Cellular Reproduction
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Cellular Reproduction
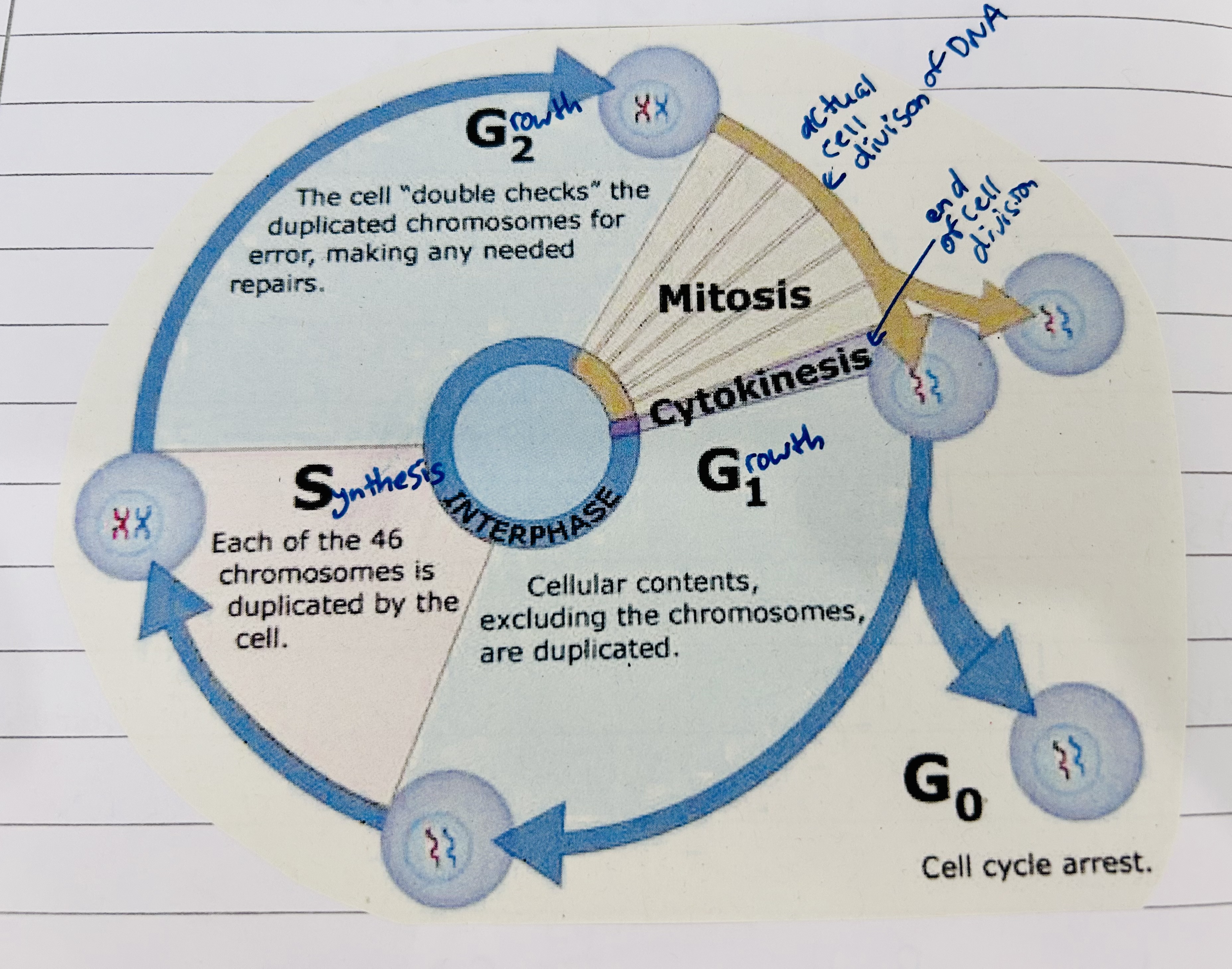
