Physical Geography - Water and Carbon Cycles
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
biogeochemical cyces
refers to cycles involving biotic and abiotic components eg the water cycle and the carbon cycle
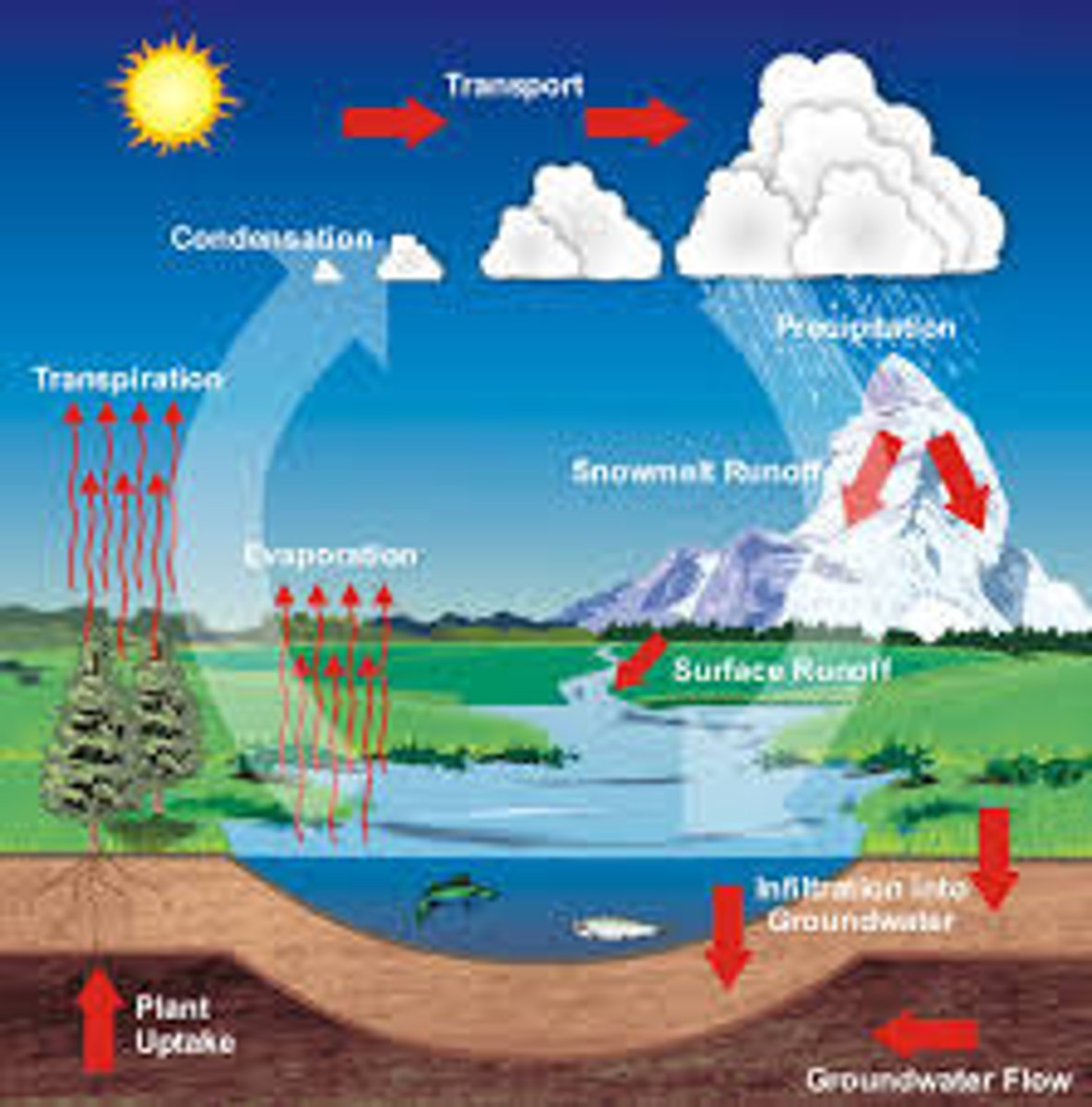
water cycle
heat from sun - evaporation - condensation - precipitation - surface runoff - stream flow - infiltration - throughflow - percolation - groundwater flow - interception - evapotranspiration
systems are
- bounded
a generalisation of reality
have inputs, outputs, stores ad flows (about movement of matter or energy)
- are studied at a range of scales from local to global
albedo effect
lighter surfaces reflect light/ sun's energy eg snow/ice, darker surfaces absorb light/sun's energy eg concrete/water
positive feedback loop in the carbon cycle
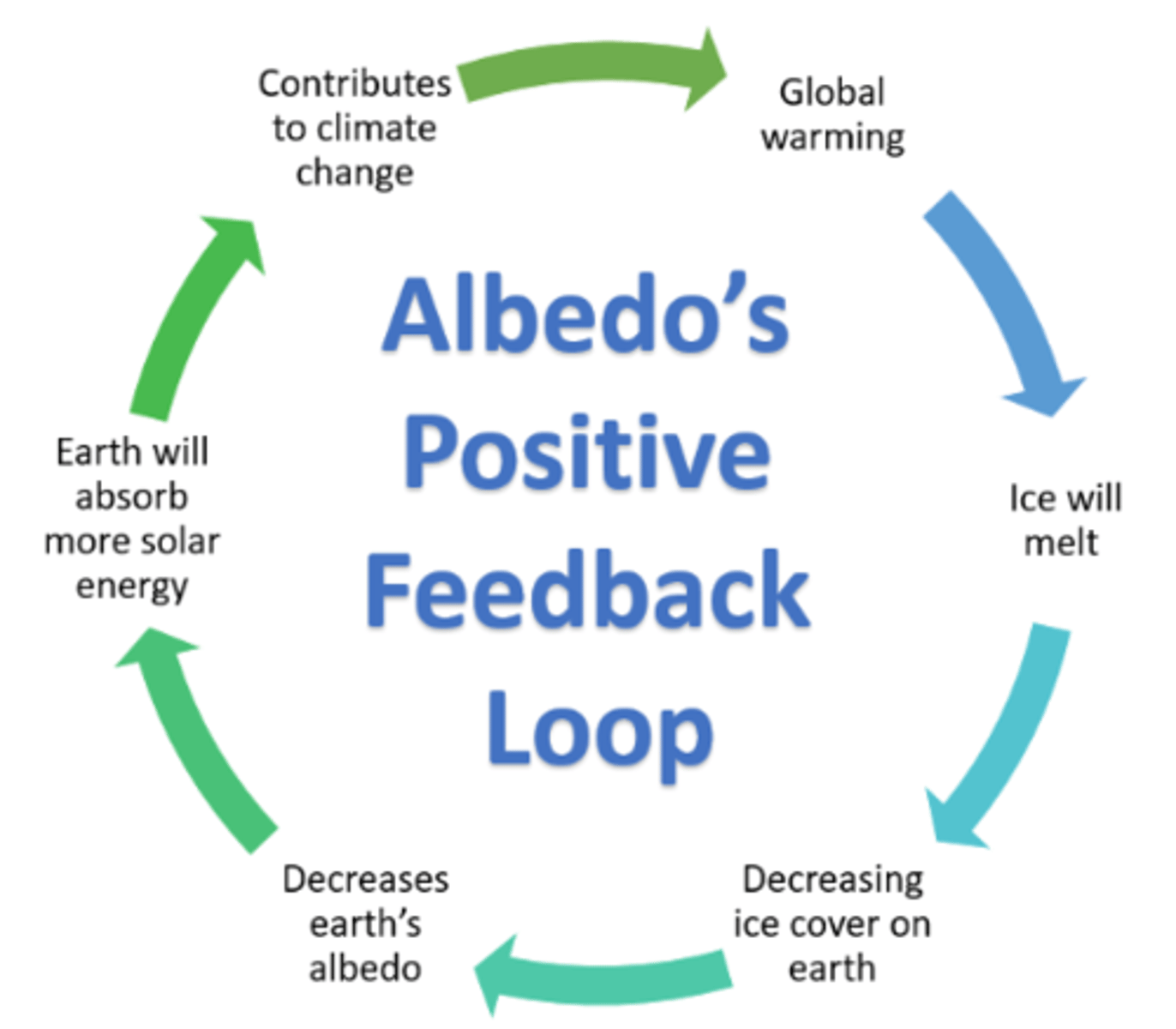
negative feedback loop for the carbon cycle
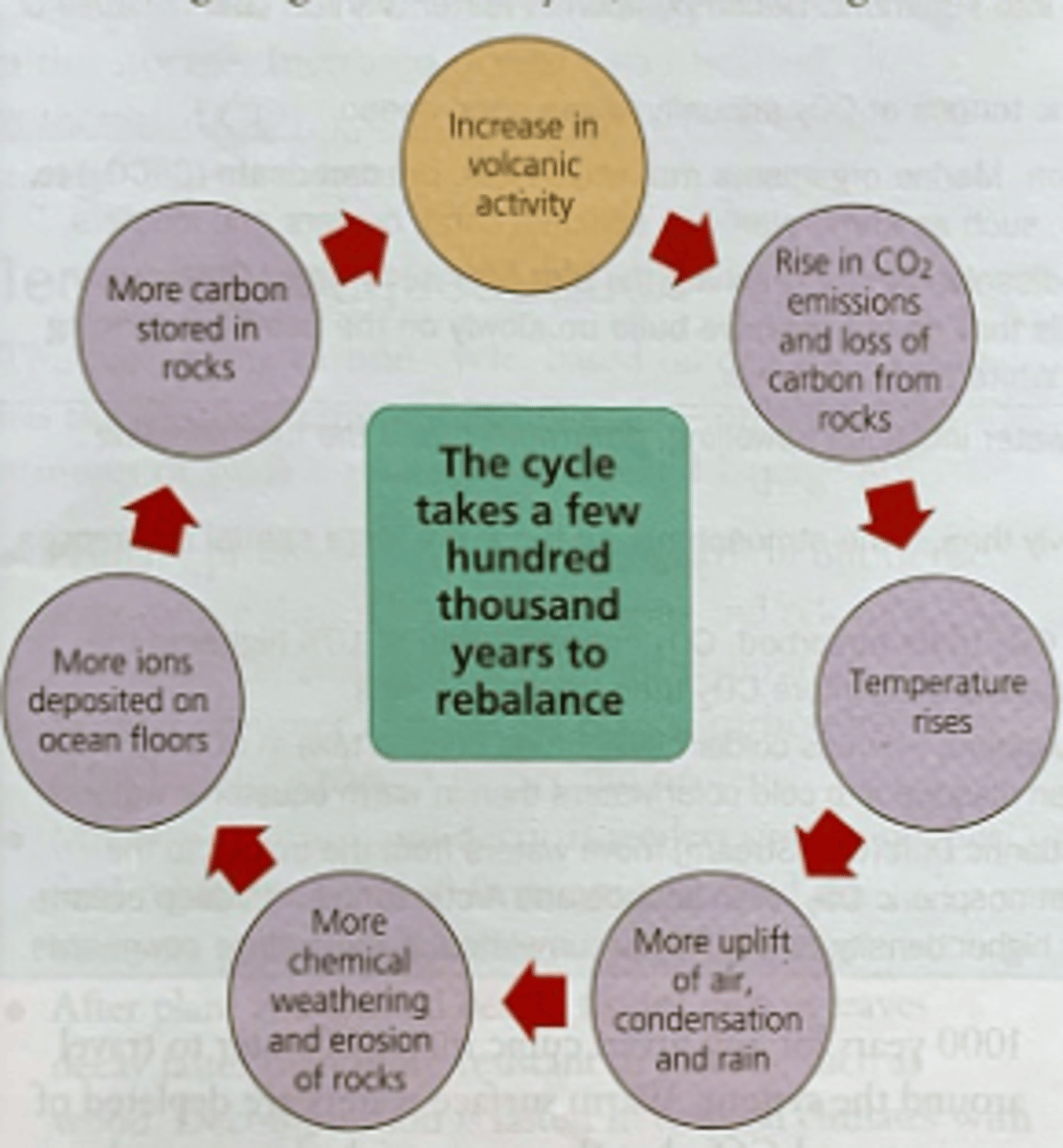
closed system
transfer of energy in and out but not matter
dynamic equilibrium
the inputs and outputs within a system are balanced
open system
transfer of energy and matter in and out
boundary
the edge of the system (encloses the system)
flow/transfer
the movement of matter within systems
input
energy or matter going in
store/component
