Introduction to Material Selection in Design
1/514
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
515 Terms
What are materials in the context of architecture and interior design?
Materials are the basic building substances used to create built environments, providing form, shape, variety, and distinction to interior spaces.

How do materials contribute to interior spaces?
They provide physical and psychological form to the space, structure, finishes, and contents for human use.
What are some examples of materials used in construction?
Stone and wood can be used as construction elements to enclose space and provide protection and privacy.
How have materials changed over time?
Materials evolve as technology advances, introducing new materials and new uses for existing ones.

What will Chapter 14 focus on regarding materials?
It will show how materials serve specific functions within a building, such as wood used in flooring or wall coverings.
What was the common practice for building materials before the nineteenth century?
Most buildings were constructed of local or indigenous materials, with high-quality materials like marble imported for significant structures.
How did manufacturing processes and transportation affect material use after the nineteenth century?
They created greater opportunities for materials to be used beyond their regional borders and in various building types.
What are 'green' building materials?
Materials that help reduce environmental impact associated with extraction, processing, fabrication, shipping, and installation.

What benefits do green building materials provide?
They promote conservation of nonrenewable resources and encourage reuse and recycling practices.
How can materials be reused or recycled?
Used brick and timber can be reclaimed for new structures, and newspapers can be recycled into insulation.
What is a major concern regarding biodegradable materials?
The impact of consumer products thrown into landfills and the waste from packaging materials.

What can discarded wood be turned into?
Sawdust, particleboard, or can be burned for fuel.
What is the impact of overusing rare natural materials?
It can lead to environmental degradation, such as the destruction of rainforests for exotic woods.

What is 'sick building syndrome'?
A condition caused by low levels of indoor pollutants, leading to irritations and health issues for occupants.
What are some symptoms of sick building syndrome?
Eye, nose, throat, and lung irritations, headaches, lethargy, and difficulty concentrating.

Why is it important for designers to be aware of material selection?
To minimize environmental impact and promote sustainability in building practices.

What role do new technologies play in material selection?
They lead to new design ideas and innovative uses for both new and old materials.
What is the significance of using local materials in construction?
Local materials reduce transportation costs and environmental impact while supporting local economies.
How can designers contribute to environmental preservation?
By avoiding the use of rare and exotic materials when more sustainable options are available.

What is the relationship between materials and the psychological aspect of space?
Materials can influence the mood and perception of a space, affecting how occupants feel and interact within it.

What is the importance of surface treatments in design?
Surface treatments enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of materials, contributing to the overall design.

How do materials provide durability in design?
Certain materials are chosen for their strength and longevity, ensuring that structures withstand wear and environmental factors.

What is the impact of packaging materials on waste?
Packaging contributes significantly to waste, complicating the environmental issues associated with building materials.
What are common sources of hazardous gases in interior environments?
Hazardous gases can be produced from materials such as paints, carpets, glues, particleboard, and man-made textiles.

What is the role of an interior designer regarding material selection?
An interior designer must understand the potential hazards of materials before specifying them for use in closed environments.
What is an example of an indigenous material used in Southwestern architecture?
Adobe is an indigenous material that gives Southwestern architecture a distinct look.
How can materials be categorized based on their state?
Materials can be categorized as natural, converted, or artificial.
What are natural materials?
Natural materials are those found in nature, including both organic (from plants and animals) and inorganic (such as soil, clay, and stone) substances.
What happens to clay when it is fired at high temperatures?
When clay is fired at high temperatures, it is converted into ceramic, a new material with different characteristics.
What are artificial materials?
Artificial materials are created through man-made processes, such as plastics, which are made from petroleum and chemicals.
What are metamaterials?
Metamaterials are created with artificial properties that may not be found in nature, often used in specialized fields like aerospace and electrical engineering.
What should be the primary consideration in material selection for interior design?
Materials should first be selected for their functional qualities, such as durability, sustainability, and ease of maintenance.
What aesthetic factors should be considered when selecting materials?
Materials can be chosen for their surface appearance, such as color and texture, but this is often secondary to functional qualities.
Why might heavy, rough textures and dark colors be inappropriate for a children's play area?
