Chap 24 Aquatic Ecosystems
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
aquatic ecosystem
An ecosystem located in a body of water
- classified based on features of the physical environment

Salinity
the amount of salt in water
- is a major feature that influences aquatic organisms

freshwater ecosystem
bodies of water with Low salt levels
- Lentic
- Lotic

Lentic
non-flowing water
----------------
EXAMPLE:
- ponds
- lakes
- wetlands

Lotic
flowing water
----------------
EXAMPLE:
- rivers
- streams

marine ecosystem
bodies of water with high salt levels
-----------------
- Open water
- coastal

What makes the ocean salty?
Erosion of rocks and minerals

Abiotic factors in aquatic systems
- oxygen
- temperature
- light
How can oxygen impact aquatic systems
Limiting oxygen would allow decomposers to consume large quantities of oxygen needed for respiration
(especially during the summer)
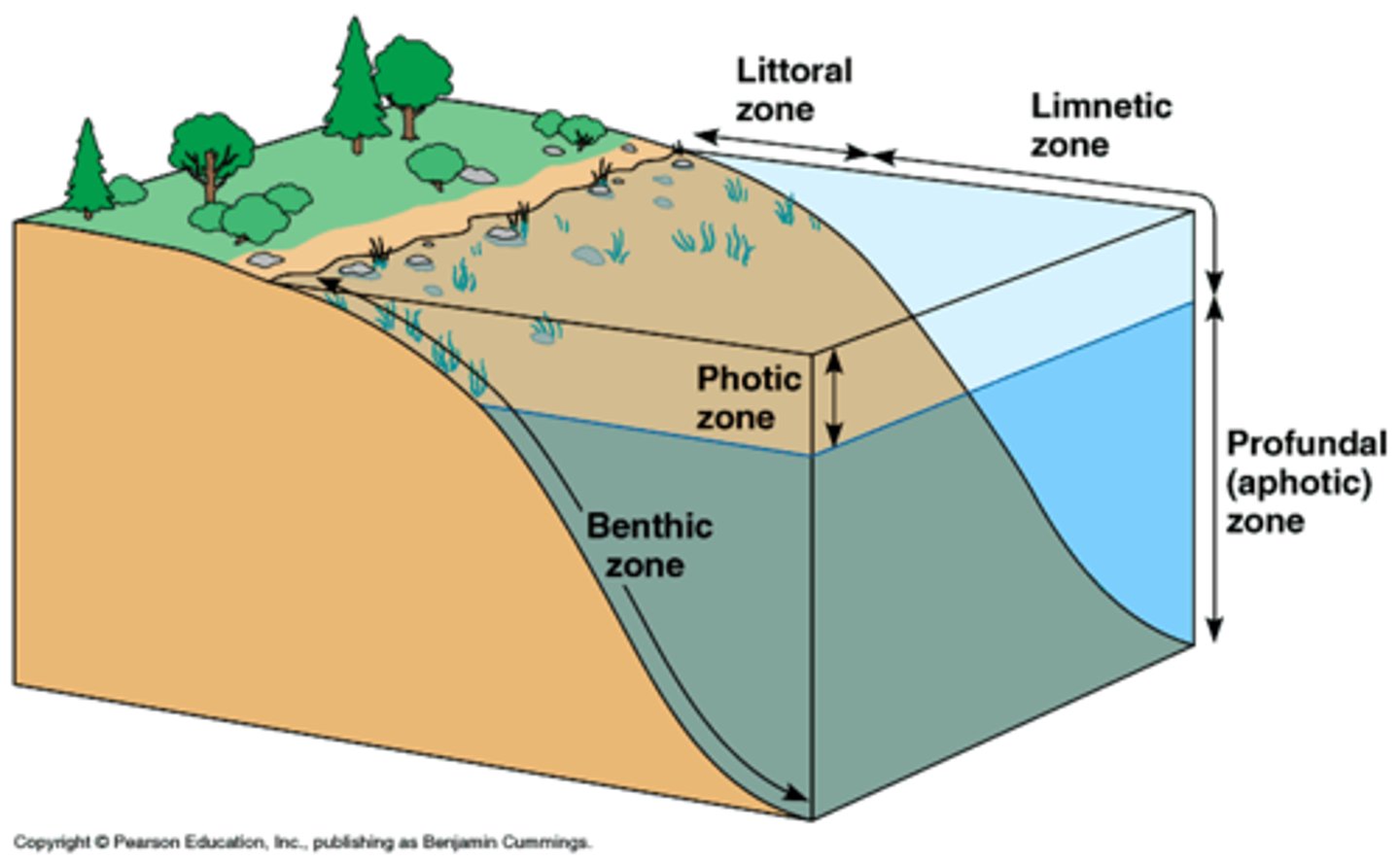
Horizontal zones (lakes and pond)
- littoral zone
- limnetic zone
littoral zone
shallow water zone with light reaches the bottom
- near shore
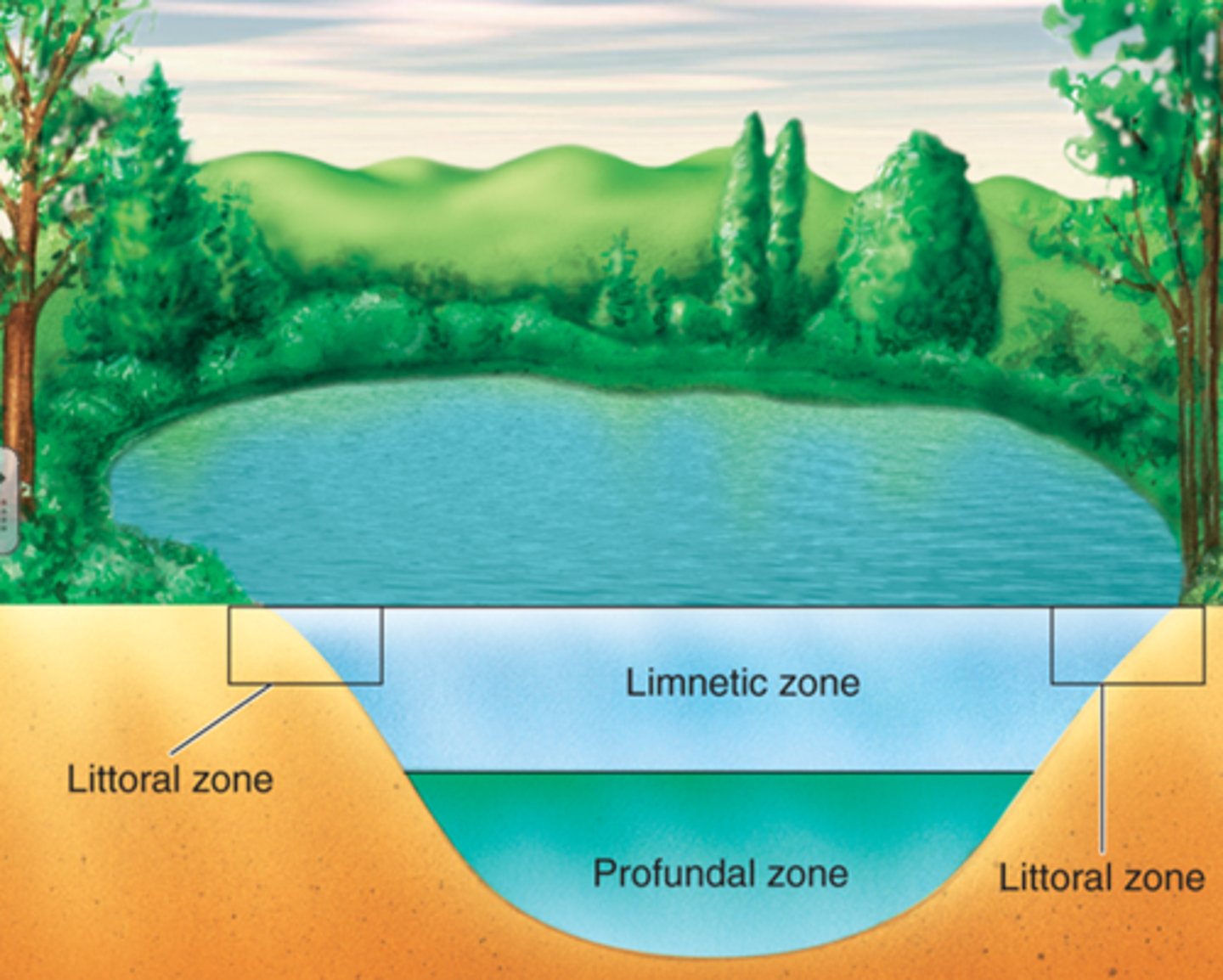
limnetic zone
open water that extends to the depth of light penetration
- further away from shore
Plankton
Tiny organisms that float/drift in the water
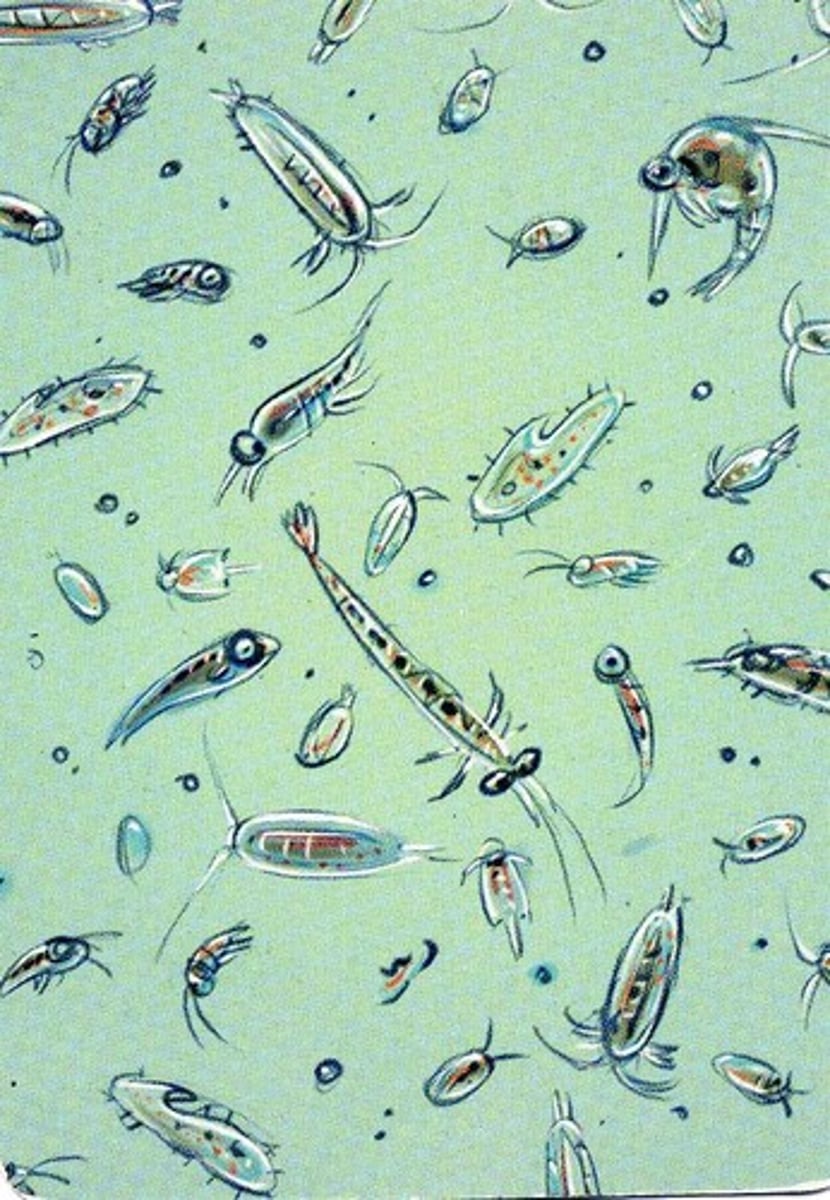
Nekton
free-swimming animals that can move throughout the water column

