Poultry Nutrition
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Feed additives
Substances added to feed for specific functions.
Nutritional needs
Essential dietary requirements for poultry health.
Egg production impact
Influence of laying on nutritional requirements.
Growth rates effect
Nutritional adjustments based on growth speed.
Feed cost
70% of total poultry production expenses.
Dietary enzymes
Substances enhancing feed efficiency and nutrient absorption.
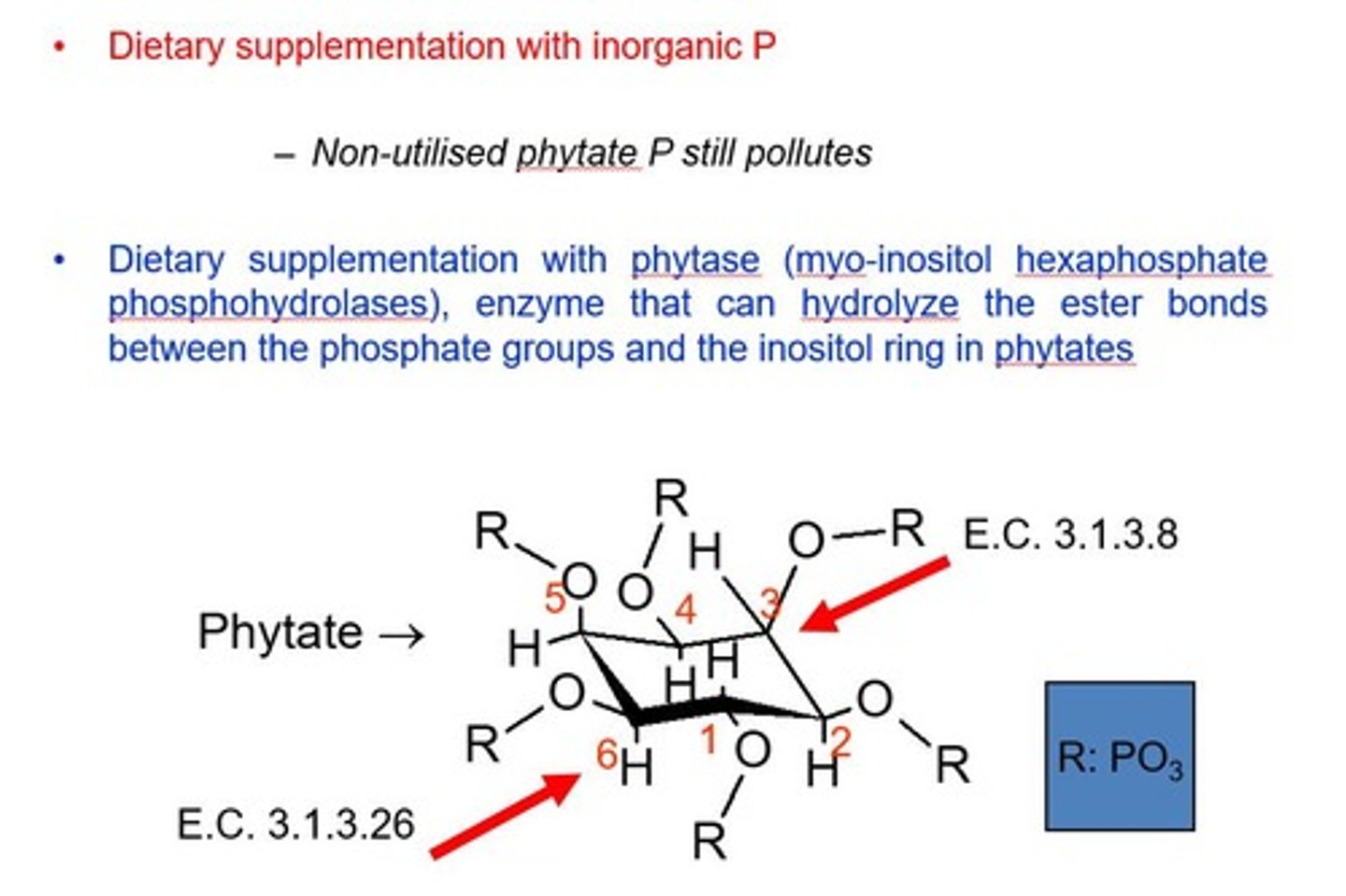
Phytases
Enzymes that increase phosphorus availability from phytate.
