Lower Extremity Injuries: Diagnosis and Treatment Overview
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
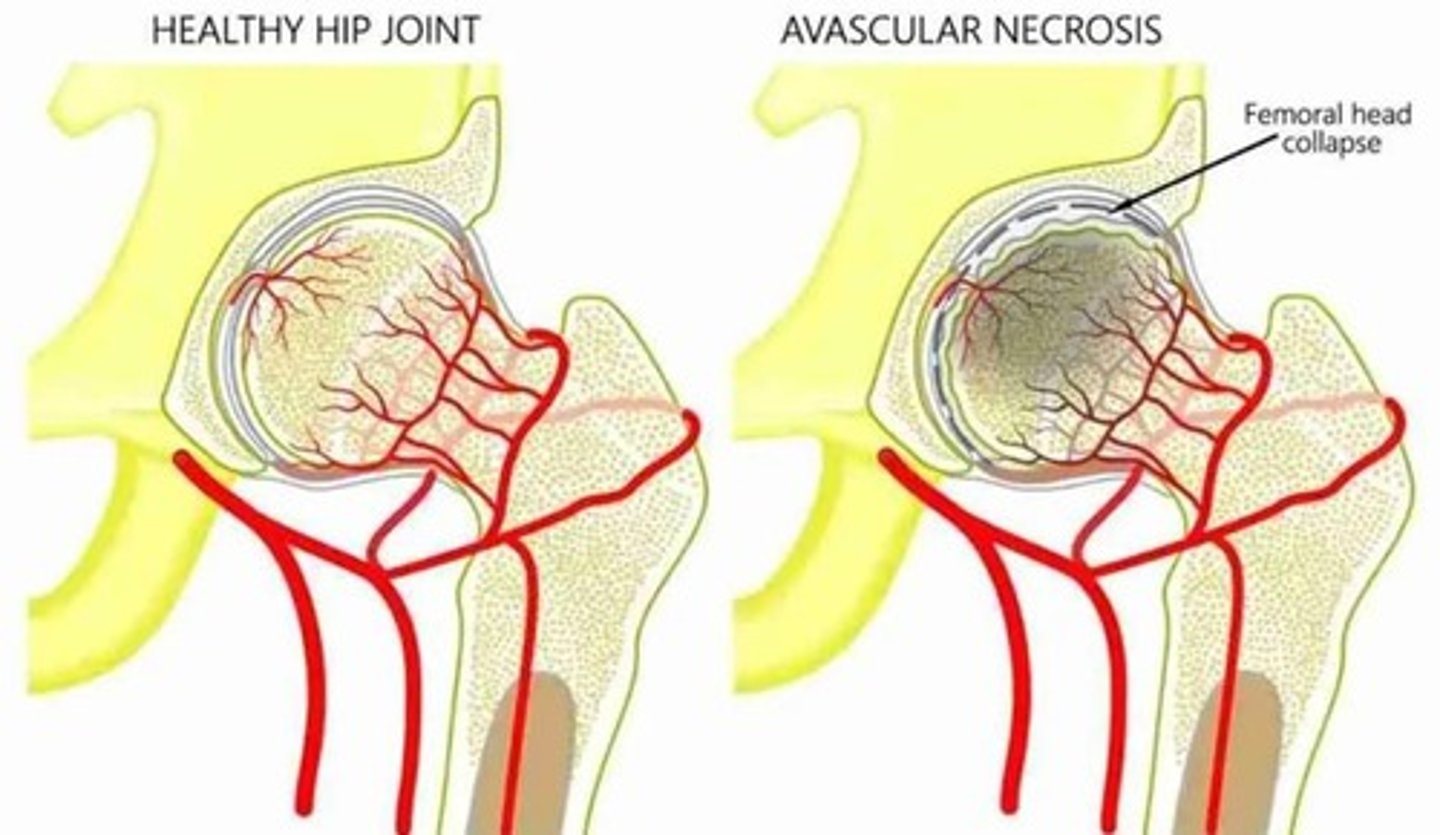
Avascular necrosis
Bone tissue death due to interrupted blood supply.
