6.1Oncology Flashcards: Chemotherapy Terms & Definitions
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
After exposure to a carcinogen, which of the following occurs FIRST? (select all that apply)
A. activation of protooncogenes
B. defects in terminal differentiation
C. inactivation of tumor-suppressor genes
D. inactivation of genomic stability genes
A. activation of protooncogenes
C. inactivation of tumor-suppressor genes
D. inactivation of genomic stability genes
Once a cell undergoes genetic change and becomes an initiated cancer cell, what happens next?
A. genetic change
B. selective clonal expansion
C. NK cell activation
D. adaptive immune response
B. selective clonal expansion
In the selective clonal expansion stage of carcinogenesis, which of the following occur? (select all that apply)
A. defects in terminal differentiation
B. defects in growth control
C. resistance to cytotoxicity
D. defects in programmed cell death
A. defects in terminal differentiation
B. defects in growth control
C. resistance to cytotoxicity
D. defects in programmed cell death
What viruses can cause cancer? (Select all that apply)
A. HIV
B. Influenza
C. EBV
D. HPV
C. EBV
D. HPV
What outside factors can cause cancer? (select all that apply)
A. benzene
B. asbestos
C. ionizing radiation
D. UV light
A. benzene
B. asbestos
C. ionizing radiation
D. UV light
definition: a term for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and can invade nearby tissues
A. cancer
B. oncogenes
C. tumor suppressor genes
D. metastasis
A. cancer
definition: gene that is a mutated form of a gene involved in normal cell growth
A. cancer
B. oncogenes
C. tumor suppressor genes
D. metastasis
B. oncogenes
definition: type of gene that makes a protein called a tumor suppressor protein that helps control cell growth
A. cancer
B. oncogenes
C. tumor suppressor genes
D. metastasis
C. tumor suppressor genes
Which of the following is NOT one of the top 4 most prevalent cancers in males?
A. prostate
B. non-hodgkin lymphoma
C. colon & rectum
D. urinary bladder
B. non-hodgkin lymphoma
note: the 4 most prevalent in males are prostate, lung&bronchus, colon&rectum, and urinary bladder
Which of the following is NOT one of the top 4 most prevalent cancers in females?
A. breast
B. kidney&renal pelvis
C. colon & rectum
D. lung & bronchus
B. kidney&renal pelvis
note: the 4 most prevalent in females are breast, lung&bronchus, colon&rectum, and uterine corpus
What cancer is the leading cause of death in both male and females?
A. colon and rectum
B. urinary bladder
C. non-hodgkin lymphoma
D. lung and bronchus
D. lung and bronchus
What phase of the cell cycle: resting phase, quiescent
A. G0
B. G1
C. S
D. G2
E. M
A. G0
What phase of the cell cycle: synthesis of various enzymes that are required in S phase, mainly those needed for DNA replication
A. G0
B. G1
C. S
D. G2
E. M
B. G1
What phase of the cell cycle: the amount of DNA in the cell has effectively doubled, thought the ploidy of the cell remains the same
A. G0
B. G1
C. S
D. G2
E. M
C. S
What phase of the cell cycle: DNA synthesis ceases, protein and RNA synthesis continues and the microtubular precursors of the mitotic spindle are produced
A. G0
B. G1
C. S
D. G2
E. M
D. G2
What phase of the cell cycle: rates of protein and RNA synthesis decrease. mitosis occurs
A. G0
B. G1
C. S
D. G2
E. M
E. M
What chemotherapy drugs work in the M phase (select all that apply)
A. antimetabolites
B. Taxanes
C. vincas
D. etoposide
B. Taxanes
C. vincas
What chemotherapy drugs work in the G1 phase (select all that apply)
