L12 Corneal Degenerations
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
two conditions that causes corneal thinning
terrien marginal degeneration
furrow degeneration
diseases leave ____ are:
calcific band keratopathy
limbal girdle of vogt
corneal arcus
lipid degeneration
iron deposits
amyloid deposits
deposits
_____ ____ consists of
crocodile shagreen
salzmann nodular degeneration
spheroidal degeneratoin
corneal keloids
hassall henle bodies
cornea farinata
remodulated tissue
terrien marginal degeneration usually affects who (2)
20-40s but can occur in childhood
male
terriens marginal degeneration is characterized by slowly progressive bilateral thinning of peripheral cornea. It begins ______ then spreads _____
superior, circumferential
terriens marginal degeneration is accompanied by (3)
neovascularization, peripheral opacification, lipid deposition
terrien's marginal degeneration can be associated with
episcleral or scleral inflammation
terrien marginal degeneration
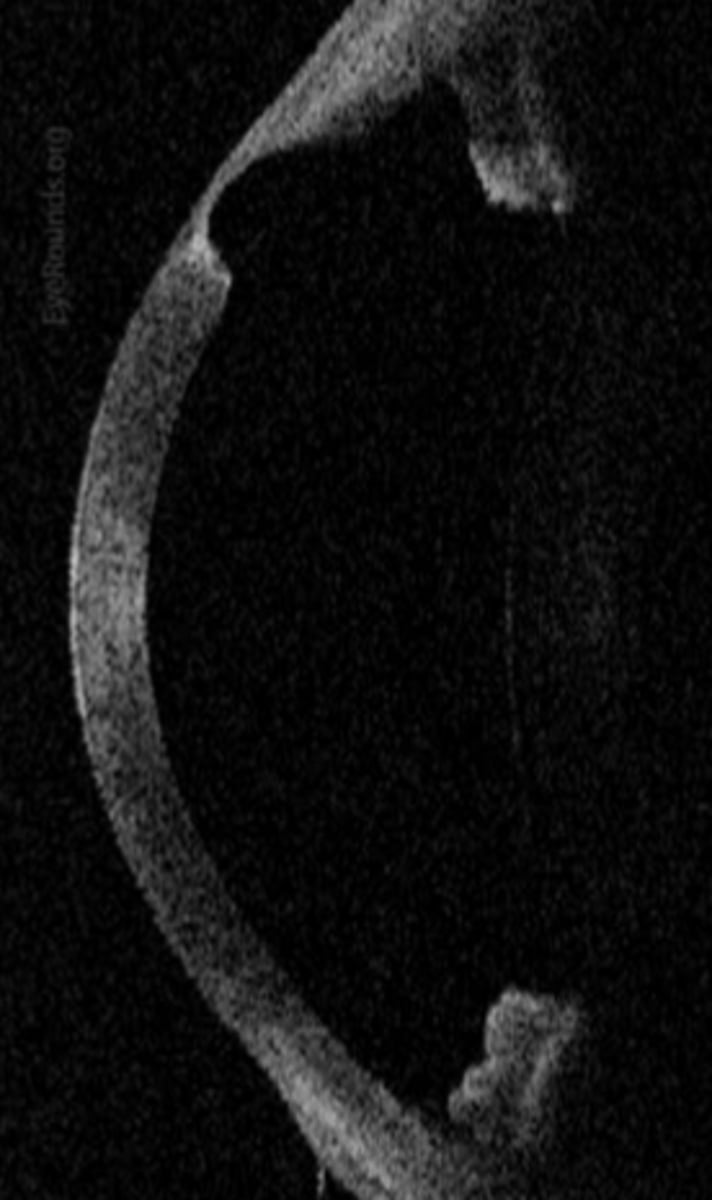
___ progression
1. superficial punctate and anterior stromal opacities superiorly
2. linear deposits at leading edge with vascular pannus circumferential thinning
3. ends with steepening in area of thinning leading to irregular astigmatism / high ATR astigmatism
terrien marginal degeneration
terrien marginal degeneration is occularly significant due to ______ corneal astigmatism, high _____ and high risk for _____
irregular, ATR, perforation
what are differentials for TMD (2)
mooren ulcer (pain & ulcer)
furrow degeneration (lack astig. shift)
what is the tx for TMD (2)
special CL for vision
surgery intervention for perforation or high risk of it
what is another name for furrow degeneration (2)
senile furrow degeneration and marginal furrow degeneration
furrow degeneration tends to affect who
older pts like 60+
furrow degeneration is characterized by ?
painless, non inflammatory peripheral thinning in avascular zone between arcus and limbal vascular arcade
furrow degeneration has areas of thinning that are similar or equal ______ ____ resulting in no ____ shift
tensile strength, astigmatic
what is the treatment for furrow degeneration
asymptomatic with no treatment
(calcific) band keratopathy affects who
any age
(calcific) band keratopathy has two forms:
calcific and non calific
(calcific) band keratopathy is characterized by calcium deposits in ______ layer located ____ along horizantal axis
bowman, interpalpebral
when (calcific) band keratopathy progresses, ____ ____ and ____ ___ can occur
avascular pannus, epithelial atrophy
besides calcific and non calcific, what are the two forms (calcific) band keratopathy can have
primary and secondary
can (calcific) band keratopathy affect vision? why?