vertical zones
- Profundul zone
- Benthic zone
Profundul zone
beyond the depth of effective light penetration
- where respiration balances photosynthesis
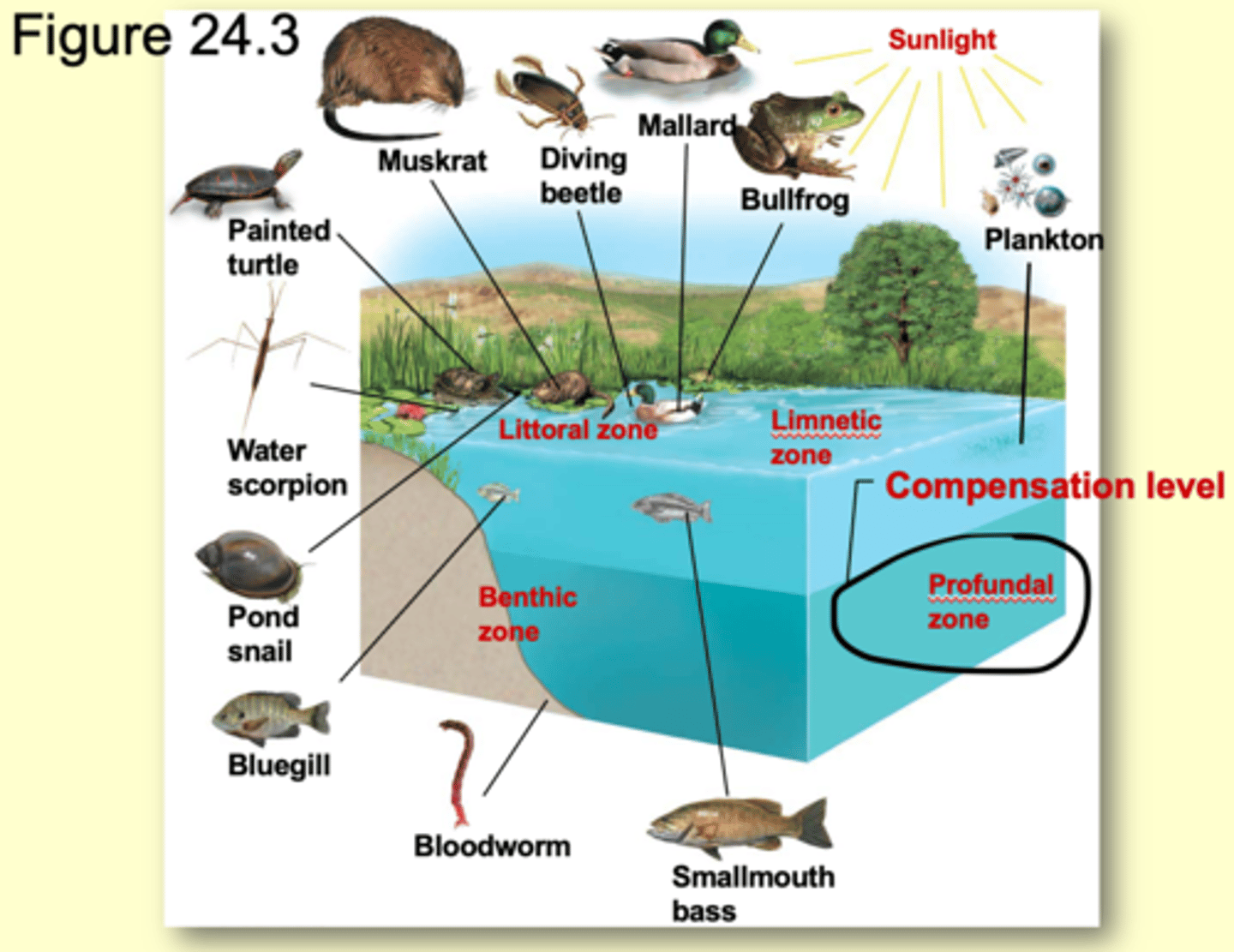
benthic zone
bottom region that is the primary place of decomposition
- muddy bottom of the lake/pond
What lives in the benthic zone?
anaerobic bacteria

How do Benthic zone organisms get there food?
Either by:
- sunken dead organisms
- waste products

Oxygen levels in vertical zones
- oxygen may be limiting
- less plant life
- little to no light (for photosynthesis)
which zone is life most abundant in ponds and lakes?
Littoral
- most source of food
- most source of soil
- most source of sunlight
--------------------
- is rich in diversity of animals associated with emergent and floating plants

Invertebrates (littoral zone)
- snails
- protists
- dragonflies
- diving insects

vertebrates (littoral zone)
- fish
- birds
------------------
- many species of fish have compressed bodies that allow them to move through aquatic plants

