Understanding Errors in Chemical Analyses
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
mean, arithmetic mean, and average
the quantity obtained by dividing the sum of replicate measurements by the number of measurements in the set
median
is the middle result when replicate data are arranged in order of size
precision
the closeness of results to others that have been obtained in exactly the same way; describes the reproducibility of measurements
accuracy
the closeness of a measurement to the true or accepted value and is expressed by the error; measures agreement between a result and its true value but precision describes the agreement among several measurements
absolute error
the difference between the measured value and the true value; E = xi - x
relative error
the absolute error divided by the true value
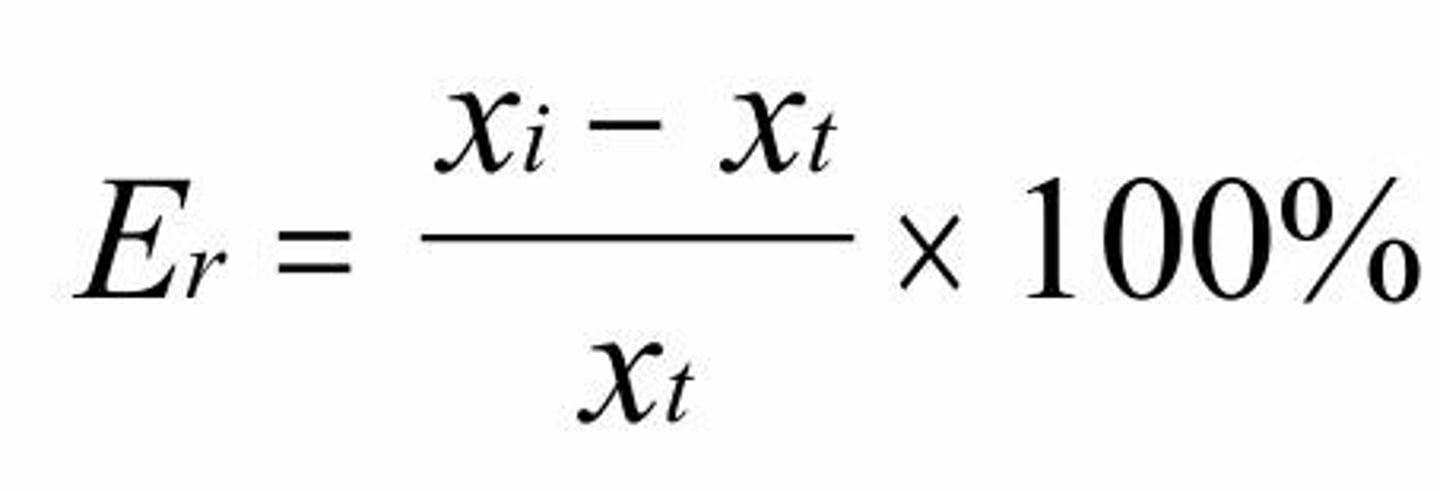
random or indeterminate errors
errors that affect the precision of measurement; causes data to be scattered more or less symmetrically around a mean value
systematic or determinate errors
errors that affect the accuracy of a result; this type of error causes the mean of a set of data to differ from the accepted value
gross errors
usually occur only occasionally, are often large, and may cause a result to be either high or low; this error causes the result to differ significantly from the rest of the results
bias
measures the systematic error associated with an analysis; has a definite value, an assignable cause and are about the same magnitude for replicate measurements
instrumental errors
are caused by the imperfections in measuring devices and instabilities in their components
method errors
arise from nonideal chemical or physical behavior of analytical systems
personal errors
results from the carelessness, inattention, or personal limitations of the experimenter
constant errors
error that does not depend on the size of the quantity measured
proportional errors
errors that decrease or increase in proportion to the size of the sample taken for analysis
standard reference materials
are substances sold by the National Institute of Standard and Technology and Certified to contain specified concentrations of one or more analytes
blank determinations
are useful for detecting certain types of constant errors; reveal errors due to interfering contaminants from the reagents and vessels employed in analysis