BIOL1020 UQ Module 1
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
What do cells have in common?
Have a cell membrane made of a lipid-bilayer (hydrophobic head & hydrophobic tail)

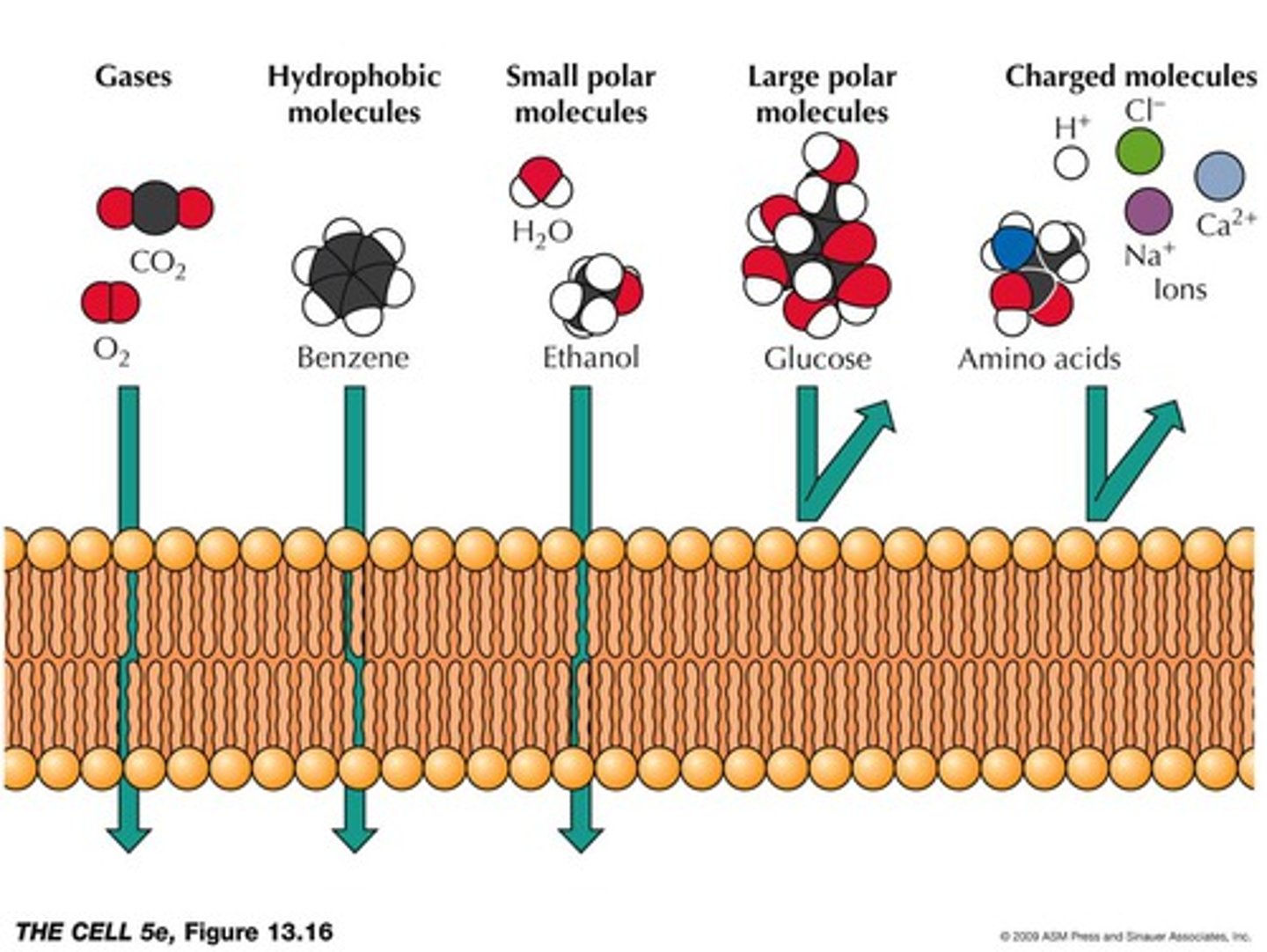
Is the lipid bilayer semi-permeable?
Yes
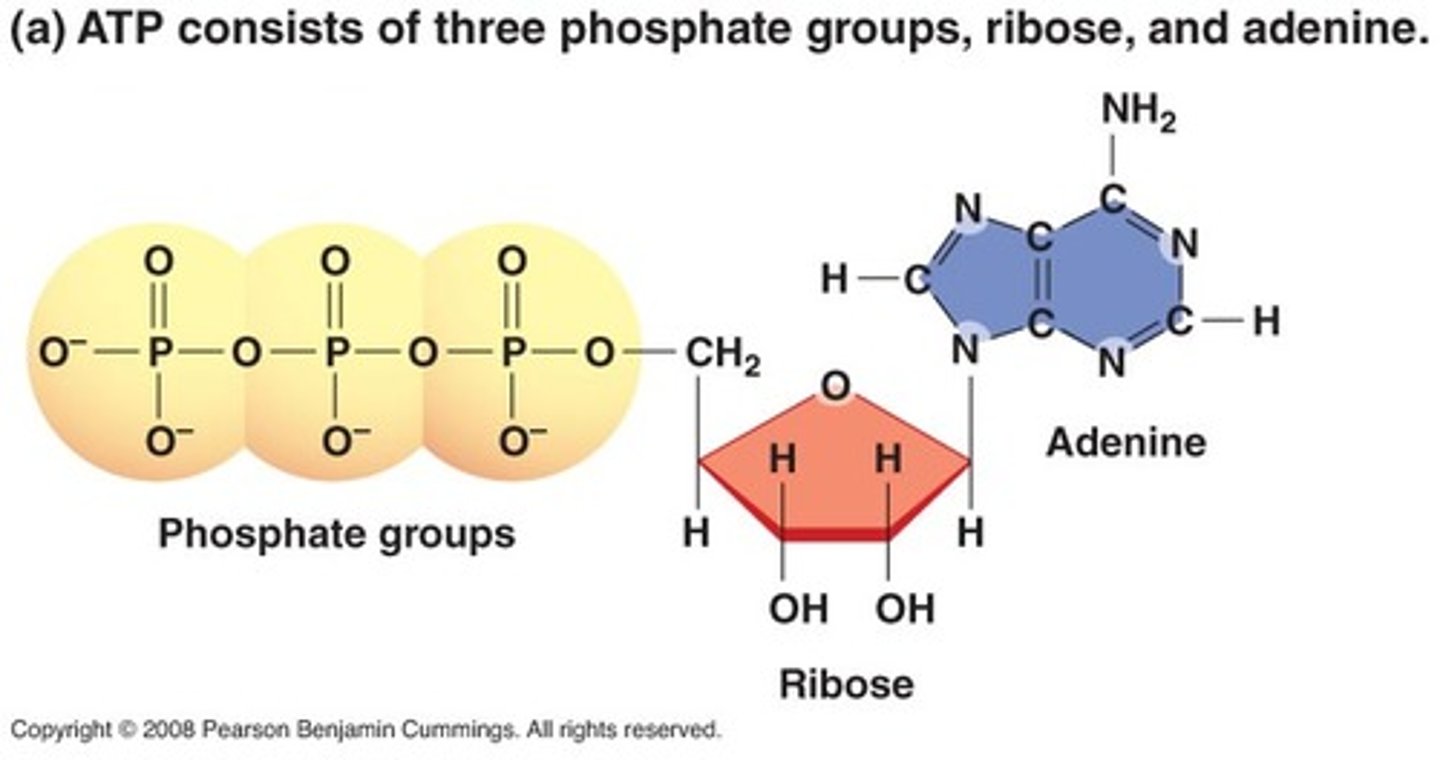
What is the most common form of energy?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
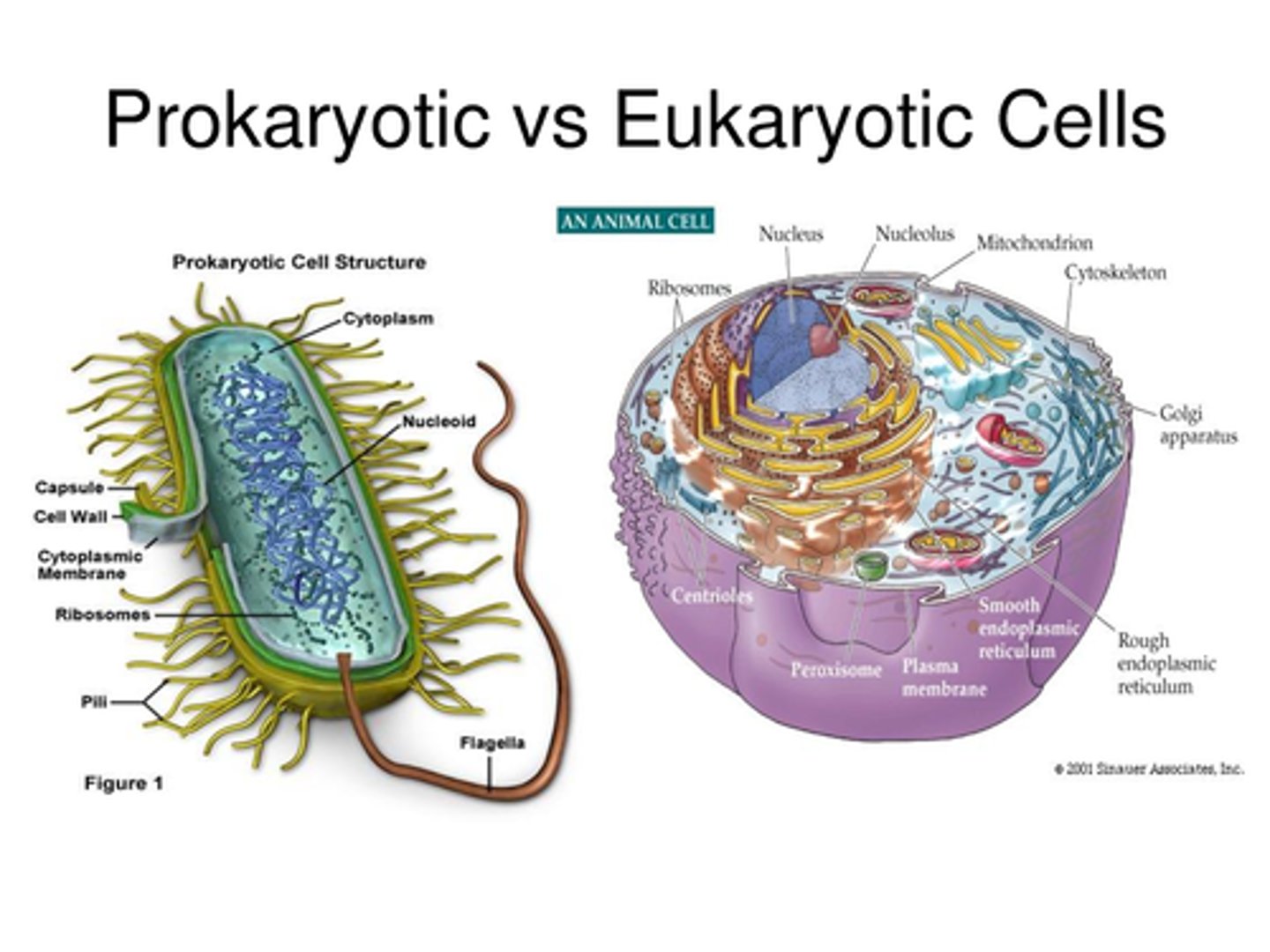
What are the different types of cells?
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
What are the basic building blocks of cells?
Macromolecules: big molecules (polymers) comprised of interconnecting individual units (monomers)
What are carbohydrates?
Macromolecules that provide fuel and structure to cells
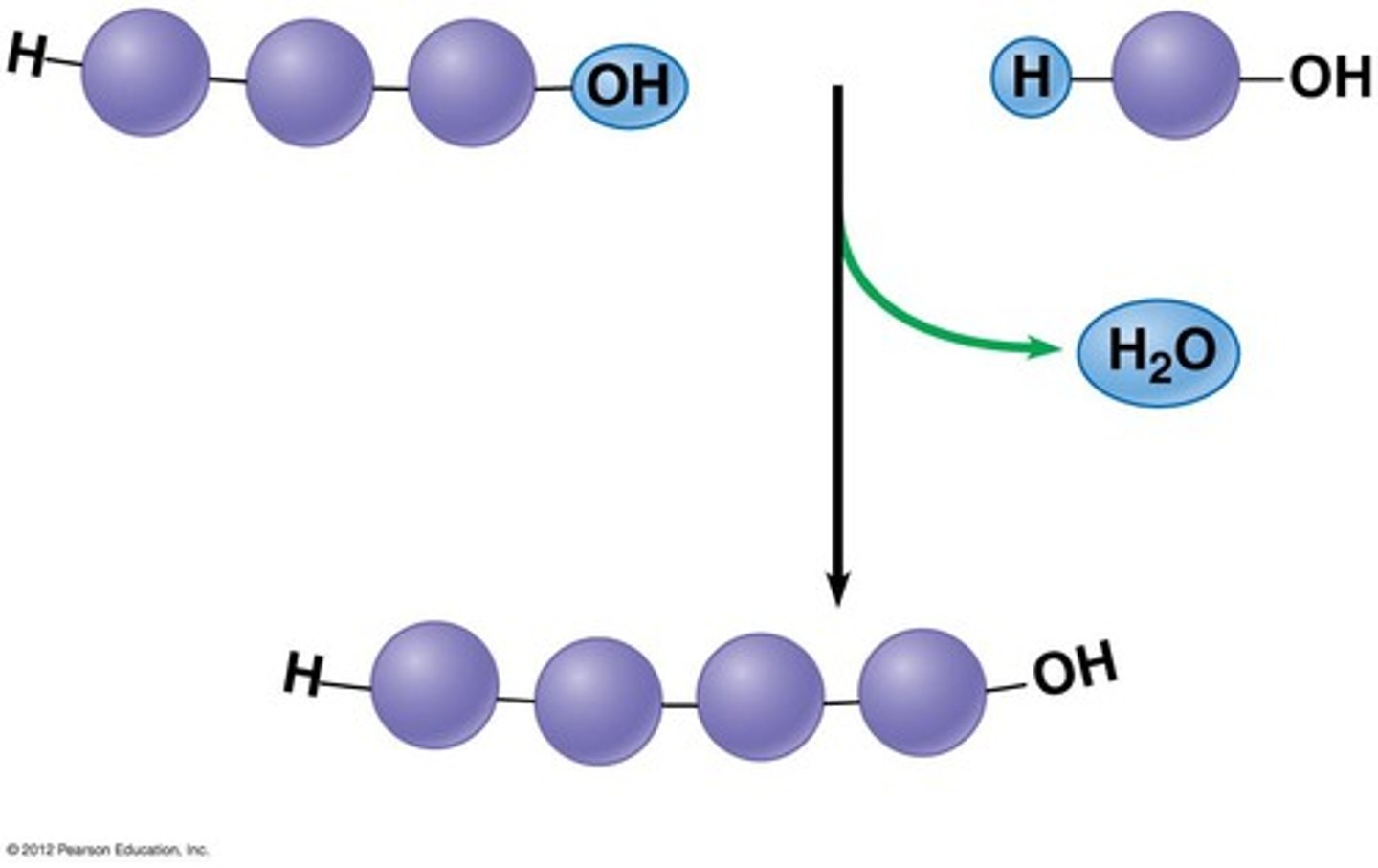
Define a dehydration reaction from polymerisation
Monomers form large polymers, the byproduct being water
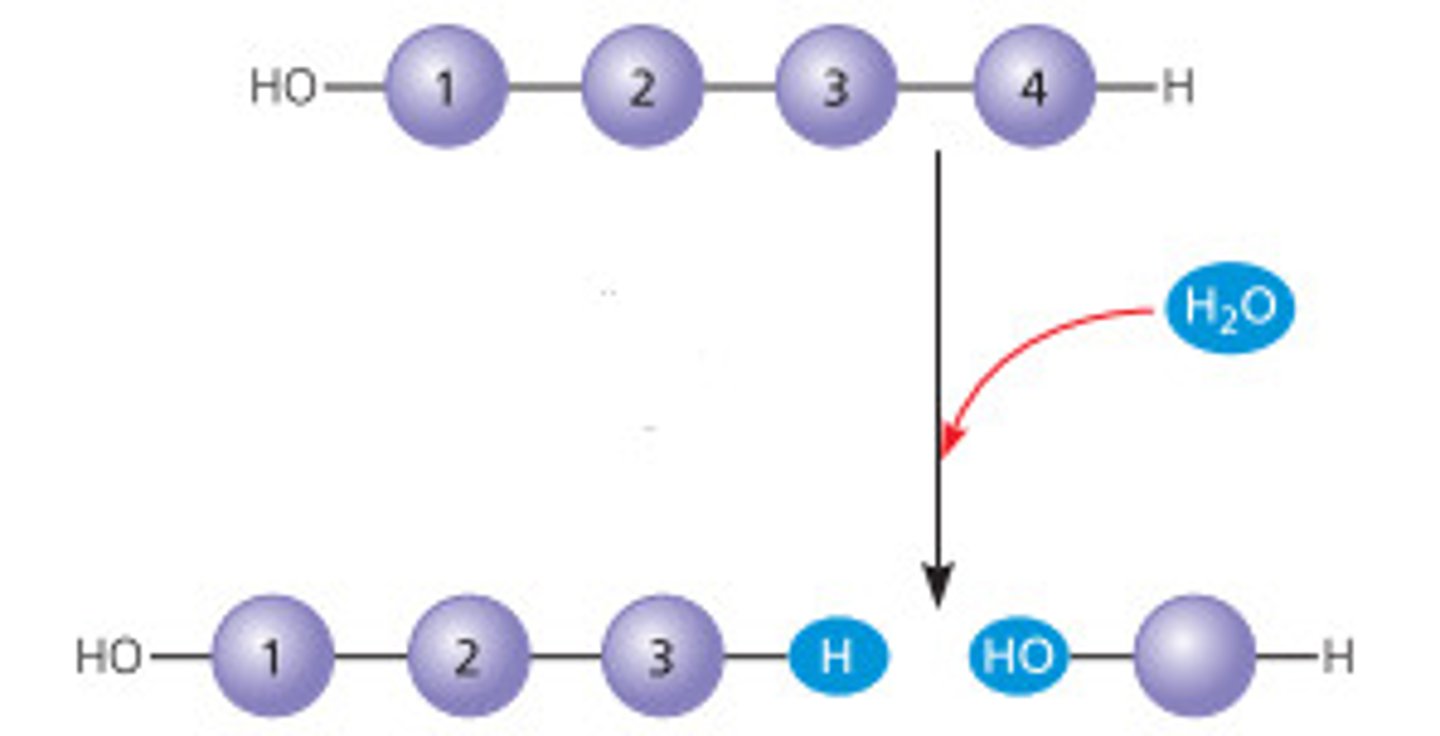
Define polymer synthesis: hydrolysis
the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
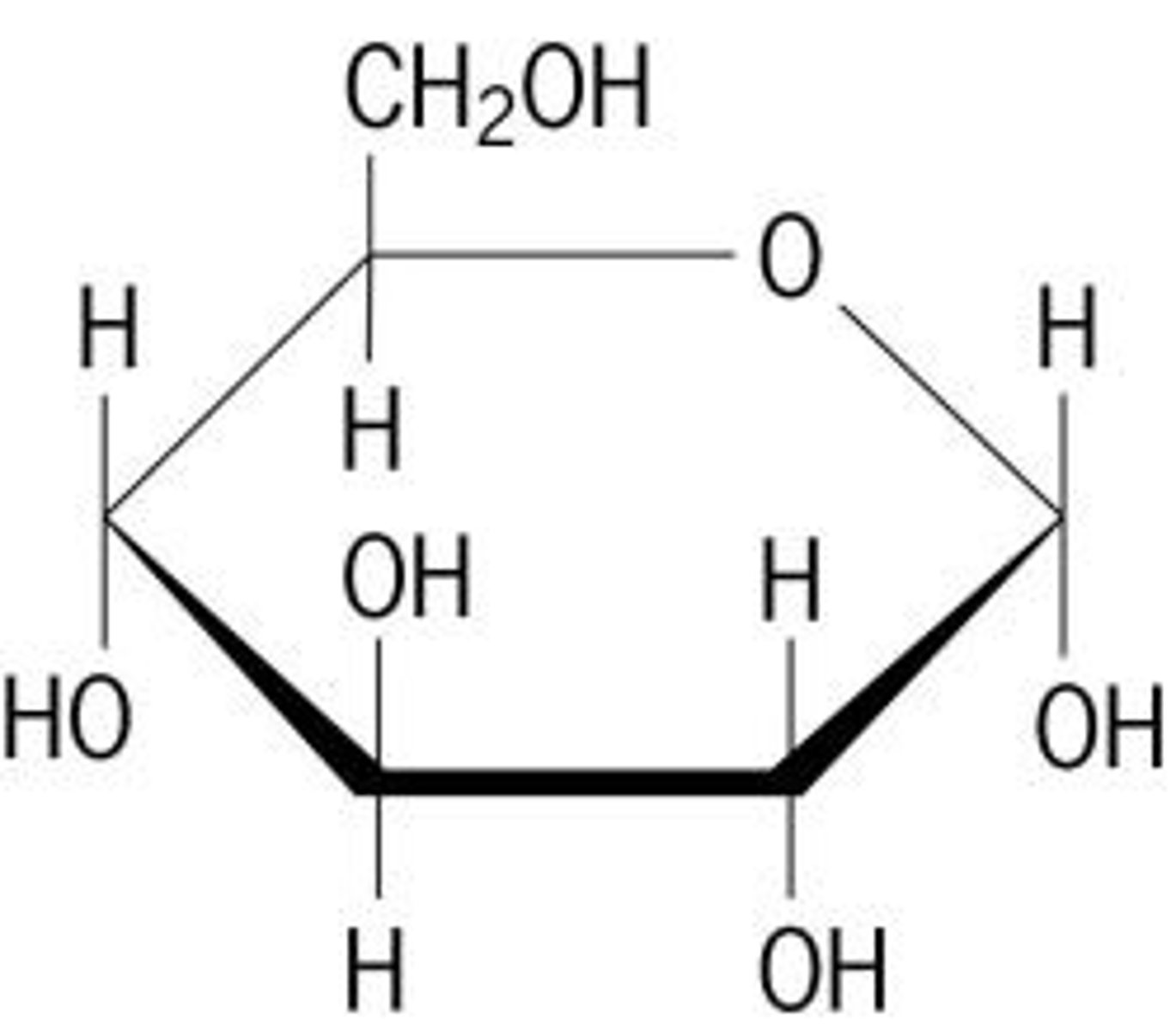
A single unit of a sugar molecule is known as?
Monosaccharides (e.g Glucose)
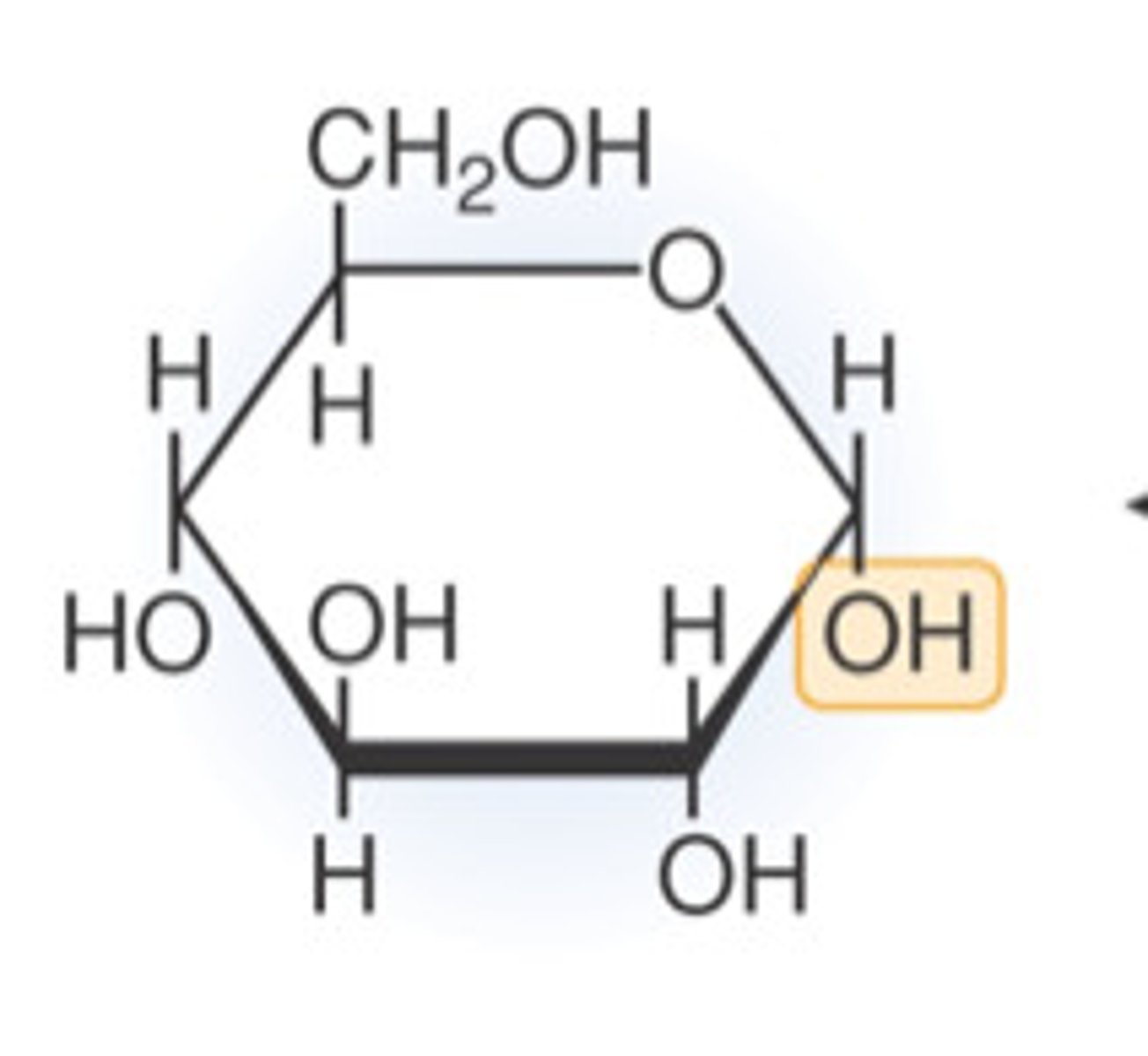
Define Disaccharides?
~ A molecule that is made up of two monosaccharides (sugar molecules)
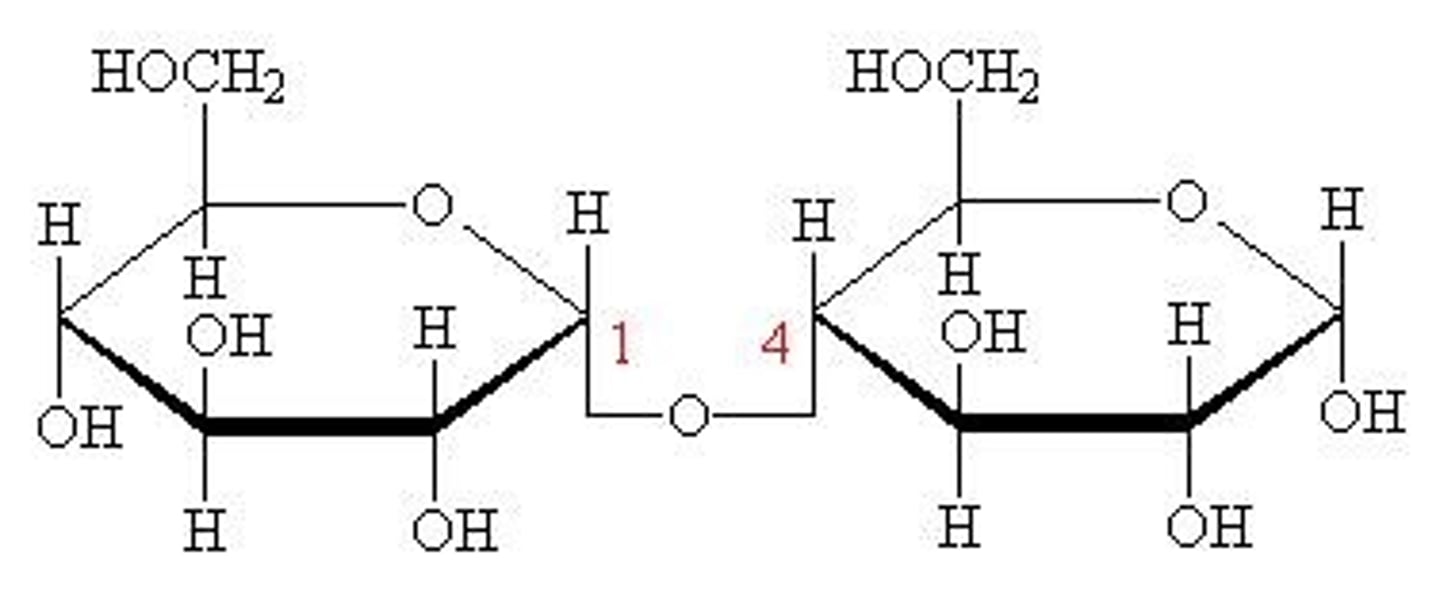
Many units of sugar molecules linked together is known as
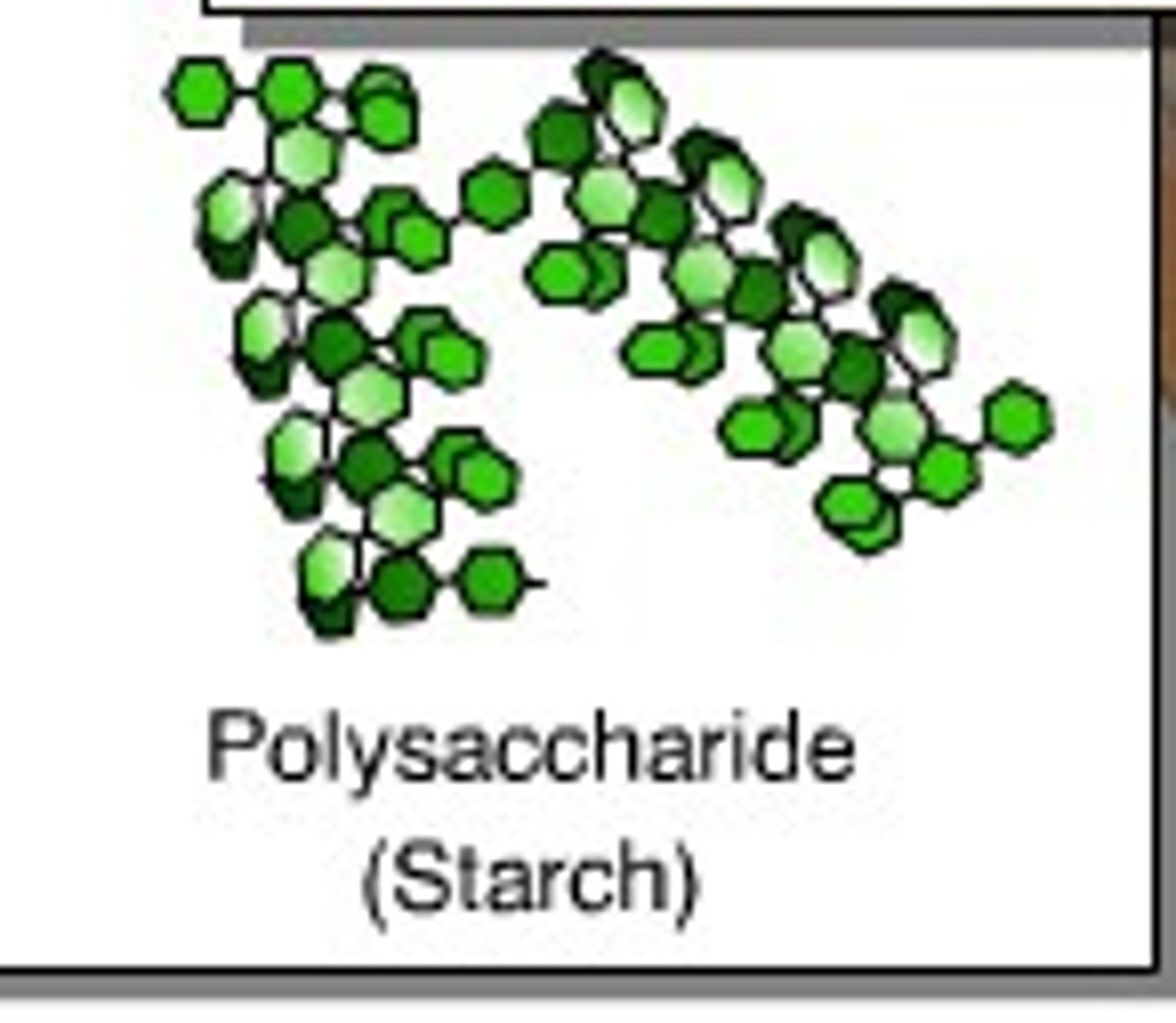
Polysaccharides
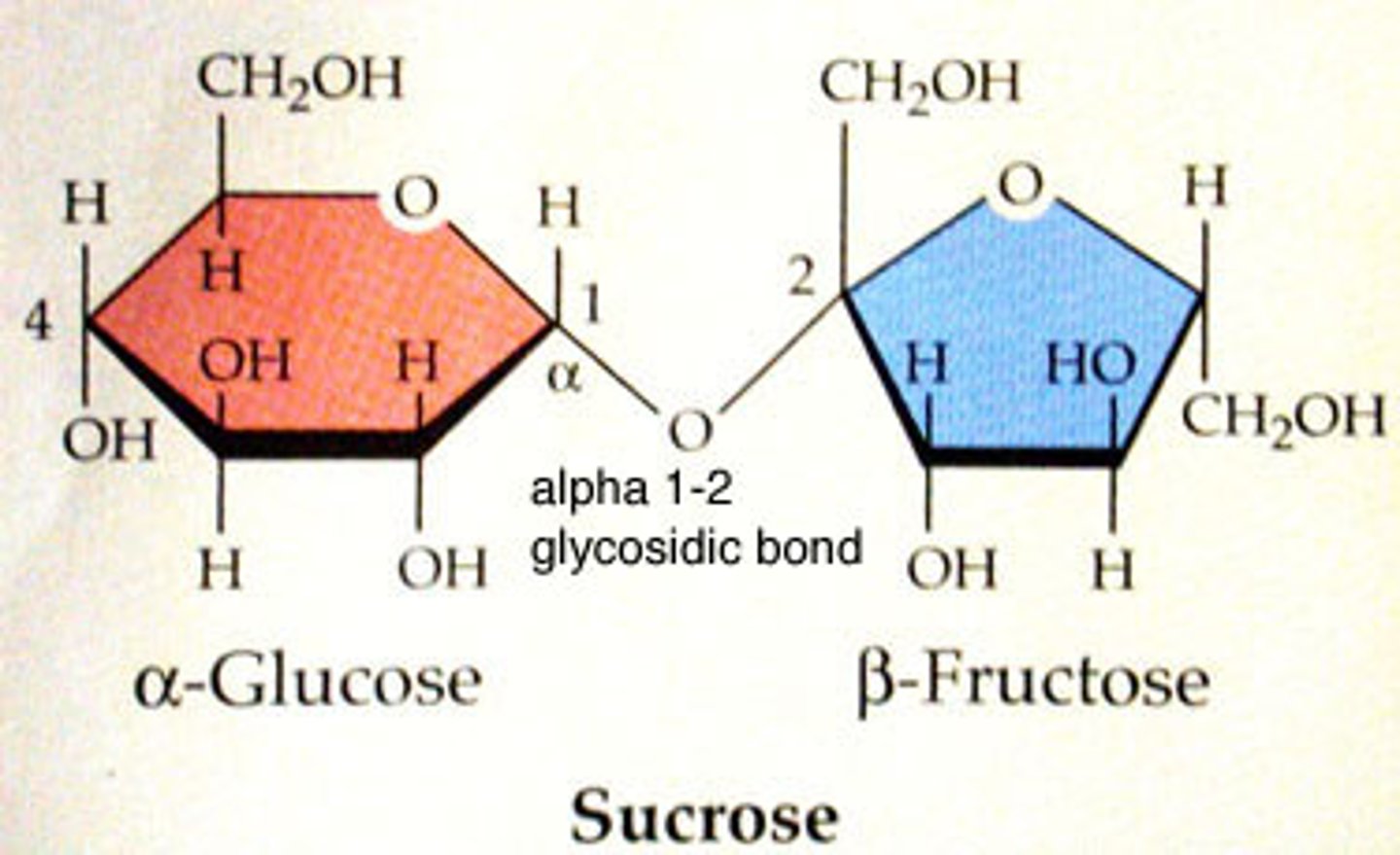
List one example of a Disaccharides?
