monomer, polymer, carbohydrates, lipids
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what is a monomer
a small basic molecular unit eg amino acid
what is a polymer
a large complex molecule composed of long chains of monomers eg proteins
what elements are carbohydrates made up of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen
name the 3 monosaccharides
glucose
fructose
galactose
name the 3 disaccharides
sucrose
maltose
galactose
name the 3 polysaccharides
starch
cellulose
glycogen
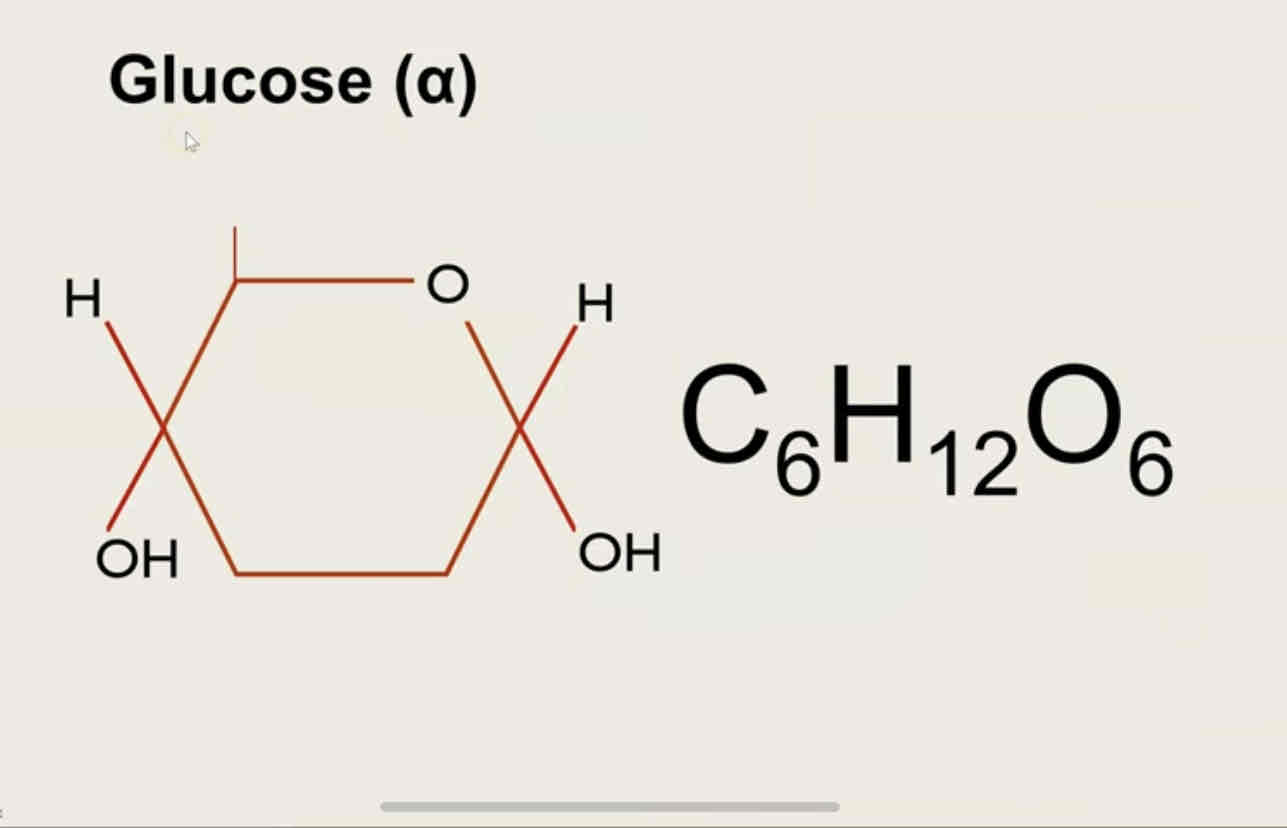
alpha glucose
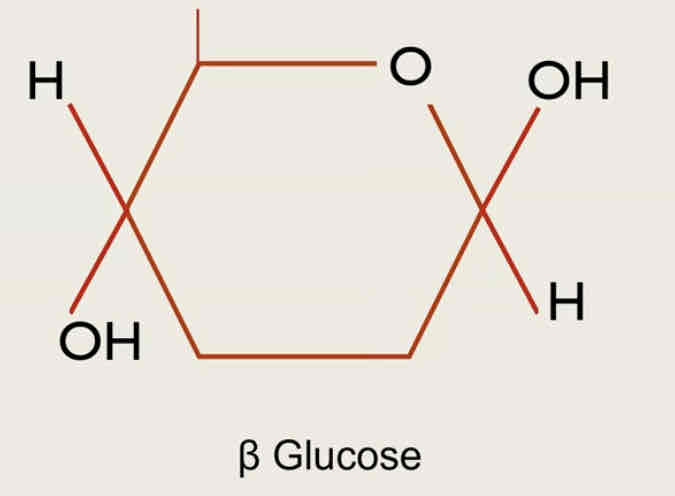
beta glucose
what is an isomer
same molecular formula but different structure
what is a disaccharide
which bonds form
which reaction forms it
a pair of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bond formed by a condensation reaction
glucose + glucose —> ________ + water
maltose
glucose + _______ —> lactose + water
galactose
glucose + _______ —> sucrose + water
fructose
what is a condensation reaction
the joining of two molecules joined together by removing water
what is hydrolysis
the splitting of molecules through the addition of water
where do bonds form in a disaccharide
1-4 glycosidic bond (2 H and 1 0)
what is a polysaccharide
what reaction forms it
many glucose monomers joined via a condensation reaction
starch
monomer and bond between them
alpha glucose
1-4 glycosidic bonds (amylose)
1-4 , 1-6 glycosidic bonds (amylopectin)
starch
function and location
insoluble store of glucose
starch grains inside of plant cells
explain starch structure and how it related to its function
made of 2 polymers. amylose which is an unbranched helix and amylopectin with is a branched molecule
the helix can compact to fit into smaller spaces. the branches increase the surface area for rapid hydrolysis into glucose. it is insoluble so won’t effect water potential
cellulose
monomer and bonds between them
beta glucose
1-4 glycosidic bonds + hydrogen bonds
cellulose
function and location
provide structural strength to cell wall
