study guide intro to perio
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
gingiva, PDL, alveolar bone, cementum
components of Periodontium
Marginal gingiva
Surrounds the tooth.
Attached gingiva
Attached to the alveolar bone.
Interdental papilla
Located between teeth
gingivodental, circular, and transseptal fibers
Gingival fibers
alveolar crest, oblique, transeptal, horizontal, interradicular, and apical fibers
PDL fibers
alveolar bone proper (lamina dura), trabecular bone, and compact bone
Alveolar bone components
lamina densa (type IV), cementum (type I and III), PDL (type I and III), and gingival fibers (type I)
collagen fiber locations
Acellular/primary cementum
Found in the cervical third, formed before tooth reaches occlusal plane, more calcified.
Cellular/secondary cementum
Found in the apical third, formed after tooth reaches occlusal plane, less calcified
Keratinized tissue
firm pink tissue that surround teeth
submandibular, submental, upper deep cervical, and lower deep cervical lymph nodes
lymphatic drainage
diabetes, smoking, and pathogenic bacteria
Risk factors
Background characteristics: genetic factors, age, gender, socioeconomic status, and stress
Risk determinants
previous history and bleeding on probing (BOP)
Risk markers
HIV/AIDS, osteoporosis, and infrequent dental visits.
Risk indicators
determine patient's risk of developing or progressing periodontal disease
Goal of risk assessment
Increases prevalence, extent, and severity
Smoking effects on periodontal diseease
E-cigarettes
Considered less harmful than traditional smoking.
Ask, Advise, Assess, Assist, Arrange
5 A’s of smoking cessation
Direct relationship with periodontitis, especially poorly controlled diabetes
relationship between Diabetes and oral health
oral hairy leukoplakia, oral candidiasis, linear gingival erythema, and Kaposi sarcoma
Oral manifestations of HIV
Continuous absence indicates periodontal stability and health
Bleeding on probing as a risk marker
Day 1 facultative/aerobic, Day 2 anaerobic, Day 14 mature microbiota, 2 years human microbiota.
bacteria colonization timeline
Commensal bacteria
Beneficial bacteria that help control pathogenic bacteria.
Pathogenic bacteria
Disease-causing bacteria.
Plaque
Resilient biofilm of bacteria and salivary glycoproteins, difficult to remove by rinsing.
Materia alba
Easily displaced white accumulation of salivary proteins and some bacteria.
Calculus
Hard deposit formed by mineralization of plaque, requires dental tools for removal.
Pellicle formation, initial adhesion, colonization, and maturation.
Phases of plaque formation
Supragingival plaque
Aerobic, found on tooth surfaces, contains gram-positive cocci.
Subgingival plaque
Anaerobic, found in gingiva, contains gram-negative rods and filaments.
tooth associated subgingival plaque
less filamentous bacteria deeper into sulcus
tissue associated subgingival plaque
gram neg rods and cocci
P. gingivalis, T. forsythia, and T. denticola
Red complex bacteria
decrease gingival inflammation decreases bleeding
effect of smoking on gingivitis
Organized structure, nutrient channels, and bacterial communication.
Biofilm characteristics
salivary flow, saliva aggregation, diet, chewing fibrous food, smoking
individual variables in plaque formation
non-specific plaque hypothesis
accumulation of plaque over time and amount of plaque is key to disease control
faster on low jaw, molars, buccal surface, and interproximally
plaque formation rates in dentition
specific plaque hypothesis
only certain plaque is pathogenic
ecological plaque hypothesis
both total amount of plaque and specific microbe contribute to disease
keystone plaque hypothesis
specific pathogen in low abundance can disrupt periodontal microbiota
Decrease in red complex bacteria, increase in Actinomyces.
Changes after SRP
Health has more facultative gram-positive rods; disease has more anaerobic gram-negative rods.
Microorganisms in health vs disease
Calculus content
70-90% inorganic, including calcium phosphate and hydroxypatite.
Calculus formation
Begins between the 1st and 14th day of plaque formation, calcification can start as early as 4-8 hours.
