PS231: Vision V (V1 & Higher Visual Cortices)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
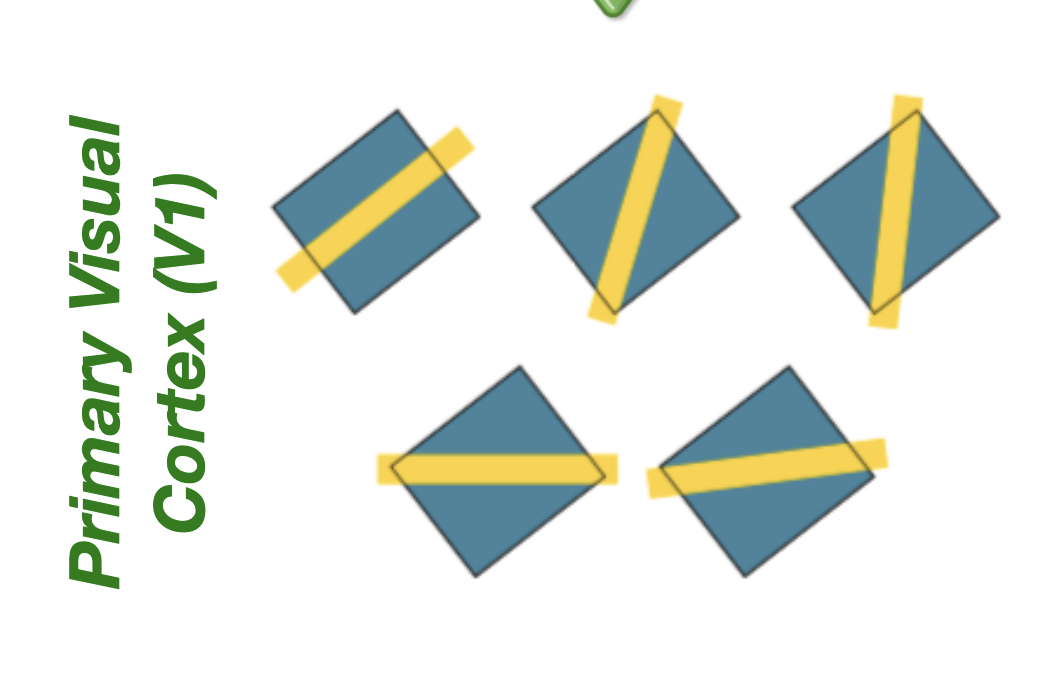
V1 “simple cell” RF
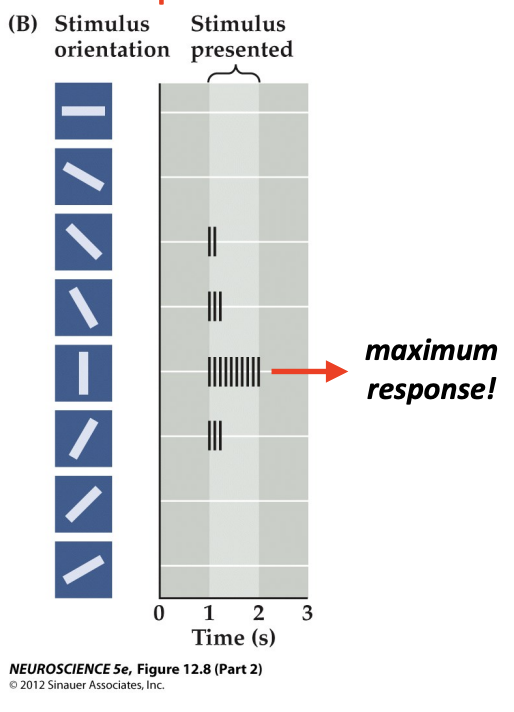
bars of light with specific orientations coming from specific locations in the visual field (more complex “orientation selectivity”)

V1 Neuron (“Simple Cell”) Receptive Field
Neurons in primary visual cortex respond to bars of light in specific orientations (known as orientation selectivity) coming from specific locations on the retina
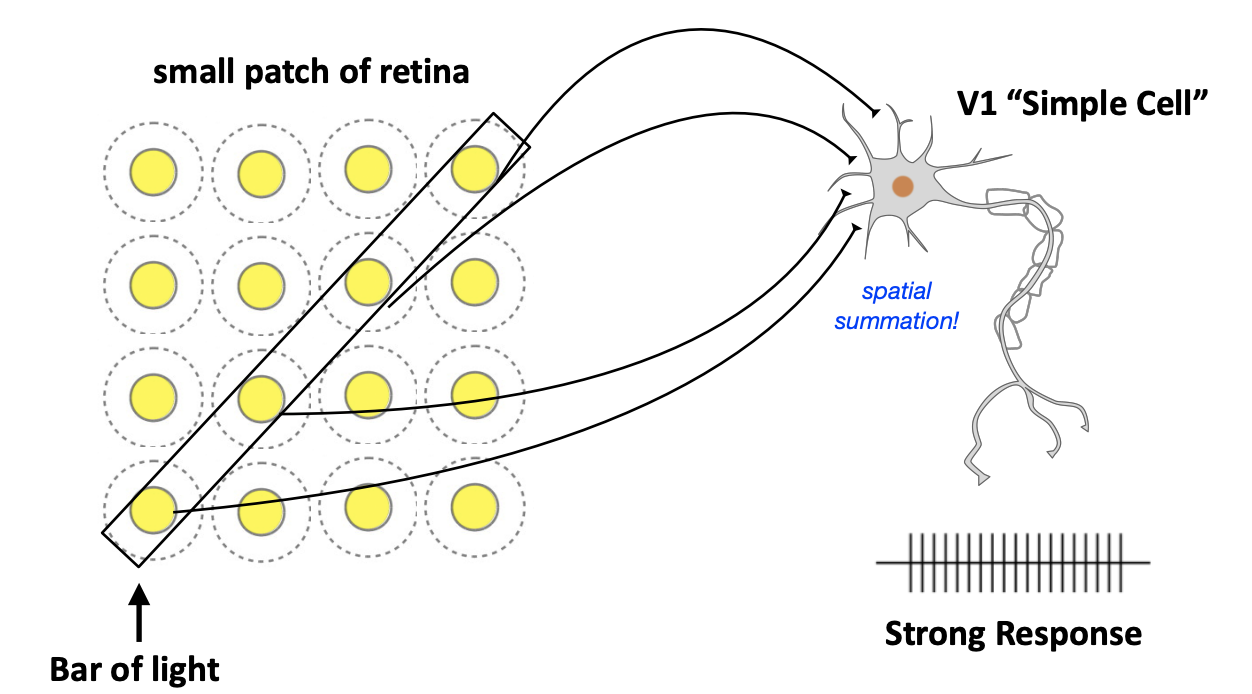