Proteases
Enzymes improving protein digestibility in poultry.
Carbohydrases
Enzymes that enhance carbohydrate digestion.
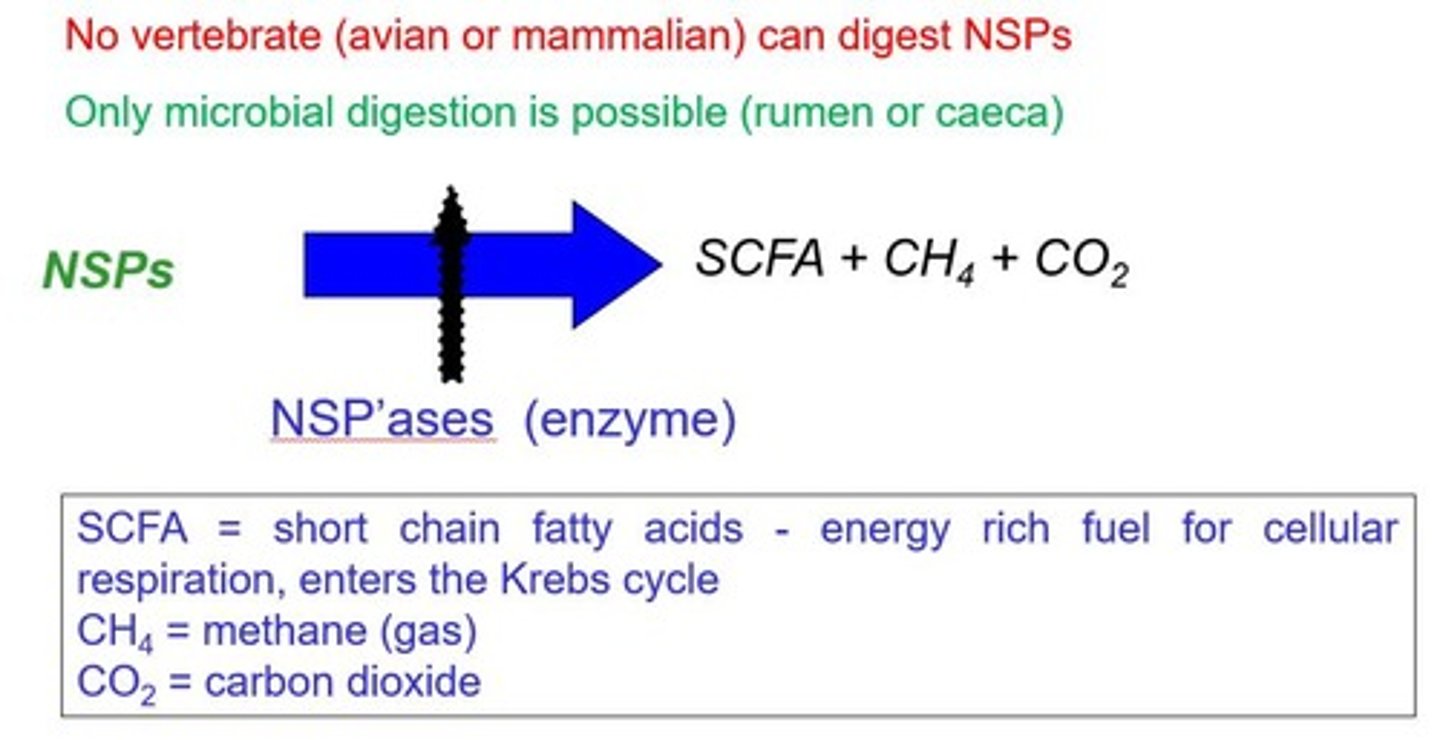
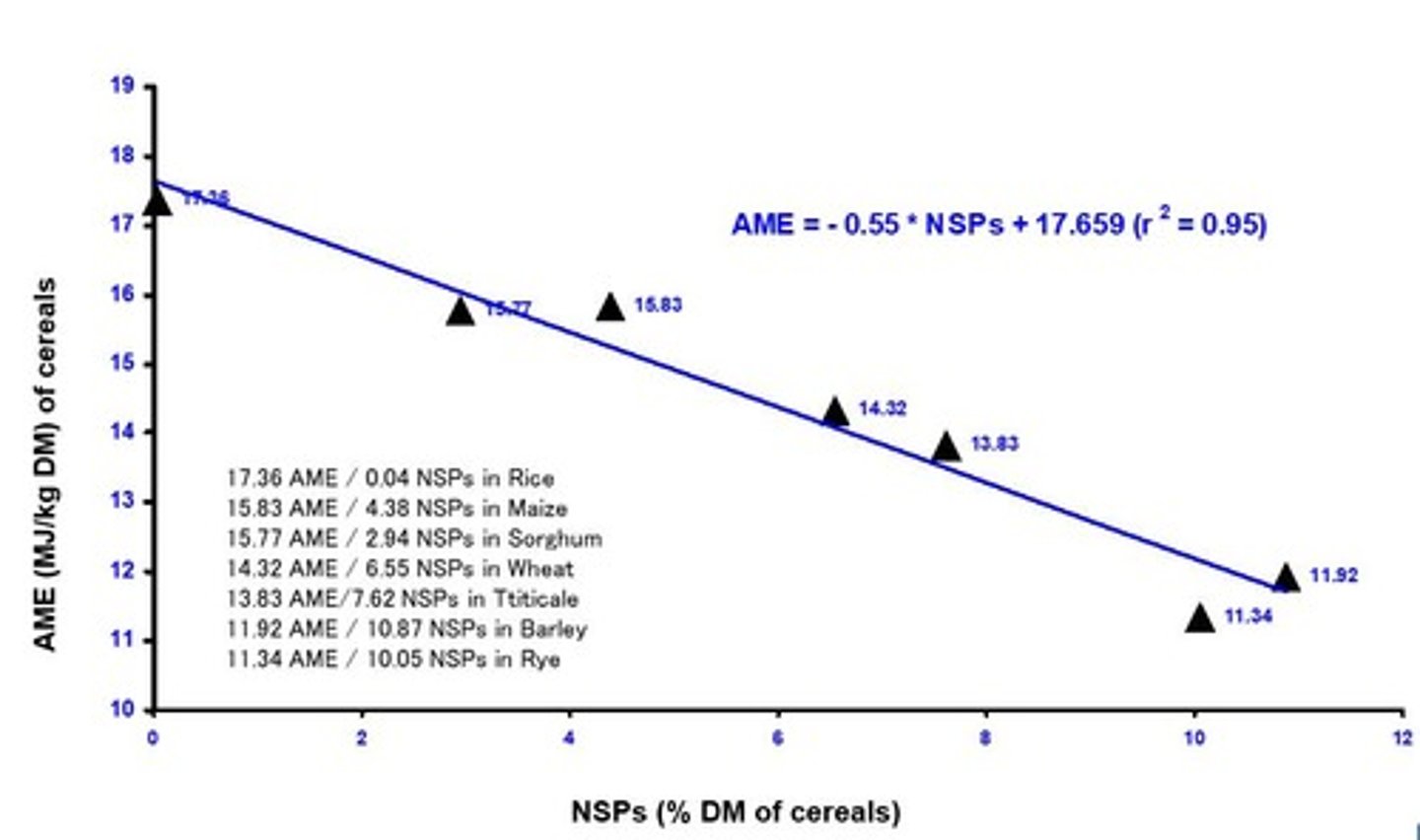
Non-starch polysaccharides
Fibers affecting nutrient digestibility in poultry.
Feed conversion ratio (FCR)
Measure of feed efficiency in weight gain.
Phytate
Organic form of phosphorus, poorly digestible by poultry.
Exogenous enzymes
Enzymes added to diets for improved digestion.
Super dosing
High levels of phytase for enhanced nutrient release.
