Ap chem unit 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
atomic number
number of protons
Mass number
# of protons + neutrons
atomic mass
the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element
- calculated using isotope abundance
- avg. Mass= (mass1)(%)+(mass2)(%)
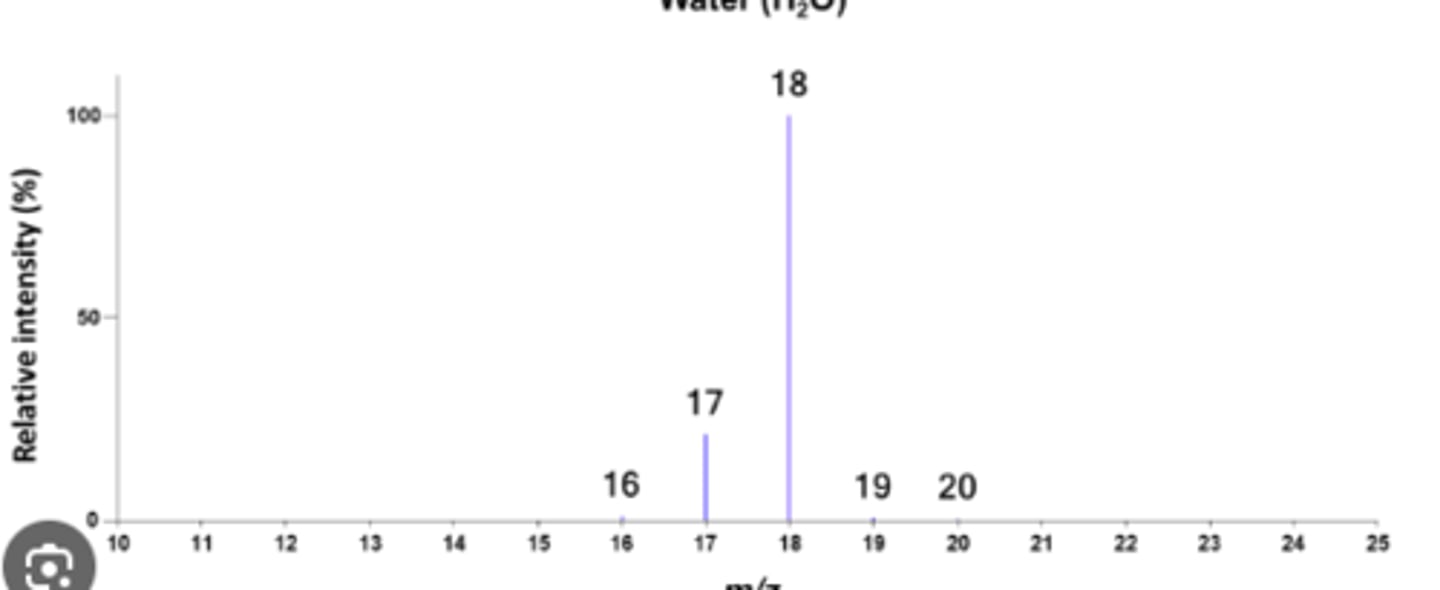
Mass Spectroscopy graph
relative abundances and masses of isotopes of an element.
- IADD ( Ionization Acceleration Deflection Detection)
- x axis is mass
- y axis is abundance (%)
Percent comp
what percent of its total mass comes from each element

empirical formula
a formula with the lowest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound
- determined form percent comp
molecular formula
show the actual molecule
- determined by (empirical to Molecular)
1. given molecular weight of substance
2. ration of molecular weight/ empirical formula - must be a whole number
3. multiply the ratio by empirical formula
Photoelectron Spectroscopy
refers to energy measurement of electrons emitted from solids, gases or liquids by the photoelectric effect, in order to determine the binding energies of electrons in a substance.