What organisms dominate the limnetic zone?
- Phytoplankton
- zooplankton
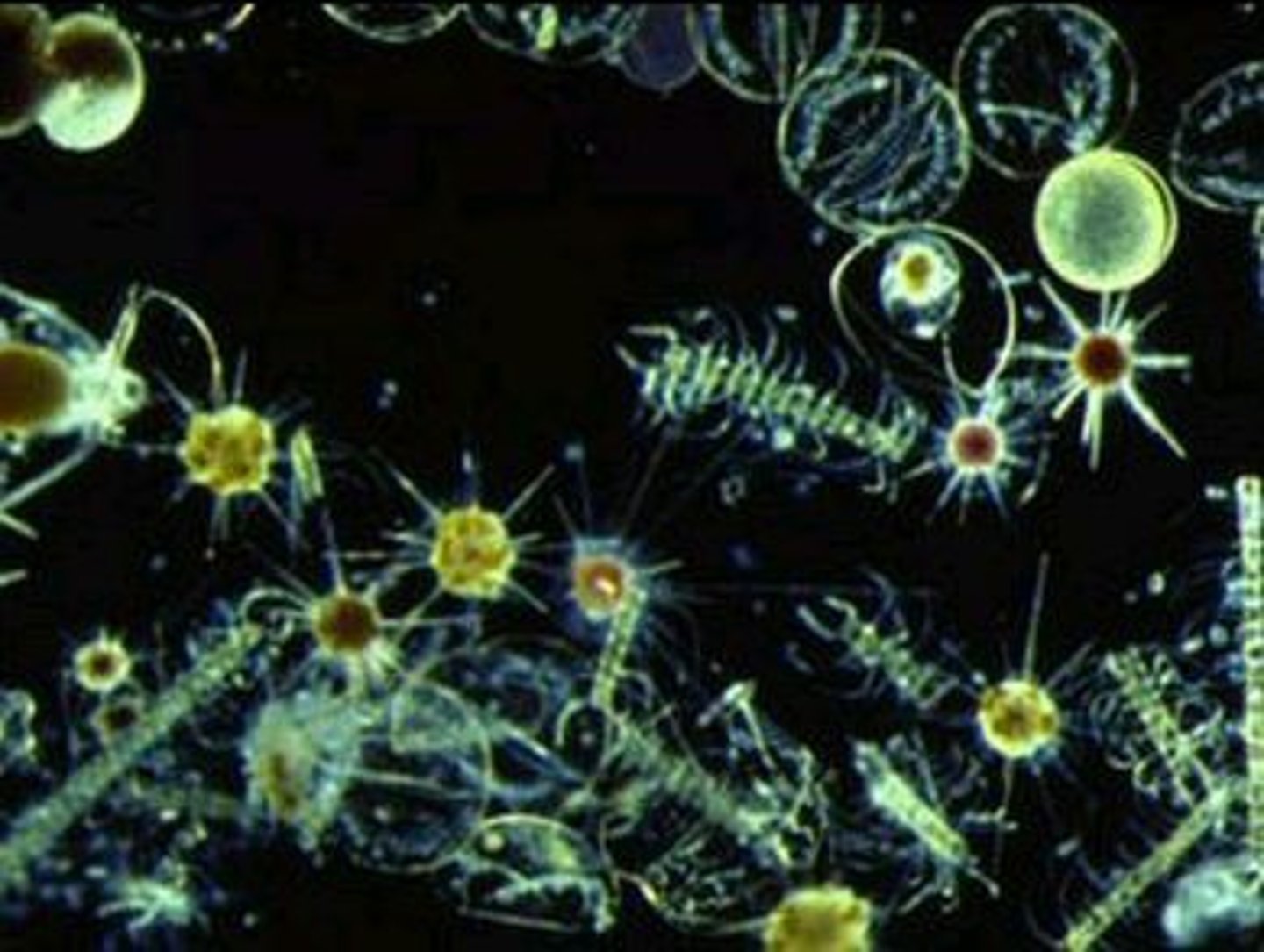
Phytoplankton
Primary producers in open water ecosystems
----------------
EXAMPLE:
- diatoms
- algae
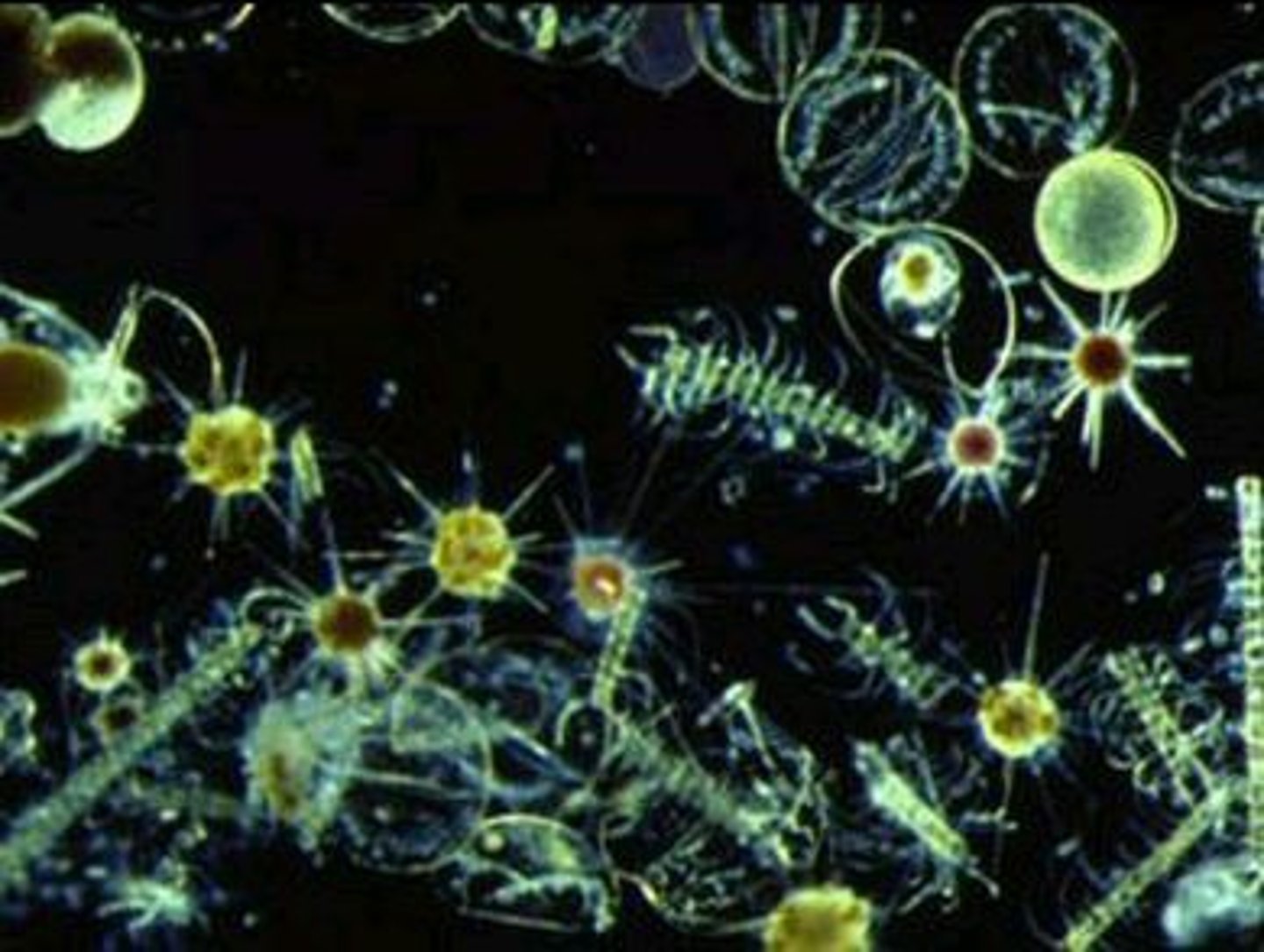
Zooplankton
small free-floating animals that form part of plankton
- feed on phytoplankton to form an energy flow in the limnetic zone
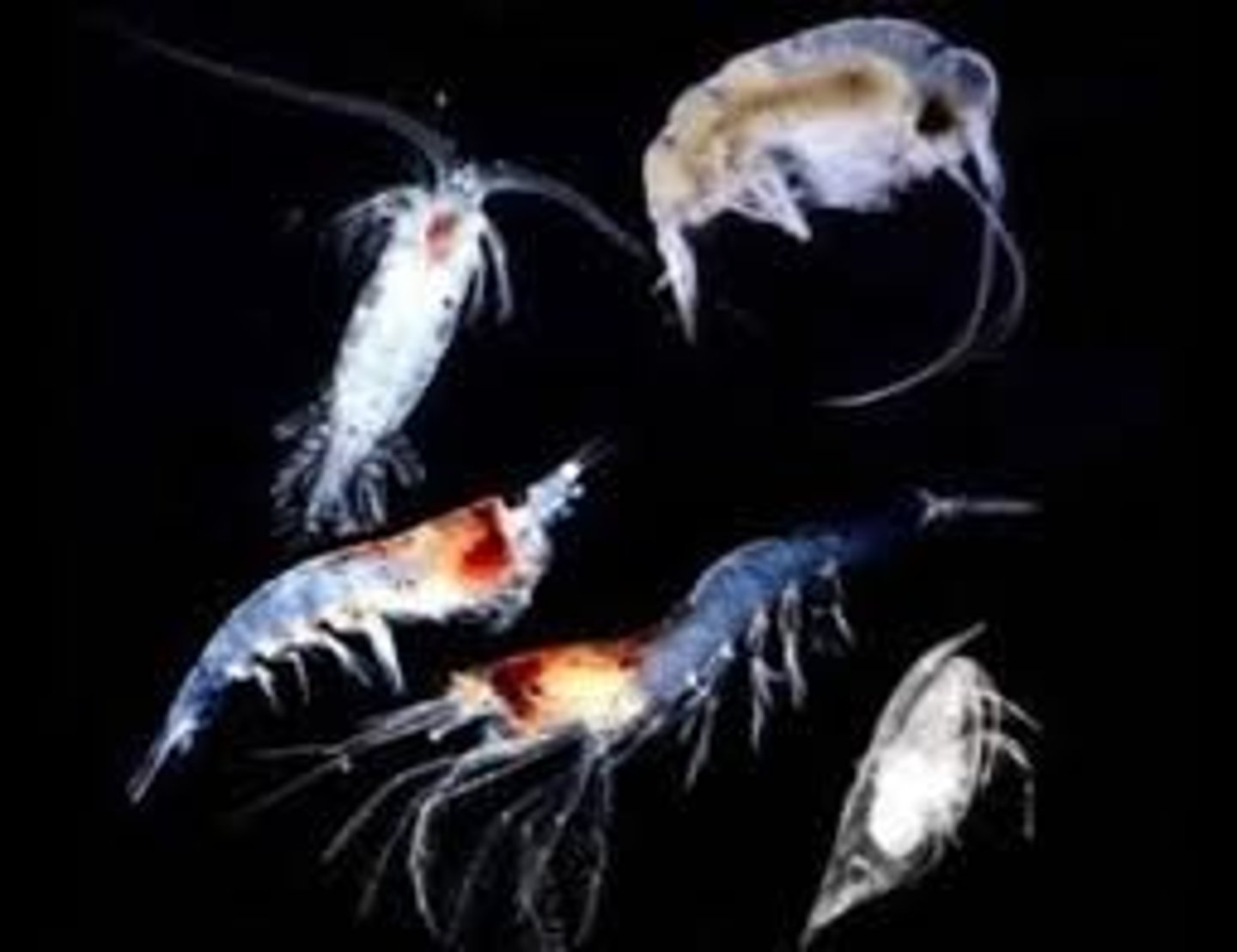

