gentics module 2
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what are amino acids binded by
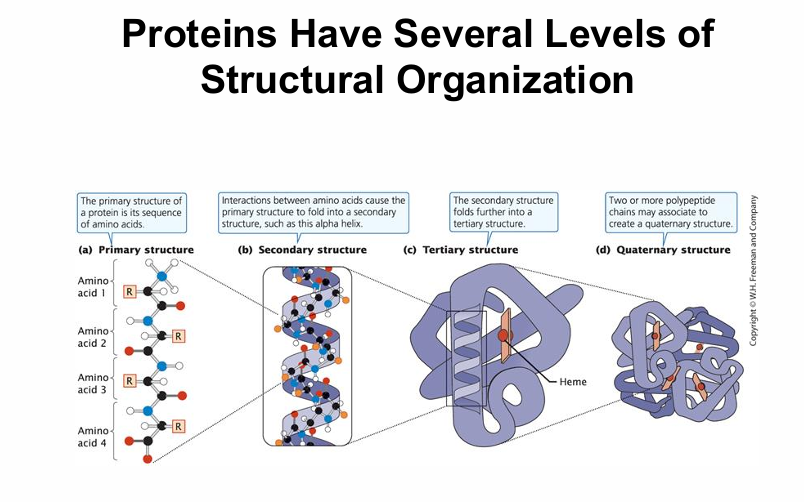
peptide bonds
DNA structures
Central dogma
the flow of genetic material into a cell, like DNA to RNA to Protein, its genotype is determined by the sequence of bases in its DNA, and pheneotype is a product of the proteins in it
what is the exception to the central dogma
many genes code for RNA molecules that do not function as mRNA, and so are not translated into proteins, sometimes RNA can flow back to DNA, called reverse transcriptase to allow the virus to reproduce in other organisms
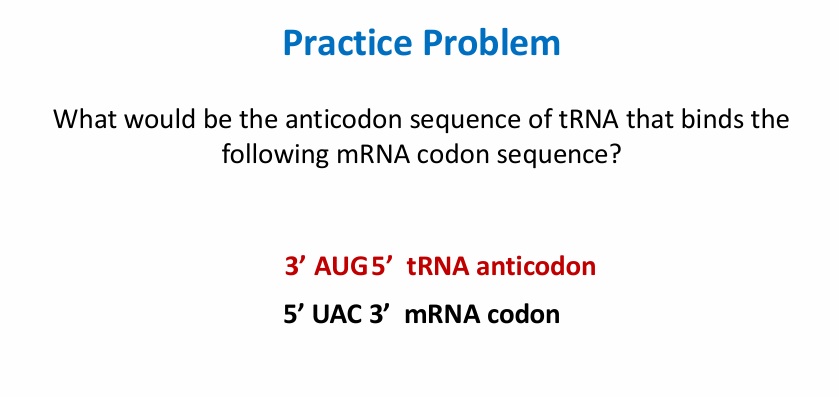
genetic code
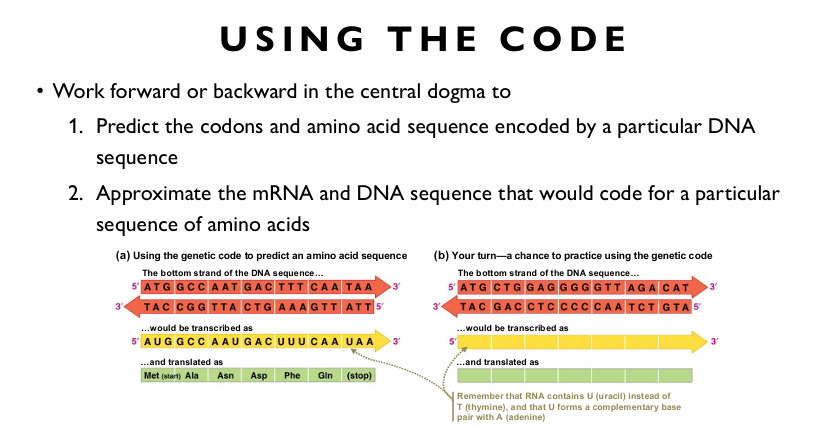
• The triplet code is redundant • Some amino acids are specified by more than one triplet code • Sense Codon • The group of three bases • Specifies a particular amino acid • There is one start codon (AUG) • Signifies the start of the protein-encoding sequence in mRNA • There are three stop codons (UGA, UAA, and UAG) • Signal the end of the protein-coding sequence
IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF THE CODE
