Nervous System and Brain Pt. 2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
bathes the external surface
what is CSF's function of the ventricles and canals?
40-70%
what percent of CSF is formed in the lateral ventricles?
up to 30%
what percent of CSF is formed in the 3rd and 4th ventricles?
100-160 mL
how much CSF is normally present at one time?
400-500 mL
how much CSF is produced in a day?
CO2; protein
CSF has more ____ and less ____ because the ependymal cells modify the filtrate from the blood plasma and capillaries of the brain
functions of CSF
bouyancy: allows brain to be its considerable size without being impaired by its weight. if it rested on the cranium the pressure would kill nervous tissue
protection: protects brain from striking the cranium when jolted. shaken child syndrome and concussions can still occur from severe jolting
chemical stability: flow of CSF rinses away wastes from the nervous tissue and regulates the environment.
lateral ventricle, interventricular foramen, third ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, fourth ventricle, foramen magendie, foramen luschka, subarachnoid space, and reabsorption in venous sinus
flow of CSF
hydrocephalus
abnormal accumulation of fluid (CSF) in the brain
increases intracranial pressure and size of ventricles over time
can cause variety of deficits
in babies: rapid increase in head size
surgical placement of shunt system to fix
10 sec
after how much time without blood flow to the brain would someone become unconscious
1-2 min
after how much time without blood flow to the brain would irreversible tissue damage occur?
4 min
after how much time without blood flow to the brain would death occur?
internal carotid artery
Supplies blood to the brain, eyes, eyelids, forehead, nose, and internal ear.
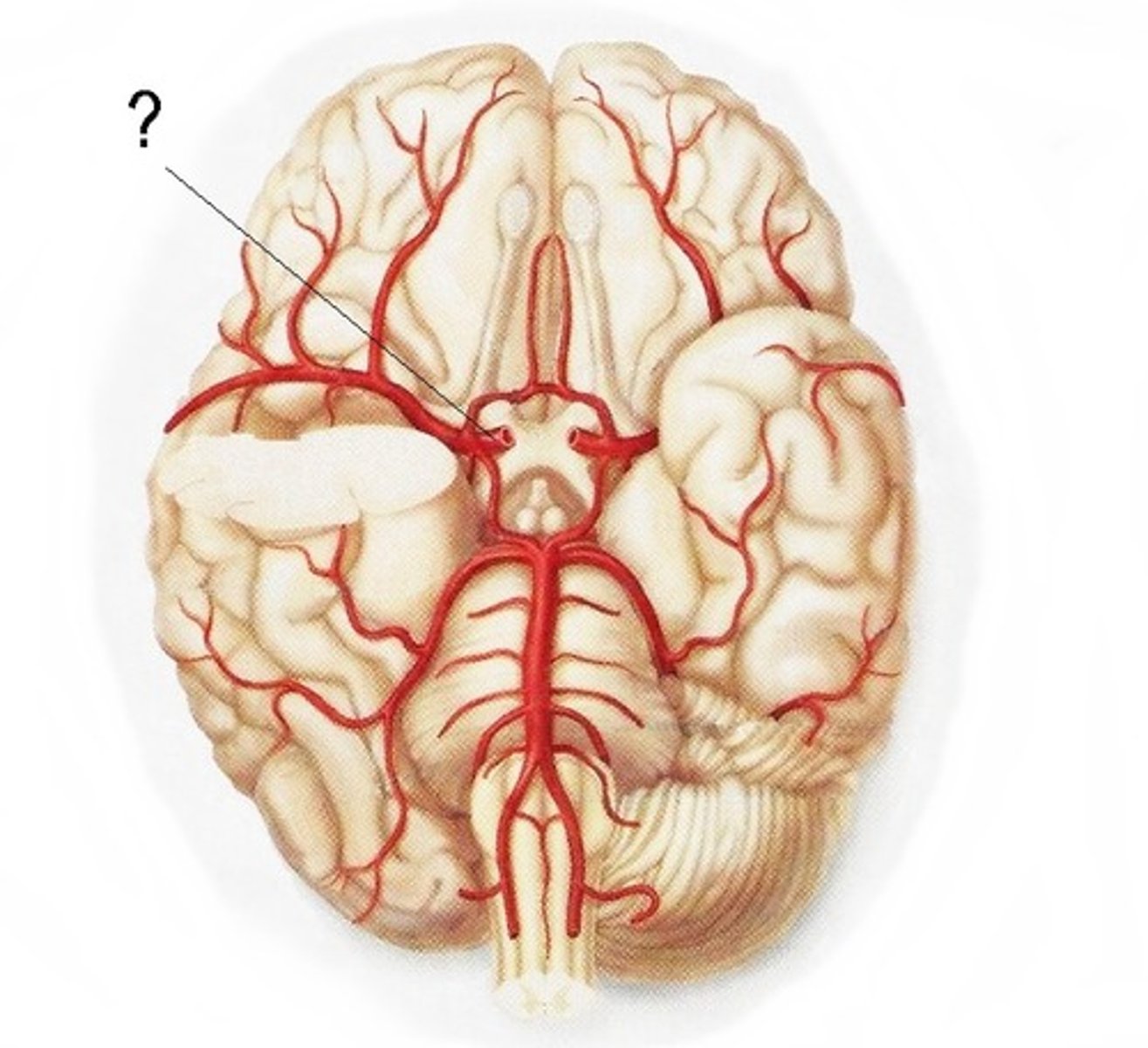
basilar artery
Serves the brain stem and the cerebellum as it travels upward
delivers to the pons
clot here is detrimental (sensory and motor info)
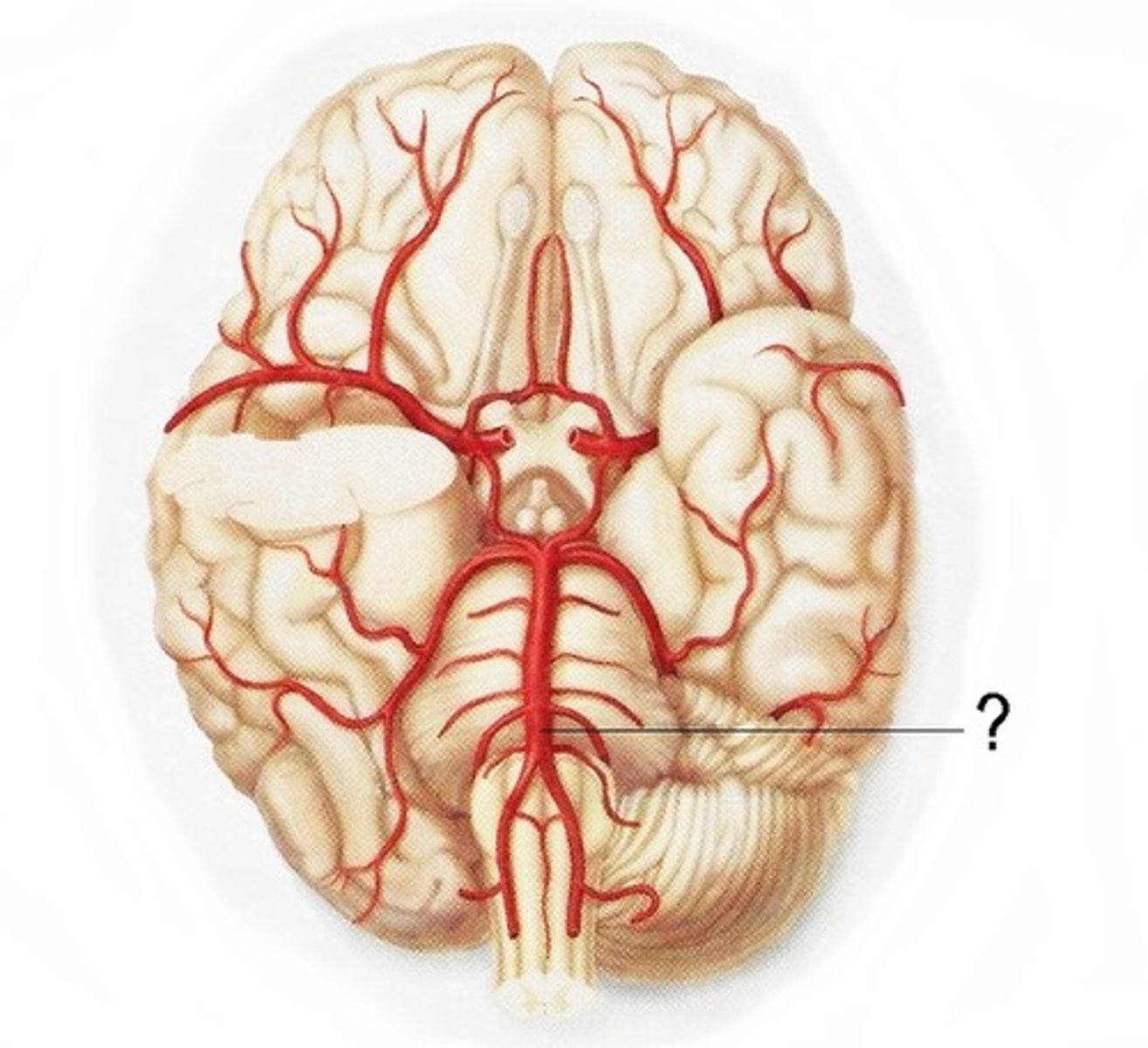
vertebral artery
delivers blood to the circle of willis
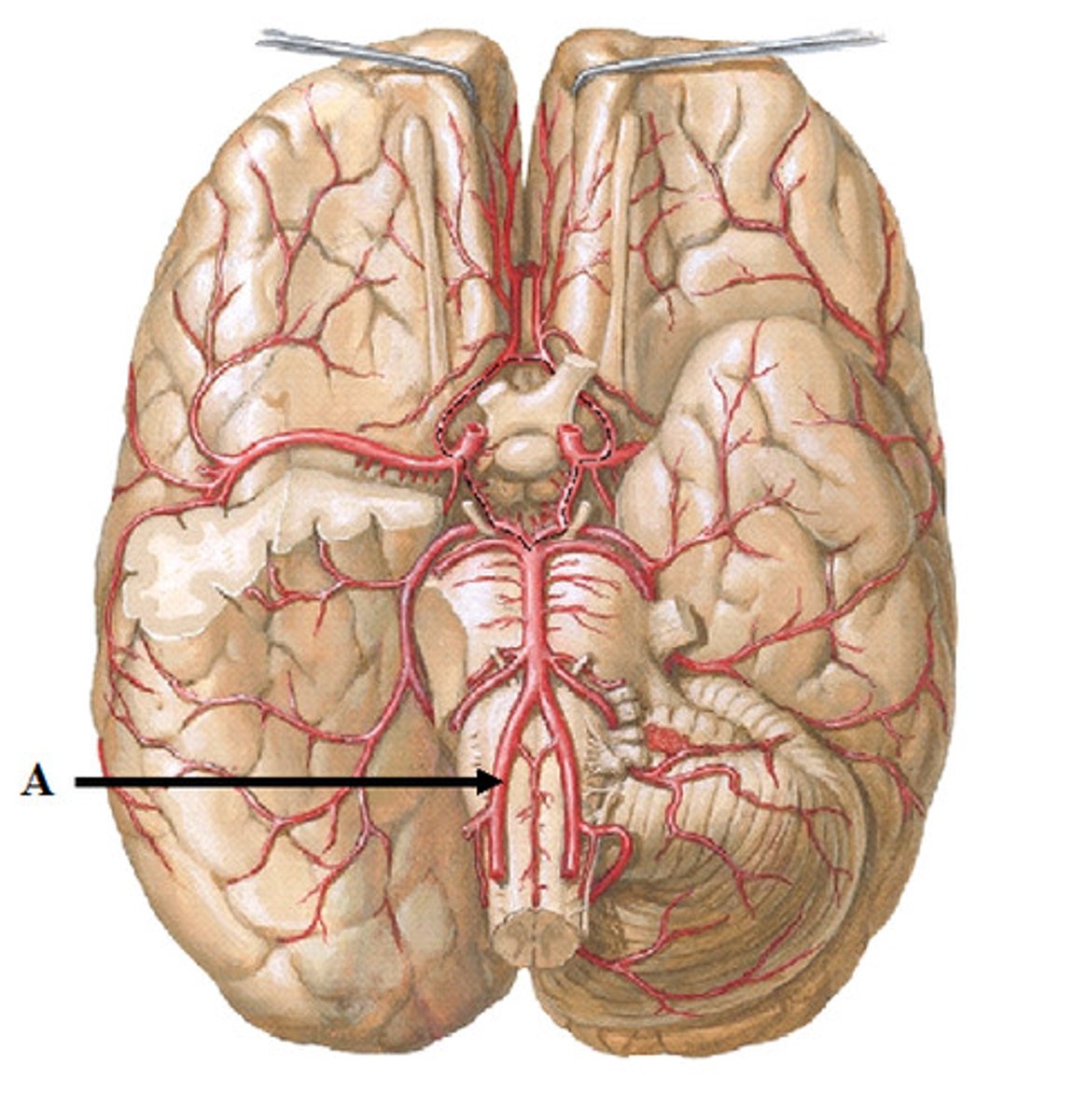
anterior cerebral artery
delivers blood to the medial part of the hemispheres
2
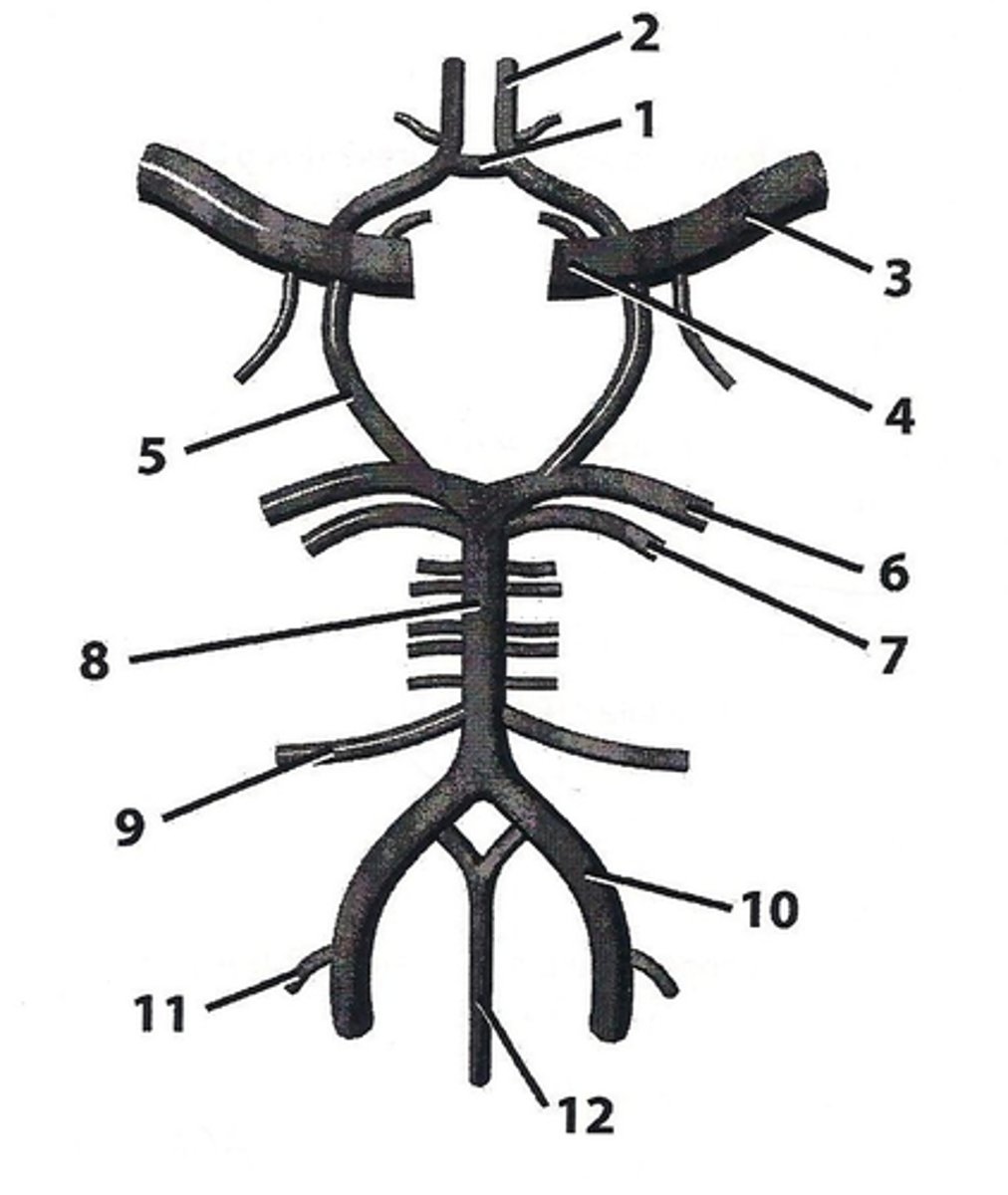
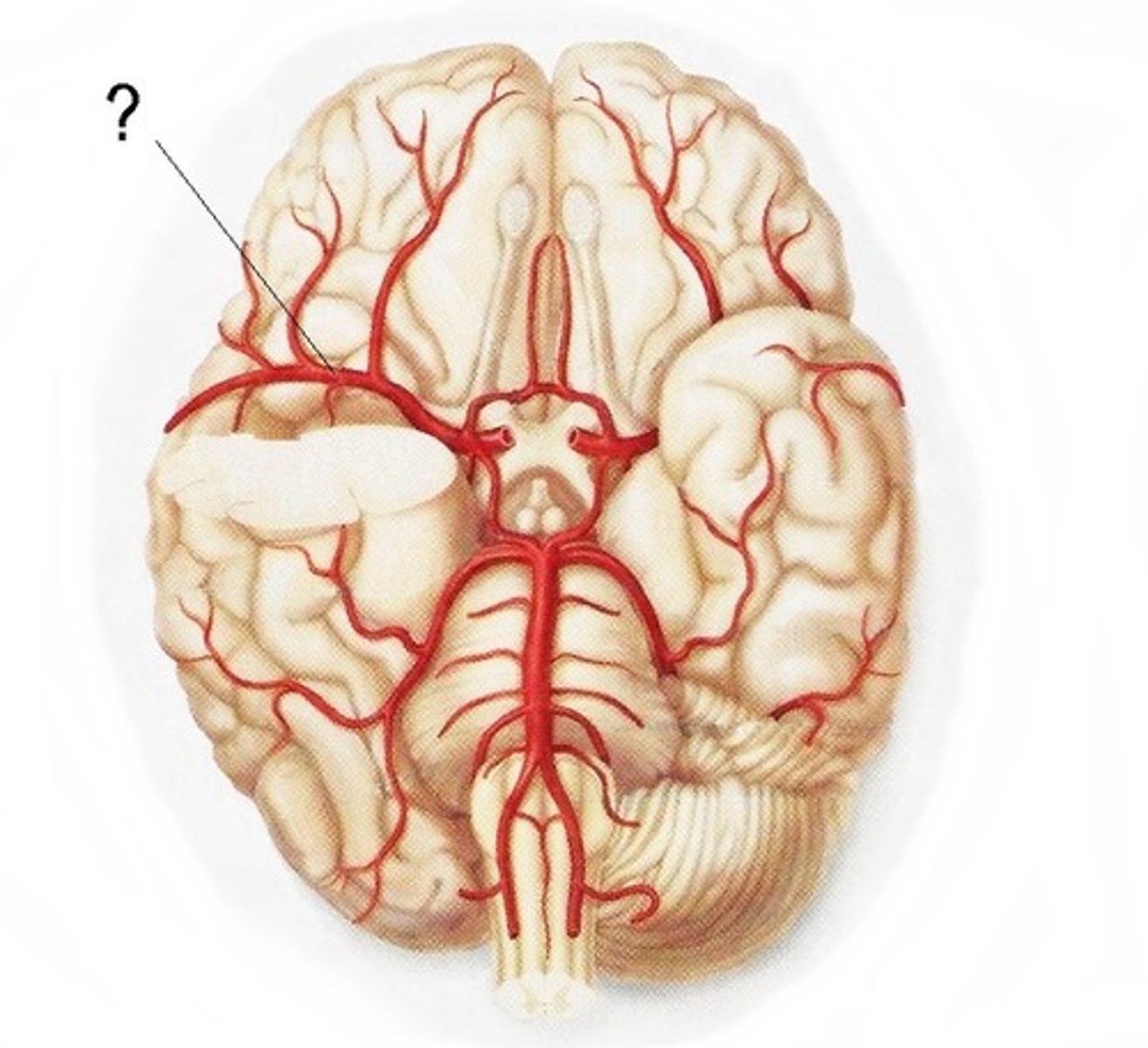
middle cerebral artery