Schematic of V1 Simple Cell Receptive Field
This V1 neuron receives input from a row of ON-center ganglion cells and so responds better to a bar of light than to any single spot of light
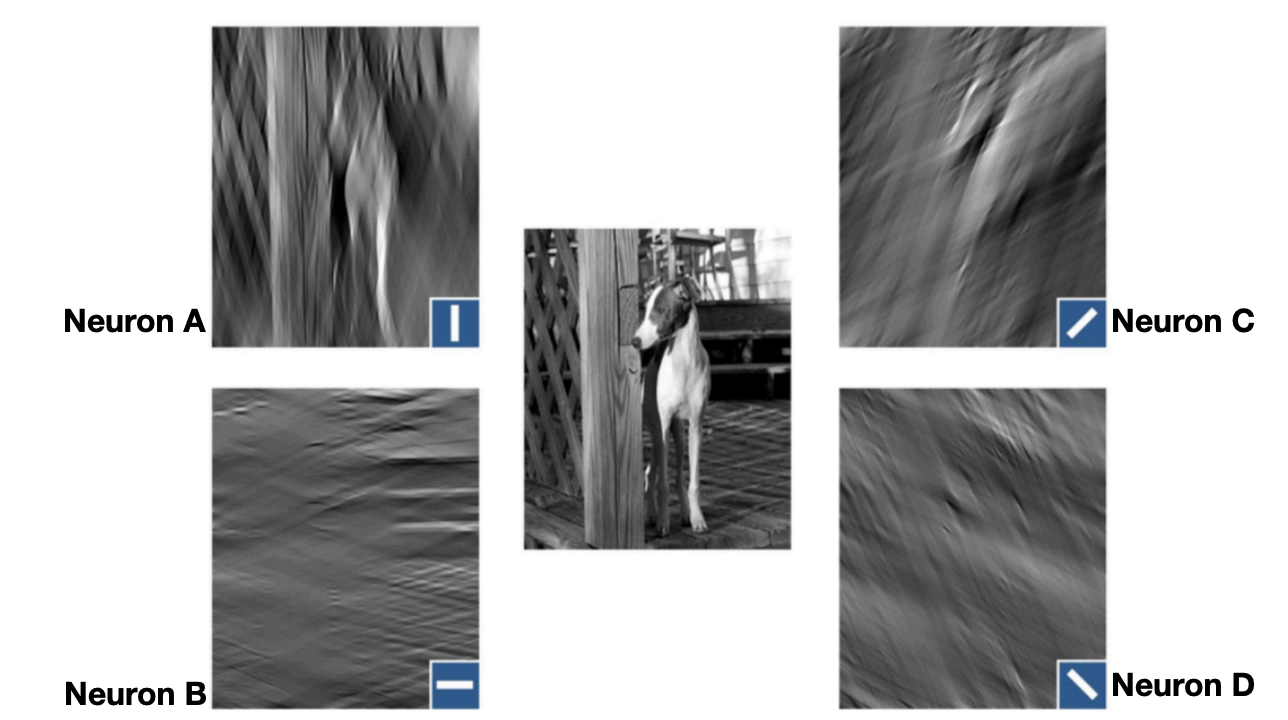
Individual V1 Neurons’ Representation of an Image
This simulation depicts what attributes of a visual image (greyhound and fence) are represented by responses of V1 neurons tuned to different preferred orientations

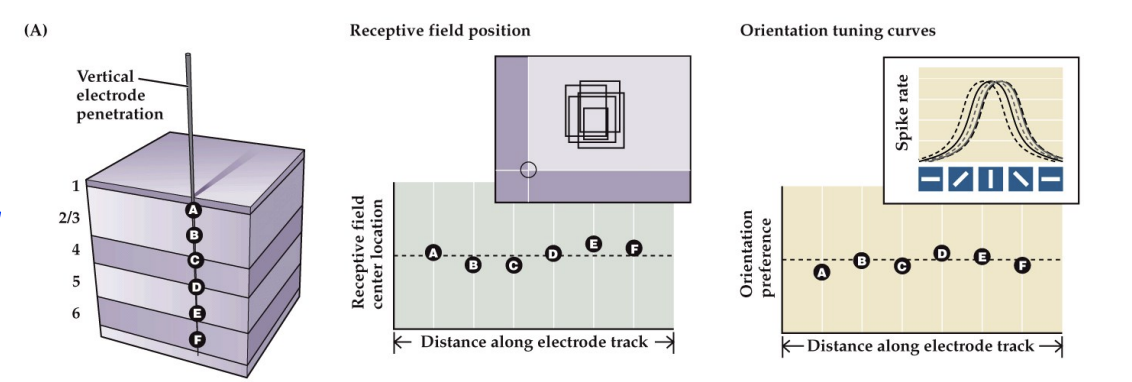
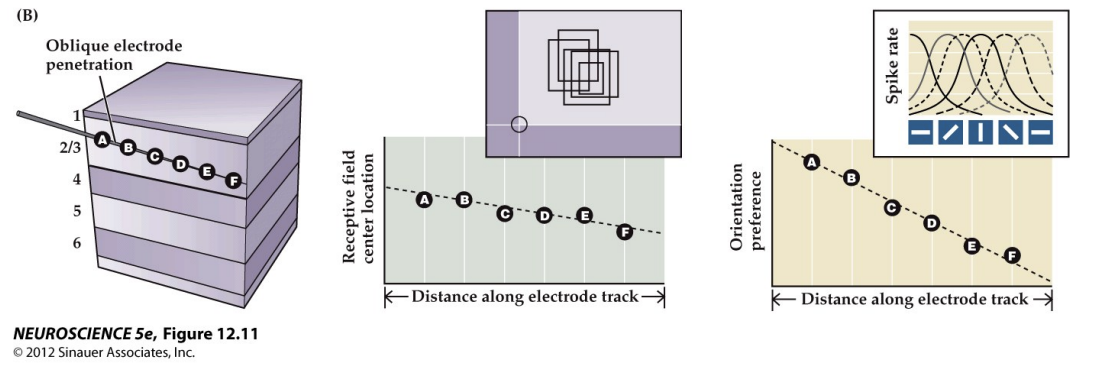
Retinotopy