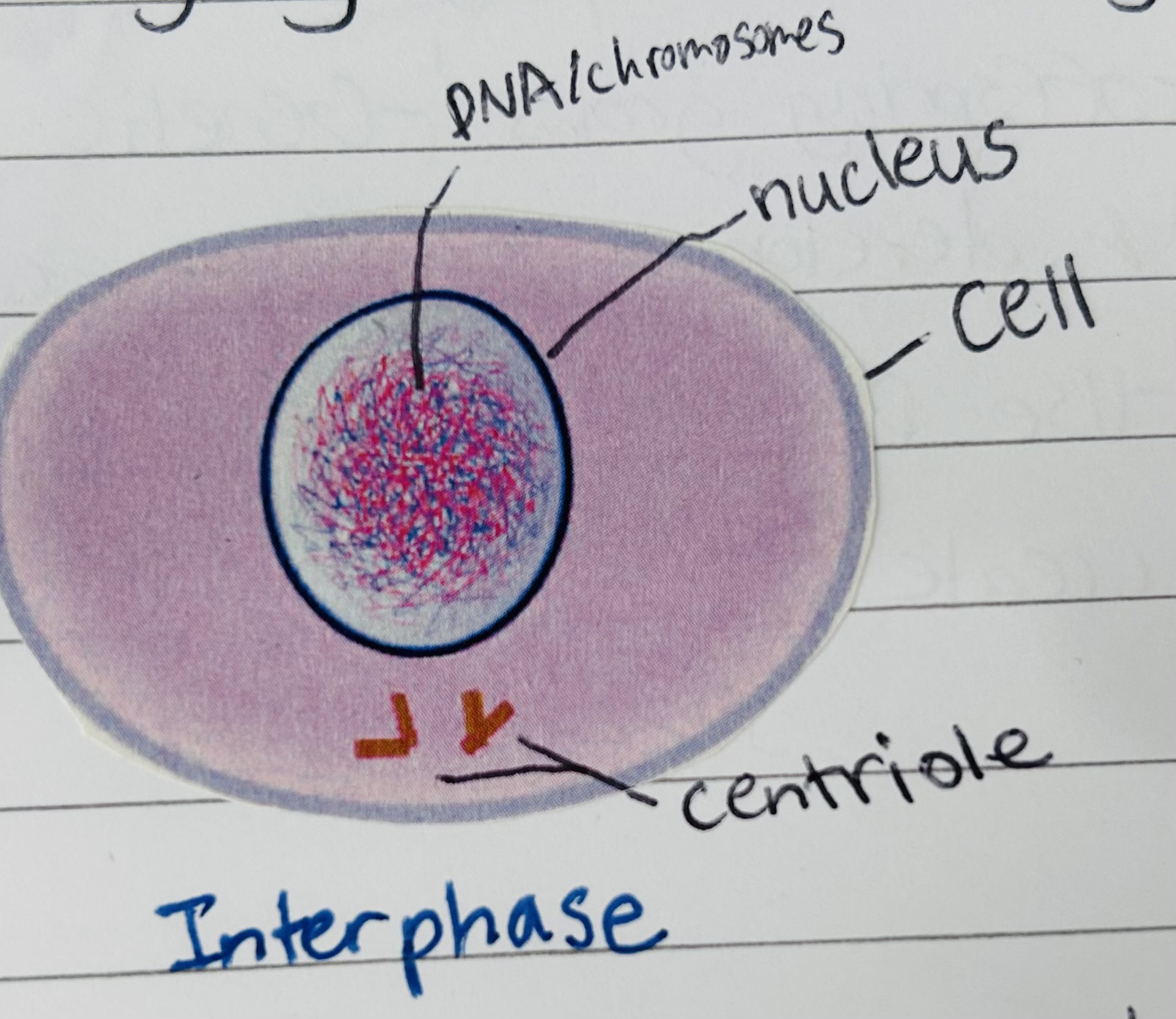
Interphase
Everything but mitosis. Longest part of a cell’s life.