delivers blood to the lateral part of hemispheres
70% of ischemic strokes occur because of a clot in this artery
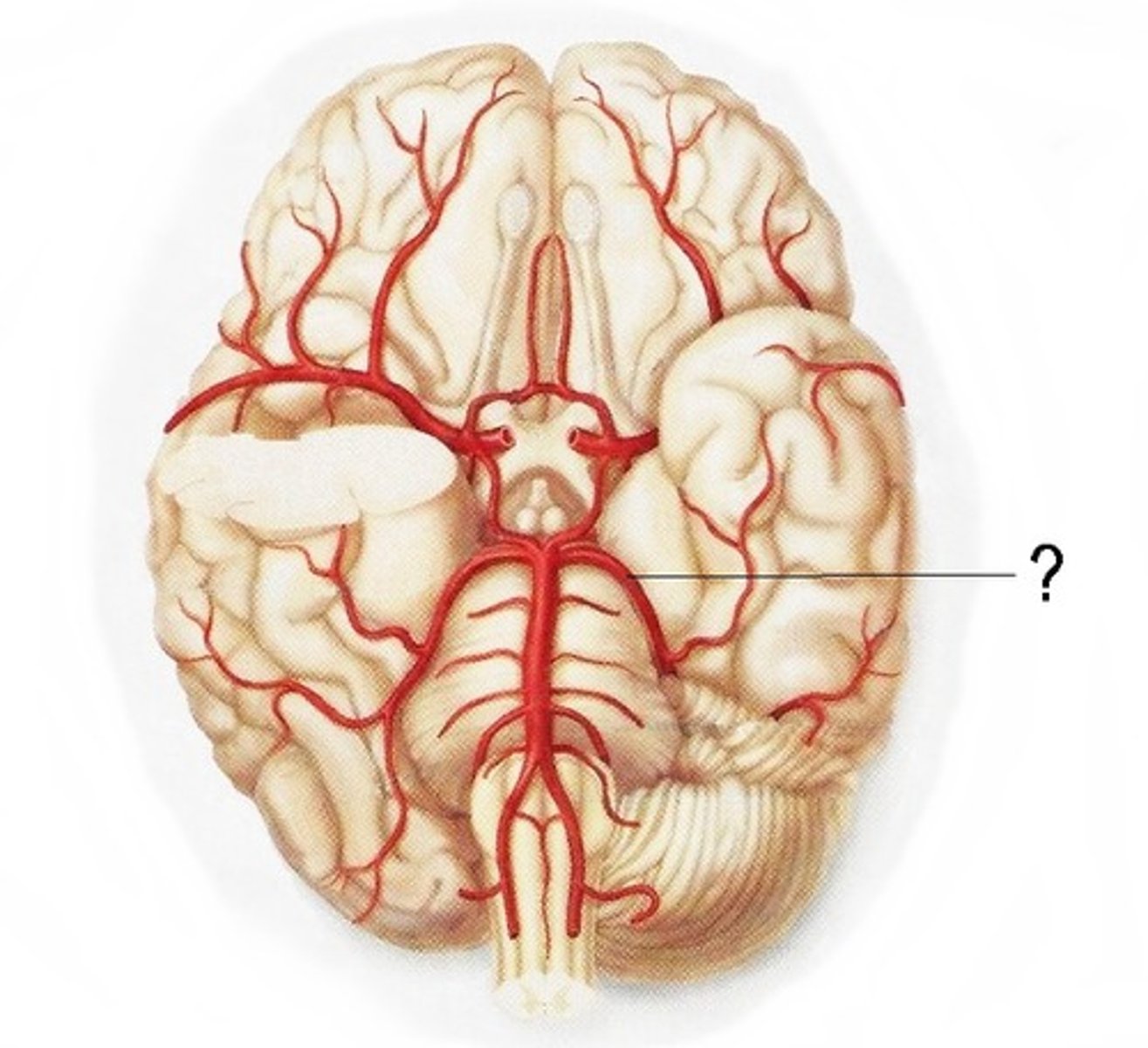
posterior cerebral artery
supplies occipital lobe
if supply is cut off, vision problems occur
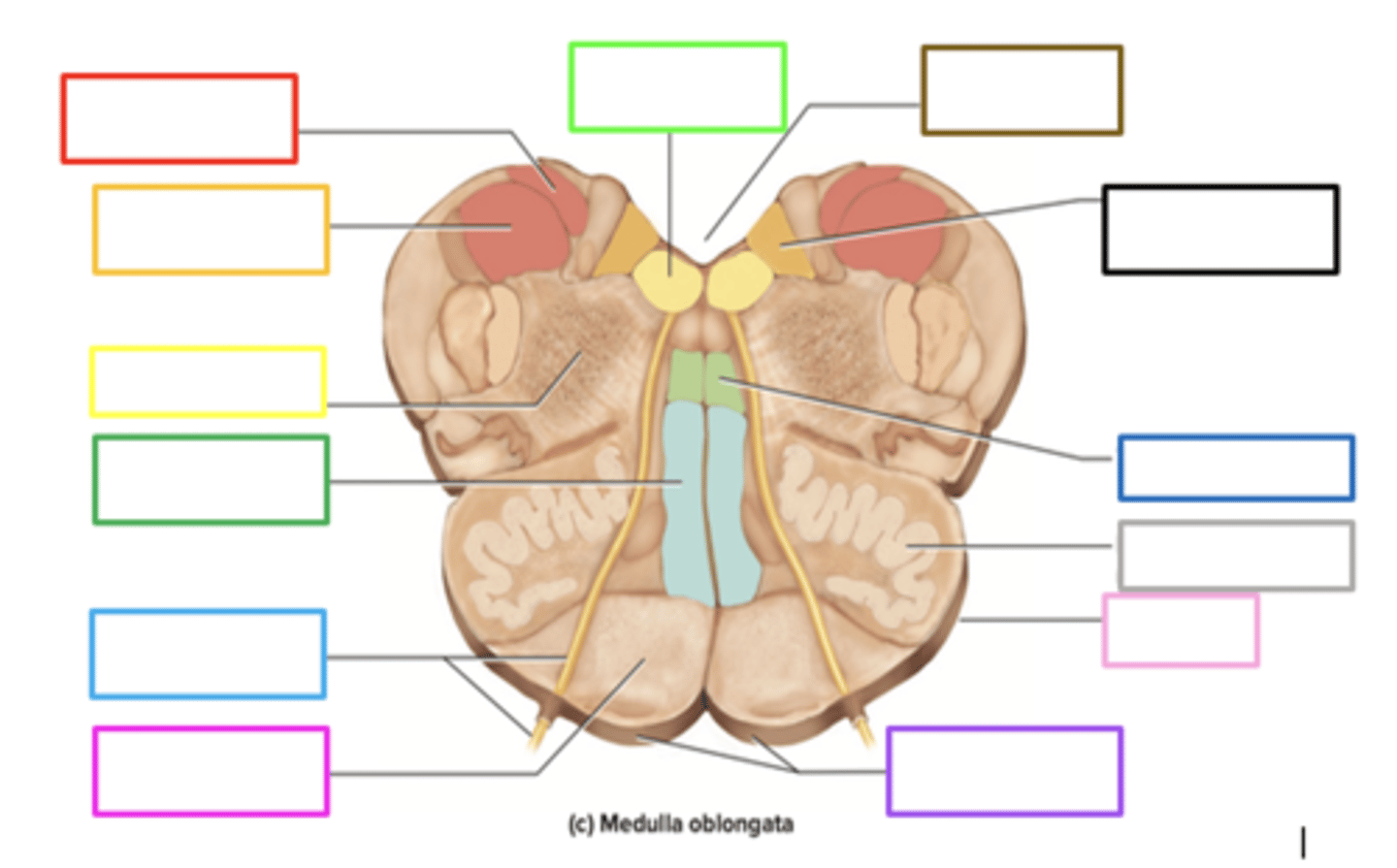
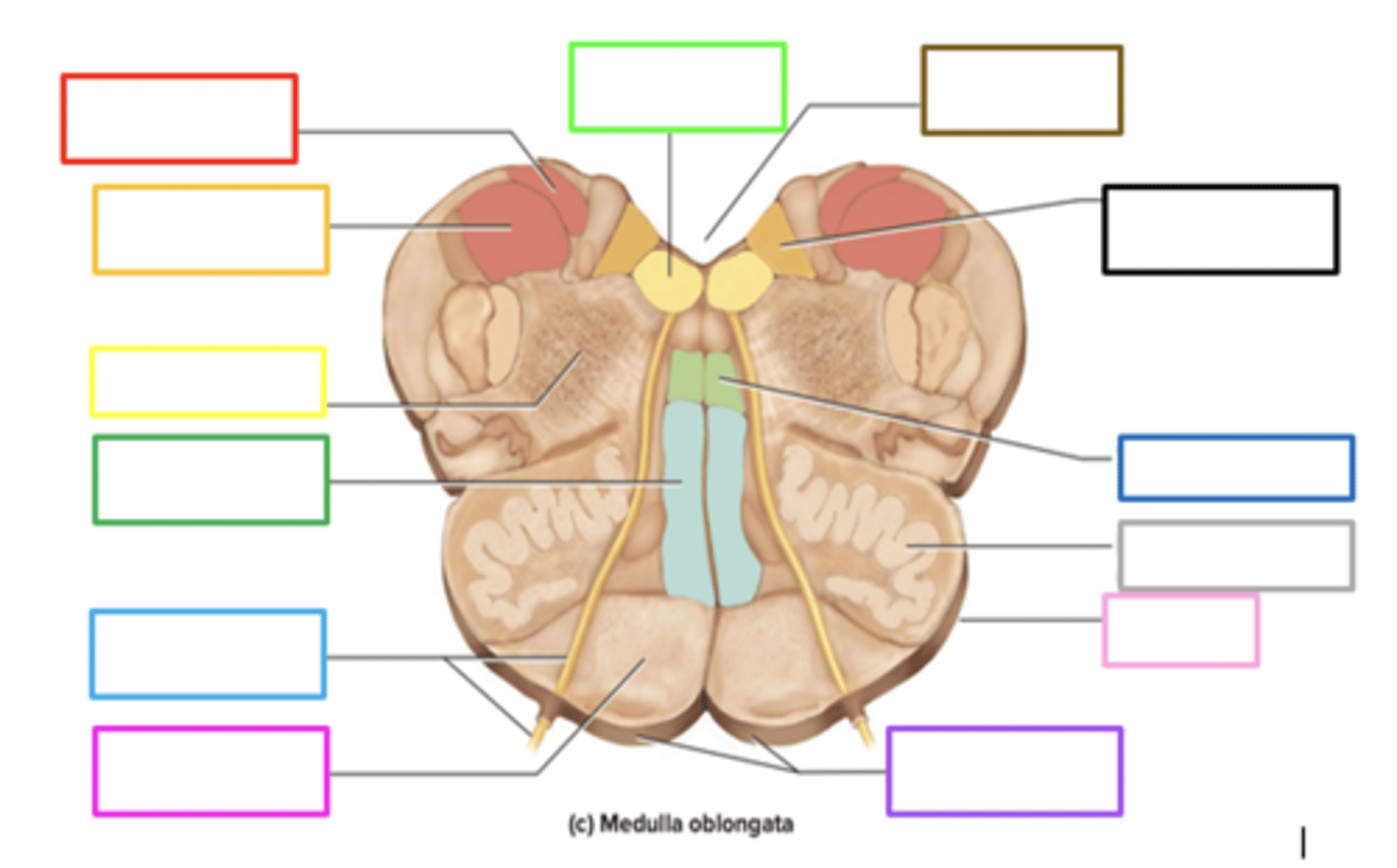
pyramids
crossing of motor fibers
carries motor signals to skeletal muscles
purple box
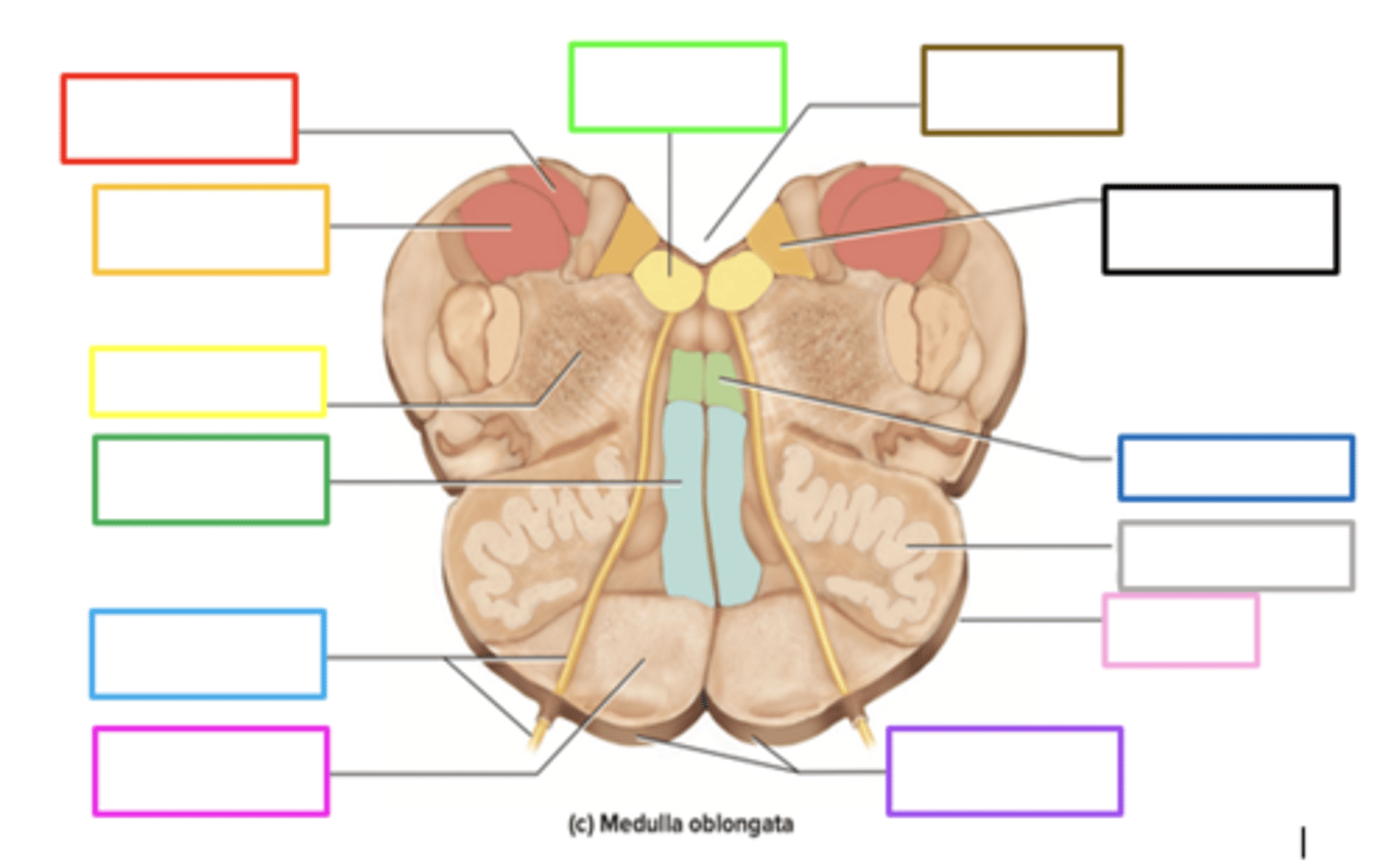
olives
prominent bulges lateral to each pyramid
has connections to the cerebellum
motor learning and coordination
light pink box
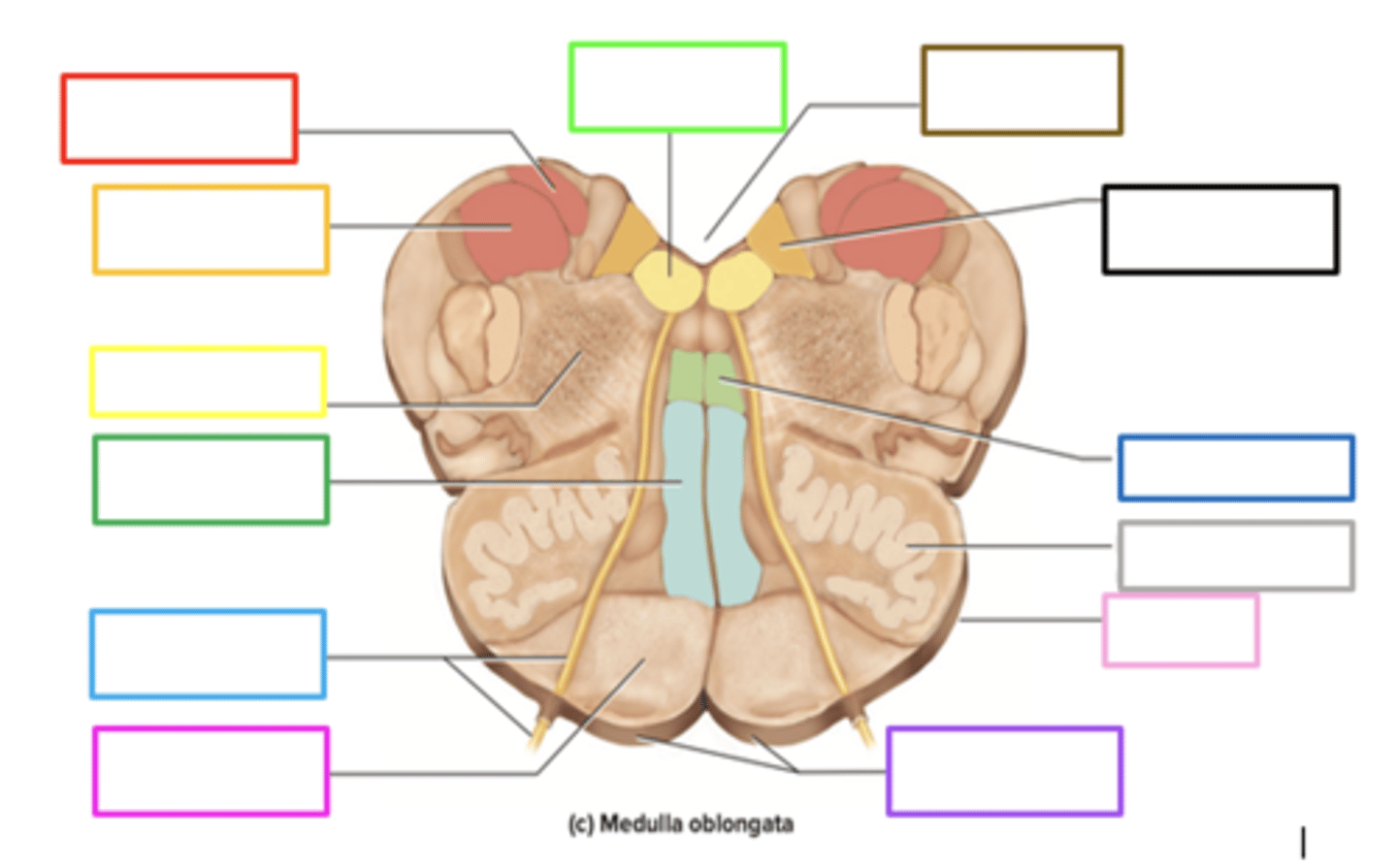
ascends upward
posteriorly, sensory info from the body of the medulla _____ to the thalamus
medulla
all nerve fibers connecting the brain to the spinal cord pass through where?
9, 10, 11, 12
what cranial nerves begin/end in the medulla?
cardiac, vasomotor, respiratory, and reflex
what are the 4 major centers of the medulla?
regulate HR
what does the cardiac center of the medulla do?
regulates if vessels are constricted/dilated
what does the vasomotor center of the medulla do?
regulates breathing