Supragingival calculus
above the gingival margin, heaviest near salviary ducts, mineral from saliva, easily removed
subgingival calculus
not site specific, mineral from GCF and inflammatory infiltrate, proximal surfaces, dense, hard tenacious
stratum corneum, stratum granulosu, sratum spinosum, stratum basale
layers of epithelium
ortho keratinized
no cell nuclei in stratum corneum
para-keratinized
cell nuclei in stratum corneum
non-keratinized
no stratum corneum and no statum granulosum
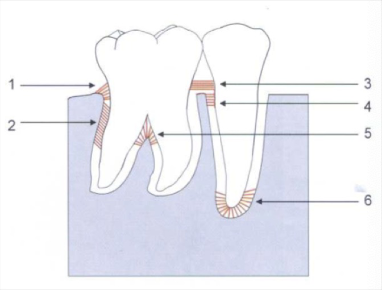
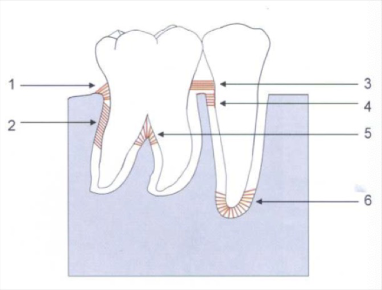
alveolar crest fiber
1) prevent tooth extrusion, resist lateral tooth movement
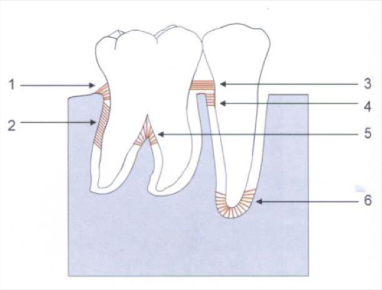
oblique fibers
2) bear and transform brunt of vertical masticatory stress
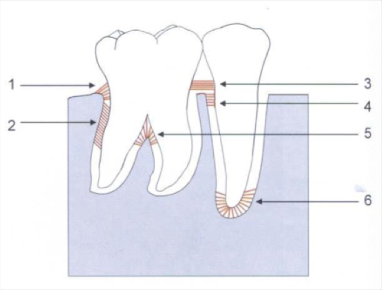
transeptal fibers
3) over the alveolar bone, no osseous attachment
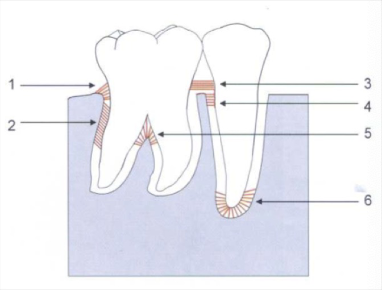
apical fibers
6) do not occur on incomplete roots
buccal, mucosa, gingva, palate, dorsum of tongue, intraoral and supragingival hard surfaces, subgingival biofilm
oral ecosystem/niches
oral epithelium
faces oral cavity, gingival margin to MGJ, keratinocytes
sulcular epithelium
small in health, oral epithelium into sulcus, no stratum corneum or granulosum
junctional epithelium
attaches gingival epithelium to tooth, allows fluid to pass, defense from bacteria
keratinocytes
producing tonofilaments and soft tissue renewal
non-keratinocytes
langerhans cells (antigen-presenting cells), merkel cells (tactile preceptors), melanocyte
horizontal fibers
4
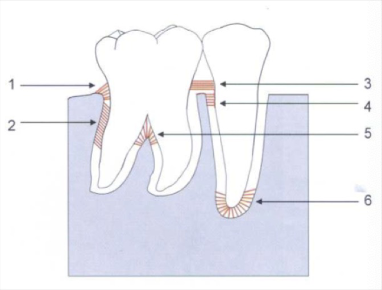
interadicular fibers
5
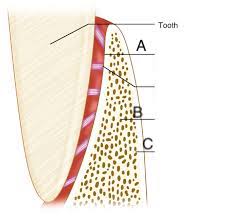
alveolar bone proper (lamina dura)
A)dense cortical plate of bone that forms the tooth socket direc tly contacts the tooth root (cribiform plate)
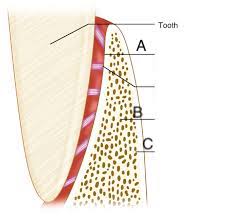
trabecular bone
B) spongy bone supporting alveolar bone
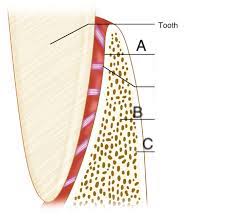
compact bone
C) towards facial formed by haveresian bone and bone lamellae