Interphase purpose
Cells grow, develop, carry on all normal metabolic functions
Mitosis
form of cell division
produces 2, genetically identical daughter cells
produces diploid cells(2n) = full set of chromosomes in each cell
Reasons for cell division
Maintenance & repair of tissues
Organism growth
Asexual reproduction for unicellular organisms
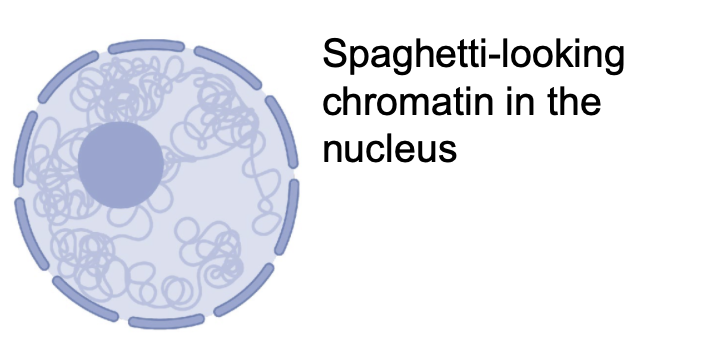
Chromatin
loosely grouped DNA – how it appears in the nucleus when the cell is not dividing
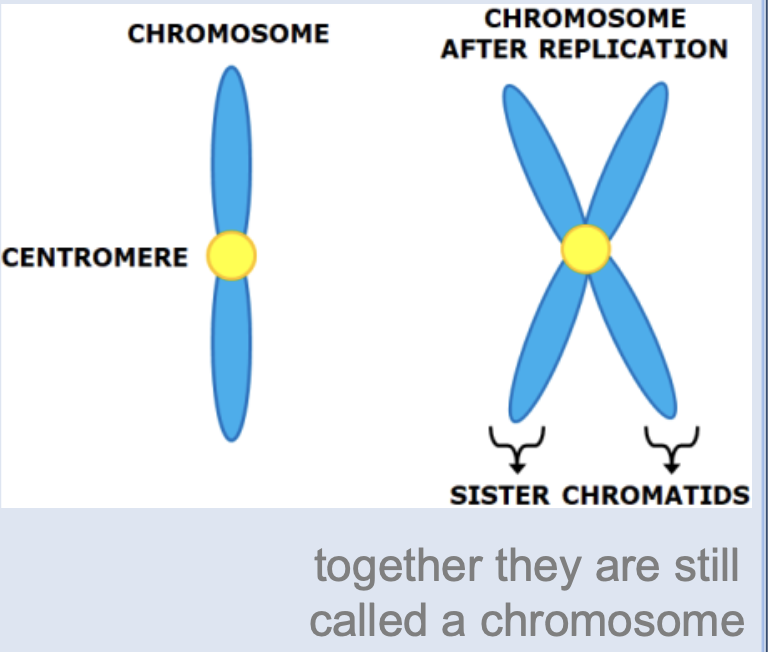