what does the respiratory center of the medulla do?
central pattern generators
neural pools that produce rhythmic signals to the muscles of breathing and swallowing
regulates vision/auditory reflex loops
what does the reflex center of the medulla do?
gracile nucleus
contains sensory info in the medulla
red box
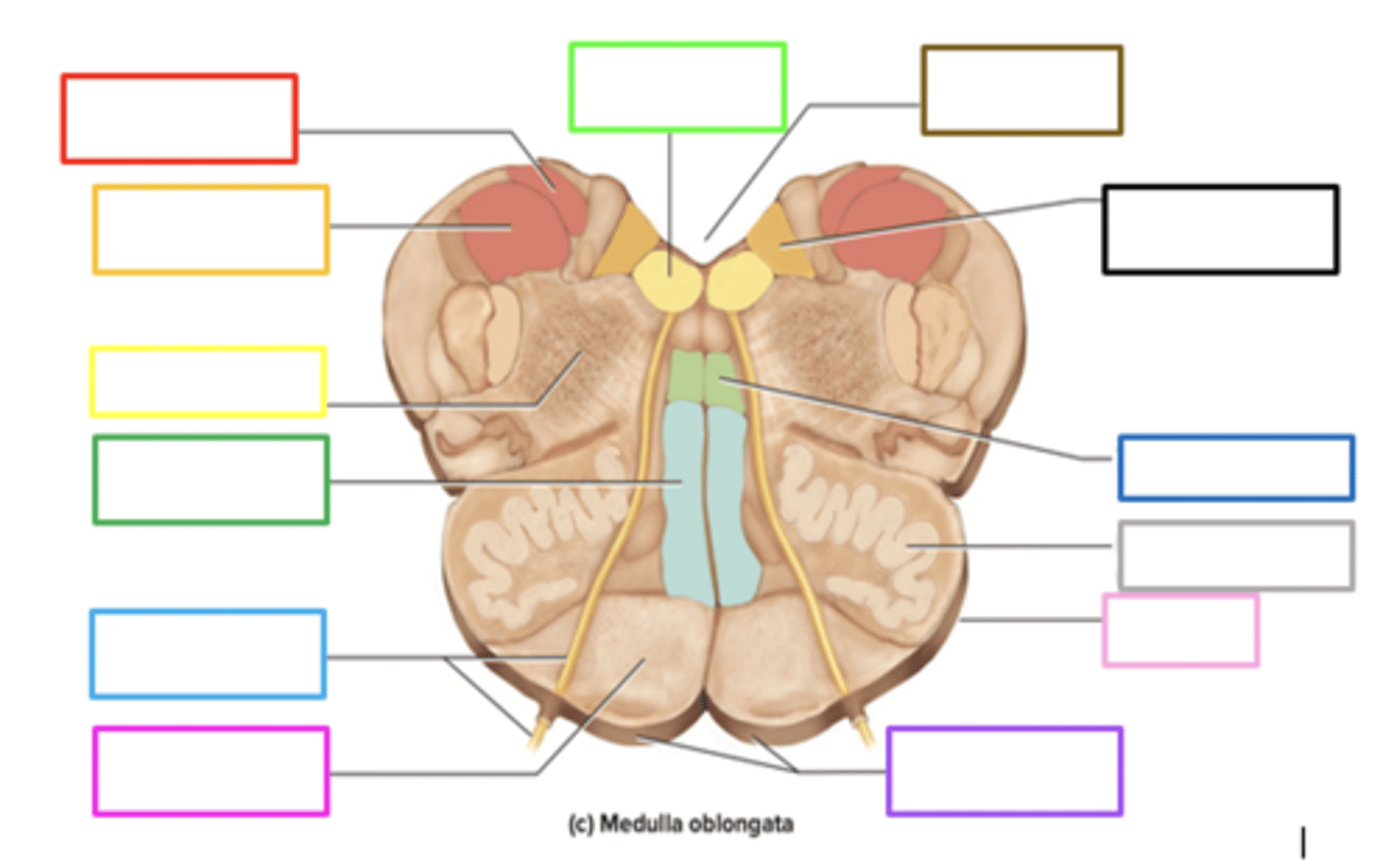
fourth ventricle
brown box
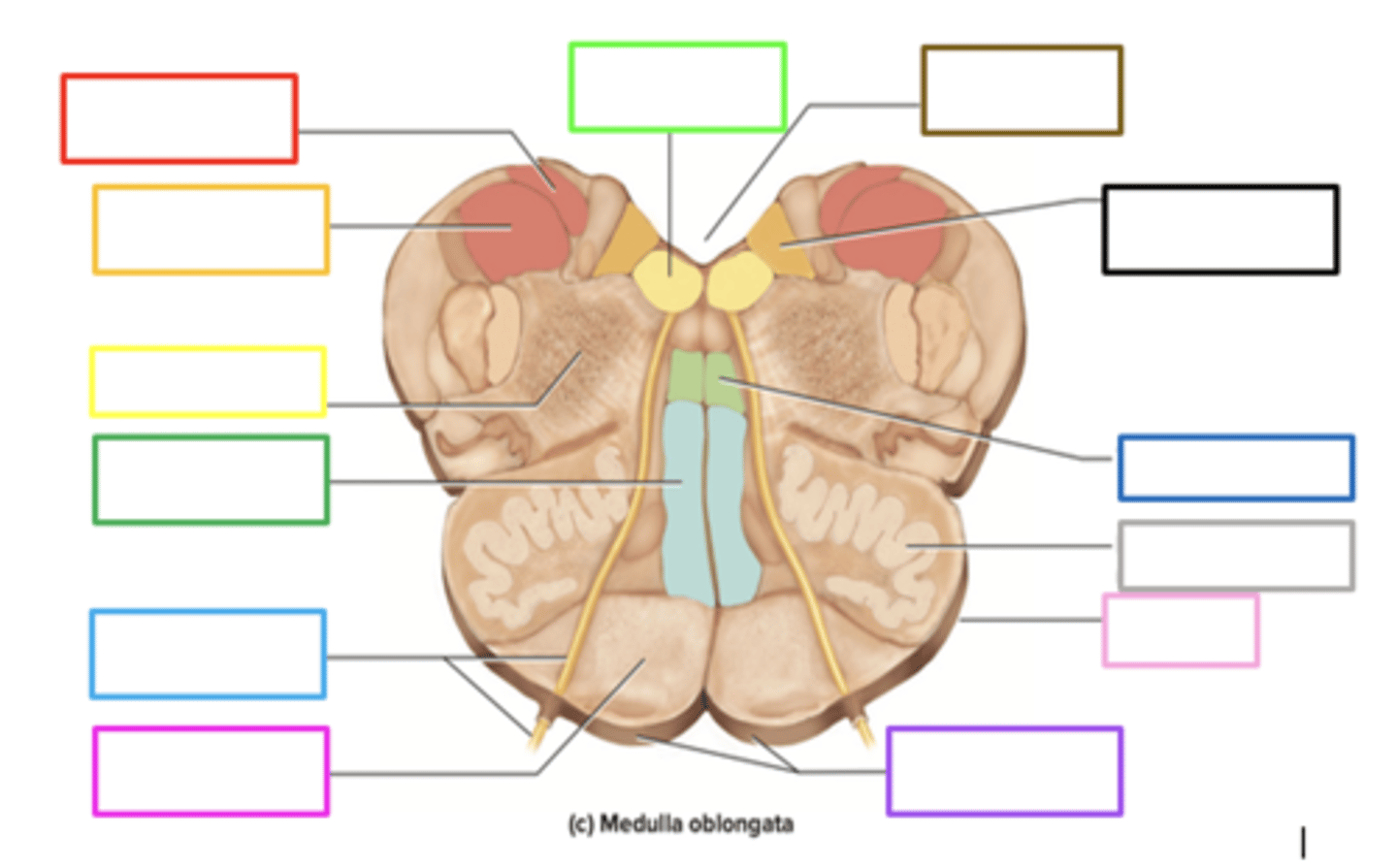
cuneate nucleus
contains sensory info in the medulla
orange box
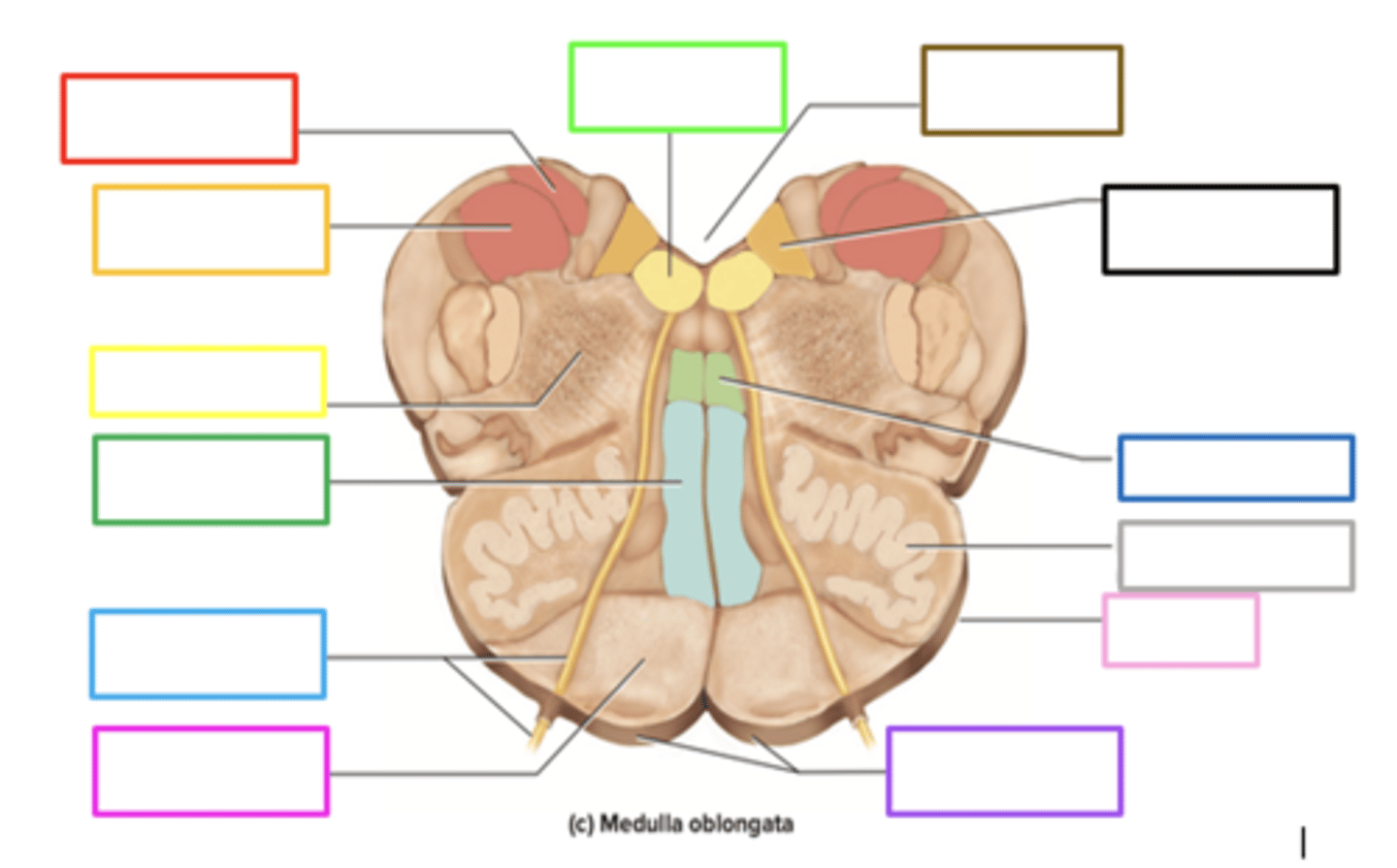
reticular formation
yellow box
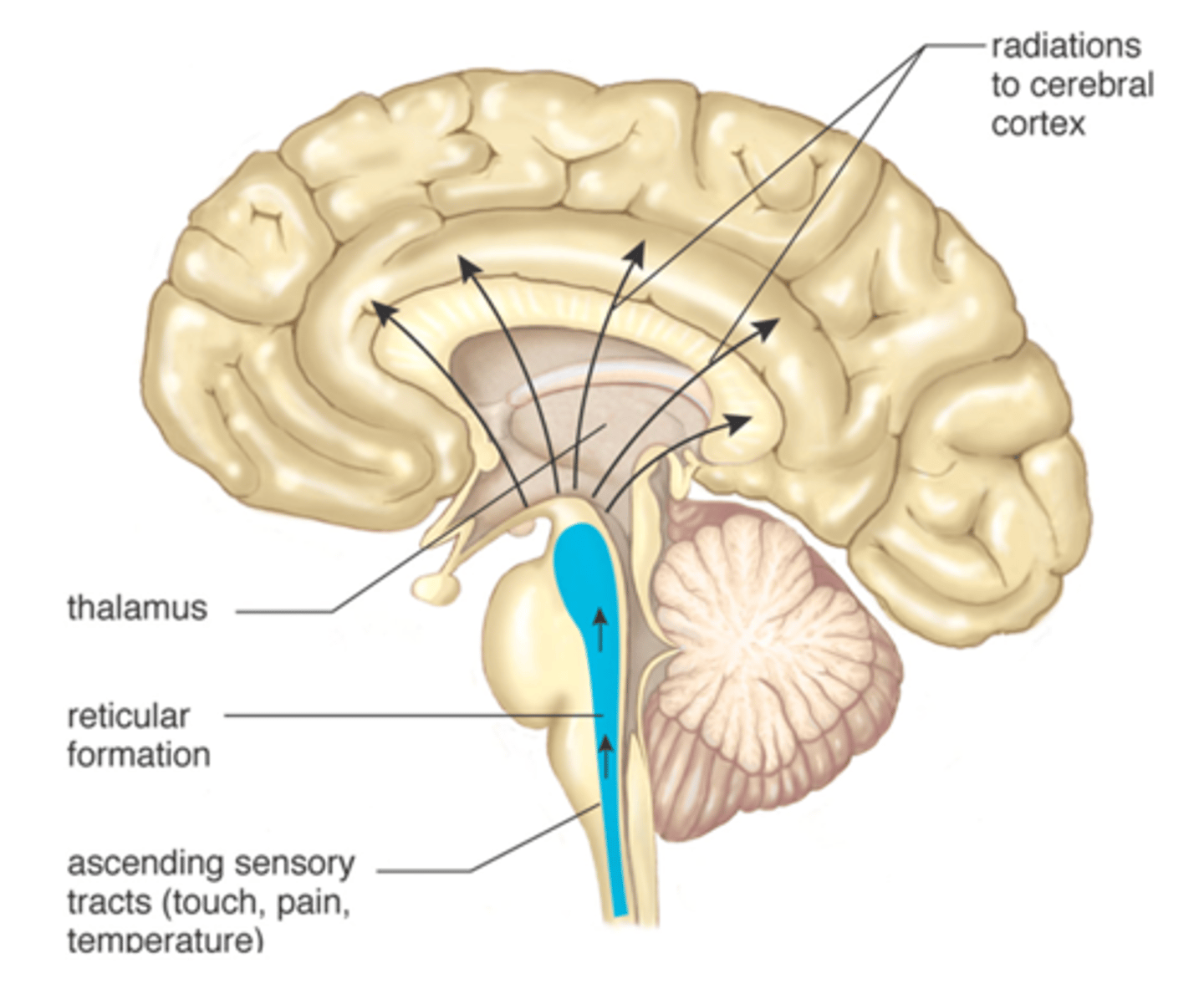
reticular formation
loose network of nuclei extending throughout the midbrain, pons, and medulla (runs vertically)
contains cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory centers
plays an important role in arousal
has connections with many areas of the cerebrum
more than 100 small neural networks within its distinct boundaries
medial lemniscus
The somatosensory pathway between the dorsal column nuclei and the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus.
green box
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
posteriorly