yes because it affects visual axis
what are the two tx options for (calcific) band keratopathy
EDTA chelation and remove with lasers
primary (calcific) band keratopathy is
- considered idiopathic
-rare presentation
secondary (calcific) band keratopathy characterization (3)
- chronic ocular inflammation
- ocular trauma
- systemic disease with elevated serum calcium or phophate
(calcific) band keratopathy can create risk of
recurrent corneal erosion
t/f (calcific) band keratopathy can alter vision
true
secondary (calcific) band keratopathy characterizition: 3
-chronic inflamation
- systemic diease with abnormal calcium metabolism
- topical/ intraocular meds that affect calcium metabolism within the eye
tx for (calcific) band keratopathy (2)
EDTA chelation - in office to remove and dissolve Ca
Excimer laser PTK to remove Ca
calcific band keratopathy presents in about ______ of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in pediatrics
1/3
pediatric bank k is associated with
uveitis
t/f in peds= inflammation, band k, cataract
true
Limbal girdle (of vogt) is seen in who
older patient. increased incidence w age
what are characteristics of Limbal girdle (of vogt) (2)
symmetric yellow- white band located at the interpalpebral limbus beneath the epithelium next to bowman
located nasal> temporal
peds bank k
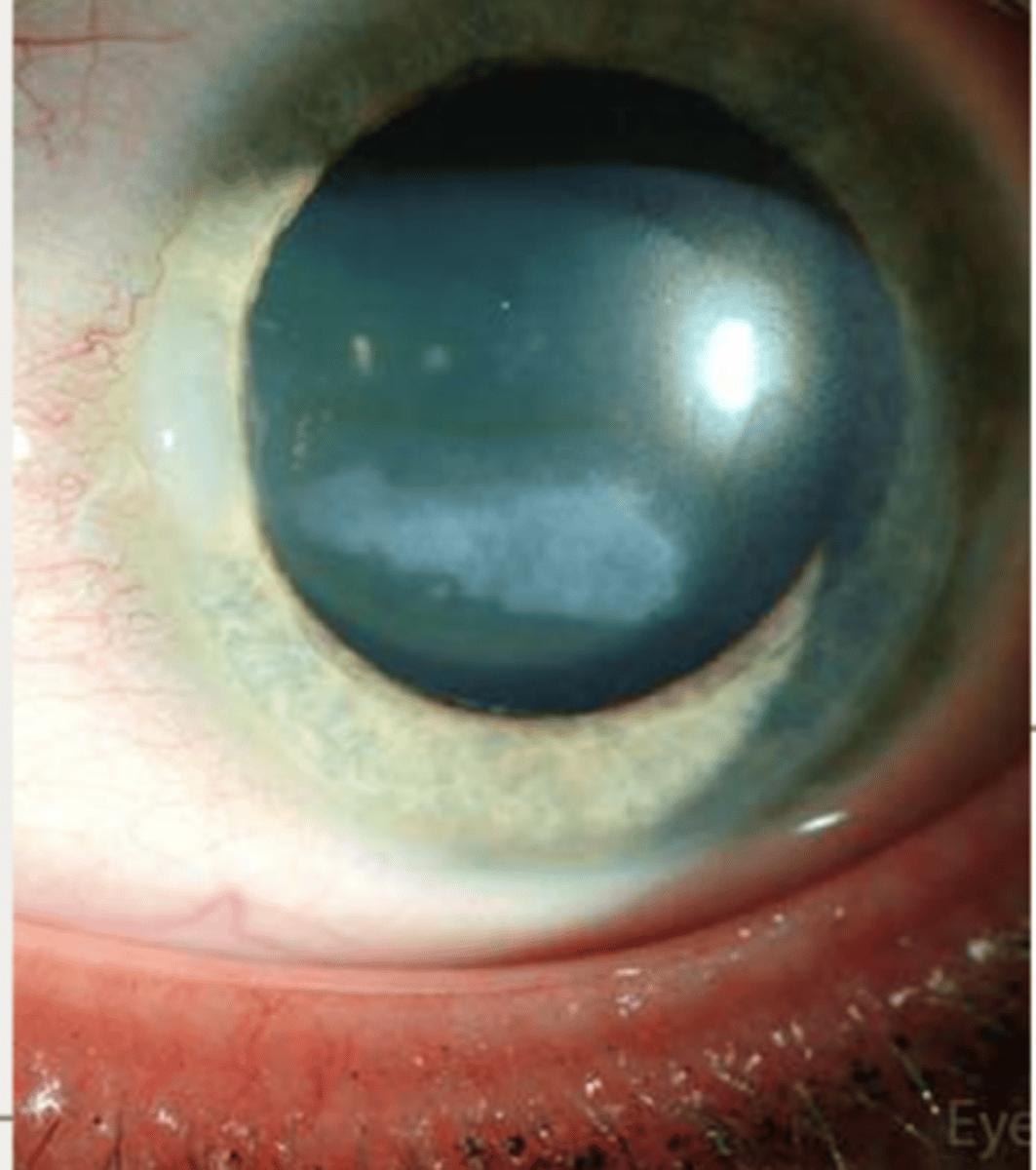