Maltose, sucrose, lactose
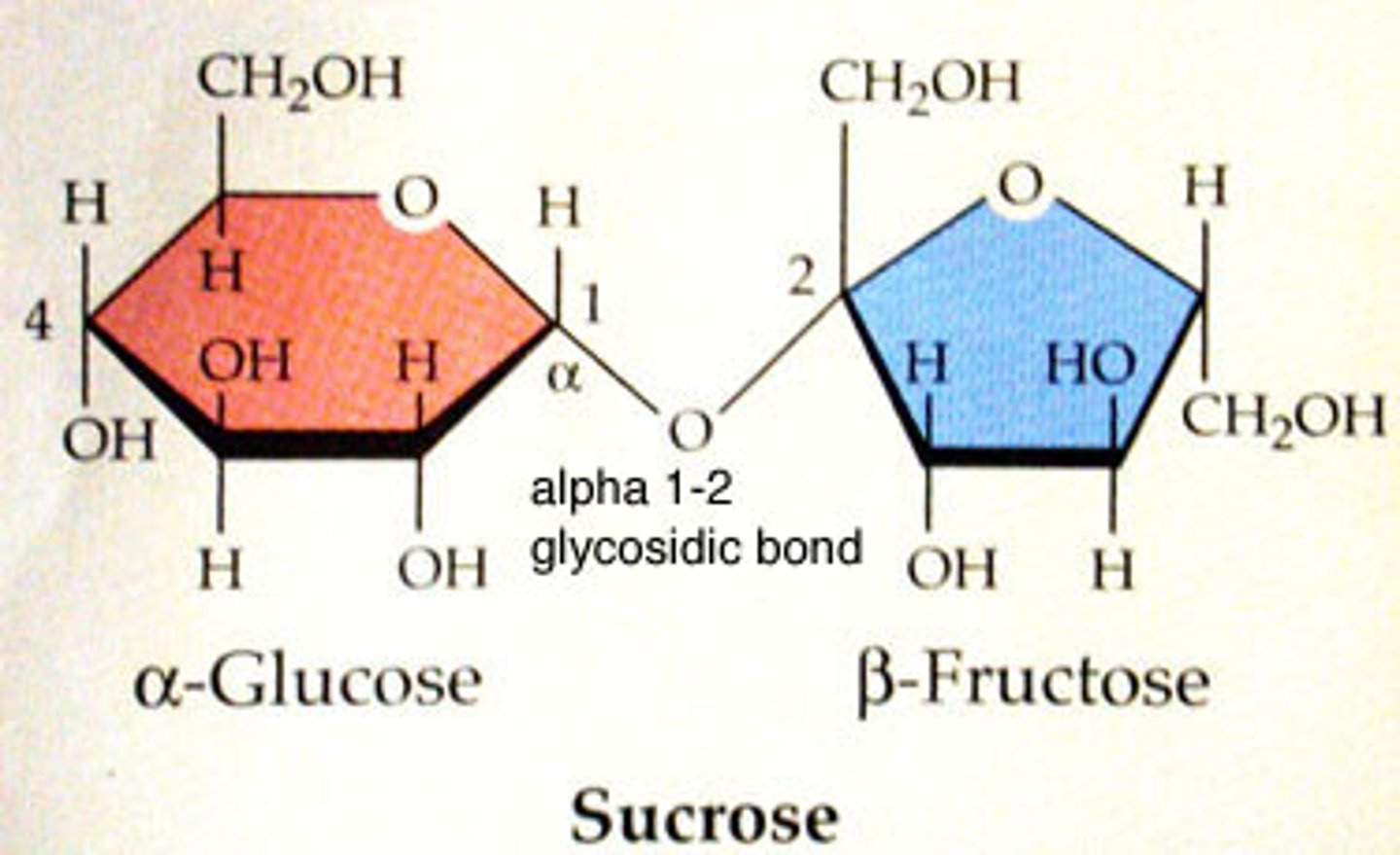
A bond between two sugar molecules are known as?
Glycosidic bond
Define stereoisomers
Compounds with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement of the atoms in space.
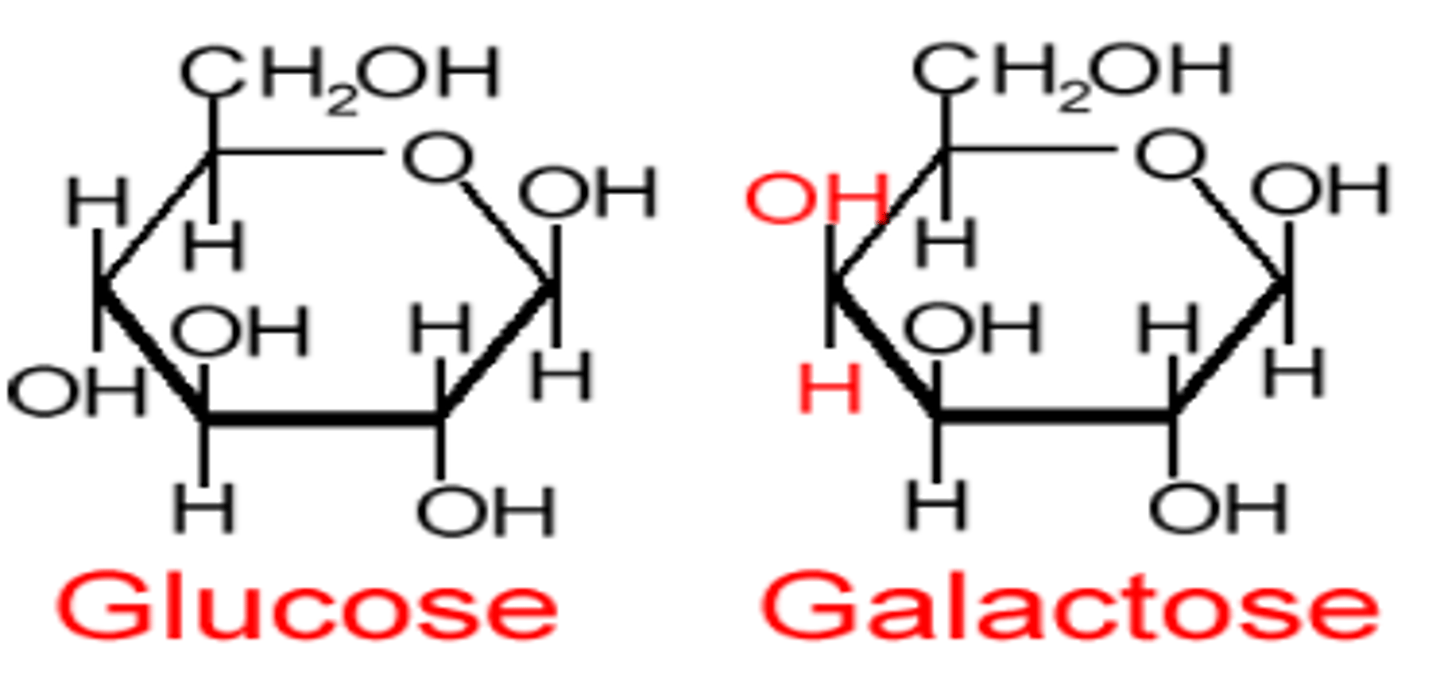
What is the difference between galactose and glucose
OH bond location at the 4th carbon (glucose is bottom, galactose is top)
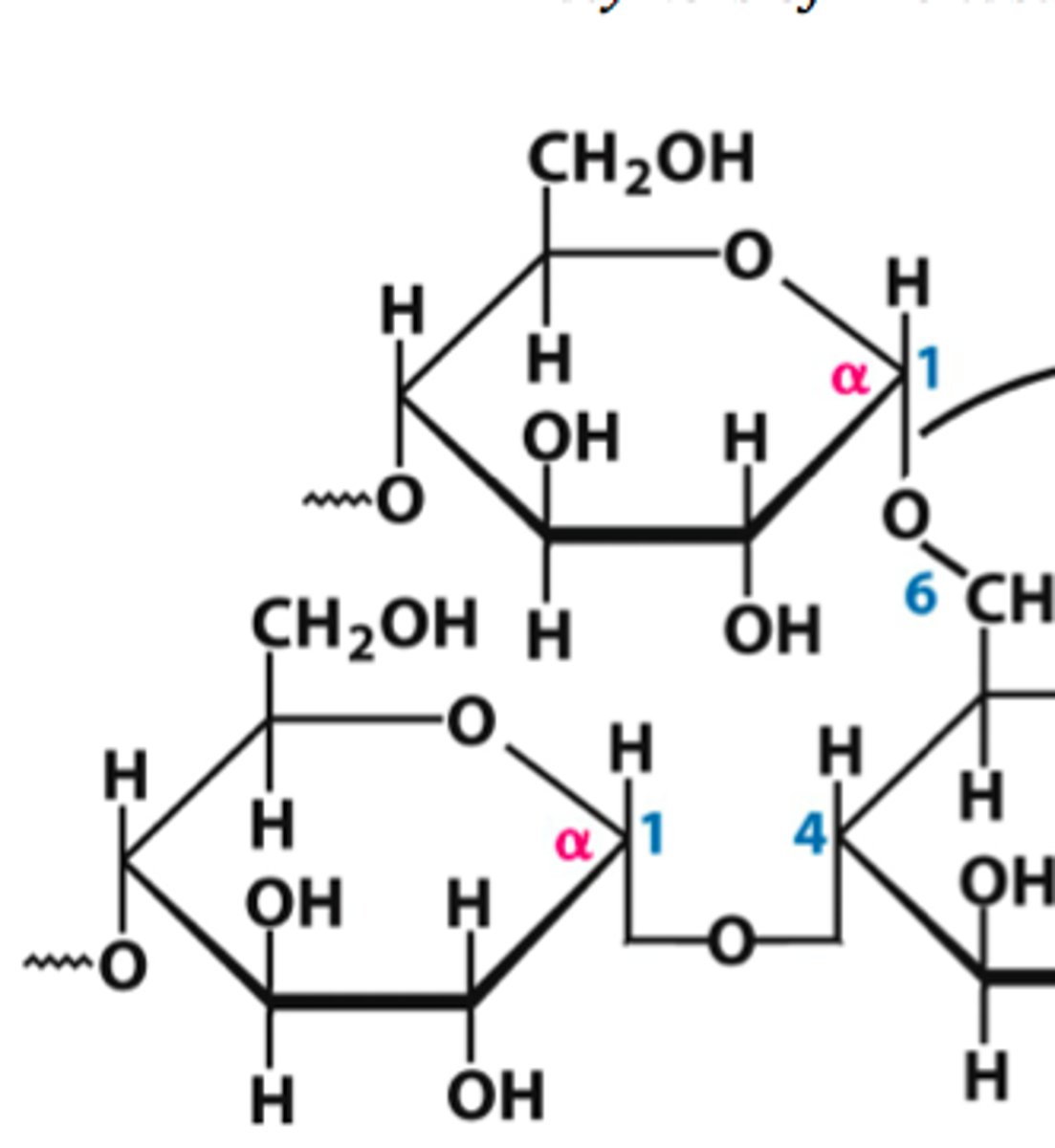
Define when α-glyosidic bonds are formed
When both carbons have the same stereochemistry
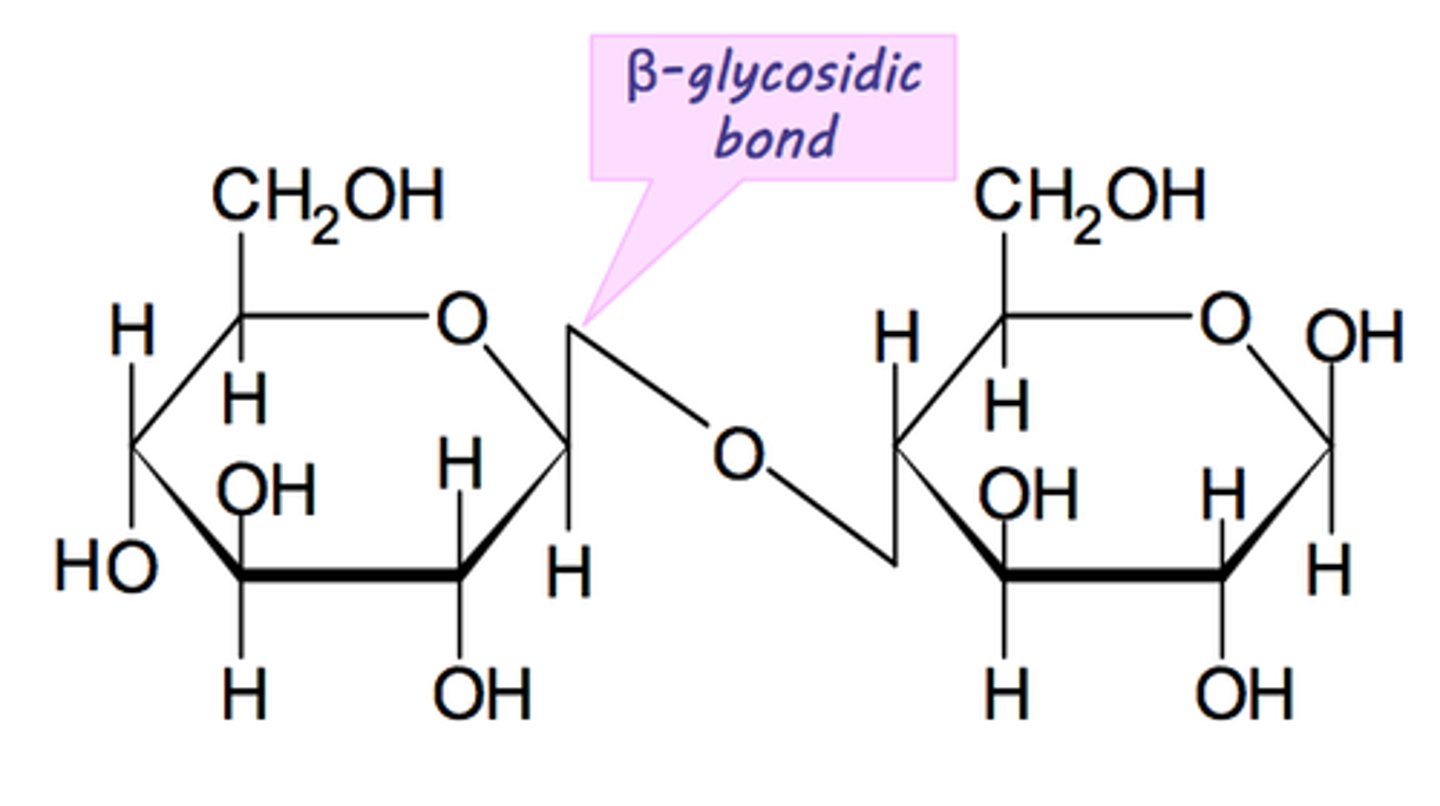
Define when a β-glycosidic bond occurs
When two carbons have different stereochemistry
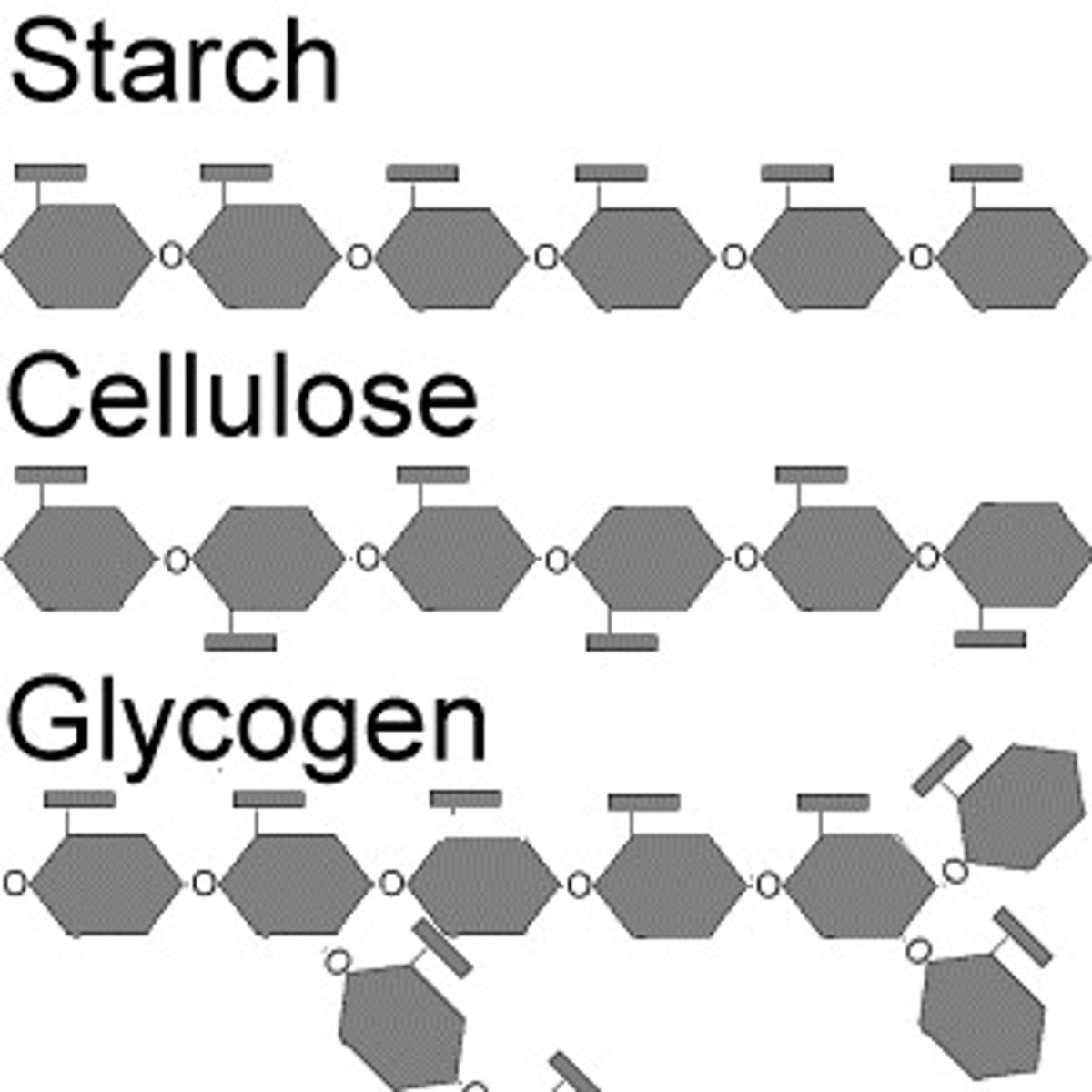
Starch is a major storage form of glucose in plants, what bonds can be formed
1-4 and a few 1-6 linkages (branching)

Glycogen is mainly located in the liver, kidneys and muscle, does this mean that it is a major storage form of glucose in animals?
Yes
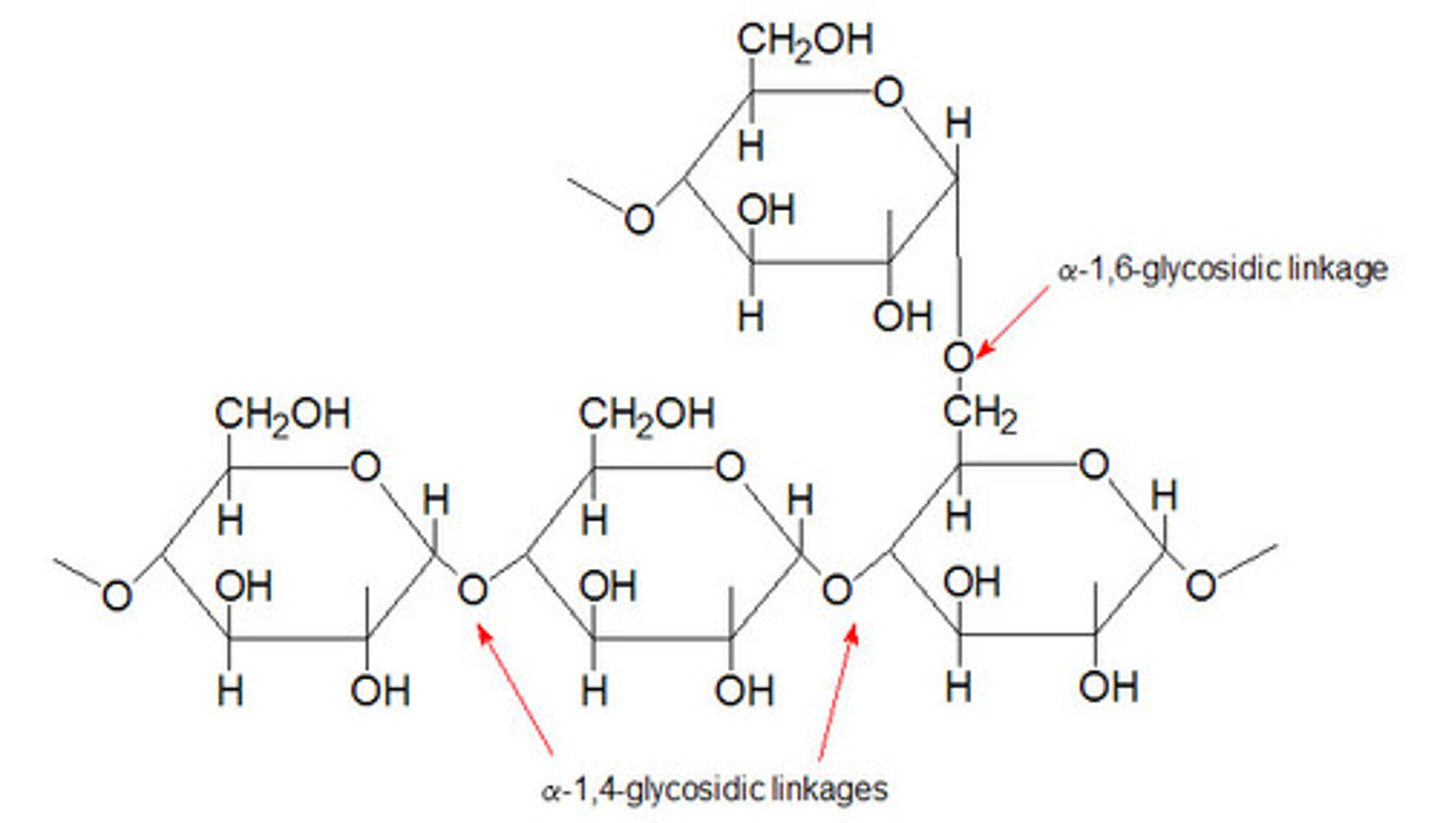
What bonds does glycogen have?
1-4, and frequent 1-6 linkages (branching)
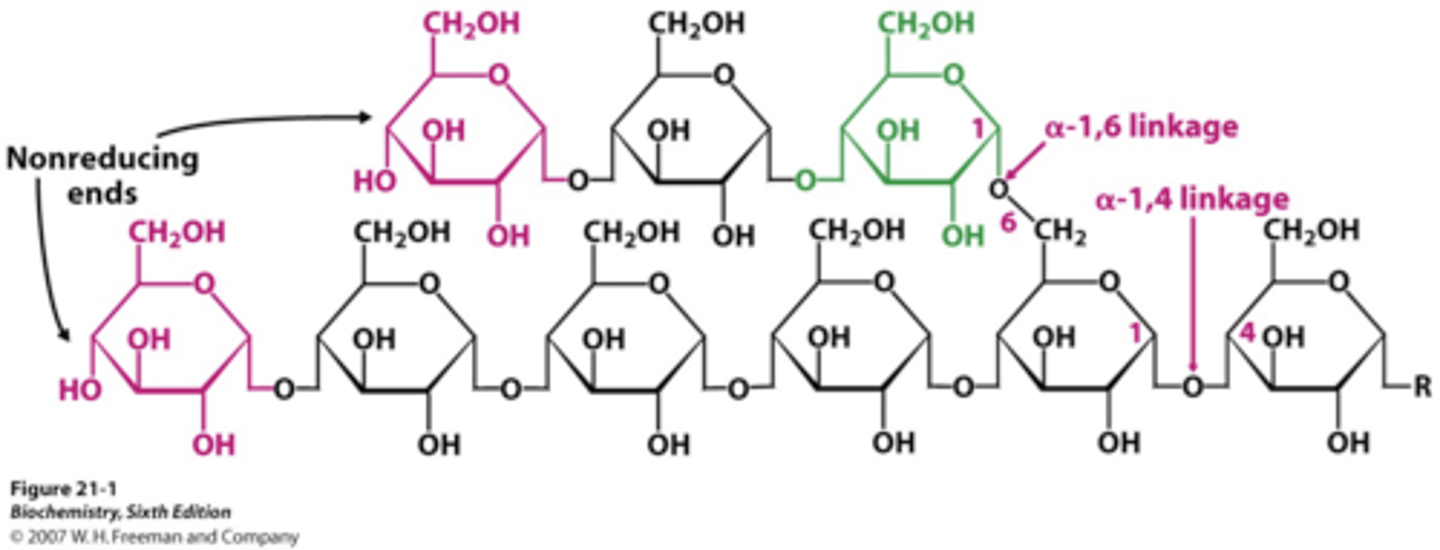
Explain why cellulose is so tough
Cellulose is in a beta configuration that is indigestible by many animals due to the lack of enzymes, this beta configuration and the lack of branching in the polymer allows for a structural plants structural integrity
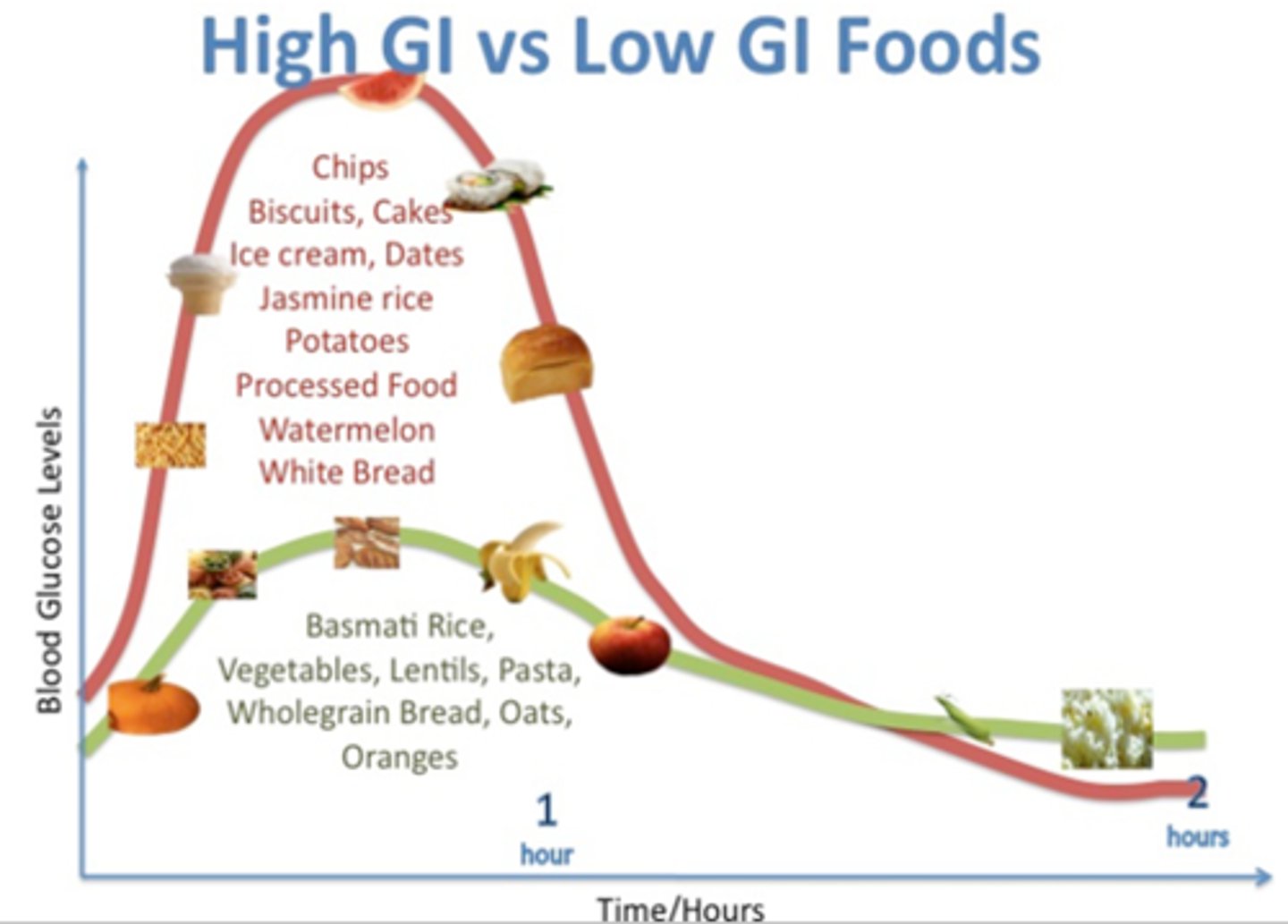
What does GI index stand for and what does it measure?
Glycaemic Index and measures how quickly your blood-glucose level rises after eating carbohydrate-containing food
What are glycoproteins?
proteins covalently bonded to carbohydrates
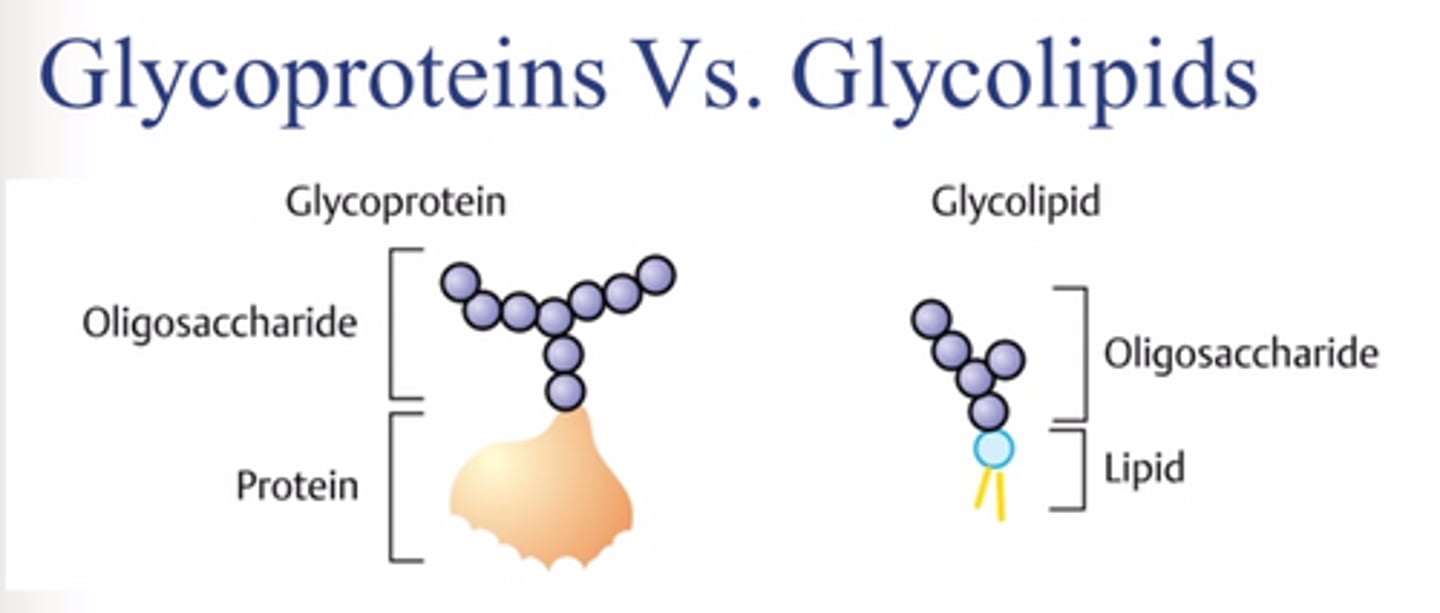
What is chitin?
a fibrous substance consisting of polysaccharides and forming the major constituent in the exoskeleton of arthropods and the cell walls of fungi.