Streams
body of flowing water confined within a channel, regardless of size

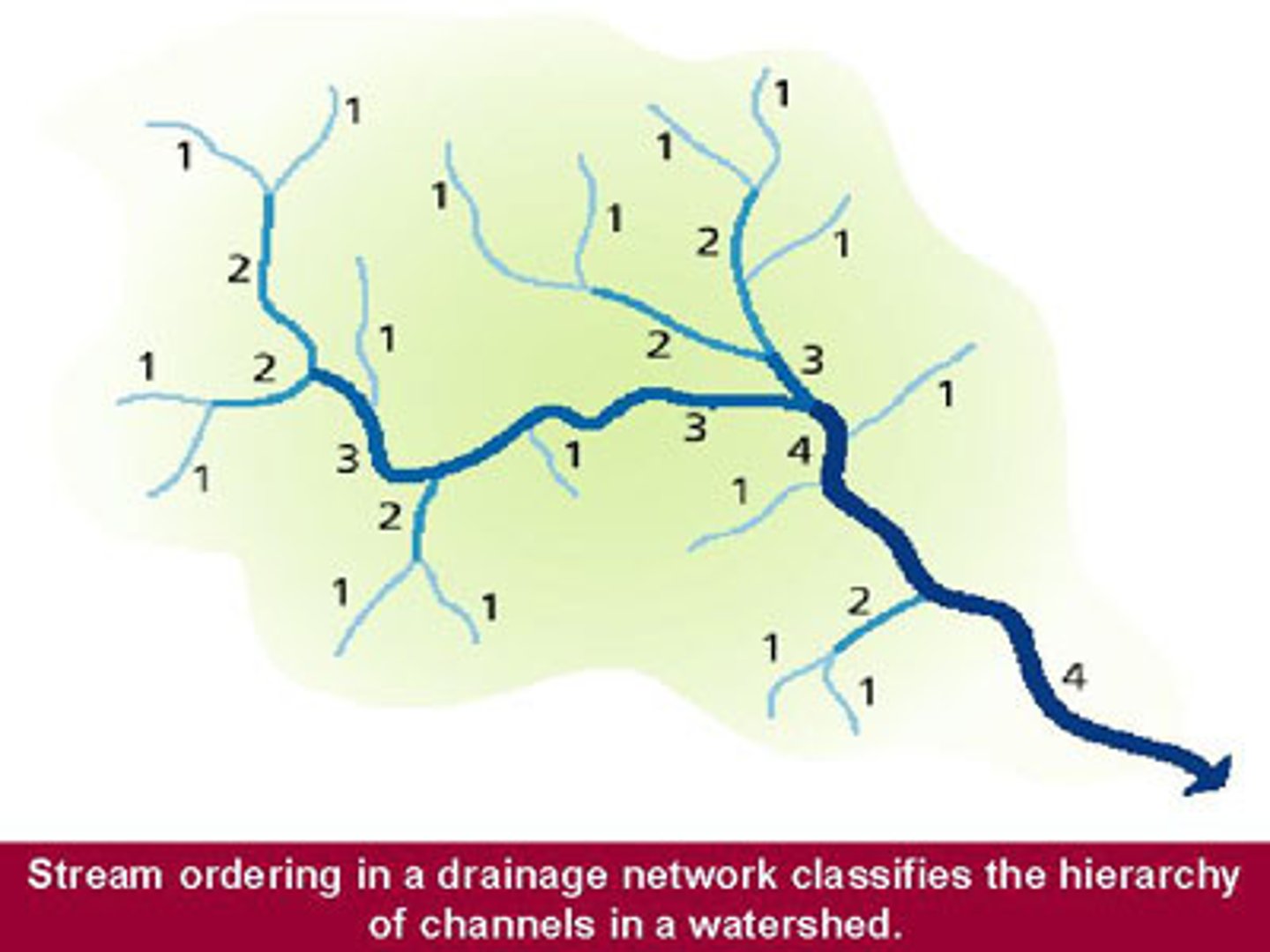
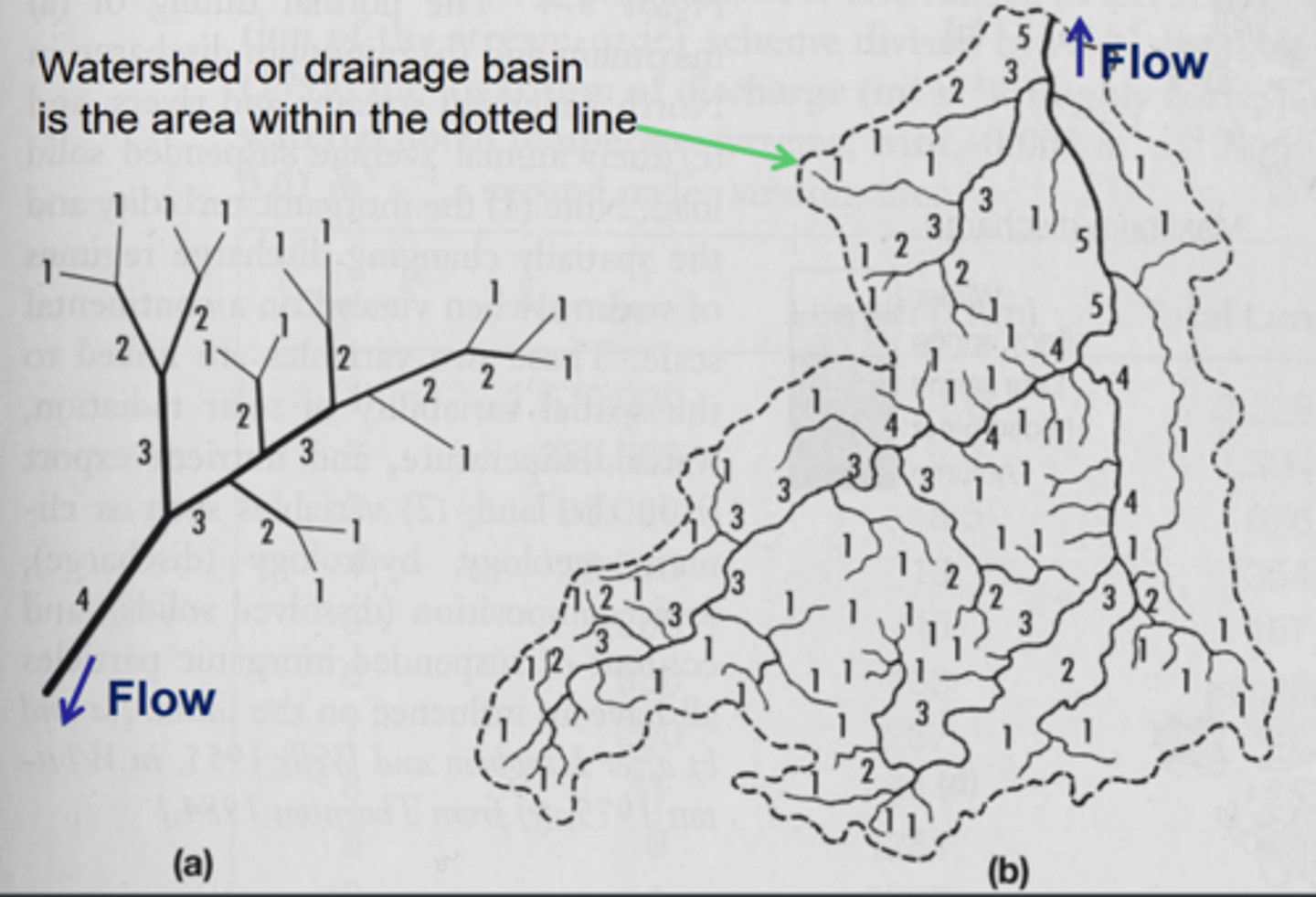
How are streams classified
according to the order of the stream
- can only increase in order when the same order of stream joins it
------------------
EXAMPLE:
- First order
- Second order
- Third order
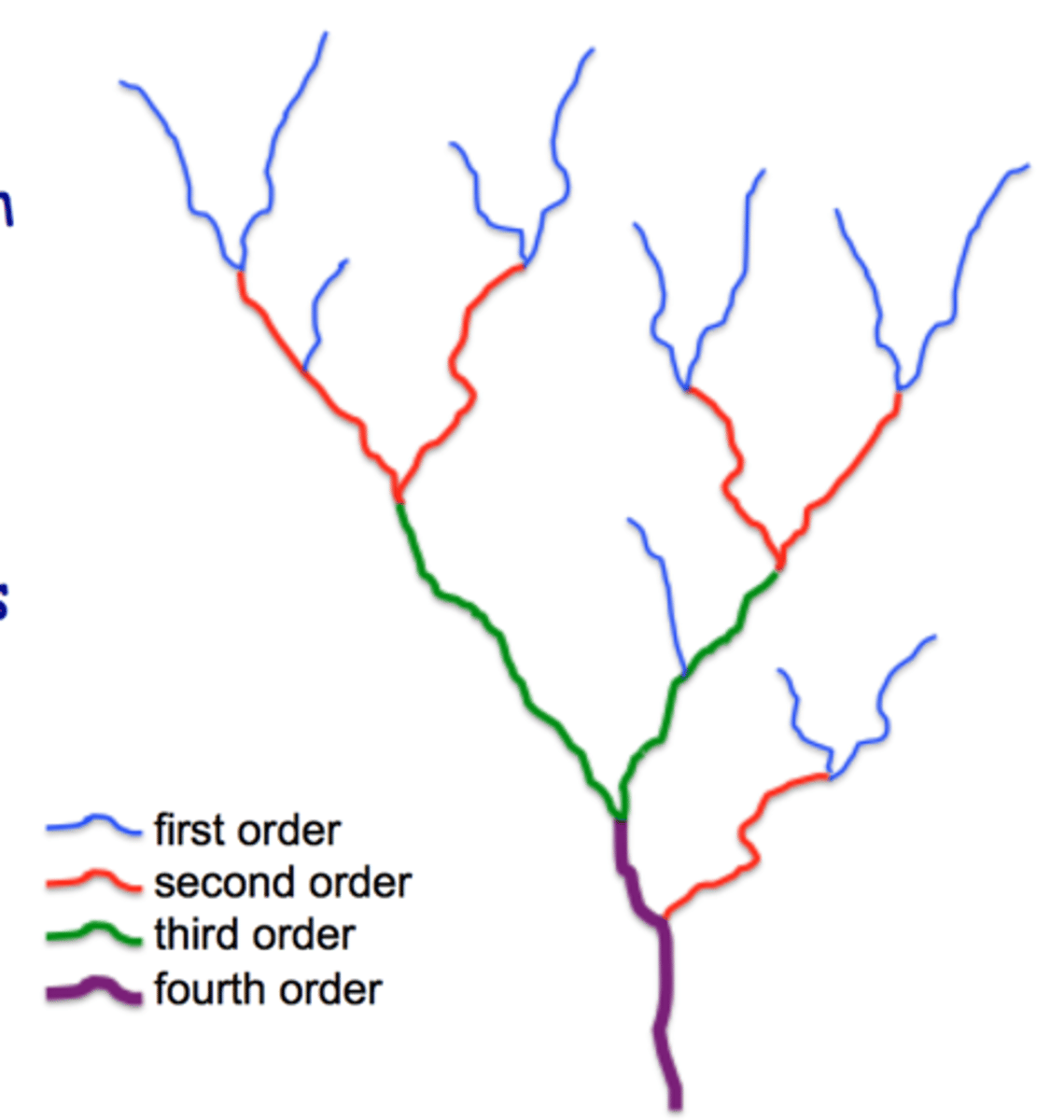
first-order stream
a small headwater stream with no tributaries
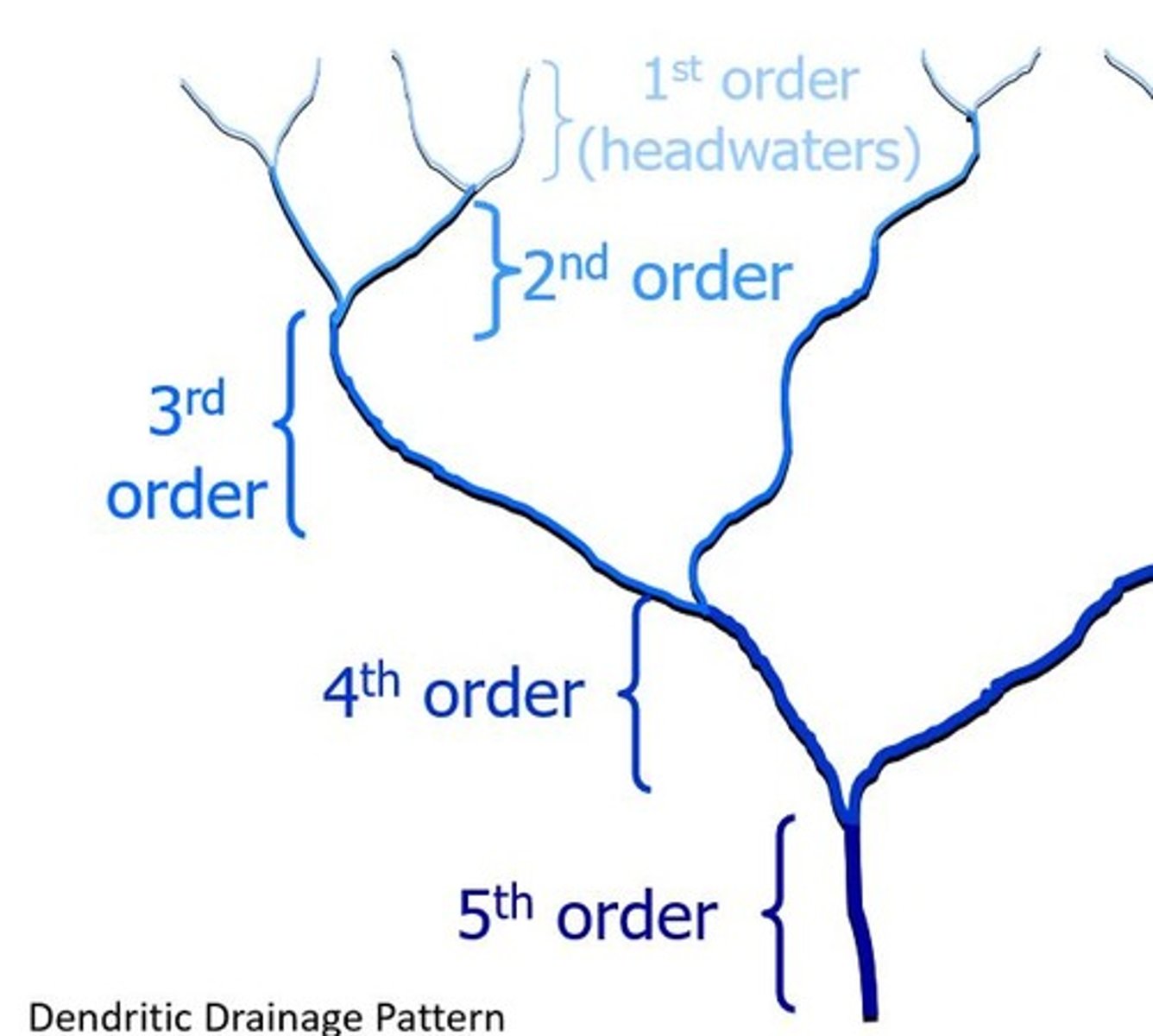
second-order stream
two first-order streams join together
third-order stream
two second-order streams join together
