Unit 1.1-1.3 Quiz Review
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Polarity
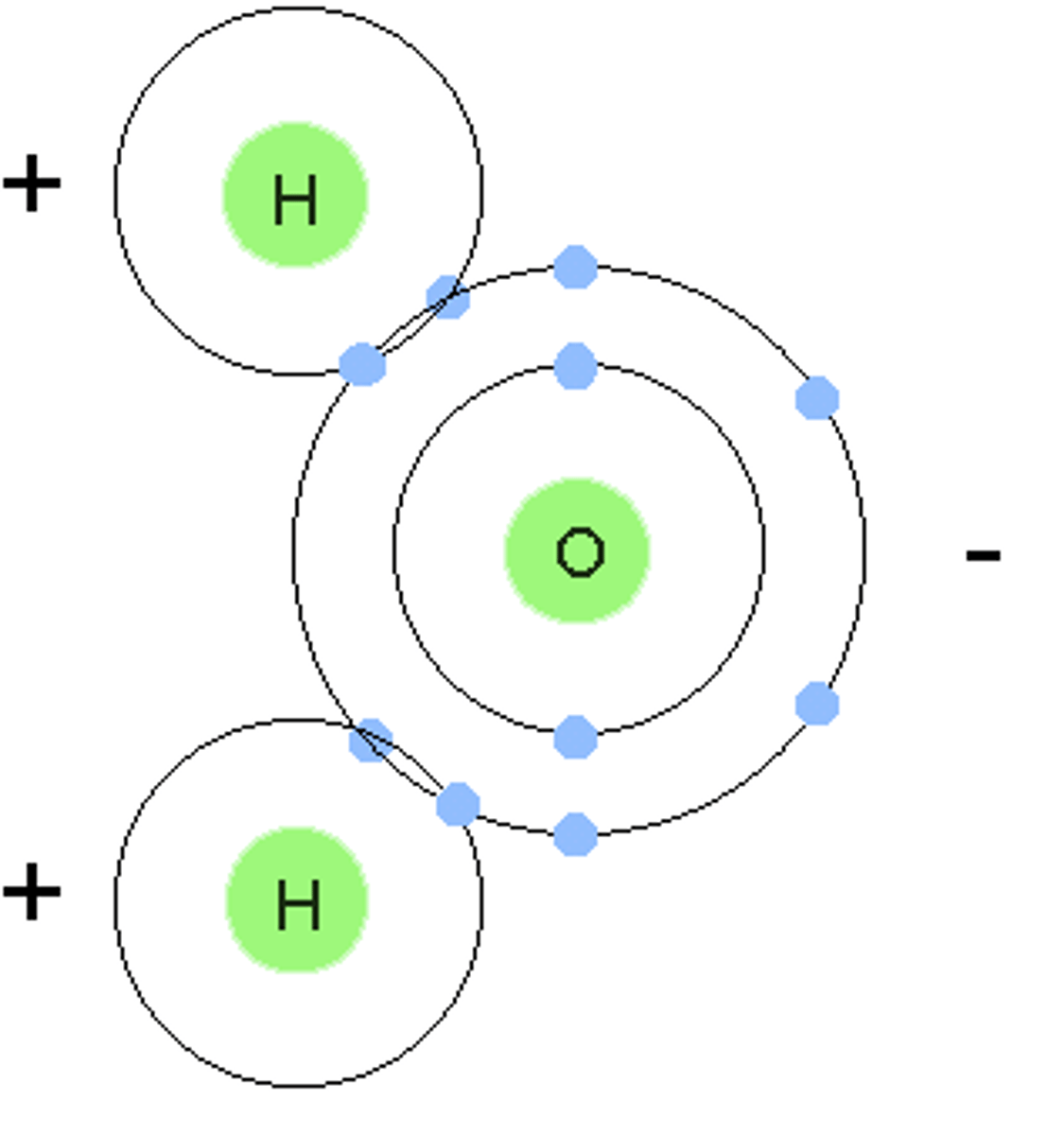
water is a polar molecule with one oxygen atom negatively charged and two hydrogen atoms positively charged.