how are the two types of Limbal girdle (of vogt) distinguished?
presence or absence of clear zone between lesion and limbus
Limbal girdle (of vogt) is considered visually _____ and does not require ____
insignificant, treatment
Limbal girdle (of vogt)
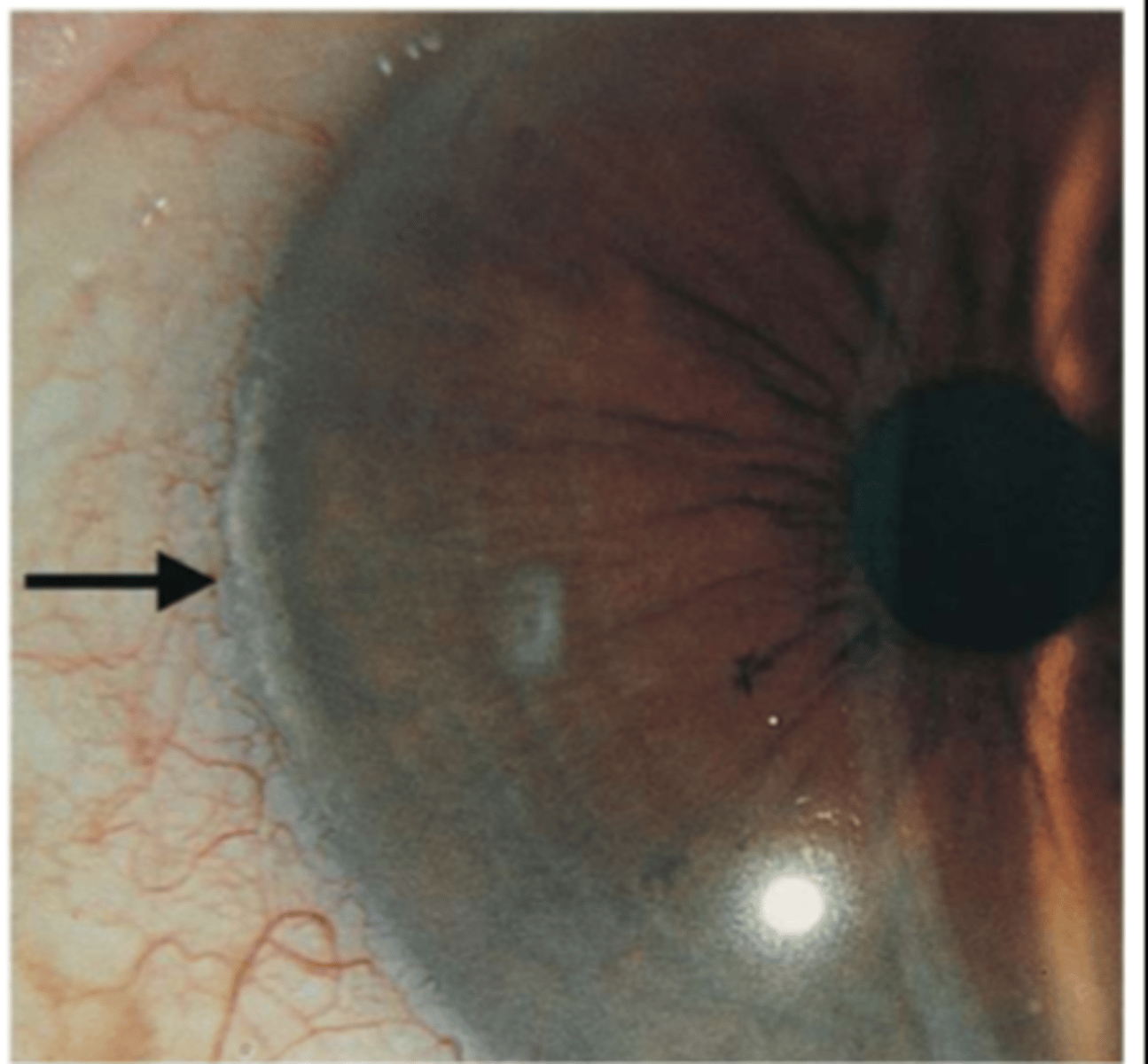
there are two types of Limbal girdle (of vogt). type 1 is the absence of _____ ____ and mainly has _____ deposits
clear zone, calcium
there are two types Limbal girdle (of vogt). type 2 has the presence of ___ ___ and is made of (3)
clear zone
made of hyaline deposits, elastic changes, hypertrophy overlying epithelium
types Limbal girdle (of vogt) type 1
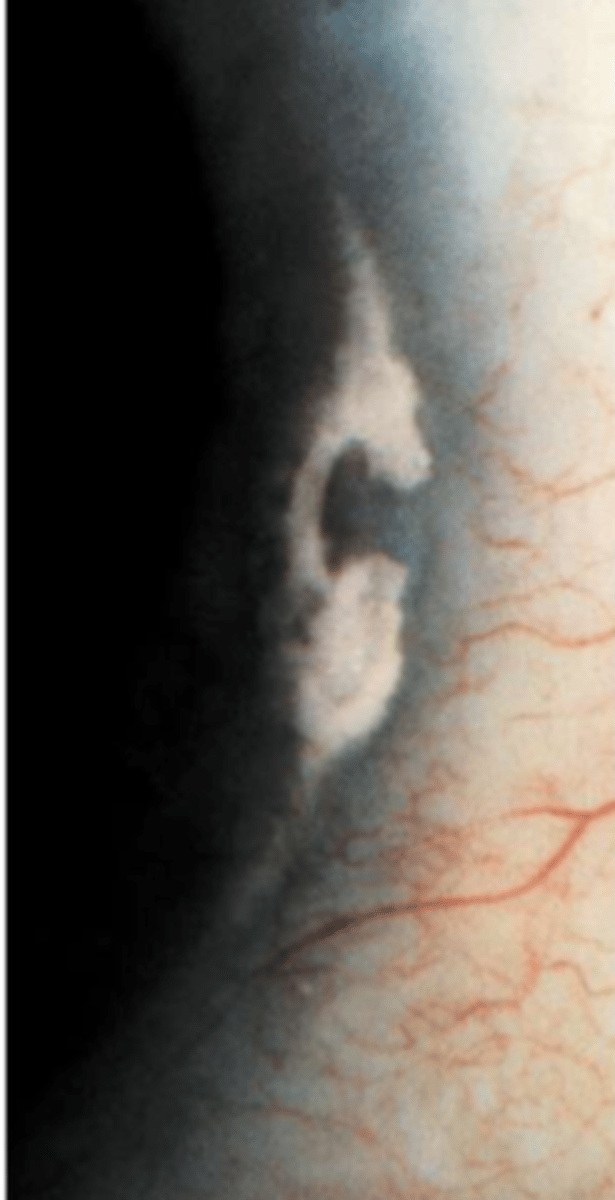
types Limbal girdle (of vogt) type 2
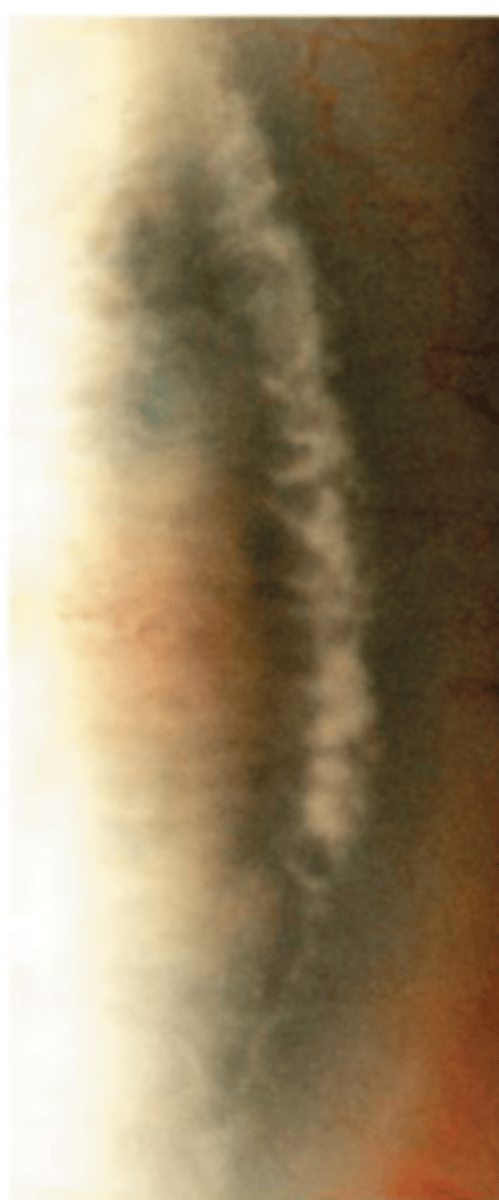
what is the term to define patients 40 and up who present with corneal arcus
arcus senilis
what is the term to define patients younger than 40 who present with corneal arcus (2)
arcus juvenilis OR posterior embryotoxin
___ ____ is can be described as
bilateral, slow progressive lipoprotein deposits in peripheral with a chance of rapid onset of hyperemia
corneal arcus
how does corneal arcus distribute itself around the limbus?
starts inferior cornea then superior cornea and then makes full ring
how does corneal arcus distribute itself within the layers of the cornea?
