chapter 6: skeletal system
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Main functions of the skeletal system/bone
Support and protection of soft tissues.
Attachment site for muscles → movement
Mineral storage and homeostasis - calcium
Hemopoiesis- blood cell production in red bone marrow
Energy (lipid) storage- in yellow bone marrow
The 3 steps for bone fracture and repair
1. Fracture Hematoma: blood gathers in area of fracture
Callus formation: osteoblasts lay down matrix in fibrocartilage
Remodeling: osteoclasts reabsorb fragments of bone and any excess callus
Compare and contrast the major features of Intramembranous and endochondral ossification
intramembranous:
most bones in the body use endochondral ossification, not Intramembranous.
Does not go thru cartilage stage
Endochondral:
most bone use this
Uses a hyaline cartilage model
Hyaline cartilage on ends of bone remains -> articular cartilage
Factors required for normal bone growth and development (length & diameter)
Bone growth in length
Occurs at epiphyseal plate
Thickness of epiphyseal plate remains constant until cartilage cells stop dividing -> epiphyseal line -> no more growth in length
Bone growth in diameter
Under periosteum, osteoblasts lay down matrix
Factors required for normal bone growth and development (Medullary Cavity)
Osteoclasts eat away at area under endosteum → larger medullary cavity
Remodeling
Osteoclasts carve out small tunnels and osteoblasts rebuild
Osteoporosis
Decrease bone mass → increase in fractures
Decrease osteoblast activity so osteoclast activity outpaces osteoblast actvity
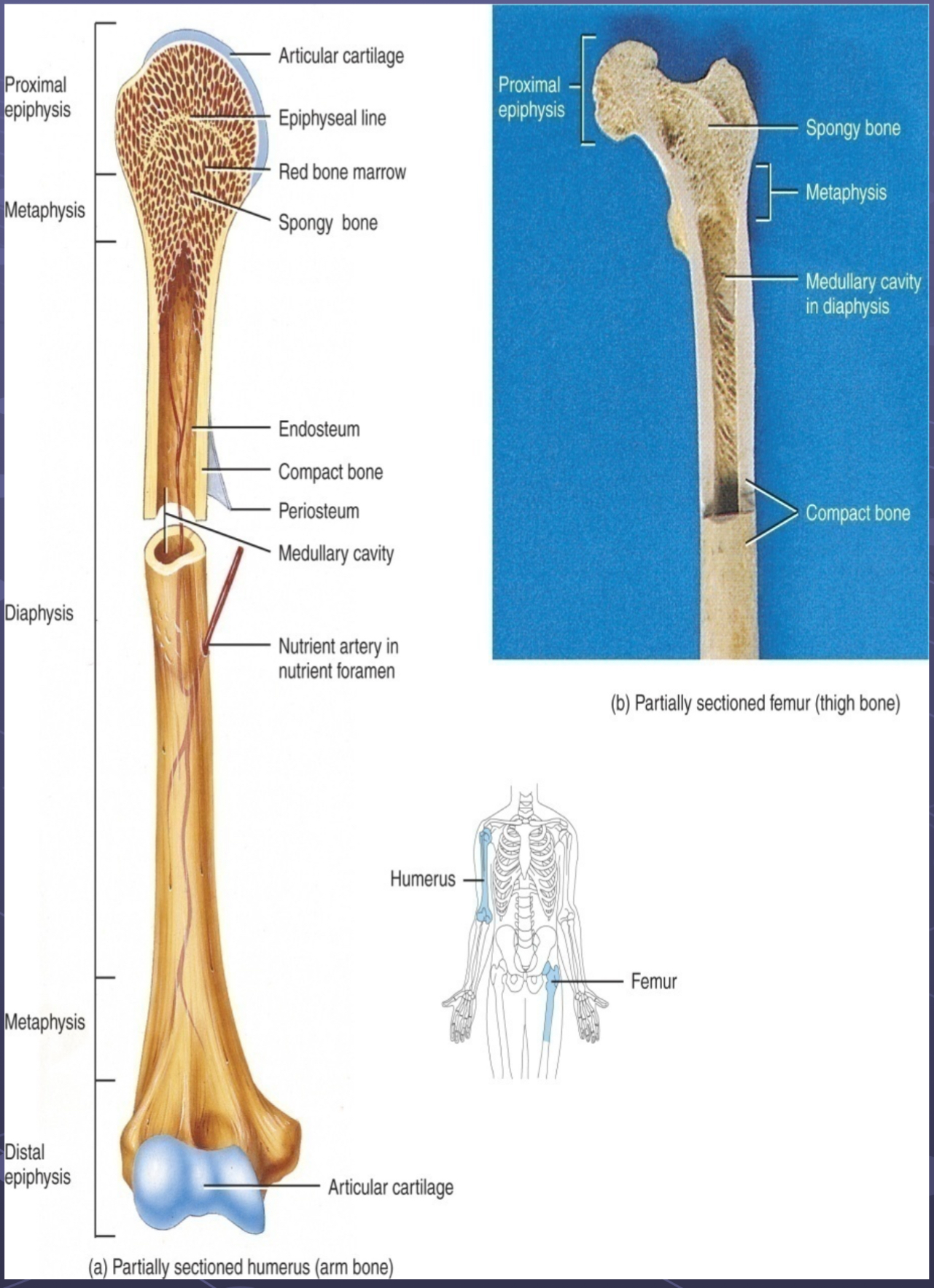
Long Bones (regions, linings/coverings and spaces)
Structure (diaphysis, epiphysis, metaphysis, medullary cavity)
