Astronomy 10: Chapters 5-8 (final)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:16 PM on 5/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
the overall process of the creation of stars and planets
nebula → molecular cloud → molecular core → solar nebula → protostellar disk →protoplanetary disk → sun, planets
2
New cards
Interstellar medium
materials in space between stars
3
New cards
protostars
formed in molecular core; has protostellar disk and then this disk is called a protoplanetary disks when planets start forming
4
New cards
thermal energy
The energy that resides in the random motion of atoms, molecules, and particles, by which we measure their temperature; pushes outwards after cloud contacts and heats up
5
New cards
magnetic fields
A field that is able to exert a force on a moving electric charge. Occurs when object has molten interior and rotates at a moderately rapid speed; collapses with turbulence as collapsing cloud resists gravity
6
New cards
Importance of a magnetic field
Protects the Earth from harmful solar wind and cosmic radiation by deflecting charged particles away from the planet.
7
New cards
Nebula Theory
explains process from Nebula to Solar System formation
8
New cards
protostellar disk
the solar nebula settles into a protosun in the center and a disk
9
New cards
protoplanetary disk
forms planets (core accretion model)
10
New cards
exoplanets
planets orbiting around stars other than the Sun
11
New cards
Conservation of angular momentum
The physical law stating that the amount of angular momentum of an isolated system does not change over time; as cloud contracts, rotation increases
12
New cards
after conservation of angular momentum…
* Collisions between particles in the cloud caused flatten into a disk (gas particles colliding reduce up & down motions)
* Spinning cloud flattens as it shrinks
* Grains in the disk accrete into planetesimals that eventually form into planets
* Spinning cloud flattens as it shrinks
* Grains in the disk accrete into planetesimals that eventually form into planets
13
New cards
Conservation of energy
The physical law stating that the amount of energy of an isolated, closed system does not change over time; Gravity causes cloud to contract and heat up
14
New cards
planetary systems consist of…
* a star
* planets/dwarf planets
* moons
* asteroids
* comets
* planets/dwarf planets
* moons
* asteroids
* comets
15
New cards
our solar system consists of…
* Terrestrial planets
* Asteroid Belt
* Jovian (gas giants) planets
* KBO (Kuiper Belt object)
* Oort Cloud
* Asteroid Belt
* Jovian (gas giants) planets
* KBO (Kuiper Belt object)
* Oort Cloud
16
New cards
Oort Cloud
A spherical distribution of comet nuclei stretching from beyond the Kuiper Belt to more than 50,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun
17
New cards
General characteristics of a solar system we have accepted from our Solar System
\
Thermal profile of a solar system and observations
Thermal profile of a solar system and observations
18
New cards
\
Thermal profile of a solar system that is hot and cools further away from the Sun
Thermal profile of a solar system that is hot and cools further away from the Sun
* Frost line/snow line: \n - Inside: Too hot for hydrogen compounds to form ices \n - Outside: Cold enough for ices to form
* Refractory: do not melt at high temps
* Volatile: melt or evaporate ate moderate temps
* Refractory: do not melt at high temps
* Volatile: melt or evaporate ate moderate temps
19
New cards
frost line
* giants formed outside of it
* terrestrials formed inside of it
* terrestrials formed inside of it
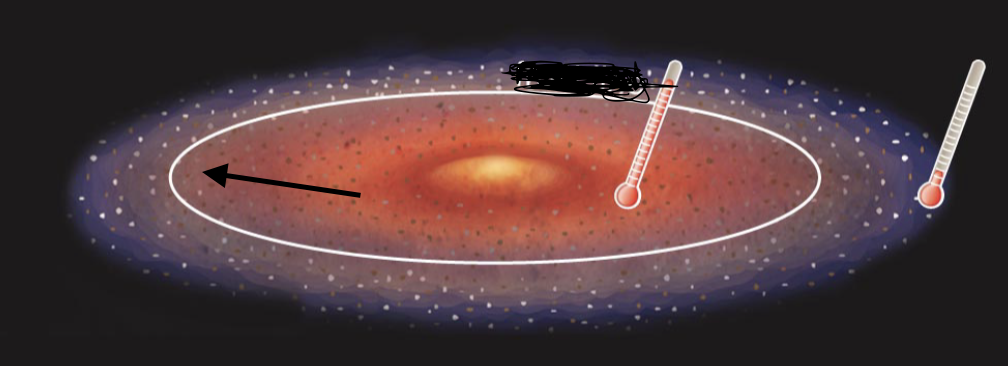
20
New cards
Solar system observations to be explained
* The large bodies orbit in same direction and plane
* There are two types of planets: terrestrial and jovian (giant planets)
* There are smaller bodies: asteroids and comets
* Notable exceptions to usual patterns:( Most likely due to bombardment/collision) odd tilt of Uranus and Venus’ retrograde rotation
* There are two types of planets: terrestrial and jovian (giant planets)
* There are smaller bodies: asteroids and comets
* Notable exceptions to usual patterns:( Most likely due to bombardment/collision) odd tilt of Uranus and Venus’ retrograde rotation
21
New cards
2 scenarios planet formation theories
1. gravitational collapse (like stars) - doesn’t explain the whole process
2. core accretion (the more acceptable theory)
* The core of planets form by planetesimal accretion; then gas is accreted
* Gas giants must form before the solar nebula dissipates (less than 10 Mys)
22
New cards
core accretion
Gas giant planet forms from dust and gas. Dust sticks together to form planetesimals, which grow by accreting more material. Once they reach critical mass, they attract gas and rapidly increase in size.