starts in decemets to bowmans and then in between stromal lamellae
___ ___ is pathophysiology is described as
- lipoproteins cross capillary walls
- elevated circulating LDL disrupts _____ junction of limbal vasculture edothelium
- _____ can accelerate it
corneal arcus, Tight, hyperemia
is corneal arcus ocularly significant in people over 40? yes or no
no
is corneal arcus ocularly significant in people under 40? yes or no
yes
corneal arcus presenting in people under 40 could show risk of _____ ____ disease and _________
coronary artery, hyperlipoproteinemia
what is hyperlipoproteinemia presenting as
premature arcus with xanthelasma
yellow near lids= xanthelasma
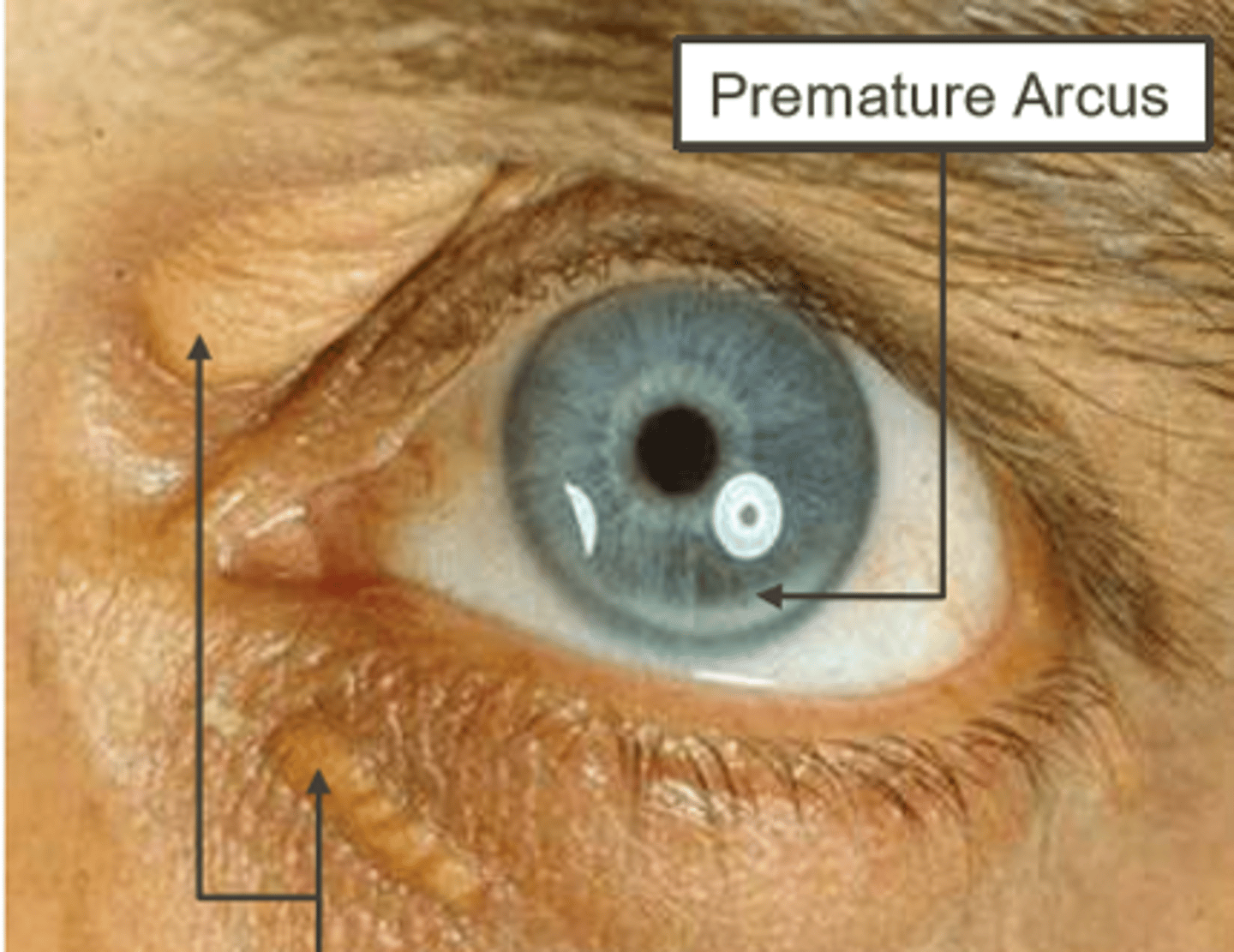
unilateral presentation of corneal arcus could mean risk of carotid artery occlusion on the side side _______ arcus
without
what are the two types of lipid degeneration
primary and secondary
______ lipid degeneration presents as
no neo or inflammation
normal lipid levels
rare
primary
what is another name for secondary lipid degeneration
lipid keratopathy
____ ___ ___ presents as or with
neo and inflammation
increased HDLs
secondary lipid degeneration
____ lipid degeneration is commonly seen with herpetic infections, ulcers, and truam
secondary
lipid degeneration
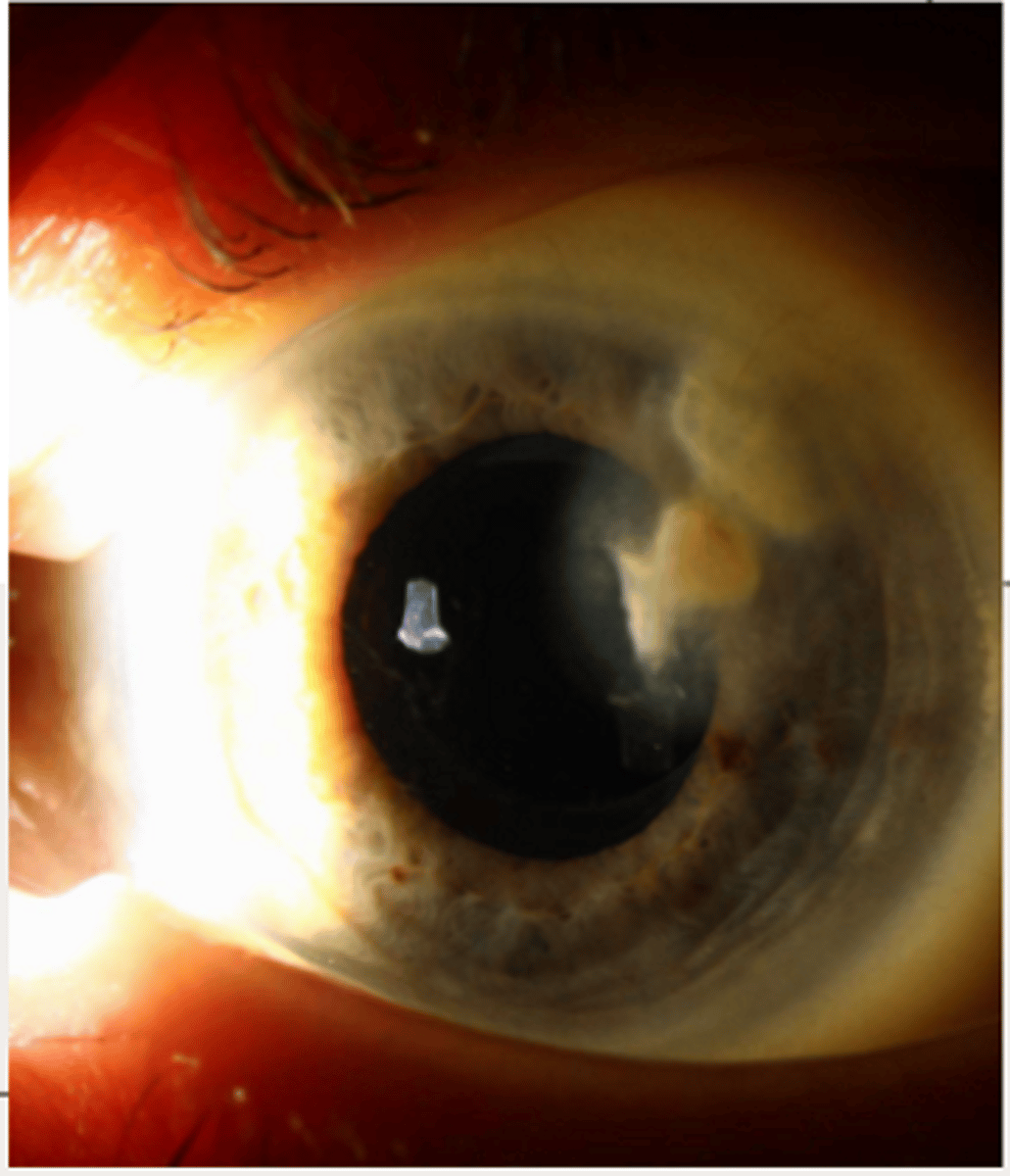
primary lipid degenerations can occur bilaterally with risk for central lipid formation and ____ formation
crystal
secondary lipid degeneration can either uni or _____. presence of white- yellw deposit with _____ vessel accompanied with other signs such as ____
bilateral, stromal, inflammation
what is the demographics for lipid degeneration
depends on etiology
lipid degeneration is characterized by (3)
- white yellow deposits in all cornea layer
- highest in midstroma
- sea fan shape with featherlike edges
- +/- crystals
can lipid degeneration affect vision? yes or no
yes
tx for lipid degeneration for neo or vision affected?