There is a systematic, orderly mapping of orientation selectivity and receptive field position across V1
Within each column of V1, each neuron has similar response properties
Across columns, neurons exhibit an orderly progression of response properties
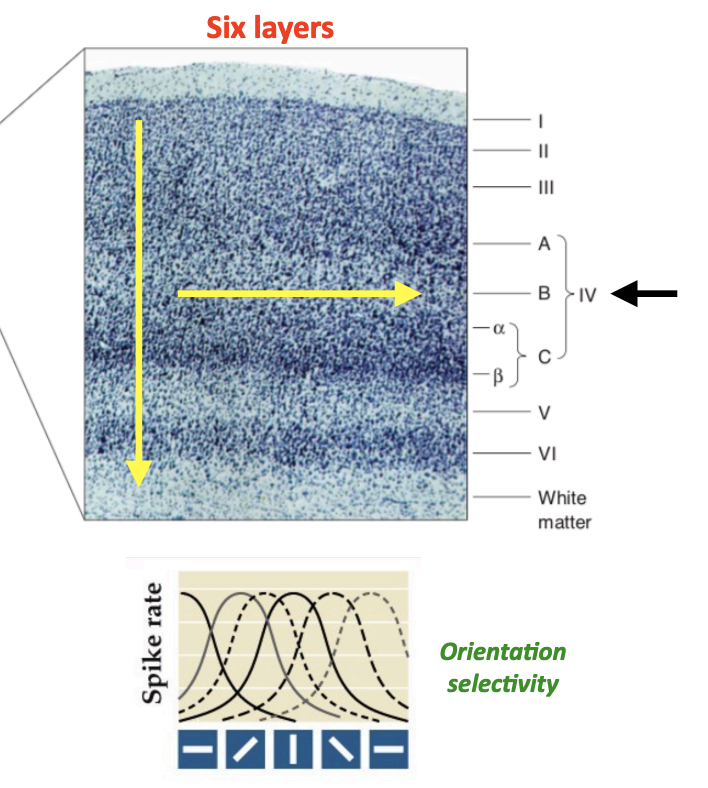
Within a column
Across a column
Dorsal stream
(“where/how” pathway): Visual motion analysis and visual control of action
Ventral stream
(“what” pathway): Recognition of color and complex objects, including faces
V2
Responds to similar stimuli as V1 but also contours and important for visual memory