Chromosome
compact, condensed DNA organized in preparation for replication and cell division
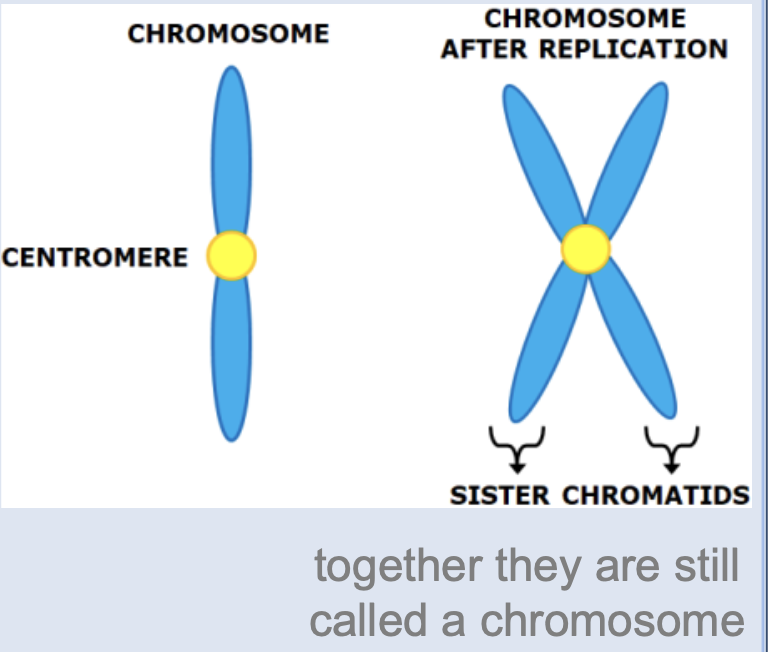
Sister chromatids
after DNA makes a copy of itself, each copy is referred to as a sister chromatid
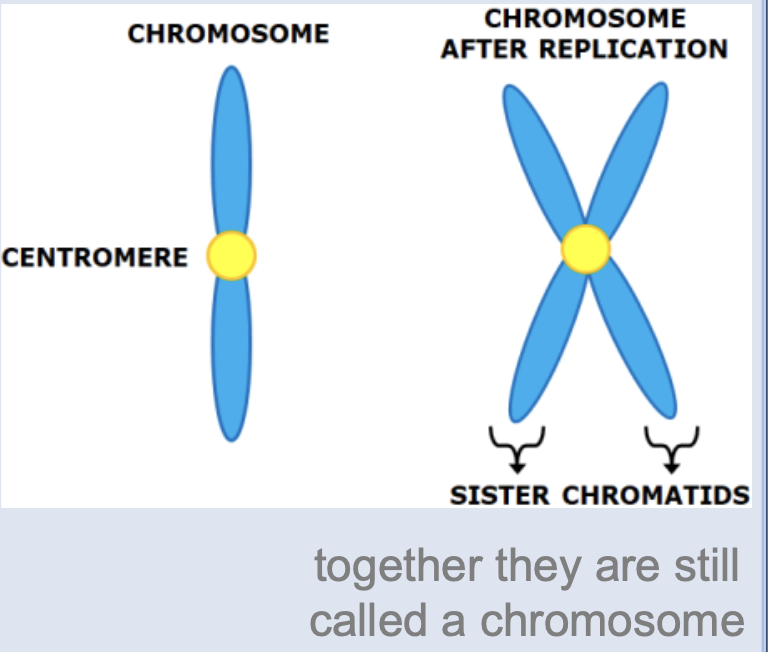
Centromere
holds sister chromatids together
Centriole
cytoskeleton structures that assist in forming the spindle fibers during mitosis
Phases of Mitosis
PMAT
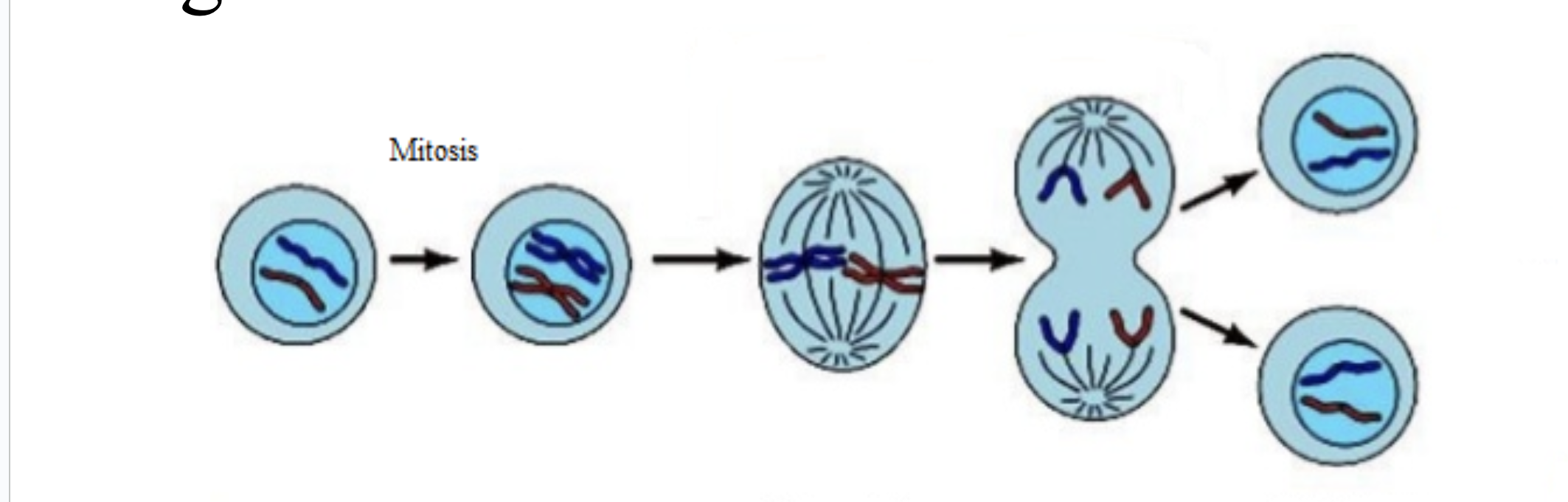
Prophase