They would create an unsuitable atmosphere, whereas they might be appropriate for creating a rustic mood in a restaurant.
What are some functional characteristics to consider when selecting materials?
Appropriateness, durability, ease of maintenance, safety, insulation, acoustical properties, and compliance with regulations.
What is the importance of understanding material characteristics in interior design?
Understanding material characteristics helps designers select appropriate materials for the intended use and atmosphere.
What is the difference between organic and inorganic materials?
Organic materials come from living organisms, while inorganic materials are nonliving substances.
How can converted materials differ from their natural state?
Converted materials are processed or manufactured into different forms, possessing new characteristics and uses.
What is an example of a converted material?
Ceramic is an example of a converted material made from fired clay.
What is the significance of ecological and economic factors in material selection?
These factors ensure that materials are sustainable and economically viable for the intended design.
What criteria should be included in a checklist for material selection?
Criteria should include functional characteristics, aesthetics, ecological and economic factors.
What is the impact of material selection on the atmosphere of a space?
Material selection can significantly influence the mood and suitability of a space for its intended use.
How do regulations and codes affect material selection?
Regulations and codes govern safety and performance standards that materials must meet.
What is the relationship between material properties and interior design?
Material properties influence the aesthetic and functional outcomes of interior spaces.
What is the role of aesthetic judgment in material selection?
Aesthetic judgment helps designers choose materials that create the desired visual impact and mood.
Why is it important for designers to be knowledgeable about materials?
Knowledge about materials allows designers to make informed choices that enhance safety, functionality, and aesthetics.
What are the aesthetic considerations in design?
Appropriateness to the design concept, surface qualities (texture and pattern), color and light reflection and absorption qualities, visual suitability to intended mood or atmosphere, balance, size, and proportion of the space.
What ecological considerations should be taken into account in design?
Environmental impact for acquisition, efficient manufacturing processes, recyclable content (postindustrial and postconsumer), renewable resources (sustainably managed sources), capability to be recycled or reusable, nontoxicity to users (minimal chemical emissions), moisture resistance and inhibiting growth of biological contaminants.
What are the economic considerations or life-cycle assessment factors in design?
Initial cost of material, shipping, and installation; availability of material; cost of maintenance and possible replacement, recycling, or minimizing waste if discarded.
Why is wood considered a major material for buildings and furniture?
Because of its abundance in nature, ease of acquisition and workability, excellent insulation properties, and renewability.
How many species of trees are used commercially as building materials?
About 100 species.
What are the characteristics of wood as a material?
Wood is organic, renewable, biodegradable, and recyclable.
What forestry practices are becoming more common for sustainable wood sourcing?
Practices that create well-managed forests and encourage tree growth to match or exceed annual harvesting.
What is the difference between lumber and timber?
Lumber refers to boards of various sizes, while timber refers to boards that exceed five inches (127 mm) in width and thickness, primarily used for structural support.