headwater streams (orders)
1-3
medium-sized streams (orders)
4-6
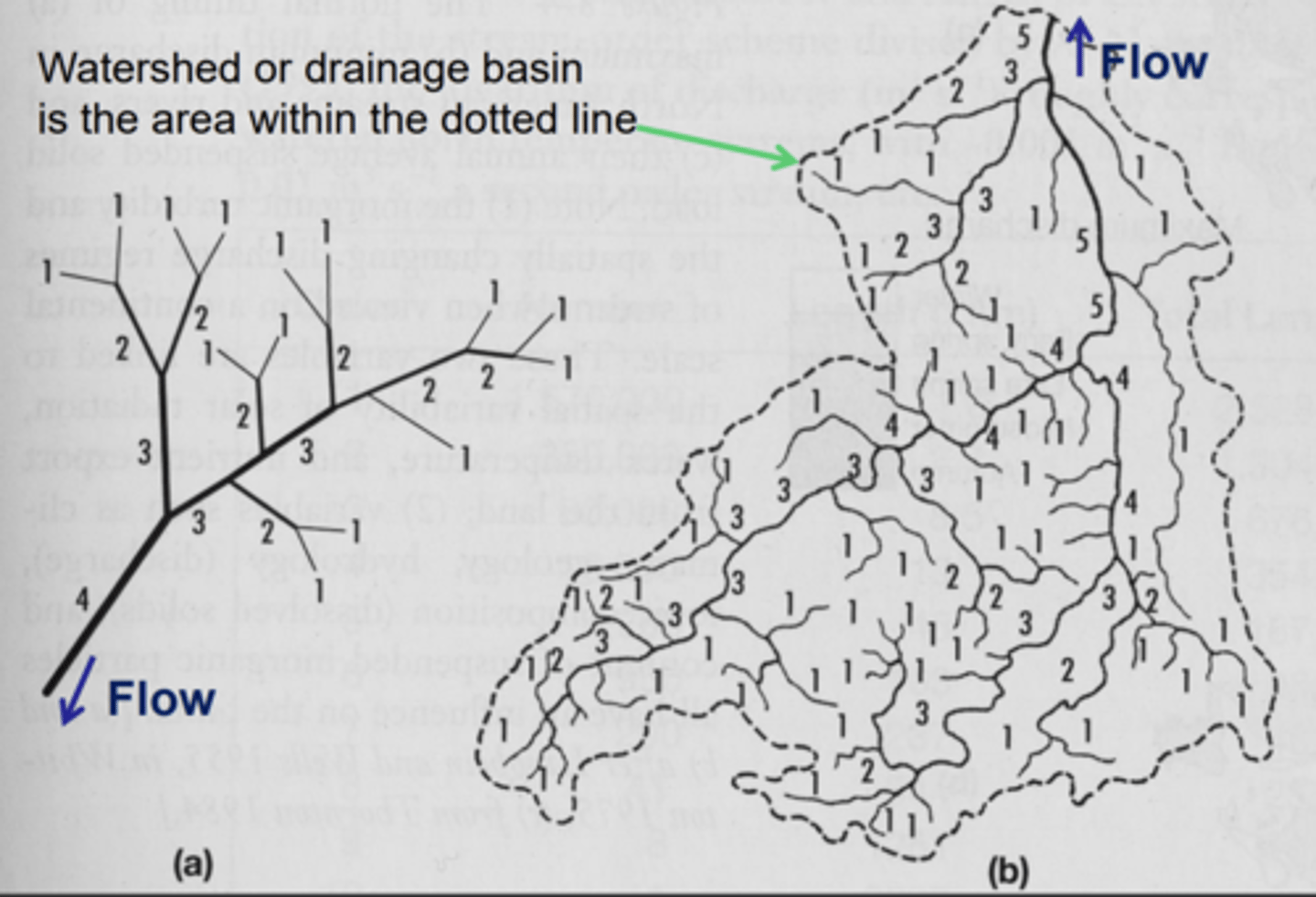
Rivers (orders)
+6
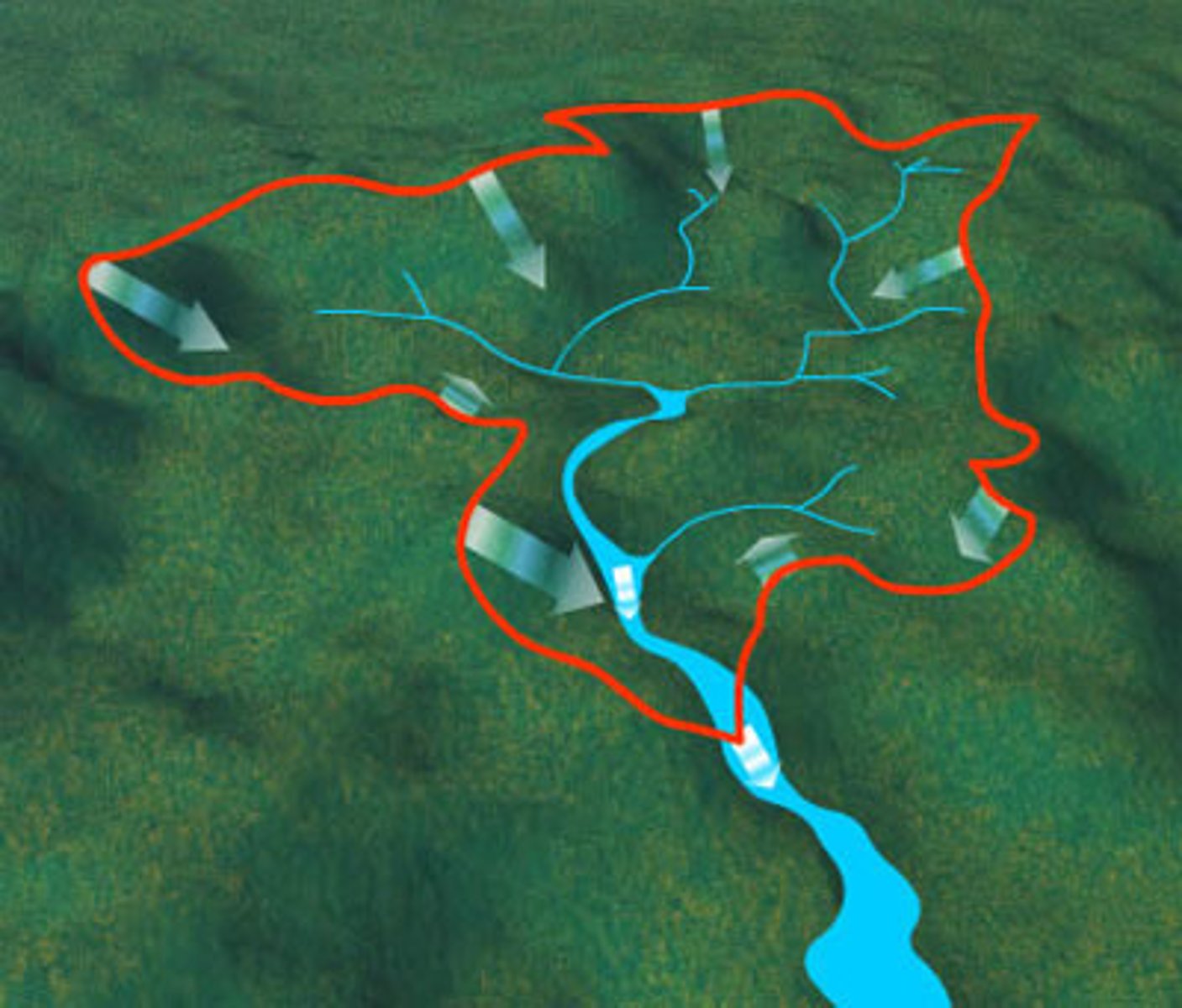
Watershed
all water runoff drains into a single body of water
How does current velocity affect species composition?
- Faster water increases O2 levels due to the mixing of air
- influences the topography of the stream bed
- can disrupt fragile/ small organisms (or mix nutrients)
Current velocity is affected by...
- shape and steepness
- intensity of rainfall or rapidity of snow melt
shape and steepness (current velocity)
FACTORS:
- width
- depth
- bottom roughness