Coulomb's Law
- higher charges and smaller distance between charges create a stronger electrostatic force
- lower charges and larger distance between charges create a weak electrostatic force
- can explain to the periodic trends
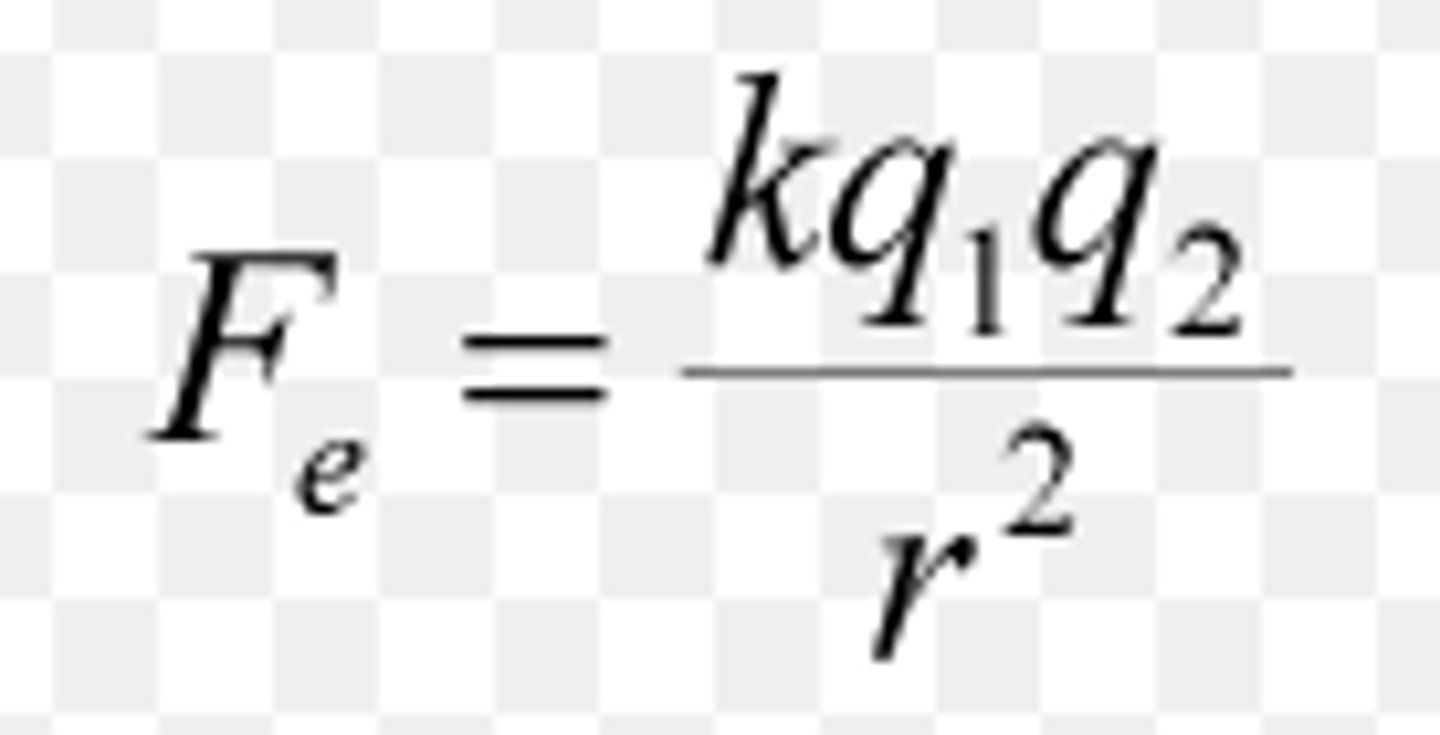
Ionization energy
energry required to remove a electron from an atom
increases across a period
- increasing effective nuclear charge (the more you go the stronger elements want to keep their electrons bc they wanna be stable - more energy)
decreases down a group
- more PELs (the farther away the electron is from the nucleus the easier it is to take it - little energy)
atomic radius
distance form the nucleus to the outer most electrons
decreases across a period
- increasing effective nuclear charge
- valence electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus, decreasing the size of the atom
Increases down a group
- increases in the orbital sizes bc of principal quantum levels
ionic radius
Anions- larger than parent atom
Cation- smaller than the parent atom
Molarity
unit of concentration

electron configuation