Structure
Diaphysis - (shaft) middle
Epiphysis - ends of long bones, proximal and distal
= spongy bone filled with bone marrow
= hemopoiesis
Metaphysis - epiphysis and diaphysis meet; contains epiphyseal plate (growth plate) in growing bone, where growth in length occurs, ossifies → epiphyseal line in adult (no more growth in length)
Medullary Cavity- yellow marrow
= fat/lipid storage
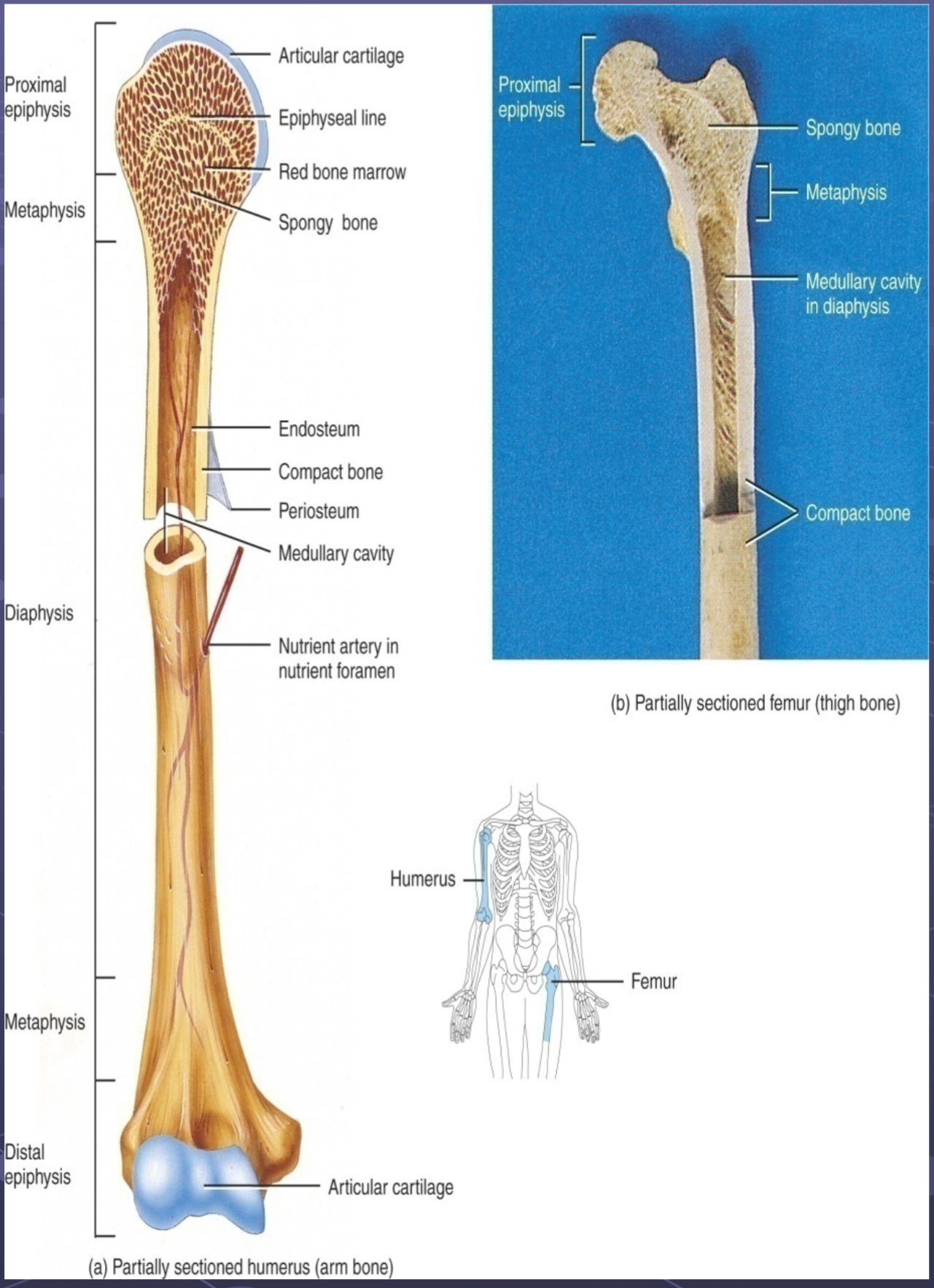
Long Bones (regions, linings/coverings and spaces)
Coverings and linings (articular cartilage, edosteum, periosteum)