lipids are grouped together to
function as a storage compound as they poorly mix with water
Fat is commonly stored in the form of
Triacylglycerol (TAG)
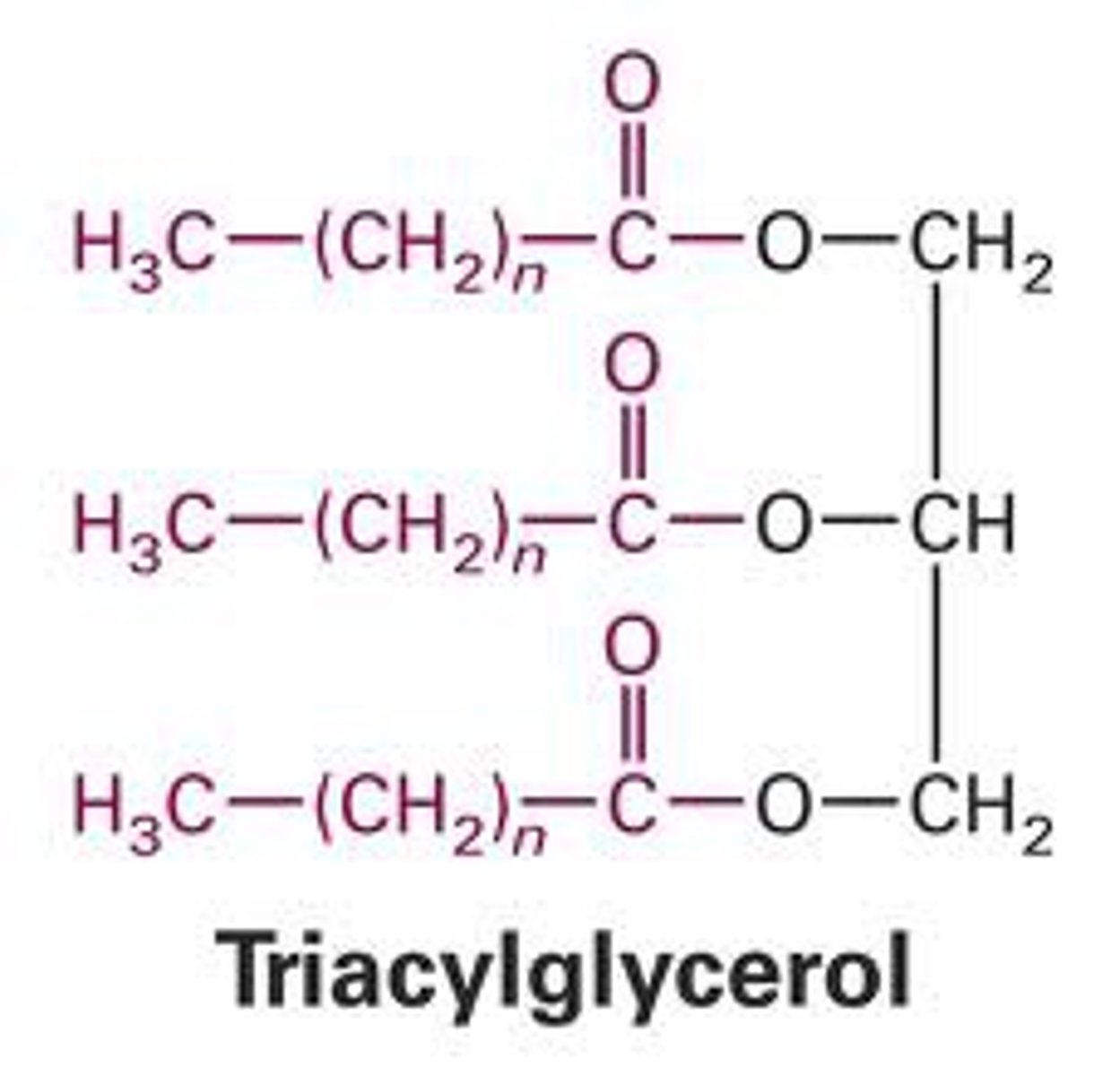
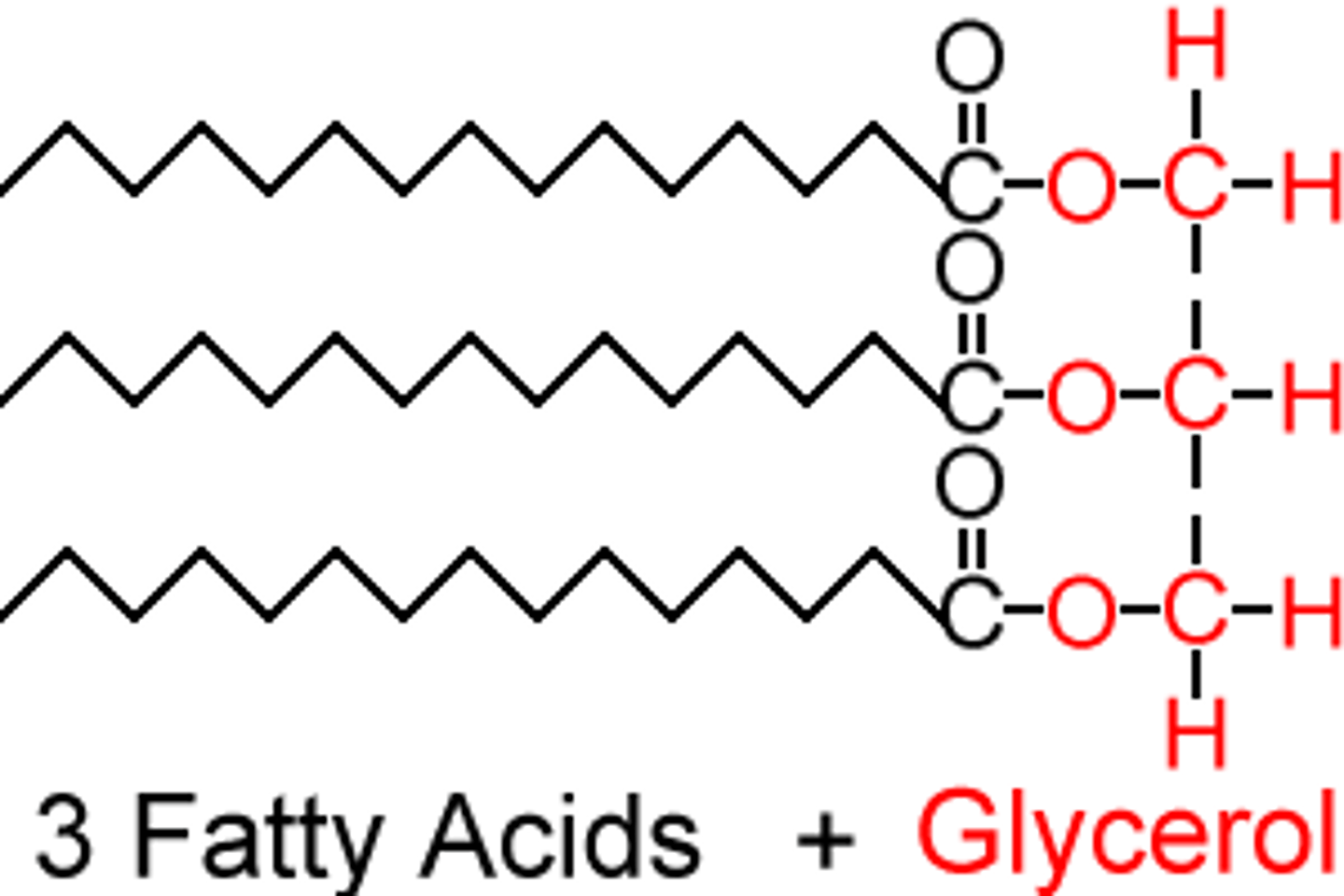
What is TAG comprised of?
non-polar hydrophobic package comprised of a glycerol headgroup, which are ester bonded to three hydrophobic fatty acid tails
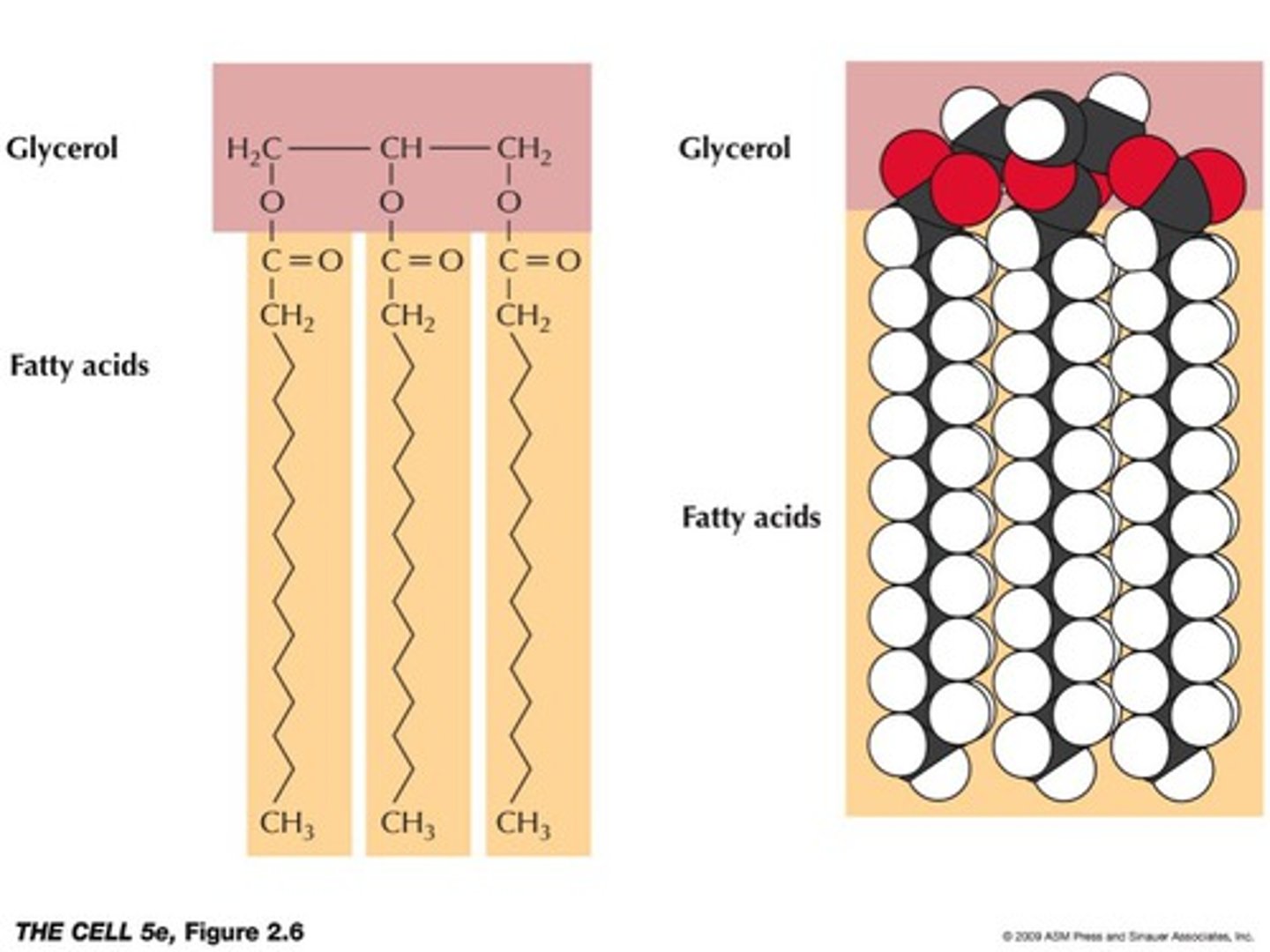
What properties does TAG allow to maximise the storage of fatty acids in its given space?
Tight non-polar hydrophobic package, which can be stacked next to each other
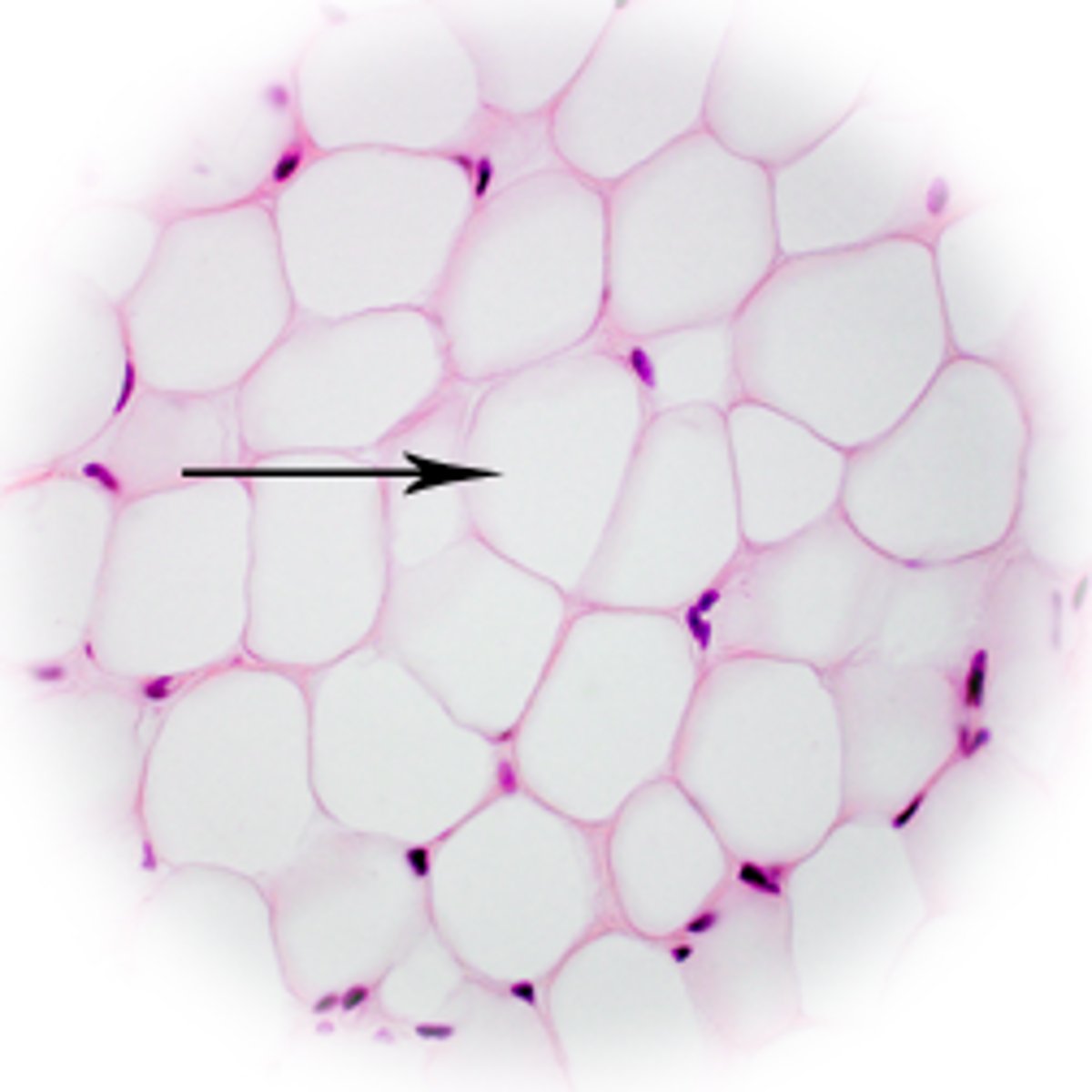
What are Adipocytes responsible for?
Cell storage - when seen through a microscope, large lipid droplets filled to the brim with fatty acid stored via TAG
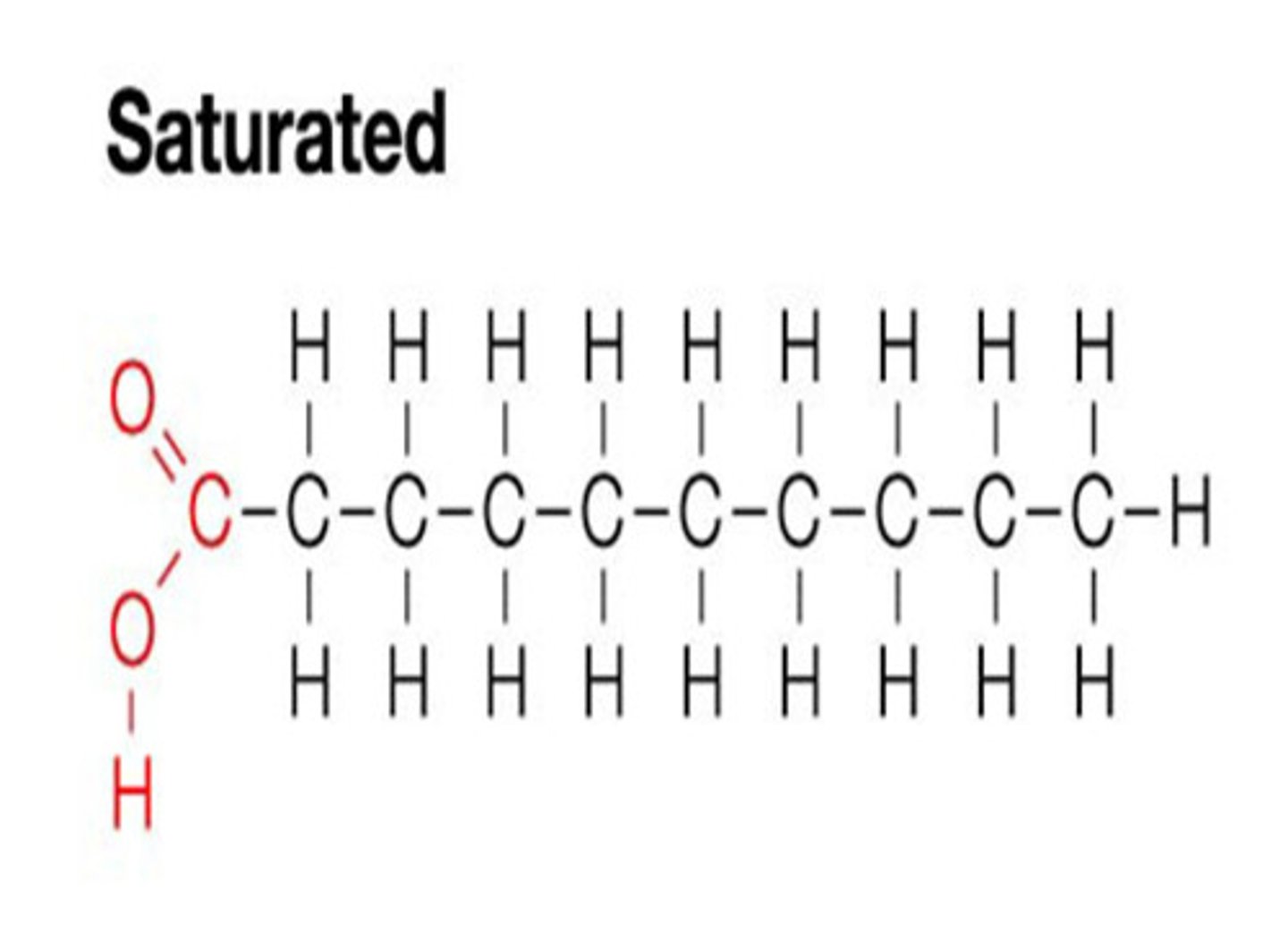
Butter is an example of what fat?
Saturated Fat

What characterises saturated fats?
No double bond, linear in shape and are packed very tightly
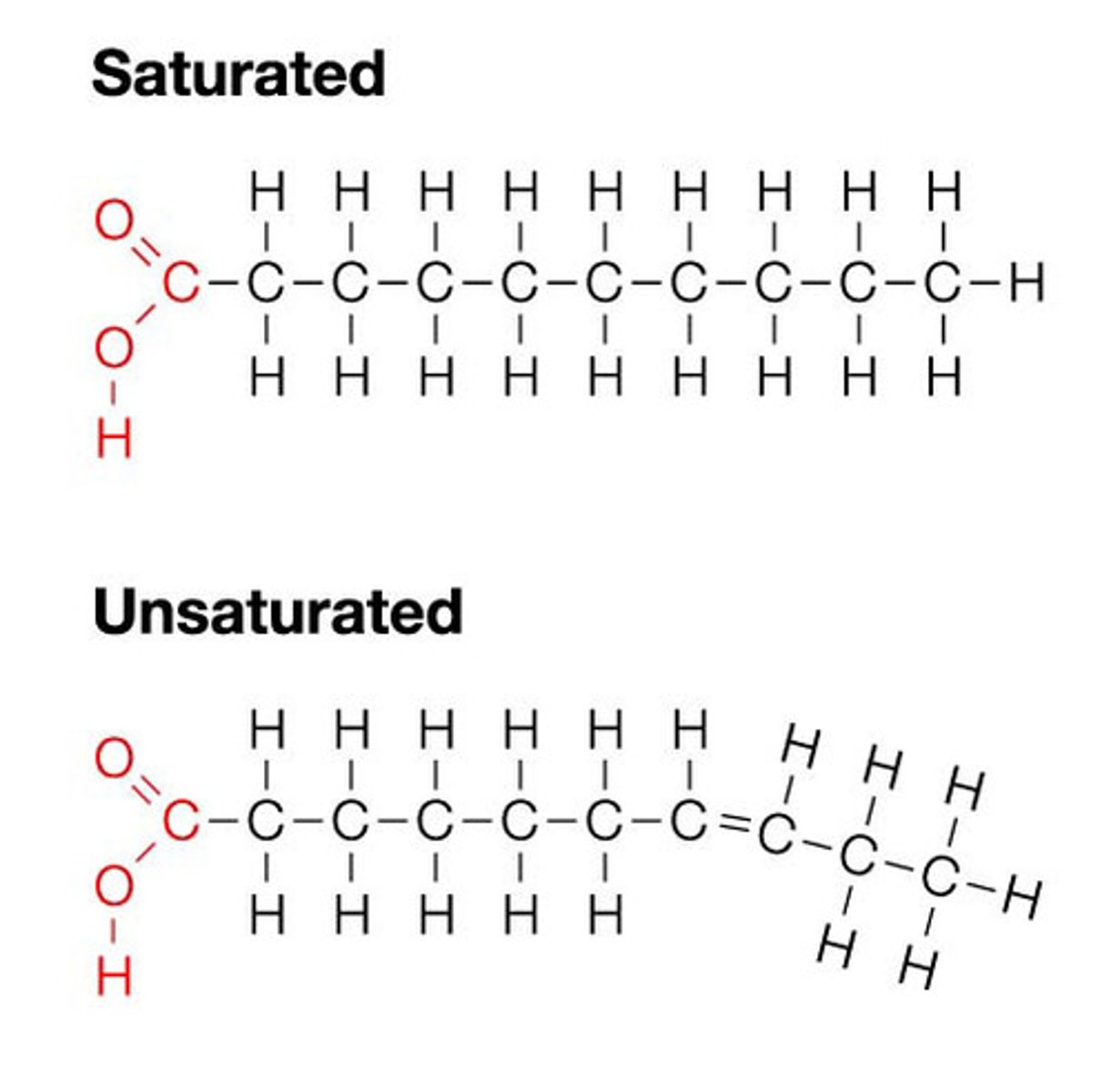
Olive oil is an example of what fat?
Unsaturated Fat

What characterises unsaturated fats?
One or more double bonds - bent and kinks and is harder to package than saturated fat
Is unsaturated fat good or bad?
good

Are saturated fats solid or liquid at room temperature?
Solid at room temperature

Are unsaturated fats solid or liquid at room temperature?
Liquid at room temperature

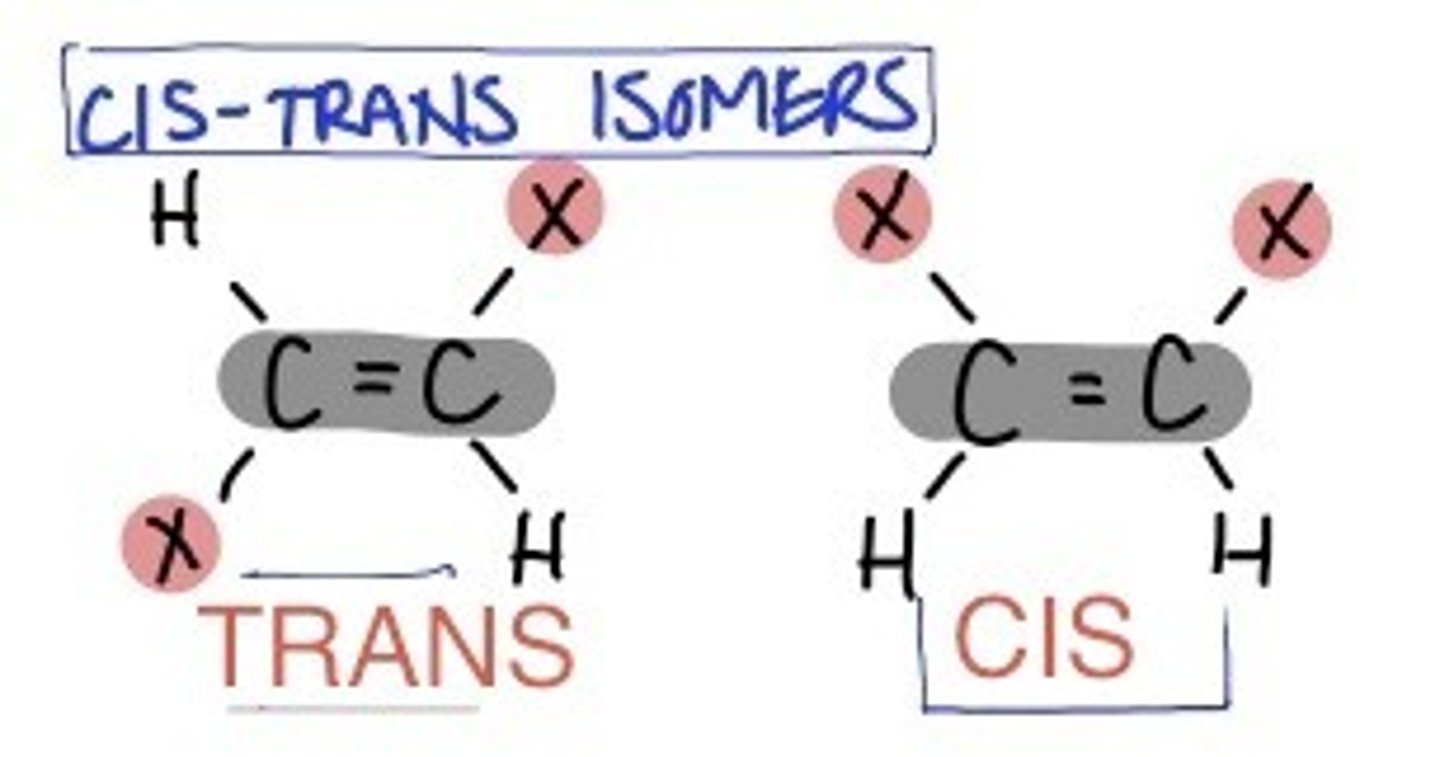
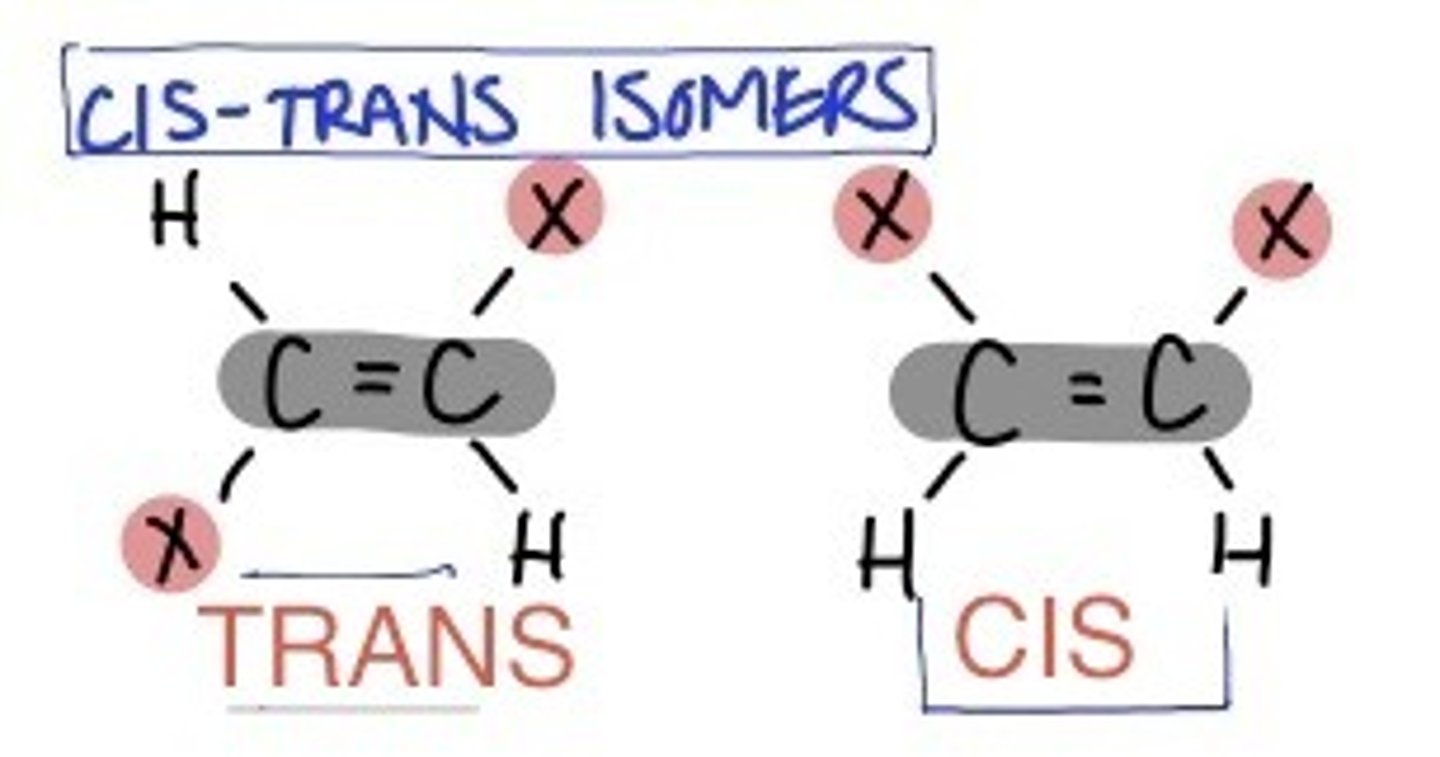
Define a cis bond
Double bonds that have hydrogen on the same side of the carbon chain - bent or kink shape
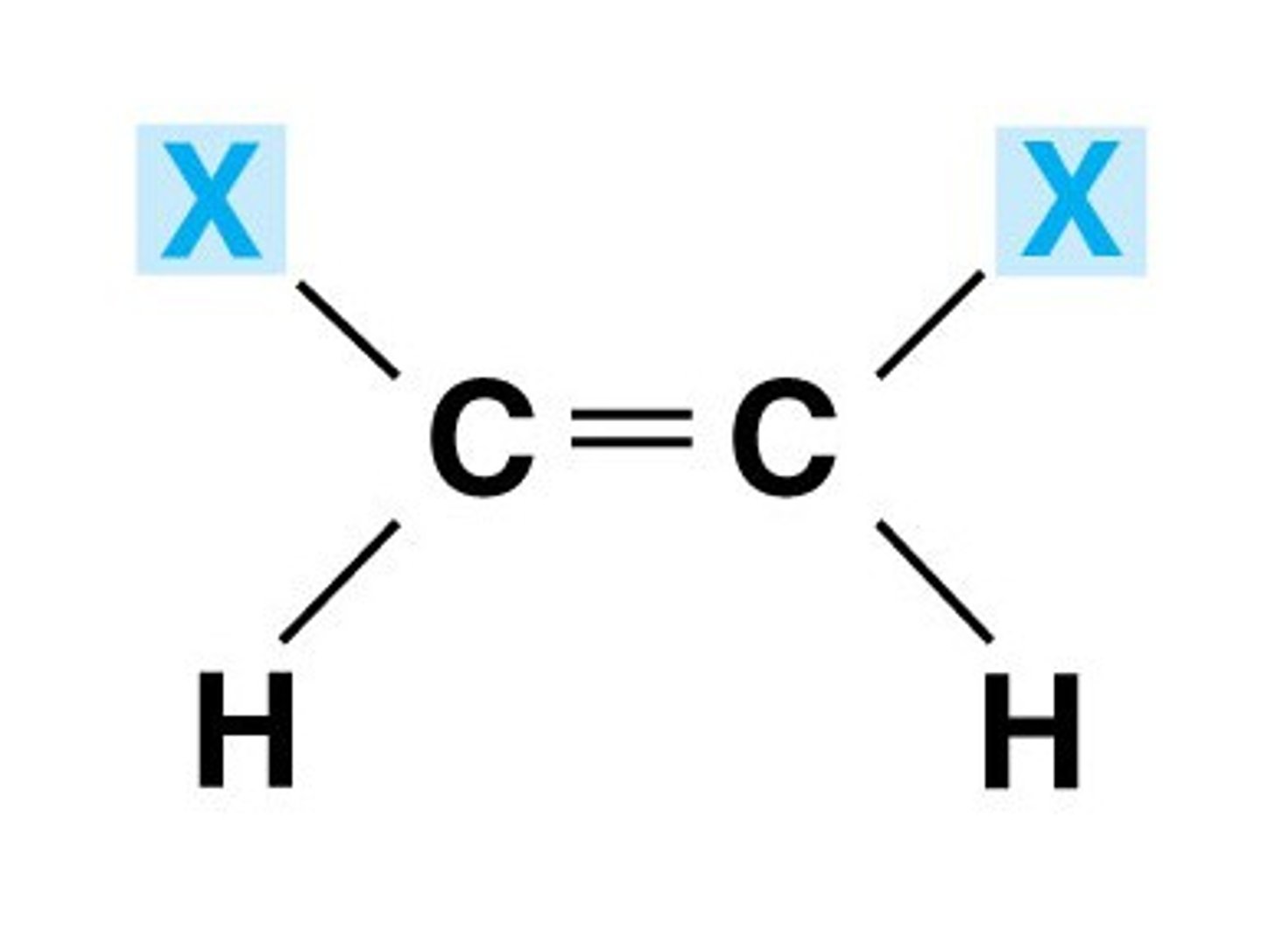
Define a trans bond
Double bonds that have hydrogen on opposite side of the carbon chain - more linear in shape
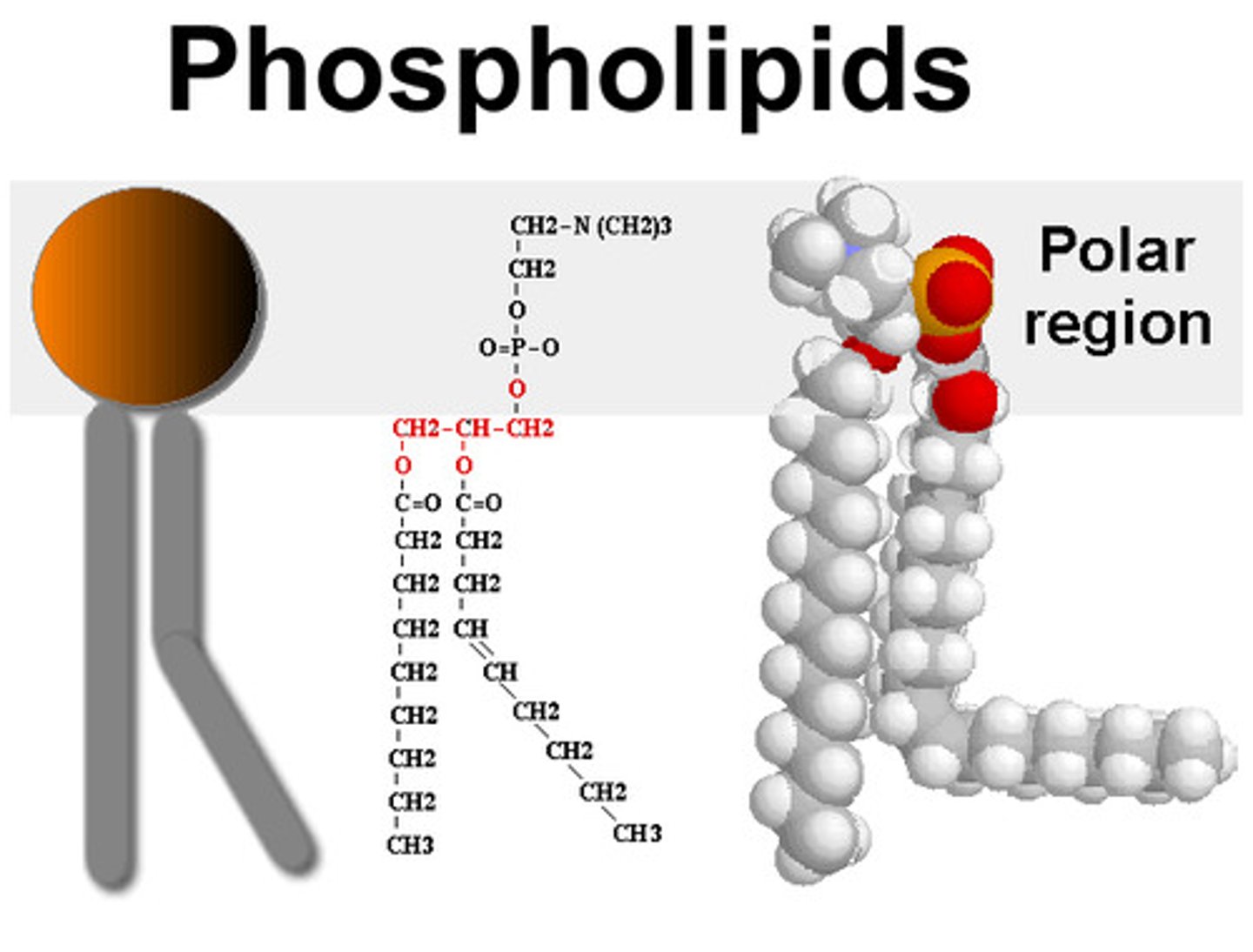
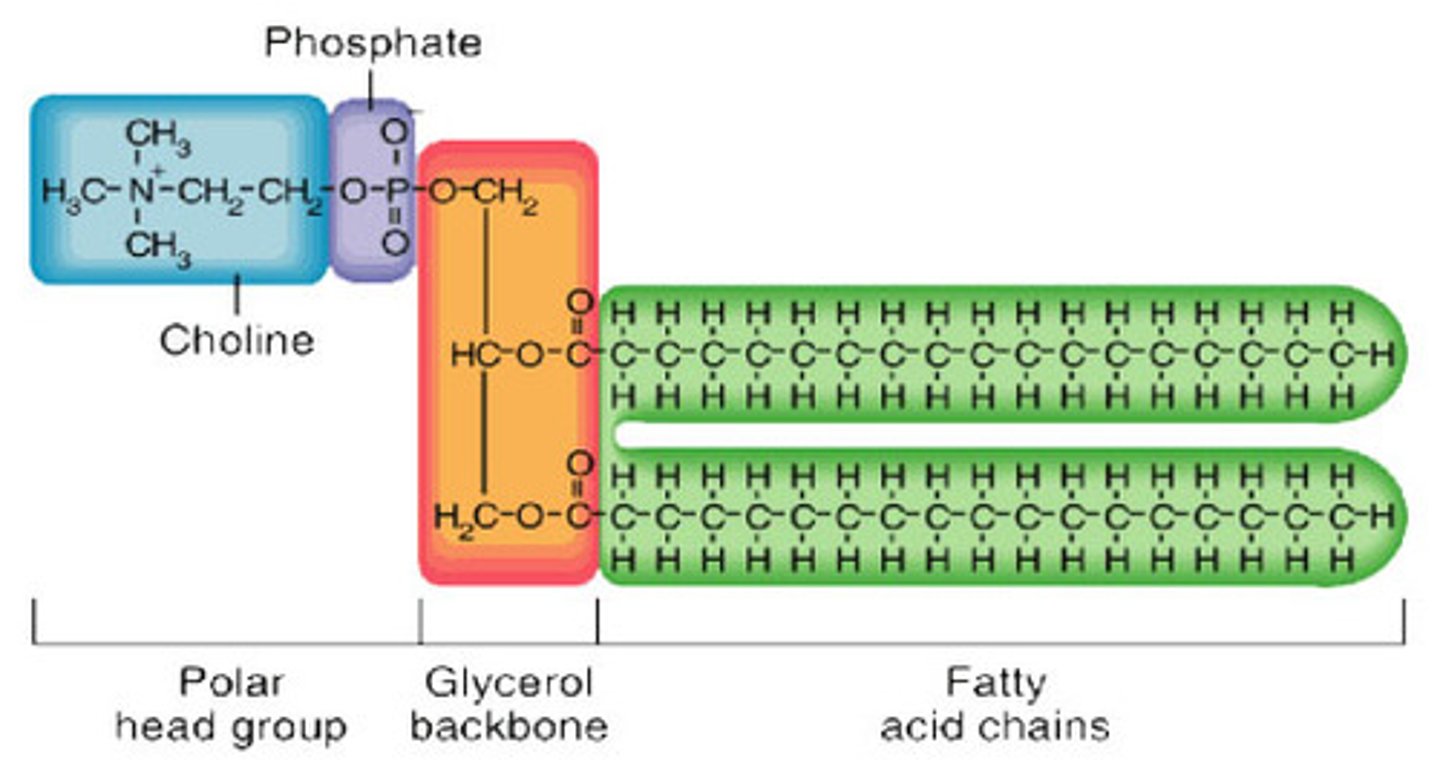
What are phospholipids made of?
