Unit 5- Radiation Therapy & Nuc Med/PET
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
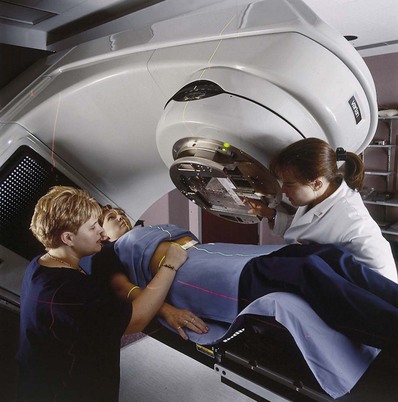
Identify the modality/capability best represented by this image:
radiation therapy
The light pipe functions to direct photons from the crystal into the _______________.
photomultiplier tube
nuclear medicine procedures in comparison to radiographic procedures:
determine the cause of disease/abnormality based on the physiological function of organs or tissue
In NM, the usage of thicker crystals allow for better imaging when using radiopharmaceuticals with higher energies, but it will have decreased resolution.
true
false
a
The only radionuclide used in Nuclear Medicine is Technetium-99m.
true
false
b
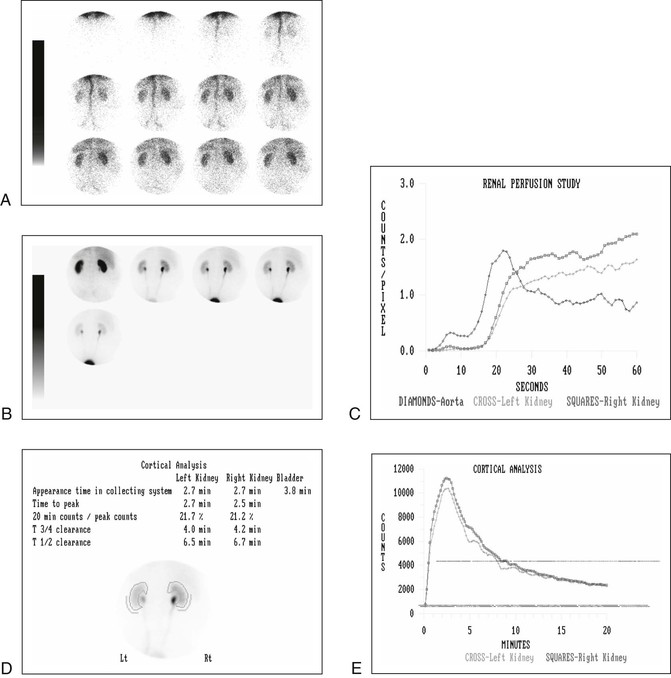
Identify the modality/capability best represented by this image:
nuclear medicine (Gamma Camera)
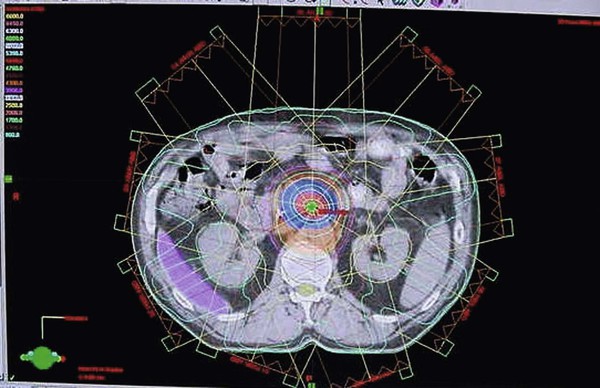
Identify the modality/capability best represented by this image:
CT Imaging w/ dosimetry planning (radiation therapy)
identify the radionuclides:
technetium
iodine
thallium
collimator
Shielding device used to limit the angle of entry of radiation
cyclotron
Device for accelerating charged particles to high energies using magnetic and oscillating electrostatic fields
decay
Radioactive disintegration of the nucleus of an unstable nuclide
detector
Device that is a combination of a scintillator and photomultiplier tube used to detect x-rays and gamma rays
gamma camera
Device that uses the emission of light from a crystal struck by gamma rays to produce an image of the distribution of radioactive material in a body organ
half-life
The time elapsed until some physical quantity has decreased to half of its original value
isotope
Nuclide of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
light pipe
Attached to the scintillation crystal to convey the emitted light to the photomultiplier tube
Parametric image
Functional image as relates to anatomical position (e.g. blood flow)
Positron
positively charged particle emitted from neutron-deficient radioactive nuclei
radionuclide
Unstable nucleus that transmutes via nuclear decay
Scintillation camera
Device that uses the emission of light from a crystal struck by gamma rays to produce an image of the distribution of radioactive material in a body organ
brachytherapy
Placement of radioactive nuclide or nuclides in or on a neoplasm to deliver a cancericidal dose.