ascending sensory tracts through the pons pass where?
anteriorly
descending motor tracts pass through the pons where?
peduncles
what are the pathways in and out of the cerebellum?
5, 6, 7, 8
what cranial nerves are within the pons?
superior cerebellar peduncle
information highway
small oval near the fourth ventricle
middle cerebellar peduncle
large lateral dark spot
information highway
medial lemniscus
in the middle of the diagram the small rectangular shape
contains sensory information
corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts
motor information descending through pyramids
rounded bulbs located posteriorly
midbrain
connects hindbrain and forebrain
contains cerebral aqueduct
3 and 4
the midbrain contains the motor nuclei of 2 cranial nerves that control eye movements. which ones?
tectum
roof of the midbrain that is posterior to the cerebral aqueduct
contains the colliculi
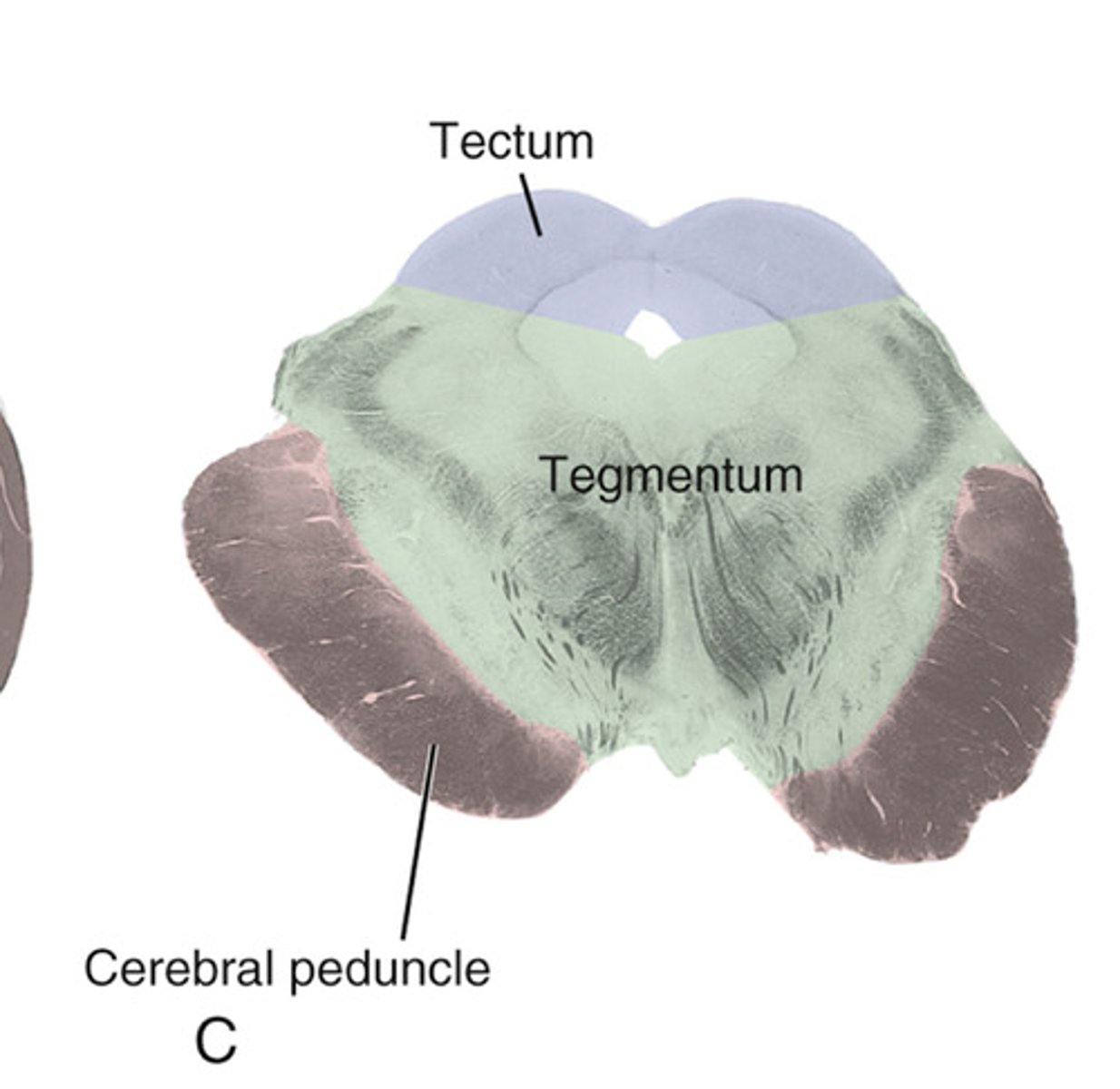
superior colliculi
visual reflexes
light in one eye and both constrict
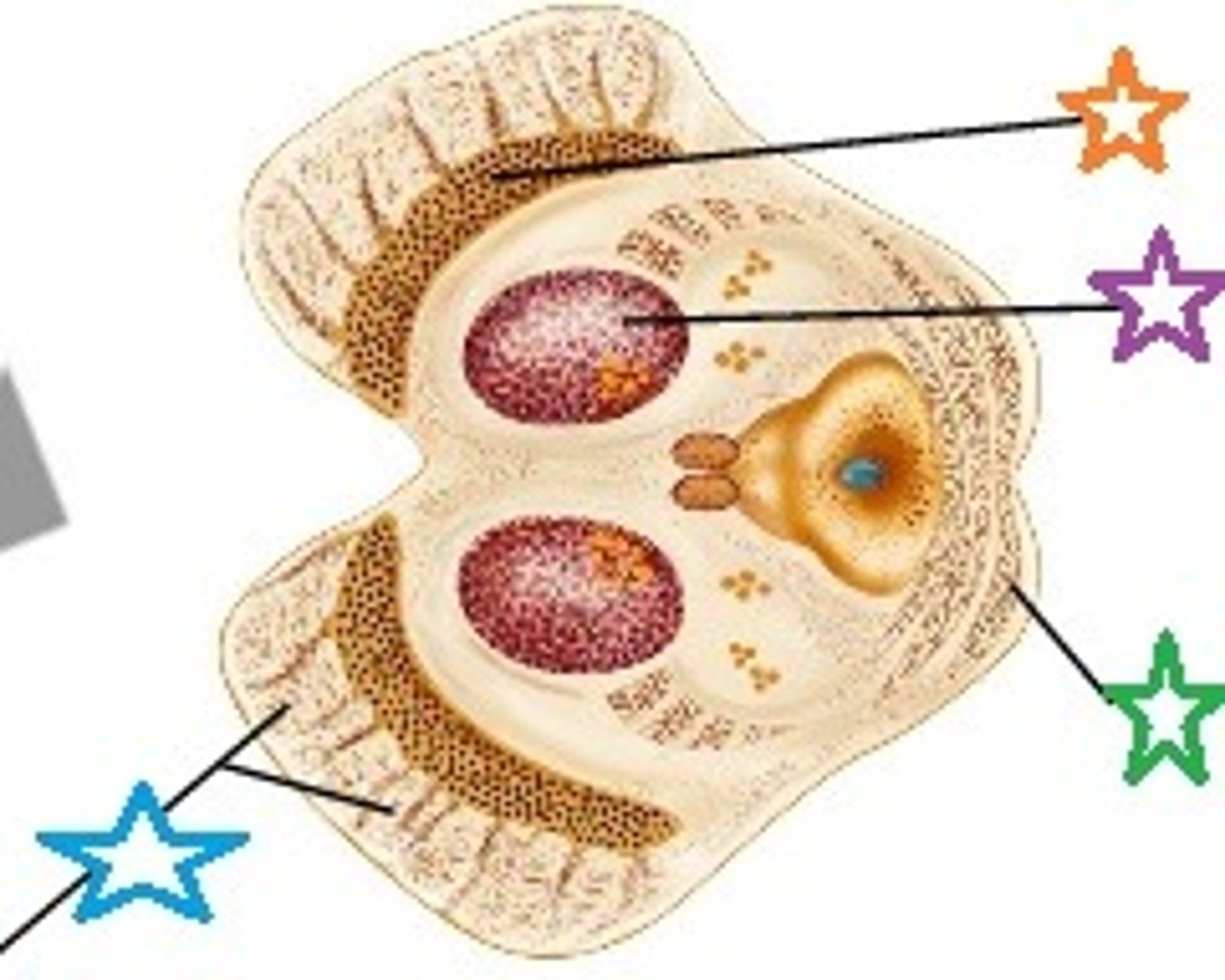
inferior colliculi
auditory reflexes
hearing something and turning to look
substantia nigra