MT (V5)
Responds to linear movement, regardless of color, and visual control of action
V4
Responds to features of intermediate complexity (e.g. geometric shapes) and color
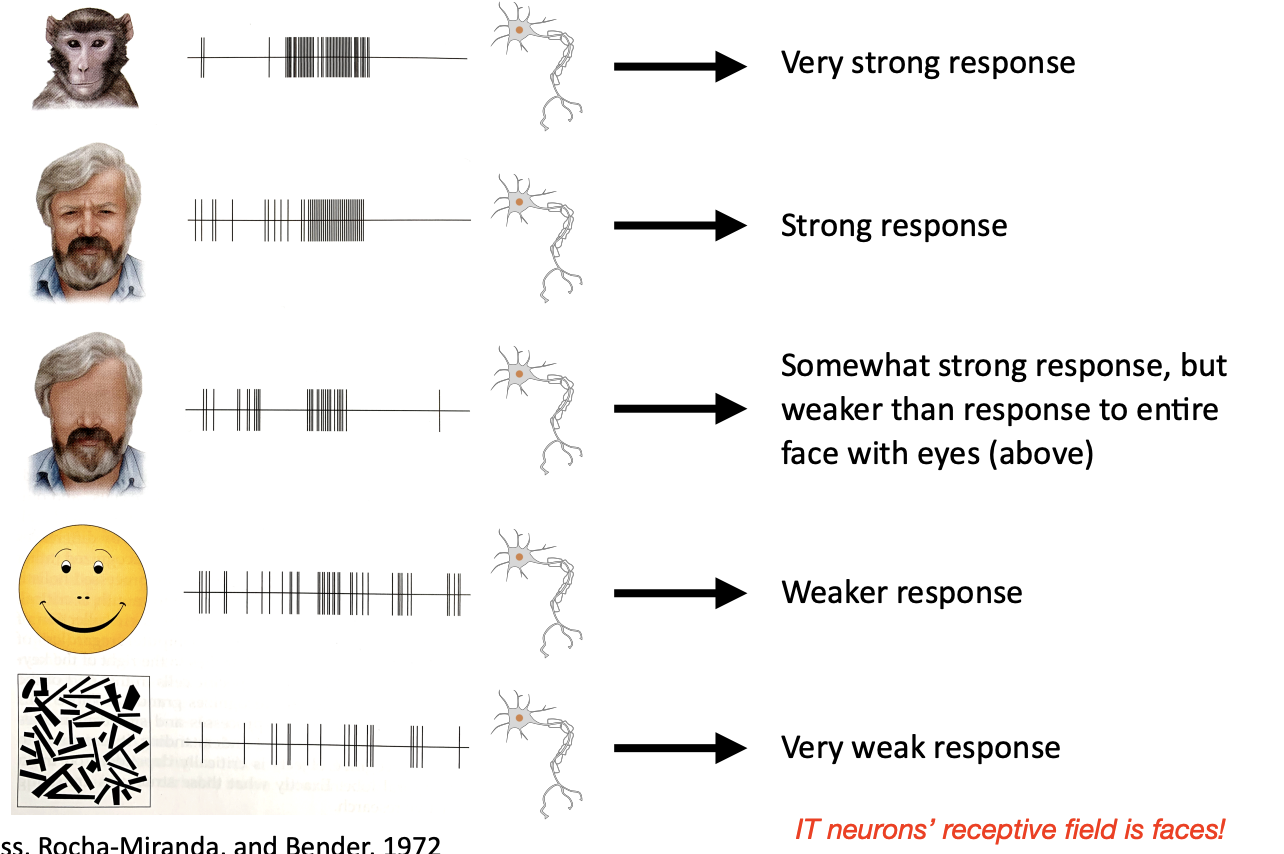
IT
Responds to complex objects, including faces! (e.g. Fusiform Face Area in IT)
Neurons in Inferotemporal Cortex (IT/FFA) of Macaque Monkeys Respond to Complex Objects, Including Faces
Visual pareidolia
The tendency to see faces in inanimate objects, shadows, clouds, abstract patterns, etc.