Chromosomes become visible when they condense into sister chromatids
Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell (the poles)
Spindle begins to form
Nuclear membrane breaks
down
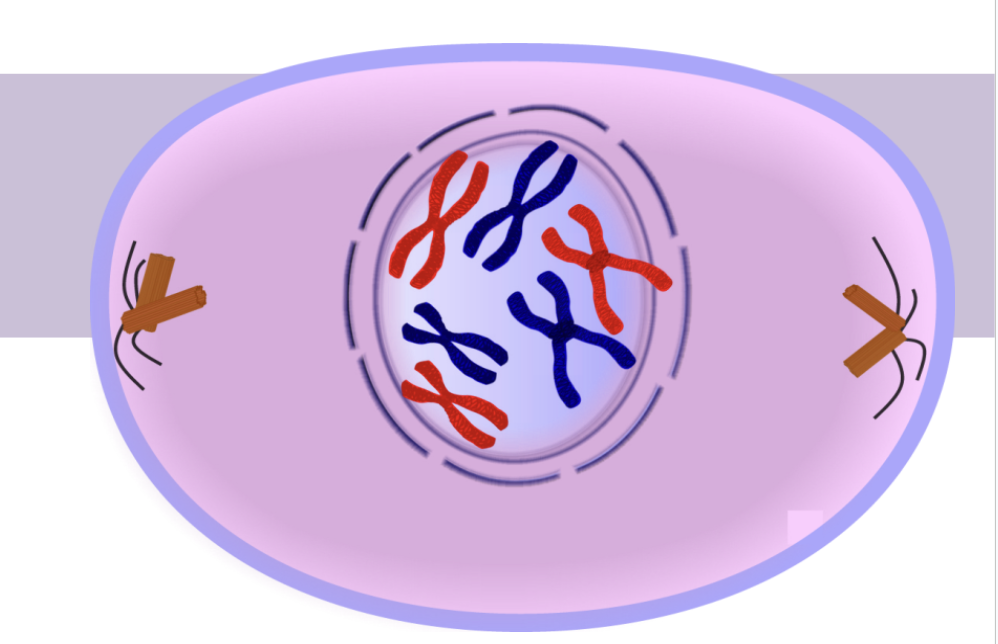
Metaphase
M = Middle!
Chromosomes line up in middle of the cell
Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres
(the center of the chromosome where 2 sister chromatids are being held together)
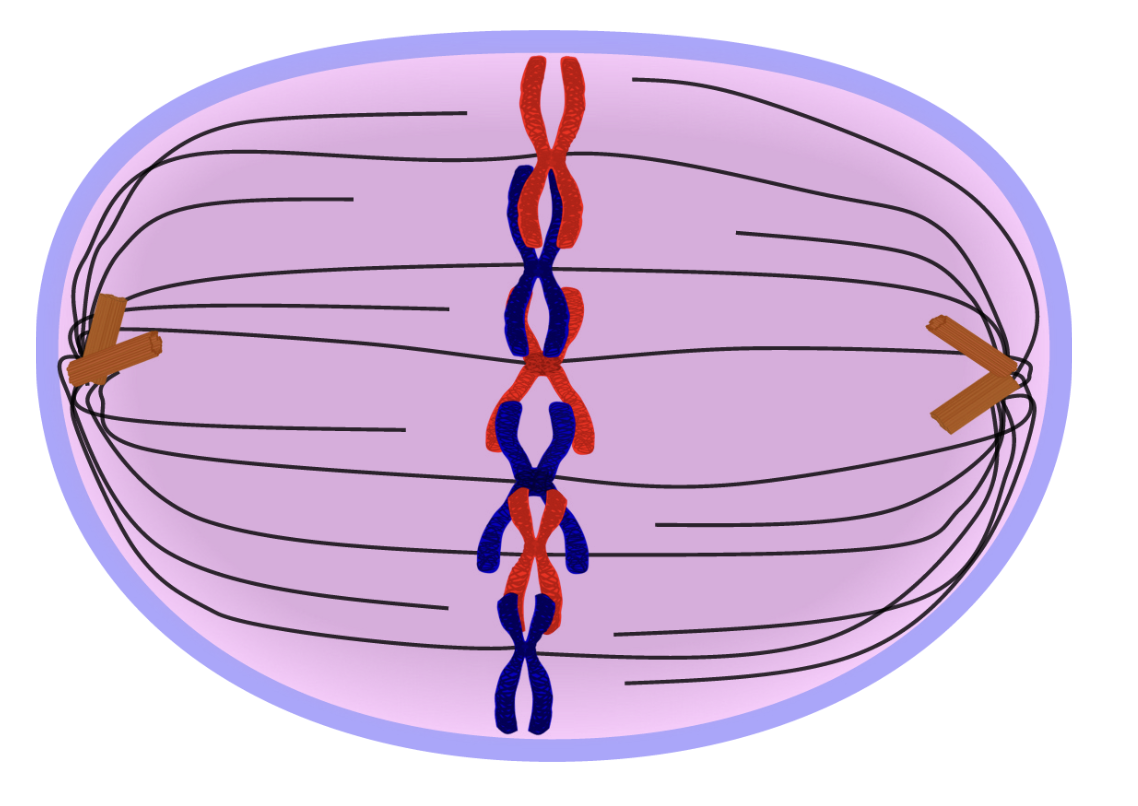
Anaphase
A = Apart or Away!