Phosphocholine group bonded to two fatty acid
What do proteins consist of?
one or more polypeptides (polymers of amino acids)
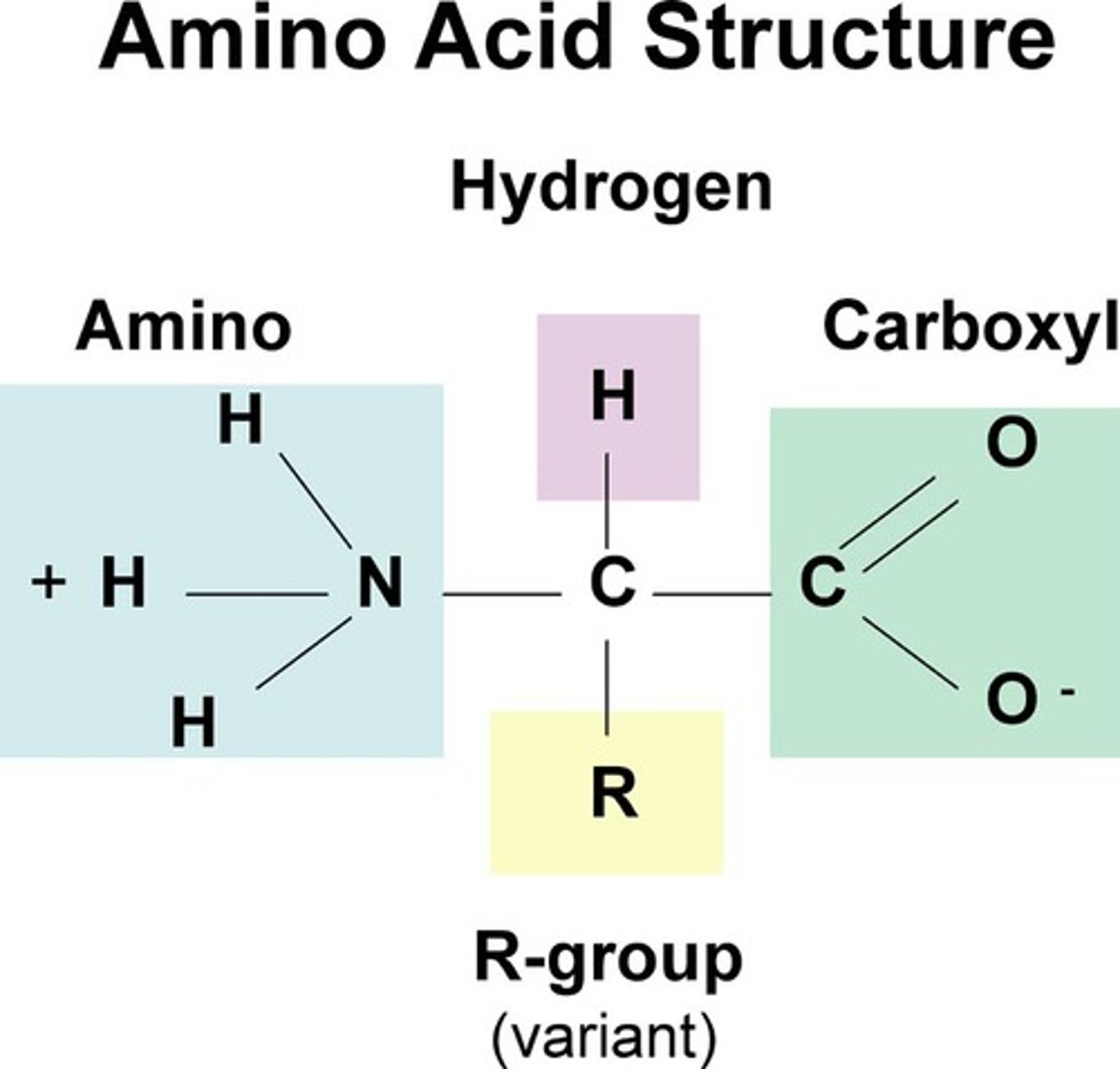
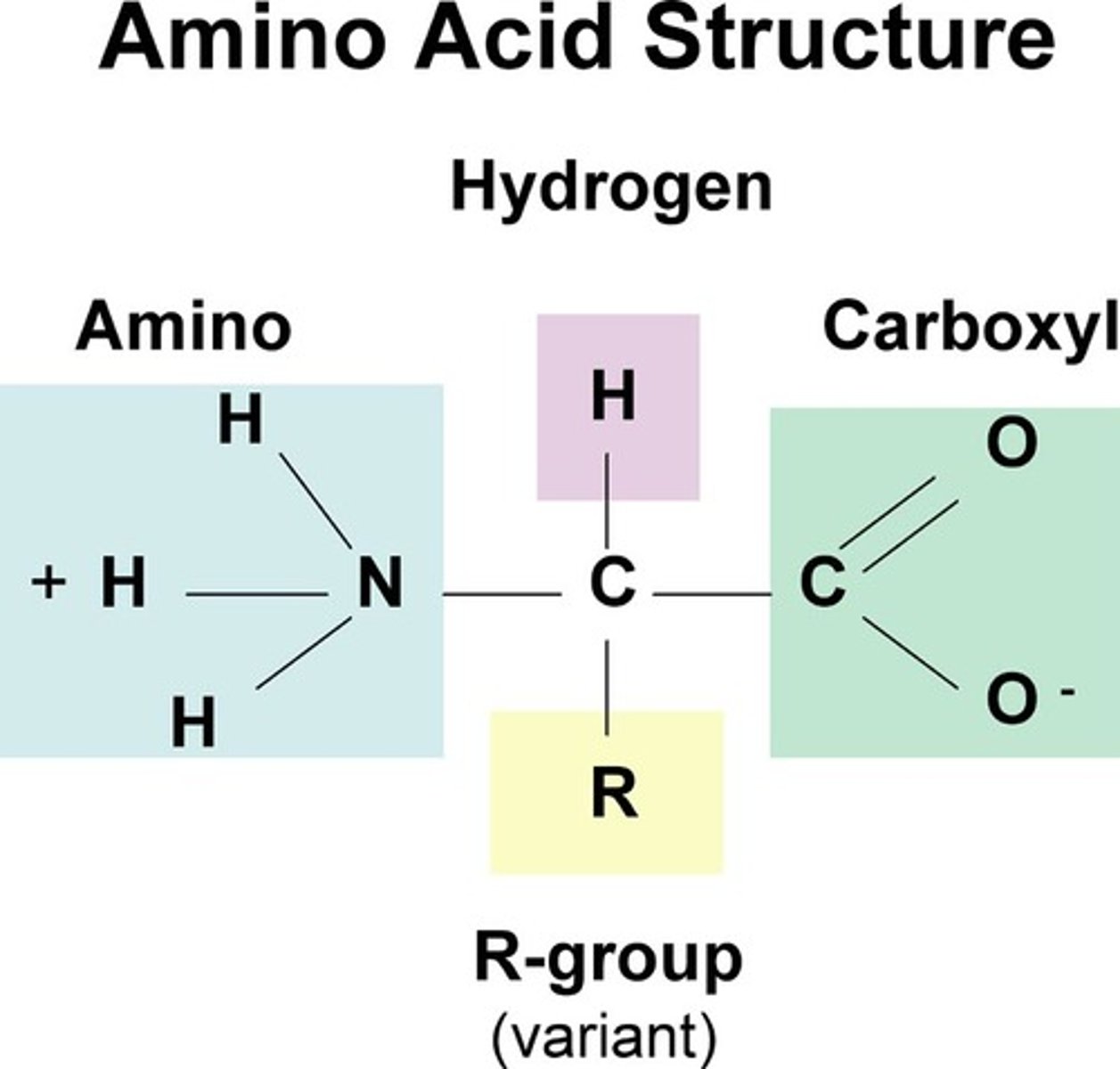
The carboxyl group in amino acids are known as the
C terminus (typically on the right side of the amino acid)
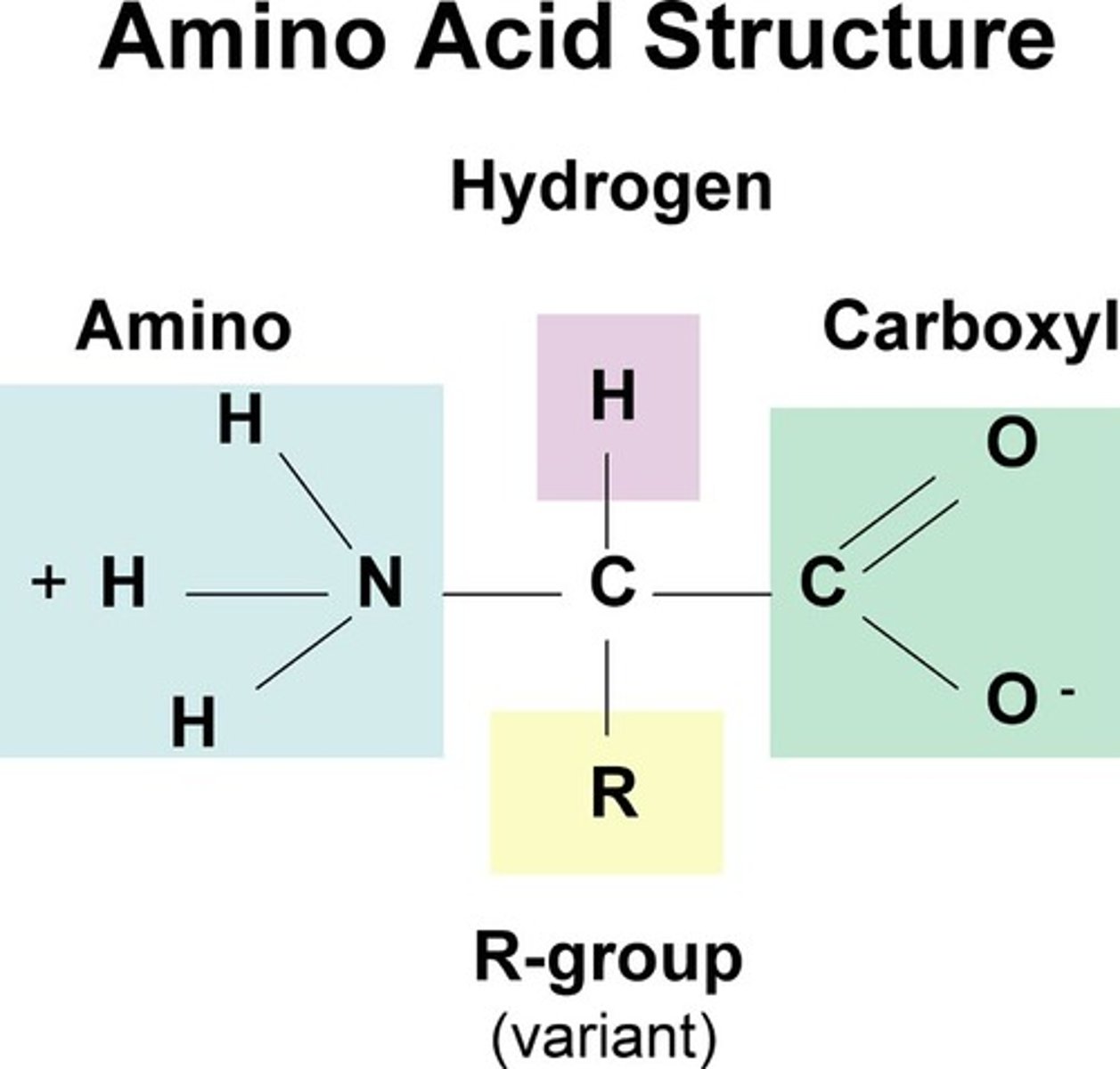
The N terminus is what group from the amino acid?
Amino group
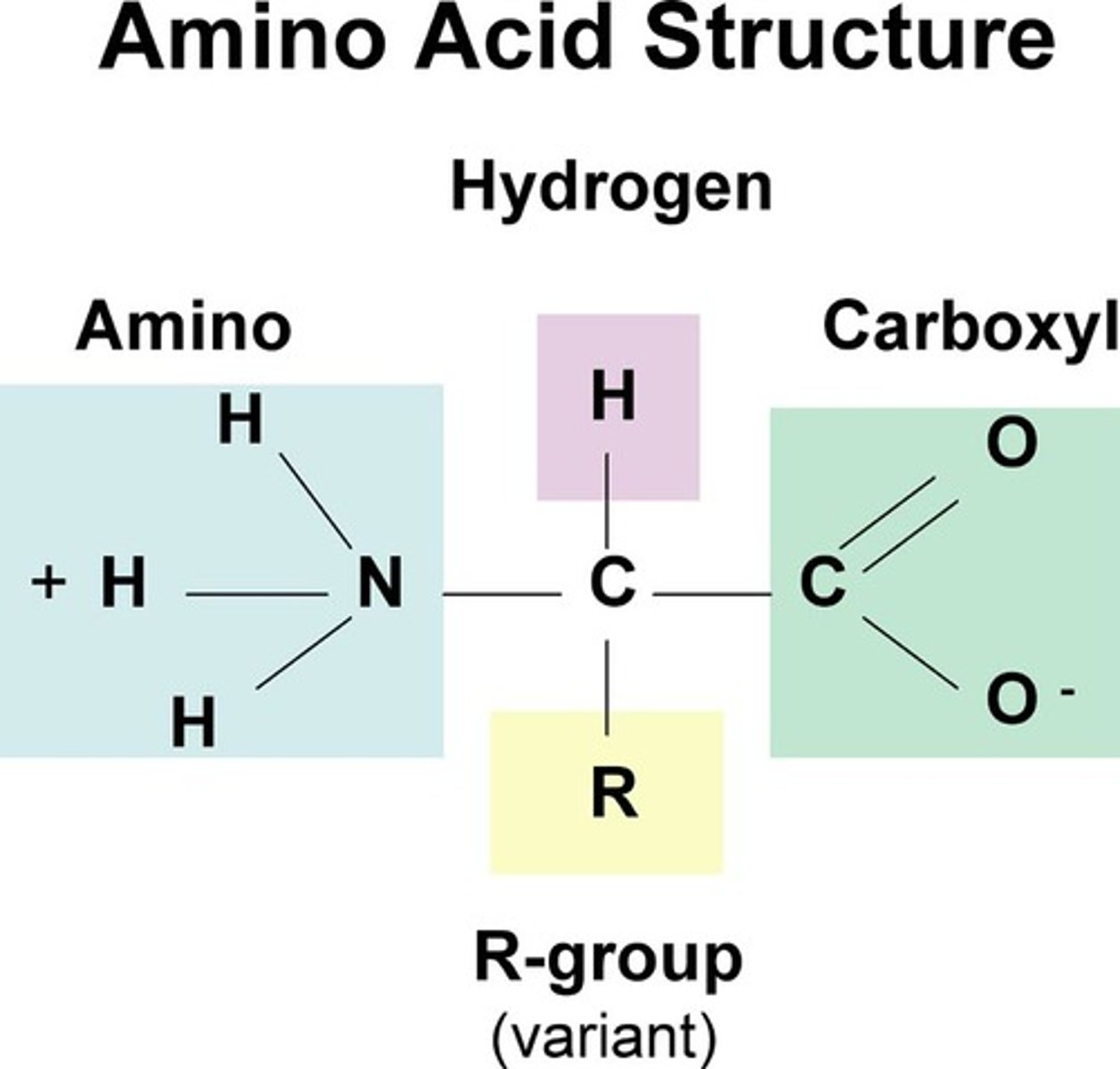
The carbon atom in between the C & N terminus is known as the
Alpha carbon
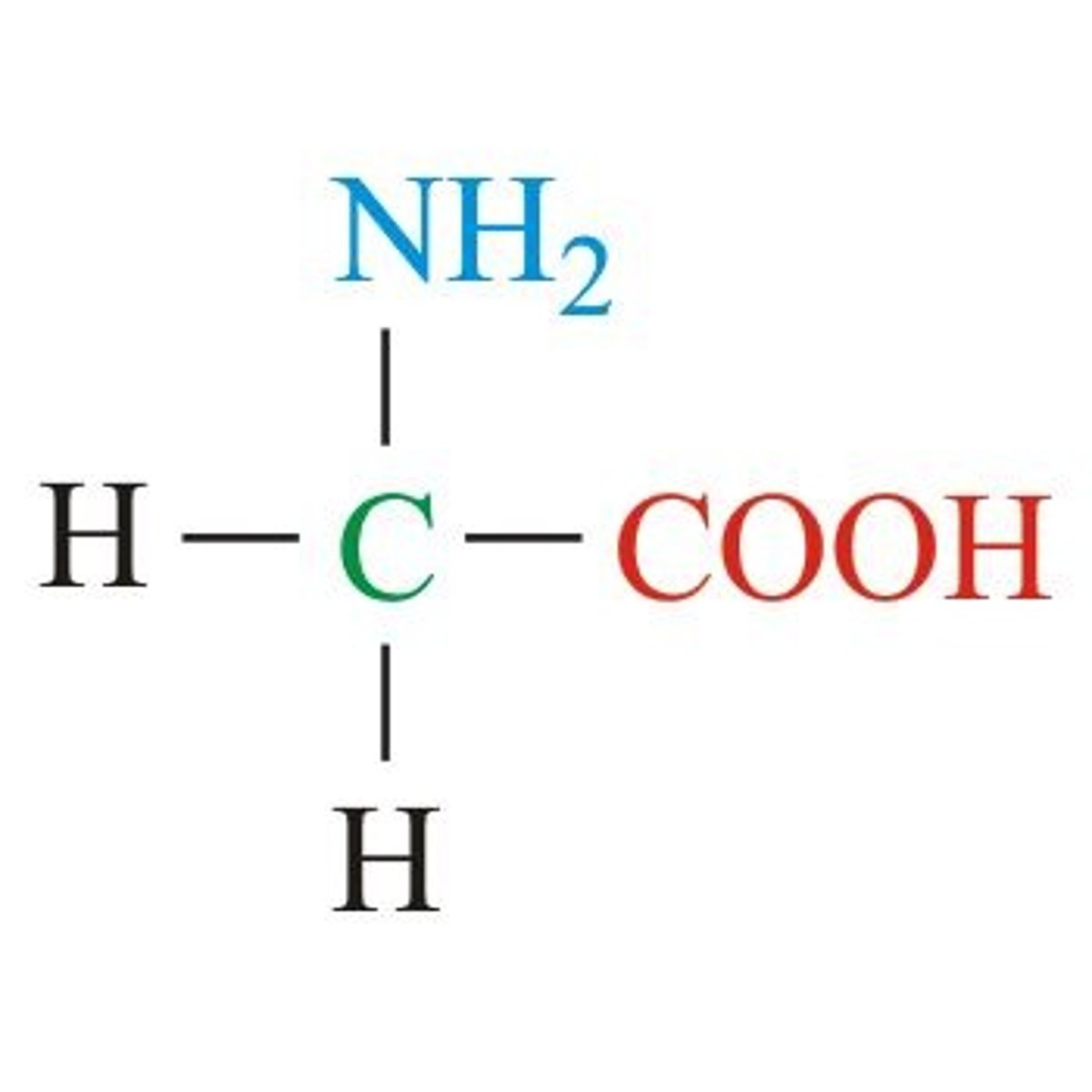
What is Glycine?
An amino acid with a non polar R group
What is Serine?
An amino acid with a polar R group
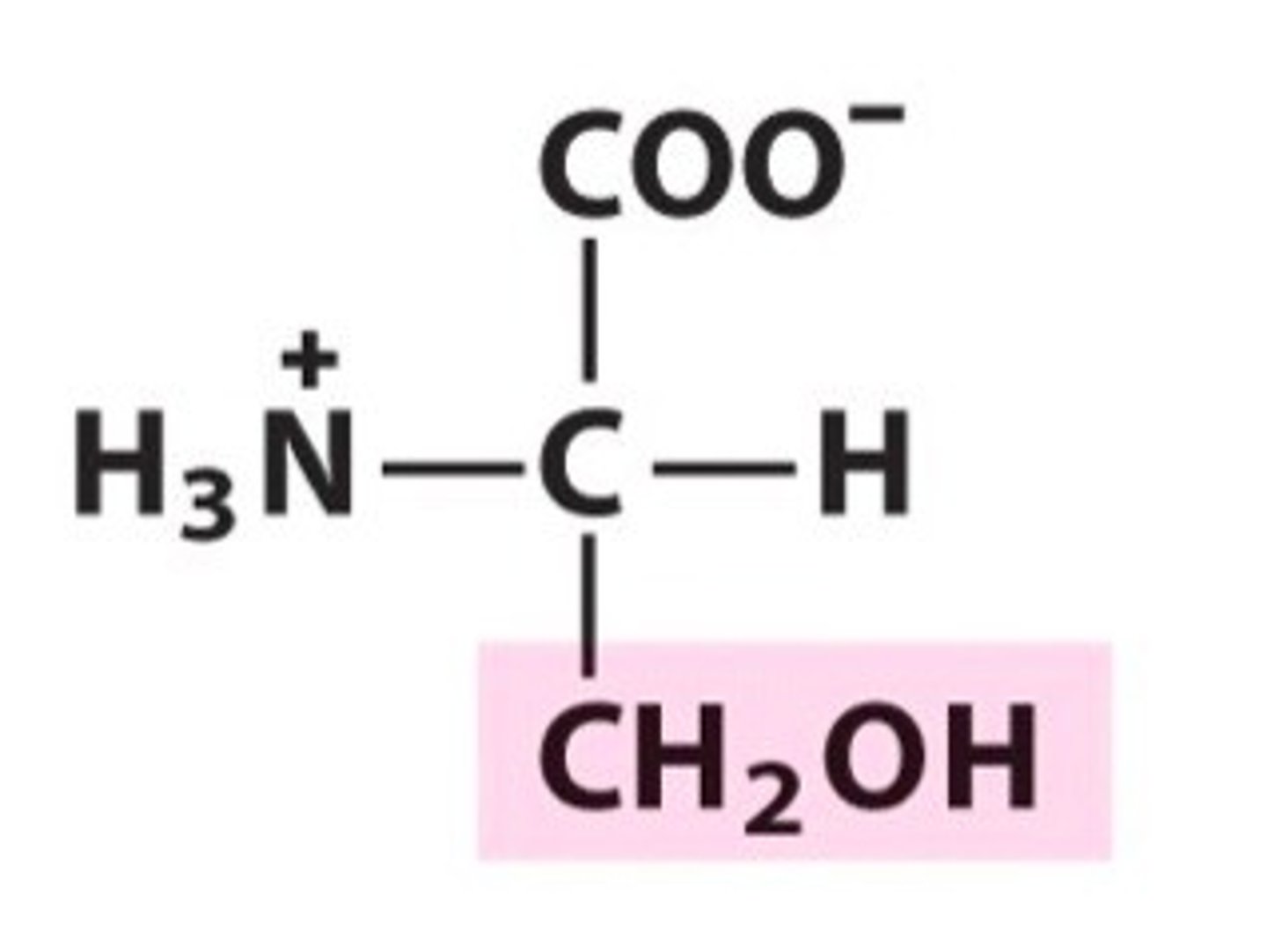
What is Aspartic Acid
An amino acid with a charged (acidic - negatively charged) R group
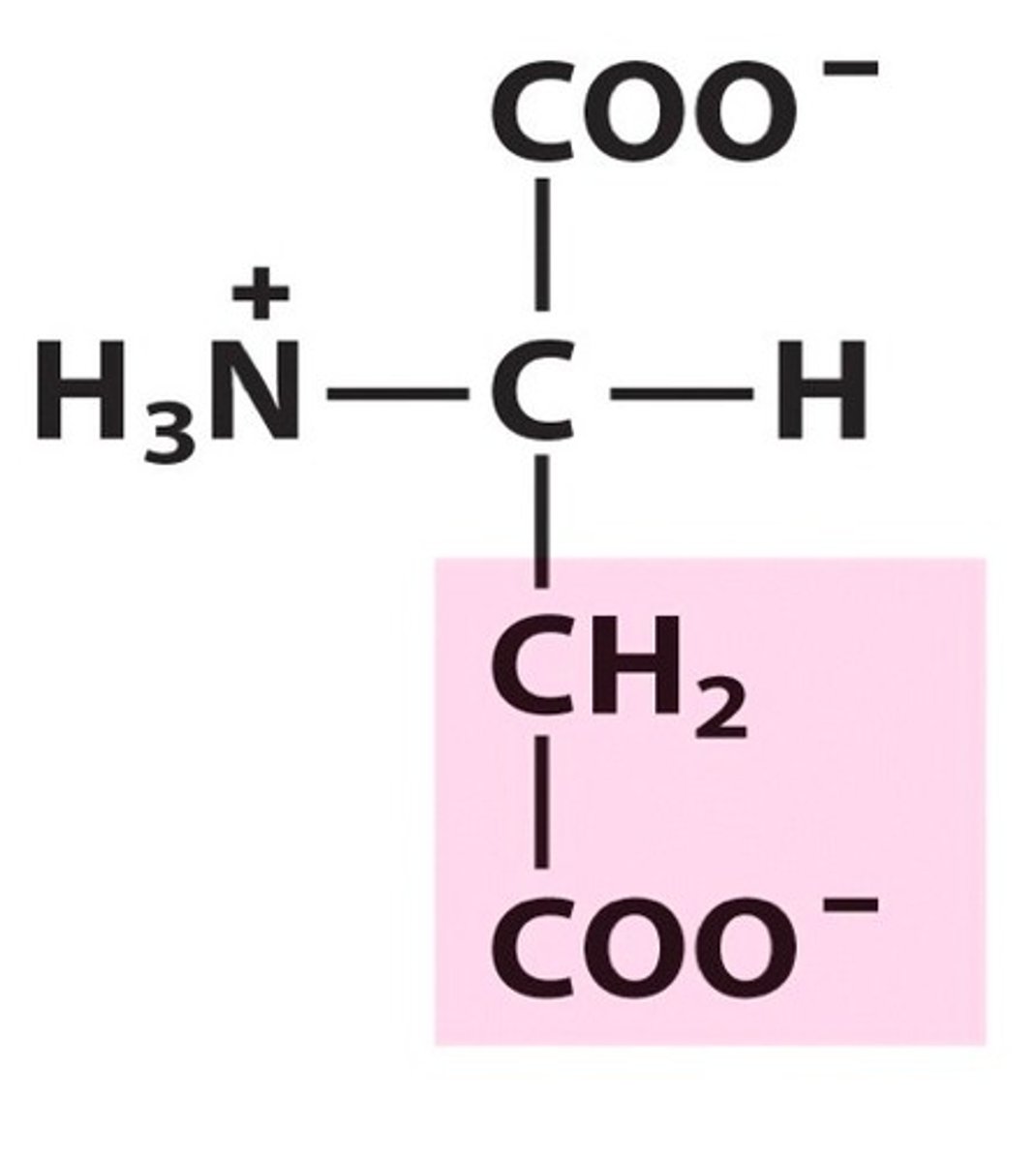
What is Histidine?
An amino acid with a charged (basic - positively charged) R group
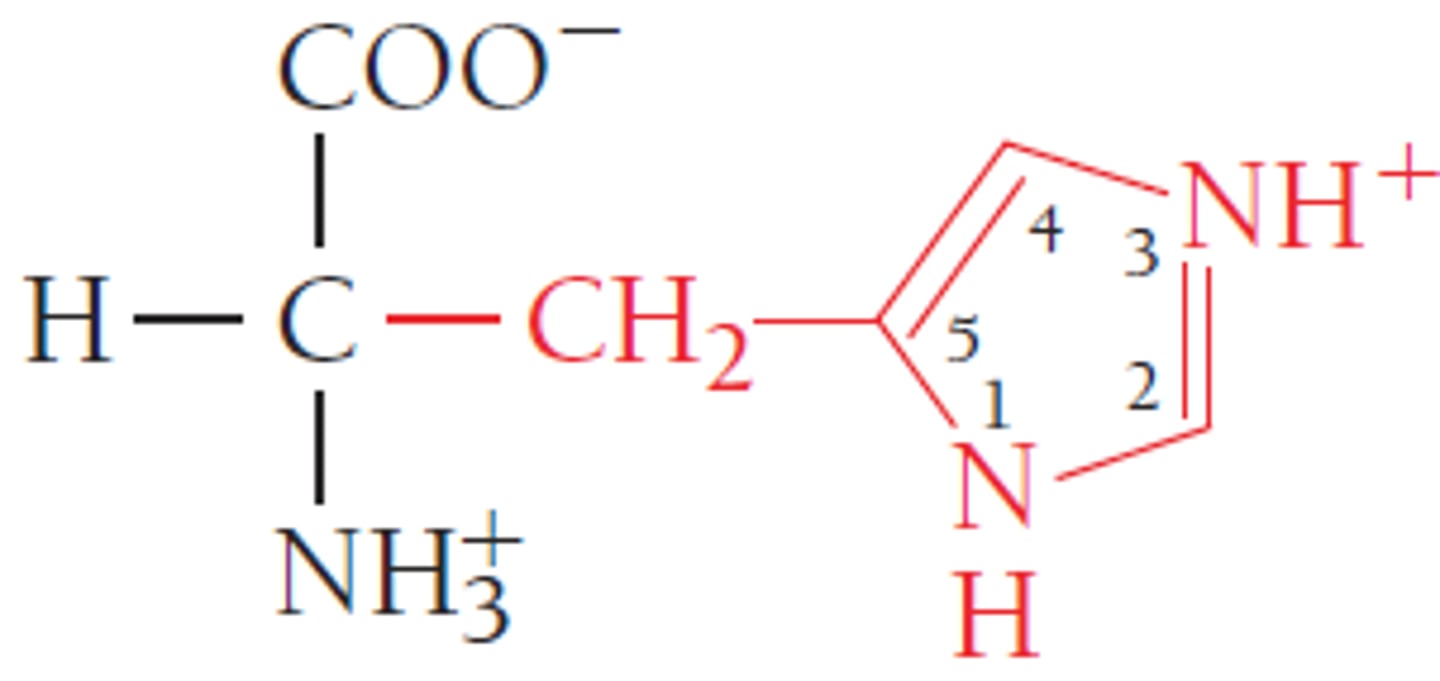
What are amino acids linked by?
peptide bonds
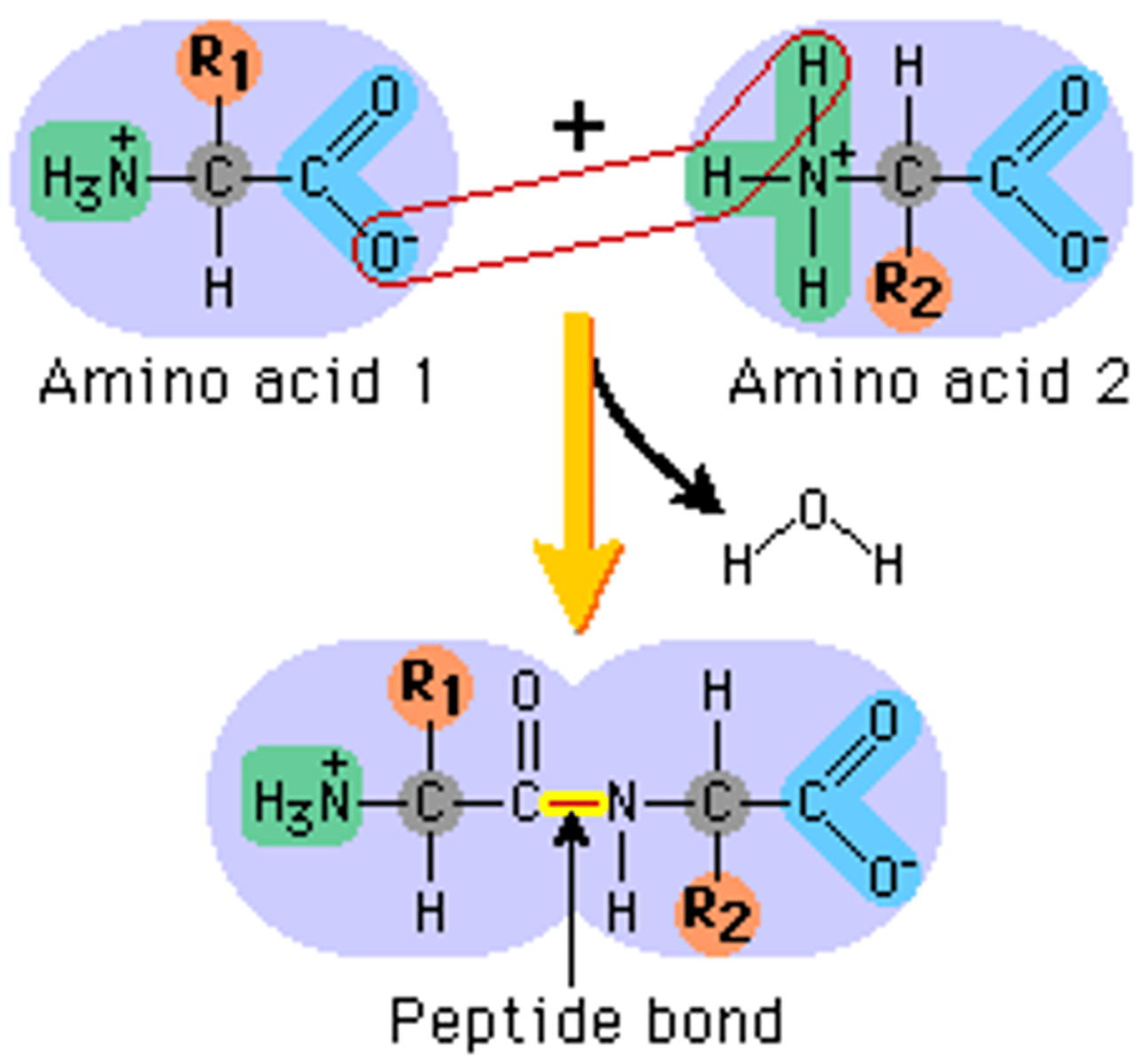
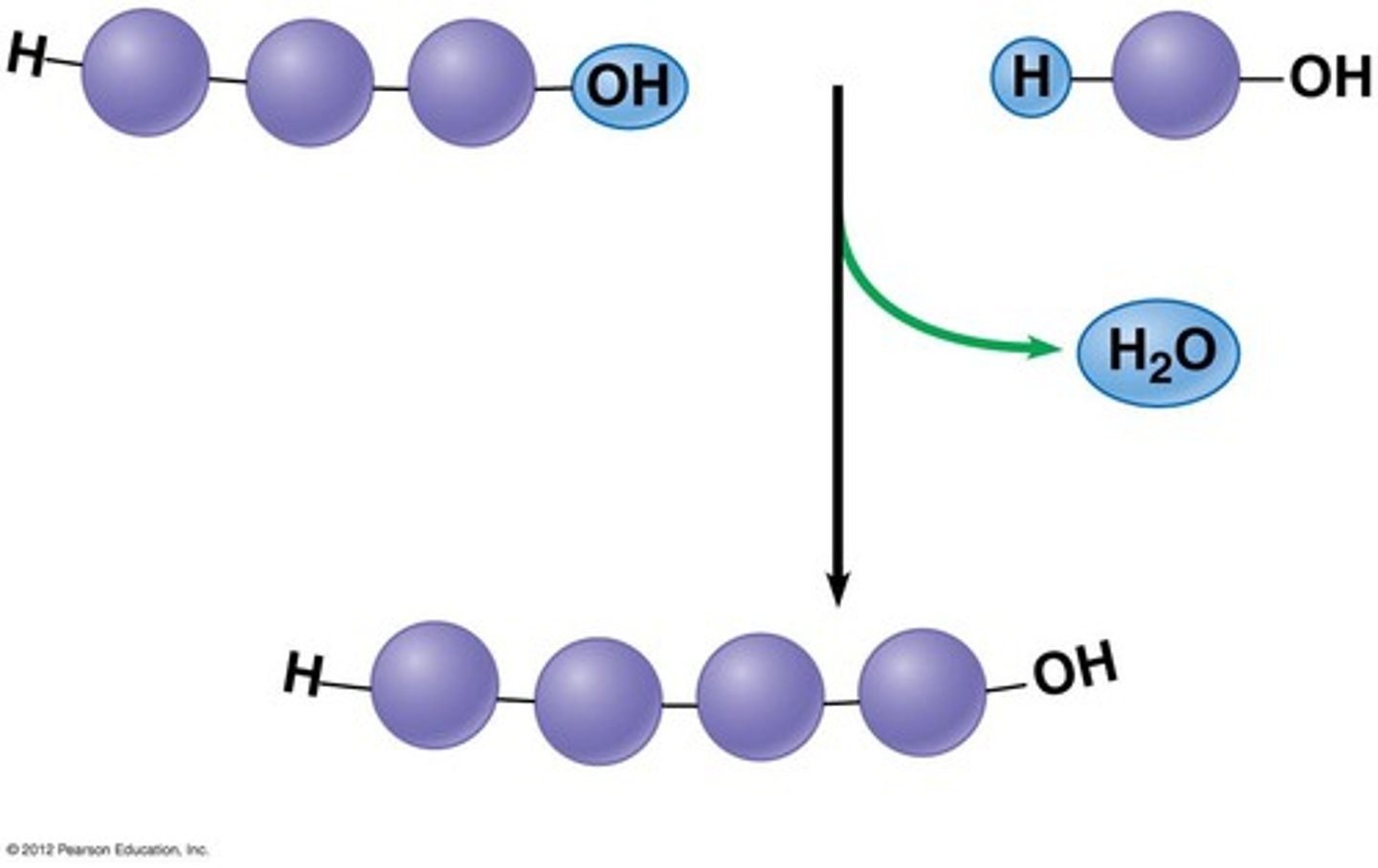
When two amino acids join what type of polymerisation occurs?