23
New cards
gravitational collapse
when the astronomical object no longer has the interior pressure to counter the gravity, so it contracts
24
New cards
planet formation ends when…
solar wind blew solar nebula away
25
New cards
A glowing, rapidly moving knot of gas and dust that is excited by bipolar outflows in very young stars.
Herbig-Haro (HH) objects
26
New cards
T Tauri variables
T Tauri variables are young stars that vary in brightness due to changes in their accretion rate. They have protoplanetary disks and are important for studying early star and planet formation.
27
New cards
asteroids
left over after accretion process; A primitive rocky or metallic body (planetesimal) that has survived planetary accretion. Also are the parent bodies of meteoroids.
28
New cards
comets
left over after accretion process; A complex object consisting of a small, solid, icy nucleus; an atmospheric halo; and a tail of gas and dust.
29
New cards
exo-planetary solar systems
* not all look like our solar system
* have many Jupiter sized planets really close to their star
* have other planets also really close to their star
* have many Jupiter sized planets really close to their star
* have other planets also really close to their star
30
New cards
2 major detection methods
radical velocity and transmit method
31
New cards
radical
\
The speed at which an object is moving in a circular path is called __________ velocity. It is perpendicular to the tangential velocity and is dependent on the radius of the circle.
The speed at which an object is moving in a circular path is called __________ velocity. It is perpendicular to the tangential velocity and is dependent on the radius of the circle.
32
New cards
Doppler effect
The change in wavelength of sound or light that is due to the relative motion of the source toward or away from the observer.
* Red shift: The shift toward longer wavelengths of light by any of several effects, including Doppler shift, gravitational redshift, or cosmological redshift.
* Blue shift: The Doppler shift toward shorter wavelengths of light from an approaching object.
* Red shift: The shift toward longer wavelengths of light by any of several effects, including Doppler shift, gravitational redshift, or cosmological redshift.
* Blue shift: The Doppler shift toward shorter wavelengths of light from an approaching object.
33
New cards
Wobble method
34
New cards
Transit Method
Method used to detect exoplanets by measuring the periodic dimming of a star's brightness as a planet passes in front of it; used by Kepler Mission
35
New cards
formation history
Earth formed 4.6 billion years ago from the inner solar nebula.
36
New cards
Interior parts of Earth
Core: Highest density; nickel and iron \n Mantle: Moderate density; silicon, oxygen, etc. \n Crust: Lowest density; granite, basalt, etc.
37
New cards
Interior Differentiation
Gravity pulls high-density material to center
lower-density material rises to surface \n Material ends up separated by density
lower-density material rises to surface \n Material ends up separated by density
38
New cards
Heating of Interior
early Earth: accretion & differentiation \n Current Earth : radioactive decay
39
New cards
Cooling of Interior (how HOT goes to COLD)
* Convection: transports heat as hot material rises and cool material falls
* Conduction: transfers heat from hot material to cool material
* Radiation: sends energy into space
* Conduction: transfers heat from hot material to cool material
* Radiation: sends energy into space
40
New cards
Geological activity that shapes the Earth’s surface
* Impact cratering
* from asteroids and comets
* Volcanism
* eruption of molten rock onto surface
* Tectonics
* Disruption of a planet’s surface by internal stresses
* Earth is only terrestrial with plate tectonics
* Erosion
* Surface changes made by wind, water, ice or debris
* from asteroids and comets
* Volcanism
* eruption of molten rock onto surface
* Tectonics
* Disruption of a planet’s surface by internal stresses
* Earth is only terrestrial with plate tectonics
* Erosion
* Surface changes made by wind, water, ice or debris
41
New cards
Greenhouse Effect
Generally a good thing when occurring naturally. But when the process is sped up through human activity, it is not good
42
New cards
Planetary sizes
small planets cool faster than large planets → heating/cooling of interior atmosphere (to have or not to have)→ erosion (water, ice, wind, debris)
43
New cards
Habitual zone
the region around a star in which planets could potentially have surface temperatures at which liquid water could exist
44
New cards
Moon
* Lowlands (Maria) à basins flooded by lava flows \n Moon formation/history (Earth was hit by Mars-sized object and ejected
* material into space, eventually accreting into our Moon
* Moon rock composition similar to that found on Earth
* material into space, eventually accreting into our Moon
* Moon rock composition similar to that found on Earth
45
New cards
Mercury
* Closest to the Sun
* No tilt
* Very slight ionic atmospherescarps
* Caloris Basin and “Rocky Road” feature just on the opposite side of Mercury from Caloris Basin→ something big hit Mercury !!! ?
