The Role of DNA & Proteins T2 W10
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards summarizing the fundamental terms related to DNA, genes, genetic code, and protein structure/function discussed in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is the structure and function of a cell dependen
Type of proteins produced in cell
Proteins link with genotype
Proteins provide the essential link between the coded instructions in the DNA, called the genotype, and the functioning cell.
Phenotype
The observable traits and functions of a cell/organism resulting from gene expression.
Gene function and number of them in chromosome
•A gene is a section of a chromosome that codes for making a protein.
•The number of genes on a chromosome range from around 200-2000 genes.
Difference between genes are based on
•The difference between one gene and the next is the:
⚬Order of bases along the DNA strand.
⚬Number of bases in that section of DNA.
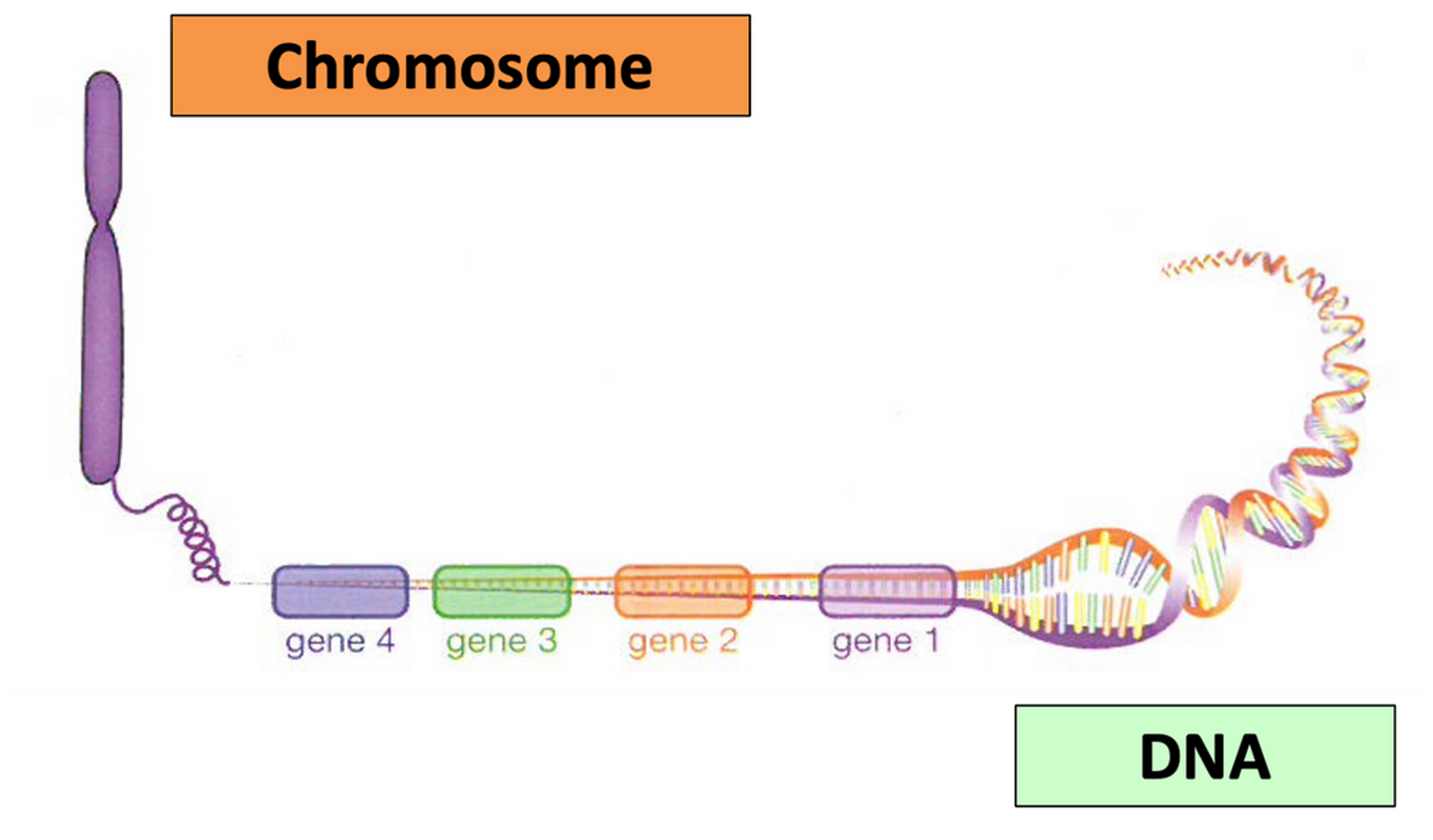
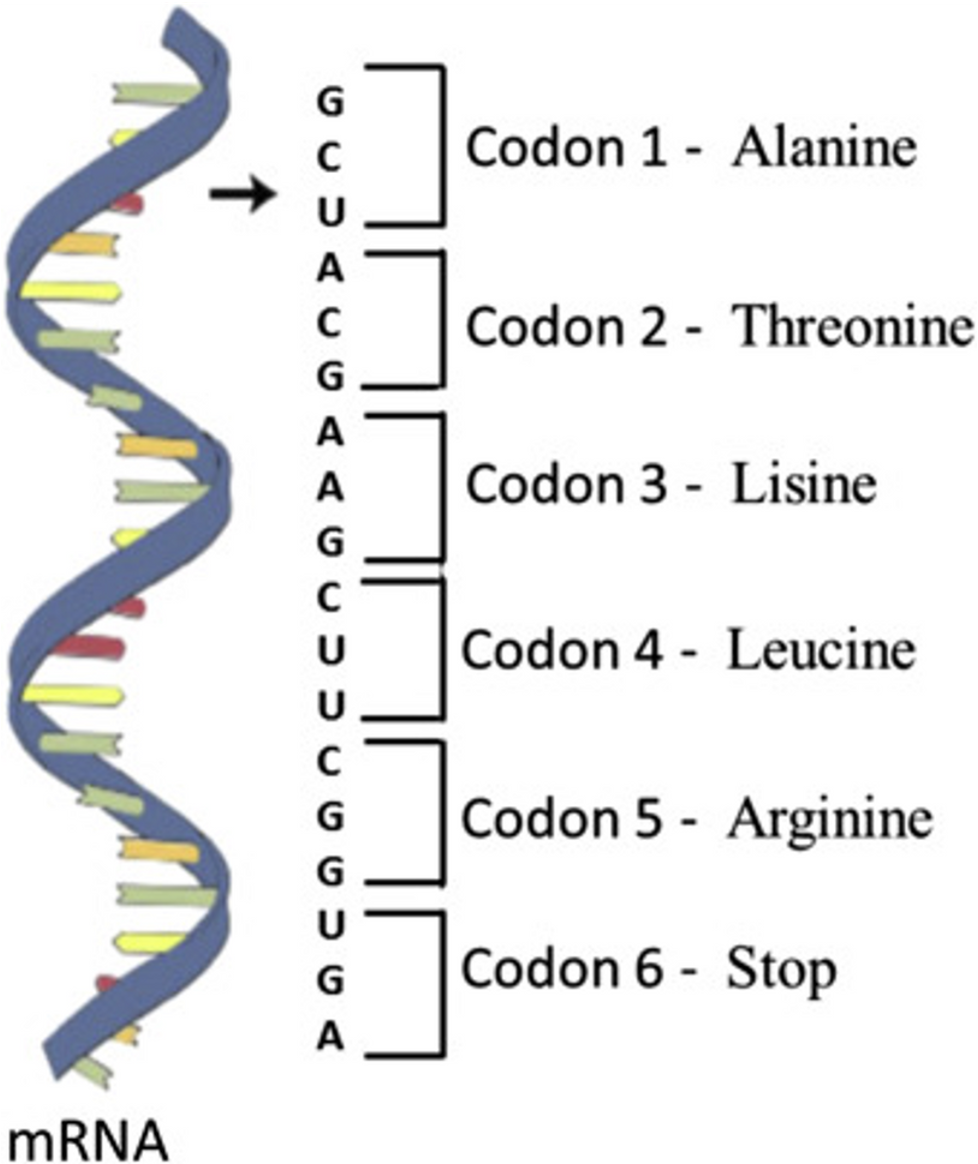
Genetic code
•The order of the bases along the DNA strand is called the genetic code.
•Each gene codes (contains instructions) for the production of a specific protein.
Elements found in proteins
•The elements found in a protein are: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
monomer (base unit) of a protein name and how many types there are
Amino acid and there are 20 different types
Name of chemical bond between 2 amino acids
Peptide bond
Types of protein structures
Primary structure, secondary strucutre, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure.
Protein primary structure
•Specific sequence of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds
Protein secondary structure
•Interactions of the nitrogen & oxygen atoms form hydrogen bonds, causing the amino acid chains to bend & coil.
Tertiary structure
•Interactions of the R group (side chains) of amino acids leads to more bonds forming, causing the protein to fold into a 3D shape.
Quaternary structure.
•Consist of more than one polypeptide chain, each forming a subunit, that interact with each other by attractive forces, forming the structure.