Spindle fibers attached to the centromere pull the sister chromatids apart
Chromosomes move toward opposite ends of cell
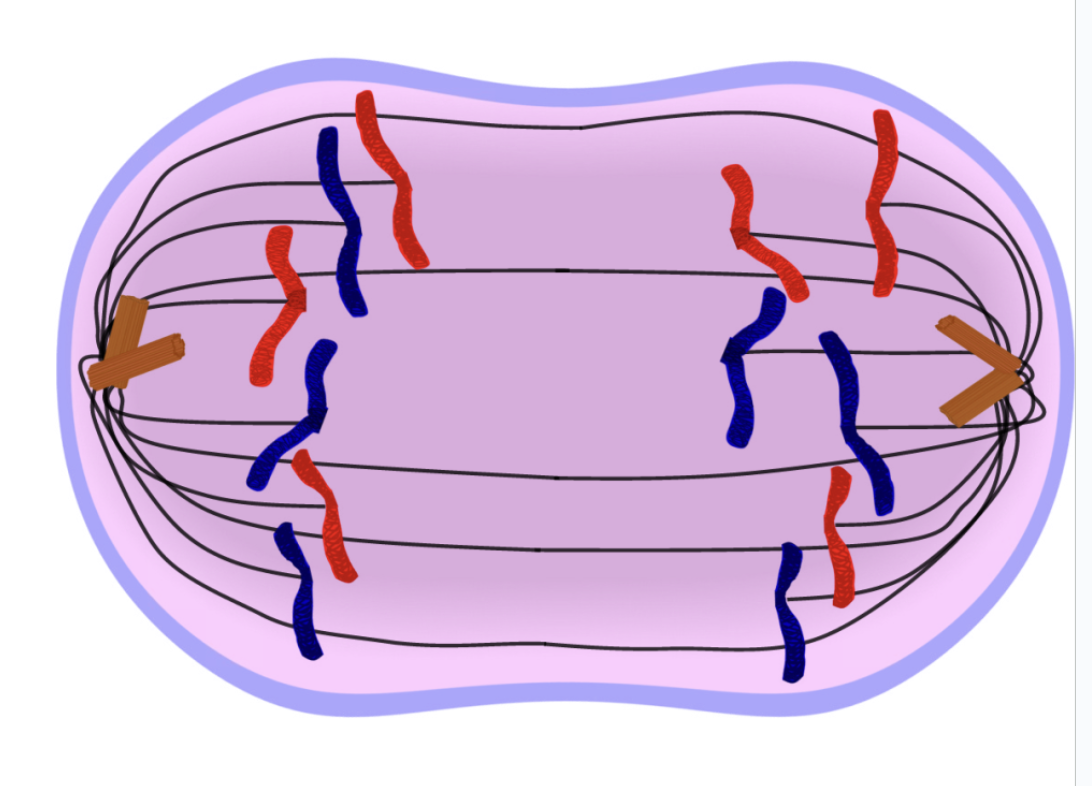
Telophase
T = Two!