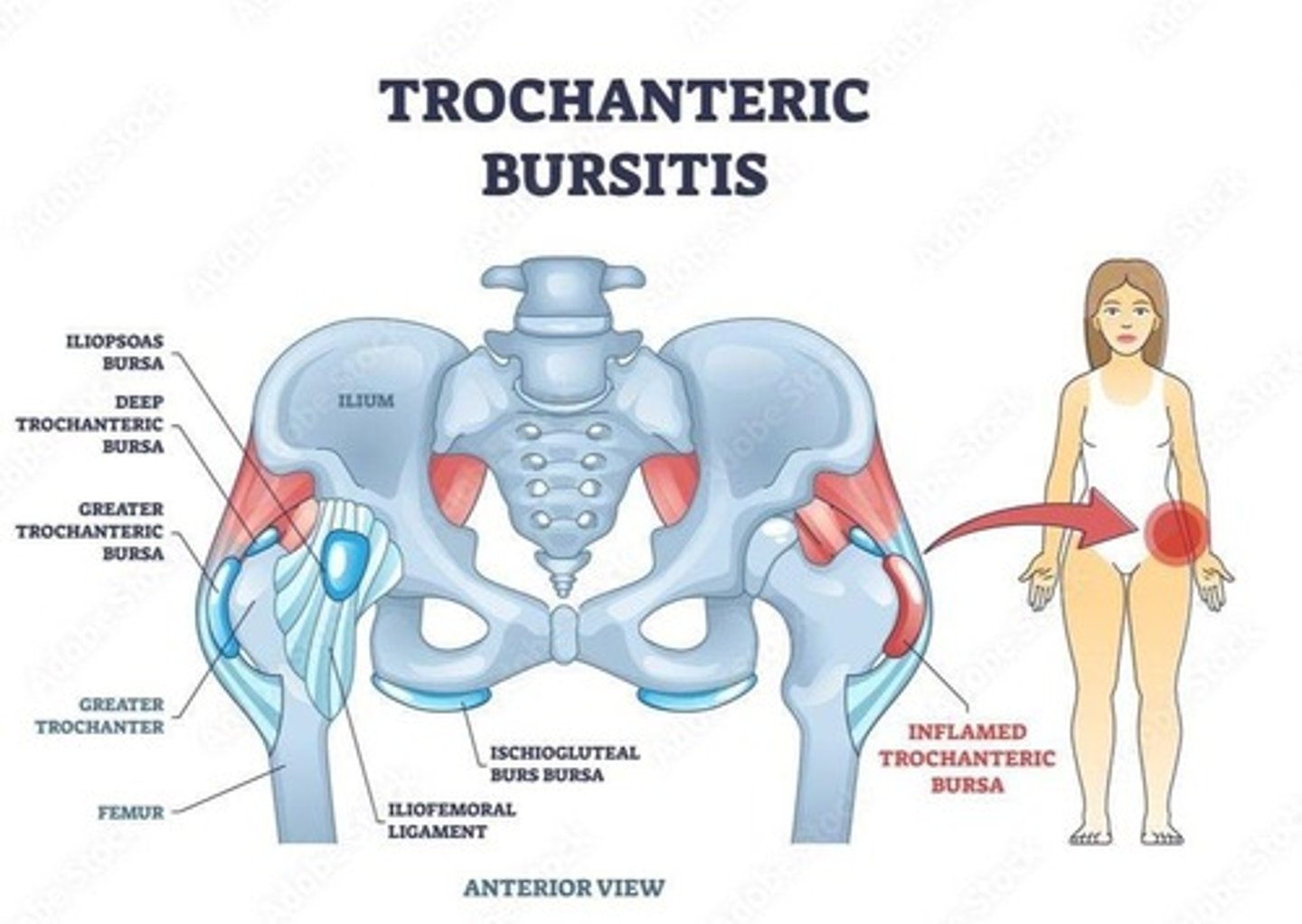
Greater trochanteric bursitis
Inflammation of the bursa near the hip.