neo = anti vegf or tx feeder vessel
vision= surgery (penetrating keroplasty)
where do iron come from and where do they deposit?
come from tear film. deposit in epithelium
what is the best way to detect iron deposisits
cobalt or red free
if there is iron in the epithelium and you use cobalt or red free how will it appear
look like a black line
iron deposits are commonly seen with (5)
- keratoconus
- filtering blebs
- pterygiums
- salzmanns nodules
- cornea surgery
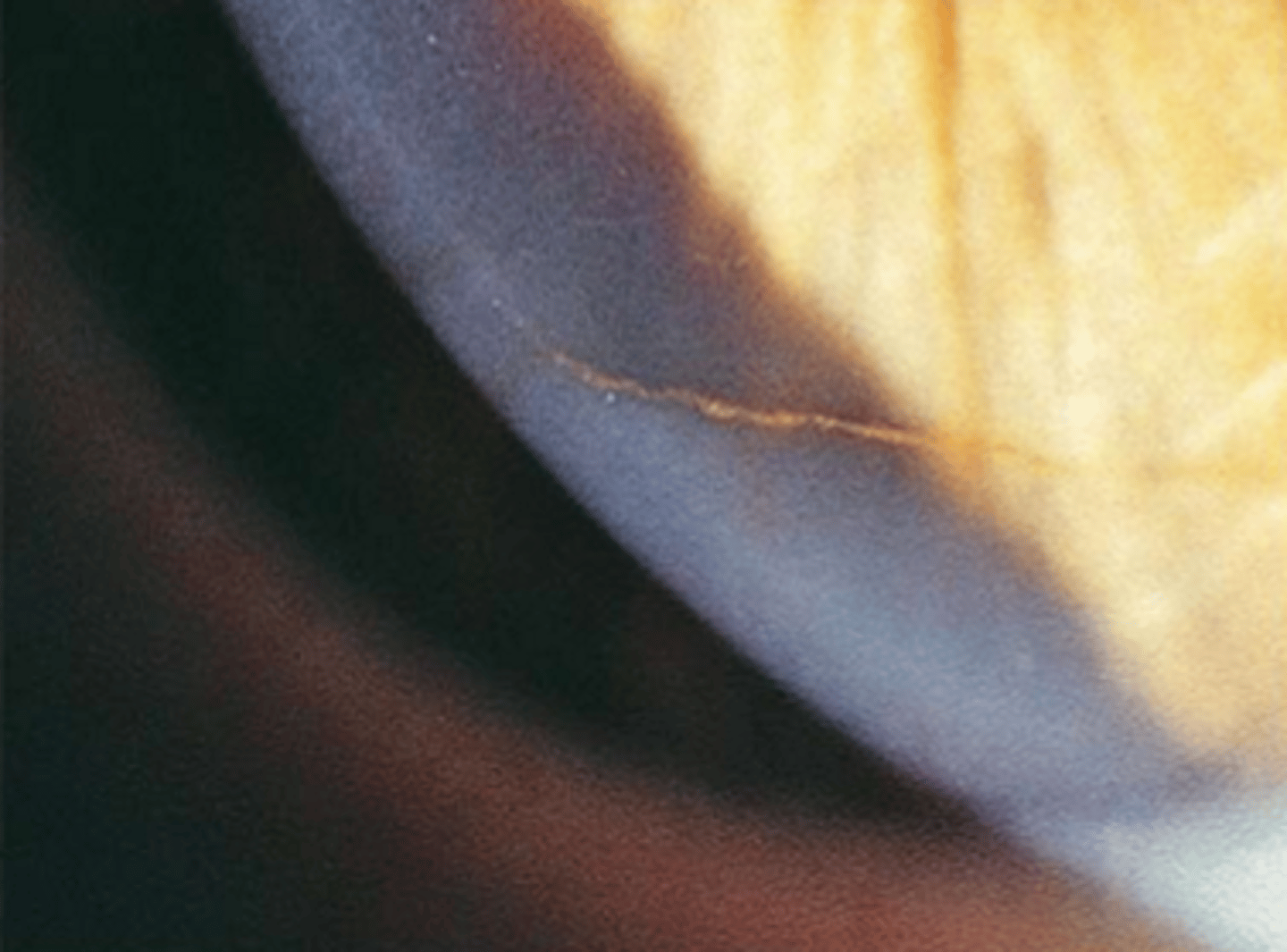
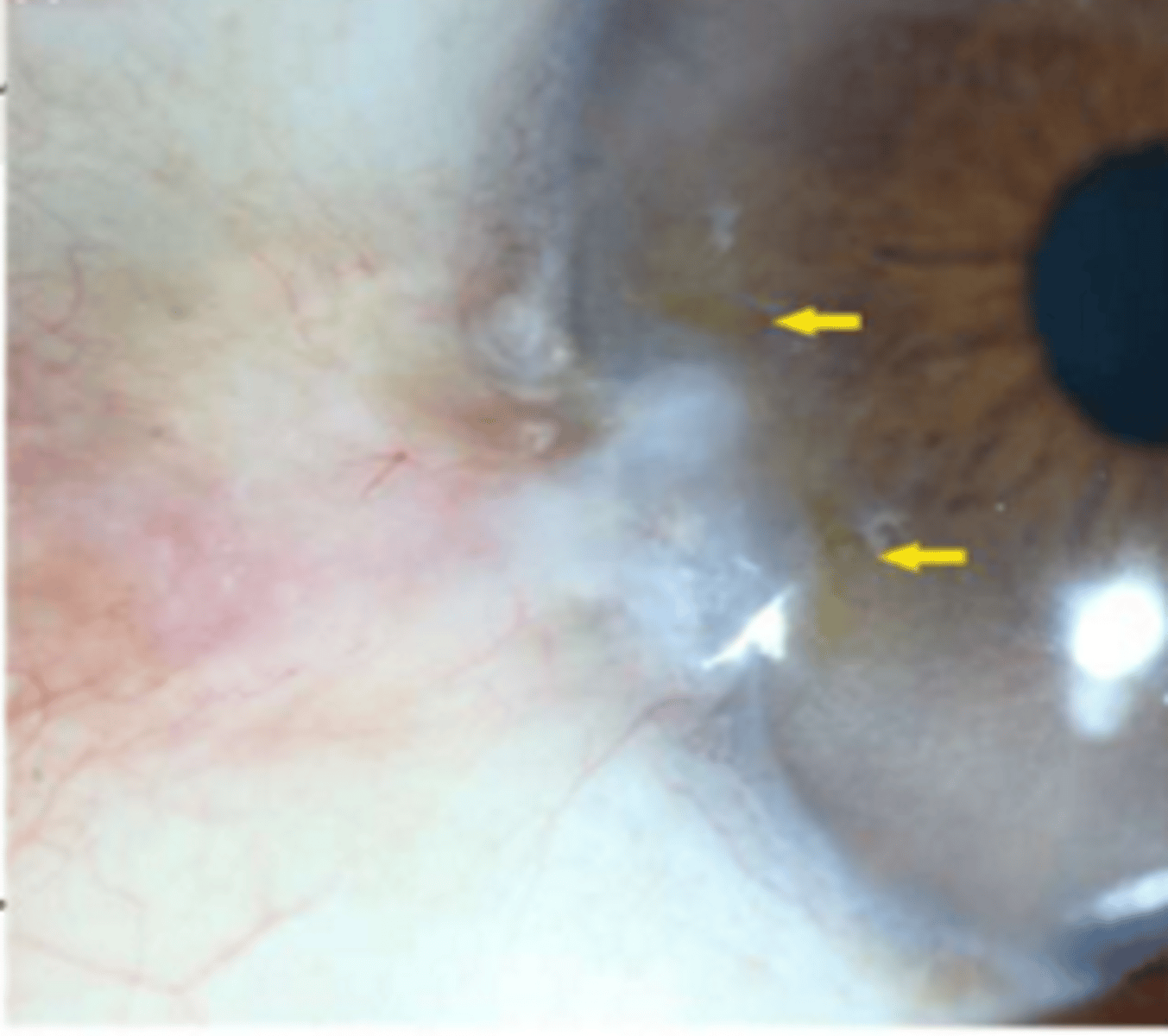
iron deposits in lower third of cornea is called
hudson-stahli line
iron deposits at leading edge of pterygium is called
stockers line
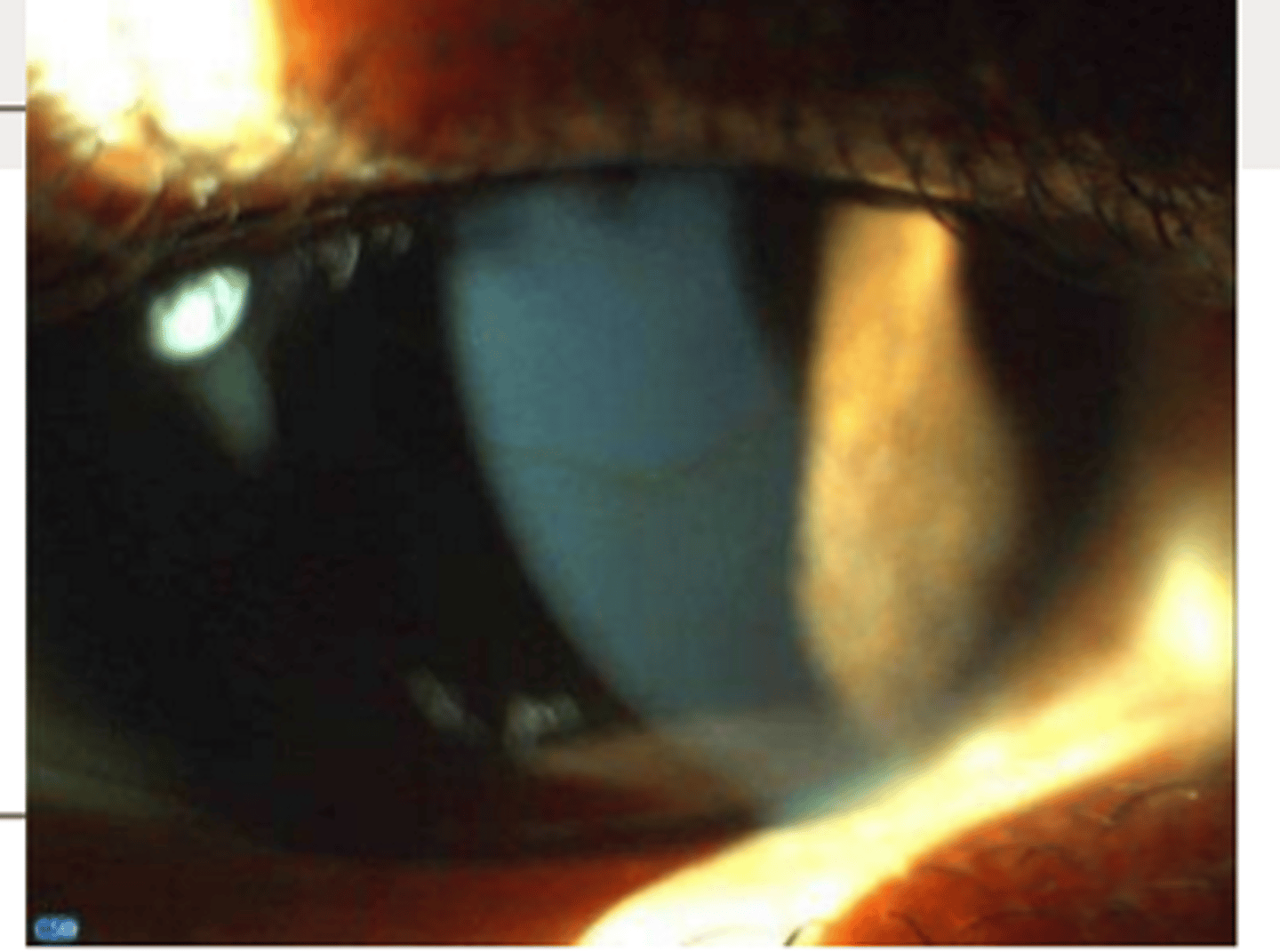
iron depositing at the base of cone in keratoconus is called
fleishers ring
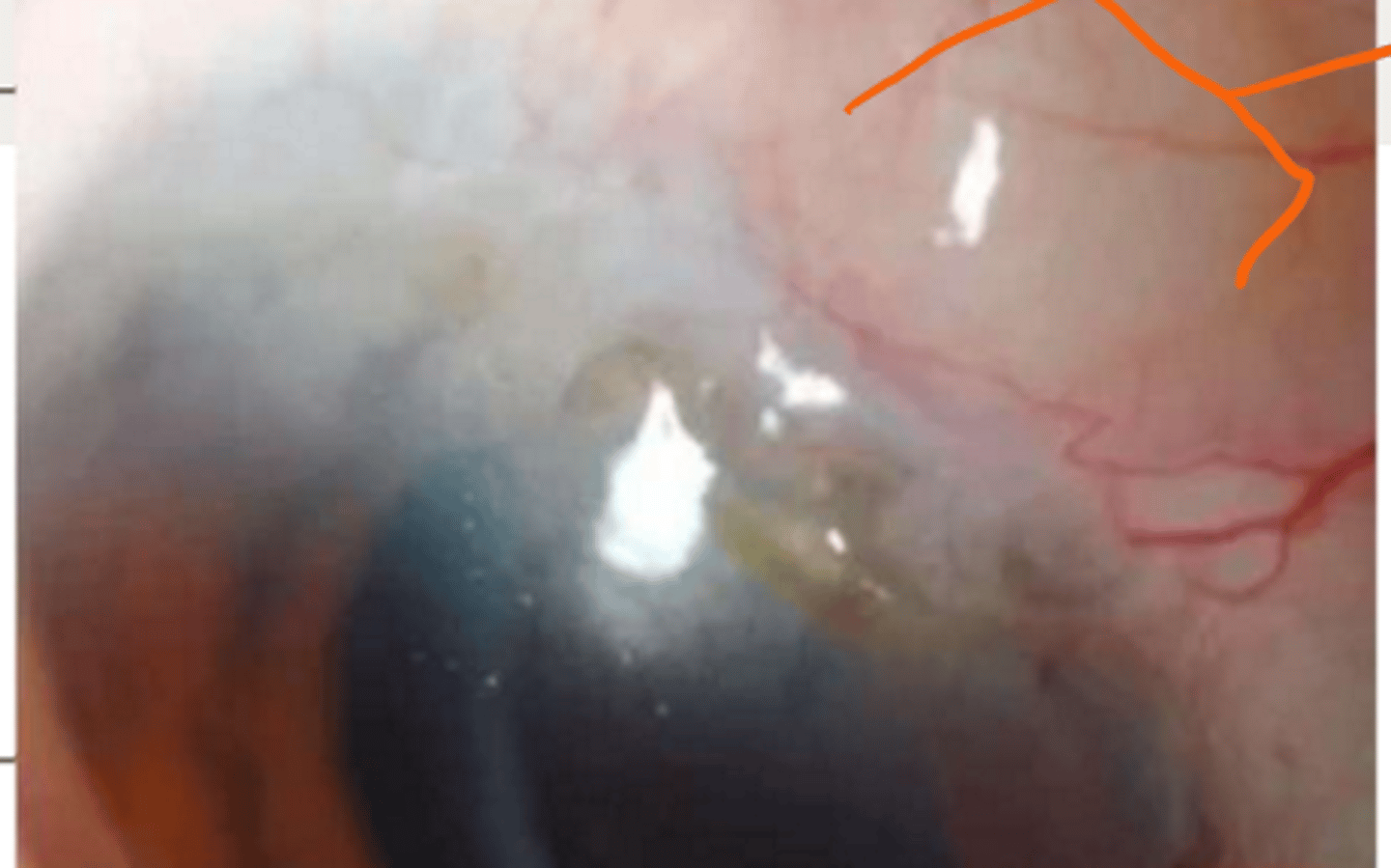
iron depositing associated with filtering blebs is called
ferrys line