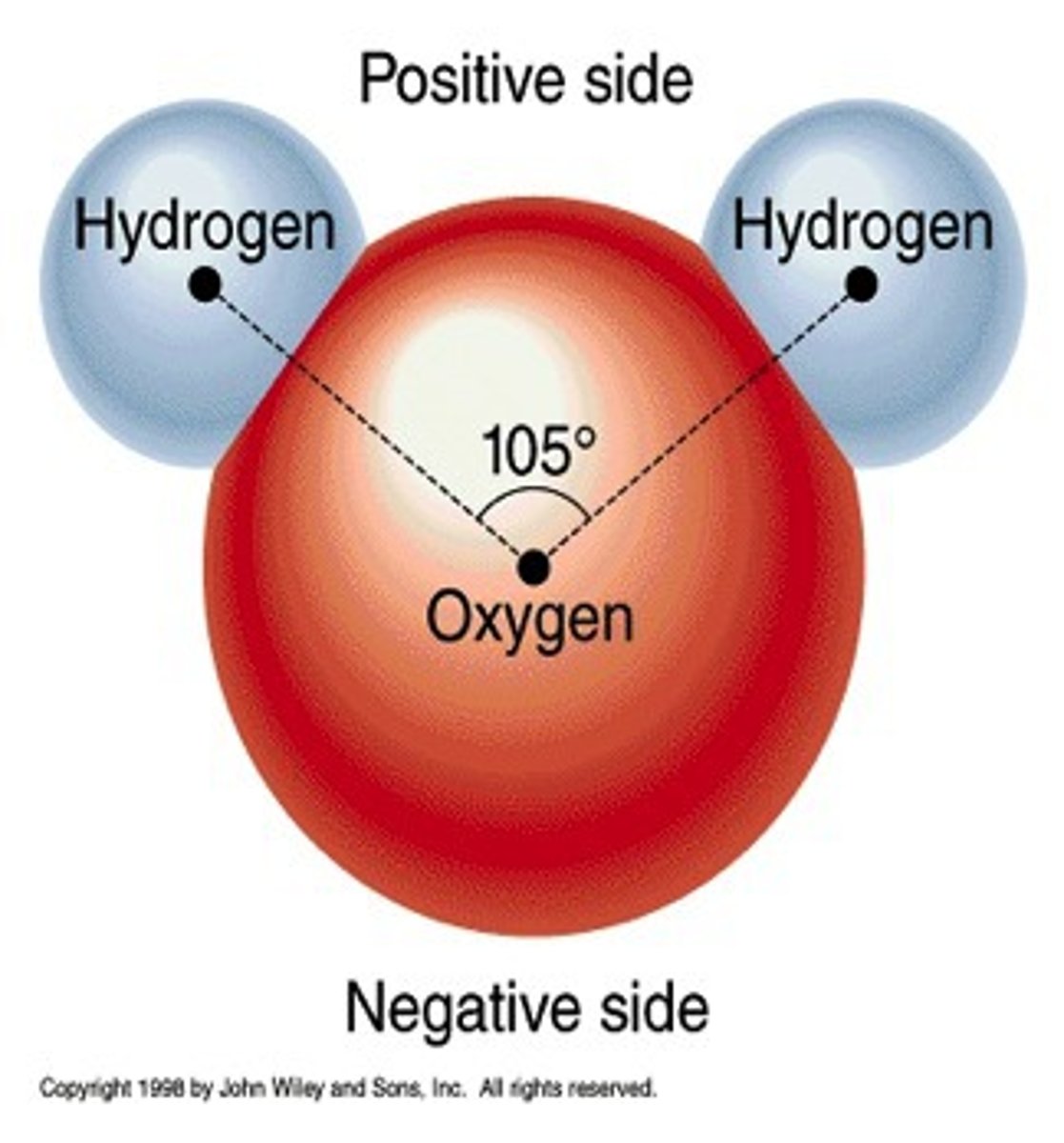
Universal Solvent
Water - due to its polarity and ability to dissolve other polar molecules