Nuclear membrane forms at each end of the cell around the chromosomes
– division of the original
nucleus is now complete
Chromosomes become less tightly coiled & appear as chromatin again
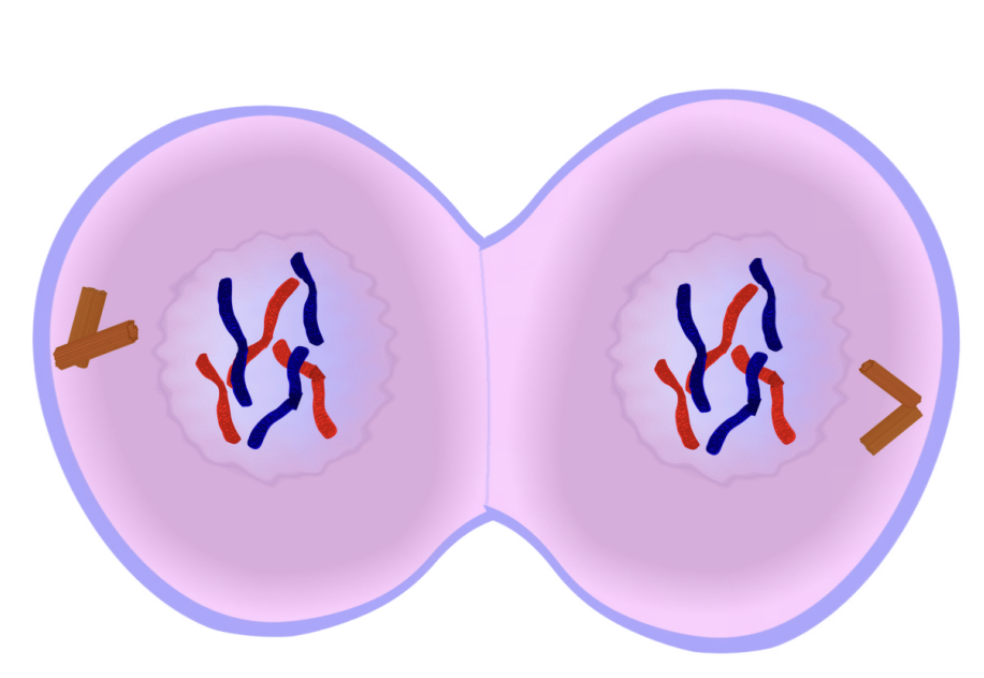
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm
forming of cell plate in plant
in animals the cleavage furrow
Animals vs Plants
