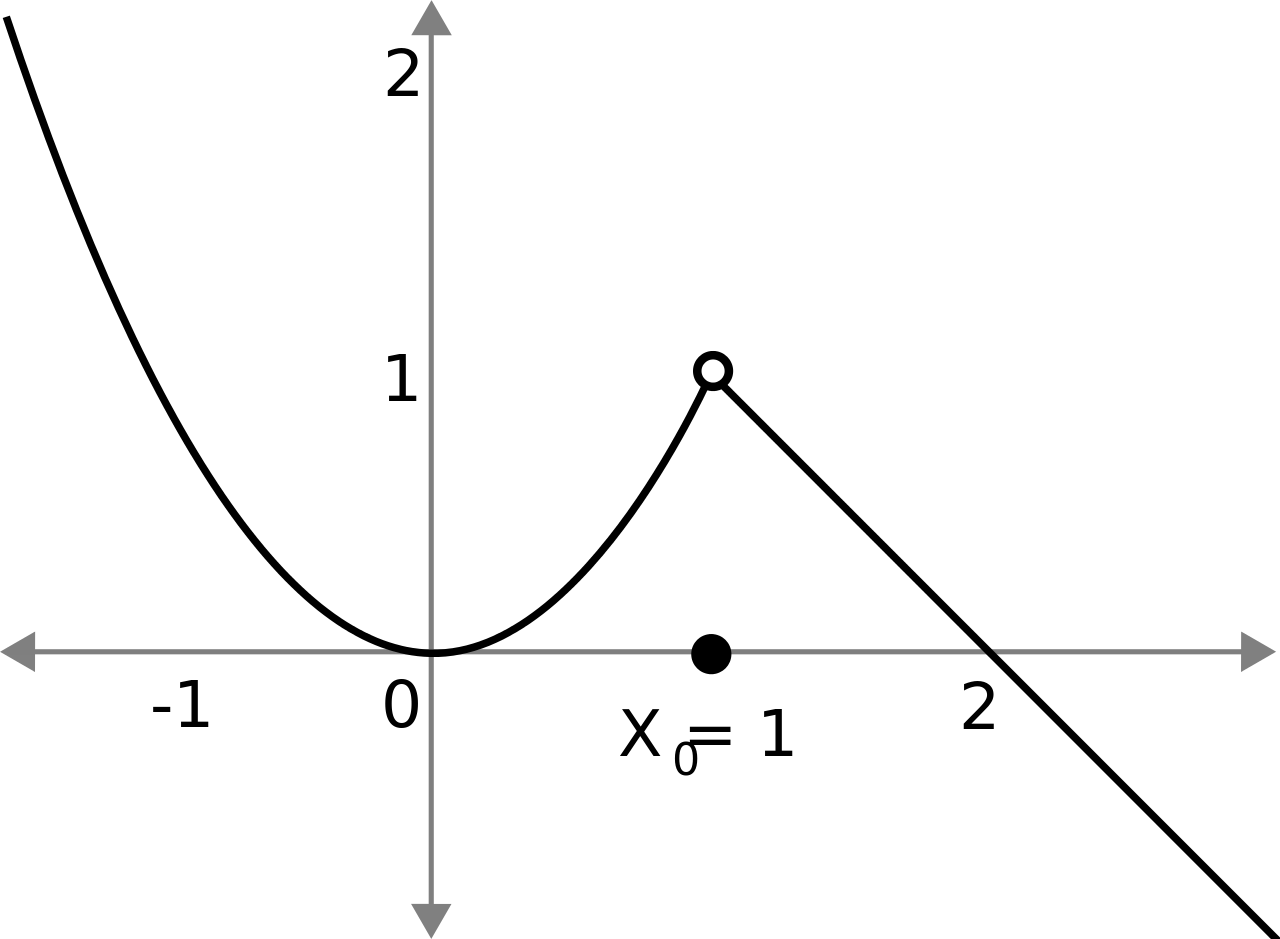
removable discontinuity
when lim x approaching c f(x) exists but isn’t equal to f©.
It’s removable as you redefine f© equal to the limit value.
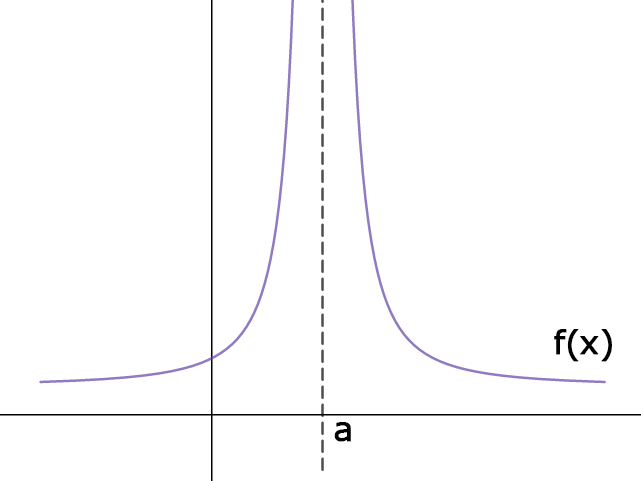
infinite discontinuity
if one/both of the one sided limitsw are infinite, then there’s a infinite disc. it’s non-removable and is when there’s a vertical asymptote.