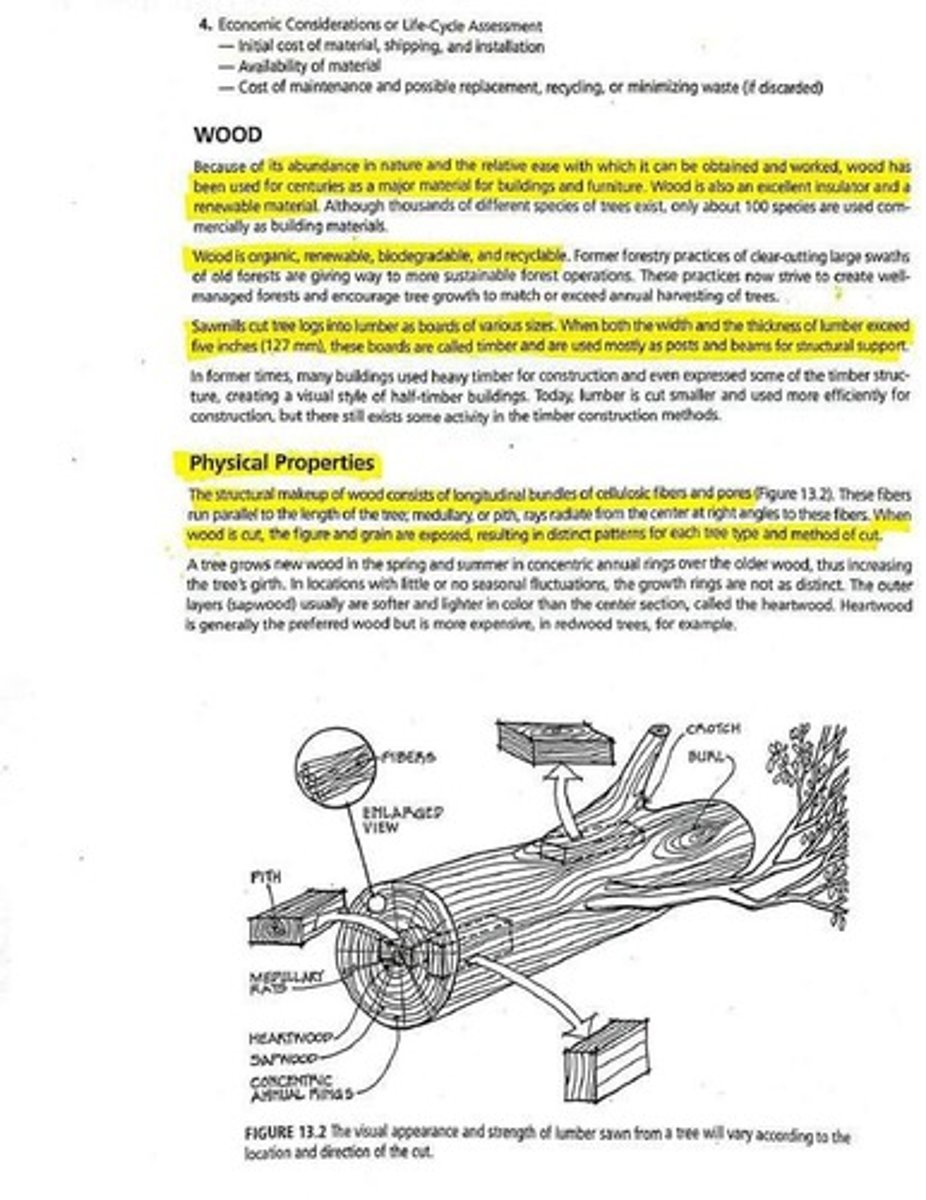
What is the significance of heartwood and sapwood in trees?
Heartwood is the center section of the tree, generally preferred for its strength and quality, while sapwood is the outer layer, softer and lighter in color.
How does the growth of a tree affect its physical properties?
The growth in concentric annual rings increases the tree's girth and influences the strength characteristics of the wood.
What is the direction in which wood can be easily split?
Wood can be easily split in a vertical or longitudinal grain direction.
What are the two types of strength that wood possesses?
Tension (resistance to bending) and compression (resistance to loads of pressure).
