Alkenes
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Explain how 3 isomeric products are formed when HY reacts with but-1-ene (3)
m1 = the major product exists as a pair of enantiomers
m2 = 3rd isomer is 1-bromobutane (minor product)
m3 = because it (m3) is formed via a primary carbocation
Identify the feature of the double bond in the E and Z isomers that causes them to be stereoisomers (1)
There is restricted rotation around the double bond C=C.
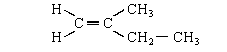
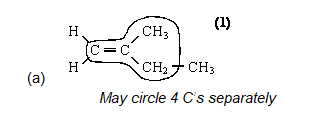
The structure of A is shown below. Circle those carbon atoms which must lie in the same plane. (1)
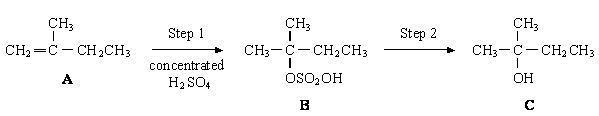
When compound A is converted into compound C, a second alcohol, D, is also formed. Alcohol D is isomeric with C but is formed as a minor product. Identify alcohol D and explain why it is formed as the minor product. (3)

State the type of intermolecular force that ocars between addition polymer chains made from hydrocarbon monomers. In your answer, explain how branching of chains affects these forces. (3)
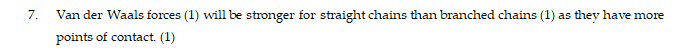
Using your answer to 8a, explain what is meant by a major and minor product and identify these products from your chosen reaction give a reason for your answer.