contains matter or energy
output
energy or matter going out
feedback
if the equilibrium of a system is upset by a change in one of the elements
positive feedback
where the effects of an action are amplified or multiplied by subsequent knock-on effects (negative outcome)
negative feedback
where the effects are of an action are nullified by its subsequent knock-on effects (positive outcome)
atmosphere
the layer of gases surrounding the planet (air)
lithosphere
solid, outer part of the Earth, includes the brittle upper portion of the mantle and the crust, the outermost layers of the Earth's structure (land)
hydrosphere
includes water that is on the surface of the planet, underground and in the air (liquid water)
biosphere
is made up of the parts of Earth where life exists. The biosphere extends from the deepest root systems of trees to the dark environment of ocean trenches, to lush rainforests and high mountain tops
cryosphere
is the frozen ice and snow on the planet (frozen water)
aquifer
a body of permeable rock which can contain or transmit groundwater
pedosphere
liquid water contained within soil, may sometimes be frozen
precipitation
transfer of water from the atmosphere to the ground
evaporation
transfer of water from liquid state to gaseous state, the vast majority occurs from the ocean to the atmosphere
evapotranspiration
evaporation combined with transpiration
condensation
transfer of water from a gaseous state to a liqquid state
sublimation
transfer from a solid state to a gaseous state and vise versa
interception
water intercepted and stored on leaves of plants
overland flow/ surface runoff
transfer of water over the land surface
infiltration
transfer of water from the ground surface into soil, wheere it may then percolate into underlying rocks
throughflow
water flowing through soil towards a river channel
percolation
water soaking into rocks
groundwater flow
transfer of water very slowly through rocks
accumulation
the addition of material to the store of ice through snowfall
ablation
the loss of material from the store of ice, occuring through melting, evaporation and sublimation
seasonal changes in the cryosphere
these occur through accumulation and ablation
glacial period
is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. More water is stored in ice than currently.
interglacials
are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods with less ice on the plant. The last glacial period ended about 15,000 years ago. They experience a reduction in the volume of ice and the hydrological cycle behaves much like it does today