An area of the midbrain that is involved in motor control and contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons
in Parkinson's disease this structure loses its dark color
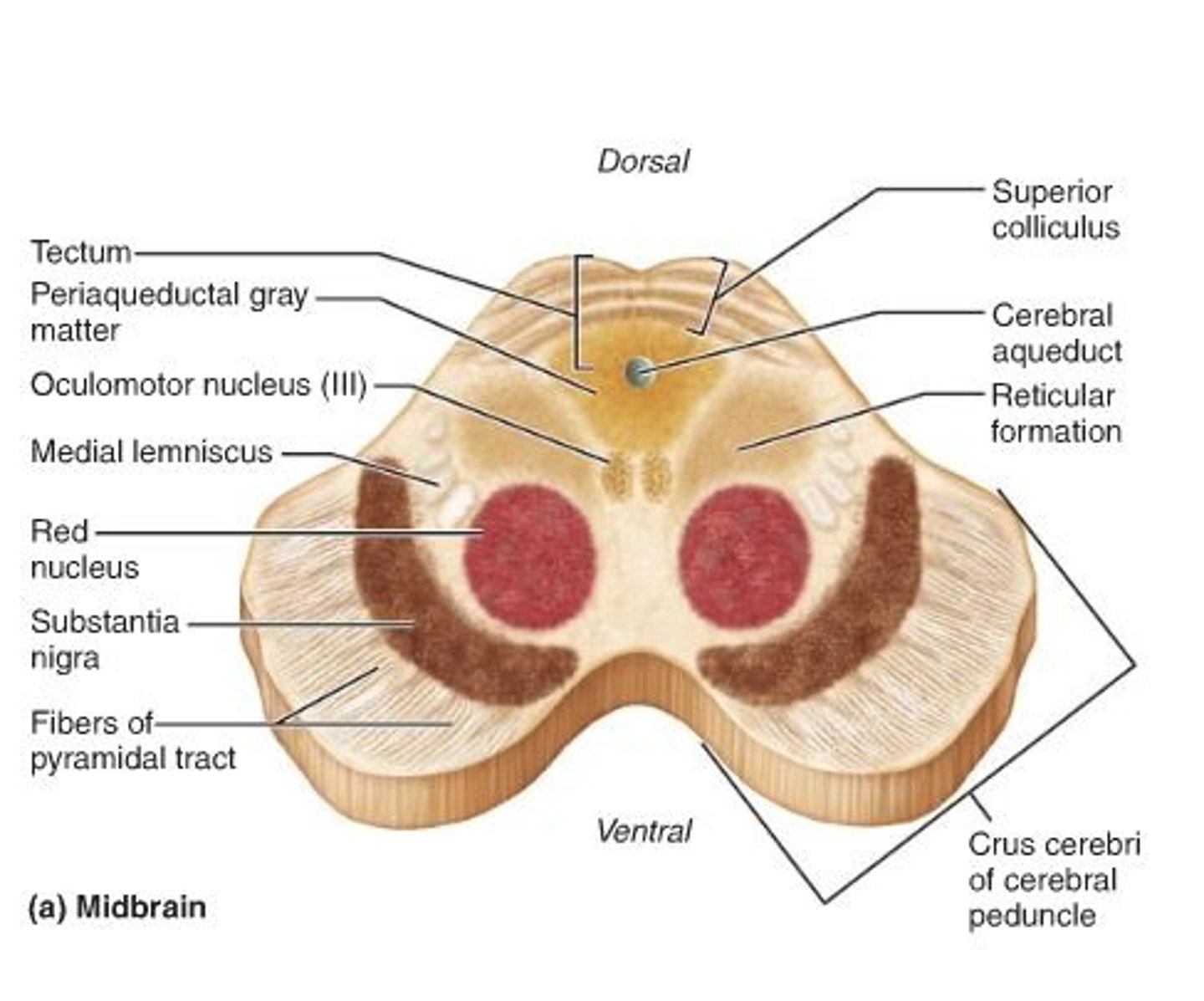
cerebral peduncle
between the brainstem and cerebrum
blue star
functions of RF
somatic motor control
CV control
Pain modulation
Sleep and consciousness
Habituation
somatic motor control
RF adjusts muscle tension to maintain tone, balance, and posture during movement
CV control
cardiac and vasomotor centers of medulla oblongata
pain modulation
RF acts in the spinal cord to block the transmission of pain signals to the brain
nociception: pain sensation
sleep and consciousness
Reticular formation plays a central role in consciousness, alertness and sleep
Injury here can result in irreversible coma (no signals from RF to keep you awake)
Habituation
tendency of the brain to stop attending to constant, unchanging information
EX: feeling clothes on skin, sitting on a chair/couch
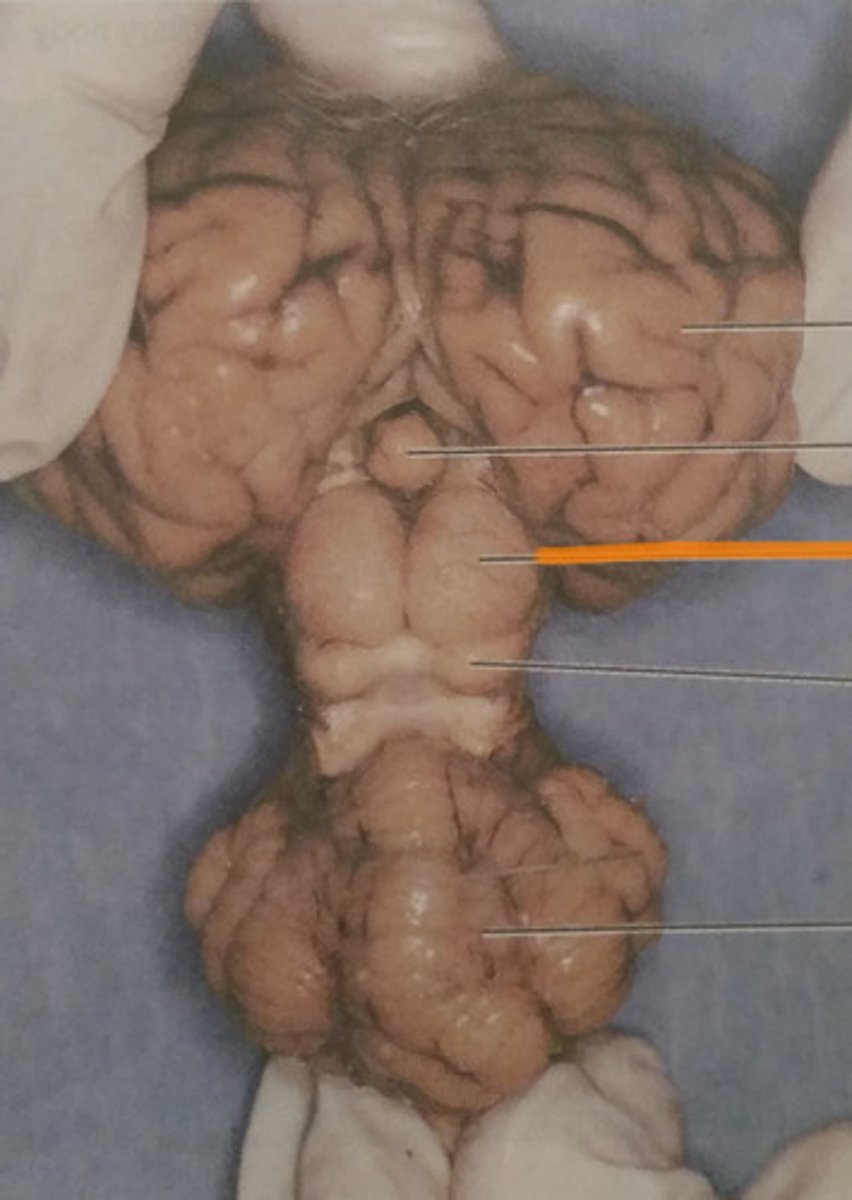
cerebellum
what is the largest part of the hindbrain?
vermis
what connects the R and L hemispheres of the cerebellum?