A. asparaginase
B. Taxanes
C. steroids
D. etoposide
A. asparaginase
C. steroids
What chemotherapy drugs work in the S phase (select all that apply)
A. antimetabolites
B. camphothecins
C. steroids
D. etoposide
A. antimetabolites
B. camphothecins
What chemotherapy drugs work in the G2 phase (select all that apply)
A. bleomycin
B. camphothecins
C. steroids
D. etoposide
A. bleomycin
D. etoposide
Cell kill is proportional to dose (linear dose response curve)
A. non-cell phase specific
B. cell phase specific
C. both
A. non-cell phase specific
only effective against cells in that portion of the cell cycle
A. non-cell phase specific
B. cell phase specific
C. both
B. cell phase specific
most effective in S phase
A. non-cell phase specific
B. cell phase specific
C. both
A. non-cell phase specific
schedule dependent
A. non-cell phase specific
B. cell phase specific
C. both
B. cell phase specific
examples: cyclophosphamide, cisplatin, carboplatin, doxorubicin
A. non-cell phase specific
B. cell phase specific
C. both
A. non-cell phase specific
examples: 5-FU, methotrexate
A. non-cell phase specific
B. cell phase specific
C. both
B. cell phase specific
TNM system: indicates the size of the tumor
A. T
B. N
C. M
A. T
TNM system: extent and spread of regional lymph node involvement
A. T
B. N
C. M
B. N
TNM system: indicates whether the cancer has spread to other parts of body such as lungs or bones. presence or absence
A. T
B. N
C. M
C. M
What does M0 mean in TNM system
no metastasis
What does M1 mean in TNM system
metastasis
In TNM system, what indicates largest tumor
A. T1
B. T2
C. T3
D. T4
D. T4
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ECOG has a grading system for cancer patient performance status. What grade does this describe: fully active
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
F. 5
A. 0
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ECOG has a grading system for cancer patient performance status. What grade does this describe: restricted in strenuous activity but ambulatory. able to carry out light work
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
F. 5
B. 1
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ECOG has a grading system for cancer patient performance status. What grade does this describe: ambulatory and capable of all self-care, but unable to carry out any work activities. up more than 50% of waking hours
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
F. 5
C. 2
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ECOG has a grading system for cancer patient performance status. What grade does this describe: capable of only limited self care, confined to bed or chair more than 50% of waking hours
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
F. 5
D. 3
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ECOG has a grading system for cancer patient performance status. What grade does this describe: completely disabled. cannot carry on any self care. totally confined to bed or chair
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
F. 5
E. 4
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ECOG has a grading system for cancer patient performance status. What grade does this describe: dead
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
F. 5
F. 5
For chemotherapy dosing you want to enhance efficacy and decrease ____________
toxicity
If BSA is ____________ doses are often capped
A. >= 1
B. >= 2
C. >= 3
D. >= 4
B. >= 2
KNOW BSA FORMULA
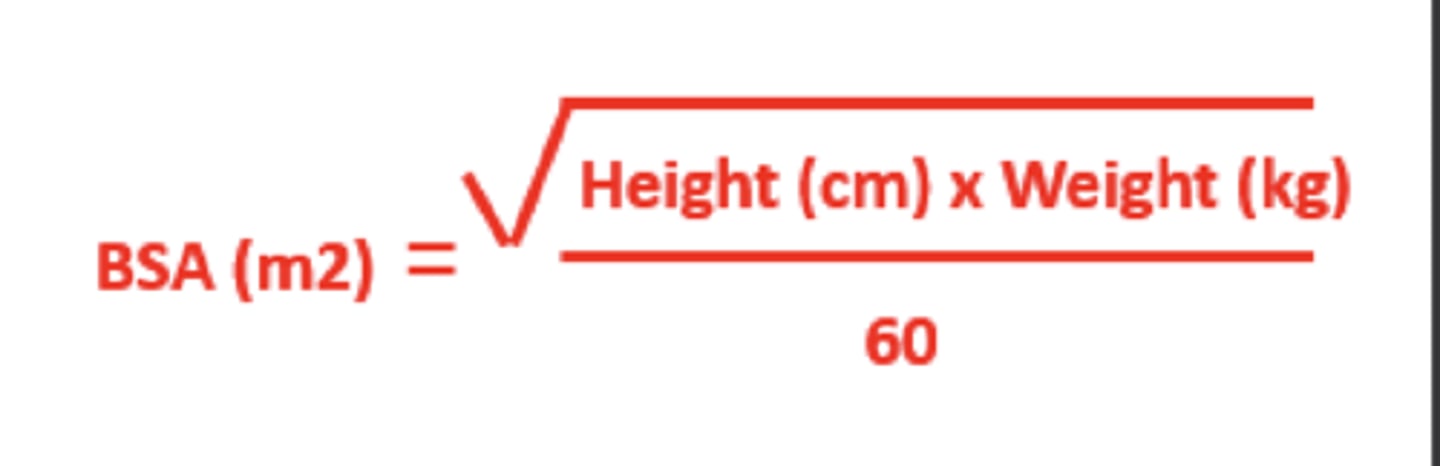
For pediatrics is the dosing usually higher or lower?