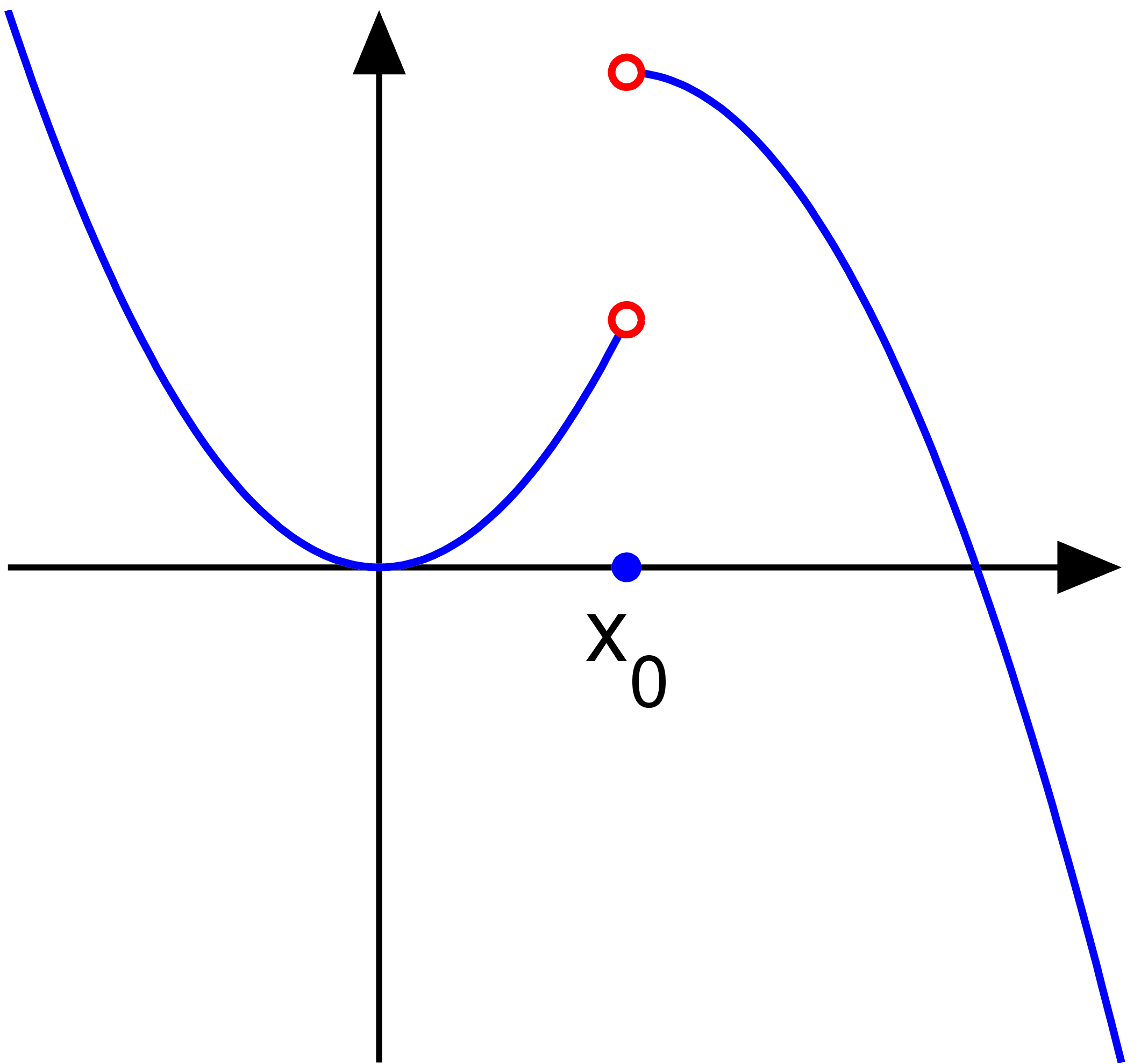
jump discontinuity
if one sided limits of a function approaching diff sides are not equal then it’s a jump discontinuity and non removable.
Squeeze Theorem
if h(x) < f(x) < g(x)
and lim of h(x) and g(x) approaching the same thing is c, f(x) approaching that is also c
Infinite Limits
if degree in n < d = lim is 0
d > n = lim is infinity/-infinity, when it’s equal, divide coeficients
Horizontal Asymptote
top < d, y= 0
d > top = none, slant
equal = divide coefficients
d/dx (sinx)
cos x
d/dx (cos x)
-sin x
d/dx (tan x)
sec² x
d/dx (cot x)
-csc² x
d/dx (sec x)
secxtanx
d/dx (cscx)
-cscxcotx
d/dx (e^u)
u’
d/dx (a^u)
ln a a^u u’
d/dx ln u
u’ / u
d/dx log a u
u’ / ln a * u
tangent line
y - f'(a) = f’(a) (x-a)how
how to solve implicit differentiation
everytime you take derivative of y, replace it with dy/dx.
how to know if a function has a inverse function
if it passes horizotal line test, one to one, and strictly incr/decr
slopes of inverse functions
reciprocal
d/dx (arcsin u)
u’/(sqrt(1-u²))
d/dx (arccos u)
-u’/(sqrt(1-u²)
d/dx (arctan u)
u’/1+u²
d/dx (arccot u)
-u’/(1+u²)
d/dx (arcsec u)
u’/(|u| sqrt(u² - 1)
d/dx (arcsc u)
-u’ / (|u| sqrt(u² - 1))