Dehydration (water is produced)
There are four different structures for proteins, what are the names?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
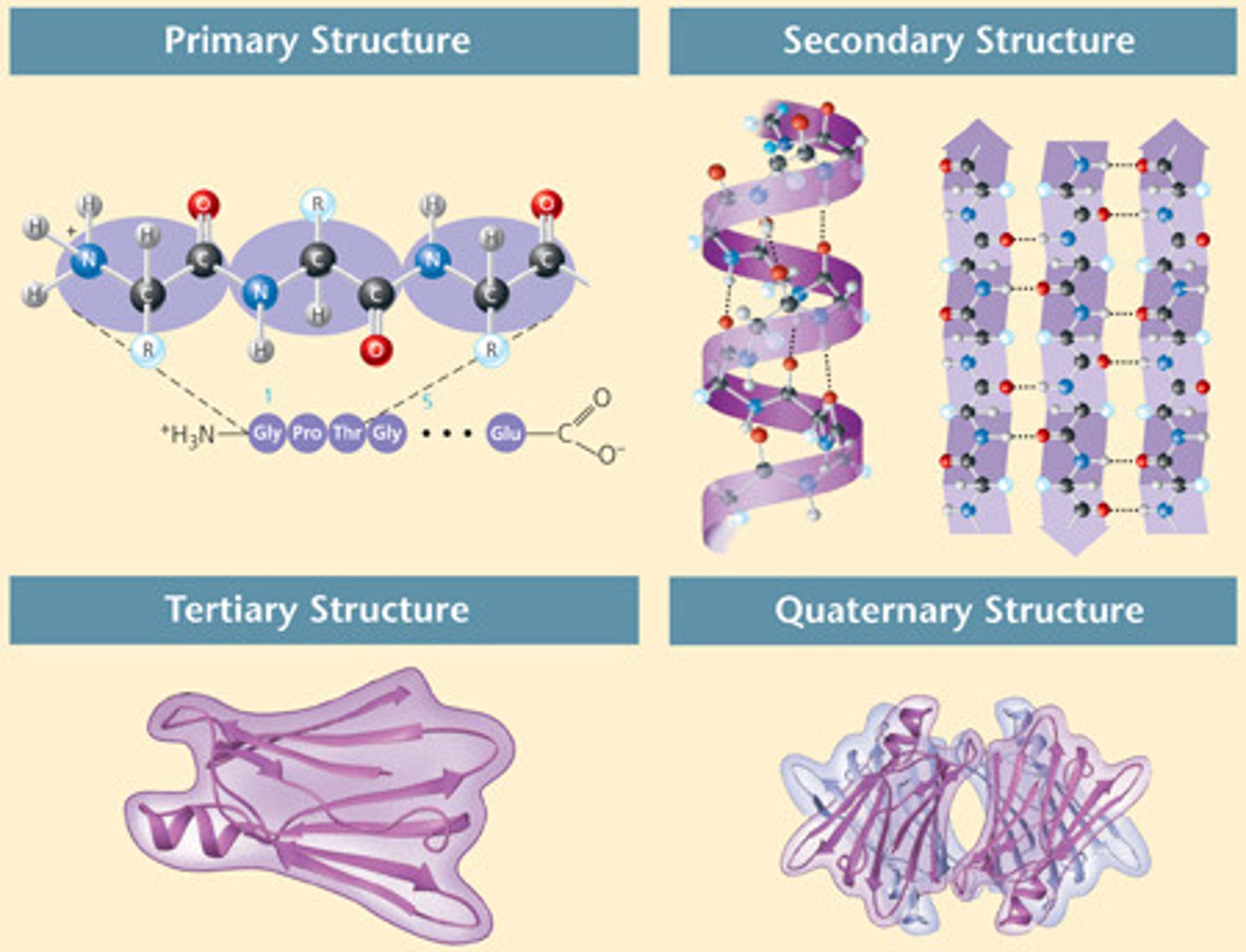
Define what the primary structure of a protein is
Amino acid sequences
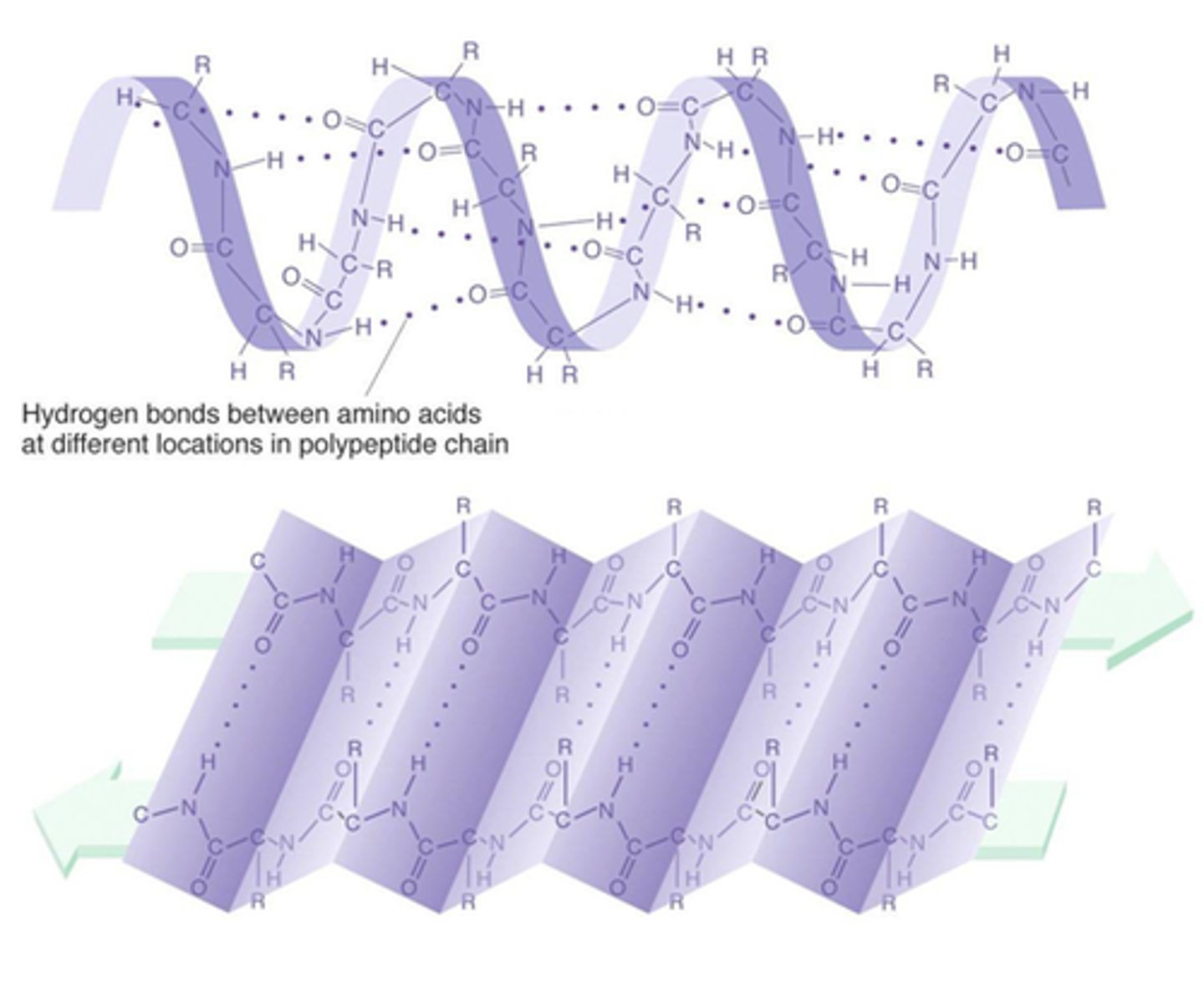
Define what the secondary structure of a protein is
Coils and folds (alpha) & Flat folds in the polypeptide (beta)
Define what the tertiary structure of a protein is
Globular 3D folding
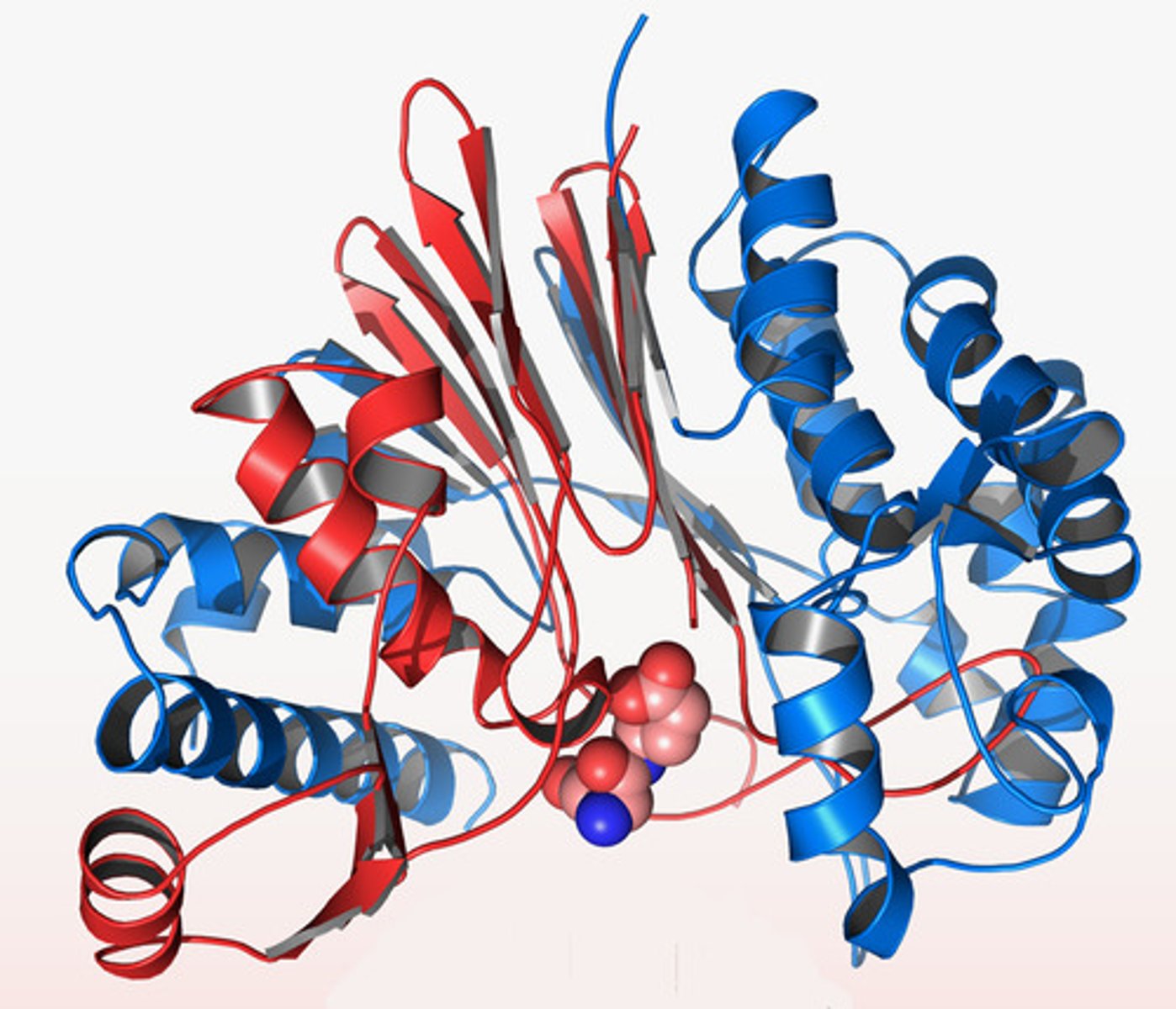
Define what the quaternary structure of a protein is
Multiple subunits of proteins to form multisubunit protein
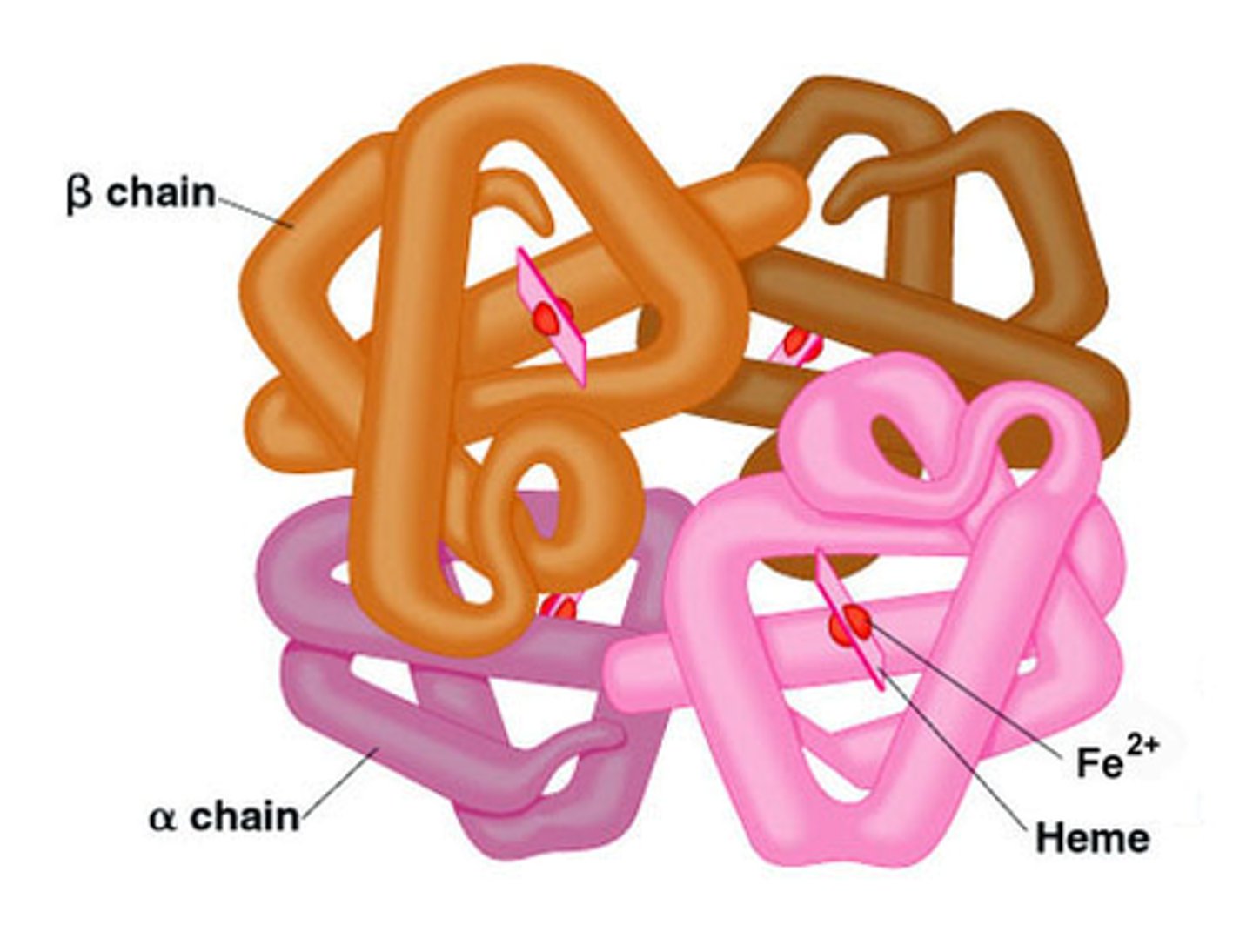
True or False: Enzymes are highly specific catalysts
True - this is specifically determined by protein structure, due to their 3D structure
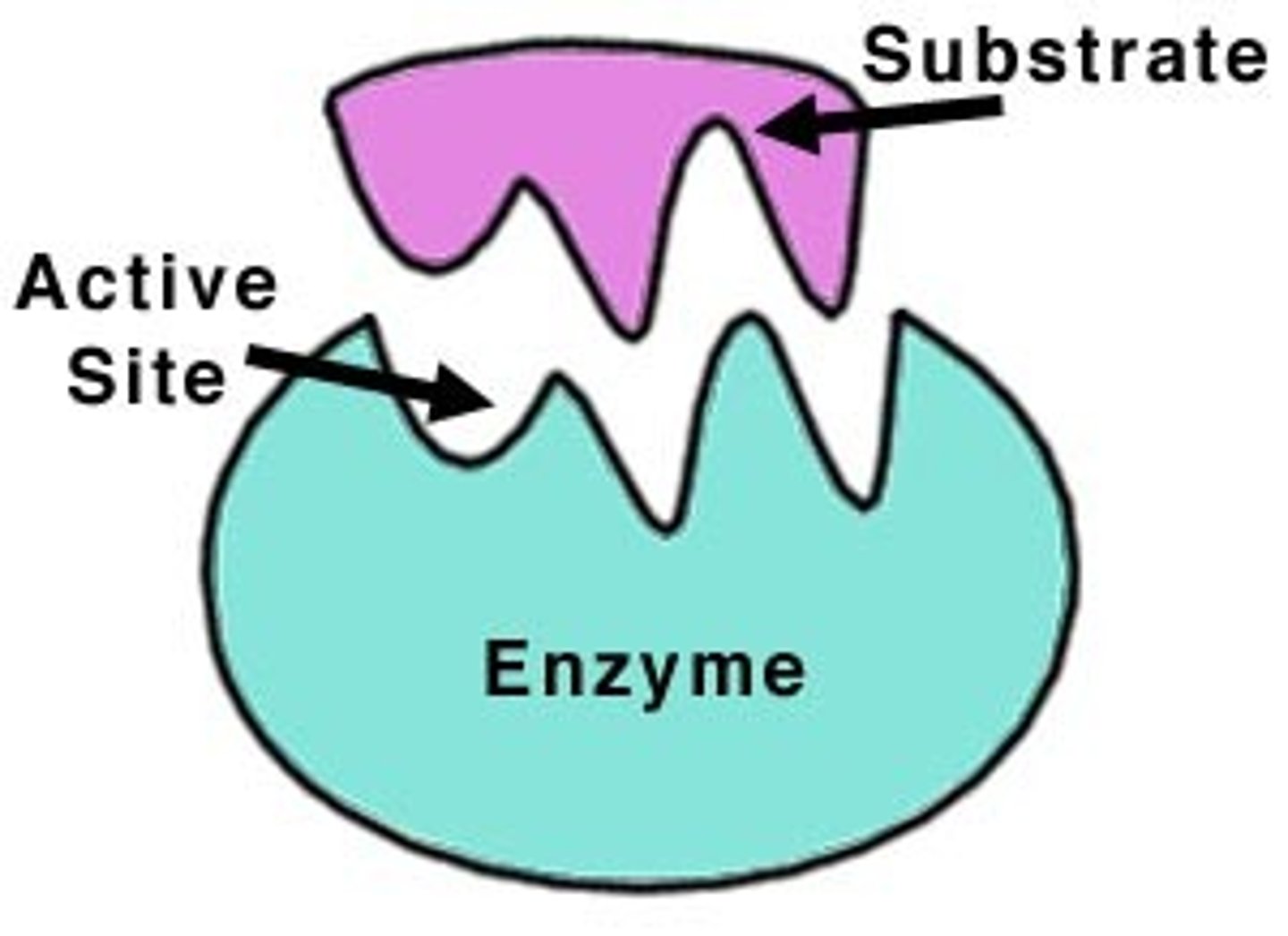
True or False: The 3D structure of an enzyme is fixed
False: The 3D structure of an enzyme is not fixed, and its shape can be influenced by the binding of as substrate
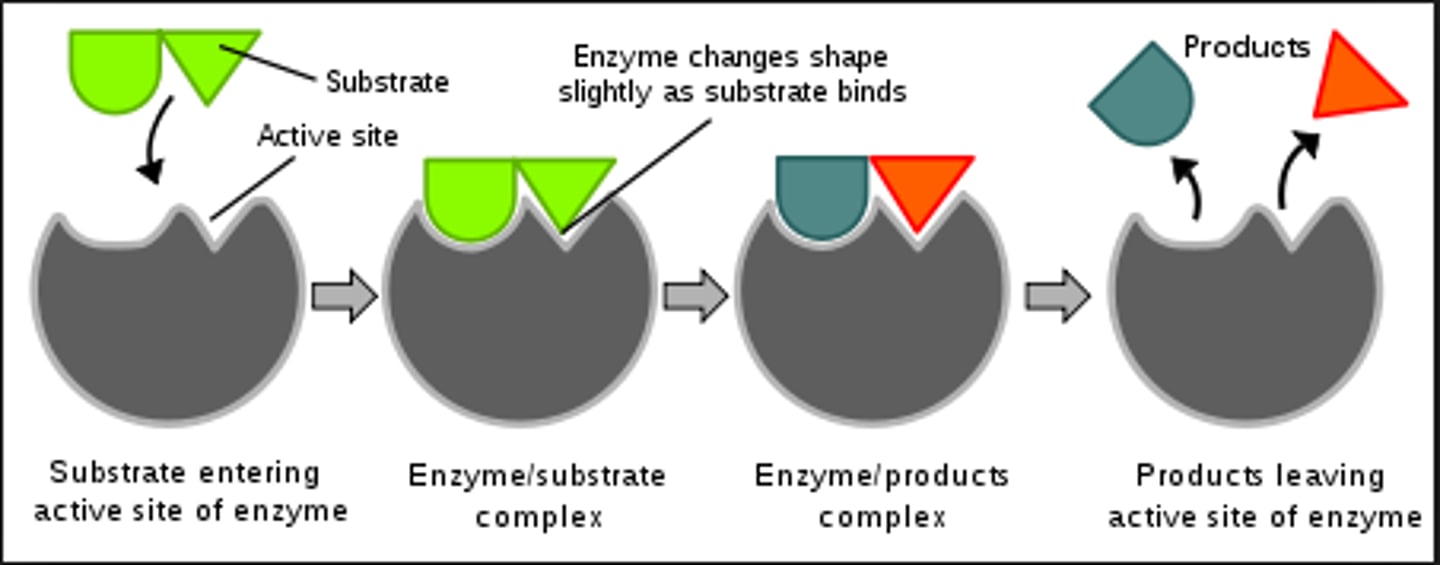
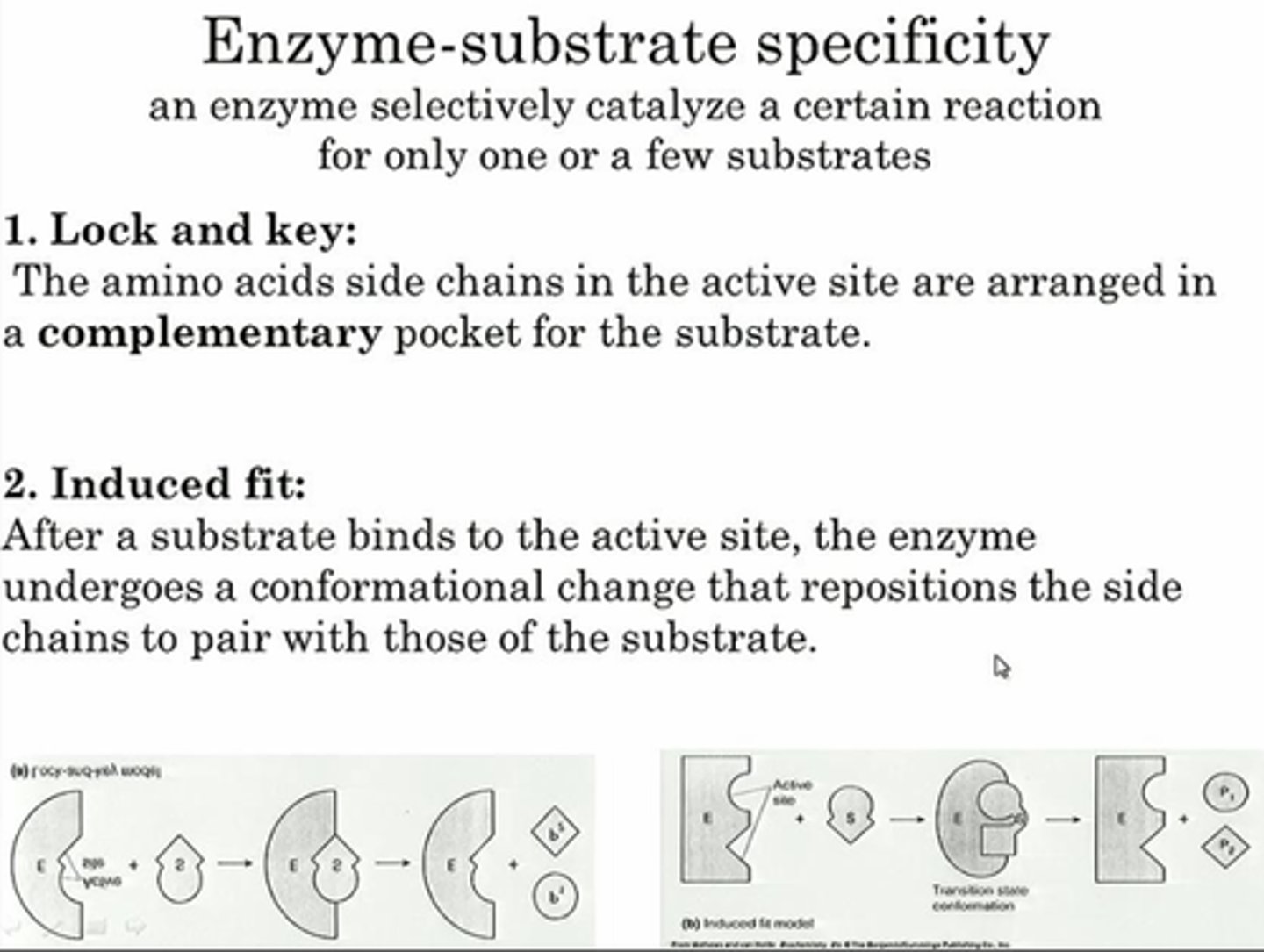
There are two models that described the relationship between an enzyme and substrate, state both and mention the outdated model
Lock & Key Model (outdated) and Induced-Fit Model (Current)
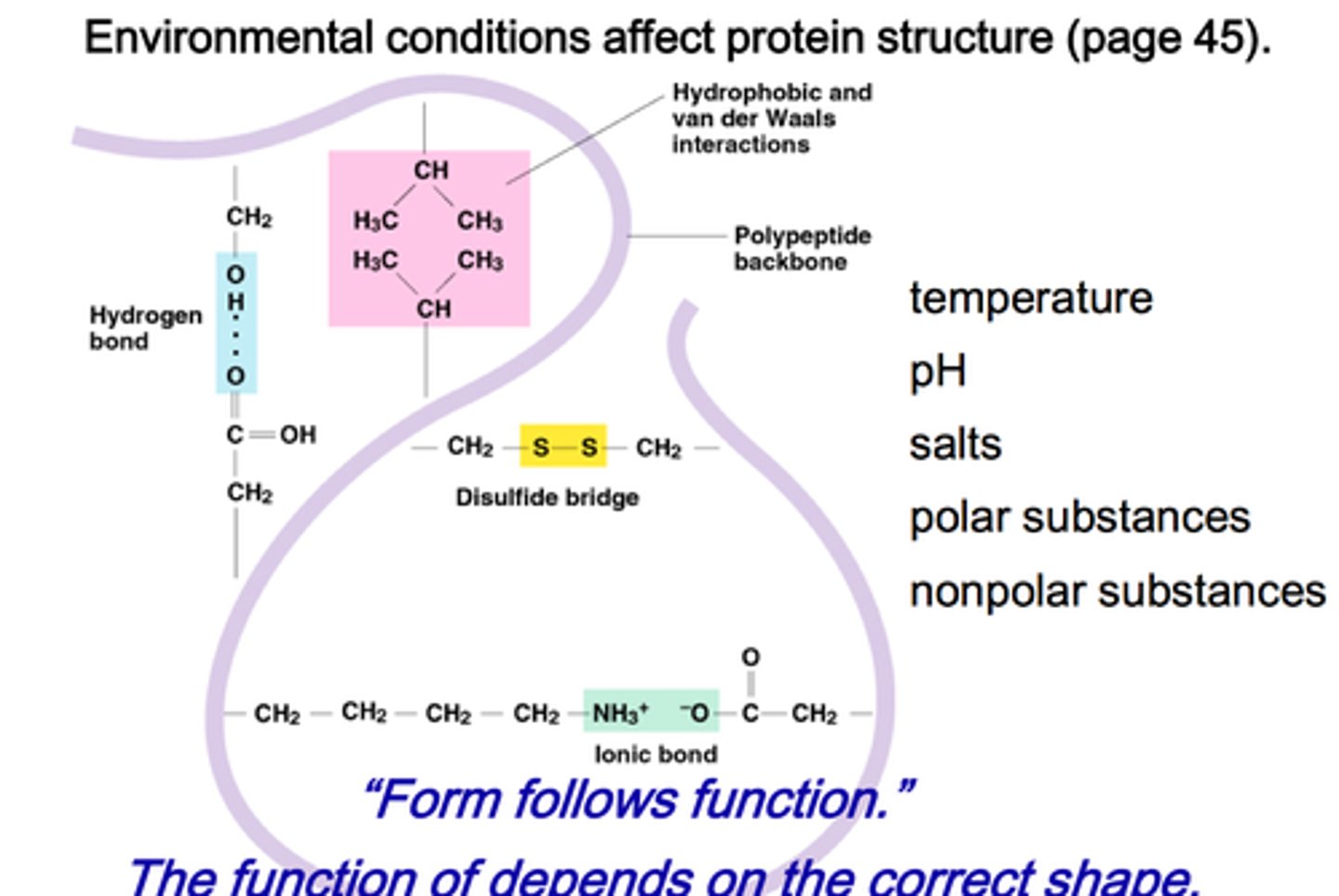
There are many aspects that cause a protein to denatures, list these factors.
pH, salt concentration, temperature, other aspects in its environment being altered - these factors cause the chemical bonds and interactions within a protein to be destroyed
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic blueprint, however, for it to be function it must be
Copied temporarily to RNA (ribonucleic acid)
There are five nucleotides, name all of them
Adenine - A
Thymine - T
Guanine - G
Cytosine - C
Uracil (RNA) - U
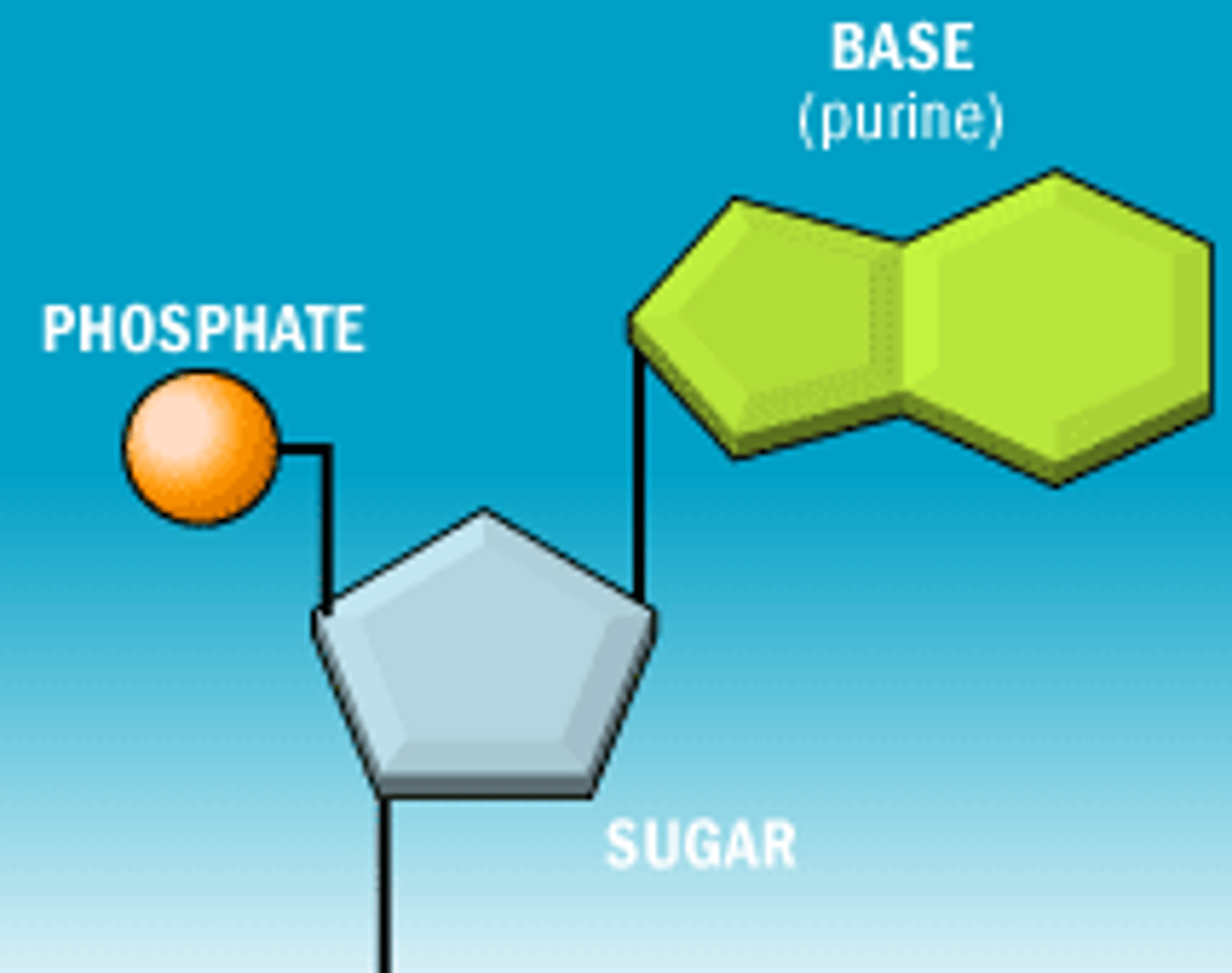
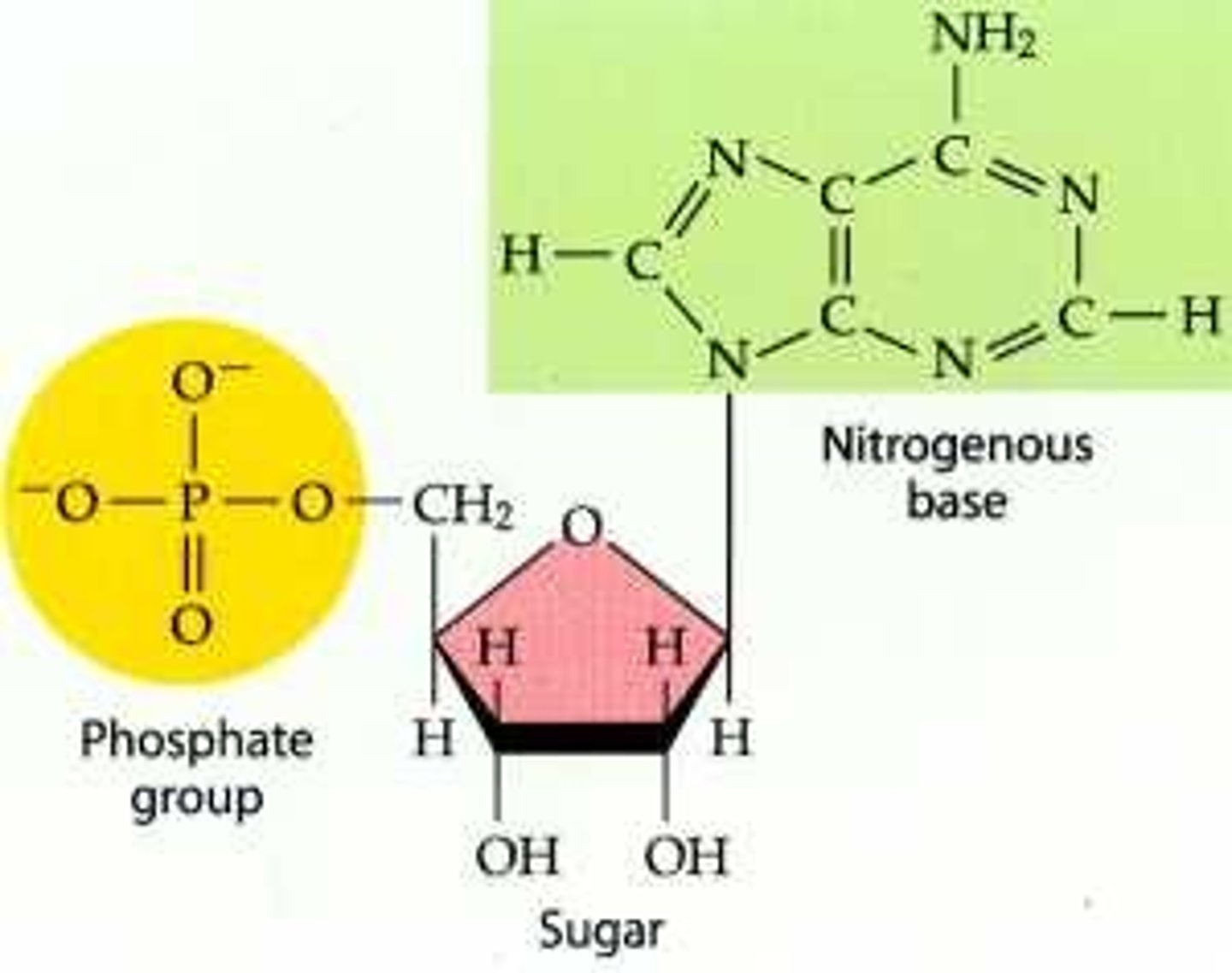
What is the structure of nucleic acids
Phosphate group, sugar (pentose) and nitrogenous base
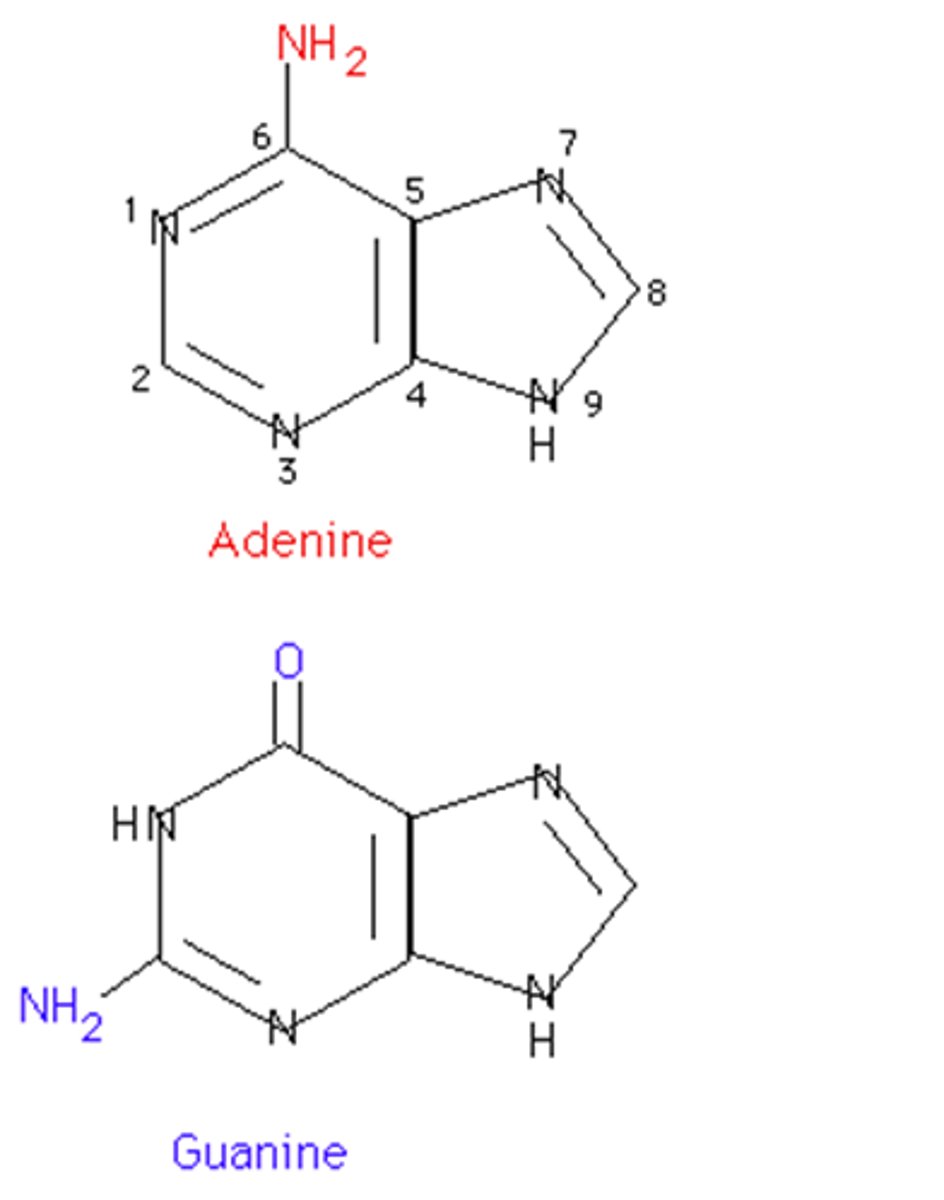
Which nucleotides are purines?
