Orgo 2 Exam 2
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
friedel-craffs alkylation
limitations
any alkyl halide can be used (single bonds only)
impossible to stop at mono-alkylation (multiple substitutions)
wont react if theres a strong deactivator
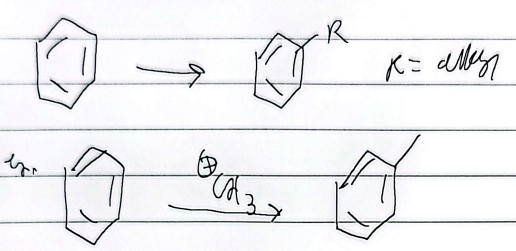
friedel-acylation
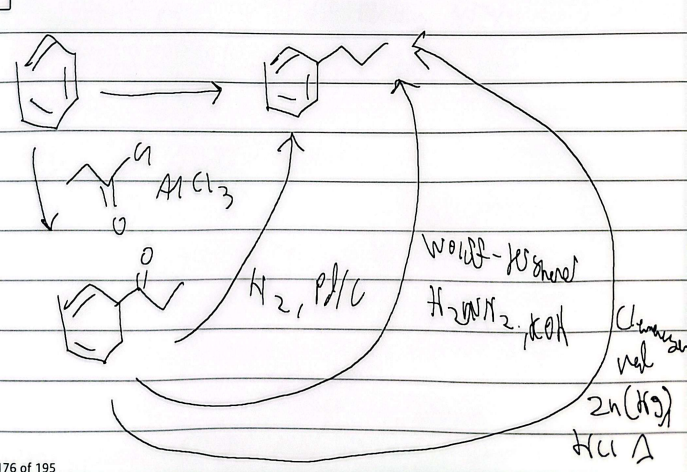
reduction
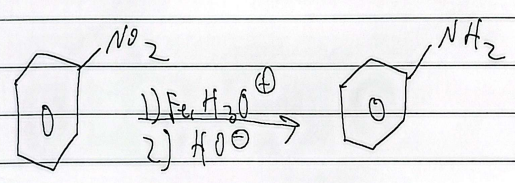
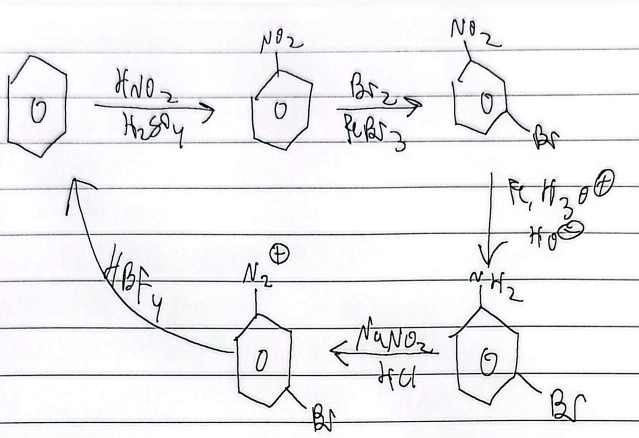
diazonium
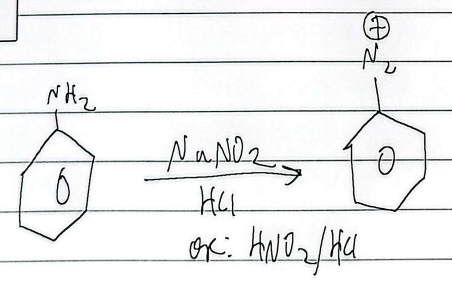
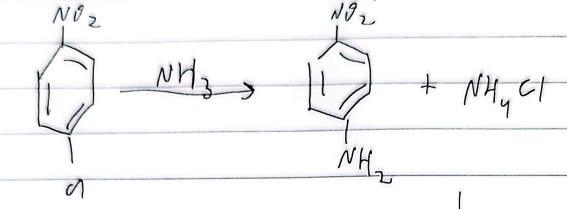
aromatic rxns
activating groups
faster rxn, lone pair e- directly connected to benzene, neg or partial neg charge
ortho/para director
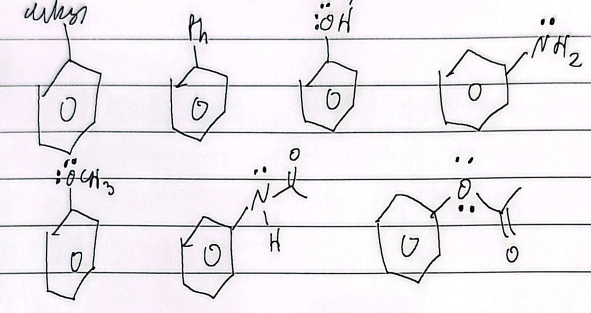
deactivating groups
slower rxn, pos or partiall pos charge
meta director
exception: halogens ortho/para deactivators