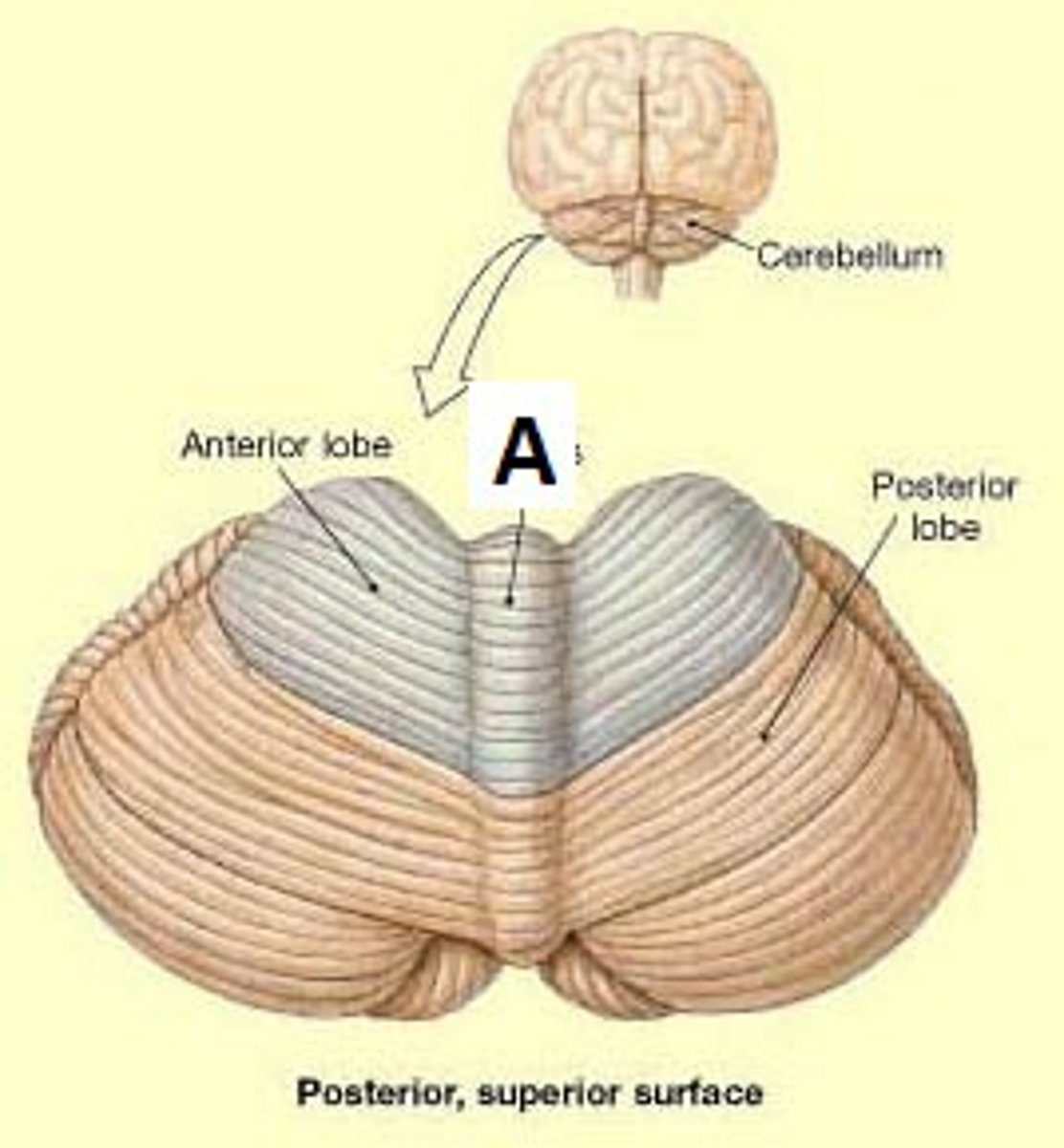
100 billion
the cerebellum contains more than half of all the brains neurons. about how many?
arbor vitae
white matter of the cerebellum
folia
folds of the cerebellum
gray matter contained here
four deep nuclei in each hemisphere
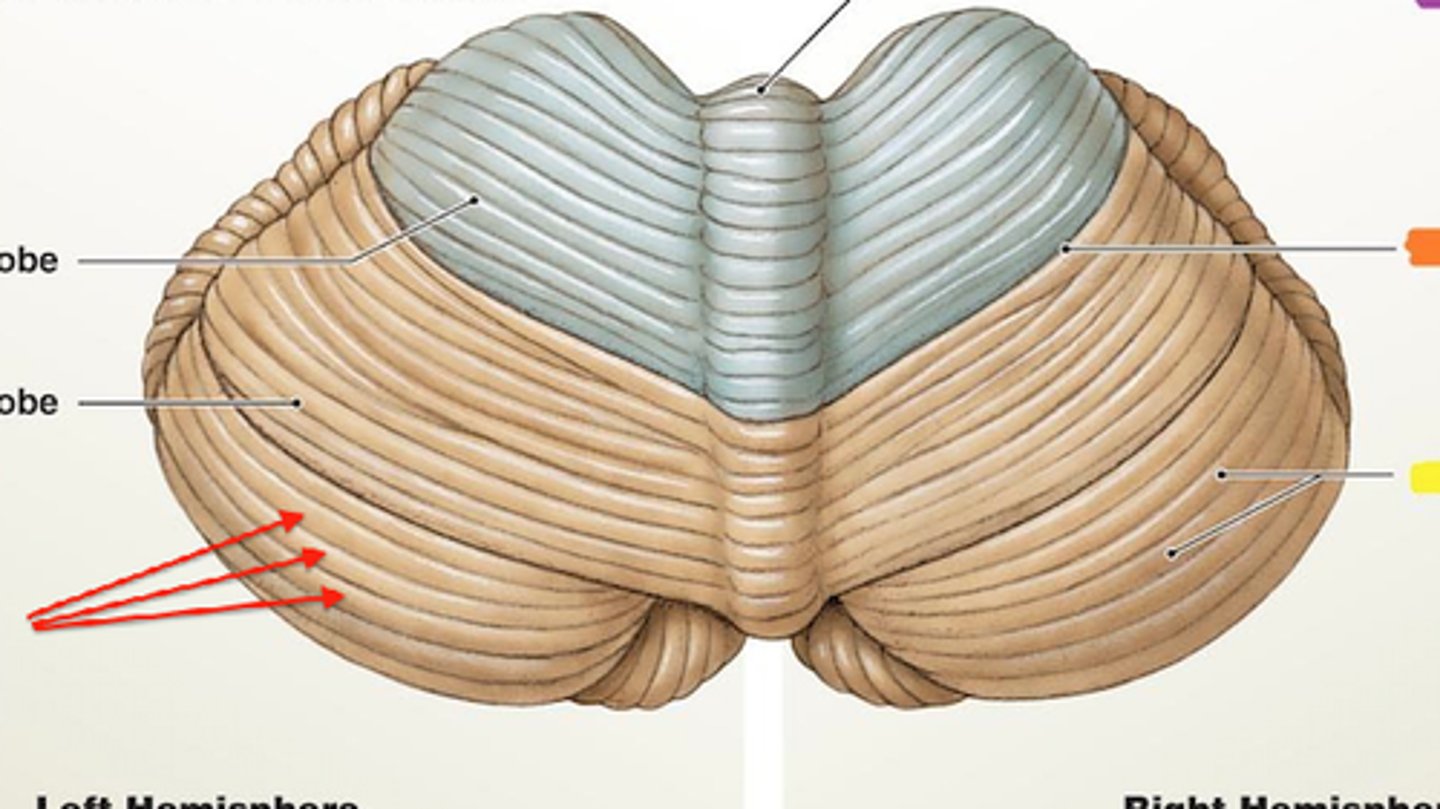
cerebellar functions
monitors muscle contractions and aids in motor coordination, evaluation of sensory input
timekeeping center
planning and scheduling tasks
evaluation of sensory input
- Comparing textures without looking at them
- Spatial perception and comprehension of different views of three-dimensional objects belonging to the same object.
timekeeping center
predicting movement of objects
helps predict how much the eyes must move in order to compensate for head movements and remain fixed on an object
planning and scheduling tasks
partly happens in the cerebellum and partly occurs in the frontal lobe
chiari malformation
part of cerbellum herniates down through foramen magnum
diencephalon
encloses the third ventricle
thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
thalamus
located in the middle of the brain