Adenine and Guanine
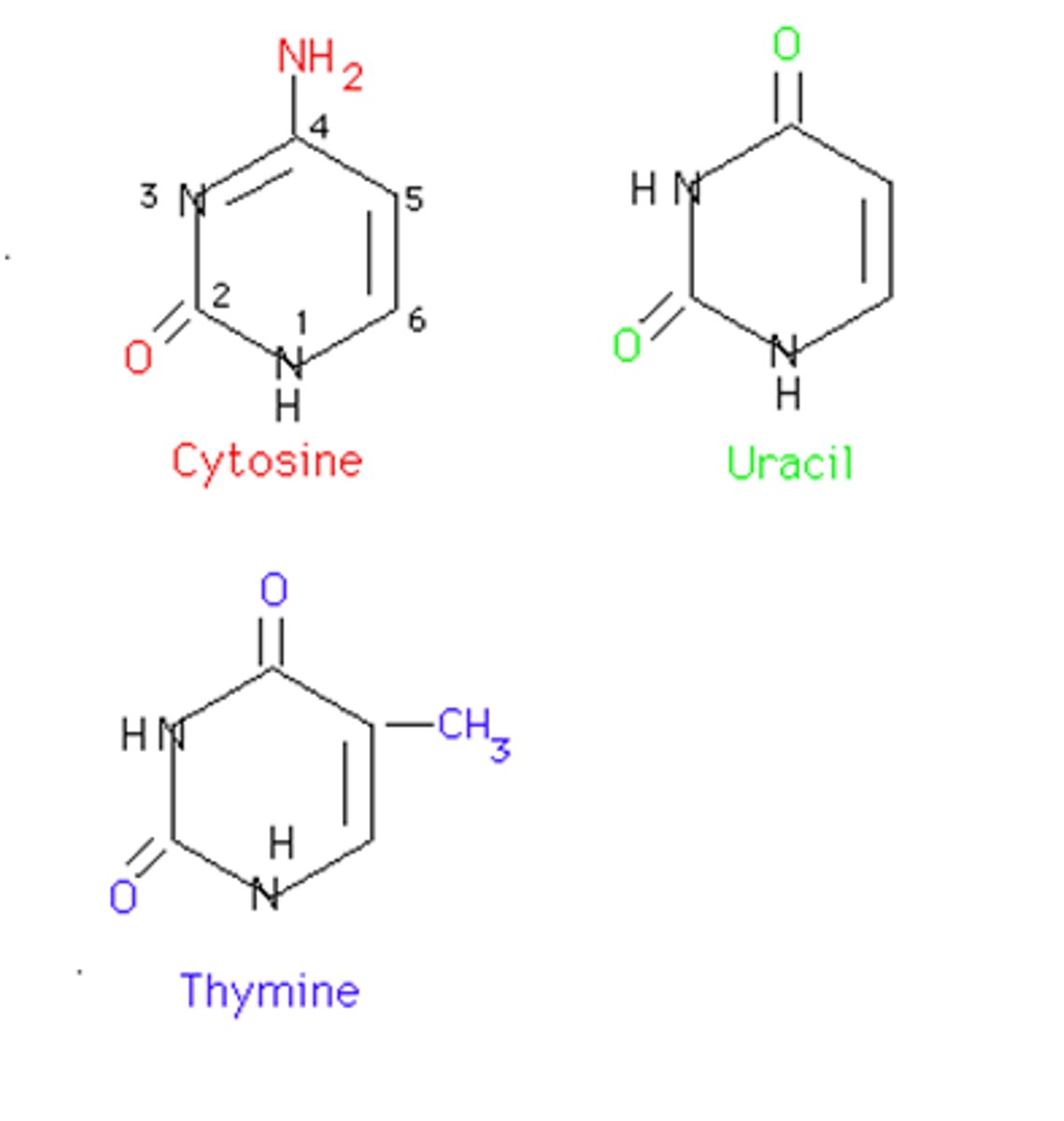
Which nucleotides are pyrimidines?
cytosine, thymine, uracil
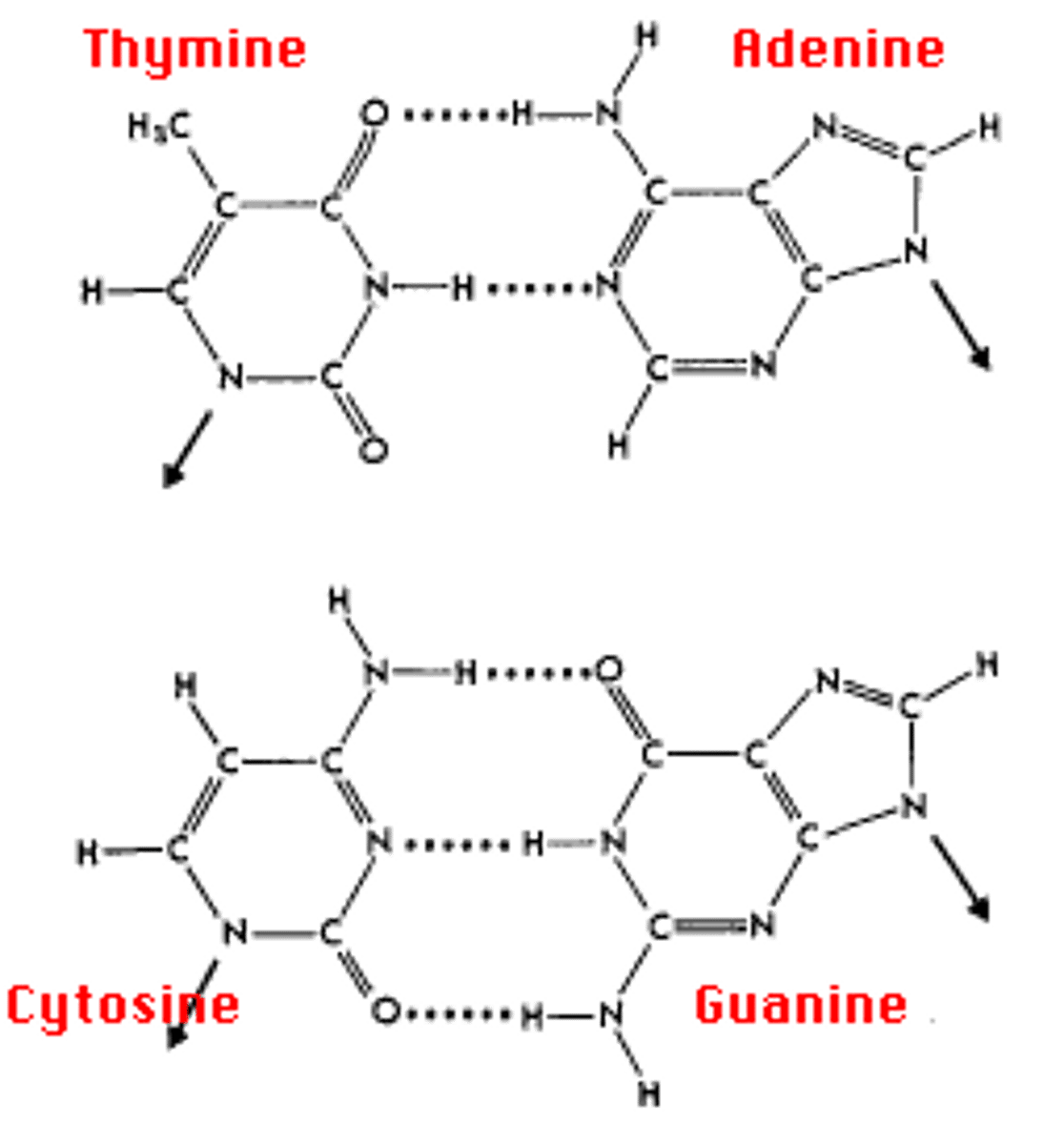
Are A=T bonds stronger than G=C bonds?
No GC bonds are stronger than AT bonds
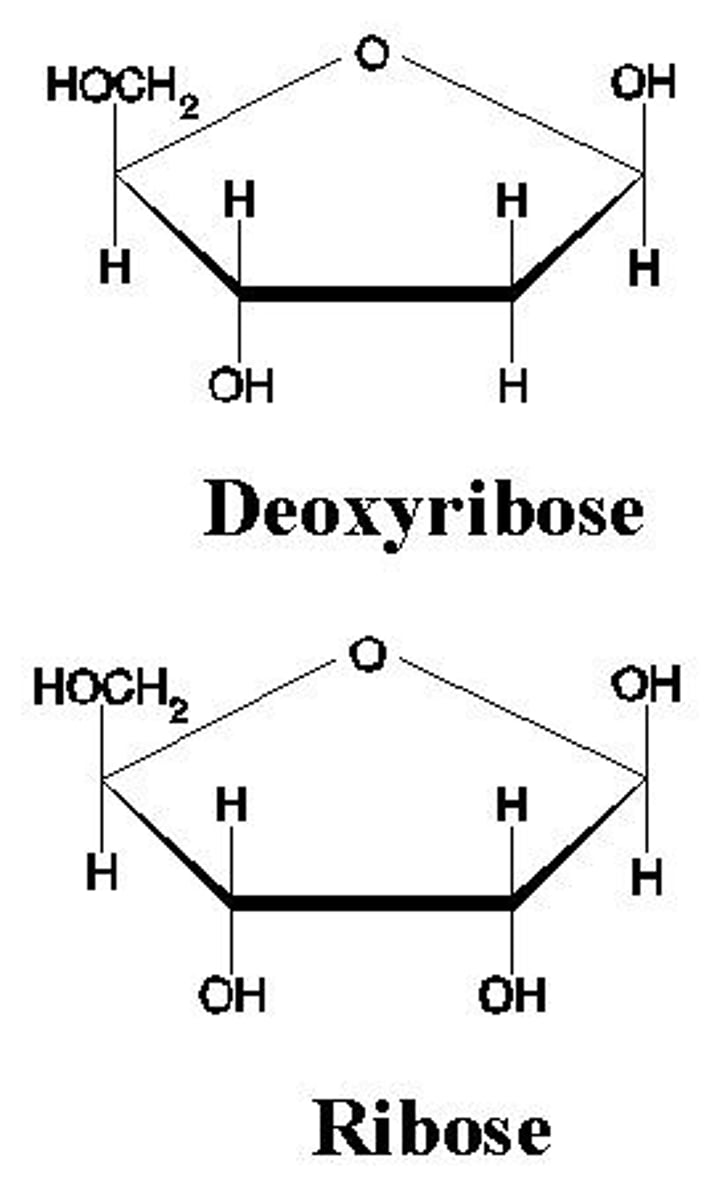
What are the differences between DNA and RNA within its pentose sugar
DNA has an OH bond to Carbon 3 & RNA has OH bonds on both Carbon 2 and 3
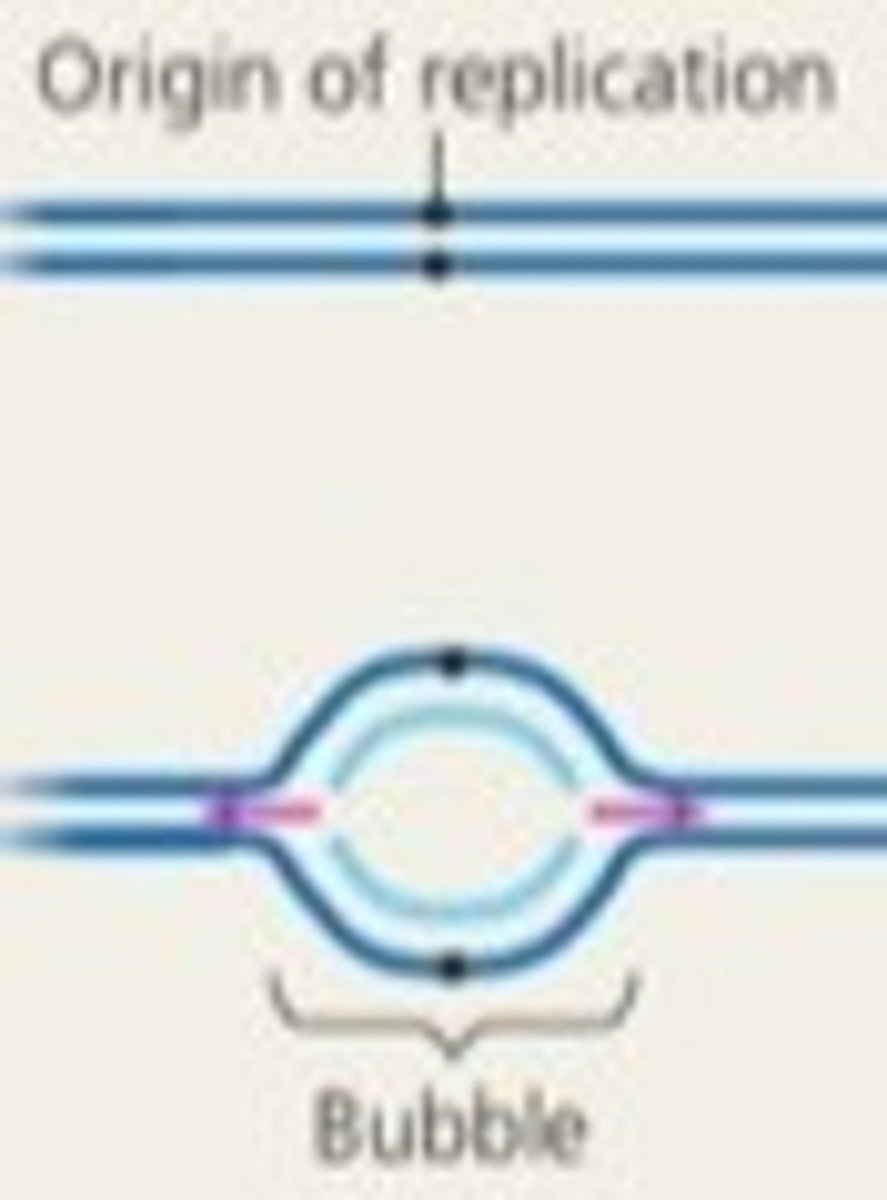
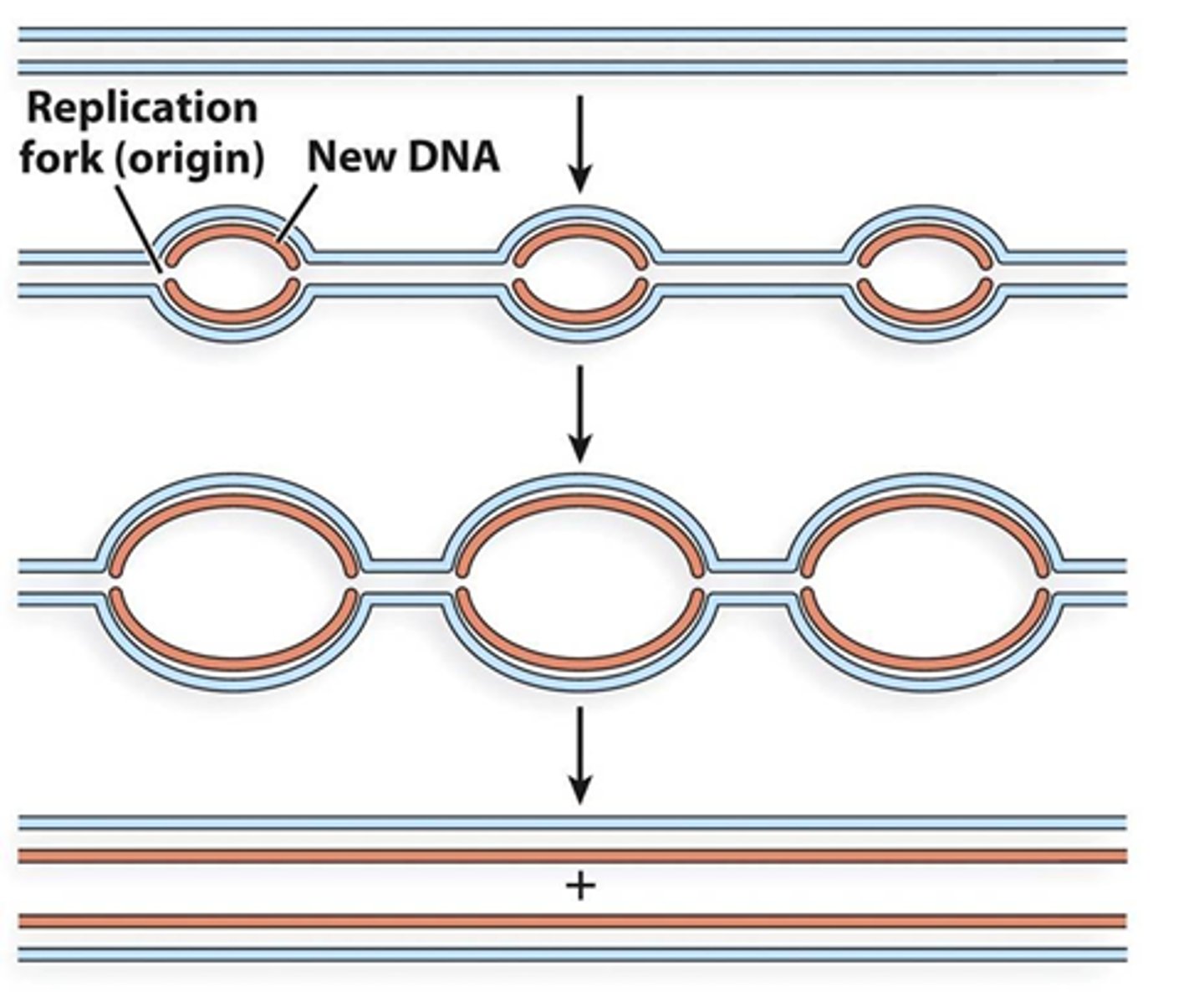
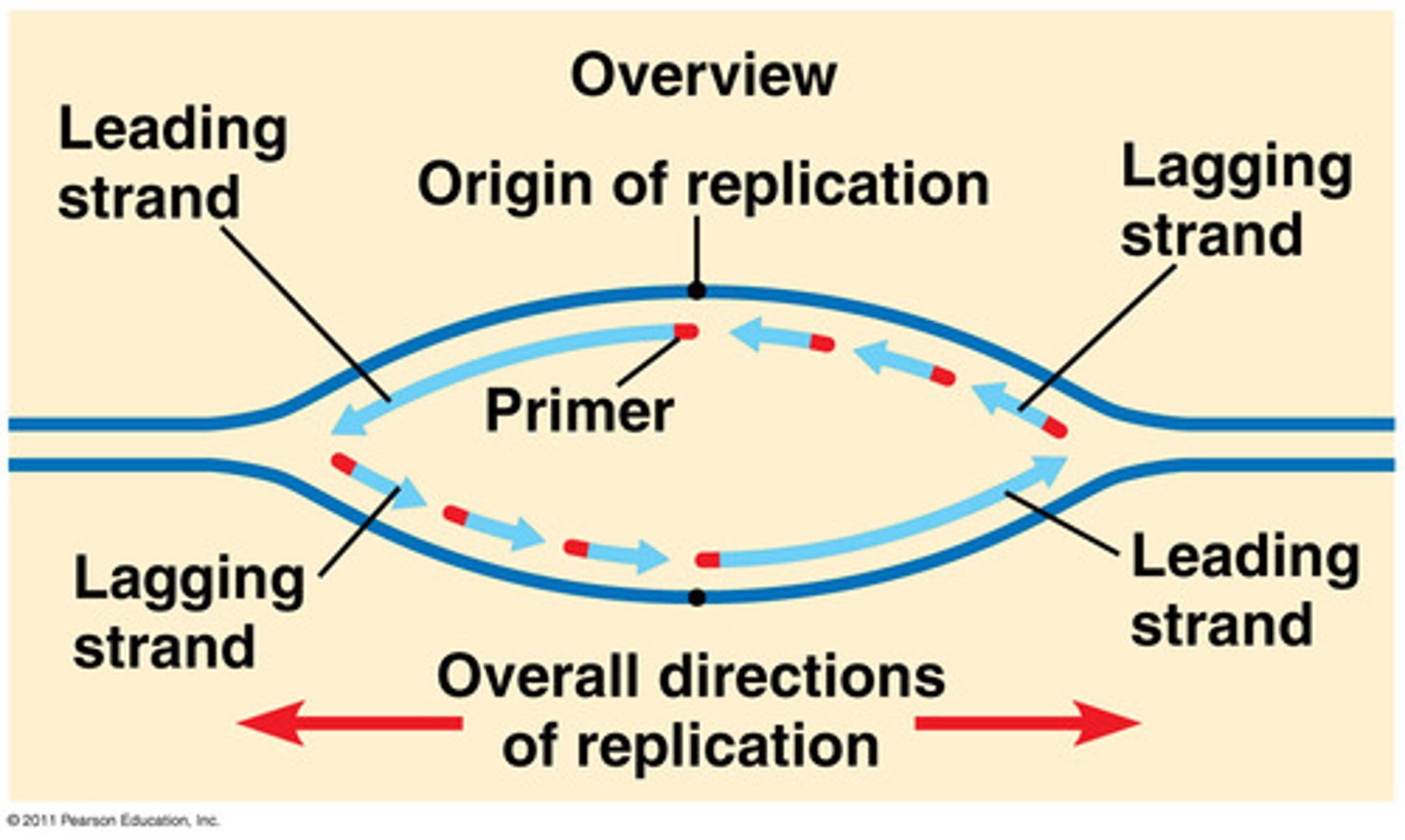
Where are the origins of replication located?
Conserved regions within a chromosome
Can enzymes go through DNA double helix structures?
No, enzymes don't have enough space to come through and copy DNA
What is it called when two DNA strands begin to seperate?
Replication fork or replication bubble
Can multiple replication bubbles be active at any time?
Yes, this is due to the size of chromosomes
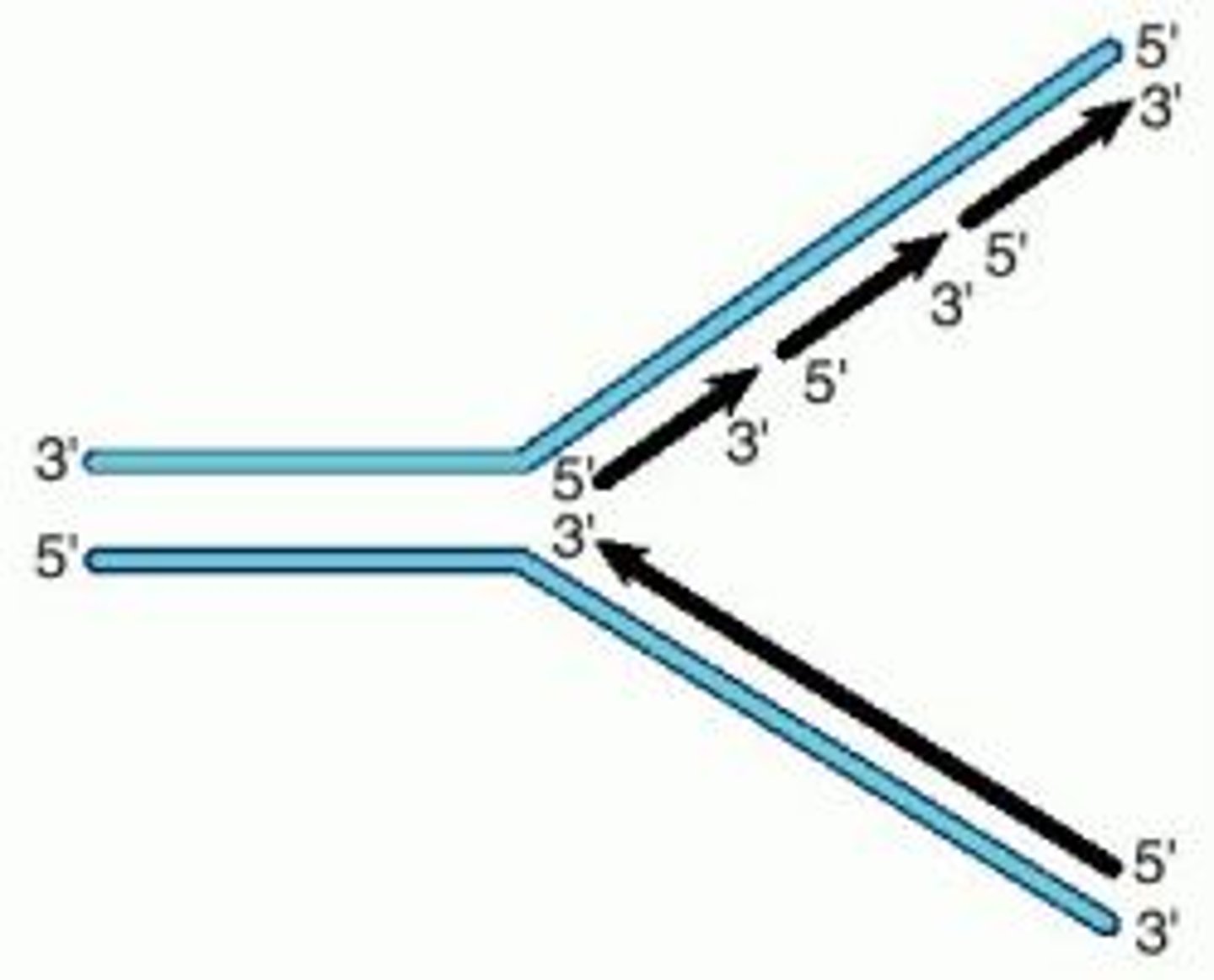
In which primer direction does replication occur?
5' to 3'
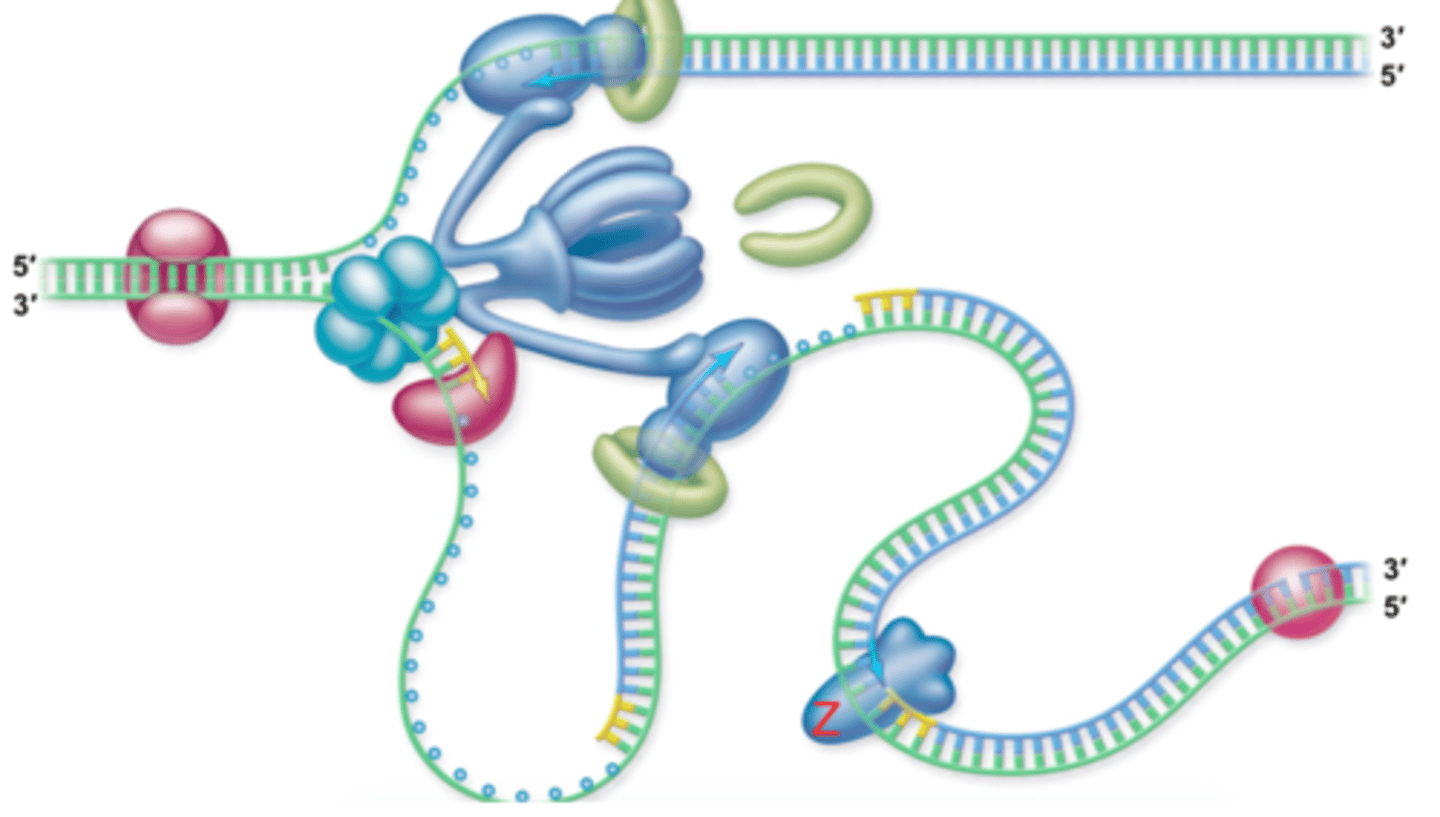
What does DNA require to replicate?
Template, polymerase and raw ingredients
What do nucleotide in their unbound form contain?