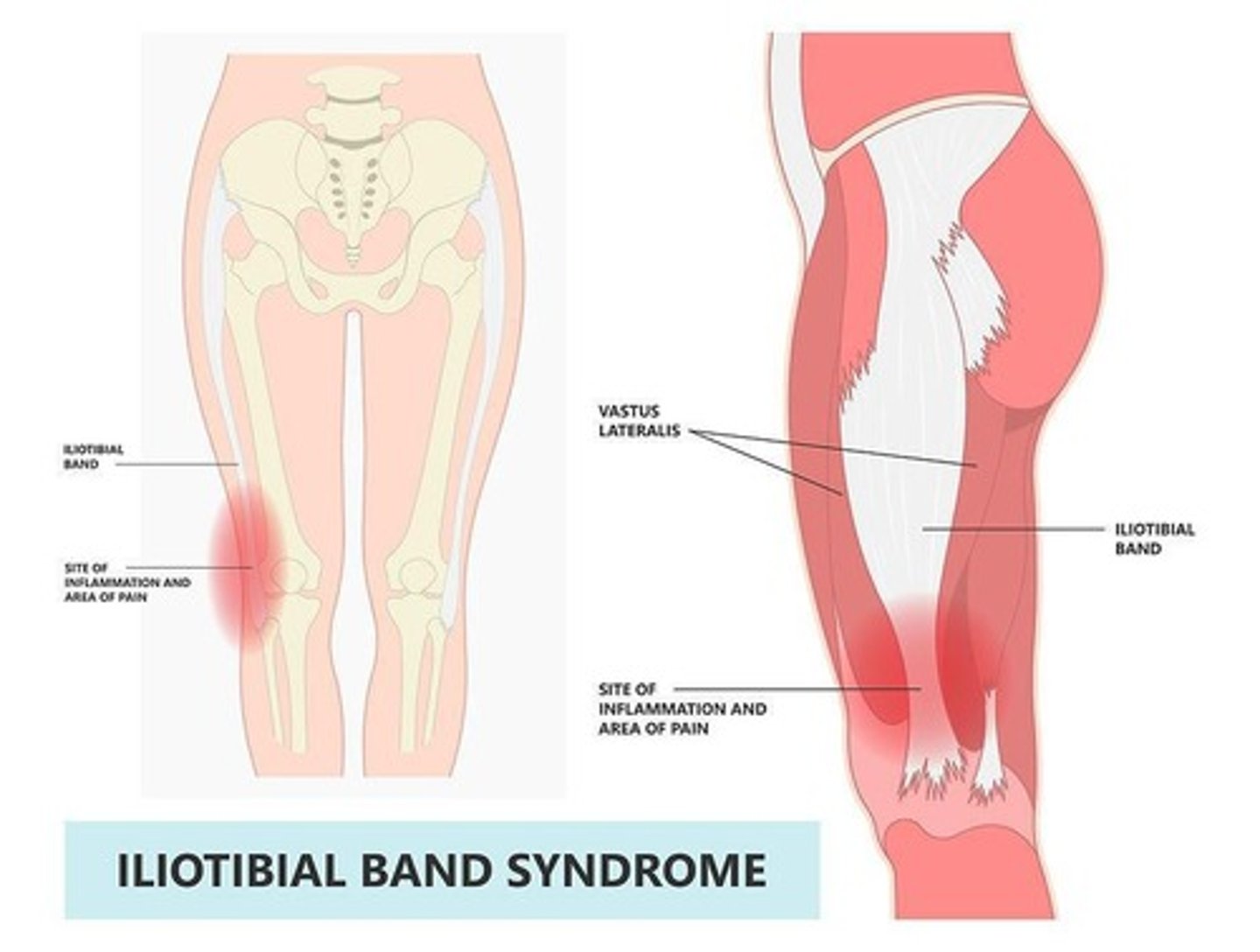
IT Band syndrome
Pain caused by friction of the IT band.
Hip fractures
Breaks in the hip bone, identified via imaging.
Quadriceps tendonitis
Inflammation of the quadriceps tendon.
Quadriceps tendon tear
Rupture of the quadriceps tendon.
Patellar tendonitis
Inflammation of the patellar tendon.
Patellar tendon tear
Rupture of the patellar tendon.
Patellar dislocation
Displacement of the kneecap from its position.
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Knee pain in adolescents due to growth.
ACL injury mechanism
Injury from sudden stops or changes in direction.
PCL injury mechanism
Injury from direct impact to the knee.
LCL injury mechanism
Injury from a force applied to the inner knee.
MCL injury mechanism
Injury from a force applied to the outer knee.
Meniscal injury mechanism
Injury from twisting motions during weight-bearing.
Ottawa ankle rules
Guidelines to determine need for ankle X-rays.
Achilles tendonitis
Inflammation of the Achilles tendon.
Achilles tendon rupture
Complete tear of the Achilles tendon.
Plantar fasciitis
Heel pain caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia.
5th metatarsal fractures
Fractures of the fifth toe bone, some need specialist.
Osteonecrosis
Another term for avascular necrosis.
Common Sites
Femoral head, talus, scaphoid affected.
Bisphosphonate Use
Associated with osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Leg-Calve-Perthes Disease
Avascular necrosis occurring in children.
Etiology of AVN
Caused by corticosteroids, alcoholism, trauma.
Clinical Presentation of AVN
Dull ache, pain with movement, decreased ROM.
Antalgic Gait
Gait pattern to avoid pain in lower extremity.
Crescent Sign
X-ray finding pathognomonic for hip AVN.
MRI in AVN
Detects changes earlier than X-ray.