There’s several theories as to why we’re good at this as a species, but the prevailing hypothesis is that it reflects our social evolution— human survival depends on others (whether we need their help or fear their violence); our brains are likely wired to quickly detect others
Studies in humans and other primates have shown, unsurprisingly, that the Fusiform Face Area (FFA) in Inferotemporal Cortex (IT) is involved in this phenomenon
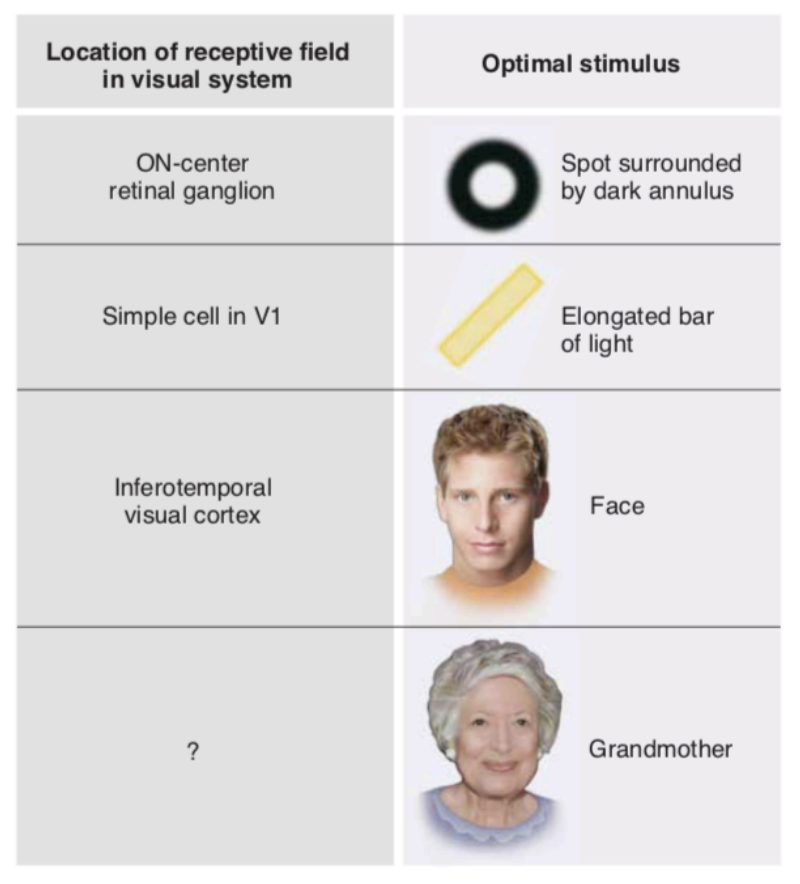
As we move up the receptive field hierarchy
we encounter neurons that respond to increasingly complex features