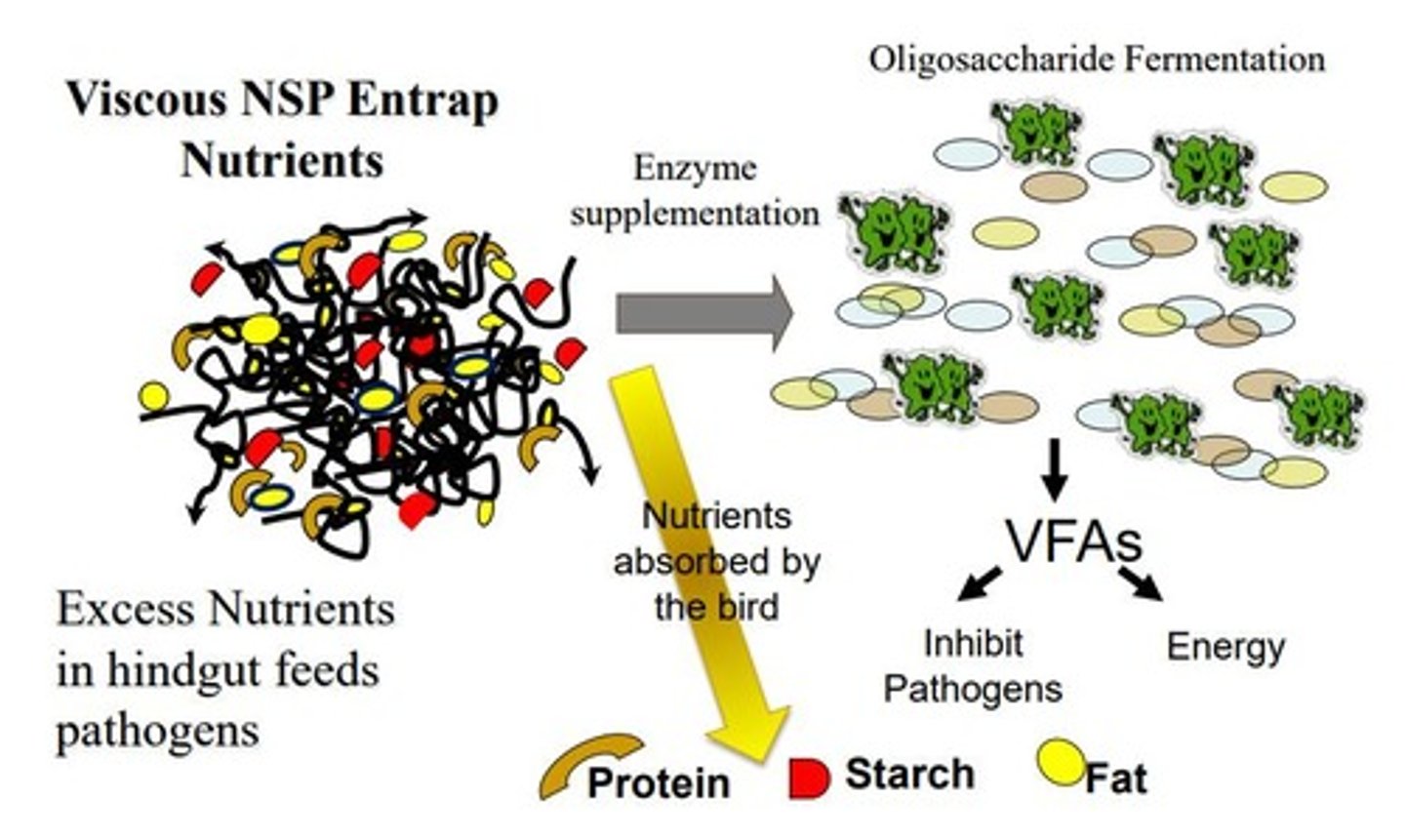
Viscous gels
Thick substances formed by soluble NSPs in gut.
Gut irritation
Discomfort caused by dietary components affecting digestion.
Nutrient bioavailability
Accessibility of nutrients for absorption by animals.
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins essential for growth.
Mortality increase
Higher death rates due to inadequate phosphorus.
Endogenous losses
Nutrient losses from the animal's own metabolism.
Water holding capacity
Ability of NSPs to retain water in the gut.
Microbial growth
Increase in gut bacteria due to poor digestion.
Maintenance costs
Expenses related to sustaining animal health.
Nutritional needs
Requirements for optimal growth and production.
Egg production impact
Influences nutritional requirements in laying hens.
Growth rates effect
Affects nutritional needs based on growth speed.
Feed cost
Feed constitutes 70% of poultry production expenses.
Exogenous enzymes
External enzymes improving digestion and growth.
Phytases
Enzymes degrading phytate, increasing phosphorus availability.
Proteases
Enzymes enhancing protein digestibility in feeds.
