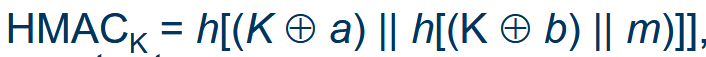1. Intro to Cryptography
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
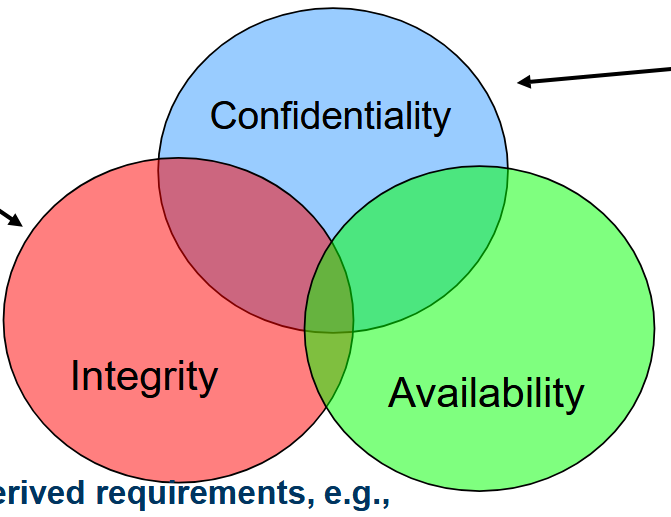
What are the 3 main security goals?
Confidentiality: Sensitive information must be protected from disclosure to unauthorized parties.
Integrity: Data integrity allows a receiver to verify that data was not altered by an adversary during transmission
Availability: Ensuring systems remain operational and accessible to users
What is system security?
Securing the entire system, including
the protocol,
the implementation of the protocol,
the environment/equipment where the protocol is running
What is a security attack?
Any action that compromises the security of information owned by an organization.
What are the 4 main types of security attacks?
- Interruption (attack on availability).
- Interception (attack on confidentiality).
- Modification (attack on integrity).
- Fabrication (attack on authenticity).
What is the distinction between passive and active attacks?
Passive attacks: Eavesdropping and monitoring transmissions without altering them (release of message contents
Active attacks: Involving some modification of the data stream (masquerade/impersonation, replay, modification of message contents, denial of service).
What is the Dolev-Yao threat model?
In the Dolev-Yao threat model, the adversary (Eve) has complete control of the entire network and can:
Obtain any message passing through the network.
Initiate and participate in conversations as a legitimate user.
Become the receiver of messages.
Send messages to anybody through impersonation.
Access any message sent through the network.

What is Kerckhoffs' principle?
A cryptographic system should be secure even if everything about the system, except the key, is public knowledge. The secrecy of the encoded message should depend entirely on the secrecy of the key, not on the secrecy of the algorithm.
Why is Kerckhoffs' principle important?
Algorithms are very hard to change (built into soft-/hardware).
Peer review (find faults before attackers can exploit).
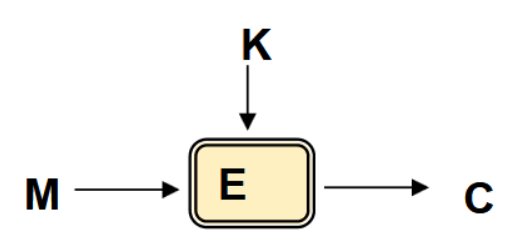
What is the basic terminology of ciphers?
Plaintext (m): The original message
Encryption function (E): The transformation function
Key (k): The secret parameter controlling the encryption
Ciphertext (c): The produced encrypted message, c = Ek(m)
Decryption (D): The reverse process, m = Dk(c)
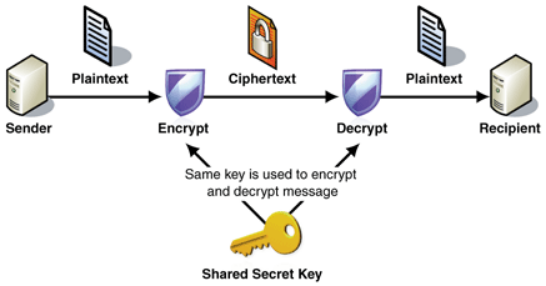
What is symmetric encryption?
Both the sender and recipient share a common key for encryption and decryption.
-> Also known as private-key encryption
What is a block cipher?
A method that takes two inputs:
a k-bit key K
an L-bit plaintext M
=> to return an L-bit encryption C = E(K, M)
It is a permutation on L-bit strings, creating a one-to-one mapping that allows for decryption.
What is the relationship between key size and security in symmetric encryption
Larger keys provide more security against brute force attacks.
Key sizes need to increase over time to maintain security levels as computing power increases.
What are the common modes of operation for block ciphers?
- Electronic Code-Book (ECB)
- Cipher Block Chaining (CBC)
- Counter (CTR)
What is a weakness of Electronic Codebook (ECB) mode?
It is deterministic - the same plaintext block always produces the same ciphertext block, which can reveal patterns in the data and compromise security.