intensity of rainfall or rapid snowmelt (current velocity)
FACTORS:
- how fast
- how strong
- how much pressure
------------------
HINT: think of it as blood pressure (how much blood is circulating through your veins)

Formula for streamflow
(m^2) x (meter/second) = m^3/sec
Organisms living in flowing water
face the challenge of staying in place instead of being swept downstream
- probably due to the shape of fish (more thinner)
animals living in fast water streams have number of adaptations such as....
- streamed lined form
- flattened bodies and broad
- protective cases
- sticky undersurfaces
stream lined form (fast-water streams)
allows for fish to have less resistance to water current
Flattened bodies and broad, flat limbs (fast-water streams)
allows for many insect larvae to cling to the underside of stones where the current it weak

protective cases (fast-water streams)
cement some larvae to the bottom of stones

sticky undersurfaces (fast-water streams)
helps snails and planaria to cling tightly and move on stones/rubble in the current

plant body form (fast-water streams)
- water moss and filamentous algae cling to rocks by strong holdfasts
- some algae grow in cushion like colonies or form sheets that lie flat against substrate surfaces
Oceans
large bodies of salt water
- marine environment covers 70% of Earth's surface and is deep (some places > 10 km)
Oceans (sunlight)
the surface area recieving sunlight is relatively small compared to its total volume
What are the seas interconnected by
currents
- influenced by wave actions and tides and characterized by salinity
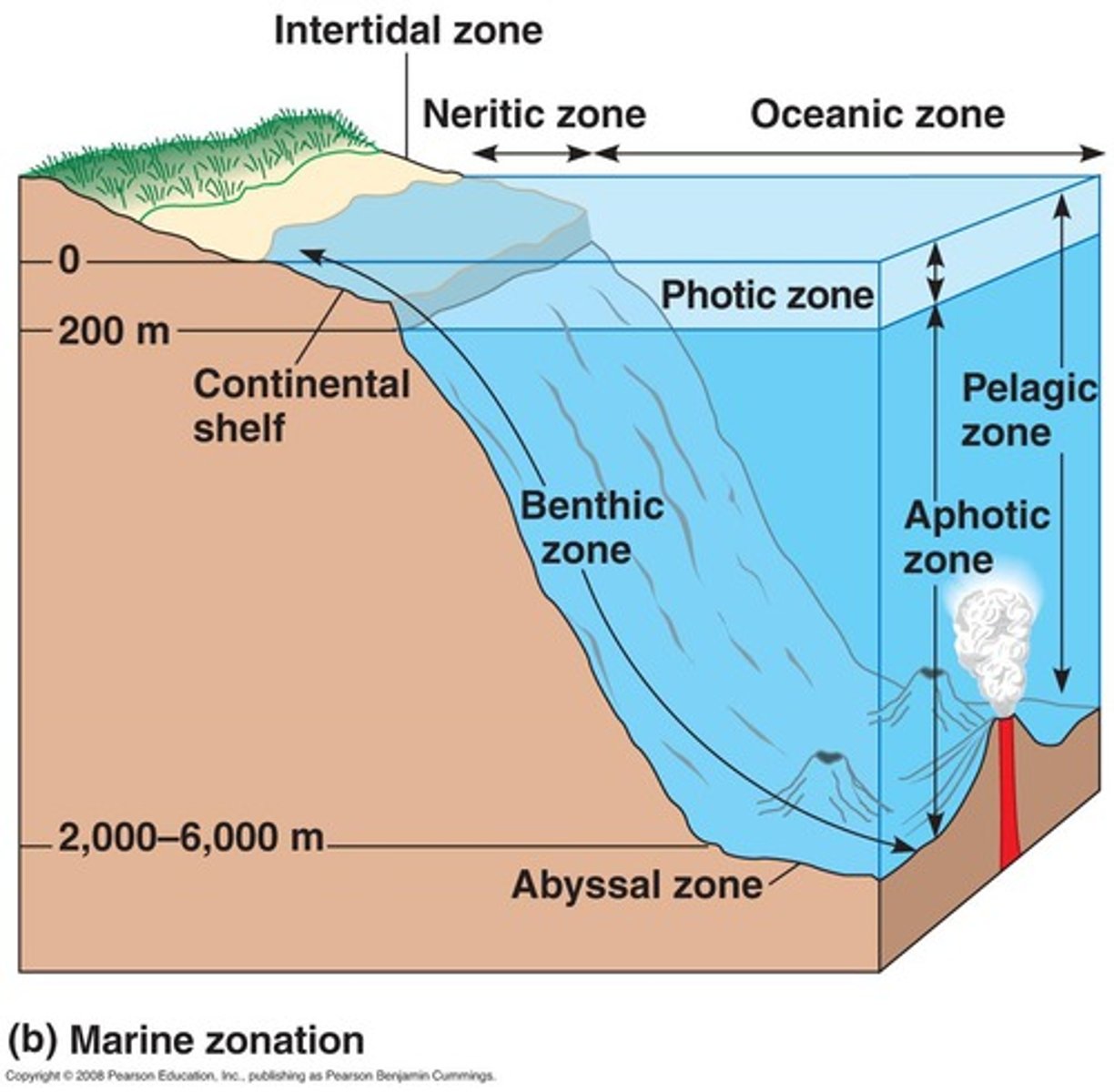
benthic zone (ocean)
the bottom region of oceans and bodies of fresh water
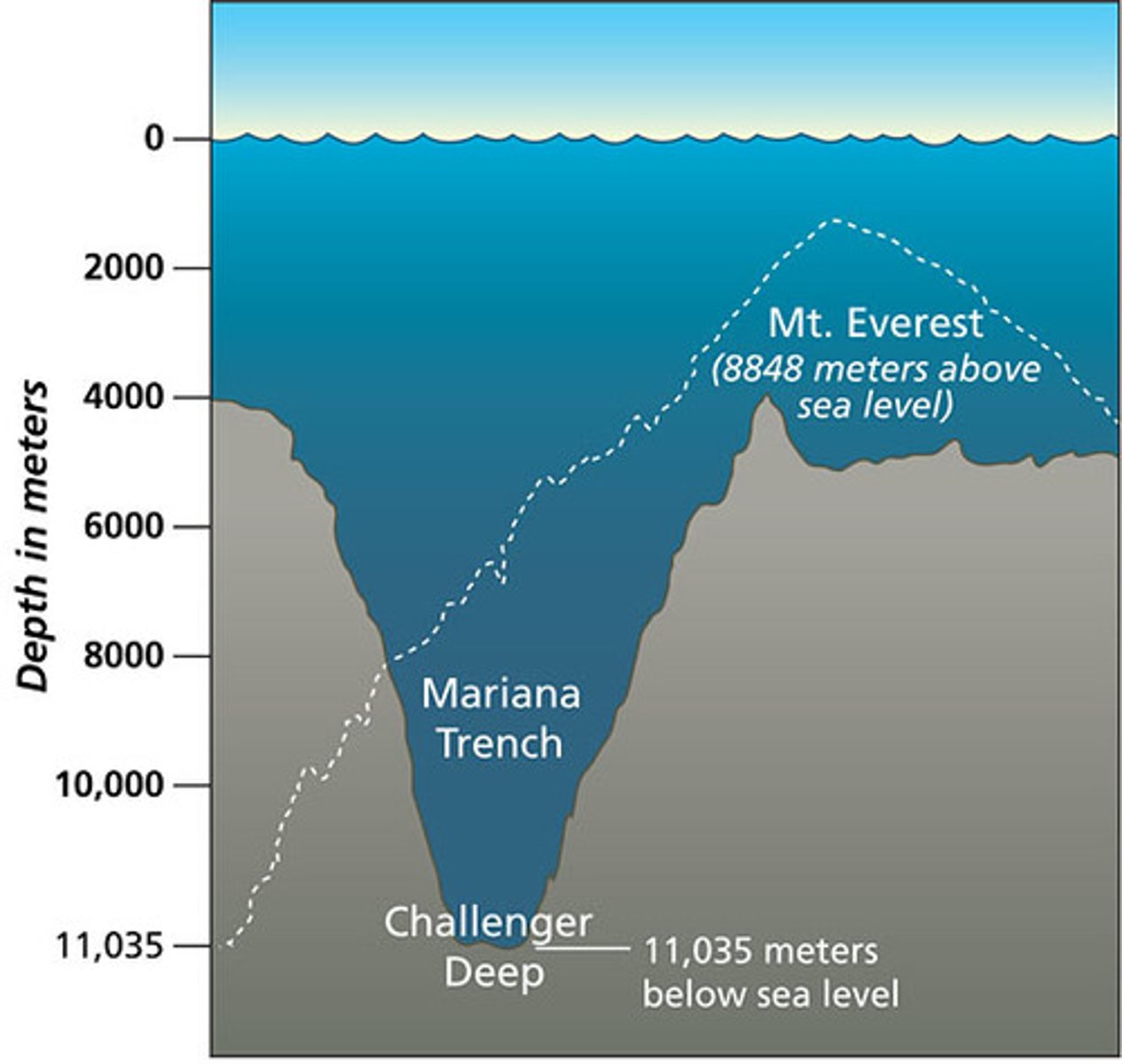
pelagic zone (ocean)
whole body of water (open water zone)
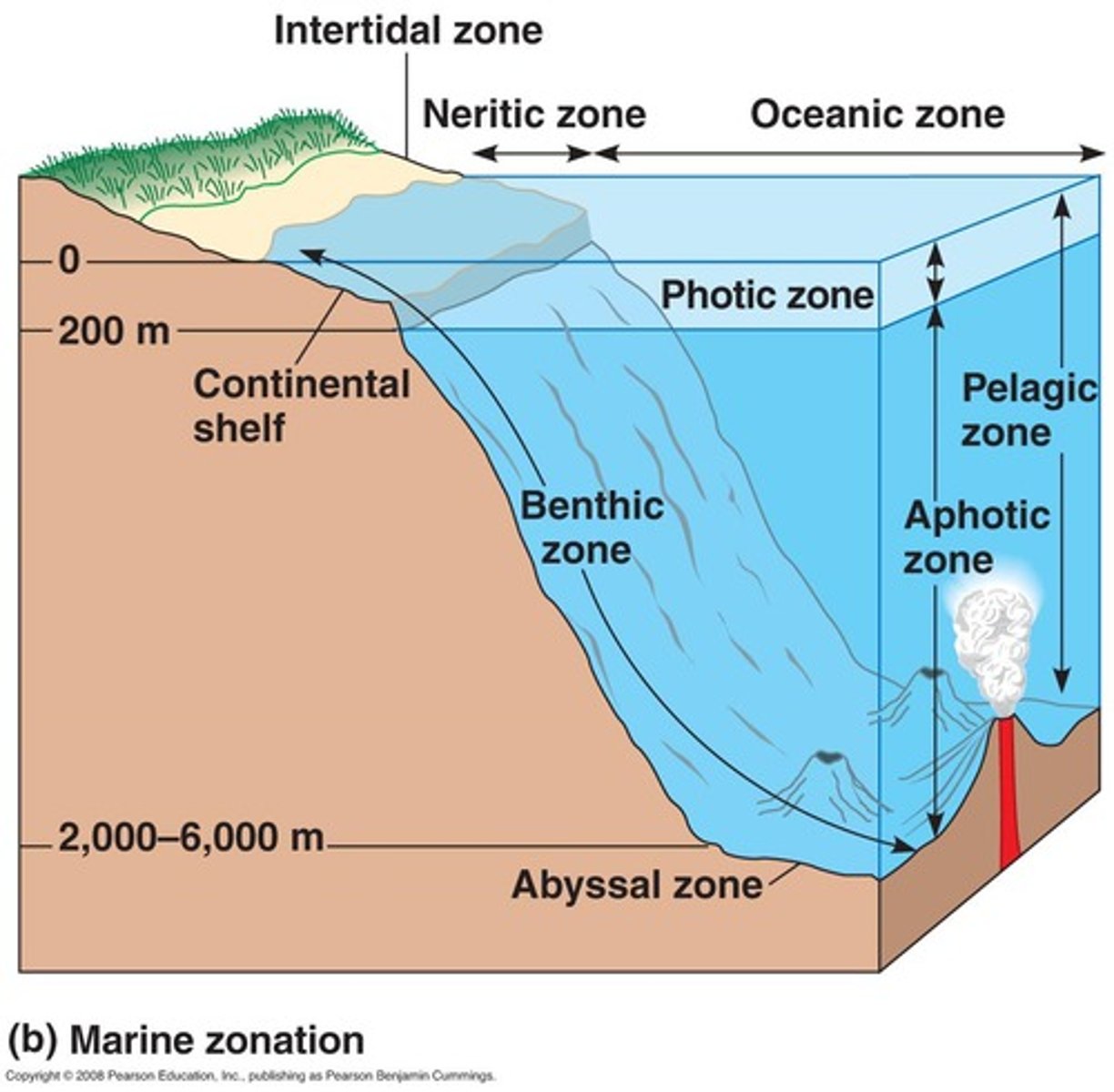
What are some ways life is tougher down the 6000m depth (ocean)
- more pressure
- less visibility
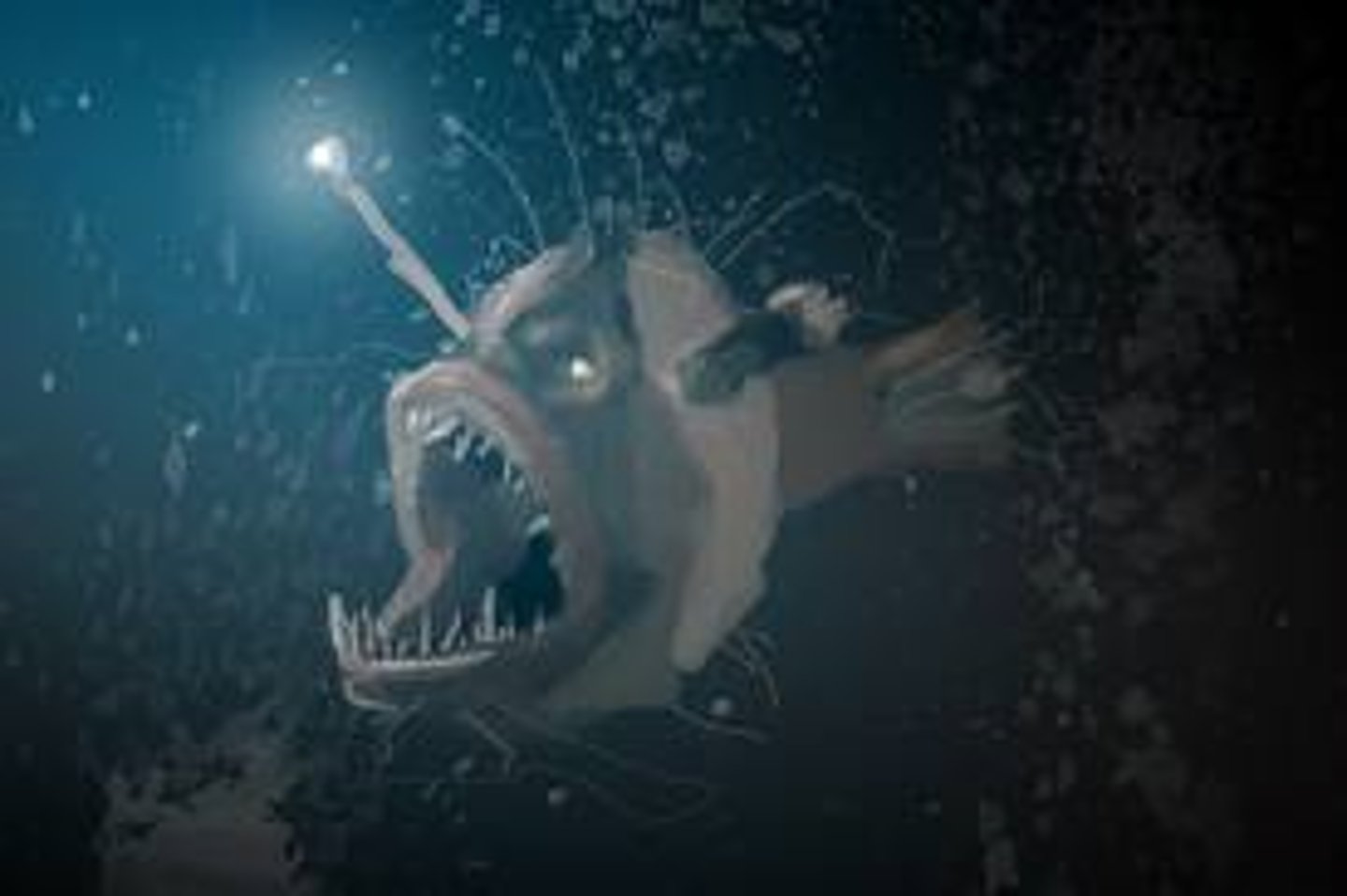
angular fish
Male:
- smaller in size and only stick to the female just to reproduce
-----------------
Female:
- bigger in size and have a hunting feature