* large core most likely due to massive impacts that blew away the mantle during formation
* No tilt
* Very slight ionic atmospherescarps
* Caloris Basin and “Rocky Road” feature just on the opposite side of Mercury from Caloris Basin→ something big hit Mercury !!! ?
* large core most likely due to massive impacts that blew away the mantle during formation
46
New cards
Venus
* not as mountainous and not as rugged as Earth; just nasty terrain
* the surface is mainly gently rolling plains;
* Only Venus has: “pancakes”/Coronae craters, shield volcanoes
* acid rain
* extremely high atmospheric pressure (92 atm) Greenhouse Effect went into “overdrive”
* Rotates cw (clockwise) → (planet knocked over upside down?)
* Very slow rotator → longer rotation time than orbit time
* Atmosphere rotates very quickly → once in 4 days
* One hot planet: 900F everywhere
* We can see phases, like the Moon
* the surface is mainly gently rolling plains;
* Only Venus has: “pancakes”/Coronae craters, shield volcanoes
* acid rain
* extremely high atmospheric pressure (92 atm) Greenhouse Effect went into “overdrive”
* Rotates cw (clockwise) → (planet knocked over upside down?)
* Very slow rotator → longer rotation time than orbit time
* Atmosphere rotates very quickly → once in 4 days
* One hot planet: 900F everywhere
* We can see phases, like the Moon
47
New cards
Mars
* rotates just 40 mins longer than Earth
* tenth of Earth’s mass
* half Earth’s radius
* shield volcanoes:
* Olympus Mons → highest & largest in the Solar System
* Tharis range
* Vallis Marineris
* Hellas & Argyre basins
* Many features believed to be caused by water flows
* Thin atmosphere mostly CO2
* Has a tilt (about 25O) → has seasons
* Has been explored by orbiting and roving probes, A LOT!
* Life on Mars? Still searching and hoping.
* tenth of Earth’s mass
* half Earth’s radius
* shield volcanoes:
* Olympus Mons → highest & largest in the Solar System
* Tharis range
* Vallis Marineris
* Hellas & Argyre basins
* Many features believed to be caused by water flows
* Thin atmosphere mostly CO2
* Has a tilt (about 25O) → has seasons
* Has been explored by orbiting and roving probes, A LOT!
* Life on Mars? Still searching and hoping.
48
New cards
Formation history for giant planets
Giants formed 4.6 billion years ago → core accretion
49
New cards
Gas planets
Jupiter and Saturn
50
New cards
Water/icy planets
Uranus and Neptune
51
New cards
General knowledge for Jovians (giant planets)
* are made of mostly gases (H, He, H2 O, CH4 (methane), NH3 (ammonia) )
* have rock/ice cores
* do not have solid surfaces: gases --> liquid & solid at high pressure
* have ring systems and many moons
* formed faster than terrestrials (less than 3 – 5 Myrs)
* large because they accumulated gas directly from the solar nebula (true for Jupiter and Saturn)
* are far from the Sun
* have rock/ice cores
* do not have solid surfaces: gases --> liquid & solid at high pressure
* have ring systems and many moons
* formed faster than terrestrials (less than 3 – 5 Myrs)
* large because they accumulated gas directly from the solar nebula (true for Jupiter and Saturn)
* are far from the Sun
52
New cards
Jupiter
* largest and contains ¾ of total Solar System planetary mass
* Red Eye storm
* core is liquid rock and water
* very strong magnetic field
* rotation period of 9.94 hours
* magnetic field aligned with axis
* Red Eye storm
* core is liquid rock and water
* very strong magnetic field
* rotation period of 9.94 hours
* magnetic field aligned with axis
53
New cards
Saturn
* has the largest set of rings
* core is liquid rock and water
* is a gas planet
* rotation period of 10.56
* magnetic field aligned with axis
* core is liquid rock and water
* is a gas planet
* rotation period of 10.56
* magnetic field aligned with axis
54
New cards
Uranus
* axis of rotation is in the plane of the Solar System
* 98° tilt (maybe due to collision)
* there’s weather change
* alike to Neptune
* has liquid core
* rotation period of 17.23 hours
* magnetic field is upside down
* 98° tilt (maybe due to collision)
* there’s weather change
* alike to Neptune
* has liquid core
* rotation period of 17.23 hours
* magnetic field is upside down
55
New cards
Neptune
* \
* crosses orbits with Pluto but will never collide
* has a liquid core
* is alike to Uranus
* rotation period of 16.10 hours
* magnetic field is off center from axis
* crosses orbits with Pluto but will never collide
* has a liquid core
* is alike to Uranus
* rotation period of 16.10 hours
* magnetic field is off center from axis
56
New cards
Roche limit
distance from object where another smaller object can broken apart because of gravity
* closer object gets to bigger object, the more the smaller object will stretch until it breaks
* Ex.: Saturn’s rings
* closer object gets to bigger object, the more the smaller object will stretch until it breaks
* Ex.: Saturn’s rings