How does the Electronic Codebook Book (ECB) work?
The message is broken into blocks which are
encoded independently of the other blocks.
=> Easy to parallelize.
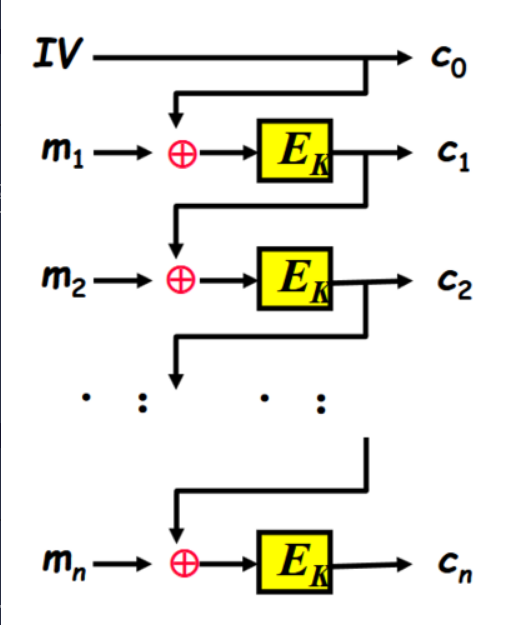
How does Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) mode work?
Each plaintext block is XORed with the previous ciphertext block before encryption.
- The ciphertext of each block is dependent on all previous blocks.
- An Initial Value (IV) is used for the first block (random).
What is an advantage of Counter (CTR) mode?
Counter mode allows for parallel encryption, making it useful for high-speed network encryptions.
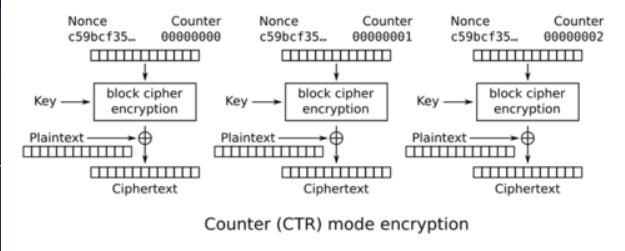
How does Counter (CTR) mode work?
- IV is combined with a Counter.
- IV/Counter is encrypted with a key and XORed to plaintext.
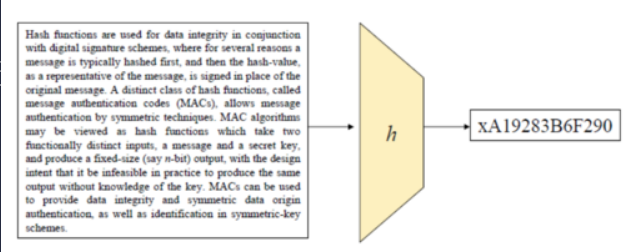
What is a hash function?
A hash function is a deterministic, efficient function that maps binary strings of arbitrary length to binary strings of a fixed length (the hash value).
What are the 2 key properties of cryptographic hash functions?
1. One-Way Property
- It should be difficult to find the input of any particular hash.
2. Weak Collision Resistance
- It should be difficult to find a message with the same hash value as a given message.
3. Strong Collision Resistance
- It should be difficult to find two different messages with the same hash value.

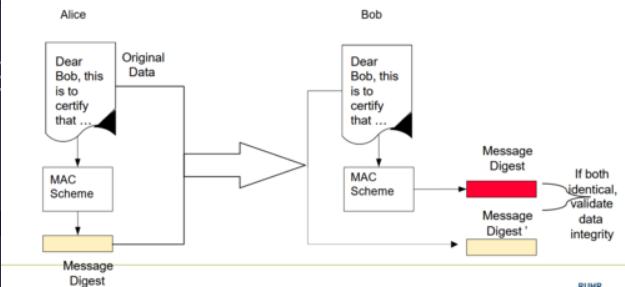
What is a Message Authentication Code (MAC)?
A hash function with a key, providing both authentication and integrity. It creates a check-value sent with data to verify its integrity.
What are the types of forgeries against MAC schemes?
Selective forgery: The adversary can produce a new message-MAC pair for a message of their choice.
Existential forgery: The adversary can produce a new message-MAC pair but has no control over the message content.
What are the components of a Message Authentication scheme?
- G: A key generation algorithm that returns a key.
- T: A tagging algorithm that takes the key and message to produce a tag.
- V: A verification algorithm that takes the key, message, and tag to verify integrity.
What is public-key (asymmetric) cryptography?
Involves 2 different keys:
- Public key => Known by anyone, used to encrypt and verify signatures.
- Private key => Only known by the recipient, used to decrypt messages and sign signatures.
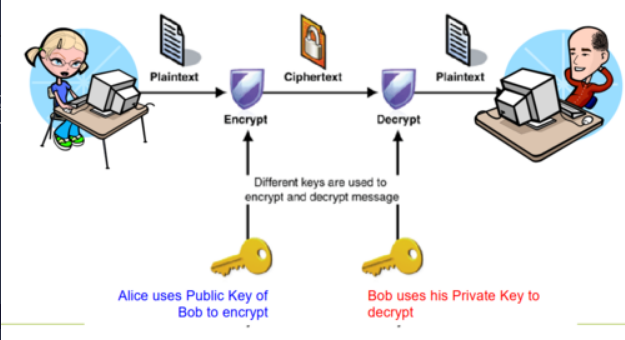
What are the benefits of public-key cryptography?
- Key distribution
- Digital signatures
What mathematical "hard problems" are used in public-key cryptography?
- Factoring large numbers into primes.
- Discrete logarithm problem.
Performance: RSA vs. ECDSA
Key Generation => ECDSA is way faster.
Signature Generation => RSA is faster for smaller, ECDSA for larger key lengths.
Signature Verification => RSA is way faster.
What are 2 requirements derived from the 3 main Security Goals?
Authentication => Who is Who?
Access Control => Only selective access is authorized.
What is an HMAC?
Hash-based Message Authentication Code
Includes padding constants (a, b) to prevent Length Extension Attacks.