• It is redundant • All amino acids except two are encoded by more than one codon (synonymous) • It is unambiguous • One codon never codes for more than one amino acid • Non-overlapping—Codons are read one at a time • It is nearly universal • All codons specify the same amino acids in all organisms • With a few minor exceptions • It is conservative • The first 2 bases are usually identical when multiple codons specify the same amino
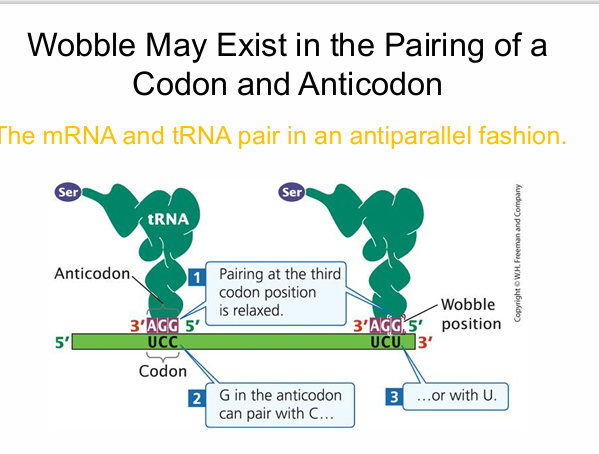
Through wobble, a single tRNA anticodon can pair with more than one mRNA codon.
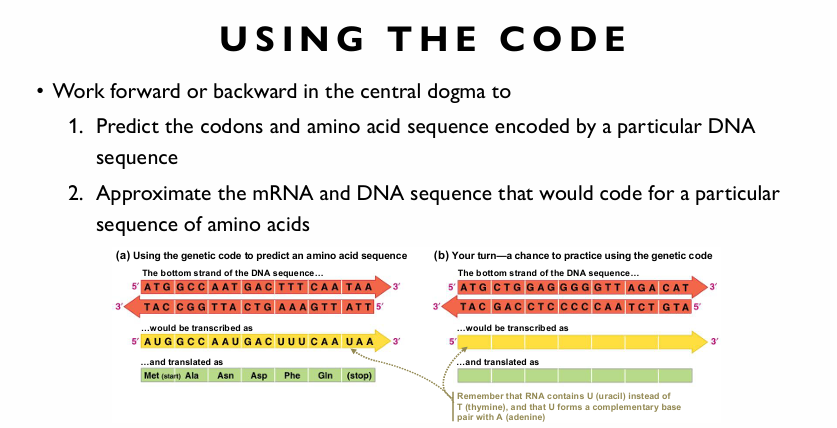
AUG met is start, and UAA,UAG, and UGA stop
There are different types of mutations • Point mutations result from a single base change • Chromosome-level mutations • Are larger in scale 30 • Often result from the addition or deletion of chromosomes from the individual’s karyotype
MUTATIONS HAVE VARYING EFFECTS ON ORGANISMS • Mutations fall into one of three categories: 1. Beneficial mutations increase the fitness of the organism 2. Neutral mutations do not affect an organism’s fitness • Silent mutations are usually neutral 3. Deleterious mutations decrease the fitness of the organism • Most mutations are neutral or slightly deleterious • Some mutations are not in coding regions but can still affect phenotype by affecting gene expression