Articulate cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Covers ends of bones/joint surfaces → reduces friction, acts as shock absorber
Endosteum
Membrane lining the medullary cavity
Contains osteoclasts which helps break down bone to make medullary cavity larger
Periosteum
Tough membrane covering outer surface of bone (not cartilage)
Growth in diameter occurs under this
Osteoclasts = new bone
Tendons and ligaments attach here
Does not cover bone ends
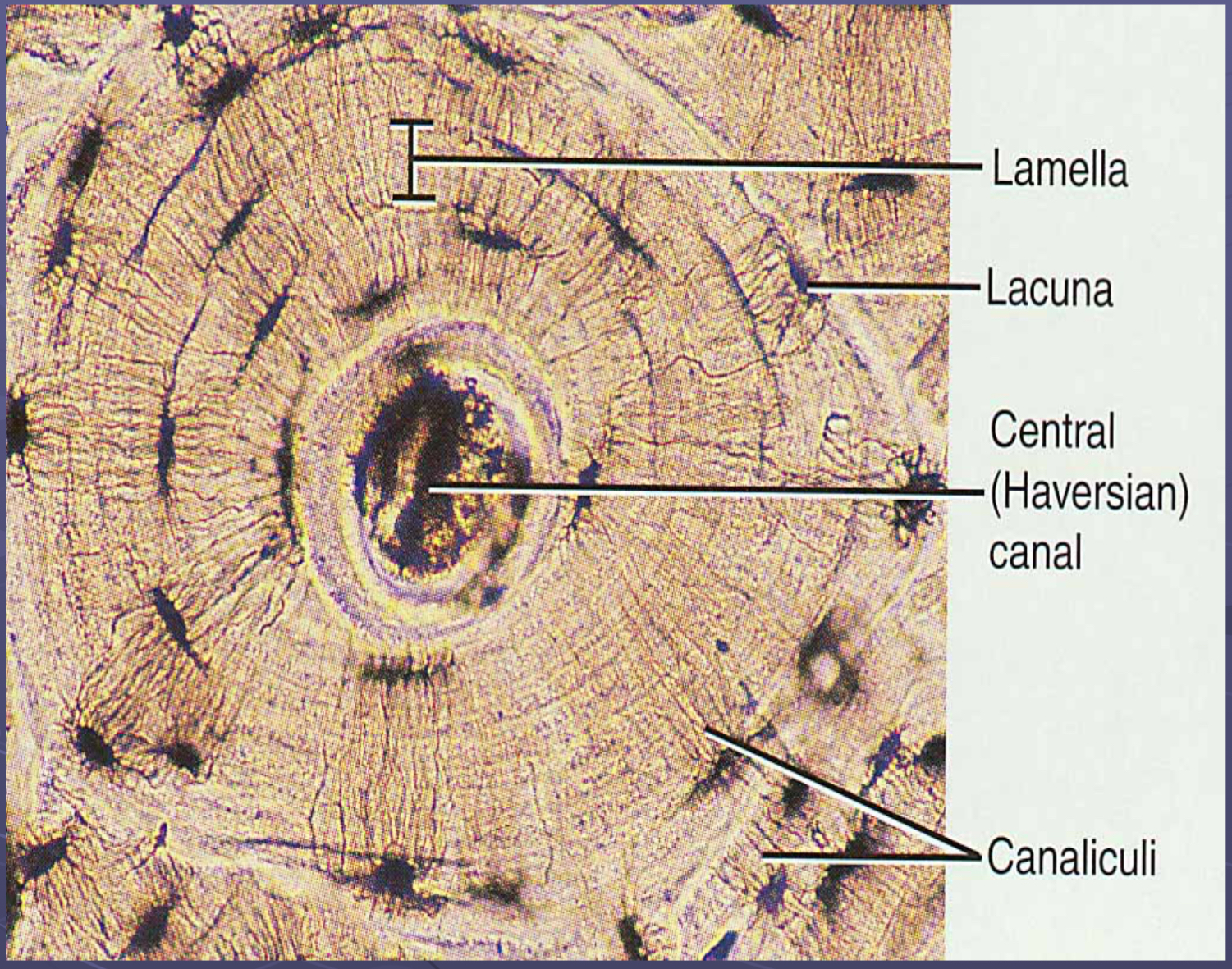
Parts of compact bone (osteon, lamelle, canaliculi, lacunae, central canal, perforating canals, interstitial lamelle, etc)