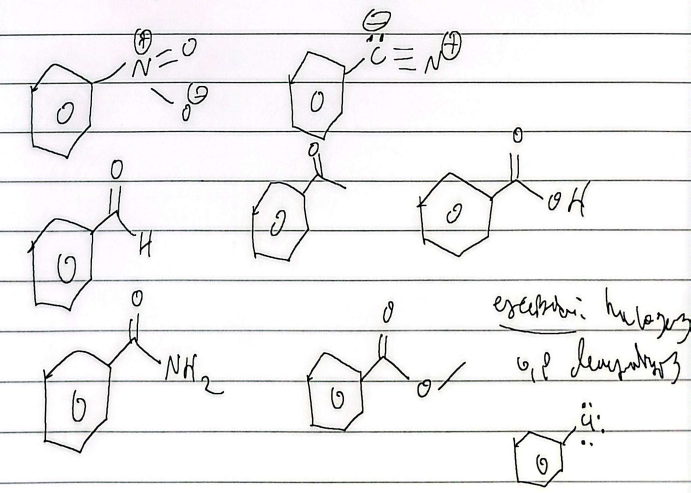
NAS
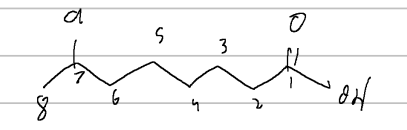
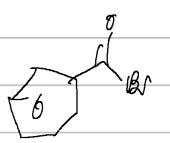
3-chloro-4-cyclohexylbutanone
IUPAC
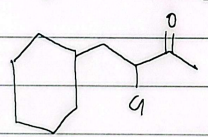
2-ethyl-6-isopropoxy-5-oxocental
IUPAC
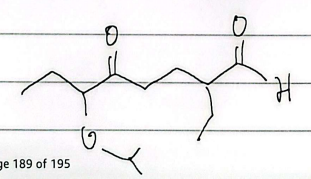
nona-4,8-diene-2,7-dione
IUPAC
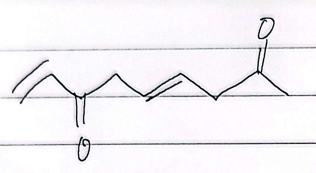
5-oxohexanedial
IUPAC
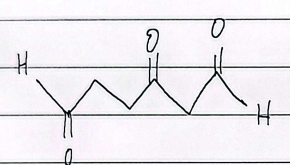
aldehydes
when naming these,
-al on end
highest priority in naming
ketones
when naming these,
-one on end
-oxo internal
cyclopentanecarbaldehyde
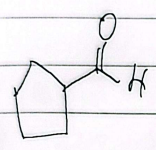
formaldehyde
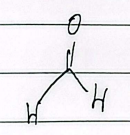
acetaldehyde
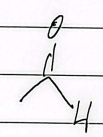
acrolein
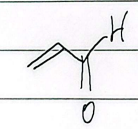
crotonaldehyde
acetone
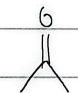
reduction