2 egg-shaped structures bilaterally
massa intermedia
the connection between the right and left thalamic nuclei
function of thalamus
sensory relay station
thalamus perception
bridge between sensory perception and cognition
sensing something and then coming to a conclusion about what it is
hypothalamus
nervous and endocrine tissue
functions:
HR and BP
body temp (shivering/sweating)
water and electrolyte balance
hunger and appetite (hormones)
activity of glands and tubes of digestive system (hormones)
sleep and wakefulness
regulates pituitary gland's regulation of growth, function of other glands, and reproductive function
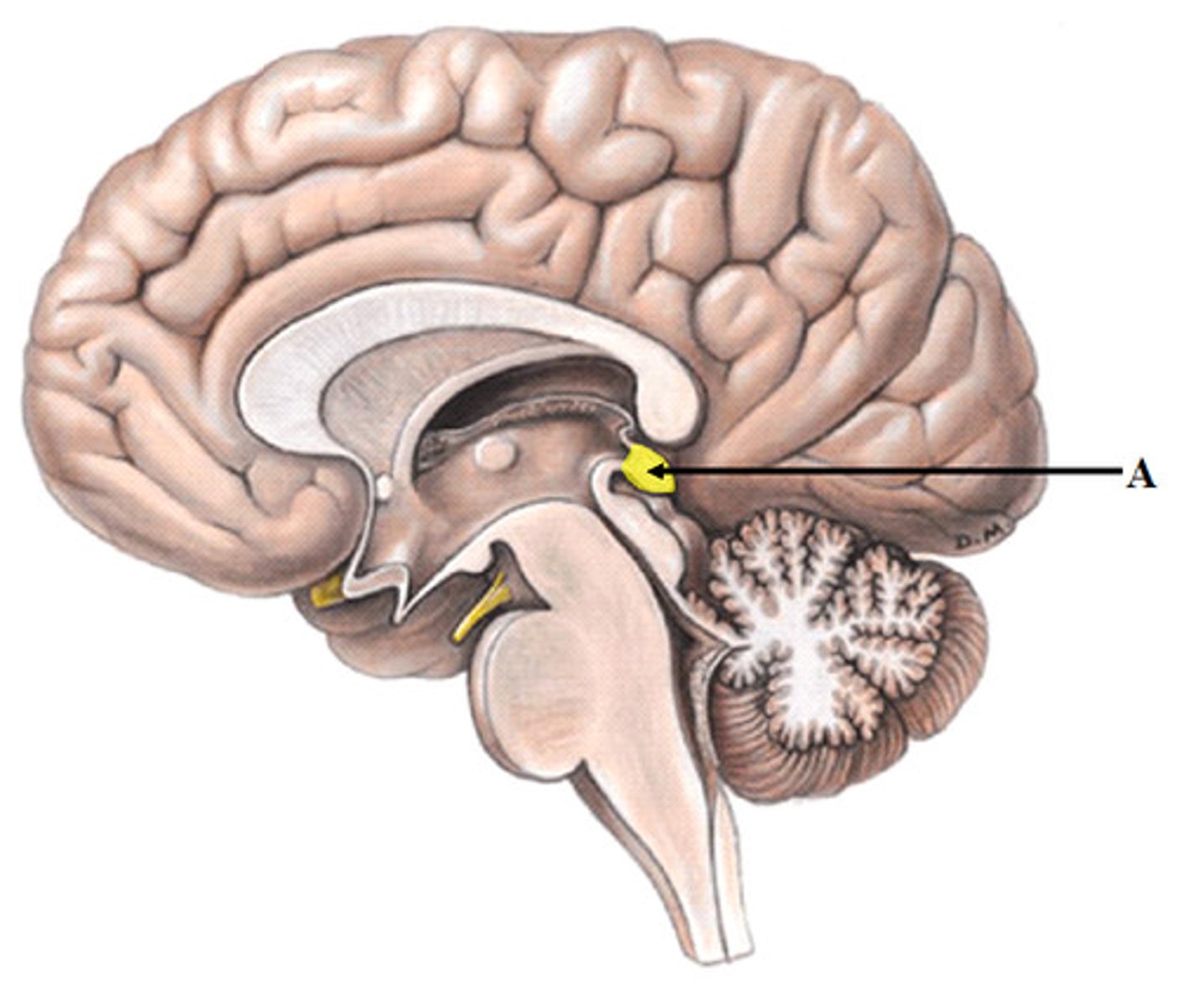
pineal gland
regulates circadian rhythms
sleep-wake cycle
metabolic changes
cerebrum
largest part of the brain
many gyri and sulci (increase surface area)
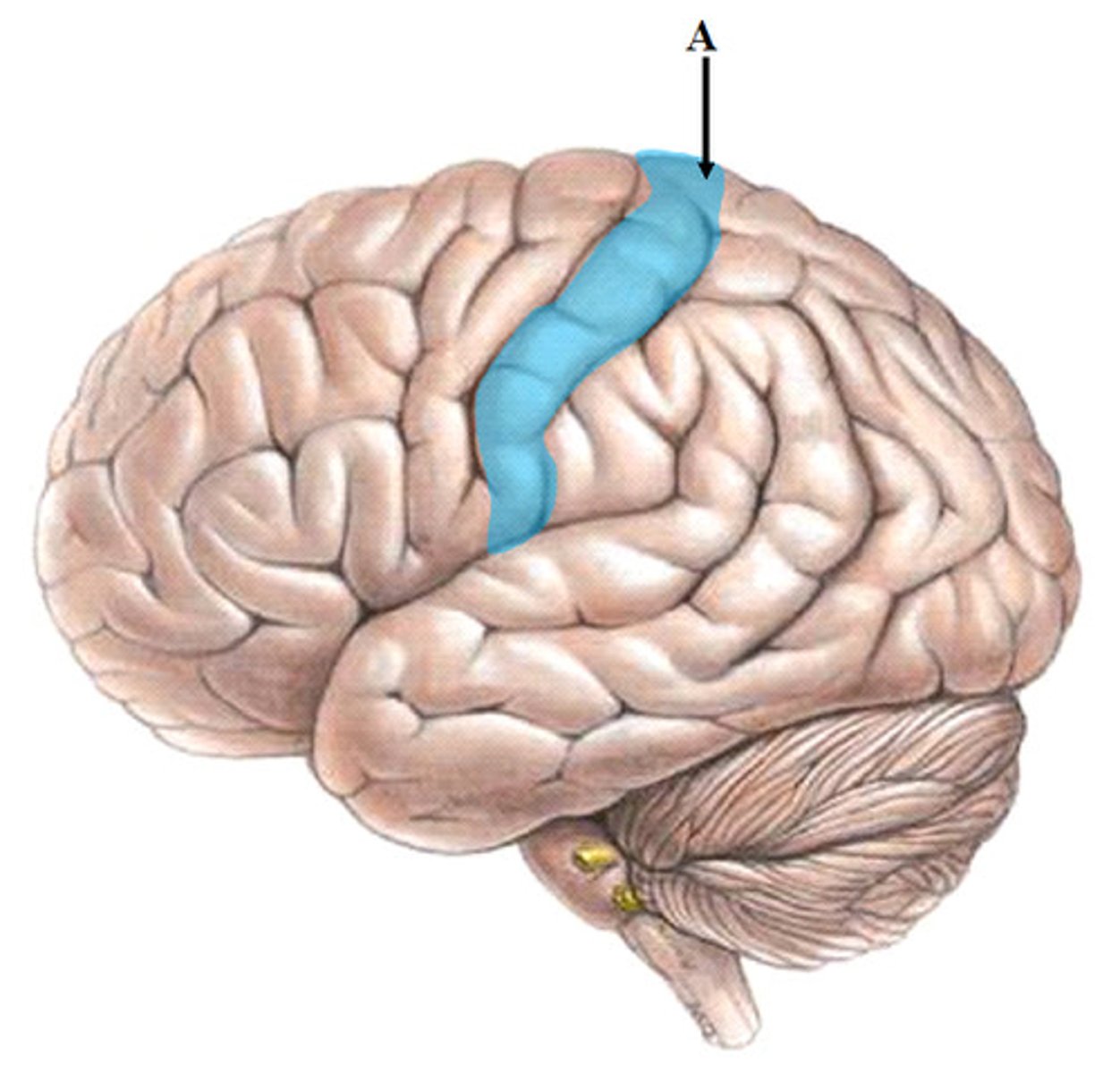
precentral gyrus
primary motor cortex
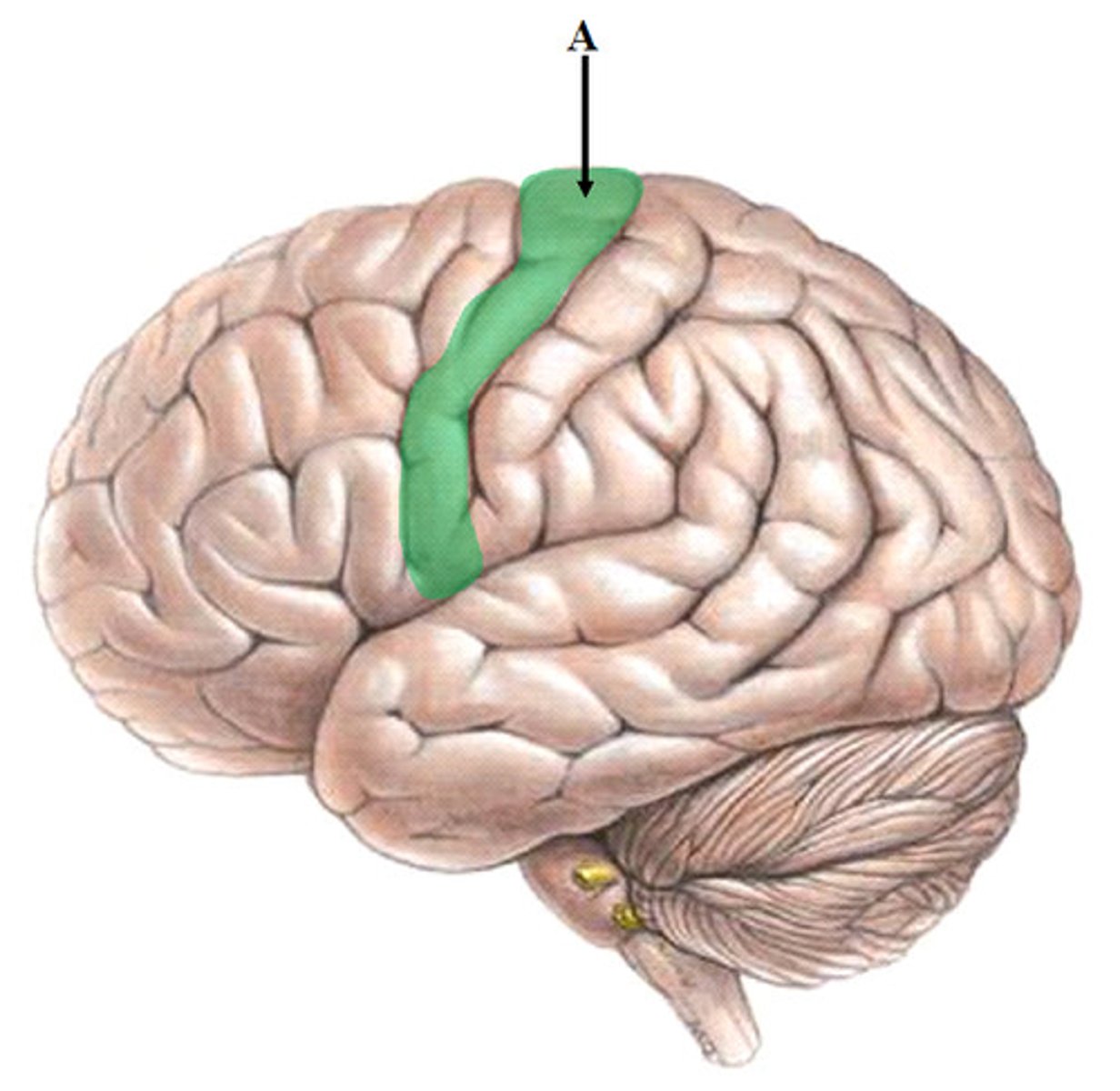
postcentral gyrus
primary sensory cortex
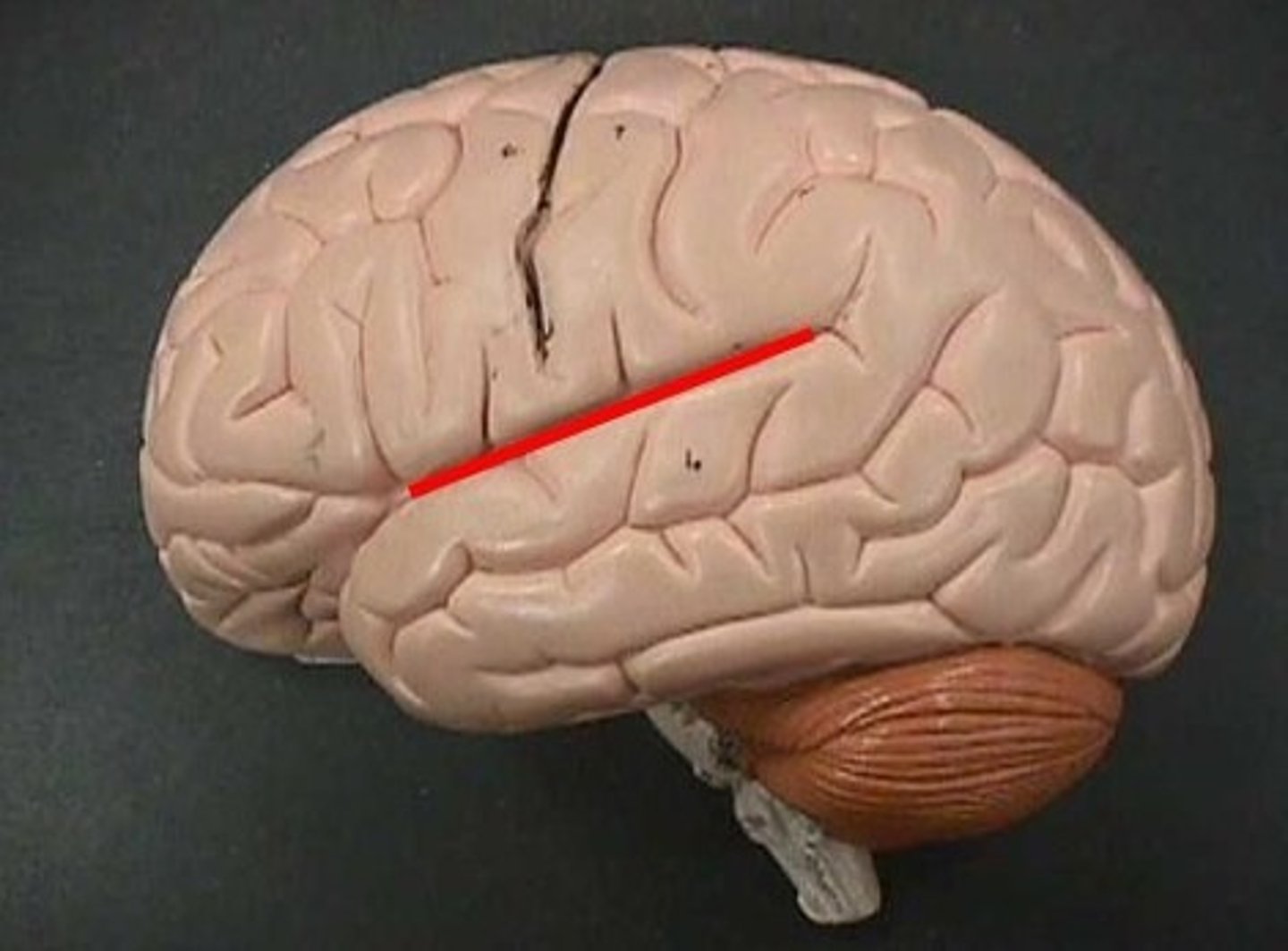
lateral sulcus
separates the parietal and temporal lobes
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates parietal and occipital lobes