Carcinogen
Any cancer-producing substance or material, such as nicotine, radiation, or ingested uranium.
Linear energy transfer
Rate at which energy is deposited as it travels through matter.
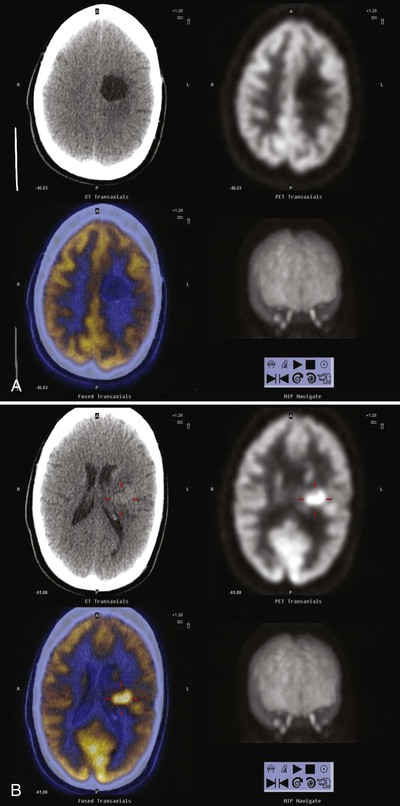
Identify the modality/capability best represented by this image:
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) (to include CT)
The latest gamma camera technology has a ______ detector system. (options: 1,2, or3)
3
Single field
used in skin cancer
Opposing ports
Treatment method used to protect a non-involved structure
Mulitfiled
three or more fields to deliver tumor dose
Rotational field
employed for centrally located lesions such as prostate cancer
Wedge field
Head and neck therapies
Shaped field
lead alloy blocks employed for a specific field
An extensive lesion greater than 5 cm prior to/without metastasis would best describe Stage 3 of the process.
true
Radiosensitivity of tissue depends on:
all of the above
Ovaries, alone, demonstrate the lowest radiation dose tolerance.
false
Iodine 123 would most likely be employed for what type of study?
thyroid function
Radiotherapy uses verification images taken weekly to ensure accuracy also known as:
port films
Most PET scans use radioactive _______ solutions(*hint* glucose).
sugar
Identify the preferred characteristics of radiopharmaceuticals
Readily available |
Half-life > preparation time |
Near-stability |
Localization efficiency |
Simple production |
Affordability |
An additional treatment after surgery is best described as:
adjunct
__________ is a radionuclide commonly used for glucose metabolism in the brain.
fluorine-18 / fluorine
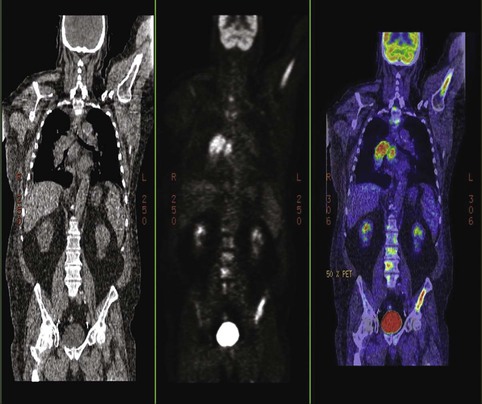
Identify the modality/capability best represented by this image:
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) (to include CT)
Equipment used to transform emissions into images recording function and anatomical areas of interest:
scintillation camera
General delivery of low intensity radiation over an extended period to a small volume of tissue after being implanted inside the patient
brachytherapy