list of shells, subshells, and orbitals electrons in an atom occupy
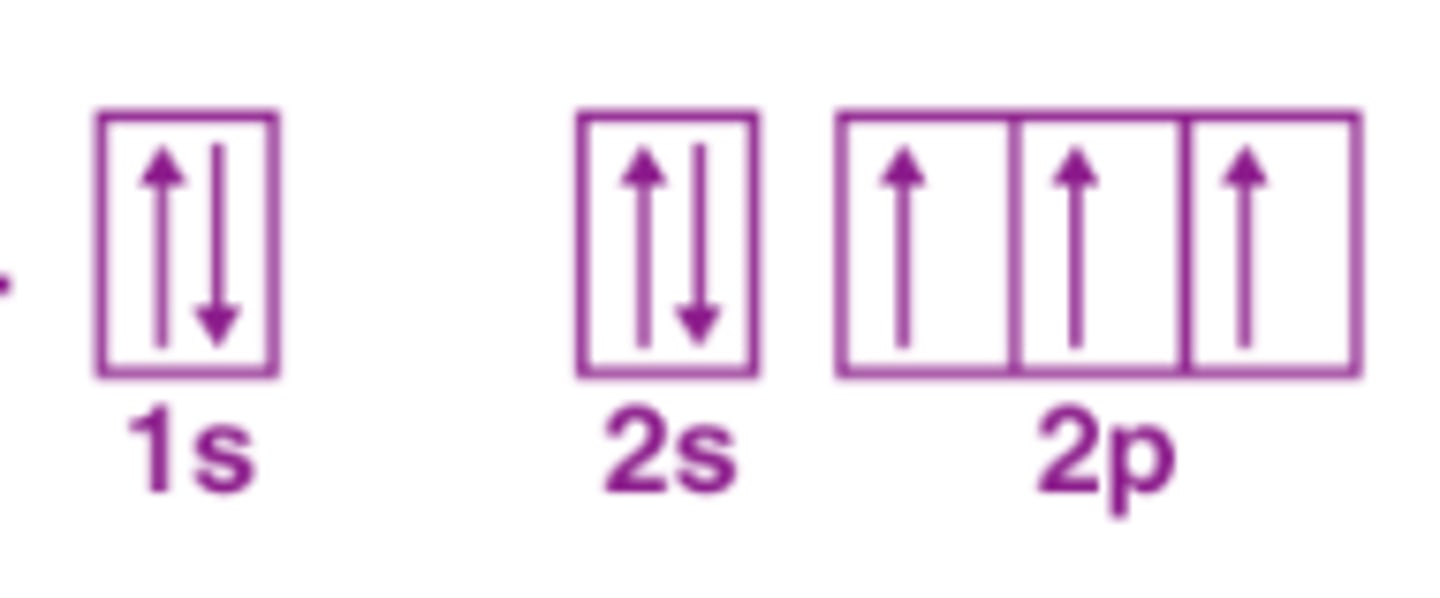
The Aufbau Principle
the rule that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first then occupy of increasing energy
The Pauli Exclusion principal
two electrons in the same orbital cannot have the same spin
Hund's principal
Electrons in a subshell will occupy empty obitals first then pair up
periodic trends
1. electrons attracted to the protons
- electron and nucleus close are strongly attracted
- more protons more strongly attracted the electron is
2. valence electrons don't feel the full pull of the nucleus b/c inner core push them away, they experience effective nuclear charge
3. add or subtract electrons to be stable
Electronegativity
measures how strongly an atom attracts valence electrons in covalent bonds
Increases across a period and decreases down a group
electron affinity
change in energy when a atom gains an electron
increases across a period and decreases down a group
Hydrate
ionic compound that contains water molecules in its structure
anhygdrate
substance that remains after water is removed