reduction

poisoned pd

gutterman ruch
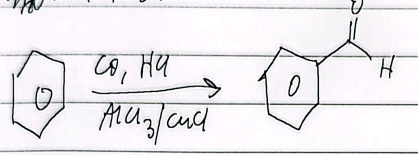
ozone cleavage
silver mirror test
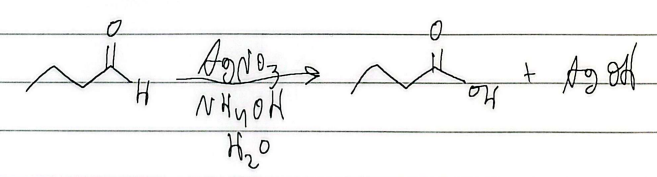
nucleophilic addition rxn
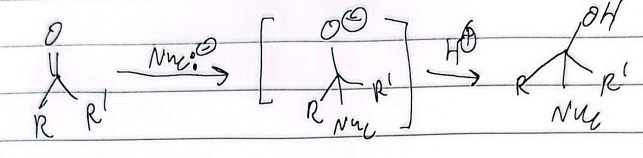
aldehydes
more reactive than ketones for two reasons:
sterics: h smaller group, more room for nucleophile to attack
electronics: alkyl gets past e- density easier, less electrophilic, attracts nucleophile more readily
acids
when naming these,
methane → methanoic acid
on chain names, drop the ending e and replace with -oic acid
heptanedioic acid
IUPAC
7-chlorooctanoic acid
IUPAC
nitrile
when naming these,
add nitrile at the end of the chain name
ethane → ethanenitrile
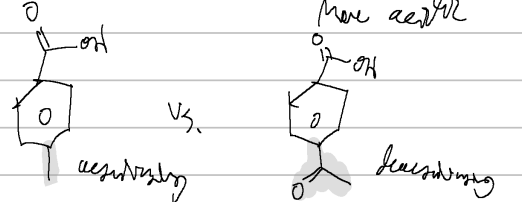
properties of carboxylic acids
dimerize, high boiling point
acidic
pka usuallly from 4-5 when in the body
right
more acidic?

right
more acidic?

right
more acidic?

right
more acidic?

right
more acidic?
CN, hydrolysis
prep of carb acids

Na2CrO7, LAH
prep of carb acids

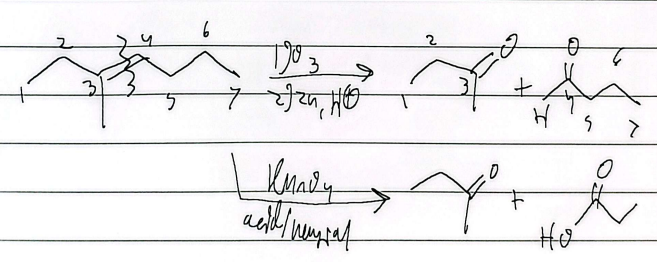
cleavage (KMnO4, acid/neutral)
prep of carb acids

cleavage (KMnO4 or O3)
prep of carb acids
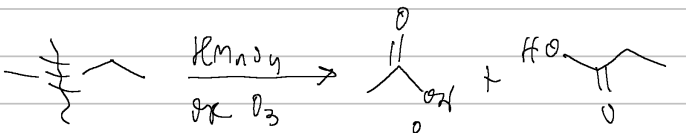
KMnO4
prep of carb acids

CO2, H3O
prep of carb acids, grignard
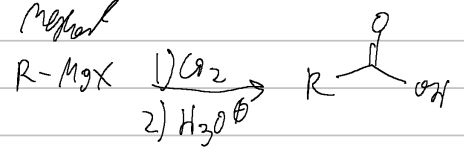
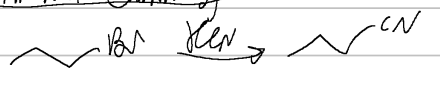
KCN
prep of nitrilles
SOCl2
prep of nitriles
degradation of a primary amide
LAH, H2O
carb acid rxn
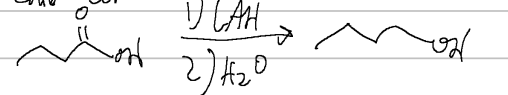
BH3, THF
carb acid rxn