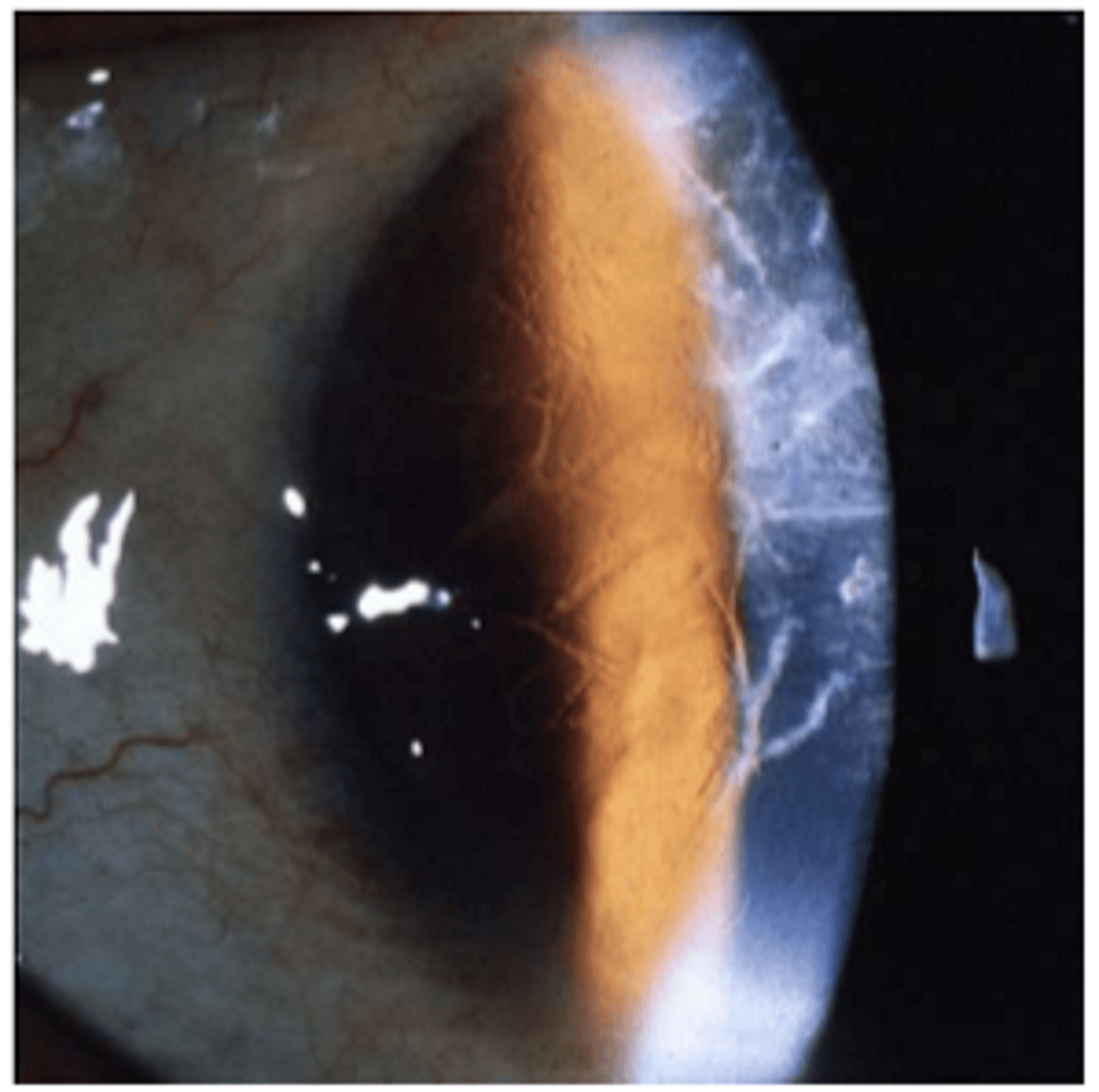
hudson stahli line
stockers line
fleishers ring
ferrys line
amyloid depositis
what is amyloid
group of hyaline proteins with starch like staining characteristics
a characteristic of amyloid deposit is they occur on ___ or _____ from systemic and localized condition
conj, cornea
amyloid deposits present in (4)
corneal dystrophy (lattice, gel. drop like cornea prblms)
trauma
chronic inflammation
degeneration (polymorphic amyloid degen.)