higher
pediatric patients can generally tolerate more toxicity EXCEPT FOR:
A. nephrotoxicity
B. neurotoxicity
C. hepatotoxicity
D. cardiotoxicity
D. cardiotoxicity
Chemotherapy terminology: following eradication of disease with surgery/radiation, chemo is given to treat microscopic disease and prevent relapse
A. adjuvant
B. neoadjuvant
C. maintenance
D. salvage
E. induction
F. consolidation/intensification
A. adjuvant
Chemotherapy terminology:prior to therapy, chemo is given to reduce the extent of local treatment
A. adjuvant
B. neoadjuvant
C. maintenance
D. salvage
E. induction
F. consolidation/intensification
B. neoadjuvant
Chemotherapy terminology: low dose chemo is given to prolong duration of remission
A. adjuvant
B. neoadjuvant
C. maintenance
D. salvage
E. induction
F. consolidation/intensification
C. maintenance
Chemotherapy terminology: following failure of other txs, therapy used to control symptoms or provide palliation
A. adjuvant
B. neoadjuvant
C. maintenance
D. salvage
E. induction
F. consolidation/intensification
D. salvage
Chemotherapy terminology: initial chemo given to achieve cytoreduction
A. adjuvant
B. neoadjuvant
C. maintenance
D. salvage
E. induction
F. consolidation/intensification
E. induction
Chemotherapy terminology: given after remission, same agents used in induction are repeated
A. adjuvant
B. neoadjuvant
C. maintenance
D. salvage
E. induction
F. consolidation/intensification
F. consolidation/intensification
What is this: toxic effect of a drug that prevents further use of the drug or means that the dosage of the drug has reached its limit and cannot be increased
A. dose limiting toxicity (DLT)
B. maximum tolerated dose (MTD)
C. dose dense
A. dose limiting toxicity (DLT)
What is this: highest dose of a drug or treatment that does not cause unacceptable side effects
A. dose limiting toxicity (DLT)
B. maximum tolerated dose (MTD)
C. dose dense
B. maximum tolerated dose (MTD)
What is this: attempt to achieve maximum tumor kill by increasing the rate of chemotherapy delivery, not by increasing dosage
A. dose limiting toxicity (DLT)
B. maximum tolerated dose (MTD)
C. dose dense
C. dose dense
Which of the following supports the rationale behind giving growth colony stimulating factors to patients? (select all that apply)
A. reduce the incidence of febrile neutropenia
B. decrease length of hospitalization
C. reduced confirmed infections/antibiotic use
D. mobilization of stem cells (bone marrow transplantation)
A. reduce the incidence of febrile neutropenia
B. decrease length of hospitalization
C. reduced confirmed infections/antibiotic use
D. mobilization of stem cells (bone marrow transplantation)
definition: biologic product that is highly similar to and has no clinically meaningful differences from existing FDA approved reference product. Expected to have same clinical result
A. biosimilar
B. generic
C. brand
A. biosimilar