Carbohydrases
Enzymes improving carbohydrate digestion and nutrient uptake.
Phosphorus (P)
Essential mineral for growth and performance.
Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSPs)
Fibers affecting digestion and nutrient availability.
Viscous gels
Formed by soluble NSPs, hindering nutrient absorption.
Nutrient bioavailability
Extent nutrients can be absorbed and utilized.
Super dosing
High levels of phytase to enhance phosphorus release.
Gut irritation reduction
Benefit of exogenous phytase in digestion.
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins, essential for growth.
Dietary nutrient availability
Accessibility of nutrients for absorption in the gut.
Microbial growth
Increased by poor nutrient digestibility and gut health.
Maintenance costs
Expenses related to sustaining animal health and performance.
NSP enzymes
Reduce digesta viscosity and improve gut health.
Symbiotic gut ecosystem
Maintains beneficial microbial populations in the intestine.
Xylanase
Enzyme that breaks down arabinoxylan in feed.
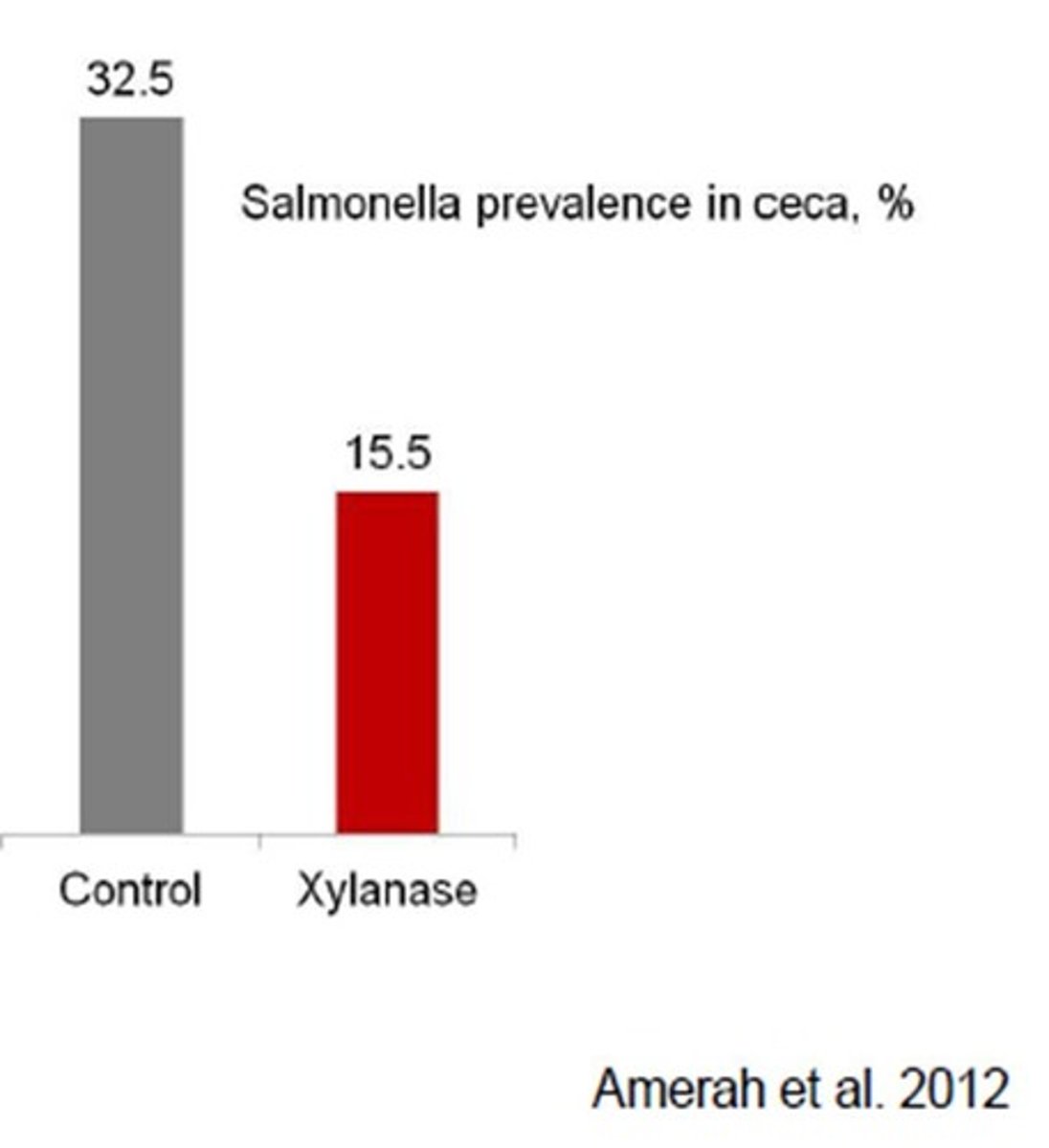
Nutrient digestibility
Improved by xylanase, reducing pathogenic bacteria.
Arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides
Prebiotics stimulating immune responses in the intestine.
Feed conversion ratio (FCR)
Measure of feed efficiency in animal production.
Exogenous NSP enzymes
Supplemental enzymes enhancing feedstuff utility and performance.
Body weight gain
Increased by enzyme supplementation in animal diets.
Dietary protein costs
Rising expenses affecting animal feed formulations.
Crude protein digestibility
Undigested protein represents opportunity for supplementation.
Supplementary proteases
Enhance protein digestibility by complementing digestive enzymes.
Protein hydrolysis
Breakdown of dietary proteins into peptides and amino acids.
Protein-starch interactions
Disrupted by proteases to improve nutrient availability.
Anti-nutrients in soybean
Degraded by proteases to enhance nutrient absorption.
Solubilization of NSP
Increased by exogenous proteases for better digestion.
Phytase access
Enhanced by proteases and xylanases to degrade phytate.
Animal performance
Improved through enzyme supplementation in feed.
Feed raw materials
Expanded options for formulating animal diets.
Digestive enzymes
Natural enzymes aiding in nutrient breakdown.
Xylanase and food safety
Reduces nutrients for pathogenic bacteria in intestines.
Caine et al. (1998)
Study on protein hydrolysis and solubility.
Emulsifiers
Enhance fat mixing in gut for digestion.
Lipases
Enzymes that break down fats in feed.
Probiotics
Live microorganisms improving gut microbial balance.
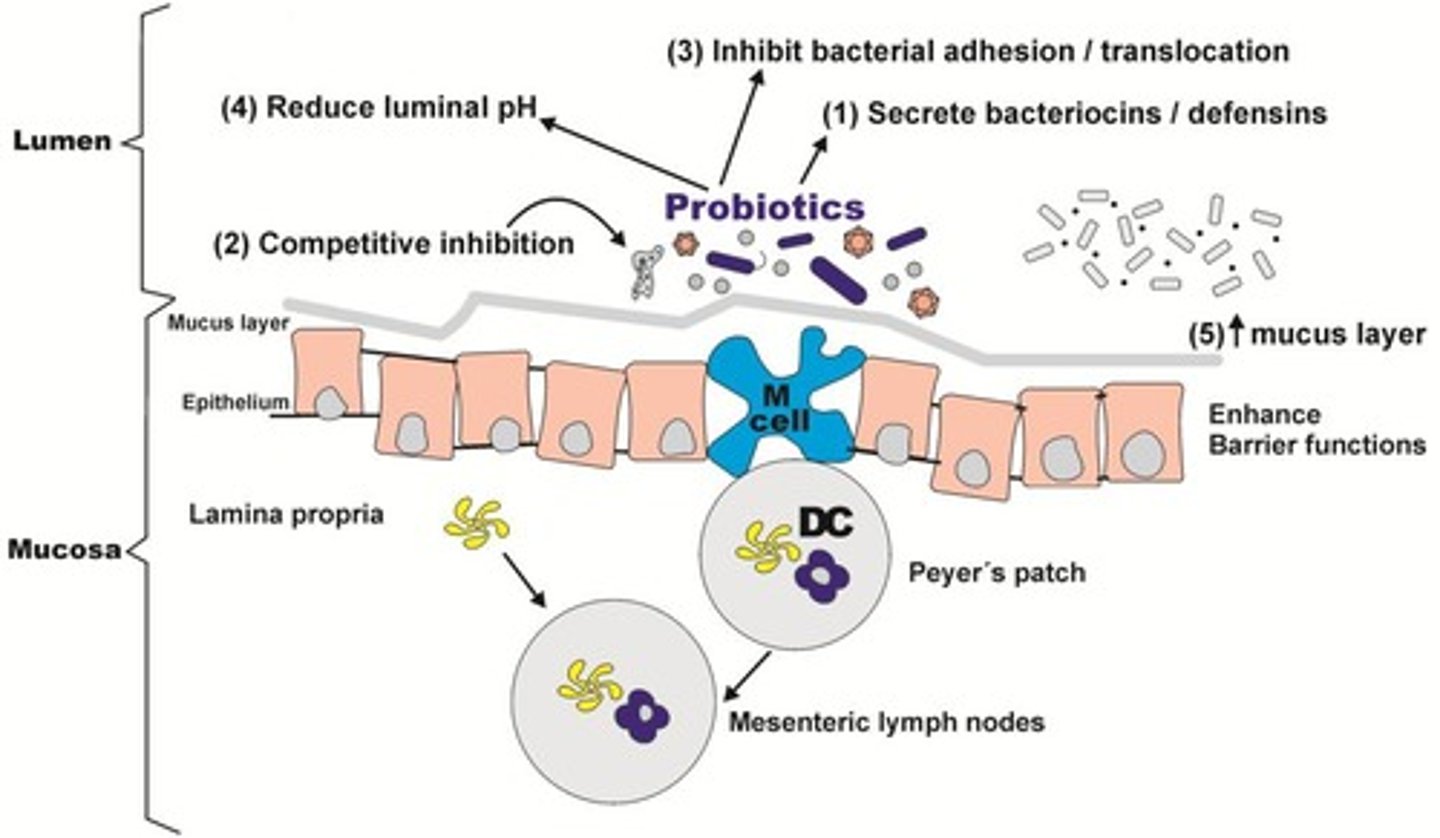
Competitive Exclusion
Probiotics colonize gut, preventing pathogen growth.
Bacterial Antagonism
Probiotics produce substances harmful to pathogens.
Immune Modulation
Probiotics stimulate immune response against pathogens.
Prebiotics
Substrates selectively used by beneficial gut microorganisms.
Oligosaccharides
Carbohydrates often used as prebiotics.
Bacillus
A genus of bacteria used in probiotics.
Enterococcus
A strain authorized for animal nutrition in EU.