t/f treatment for amyloid deposits is related to etiology
true
t/f amyloid deposits can be visually significant
true
what is polymorphic amyloids degeneration
bilateral glass like deposits made of amyloid in the central stroma that can indent decemets
polymorphic amyloids degeneration occurs in which age
>50 yrs
what is a differential for polymorphic amyloids degeneration
lattice dystrophy
does polymorphic amyloids degeneration impair vision? yes or no
no
____ ____ is bilateral, symmetric mosaic pattern opacities in the stroma
crocodile shagreen
crocodile shagreen
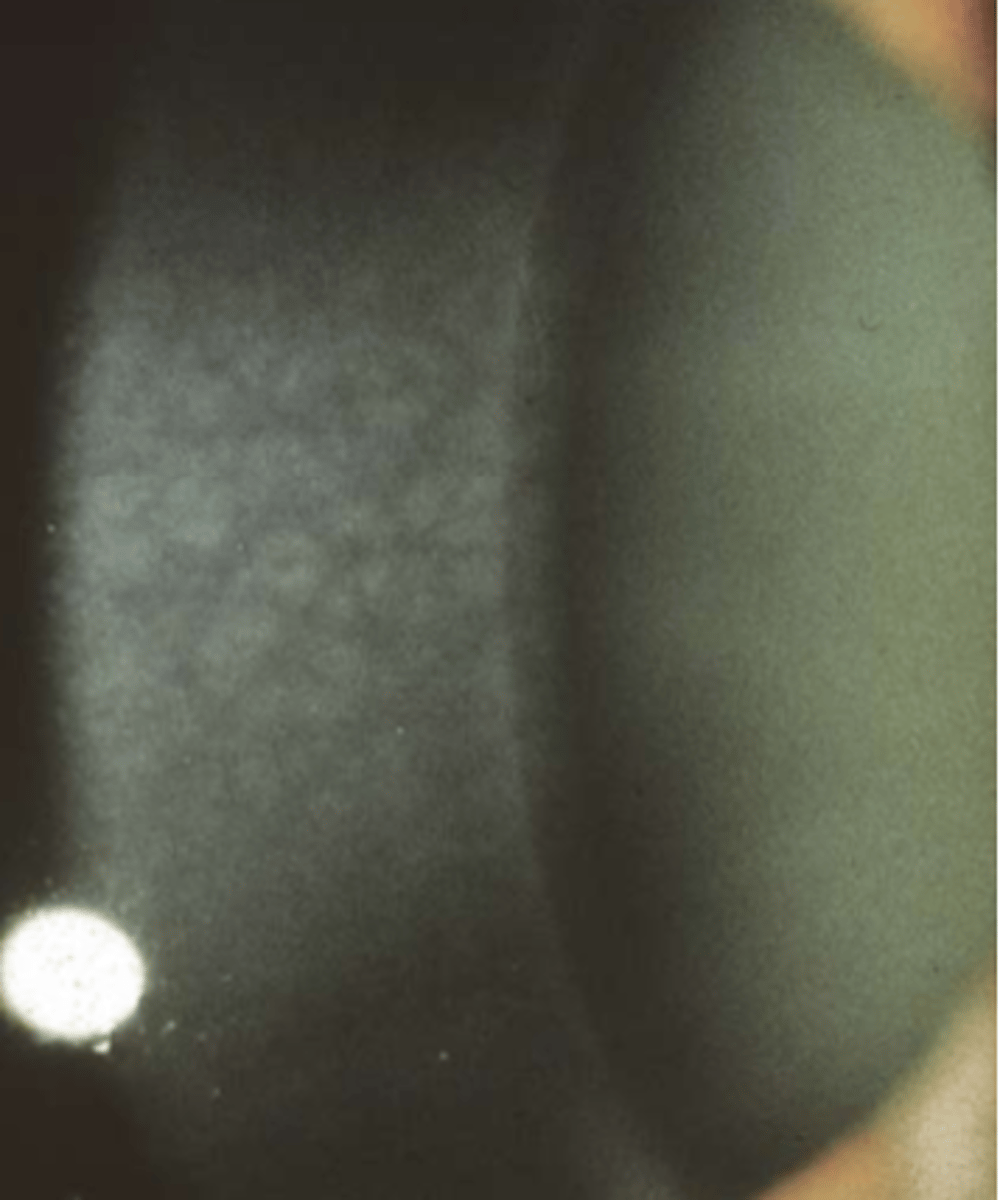
is crocodile shagreen common in the central or peripheral
more common in central but appears in peripheral
what is the composition of crocodile shagreen
reorganization of collagen lamella
what are the two types of crocodile shagreen
anterior and posterior
what is anterior crocodile shagreen assoicated with
trauma, hypotony, band - k, megalocornea, or RGP wear
what is posterior crocodile shagreen assoiciated with
age related degeneration
is crocodile shagreen ocularly significant? yes or no
no
what is the tx for crocodile shagreen
does not need treatment
Salzmann nodular degeneration affects who
middle ages
females more than males
____ ____ can be
- uni lateral or bilateral
- 0.2 to 2mm round oval, elevated, avascular, white blue gray lesions located between epithelium and bowman
- single or multiple in an annular distr.
- iron line at base of nodules is possible
- slow progression
- adjacentt to pannus or scarring
salzmanns nodular degeneration