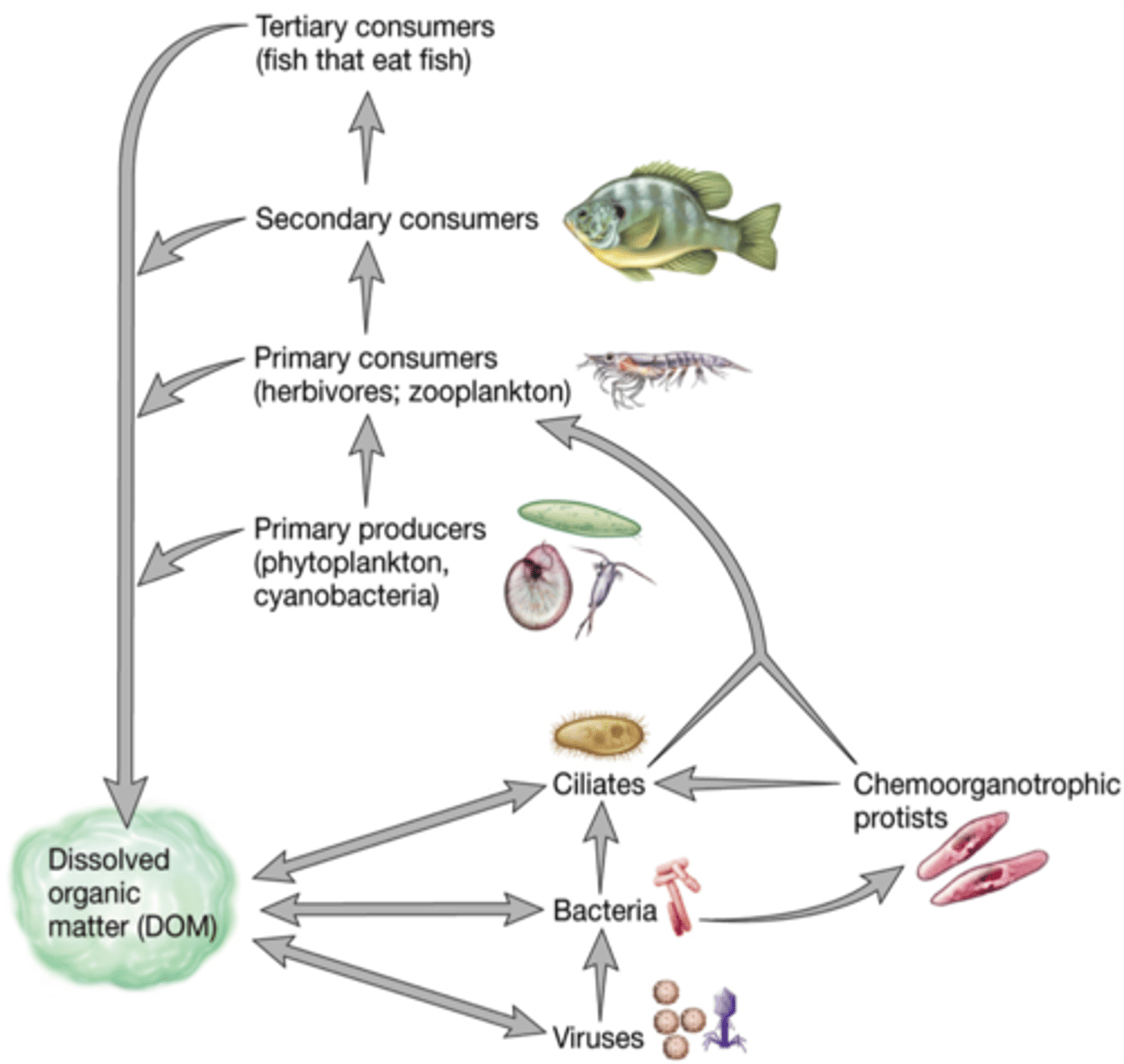
microbial loop
a cycle of production and consumption of glucose carried on by extremely small aquatic organisms
- Heterotrophic bacteria promote energy flow through the ecosystem by feeding on dissolved organic material that cannot be digested /utilized by other organisms
Human activitys (ecological issue)
can have a negative impact on water quality in freshwater and marine ecosystems
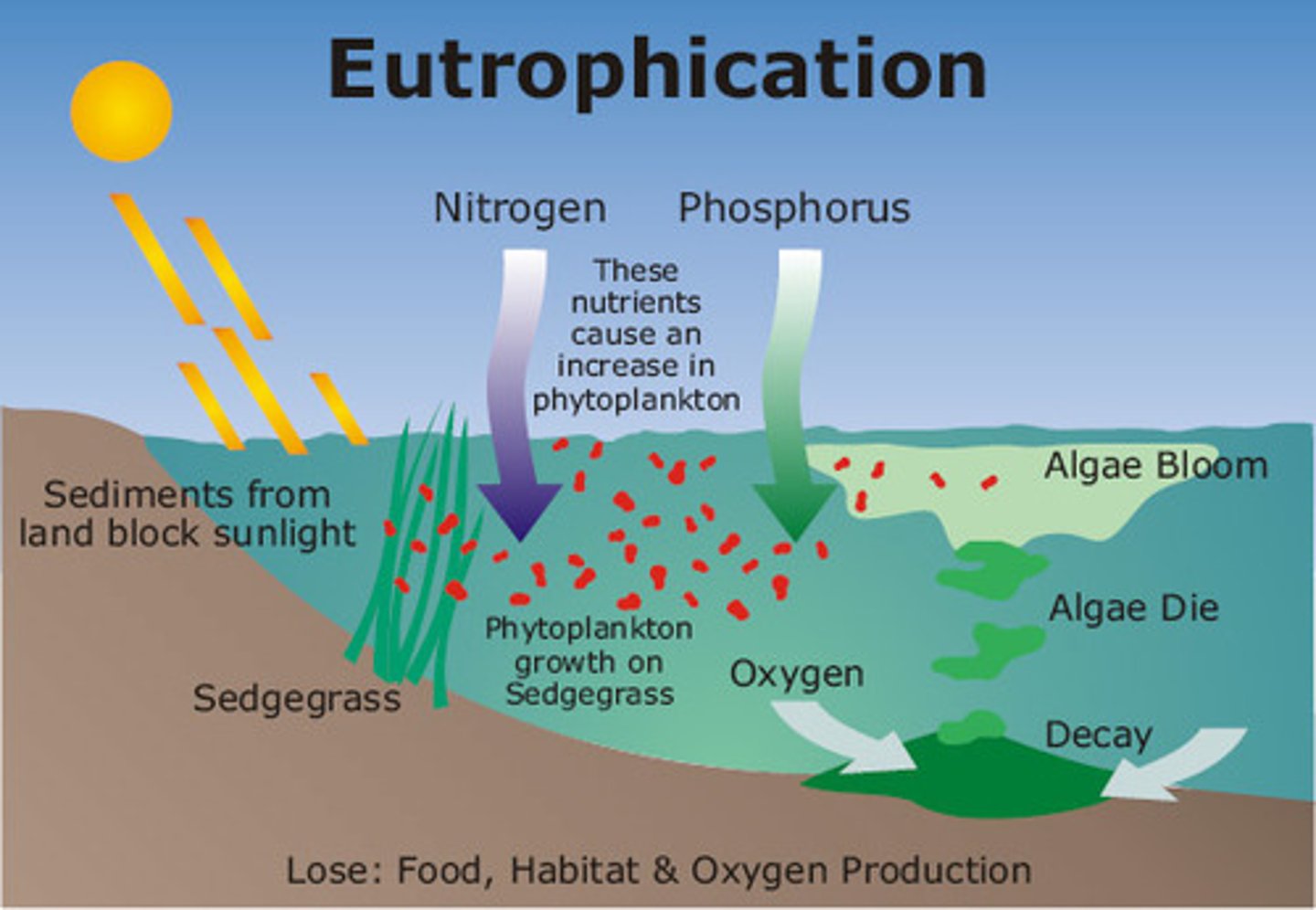
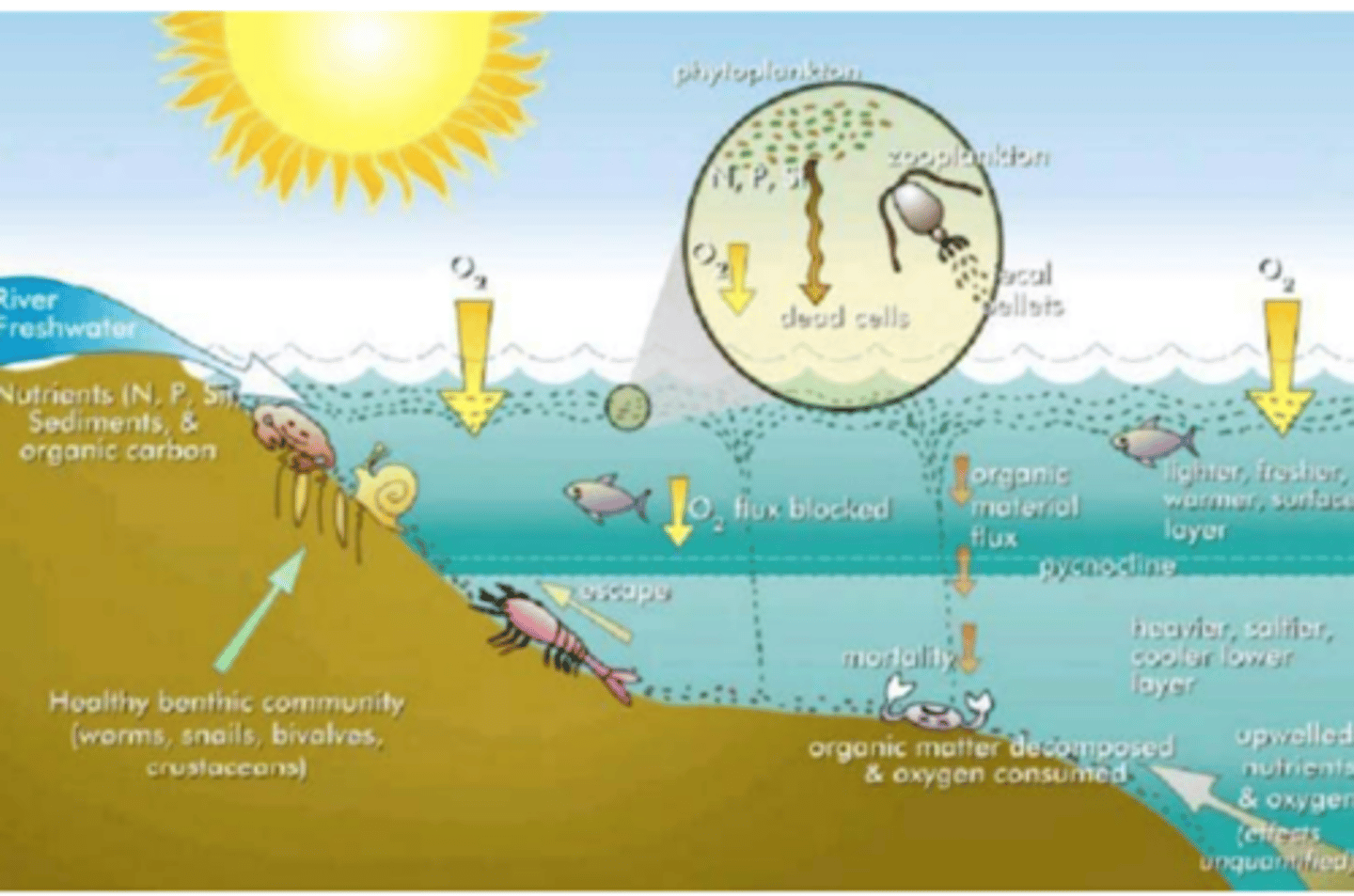
eutrophication
inputs of nitrogen and phosphorus (aquatic system that receives more nitrogen)
- normally limits the NPP
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
(energy captured by producers in an ecosystem) - (the energy producers respire)
how do humans put N and P into these systems?
- agriculture
- putting fertilizers runoffs
Limiting NPP
can lead to low oxygen levels (anoxia)
anoxia
lack of oxygen
- causing the death of aquatic organisms forming dead zones
- only caused of N and P increase NPP
Eutrophication leading to anoxia (part 1)
FROM BEGINNING TO END
1. Excess nutrients applied to the sol
2. Nutrients leach to the soil and eventually drain into the water body
3. Nutrients runoff over the ground into the body of water
4. Excess nutrients cause algal bloom