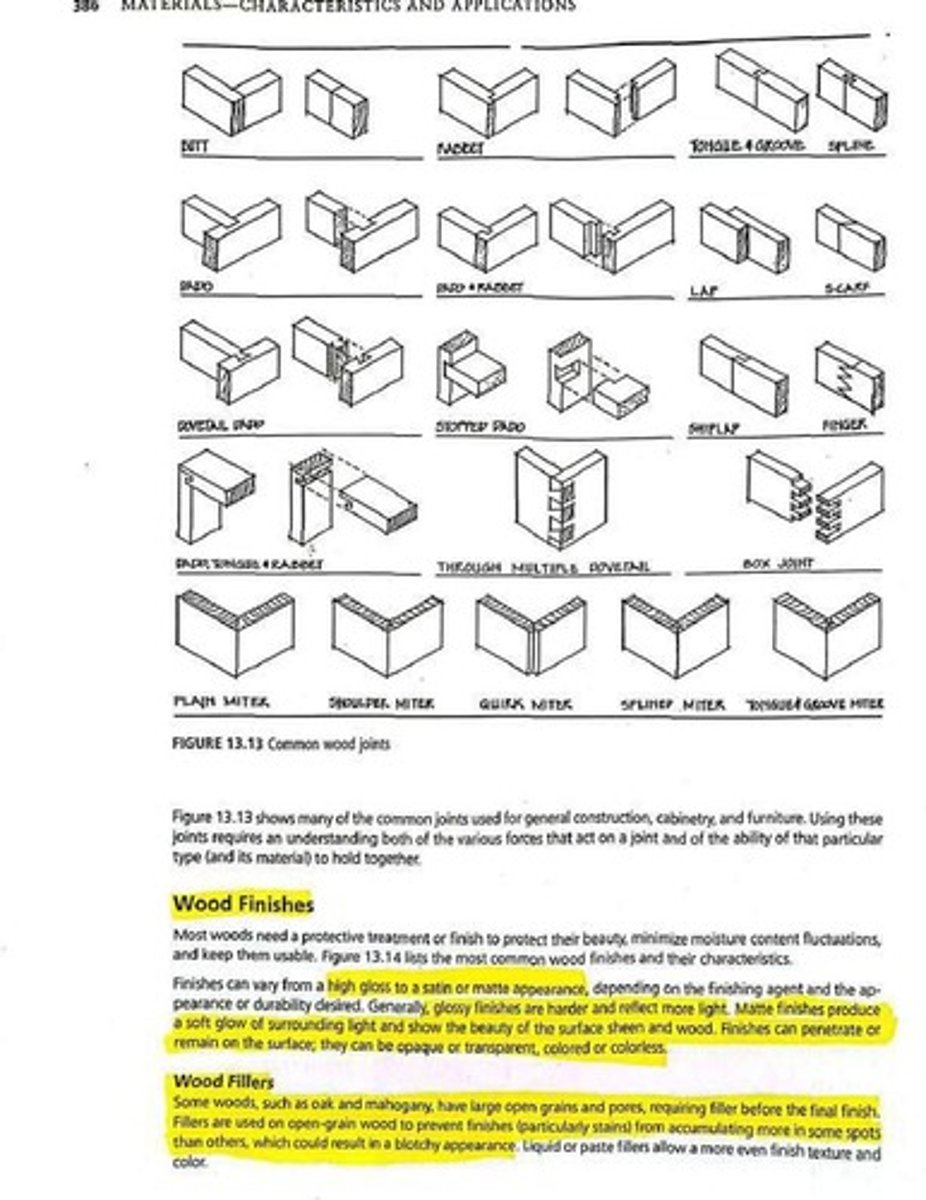
What is the purpose of grading wood?
Wood is graded according to its appearance, strength, use, and defects (such as knots and pitch pockets).
What is a knot in wood, and how does it affect the wood's properties?
A knot is generally the base of a side branch that can affect the technical and visual properties of the wood.
Why might knots be desirable in certain applications of wood?
Knots might be desirable in decorative applications, such as burl wood.
What is the role of sawmills in wood processing?
Sawmills cut tree logs into lumber, producing boards of various sizes.
What is the visual appearance of lumber affected by?
The location and direction of the cut from the tree.
What is the tensile strength of wood used for?
Tensile strength allows wood to be used in cantilever construction, such as wood decks suspended from a building.
How does the growth environment of a tree affect growth rings?
In locations with little or no seasonal fluctuations, the growth rings are not as distinct.
What is the impact of clear-cutting on forestry practices?
Clear-cutting practices are being replaced by more sustainable operations that focus on forest management and tree growth.
What are the benefits of using wood as a building material?
Wood is renewable, provides excellent insulation, and has good physical strength for construction.
What factors influence the visual and structural properties of wood?
The method of cut, the presence of knots, and the growth characteristics of the tree.
What are the aesthetic possibilities of wood?
The aesthetic possibilities for the use of wood are seemingly endless, with different wood types, grains, and colors offering a variety of natural appearances and finishing options.
