Cognitive Psychology - Exam 1
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
3 main characteristics of cognitive psychology
study of mental processes, scientific and evidence based, variety of methods (behavioral or neuroscientific methods)
Word-pair memory demo
Pairing words with imagery were more likely to imagine more word pairs, simple repetition did not noticeably improve memory
Metacognition
knowledge understanding about own cognitive processes; often inaccurate
Painting style experiment
found that mixed method of studying painting styles was more effective for identifying new painting
Interleaving
technical term for mixed learning; very beneficial when learning differences between different types of materials
Two facets of metacognition
monitoring and control
Inaccurate metacognition
people tend to overestimate their skills and abilities
Above-average effect
optimistic, can lead to overconfidence; 93% of US drivers think they are above average drivers
Dunning-Kruger effect
Degree of overestimation is greater for people with lower skill in specific area
Fluency
the degree of ease one experiences when processing information
Planning fallacy
Imagining ideal scenarios
When are metacognitive judgments poorer?
low exam scores, estimating exam scores, when information is still fresh, high fluency, easy study methods
How to improve metacognition
fluency ≠ learning, objective measures to assess learning, delayed testing
Most effective strategies for learning
practice testing, distributed practice
Less effective strategies for learning
re-reading and highlighting, summarizing, mnemonics or imagery
What factors influence failures to retrieve information?
decay (gone), interference (similar infor), lack of effective retrieval cues
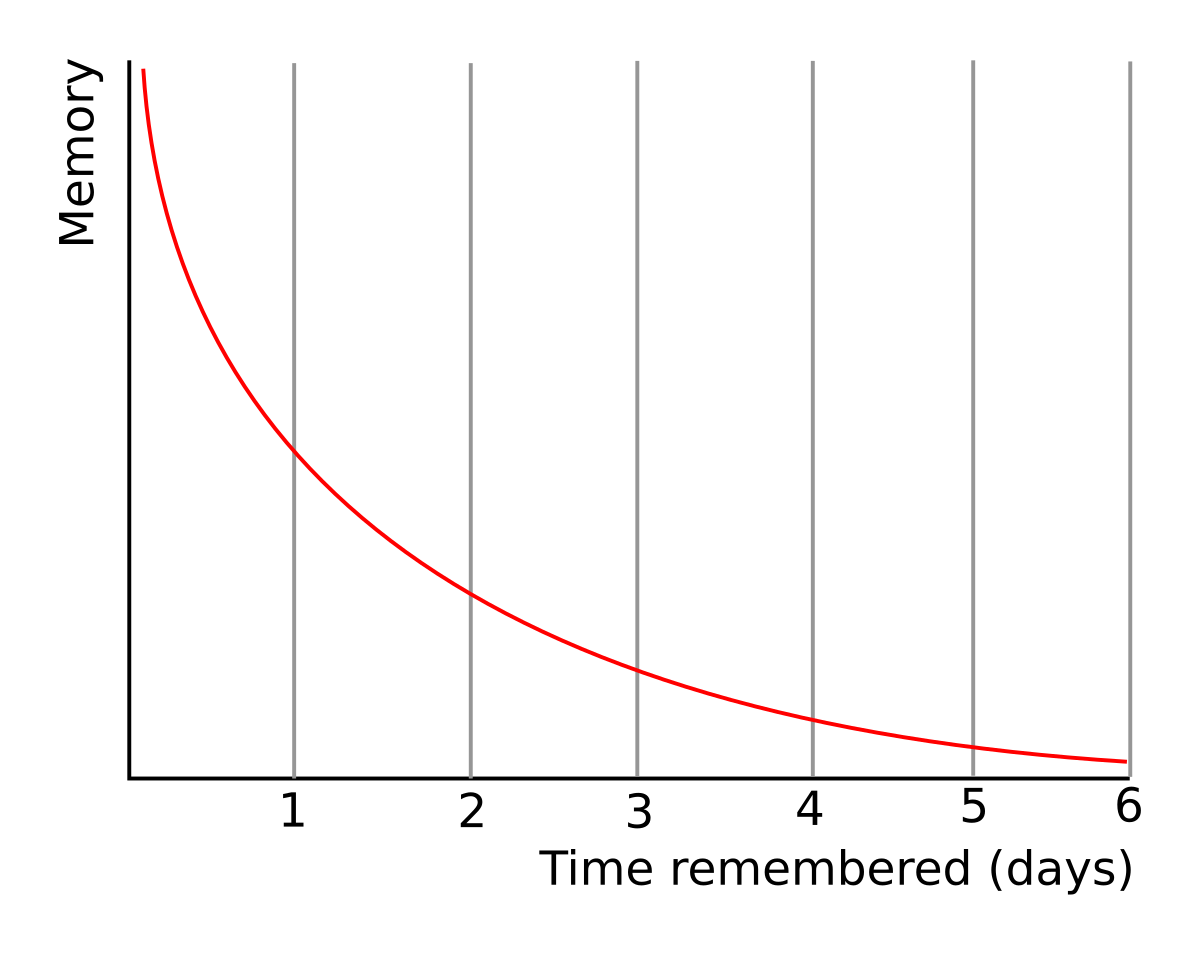
Forgetting curve
calculated saving score = (initial repetitions - relearning repetitions) / initial repetitions -> quantified what he could recall -> forgetting curve (right graph)