most animals cells can divide
Plants: mitosis only happens in special tissues called meristem
Meiosis
produces gametes (sex cells)
produces four (genetically unique daughter cells)
haploid (n) = half the number of chromosomes in daughter cells
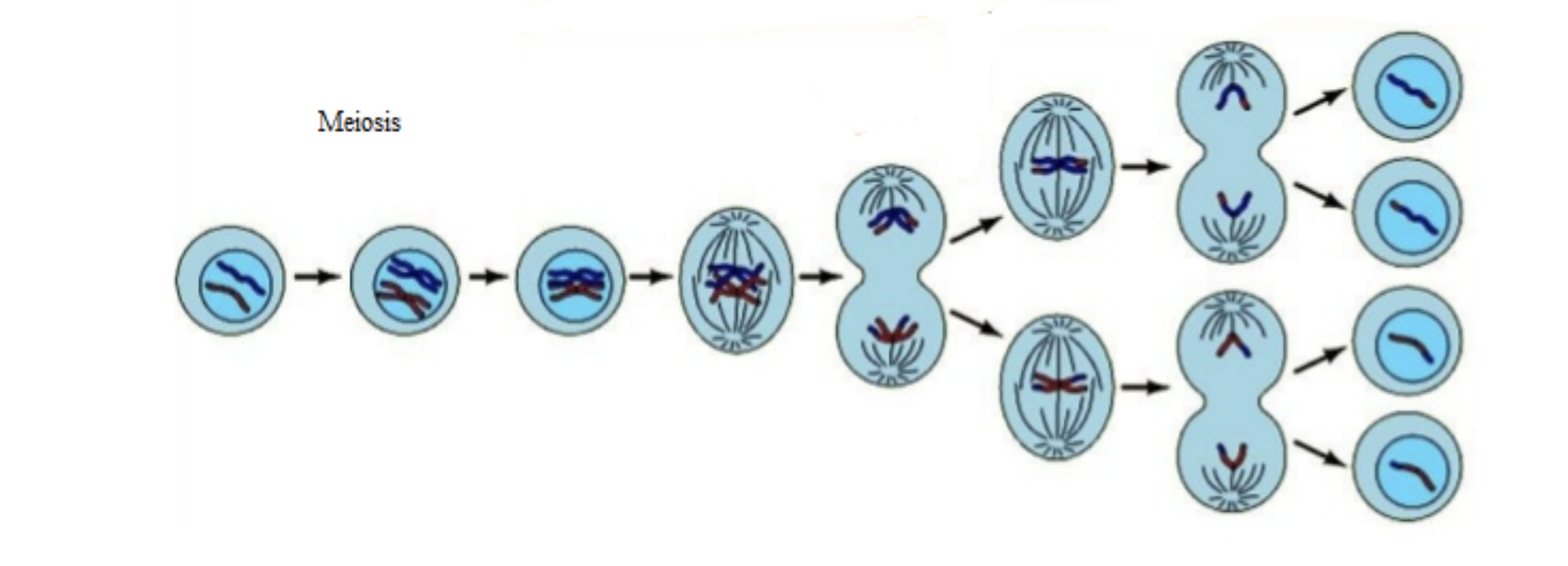
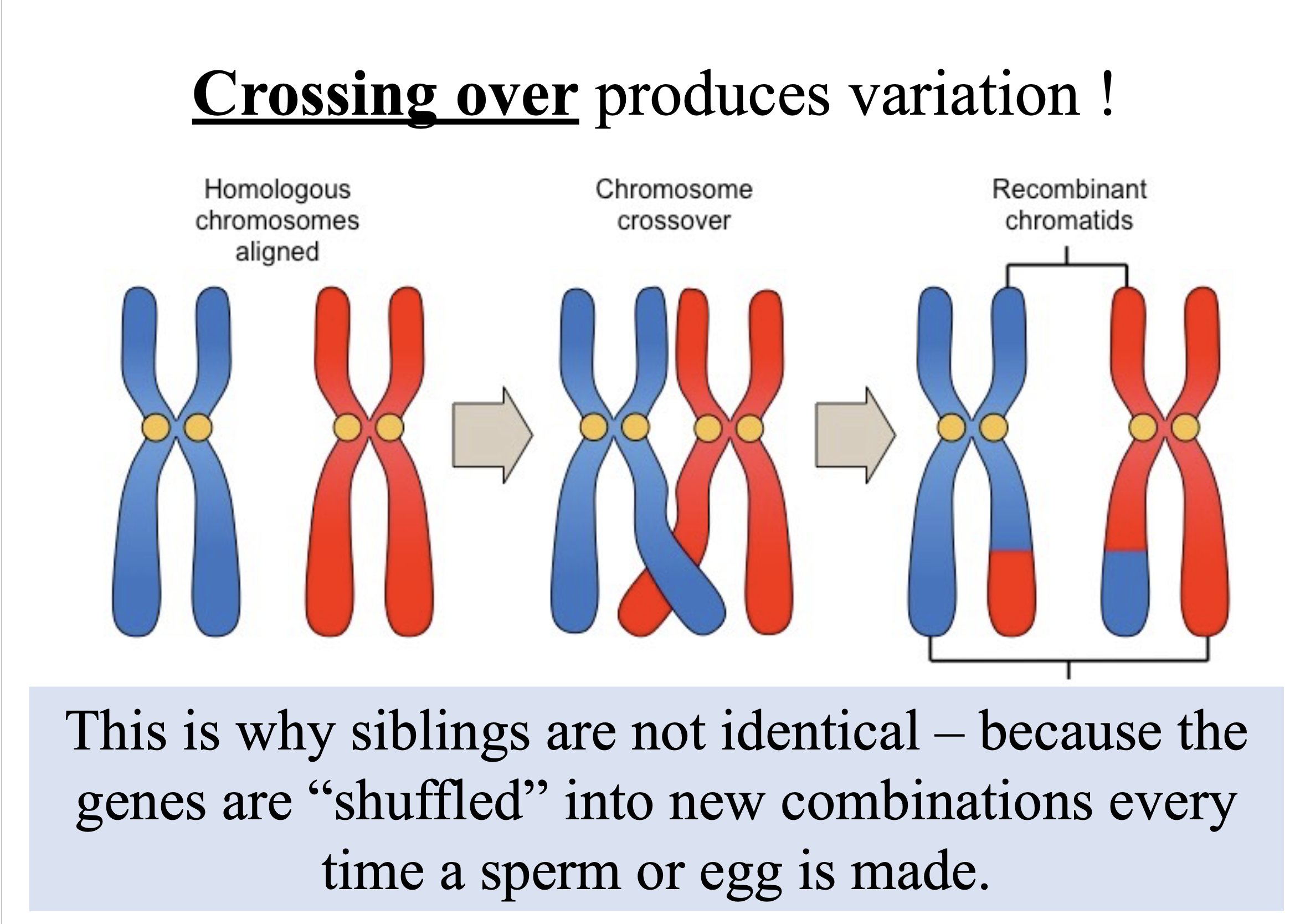
Crossing over produces variation!