BH3, THF
carb acid rxn

NAH, iodopropyl OR propanol, H3O
carb acid rxn
fischer tropsch esterification
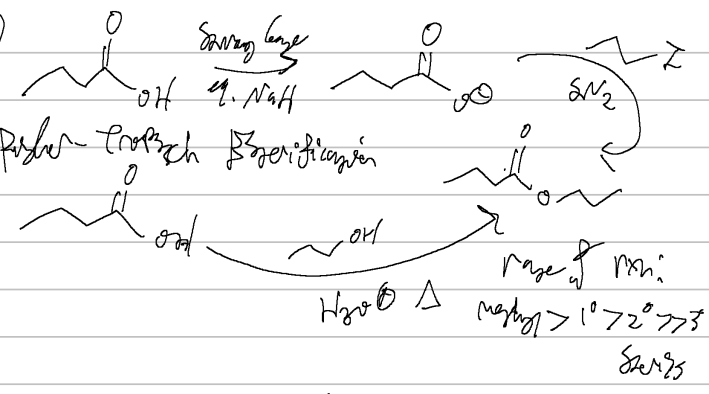
acid/base with heat
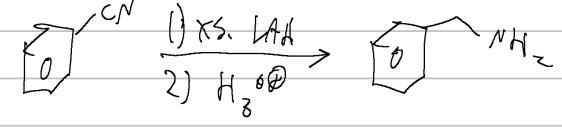
nitrile rxn
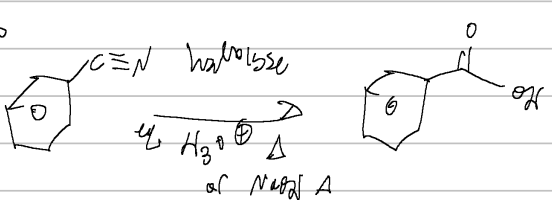
LAH, H3O
nitrile rxn
nitrile to primary amine
RMgX, H3O
nitrile rxn
grignard
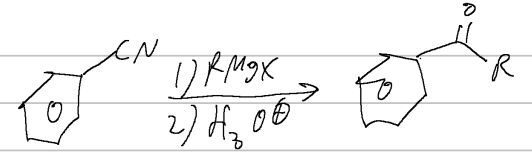
acid halides
when naming these:
formic acid → formyl chloride
propionic acid → propionyl acid
ending ic swap to yl
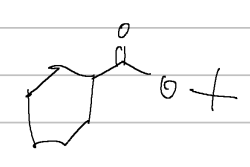
benzoyl bromide
IUPAC
esters
when naming these:
name the substituent not attached to the carbonyl first, then the parent chain
ethane → ethanoate
replace e with -oate
isopropylpentanoate
IUPAC
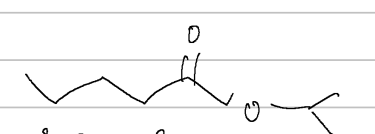
ethylethanoate (ethylacetate)
IUPAC
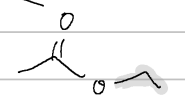
t-butylcyclohexane carboxylate
IUPAC
amides
when naming these:
ethane → ethanamide
replace e with -amide
use N- to indicate groups attached
ethanamide (acetamide)
IUPAC
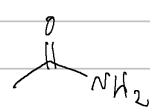
N-methylacetamide
IUPAC
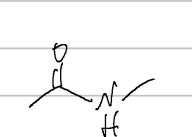
N,N-dimethylacetamide
IUPAC
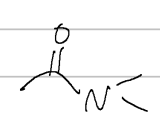
N-isopropylbutanamide
IUPAC
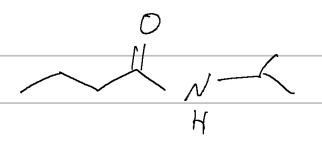
N-ethyl-N-methylacetamide
IUPAC
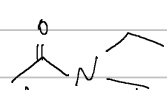
thioesters
when naming these:
name the substituent not attached to the carbonyl first, then the parent chain
ethane → ethanoate
replace e with -oate
then, add thio- in front of the parent chain
ethylthiobutanoate (ethylbutanethioate)
IUPAC
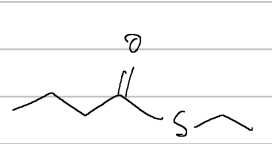
methylcyclopentanecarbothioate
IUPAC
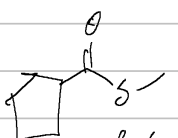
acid anhydride
when naming these;
name the substituents same as an acid then add anhydride at the end
benzoic acid → benzoic anhydride
benzoic anhydride
IUPAC
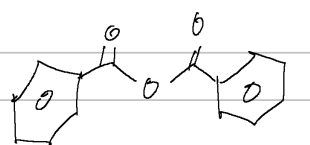
acetic benzoic anhydride
IUPAC
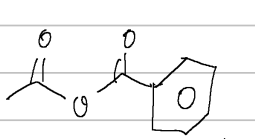
nucleophilic aryl substitution