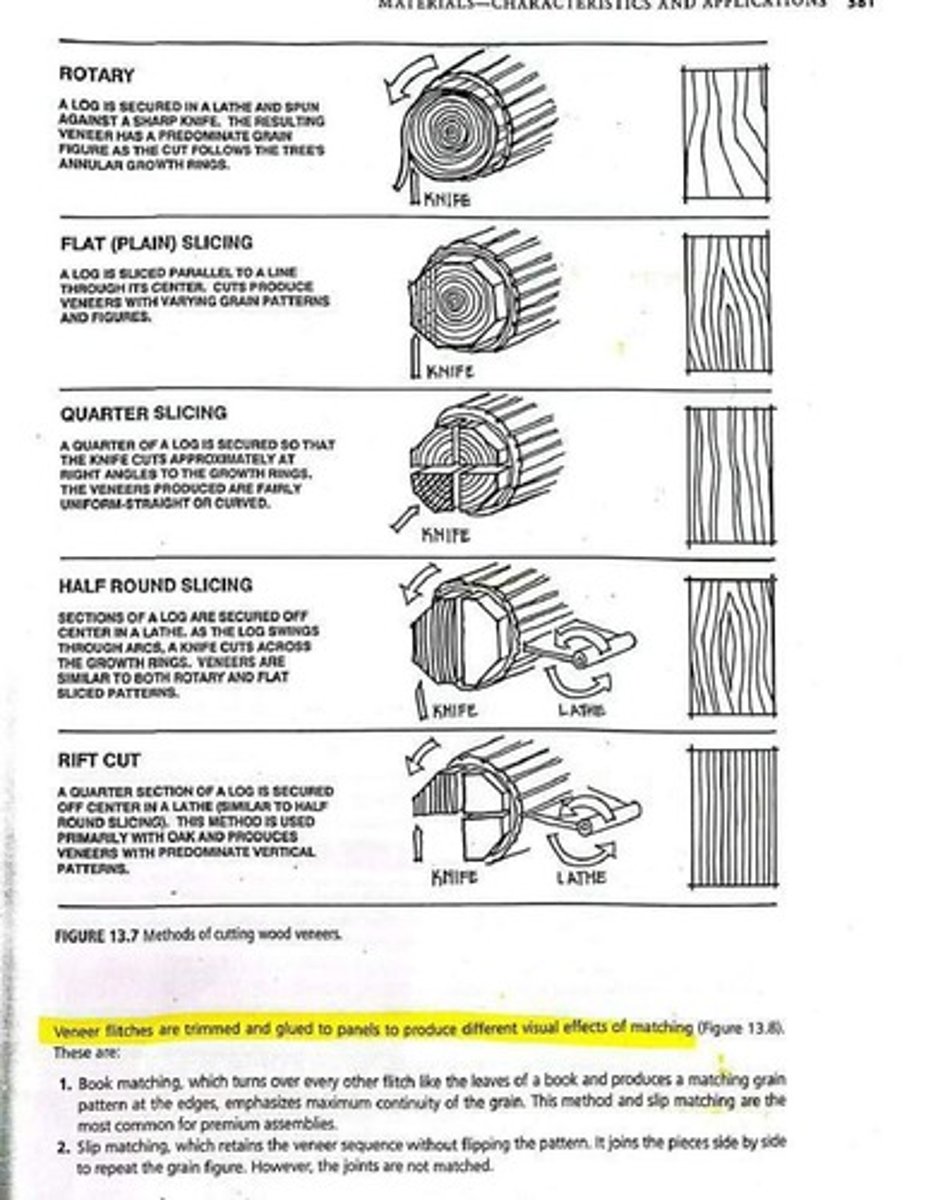
What is the difference between flat-sawn and quartersawn lumber?
Flat-sawn lumber consists of longitudinal cuts parallel to the log diameter, producing varied grain patterns but is prone to uneven wear and twisting. Quartersawn lumber is cut parallel to the radius of the log, resulting in more stable, even grain patterns and less twist as it dries.
What are the standard sizes for dimensional lumber?
Dimensional lumber is cut to specific nominal sizes, which differ from actual sizes. For example, a nominal 2x4 is actually 1.5 inches by 3.5 inches when surfaced.
How is lumber measured?
Lumber is measured in board feet, which is the volume of lumber equal to 1 inch thick, 12 inches wide, and 1 foot long.