Lactobacillus
Bacteria strain beneficial for gut health.
Pediococcus
Bacterial strain used in probiotic formulations.
Saccharomyces
Yeast species used in probiotic supplements.
Gut Microflora
Microbial community in the gastrointestinal tract.
Feed Digestibility
Efficiency of nutrient absorption from feed.
Energy Cost Reduction
Lower energy requirements due to emulsifier use.
Live Microbial Feed Supplement
Probiotics that enhance host animal health.
Strain Combination
Mix of different probiotic bacteria or yeasts.
Gastrointestinal Immune Response
Body's defense mechanism in the gut.
Synergistic Action
Combined effect of emulsifiers and bile salts.
Bactericidal Properties
Ability to kill bacteria, provided by probiotics.
Fructo-oligo-saccharides (FOS)
Prebiotic used to combat pathogens in animals.
Xylo-oligo-saccharides (XOS)
Prebiotic that supports gut health and pathogen control.
Mannan-oligo-saccharides (MOS)
Prebiotic that enhances immune function in animals.
Galacto-oligo-saccharides (GOS)
Prebiotic that promotes beneficial gut bacteria.
Synbiotics
Combination of prebiotics and probiotics for synergy.
Organic acids
Substances that alter gut microbial populations.
Digestive enzyme activity
Enhanced by organic acid supplementation in diets.
Microbial phytase activity
Increased by organic acids for better nutrient absorption.
Pancreatic secretion
Release organic acids to aid digestion.
Intestinal mucosa growth
Promoted by organic acids for improved gut health.
Plant extracts
Natural products added to animal feed for performance.
Plant secondary metabolites
Compounds derived from plants with varied nutritional value.
Essential oils
Concentrated plant extracts with potential health benefits.
Phytogenics
Plant-derived substances used to enhance animal diets.
Egg yolk pigmentation
Color influenced by carotenoids in poultry feed.
DSM Yolk Colour Fan
Scale measuring preferred yolk color intensity.
Mycotoxins
Toxic compounds produced by moulds in feeds.