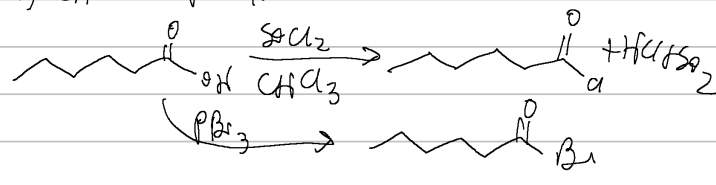
SOCl2/CHCl3 or PBr3
carb acid → acid halide
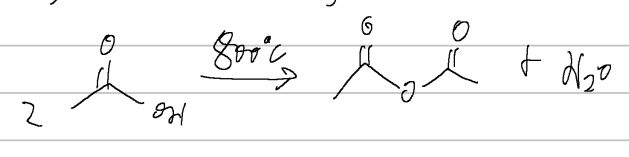
heat
carb acid → acid anhydride
NaH/iodopropane
carb acid → ester

H3O
carb acid → ester
fischer tropsch esterification

R2NH
carb acid → amide

DCCI/propylamine
carb acid → amide

LAH/H2O
carb acid → alcohol
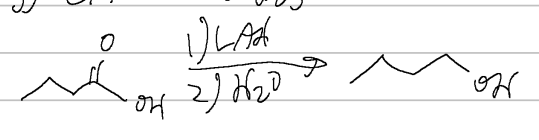
BH3, THF/H3O
carb acid → alcohol
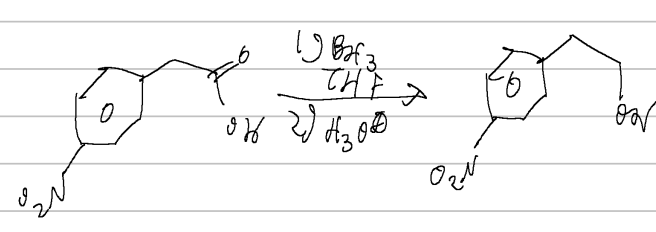
NaOH/H2O pyr
acid halide → acid

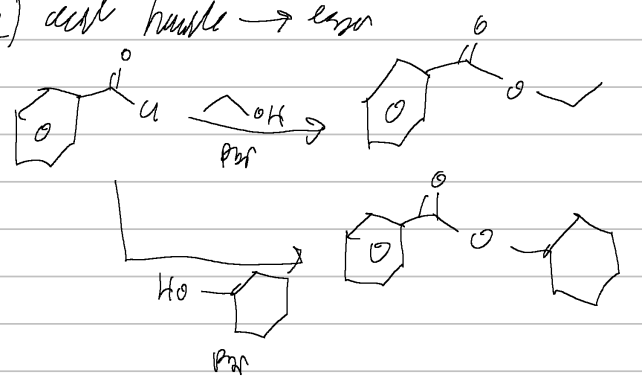
ethanol/pyr
acid halide → ester
sterics are critical here, 1 > 2 > 3
2 NH3
acid halide → amide