What is the process of seasoning wood?
Seasoning is the drying process used to improve wood's strength, stability, and resistance to decay or insect attack. It can be done naturally or quickly in kilns.
What happens to wood when it absorbs or loses moisture?
Wood expands when it absorbs moisture and contracts when it loses moisture, which can lead to checking or cracking.
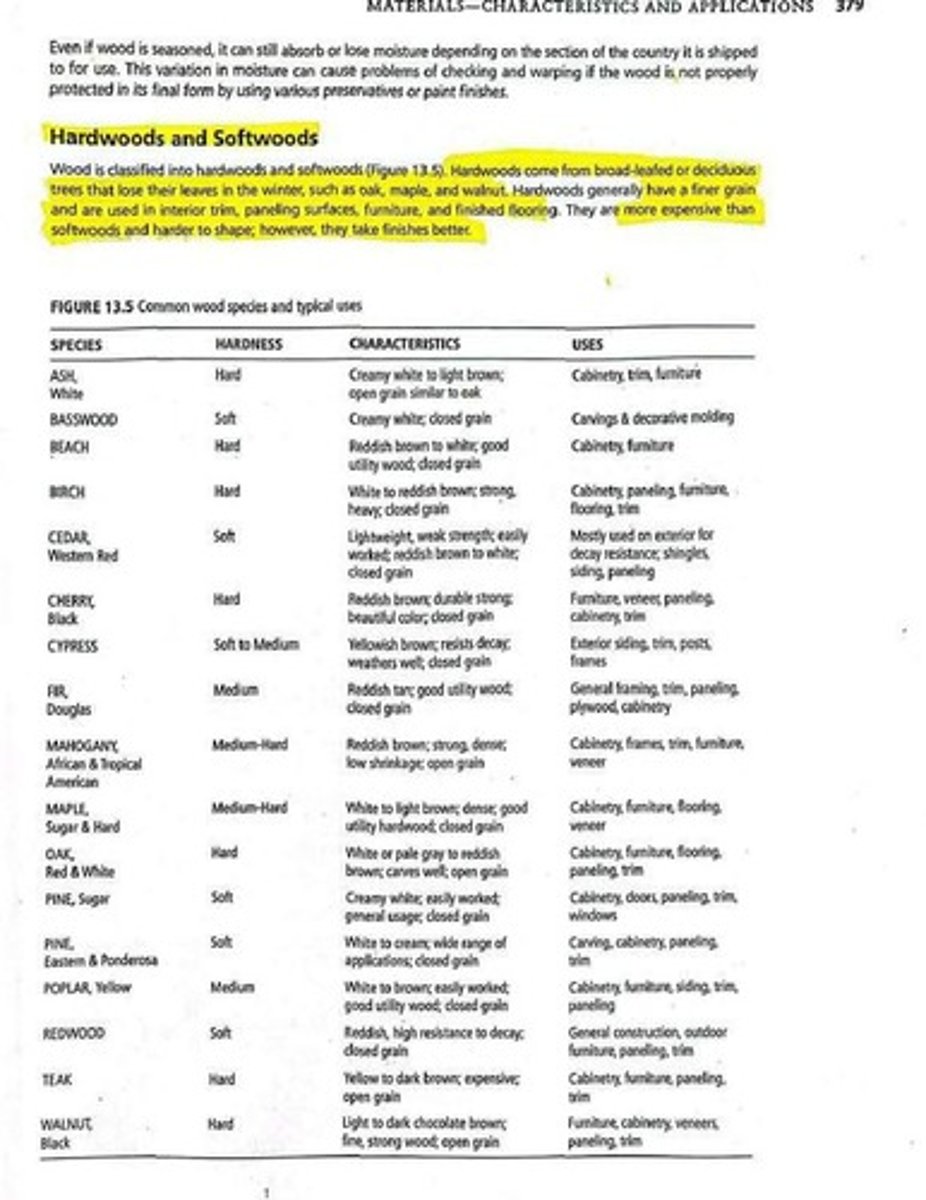
What are hardwoods and softwoods?
