Types of gene mutations
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
define species
group of individuals that share many characteristics and are able to interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring
genus and species of modern day, current humans
genus - homo
species - sapiens
homosapiens
define alleles
alternative forms of a gene
define population
group of organisms of the same species living together in a particular place at a particular time
define gene pool
sum of all alleles carried by members of a population (what genes are present - includes recessive and dominant)
define allele frequency
how often each allele of a gene occurs in a population (eg 85% blonde allele frequency and 15% brown allele frequency)
define evolution
evolution is the change in characteristics of a species over time. It is a gradual change that occurs over a number of generations, rather than a change of a particular individual or generation.
Things which influence allele frequencies changing:
Natural selection - new trait is beneficial to the selective pressures present in the population {contribute to human survival}
Chance - Genetic drift occurs whereby the characterisitics does not provide a survival advantage
what are mutations?
The result of a new allele being formed, as DNA is changed, resulting in a different variation of the trait.
define mutant
individual who expresses a characteristics as a result of a mutation
Types of mutations - classified by amoutn of DNA affected
Gene mutation - changes in a single gene so that traits normally produced by that gene are changed or destroyed. Occurs during replication of DNA before cell division
Chromosomal mutation - all or part of chromosome. this means many genes may be affected.
When do mutations have significant effects on the functioning of the cell?
If occurs spontaneously when the DNA molecule is copied during mitosis or meiosis, or when the chromosomes are separated during meiosis.
causes of mutations:
induced mutations - mutagens in the environment increase the chance of mutations occurring
spotaneous mutations - occur due to a random error in biological processes such as mitosis or meiosis.
define mutagens/ mutagenic agents:
an agent known to increase rate at which mutations occur
name mutagens/mutagenic agents:
mustard gas, formaldehyde, sulfur dioxide, some antibiotics, ionising radiation, ciaggeretes, benzene, nitrous acid
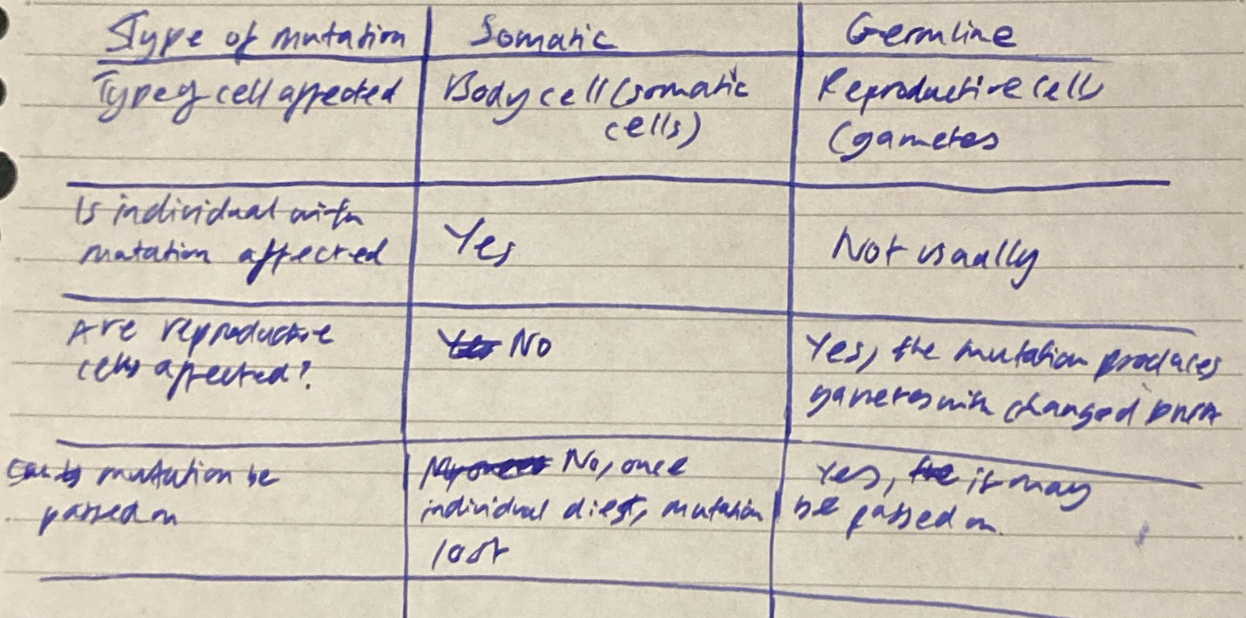
compare types of mutations - classfied by type of cell affected:
what is a point mutation
change in a single nucleotide [when reading strand to produce another, could put in nucleotide with wrong base] , just one base in the DNA sequence, can alter protein, have no effect at all [possible as mutliple codons can code for the same amino acids], or prevent protein from being produced [prevent occur if accidentally code STOP codon]
Types of point mutations:
substitution of a base- existing nucleotide replaced with another
inversion of a base- two nucleotides are switched (ATG becomes AGT)
insertion of a base - new nucleotide is added to the DNA strand [results in frameshift]
deletion of a base - nucleotide is removed from the DNA strand [results in a frameshift]
define frameshift mutations:
occur when the addition (insertion) or removal (deletion) of a base alters the reading frame of the gene. This change will affect every codon beyond the point of mutation and thus may dramatically change the amino acid sequence.
effect of point mutations - depending on which nucleotide was changed
missense mutation - cause a change in the amino acid, and therefore the protein produced.
nonsense mutation - changes the base sequence to the code to STOP. This means that the syntheiss of the portien will stop, and so a shorter portein is produced that is unlikely to be able to fulfil its function.
neutral mutations - cause a change in an amino acid; however, the amino is of the same type (functionally similar - [category of the protein is the same or similar]) and does not change the structure of the protein enough to change its function. {GAG (Glu) → GAC (Asp)}
silent mutations - does not cause any change in the amino acid, and therefore the protein produced. This is possible, as most amino acids are coded for by more than one base sequence. {GAG (Glu) → GAA (Glu)}
why most gene mutations produce recessive allele?
because gene mutations prevent gene from producing protein that will be able to function in the body
Examples of gene mutations - non lethal
Albinism, duchenne muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis
some gene mutations are considered lethal recessive - what is lethal recessive?
recessive mutations that is lethal if not masked by the dominant normal allele. These cause death of embryo or foetus (a miscarraige or spontaenous abortion) or early death of child.
because of this death before reproductive age, low amount of this allele in the population.
examples of lethal recessive gene mutations (not just carrying trait but expressing it):
Tay-Sachs disease
Sickle Cell Anaemia - caused by substitution