2 eq. dimethylamine
acid halide → amide

LAH/H3O
acid halide → alcohol
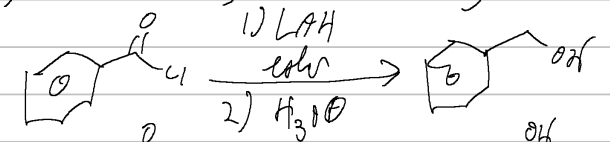
CH3MgCl/H3O
acid halide → alcohol
grignard
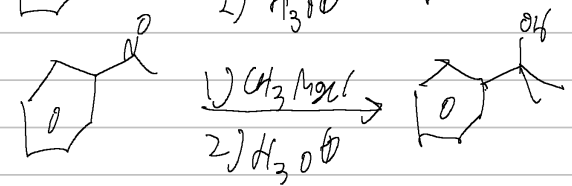
(CH3)2CuLi OR Li(O-tBu)3AlH
acid halide → ketone
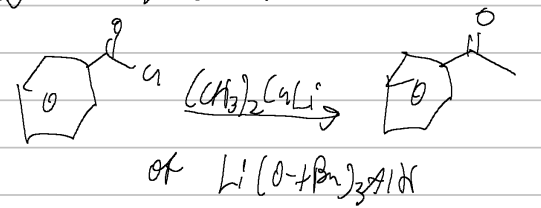
ethanol/NaOH
acid anhydride → ester

ethylamine/NaOH
acid anhydride → amide
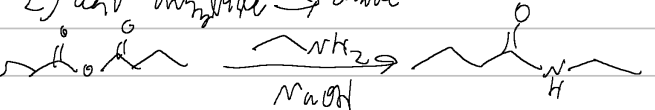
H3O
acid anhydride → carb acid
H3O
ester → carb acid
NH3/ether
ester → amide

ester to alcohol
ways for _______________
LAH
DIBAH → aldehyde
RMgX
H3O
amide → carb acid

LAH/H3O
amide → amine
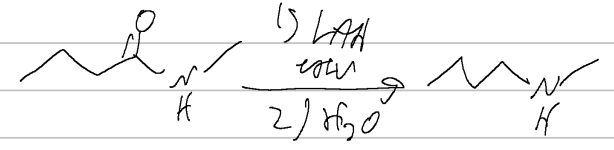
SOCl2/pyr OR P2O5/pyr OR POCl3/pyr
amide → nitrile

2-methylpropylbutanoate
IUPAC
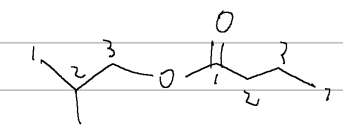
alpha carbon
bulky base vs regular base
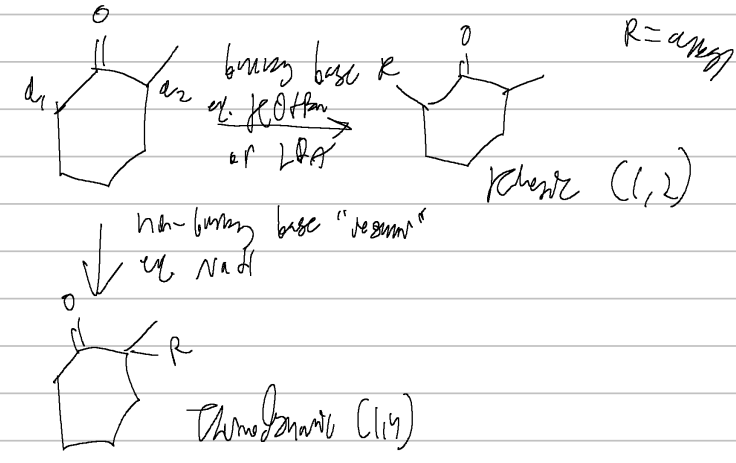
alpha carbon