cell wall of plants
describe the structure of cellulose and how it relates to its function
made up of long straight chains held together by many hydrogen bonds - fibrils
the many hydrogen bonds provides collective strength. insoluble so won’t effect water potential or osmosis
glycogen
monomer and bonds between them
alpha glucose
1-4 glycosidic bonds and many more 1-6 glycosidic bonds
glycogen
function and location
insoluble store of glucose
muscle and liver cells of animals
describe the structure of glycogen and how it relates to its function
highly branched molecule which increases surface area for rapid hydrolysis back to glucose and more points for the enzymes to attach. insoluble so won’t effect water potential.
triglyceride
reaction
what’s it’s made up of
what bonds are formed
formed via a condensation reaction between one glycerol and three fatty acids (3 waters) to form 3 ester bonds (in the carboxylic group)
phospholipid
what reaction
what’s it made up of
what bond is formed
formed via a condensation reaction between one glycerol molecule, two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group attached to a glycerol. two ester bonds form.
properties of triglycerides (4)
energy storage
large ration of C-H bonds compared to number of C atoms so a lot of energy can be stored in the molecule
metabolic water source
high ratio of H + O atoms so will release water when oxidised
insoluble
larger and hydrophobic so won’t effect water potential and osmosis
relatively low mass
a lot can be stored without increasing mass and preventing movement
properties of phospholipid (4)
hydrophilic head that attracts water when charged
the charge will repel other fats
has a hydrophobic tail so repels water and mixes with fats
polar head exposed to water and tails are not to form a phospholipid bilayer membrane which makes up the plasma membrane around cells
how do you test for lipids
dissolve sample is ethanol and shake
add distilled water and shake
if a white emulsion appears then it is positive