Hardwoods come from broad-leafed or deciduous trees and generally have a finer grain, used in furniture and flooring. Softwoods come from coniferous trees and are typically less expensive and easier to shape.
Why is it important to dry wood properly before use?
Proper drying prevents issues such as twisting, cupping, bending, or warping as the wood dries.
What is the moisture content threshold for lumber to be considered dry?
Lumber is generally considered dry when its moisture content does not exceed 19 percent.
What can cause checking and warping in wood?
Variation in moisture content, especially if wood is not properly protected with preservatives or finishes, can lead to checking and warping.
What types of finishes can be applied to wood?
Finishes include natural weathering properties and applied coats such as oils, paints, and plastics.
What is the effect of knots in wood?
Knots might be desirable in decorative applications of wood, such as burl wood.
What is the impact of drying methods on lumber characteristics?
Different sawing methods produce different characteristics in lumber; flat-sawn lumber may wear unevenly, while quartersawn lumber is more stable and wears evenly.
What are the standard lengths for lumber production?
Standard lengths for lumber are generally produced in 2-foot increments, such as 8, 10, and 12 feet.
How does the sawing method affect the grain pattern of lumber?
Flat-sawn lumber produces a variety of grain patterns, while quartersawn lumber yields more even, straight-line grain patterns.
What is the significance of using preservatives or finishes on wood?
Using preservatives or finishes protects wood from moisture variation and helps prevent checking and warping.
What types of wood are typically used for interior trim and furniture?
Hardwoods like oak, maple, and walnut are commonly used for interior trim, paneling surfaces, furniture, and finished flooring.
Why are hardwoods generally more expensive than softwoods?
Hardwoods are more expensive due to their finer grain, greater difficulty in shaping, and better finishing qualities.
What is the effect of wood seasoning on its resistance to fungi and decay?
Seasoning improves wood's strength, stability, and resistance to attack from fungi and decay.
What is the difference between rough lumber and surfaced lumber?
Rough lumber is larger than surfaced lumber, although both are referred to by the same nominal size.
What is the cathedral-like effect in wood grain?
The cathedral-like effect refers to the visual pattern created in flat-sawn lumber, which can display varied grain patterns.
What is the main disadvantage of flat-sawn lumber?
Flat-sawn lumber tends to wear unevenly and can bend or twist when drying.
What are the characteristics and uses of Ash wood?
Ash wood is hard, creamy white to light brown with an open grain similar to oak, used for cabinetry, trim, and furniture.
What are the characteristics and uses of Basswood?
Basswood is soft, creamy white with a closed grain, primarily used for carvings and decorative molding.
What are the characteristics and uses of Beech wood?
Beech wood is hard, reddish brown to white, utility wood with a closed grain, used for cabinetry and furniture.
What are the characteristics and uses of Birch wood?
Birch wood is hard, white to reddish brown, strong and heavy with a closed grain, used for cabinetry, paneling, furniture, flooring, and trim.
What are the characteristics and uses of Western Red Cedar?
Western Red Cedar is soft, lightweight, and weak in strength, reddish brown to white with a closed grain, used mostly for exterior applications like shingles and siding due to its decay resistance.
What are the characteristics and uses of Black Cherry wood?
Black Cherry wood is hard, reddish brown, durable, strong, and has a beautiful color with a closed grain, used for furniture, veneer, paneling, cabinetry, and trim.
What are the characteristics and uses of Cypress wood?
Cypress wood is soft to medium, yellowish brown, resists decay, weathers well, and has a closed grain, used for exterior siding, trim, posts, and frames.
What are the characteristics and uses of Douglas Fir wood?
Douglas Fir wood is medium, reddish tan, good utility wood with a closed grain, used for general framing, trim, paneling, plywood, and cabinetry.
What are the characteristics and uses of African and Tropical Mahogany?
Mahogany is medium-hard, reddish brown, strong, dense, has low shrinkage, and an open grain, used for cabinetry, frames, trim, furniture, and veneer.
What are the characteristics and uses of Sugar and Hard Maple wood?
Maple wood is medium-hard, white to light brown, dense, and a good utility hardwood with a closed grain, used for cabinetry, furniture, flooring, and veneer.