Osteon
Set of concentric rings= lamellae
Central canal = center of osteon
Perforating Canal
Blood vessels pass thu periosteum & horizontally into bone thru perforating canal
Lamellae
Rings
Lacunae
Spaces which contains osteocytes, between lamellae
Canaliculi
Small canals which radiate out from lacunae - contains osteocytes reaching out to contact other osteocytes
Interstitial Lamellae
Fragments of old osteons found between new osteons
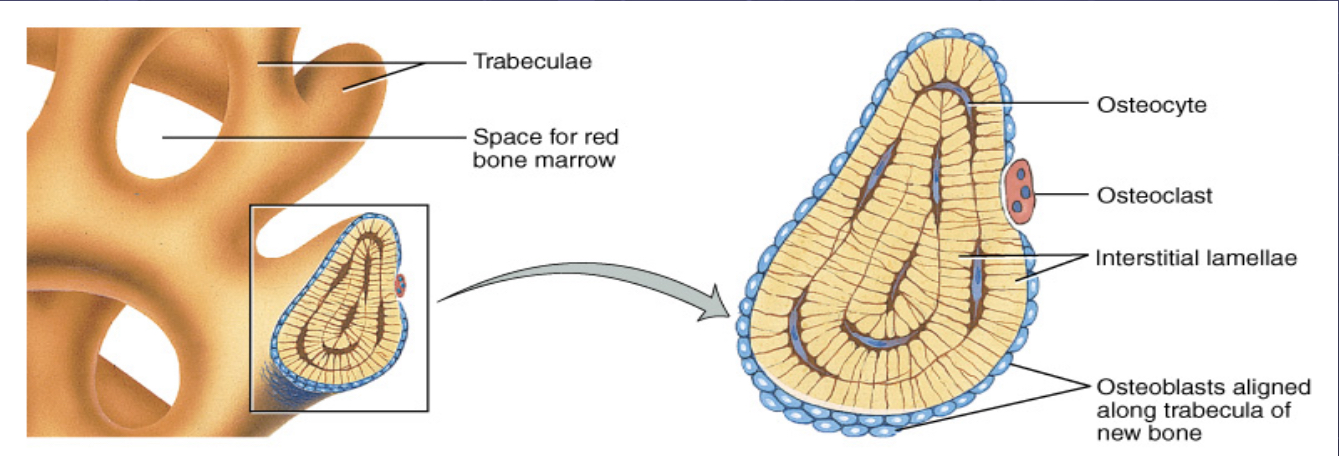
Parts of Songy Bone (Trabeculae and red bone marrow)