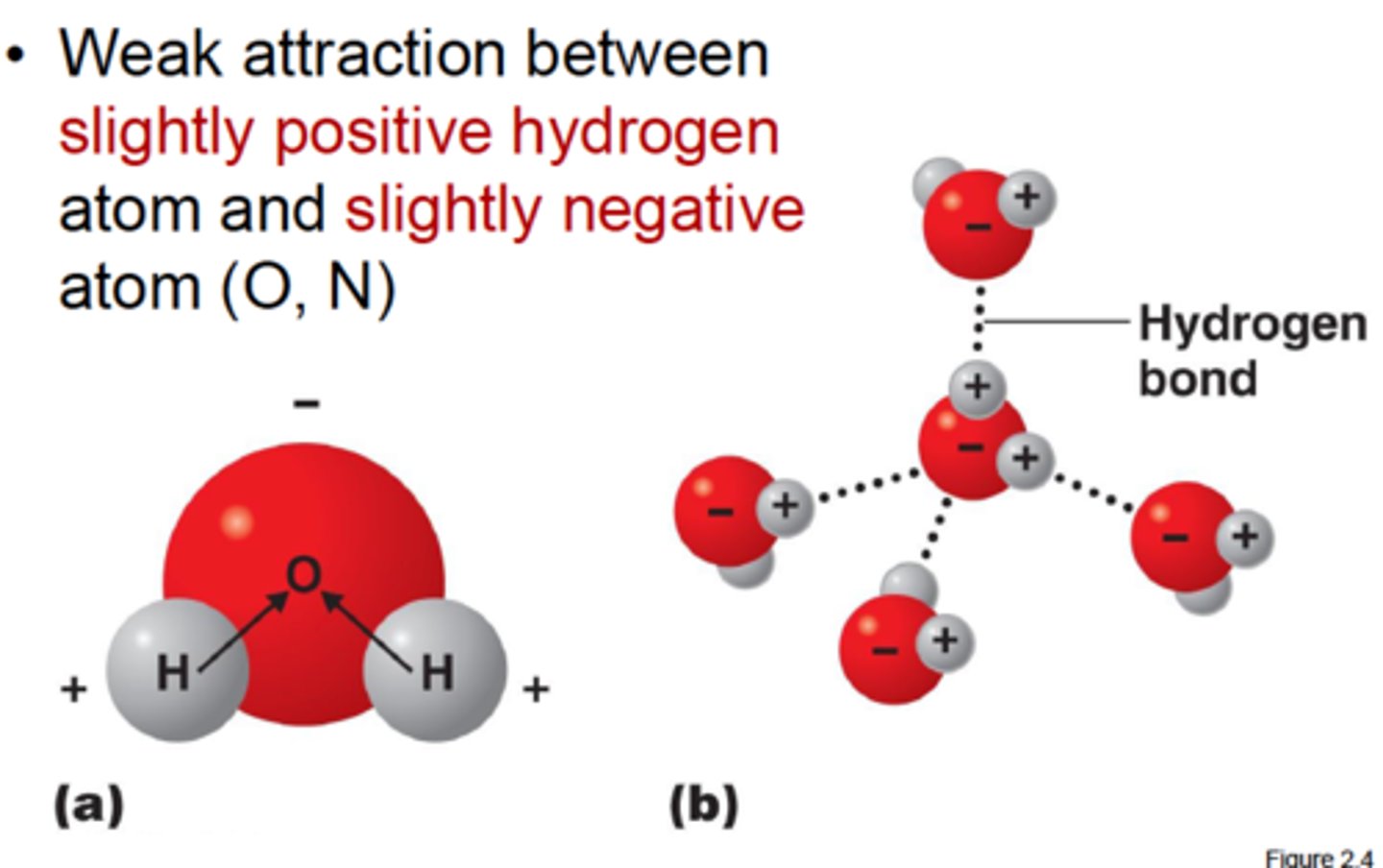
Hydrogen Bonds
The weak intermolecular bonds that form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule.