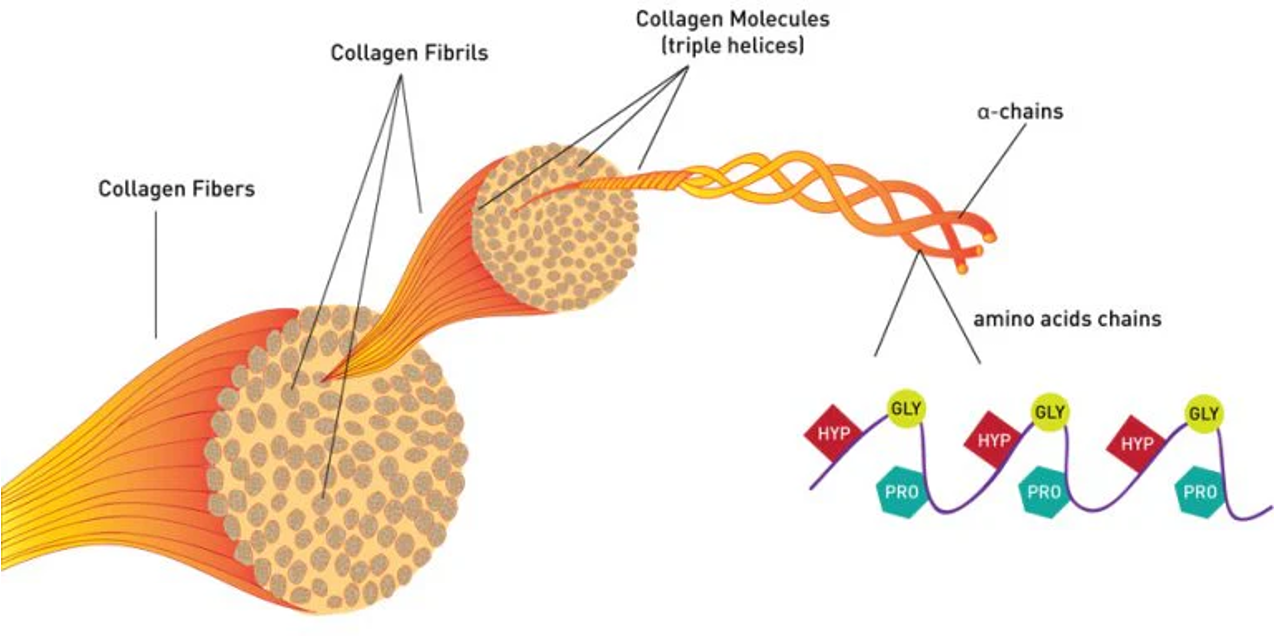
Structural proteins
Proteins that provide support and shape to cells and tissues, including collagen and keratin. e.g collagen (found in tendons & ligaments) and keratin (found in skin & nails)
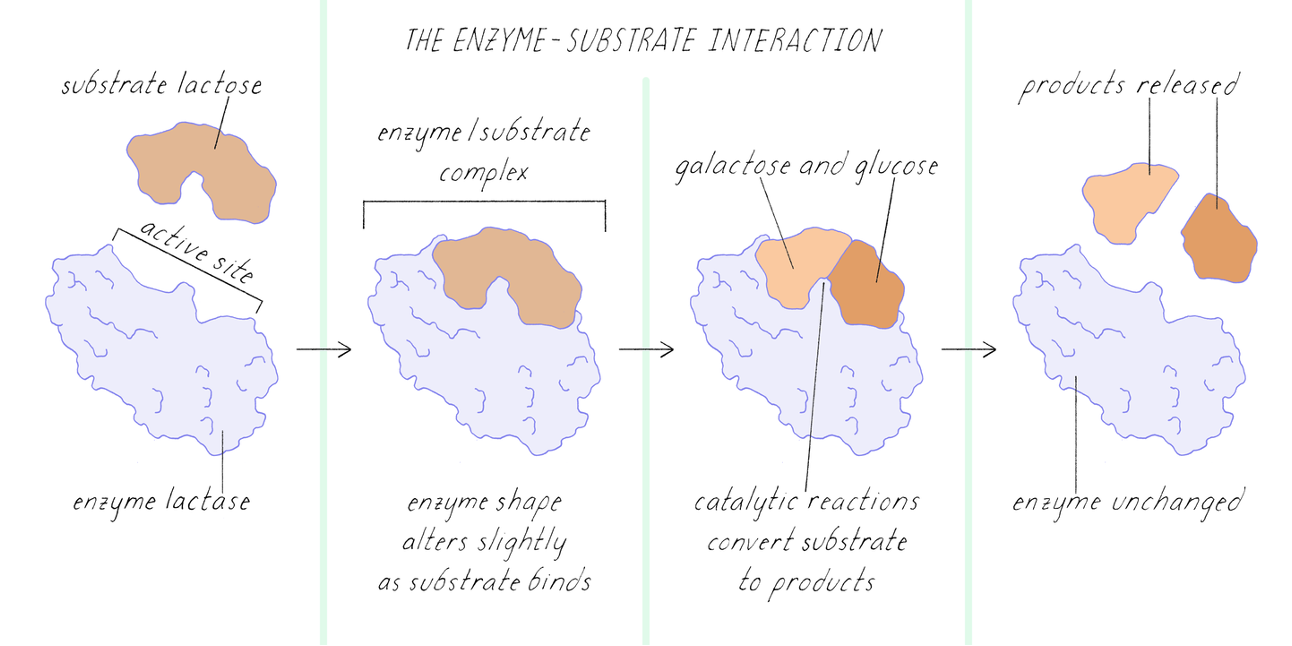
Enzyme proteins
Proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in the body without being consumed in the process. e.g. amylase (digest starch) and lactase (digest sugar in milk)
Regulatory proteins
Proteins that control the activity of genes and can regulate various cellular processes. They often include transcription factors and protein kinases. e.g. growth hormone (which stimulates growth and cell reproduction) and insulin (which controls blood glucose levels)