Location
Inside epiphysis of long bones
Inside all other types of bones
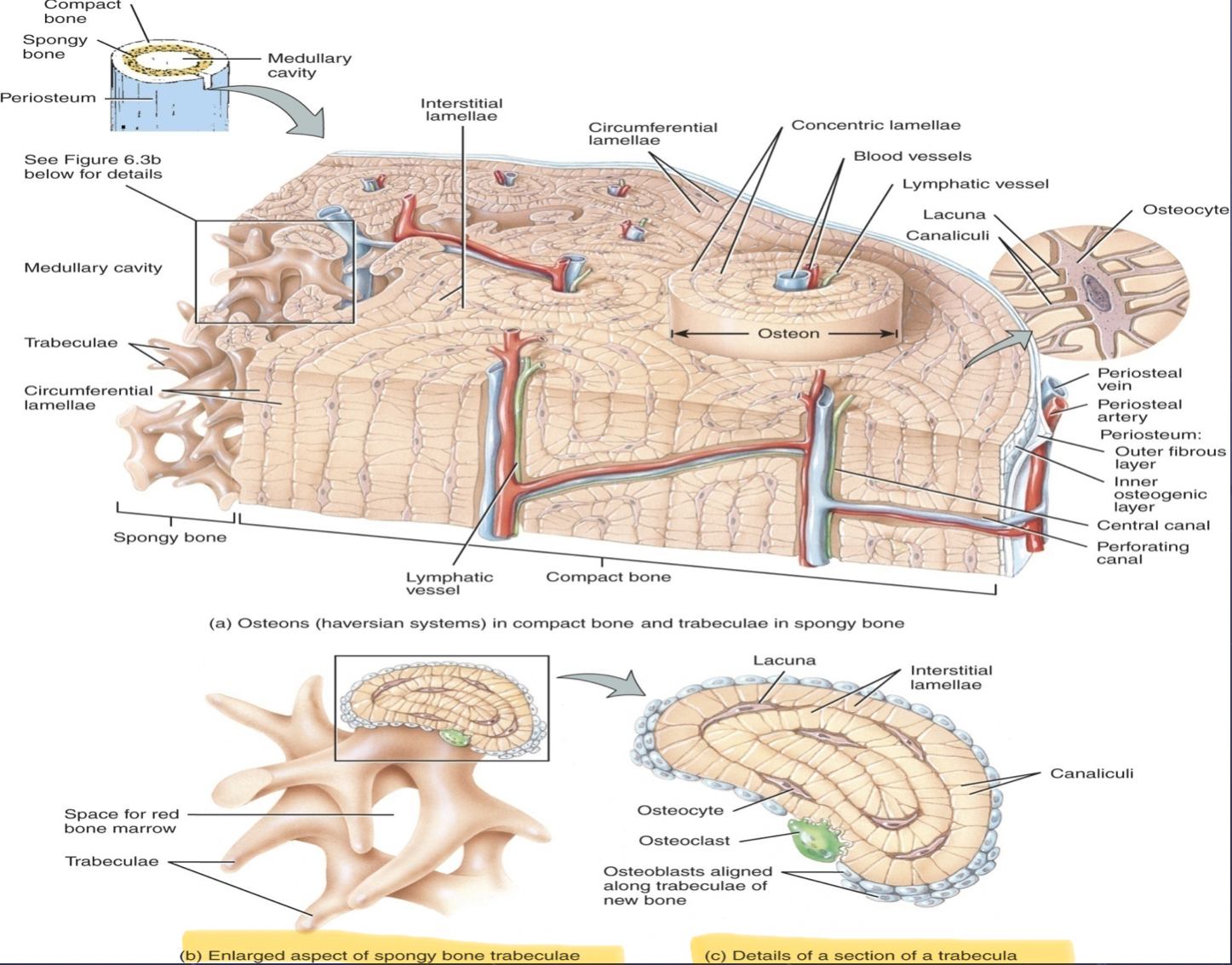
Parts of Songy Bone (Trabeculae and red bone marrow)
Open spaces which contains osteocytes reaching red bone marrow
Trabeculae
Thin shelf-like projections of bone
No true osteons
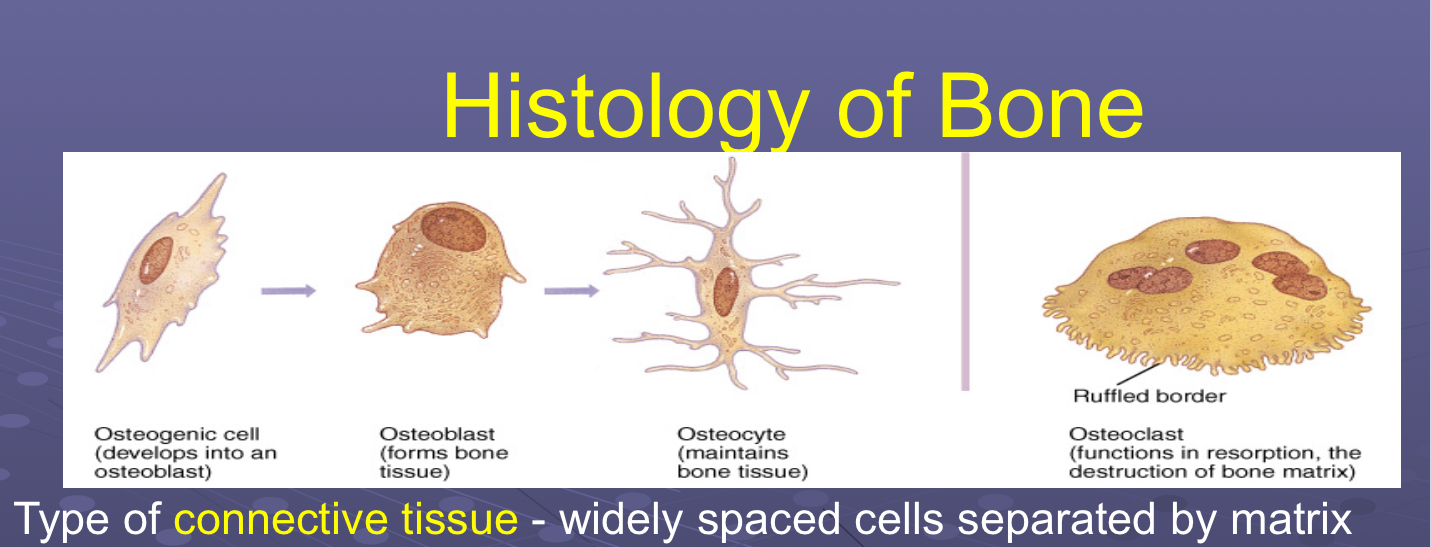
Compare and contrast 4 major cell types found in bone (osteogenic, osteocyte, osteoclast, osteoblast)
Osteogenic
Unspecialized/undifferentiated stem cells → osteoblasts
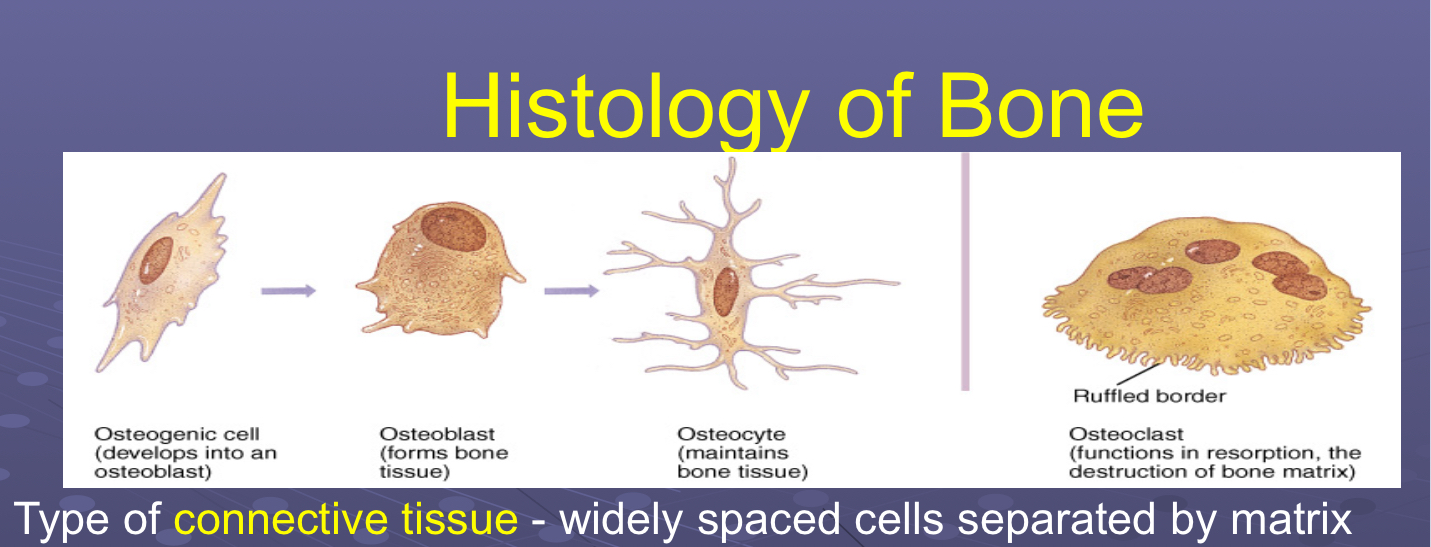
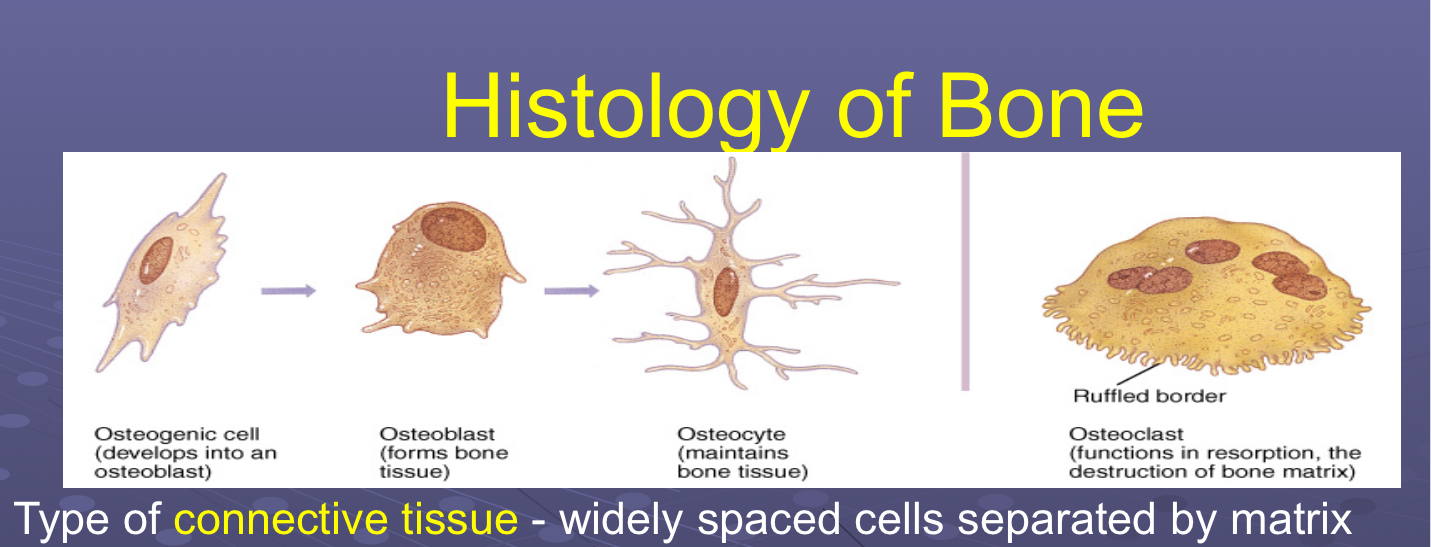