Triphosphate groups which supply polymerases with energy to catalyse the polymerising process

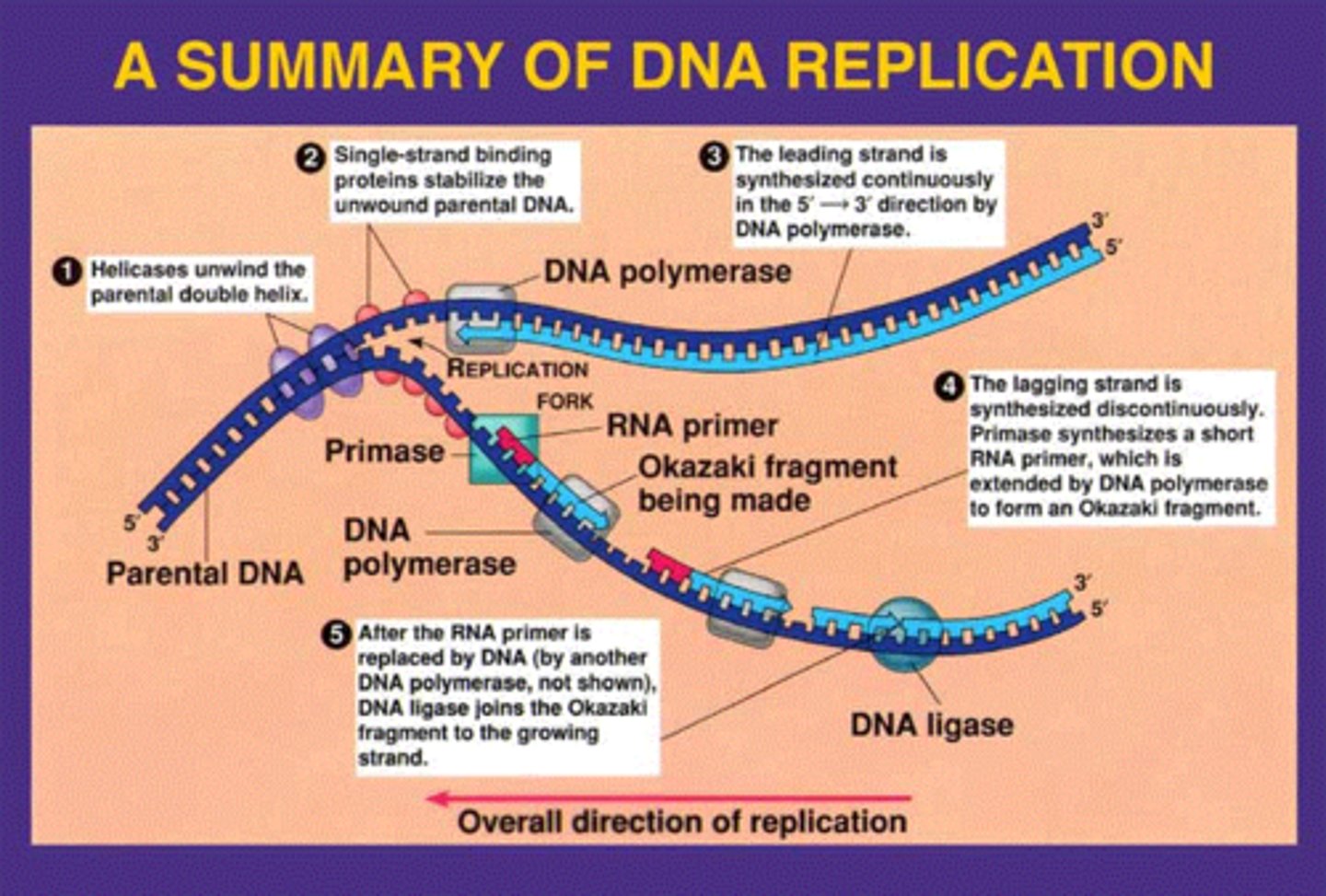
Define the function of Helicase
Helicase is an enzyme that unzips the DNA helix to give single stranded DNA - this increases coiling ahead of the replication fork
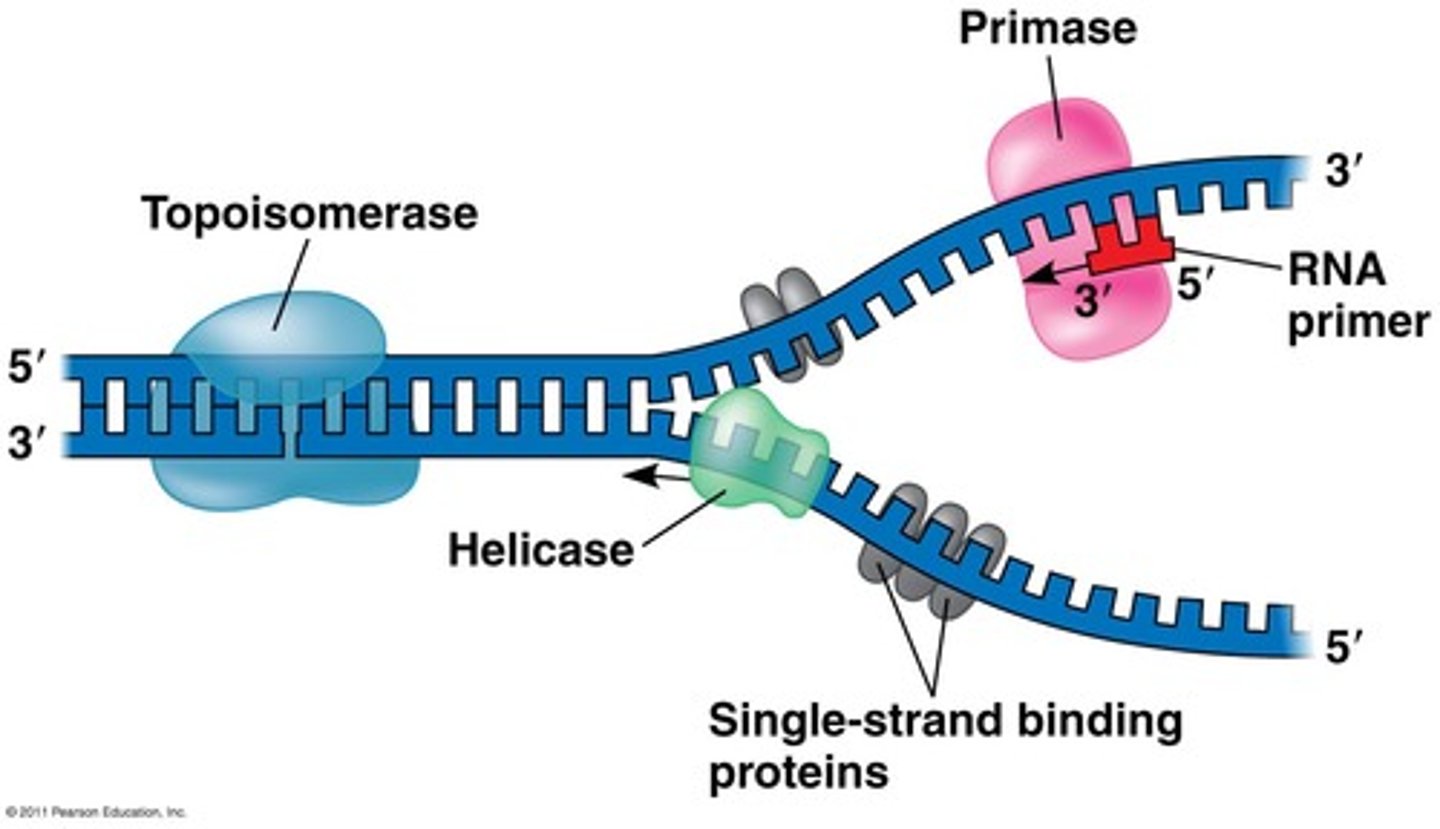
Define the function of Topoisomerase
Breaks, swivels and rejoins the parental DNA ahead of the replication fork, relieving the strain caused by unwinding
Define the function of single-strand binding proteins
Prevent the rewinding of DNA from its unwound state
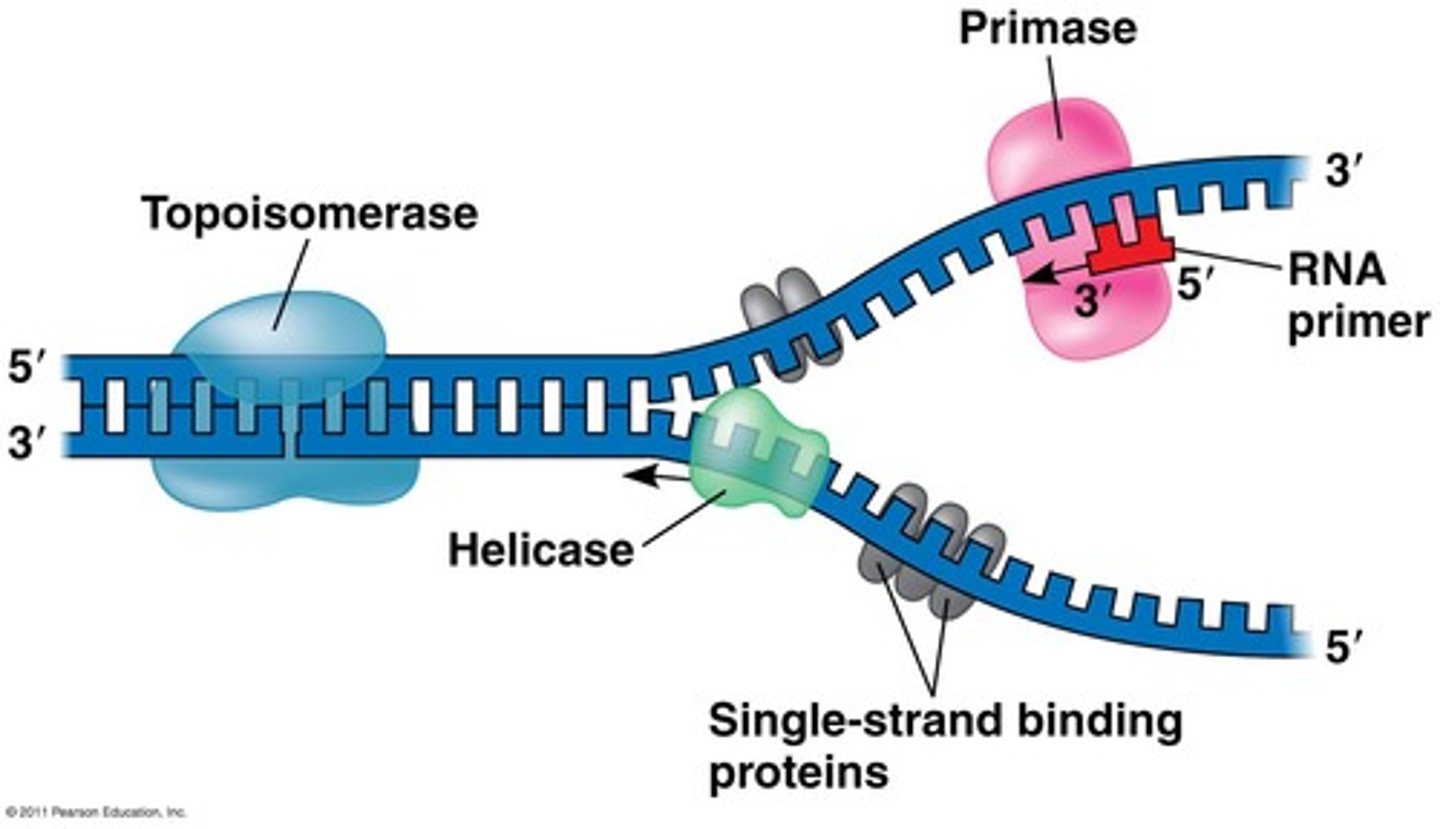
Define the function of DNA primase
Adds single-strand RNA primers which allow DNA polymerase to attach to the open strand and begin replicating
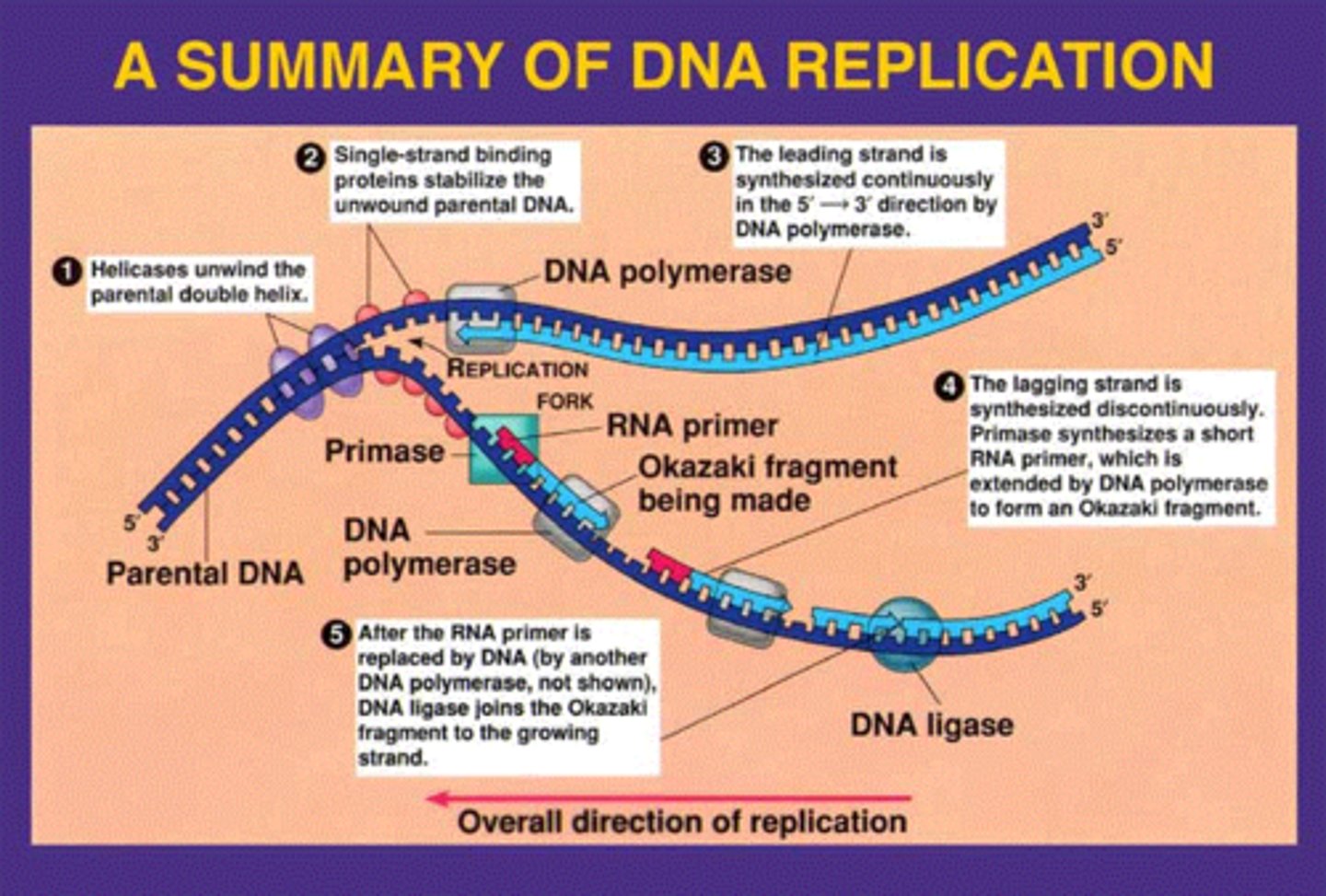
What does DNA Polymerase III do?
Builds many DNA and continues from the primer and adds complimentary nucleotides to the template.
What does DNA Polymerase I do?
Uses exonuclease activity to remove the original RNA primer and replace it with DNA
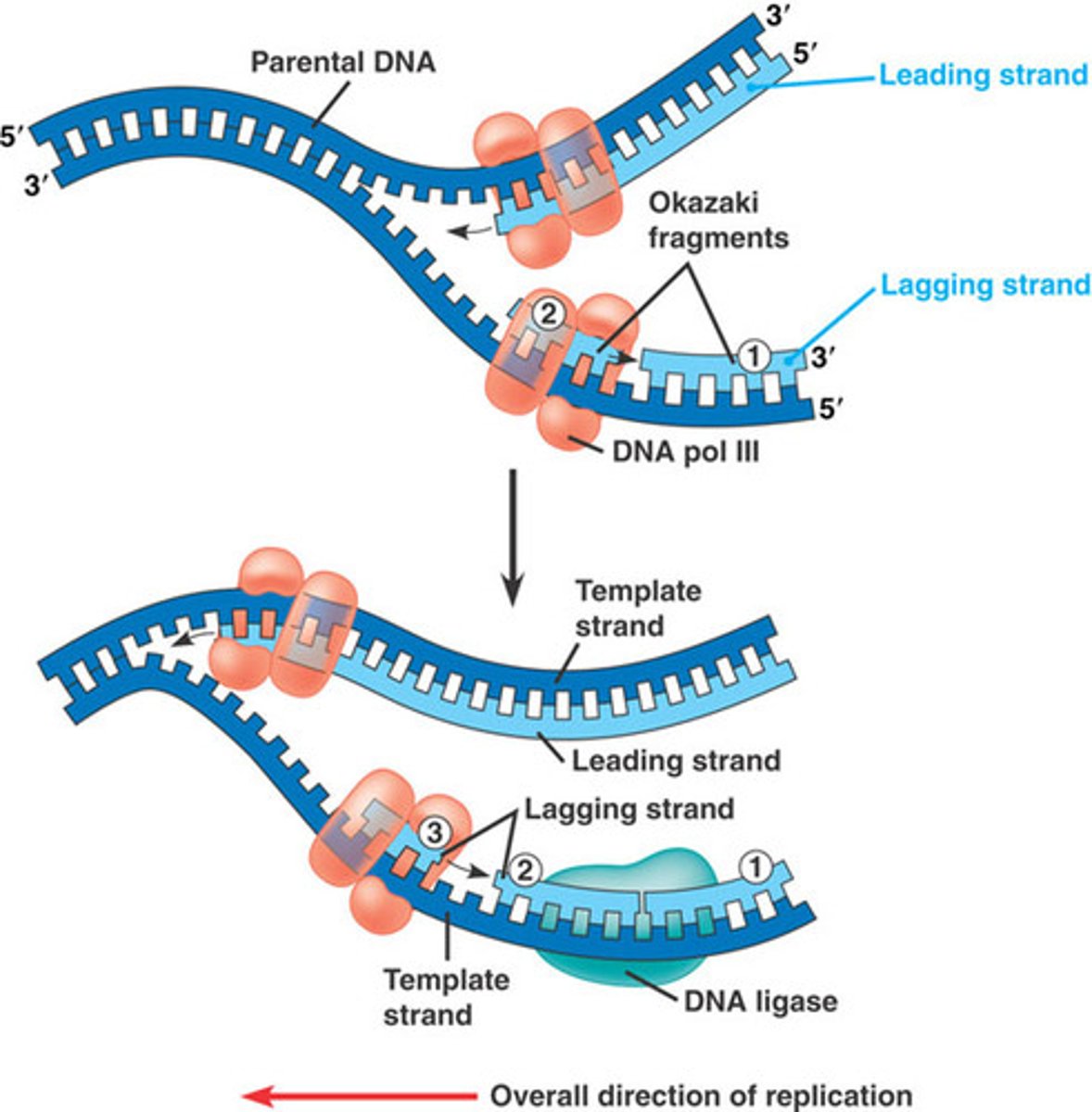
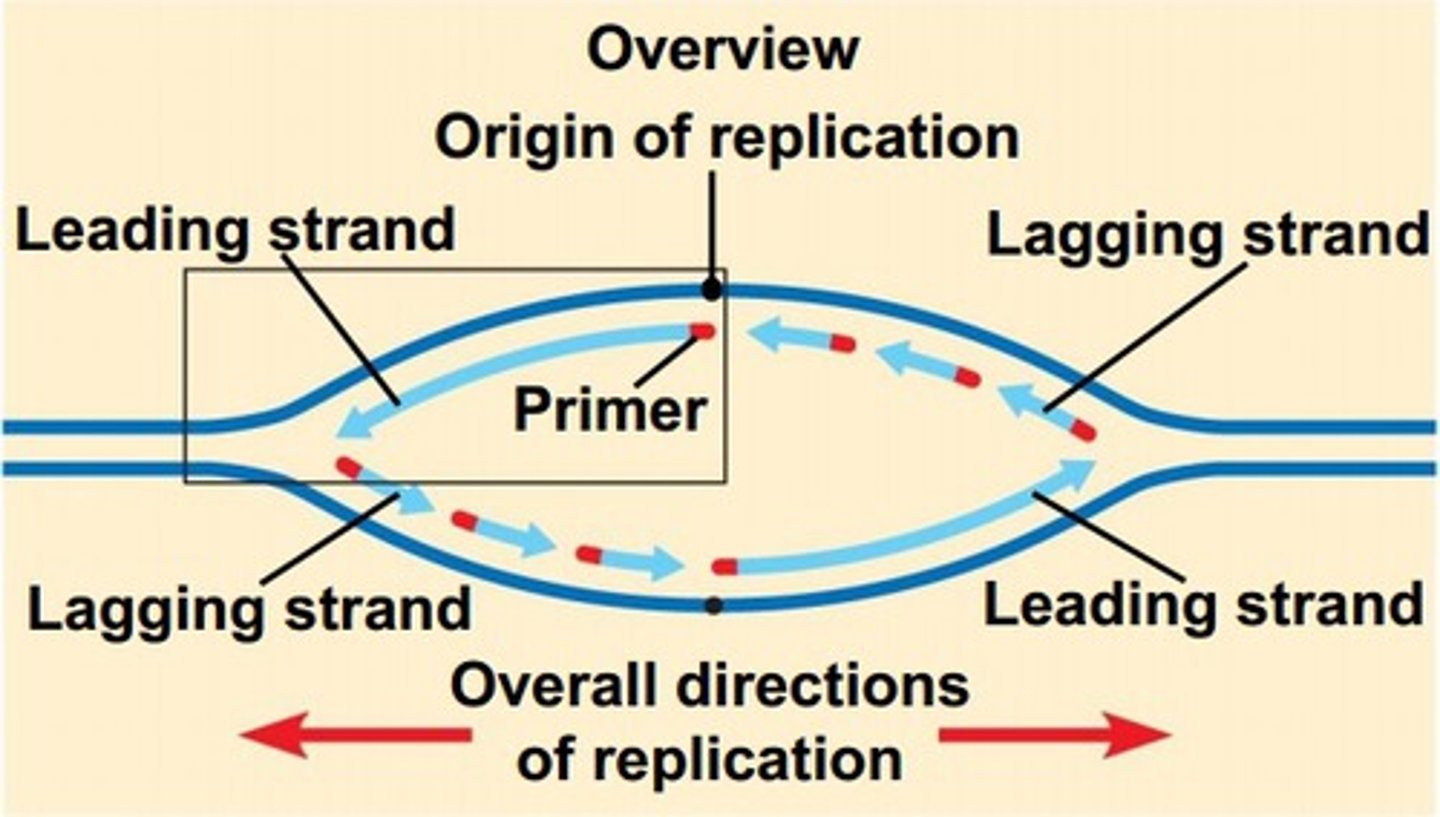
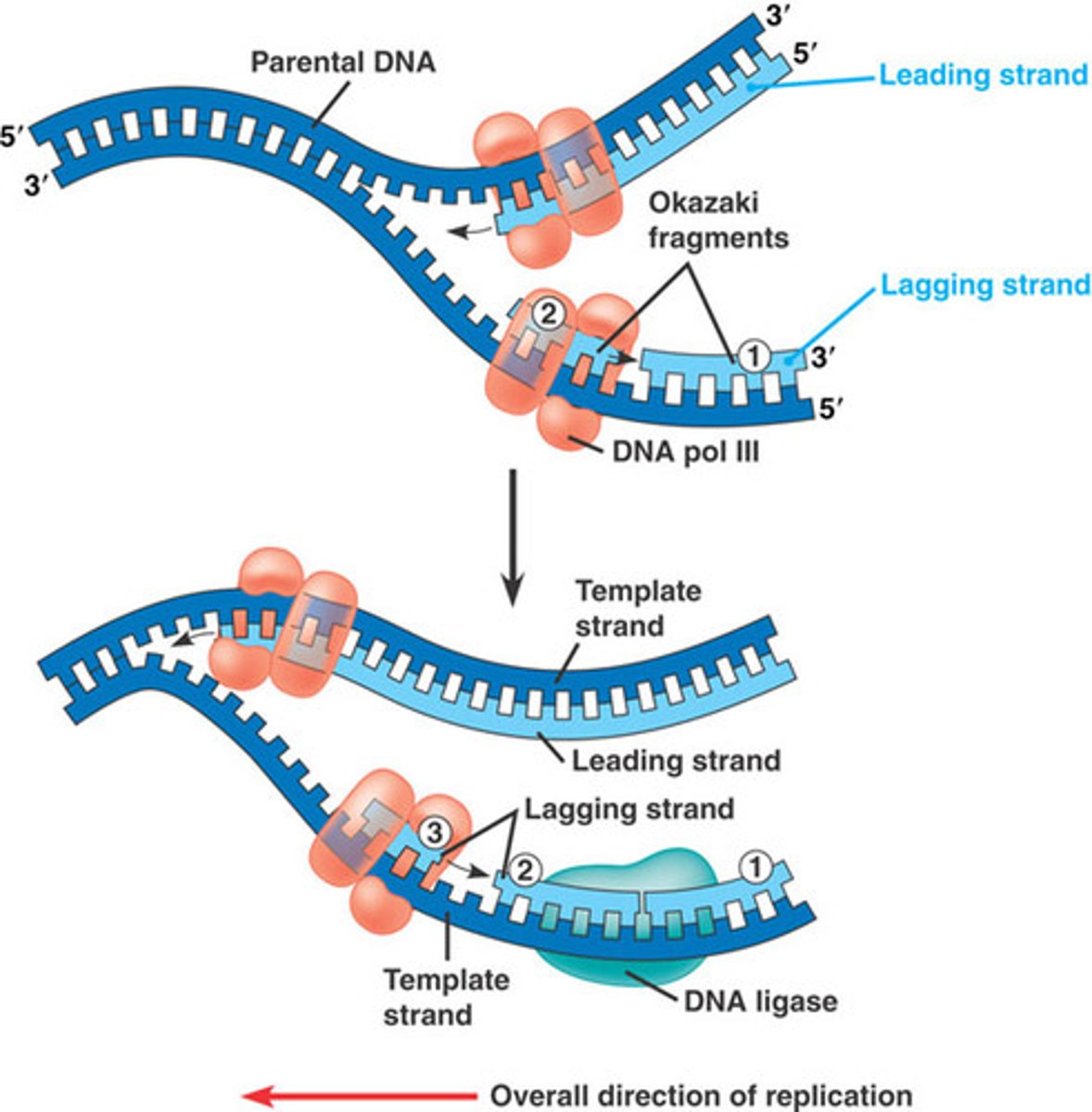
DNA has two strands, what are the names of both?
Leading and Lagging Strand
Is the synthesis of the leading strand smooth and continuous?
Yes, this is due to the primers direction 5' to 3', which allows the primase and polymerase to function smoothly and continuously
Why is it harder to synthesis the lagging strand?
Because of its 3' to 5' primers, which makes it more difficult for enzymes
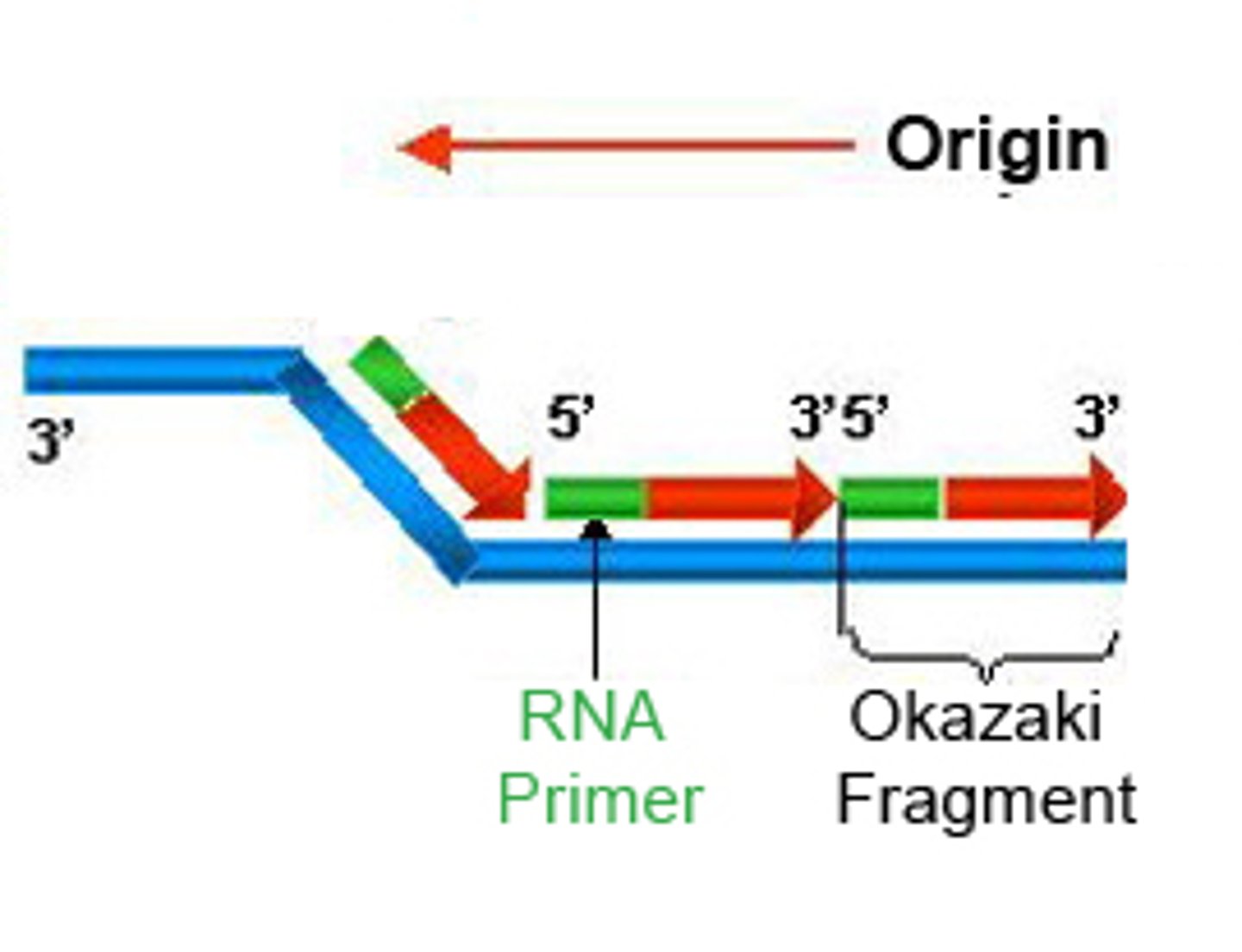
DNA primase adds several primers throughout the lagging strand which allow DNA polymerase III to come fill the gaps inbetween, the filled regions are known as the
Okazaki Fragments
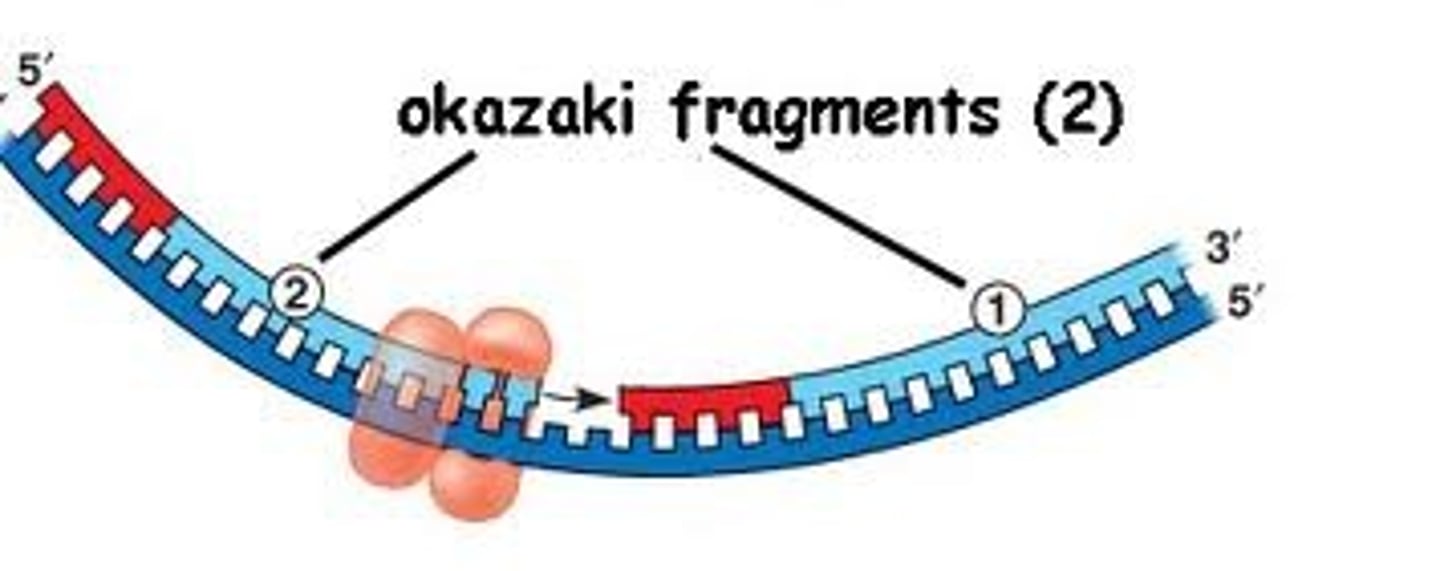
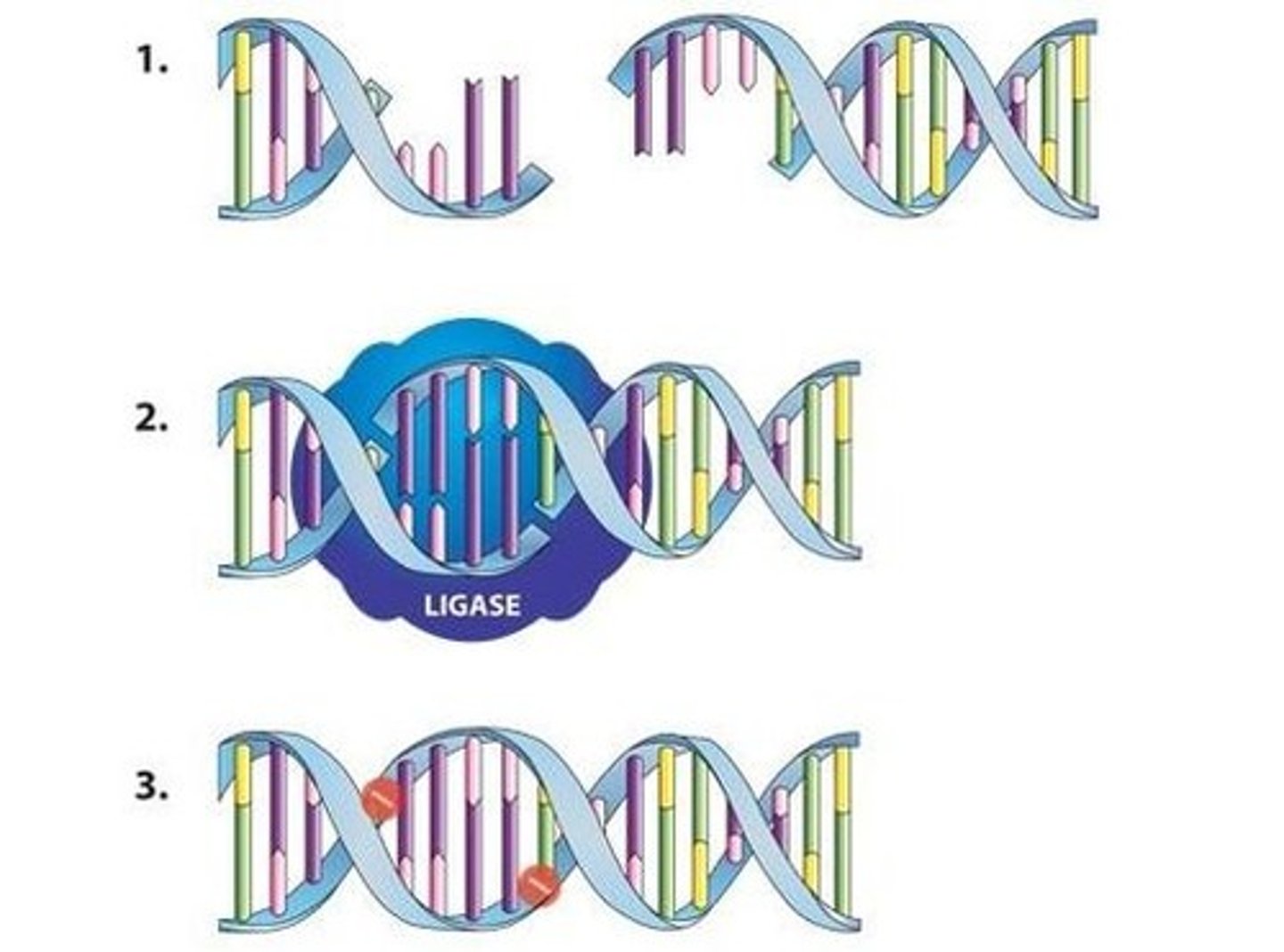
Which enzyme is responsible to fill the gaps of the Okazaki fragments from the lagging strand
DNA ligase - stitches together each of the Okazaki fragments covalently bonded, to form a continuous strand
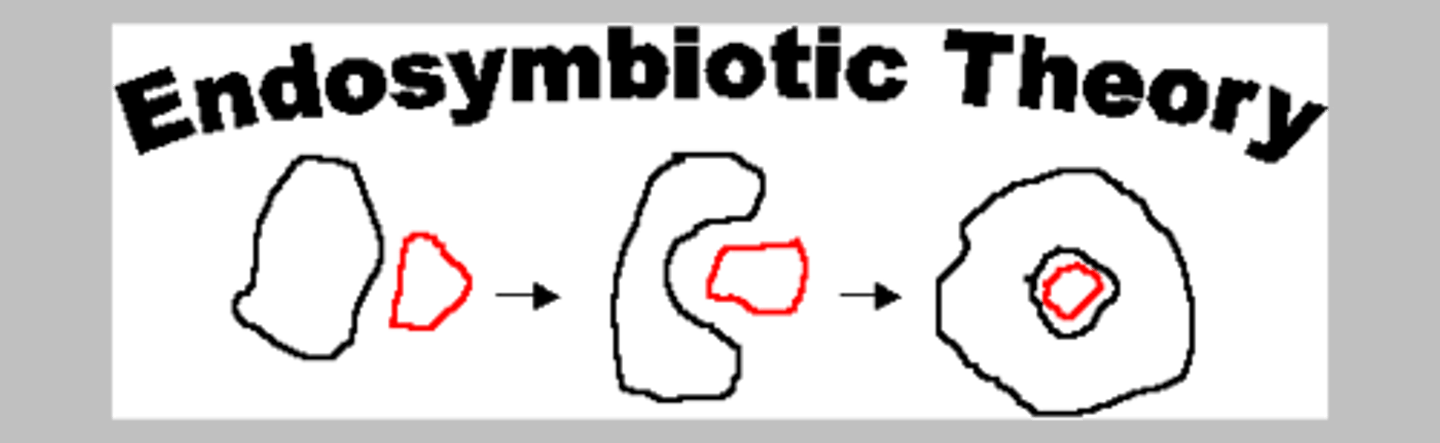
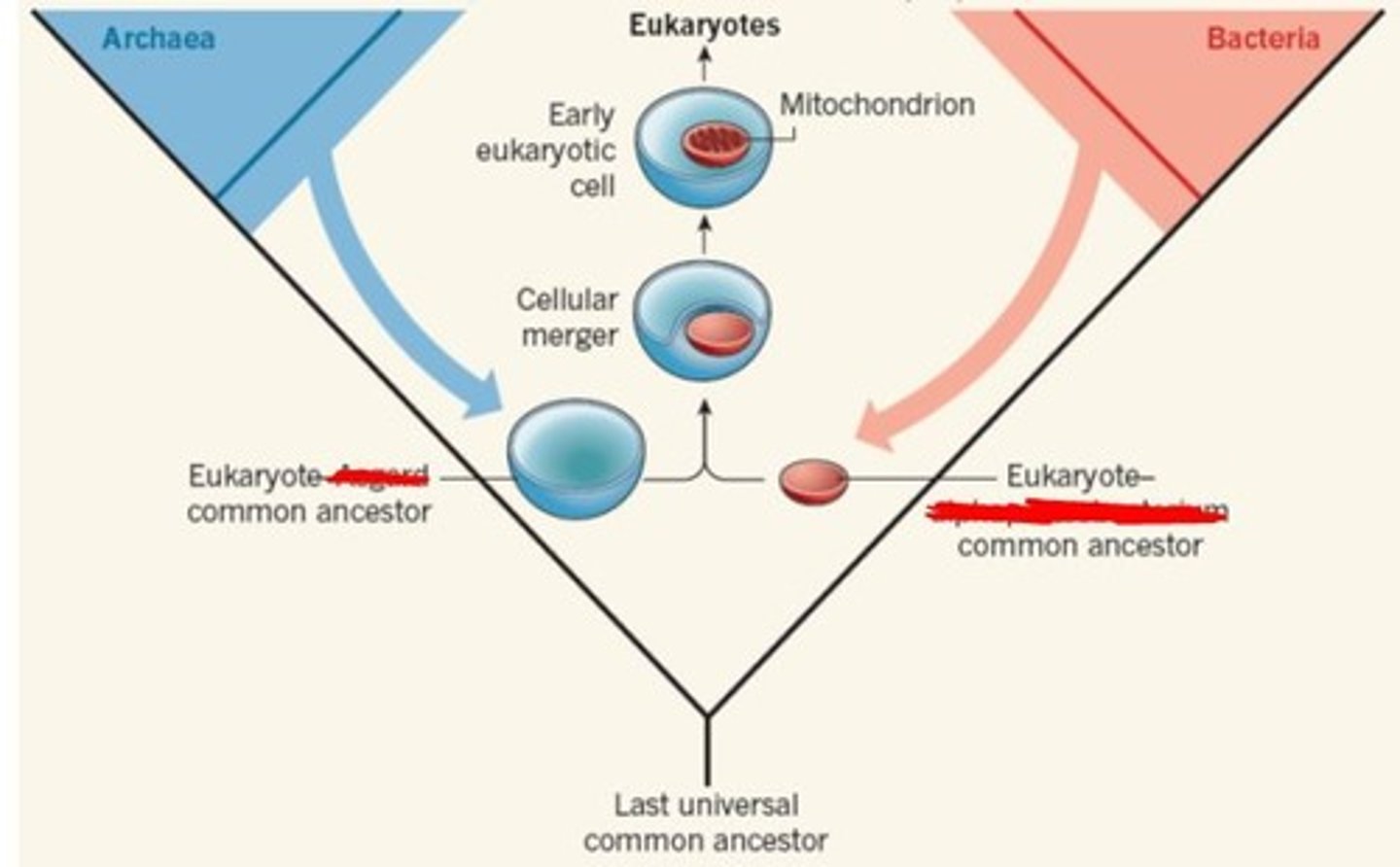
define endosymbiotic theory
origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts is that they originated as a result of a symbiotic union between free living bacteria and ancestors of eukaryotic cells
What organelles are unique to plants?