Stages of memory
encoding, storage, and retrieval
Spaced (distributed) learning
focus on repetition (effective repetition) over time vs. massed learning AKA cramming
Retrieval practice
also known as “practice testing”; deliberately recalling what you want to learn without using notes etc., retrieving knowledge tests learning and retention (testing effect)
“Do’s” for making flashcards
supplement with other study methods, simple and easy information, make your own, one prompt per card, say answers out loud, study in both directions, make within the same day (fresh info)
“Don’ts” for making flashcards
not well suited for learning high order information, don’t use flashcards as notes, don’t stop studying after multiple successful retrievals
What makes quality of encoding better?
preview information and use deep, elaborative
Deep processing
learn better when you focus on what you were learning, you’ll learn words better when thinking about their meaning as opposed to their visual appearance
Elaborative processing
Making new connections between information improves memory, two types of linking
Types of elaborative linking
elaborative rehearsal, maintenance rehearsal
procrastination
Voluntarily and unnecessarily deciding to delay a task despite intention to complete that task and knowing there will be future negative consequences for that delay
What increases likelihood of procrastination?
low conscientiousness, high impulsivity, high perfectionism, mental health challenges
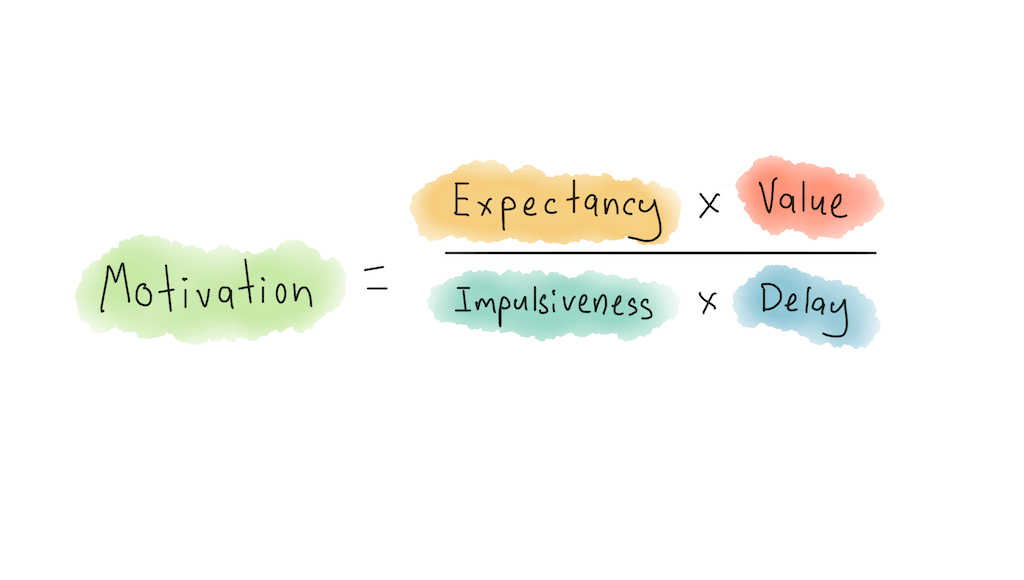
Steel’s temporal motivation theory
↑ expectancy & value = increased motivation
↑ impulsiveness & delay = lower motivation
Sirois short term mood-repair theory
Theory: coping with negative affect associated with procrastination/not wanting to do it; failure of emotional regulation
Cognitive psychology
how people remember, pay attention, and think