Compare and contrast 4 major cell types found in bone (osteogenic, osteocyte, osteoclast, osteoblast)
Osteoblasts
Bone forming/building cells → osteocytes
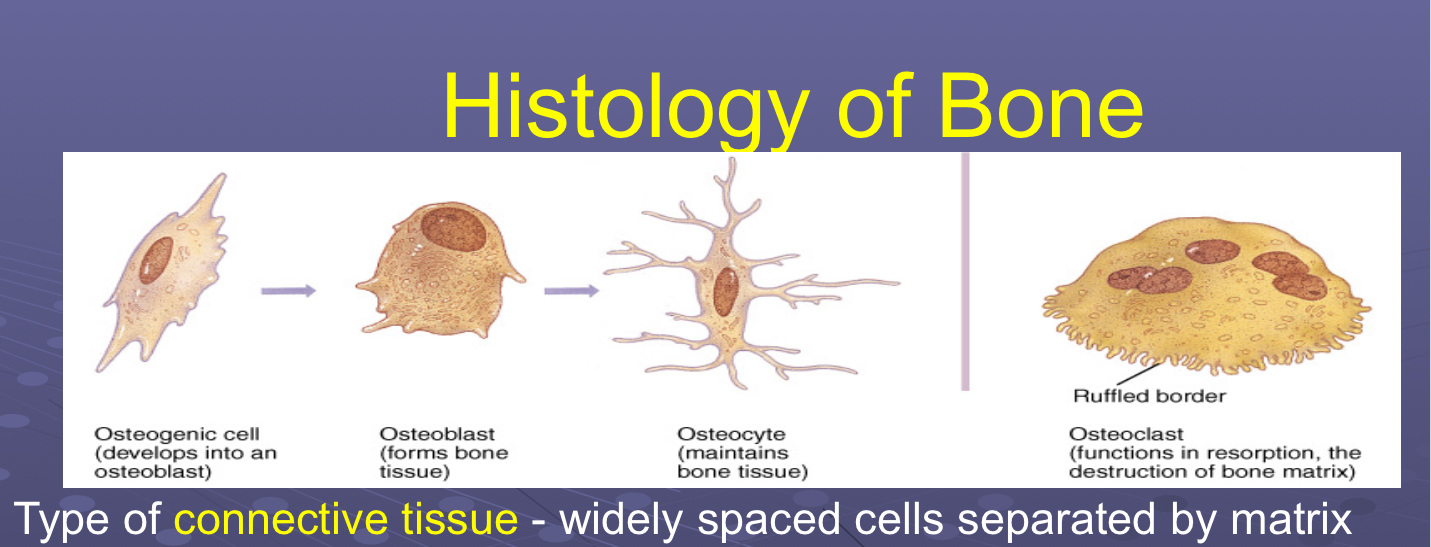
Compare and contrast 4 major cell types found in bone (osteogenic, osteocyte, osteoclast, osteoblast)
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells contained in lacunae
Compare and contrast 4 major cell types found in bone (osteogenic, osteocyte, osteoclast, osteoblast)
Osteoclasts
Break down bone (resorption) for remodeling, repair, make medullary cavity larger