Eutrophication leading to anoxia (part 2)
FROM BEGINNING TO END
5. algal bloom blocks light of the sun reaching the bottom of the water body
6. the plants beneath the algal bloom die because they cannot get sunlight to photosynthesize
7. algal bloom dies and sinks to the bottom of the lake (bacteria begins to decompose the remains using up oxygen for respiration)
8. the decomposition causes the water to become depleted of oxygen (suffocating the larger aquatic life forms to death)
Gulf of Mexico Dead Zone
threatens fisheries and food webs in the gulf
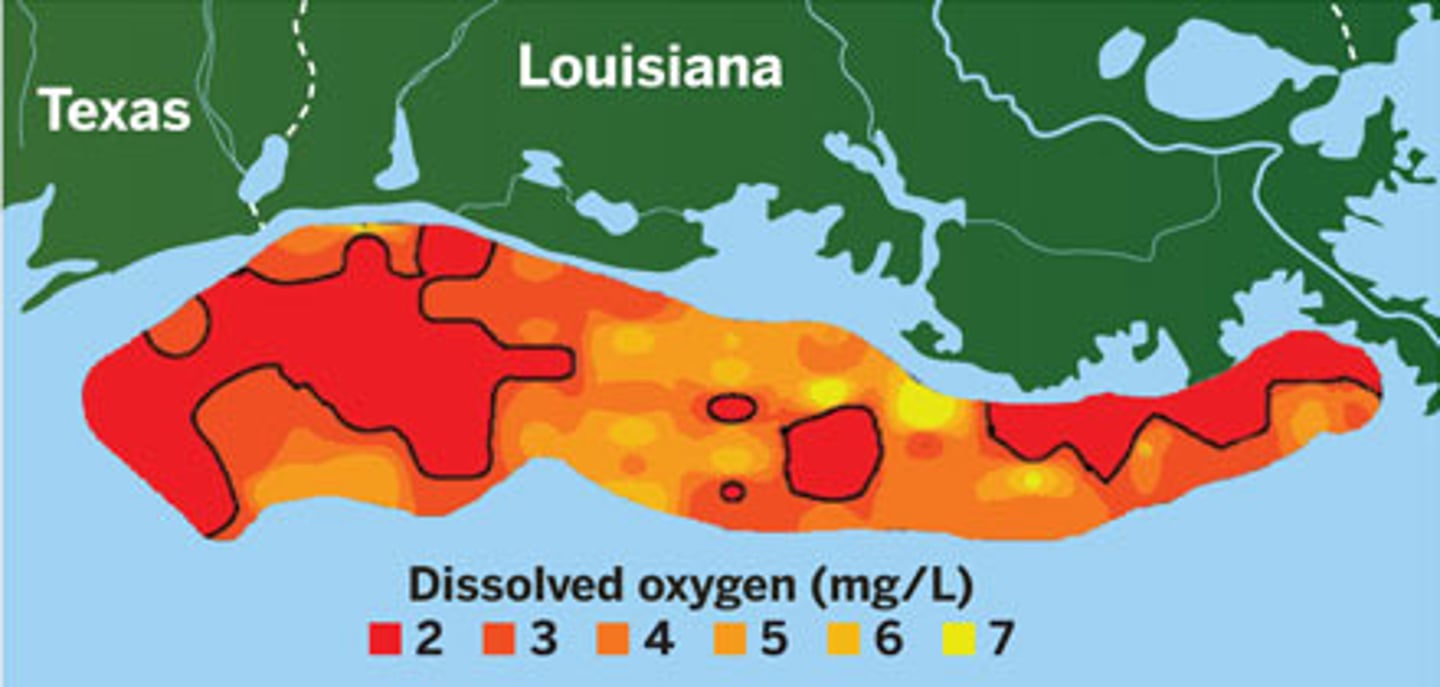
How can you fix the gulf of Mexico dead zones?
- manage nutrient inputs
- restore wetlands and riparian ecosystems
- remove/seal sediment high in N or P
- algicides
algicides
kills algae
- is rarely used because they typically rely on heavy metals that can accumulate in sediment toxic levels
Worst case scenario (climate change and sea level)
- degradation/destruction of coastal estuaries, wetlands, coral reefs, and deltas
- destruction of coastal fisheries
- flooding of low-lying countries and cities, and submersion of island nations
- Saltwater invasion of coastal aquifers
Fundamental properties of water
ice cap melt 2/3
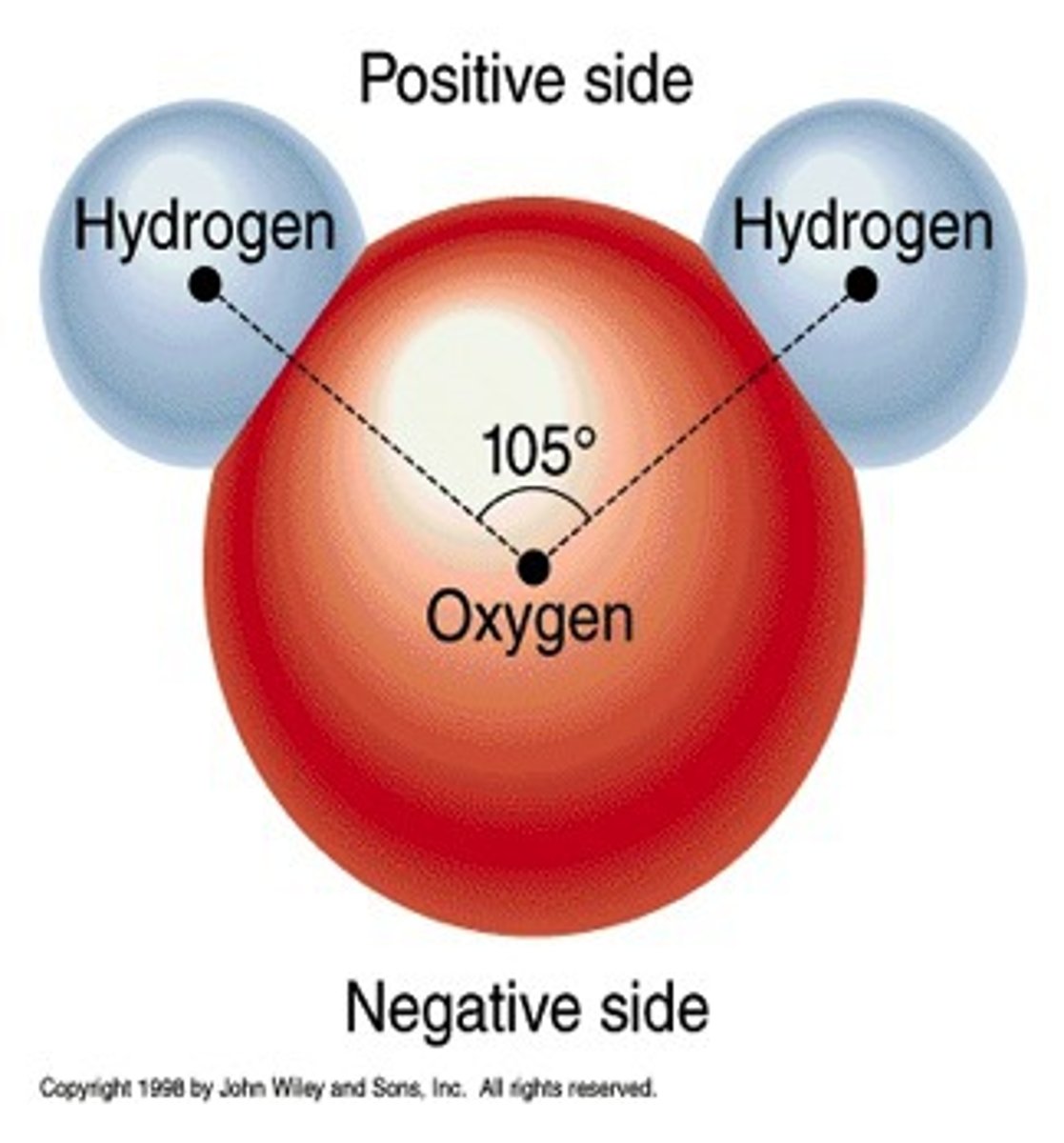
expansion of water due to warming
1/3 of rise