Non-Operative Treatment
Includes NSAIDs, activity modification, physical therapy.
Core Decompression
Surgical treatment for early-stage AVN.
Total Joint Replacement
Surgical option for advanced AVN.
Trochanteric Bursitis
Inflammation of bursa over greater trochanter.
Hip Bursitis
Common cause of lateral hip pain.
Clinical Presentation of Bursitis
Localized pain, tenderness, worsens with activity.
Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Overuse injury causing lateral knee pain.
Ober Test
Diagnostic test for IT Band Syndrome.
Pathologic Fractures
Fractures due to underlying conditions like malignancy.
Classification of Hip Fractures
Based on anatomic location: head, neck, intertrochanteric.
Inability to bear weight
Inability to support body weight on leg.
Shortened leg
Leg appears shorter than the opposite leg.
Externally rotated leg
Leg rotated outward from the hip joint.
Ecchymosis
Bruising due to bleeding under the skin.
Swelling
Increase in size due to fluid accumulation.
X-Ray
Imaging technique for visualizing bone structure.
MRI
Imaging for soft tissue and bone abnormalities.
Occult femoral neck fracture
Fracture not visible on initial X-ray.
Subcapital femoral fracture
Fracture at the femur just below the head.
Transcervical femoral fracture
Fracture through the neck of the femur.
Basicervical femoral fracture
Fracture at the base of the femoral neck.
Intertrochanteric fracture
Fracture between the greater and lesser trochanters.
Subtrochanteric femur fracture
Fracture below the trochanters of the femur.
Pathologic fracture
Fracture caused by underlying disease or condition.
Surgical fixation
Procedure to stabilize fractured bones surgically.
Fascia iliaca block
Nerve block for pain control in hip injuries.
Hemiarthroplasty
Partial hip replacement surgery.
Total arthroplasty
Complete hip joint replacement surgery.
Traumatic dislocations
Dislocations caused by high-energy impacts.
Developmental dysplasia of hip
Improper formation of hip joint in infants.
Barlow test
Test for hip dislocation by posterior movement.
Ortolani test
Test for hip reduction by anterior movement.
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
Displacement of femoral head in adolescents.
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
AVN of the hip in children.
Developmental Hip Dysplasia
Abnormal hip joint formation in infants.
Legg-Calve Perthes
Avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
Displacement of the femoral head in adolescents.
Osgood Schlatter Disease
Knee pain due to tibial tuberosity inflammation.
Quadriceps Tendinitis
Inflammation of the quadriceps tendon from overuse.
Quadriceps Tendon Rupture
Complete tear of the quadriceps tendon.
Patellar Tendinitis
Inflammation of the patellar tendon from repetitive strain.
Patellar Tendon Rupture
Complete tear of the patellar tendon.
Patella Baja
Lowered position of the patella in chronic rupture.
Patella Alta
Elevated position of the patella in injuries.
Clinical Diagnosis
Diagnosis based on physical examination findings.
X-Ray Evaluation
Imaging to assess patellar position and alignment.
US/MRI
Imaging techniques for tendon tear confirmation.
Extensor Lag
Inability to fully extend the knee actively.
Pain with Straight Leg Raise
Indicates quadriceps tendon injury severity.
Activity Modification
Adjusting activities to prevent further injury.
NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief.
Knee Immobilizer
Device to restrict knee movement post-injury.
Surgical Repair
Operation to fix torn tendons or ligaments.
Risk Factors for Rupture
Includes diabetes, obesity, and steroid use.
Palpable Defect
Visible gap in tendon indicating rupture.
Pain with Weight Bearing
Indicates severity of patellar tendon injury.
Partial Tear
Injury requiring knee immobilization for 6 weeks.
RICE Protocol
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation for injury treatment.
Cortisone Injection
Avoided treatment for knee injuries.
Patella Dislocation
Displacement of patella from femoral sulcus.
Mechanism of Injury (MOI)
Caused by quadriceps contraction and leg rotation.
Re-dislocation Rate
20-45% chance of patella re-dislocating.
Clinical Presentation
Symptoms include knee pain and effusion.
Diagnostic Evaluation
Immediate reduction of patella is critical.
X-Rays
Imaging technique for knee assessment.
Tibial Tubercle
Bony prominence where patellar tendon attaches.
Self-Limiting Condition
Condition that resolves without treatment.
Anterior Knee Pain
Pain located at the front of the knee.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Common knee pain due to patellar malalignment.
Runners Knee
Another term for patellofemoral pain syndrome.
Quad Weakness
Reduced strength in quadriceps muscle.