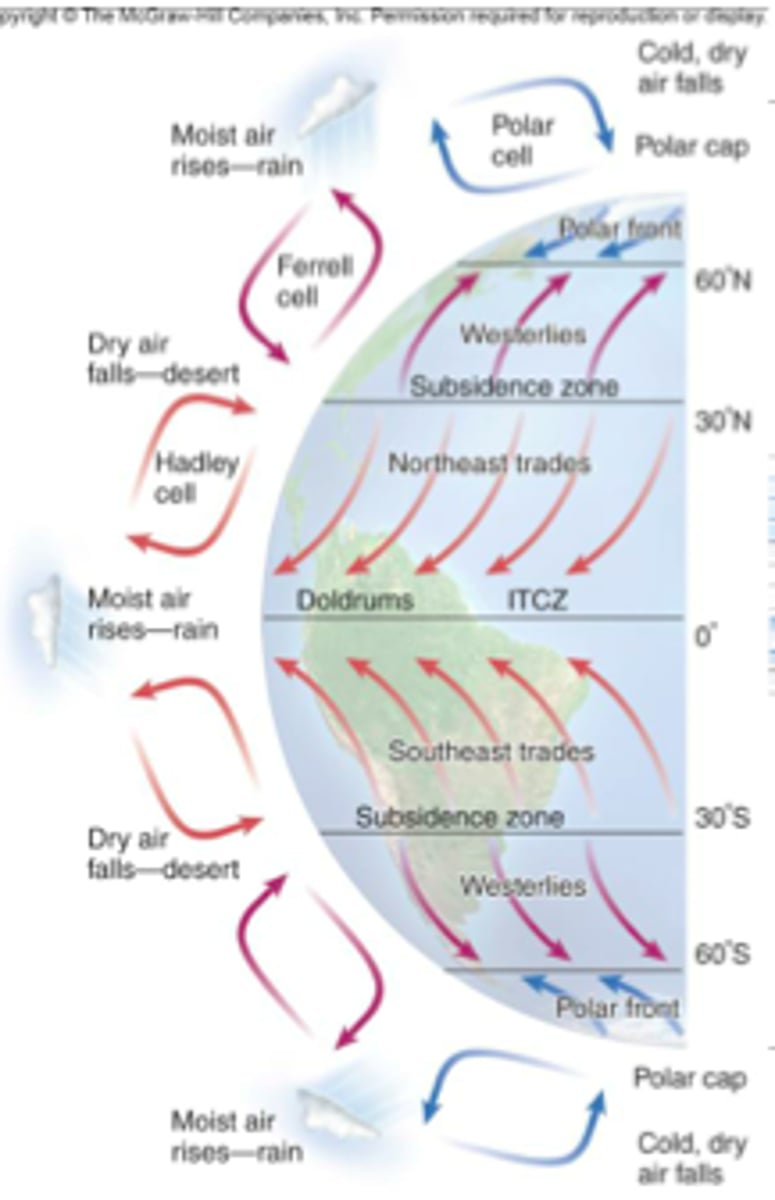
Global atmospheric circulation
Drainage basin
the area of land drained by a river and its tributaries (when it rains in this area the water finds its way into the river)
Watershed
the boundary of the drainage basin. It separates one drainage basin from another
Confluence
a point where two rivers meet
Tributary
a small river or stream that joins a larger river
Source
the starting point of a river, often a spring or lake
Mouth
the point where a river leaves its drainage basin and flows into the sea
Water balance
the balance between inputs and outputs within your system. Water balance is expressed as a % of precipitation
Surface runoff
when the ground becomes too saturated by rainwater, it can not take any more water in, any extra rain flows over ground.
Discharge
the amount of water in the river at a given time
Peak discharge
maximum discharge/amount of water in the river
Peak flow
maximum discharge in the river
rising limb
the rising water in the river
Recession/falling limb
falling flood water in the river
Baseflow
the normal amount of water you would expect in the river
Basin lag time
time difference between the peak of the rainstorm and the peak flow of the river. The shorter the lag time, the faster the flooding occurred
Peak rainfall
maximum amount of rainfall
carbon stores
lithosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, atmosphere and biosphere
carbon sink
a store that absorbs more carbon than it releases
carbon source
releases more carbon than it absorbs
four main carbon cycles
fast organic, slow organic, fast non-organic, slow non-organic
carbon budget
how much carbon is emitted by various processes compared to what can be absorbed by nature or captured by people.
impacts of changing carbon on oceans
ocean acidification, ocean warming, melting sea ice, ocean salinity, sea level rise
carbon capture and sequestration
a technology that can capture up to 90% of CO2 emissions produced from use of fossil fuels in electricity generation/industrial processes, preventing it entering the atmosphere
changing rural land use
when rural land is changed for another use - can improve carbon stores by, depends on land use, soil properties, climate and land area
renewable energy
energy derived from natural sources of clean energy, replenished at a higher rate than they're consumed. Generating renewable energy creates lower emissions than burning fossil fuels
geoengineering
the deliberate large-scale intervention in the Earth's natural systems to counteract climate change