chloroplasts, large central vacuole, cell wall, chloroplast
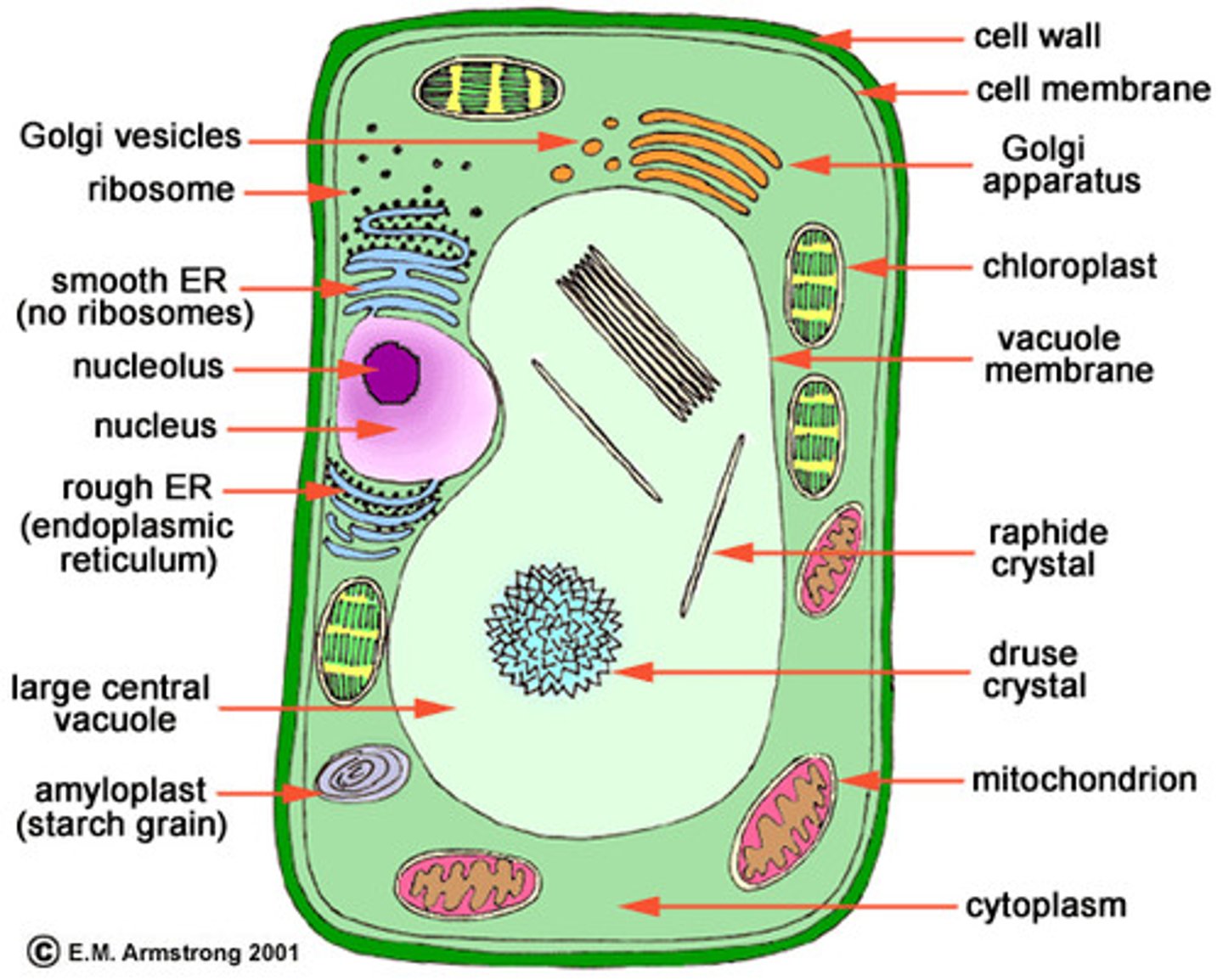
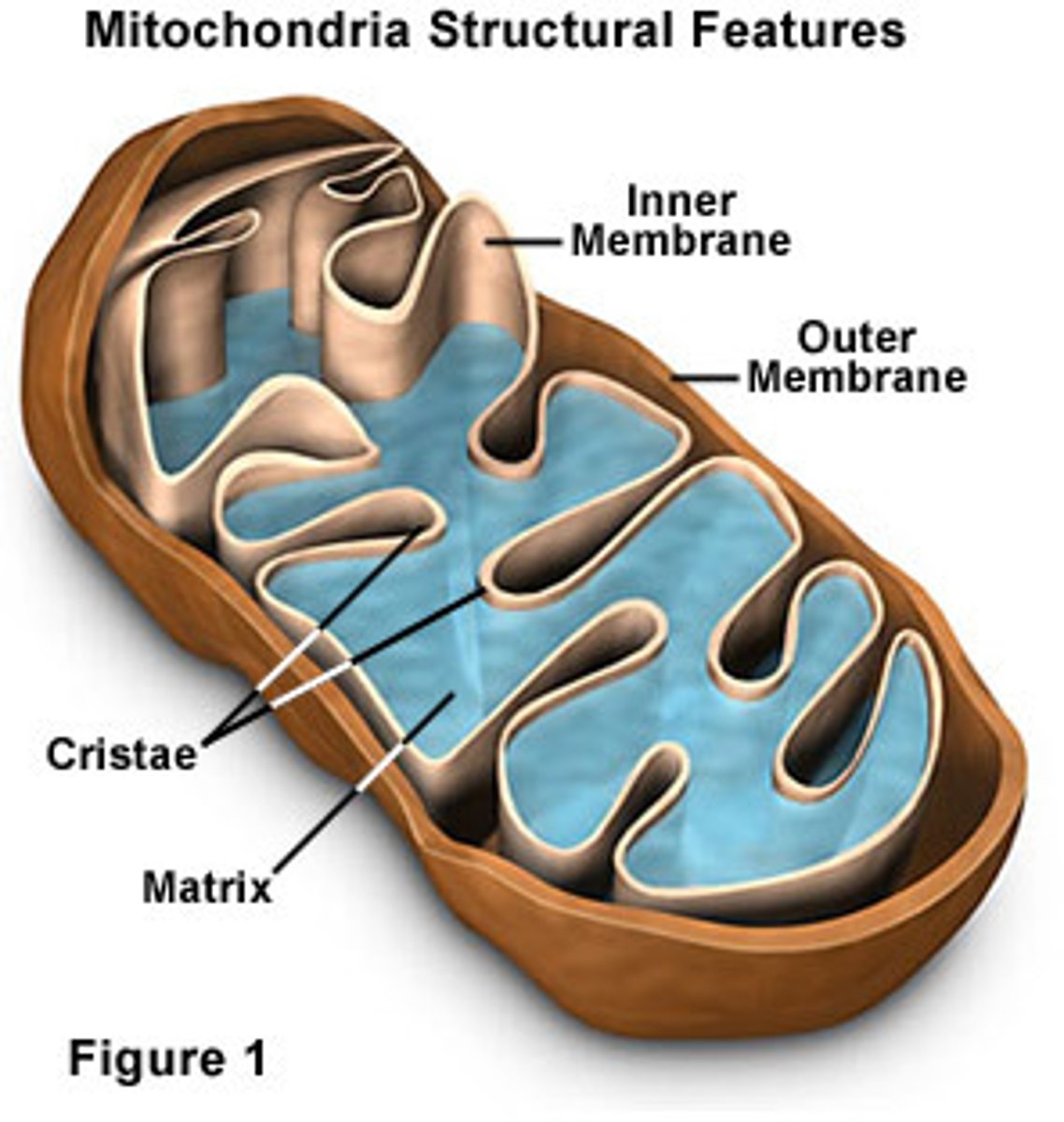
What does the mitochondria do?
Produce ATP - which is produced by the electron transport chain
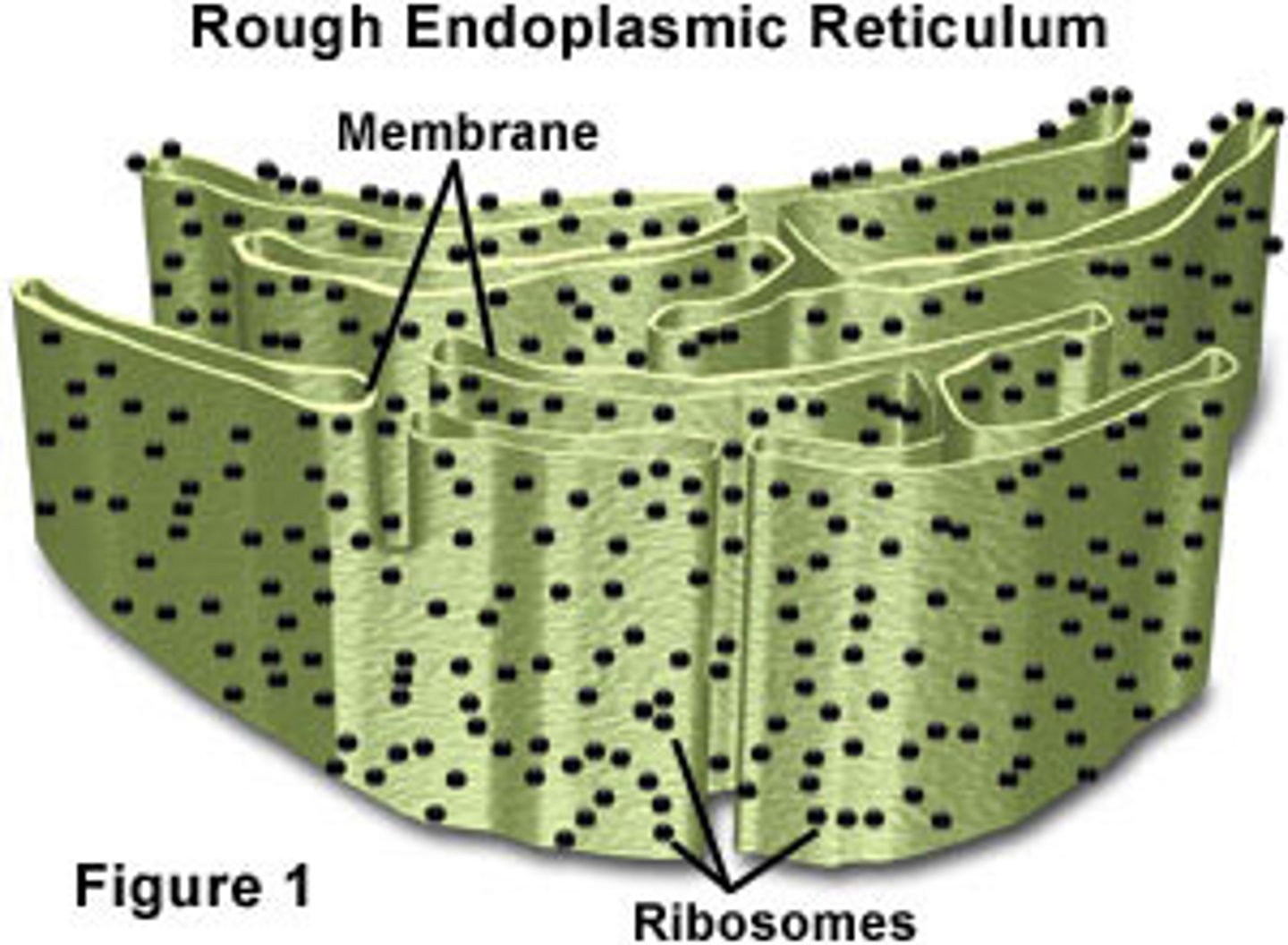
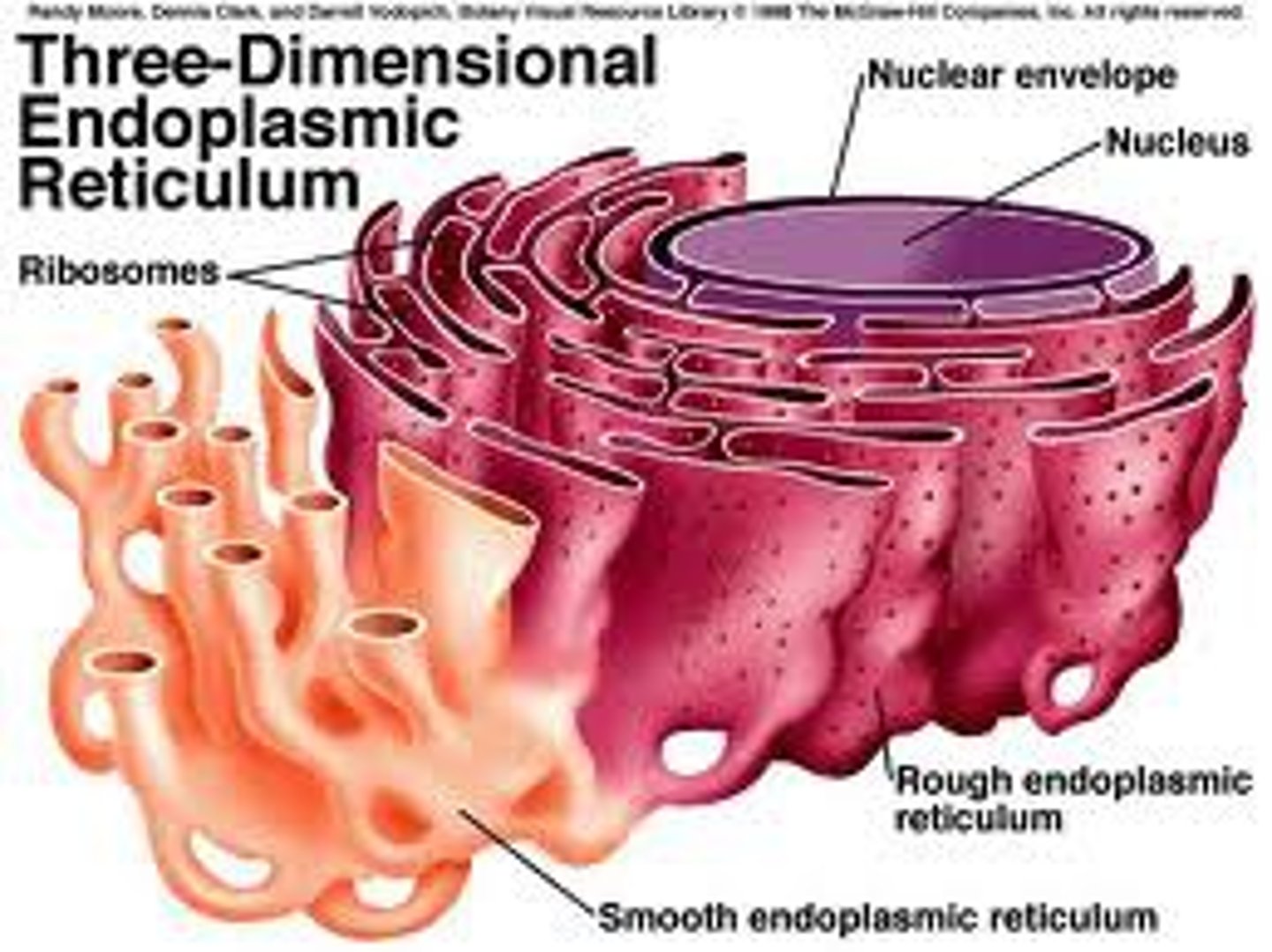
What does the endoplasmic reticulum do?
reticulated transport system that facilitates the transport of newly produced proteins around the cell
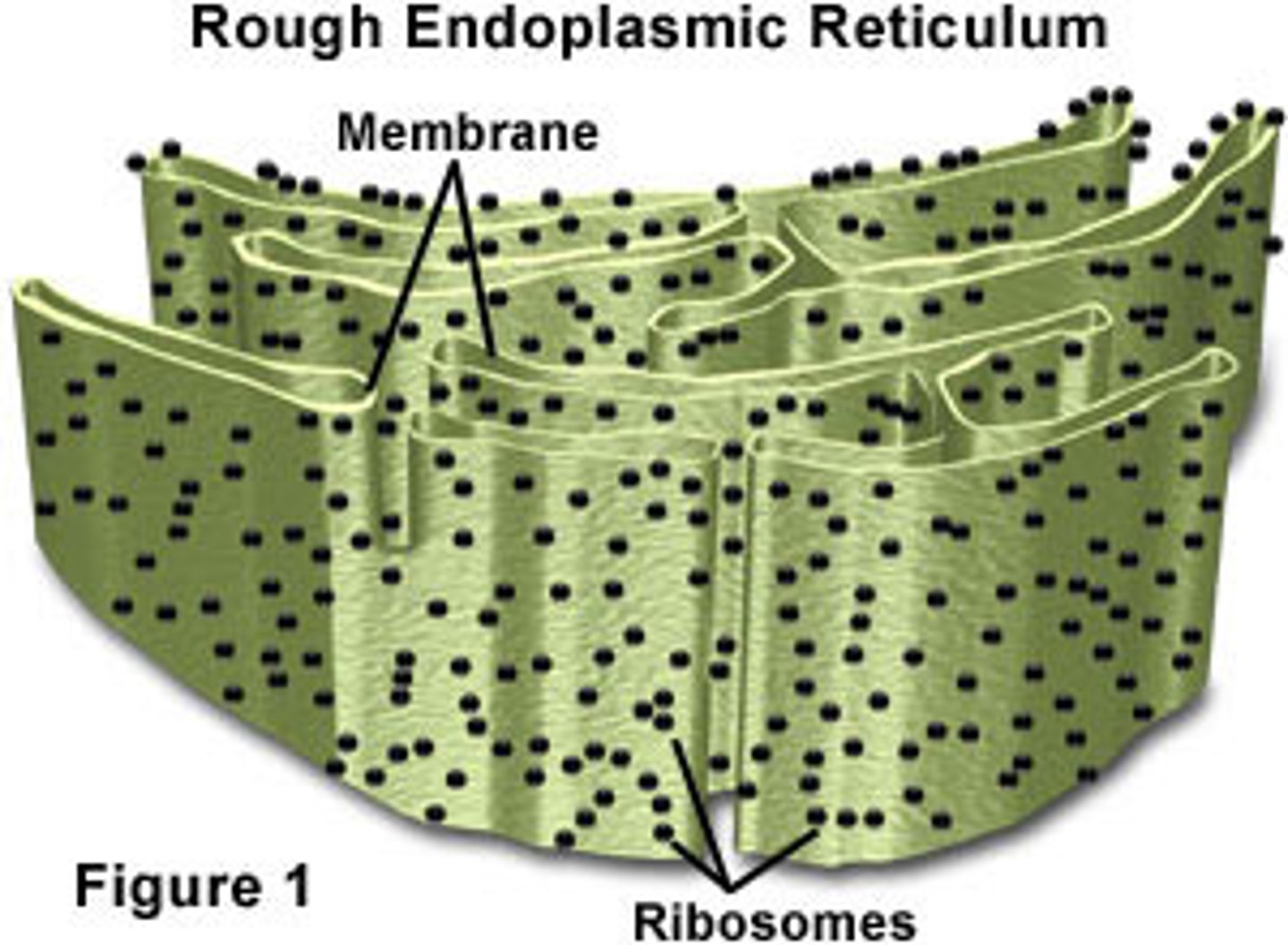
What are rough ER covered in?
Ribosomes
The endosymbiotic theory states that an ancestor had engulfed a bacterium which had an symbiont relationship with each other, producing ATP, and the rise to co-dominance, what is the class of this bacterium
Alphaproteobacterium
What does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum do?
produce lipids for other cell compartments, break down toxic organic compounds in the cell
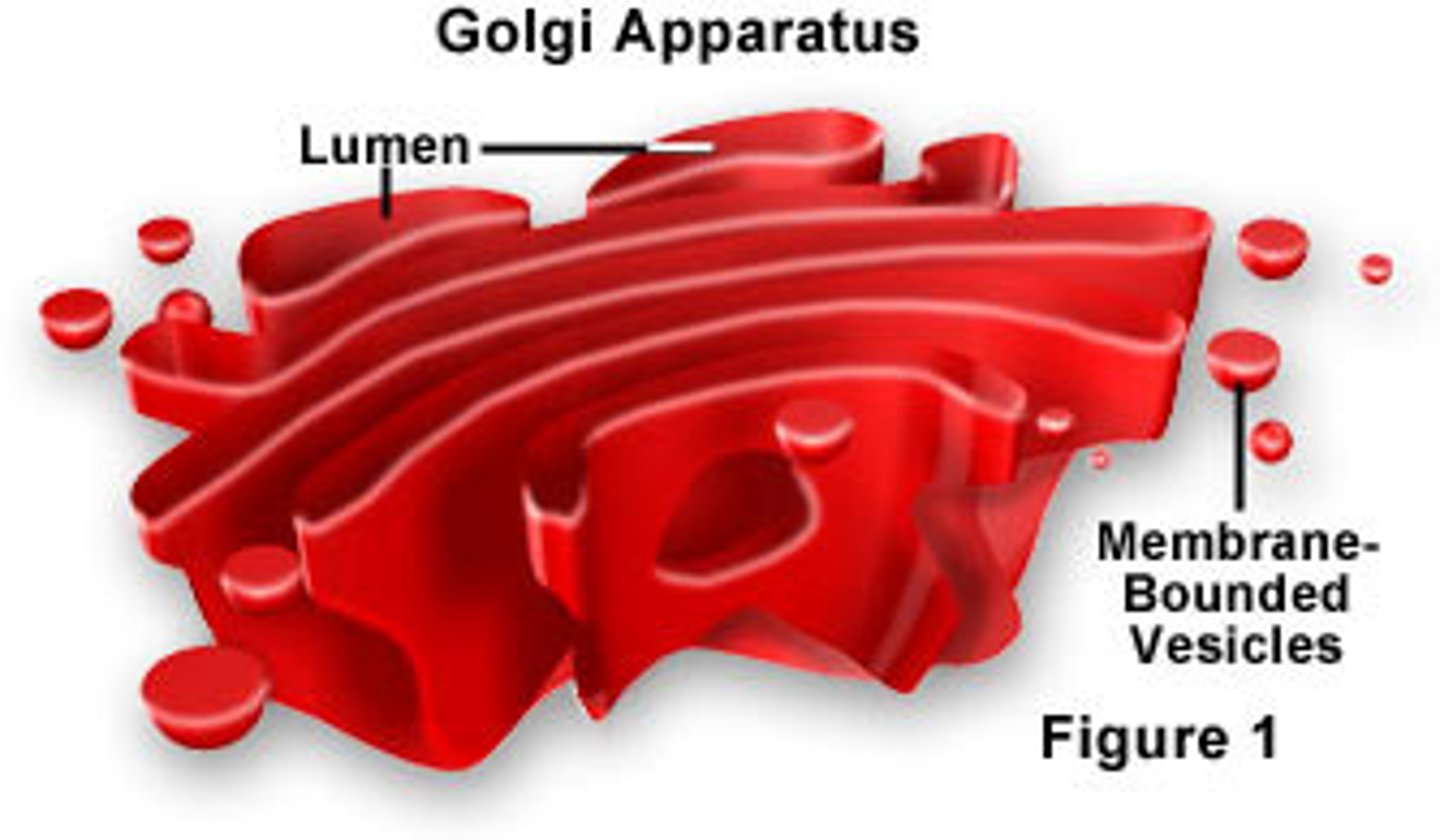
What does the golgi do?
1) Manufactures polysaccharides from simple sugars and modifies the carbohydrate tags on proteins or lipids. Some proteins are packaged into secretory vesicles to be released from the cell via exocytosis.
2) Makes lysosomes.
What does peroxisomes do?
They neutralize free radicals
Oxidize organic molecules
Detoxify alcohol and other drugs
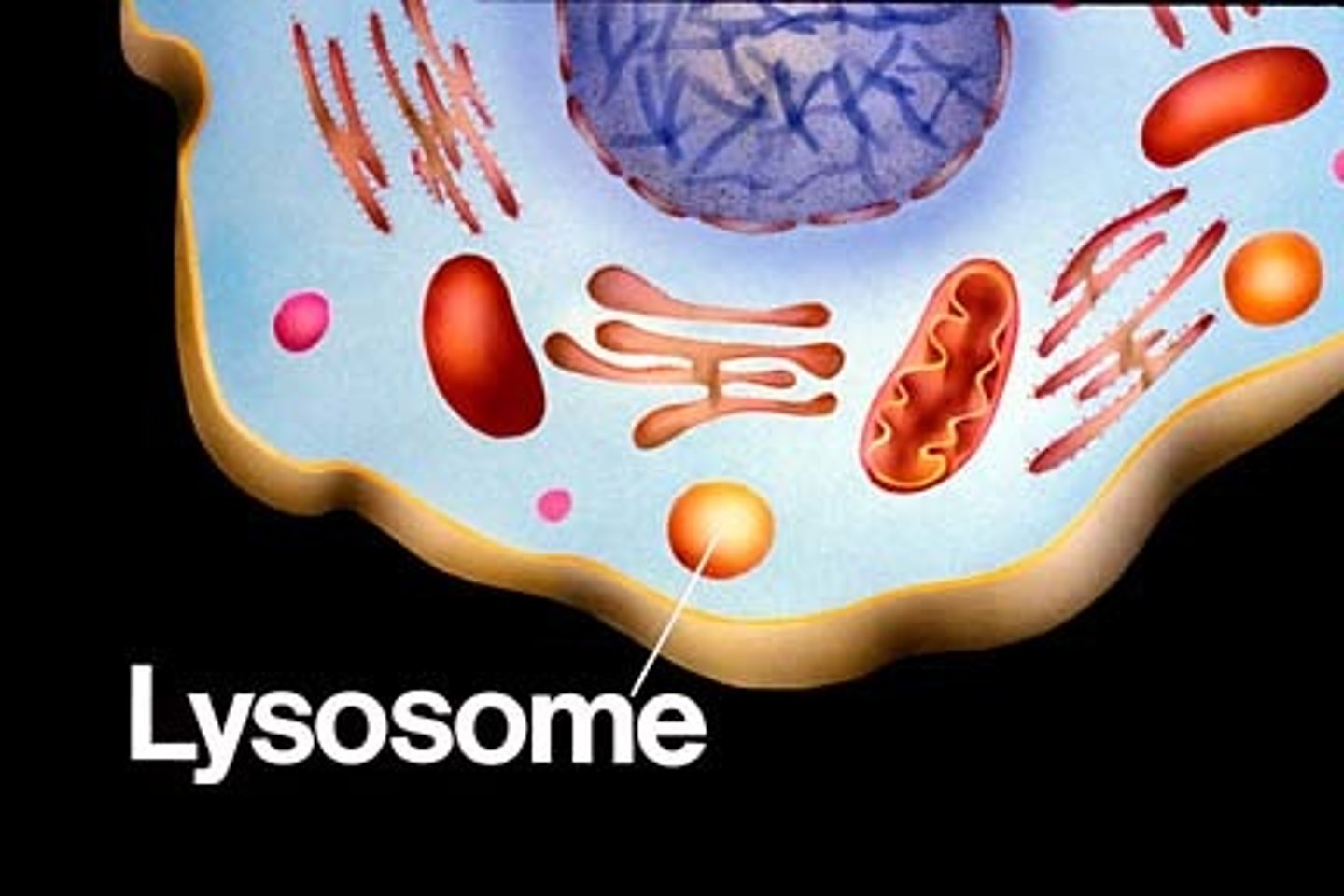
What does lysosomes do?
contains digestive enzymes and digests excess cell parts, food, or bacteria; digestion.
What does the nucleus contain?
DNA
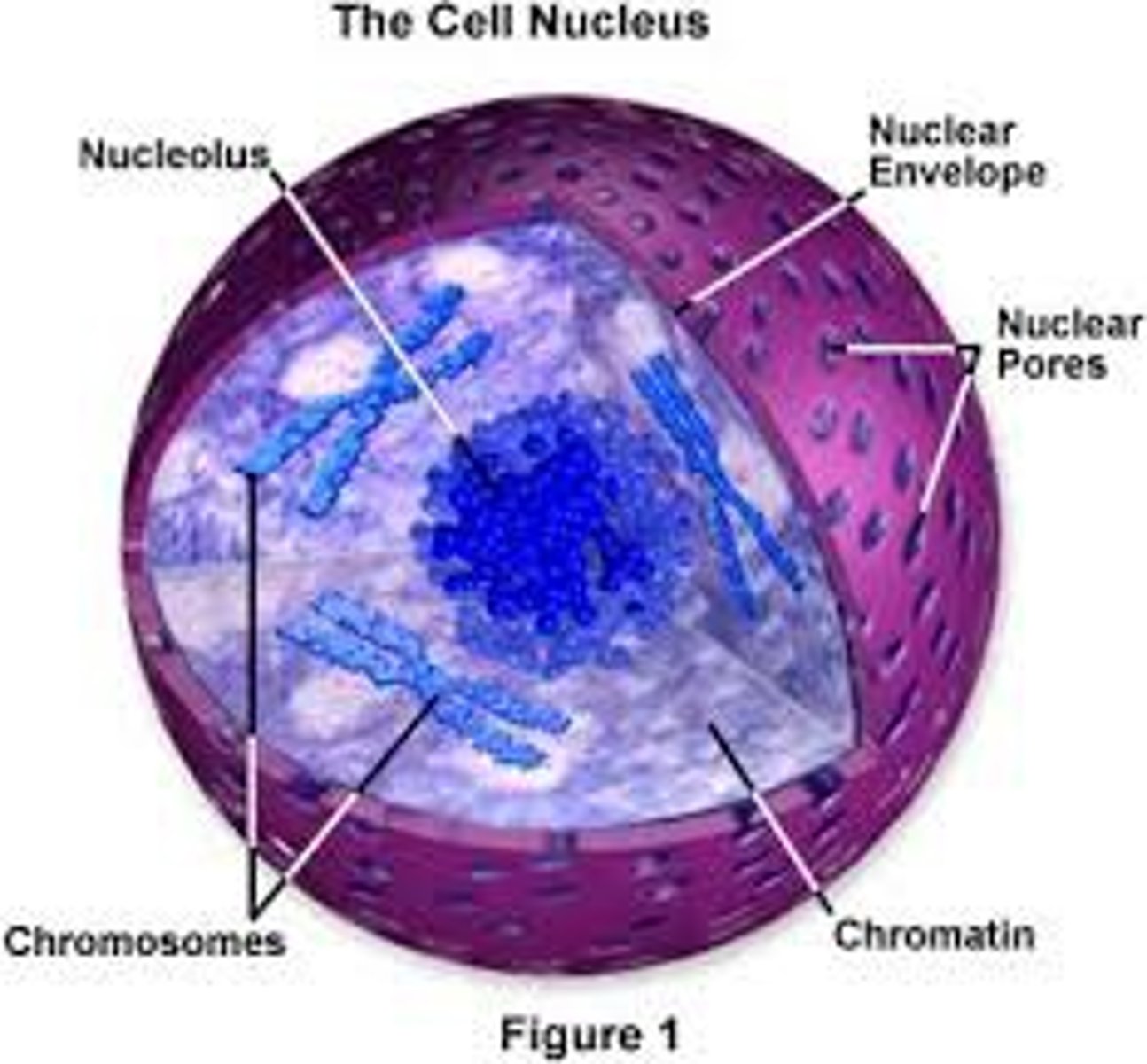
What the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound organelles such as the nucleus, while a prokaryote does not

Define energy
the capacity of a system to do work
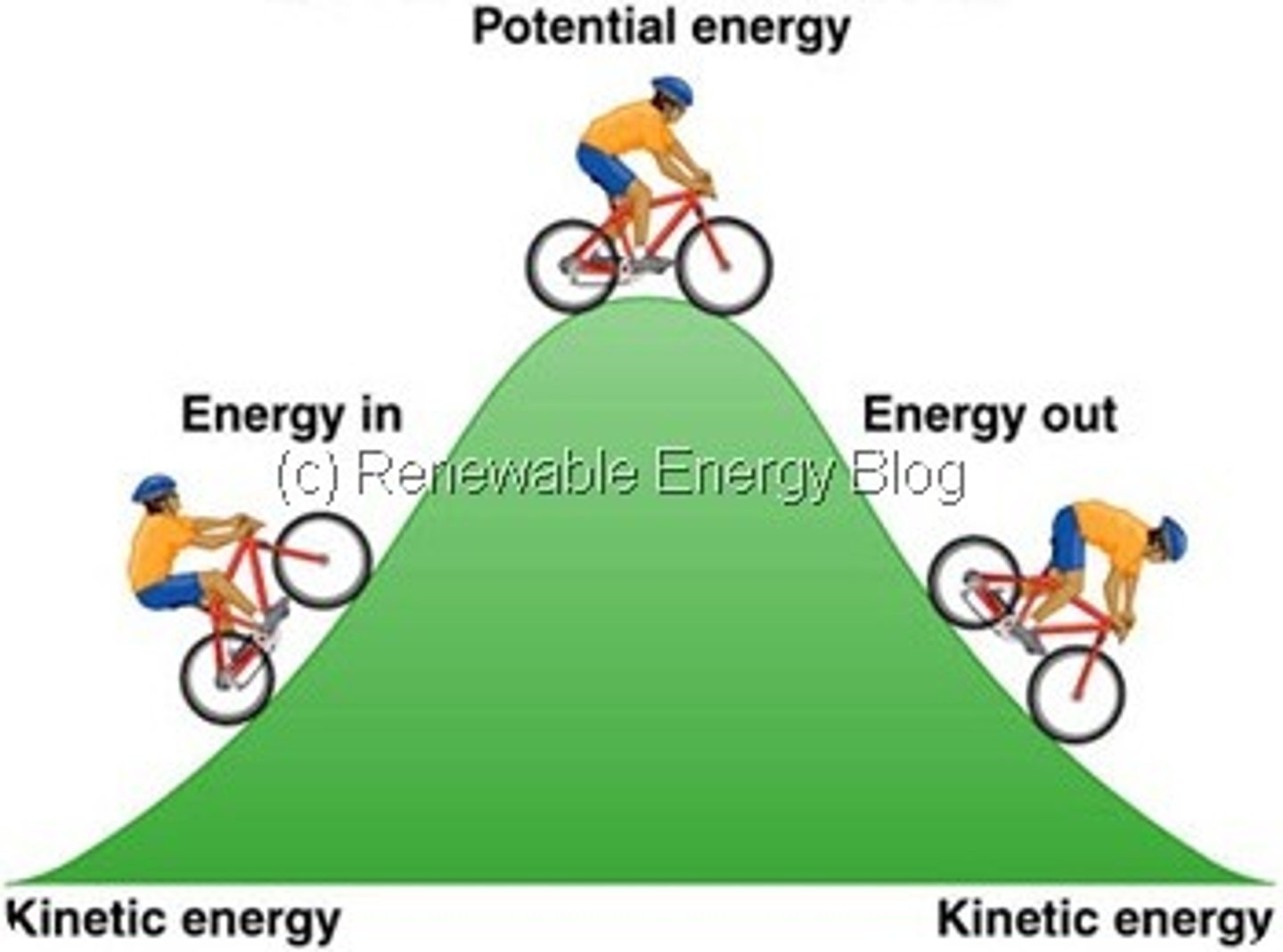
Define potential energy
energy that is stored

Define chemical energy
potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction
Define metabolism
the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life
What law does metabolism follow?
Law of Thermodynamics
