Rheumatology (1-37)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Systemic lupus erythematosus is an inflammatory, autoimmune disorder characterized by autoantibodies to nuclear antigens. Many of the clinical manifestations observed are secondary to trapped Ab-Ab complexes in capilalries of visceral structures. This is an example of what type of hypersensitivity reaction?
Type III
What race is most likely to develop lupus?
African Americans
Which patient has a genetic predisposition to developing lupus?
a. Patient with HLA DR2 and DR3
b. Patient with HLA DR1 and DR3
A
T/F A patient with lupus can have either a positive or negative ANA test result
False - revised criteria deem a negative ANA test means we cannot classify patient to have SLE.
SLE can be drug induced. When it is drug induced, what two findings do we see?
a. Brain and kidney affected
b. Brain and kidney spared
c. Gender ratio 1 to 1
d. More common in males than females
B and C
Clinical manifestations of lupus can be extremely broad and nonspecific. However, what are two findings that is more common in lupus?
a. Weight loss
b. Low grade fever
c. Vasculitis
d. Glomerulonephritis
e. Myocarditis
C and D
What is Raynaud’s Phenomenon?
It is from of vasculitis in which patient’s hand can go white from lack of blood flow, blue due to lack of oxygen, and red due to returning blood flow
T/F Arthritis and arthraldia is present in 90% of SLE patients as an early manifestation
True
What type of rash if the most characteristic of SLE?
Butterfly rash
The following are clinical manifestations of SLE. Which one is the biggest cause of morbidity and mortality?
a. Cardiopulmonary involvement
b. Renal involvement
c. Neurologic abnormalities
d. Hematologic involvement
B
Match the following term with its definition:
Anemia
Leukopenia
Thrombocytopenia
a. Lack of red blood cells
b. Low white blood cell count
c. Low platelet count
A
B
C
T/F Any young patient with a veil occlusion but otherwise clean health history should be worked up for a clotting disorder and one of the major tests we need to order is the ANA test
True - SLE commonly has clotting abnormalities and CRVO in a young patient is uncommon
There is a total of 11 criteria for the diagnosis of SLE. How many are needed to be met for a diagnosis of SLE?
4/11
The following are serologic tests that we should order for SLE patients. Which 4 are the most important according to Stephey?
a. CBC with diff
b. ANA
c. Antiphospholipid antibodies
d. Rheumatoid Factor
e. Urinalysis
f. ESR
A, B, D, F
The following are common adnexa/anterior seg findings in an SLE patient. Which one may be the first sign of the disease?
a. Keratoconjunctivitis sicca
b. Recurrent nodule and diffuse ant scleritis and episcleritis
c. Discoid lupus of lids
A
The following are neuro ophthalmic findings in SLE patients. Which one is secondary to hypertensive crisis and looks similar to IIH?
a. Optic neuritis and AION
b. Disc edema
c. Migraines and amaurosis
d. Pupillary anomalies and oculomotor issues
B
T/F In lupus retinopathy, you can find CWS with or without hemes
True
Select which of the following are tx/management strategies for SLE pts? Select all that apply.
a. Avoidance of known triggers of flares
b. Sunprotection
c. Maximization of immunomodulators
d. Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil)
All of the above
What type of toxic retina finding do we see in patients who are taking Plaquenil?
Bulls eye maculopathy
The recommended dosage for SLE patients based on their weight is what?
a. Less than or equal to 5 mg/kg
b. Less than or equal to 8 mg/kg
c. Less than or equal to 10 mg/kg
A
When managing an SLE patient, what information/tests do you need to perform? Select all that apply.
a. Weight
b. Baseline fundus exam every 5 years
c. Automated VFs
d. Spectral domain OCT
e. FAF
All of the above
OCT is important because structural changes will be seen first before functional loss on VFs
What type of automated VF do we run on Asian parents with Lupus?
a. HFA 10-2
b. HFA 30-2
c. HFA 24-2
C
What zones/layers of the retina do we need to look at for thinning in a patient taking Plaquenil?
a. RNFL
b. Ellipsoid
c. Inner retina
d. Outer retina
B and D - we need to document as a pertinent negative if not thinning and intact
What type of “sign” do we see at the macula in an OCT of a patient with Plaquenil maculopathy?
a. Lazy V sign
b. UFO sign
c. Top hat sign
B
On an FAF, will we see hyperfluorescence around the macula or hypofluorescence?
Hyper
T/F There is no tx for Plaquenil toxicity and effects are permanent and can continue even after patient has d/c treatment
True
The following are medical tx for SLE patients. Which 2 are primarily used only for symptoms and not actual treatment?
a. NSAIDs
b. Aspiring
c. Belimumab
d. Methotrexate
e. Anti TNF drugs (biologic agents)
A and B
T/F There is no official specific treatment (ie. topical steroids and oral NSAIDs) for lupus retinopathy as it can resolve with systemic treatment of SLE
True
T/F Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetrical chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammatory arthritis
True
Which of the following are true about the pathophysiology of RA? Select 2
a. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
b. T and B cells continually activated
c. MMP effects leads to destruction of joints and tissues
d. T and B cells become clumped and stuck in vasculature resulting in microvasculitis
B and C
Which of the following is NOT a clinical manifestation of RA?
a. Asymmetric polyarthritis of peripheral joints
b. Pain, tenderness, and swelling of joints
c. Worse in morning
d. Joint deformities
A - it should be symmetrical
T/F Distal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints are the most affected in RA
False - proximal not distal
Subcutaneous nodules occur in 20-25% of RA patients. What type of nodules do we see in the eye?
a. Percarditis
b. Nodular scleritis
c. Nodular episcleritis
d. Nodular retinitis
B
T/F There is no diagnostic criteria that exists for RA and a (+)RF test does not mean you have RA
True
The following are possible ant seg findings in patients with RA. Which one is the most important because it is usually associated with many autoimmune disorders?
a. Keratoconjunctivitis sicca
b. Central ulcerative keratitis (CUK)
c. Peripheral ulcerative keratitis (PUK)
d. Episcleritis
e. Scleritis
C - presents as guttering near limbus and corneal thinning with possible cells in AC and resolution results in corneal neo and subepithelial fibrosis
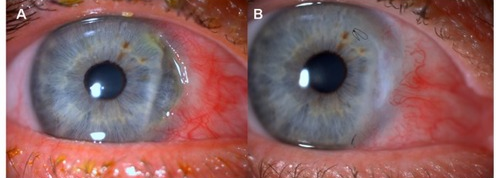
T/F PUK, recurrent episcleritis and/or scleritis are unique to RA
False - these findings can be associated with various autoimmune disorders
Which of the following is NOT a sign/symptom of diffuse anterior scleritis?
a. Slow onset with tearing and photophobia
b. Severe boring pain that radiates into forehead, brow, or jaw
c. Mainly unilateral
d. Mostly associated with underlying systemic condition
C - 50% are bilateral with unilateral cases turning bilateral in 5 years