Polar Molecule
a molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive
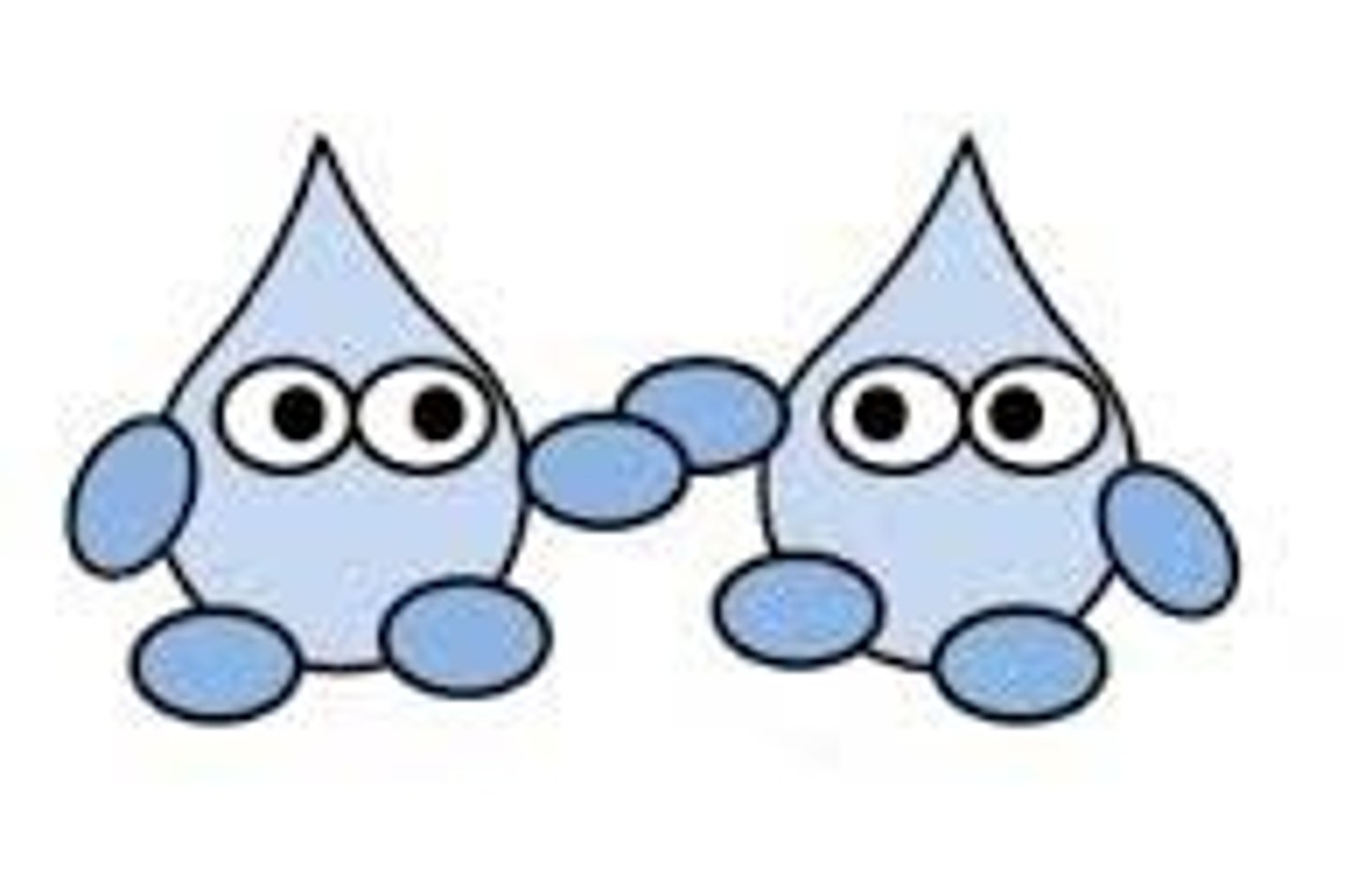
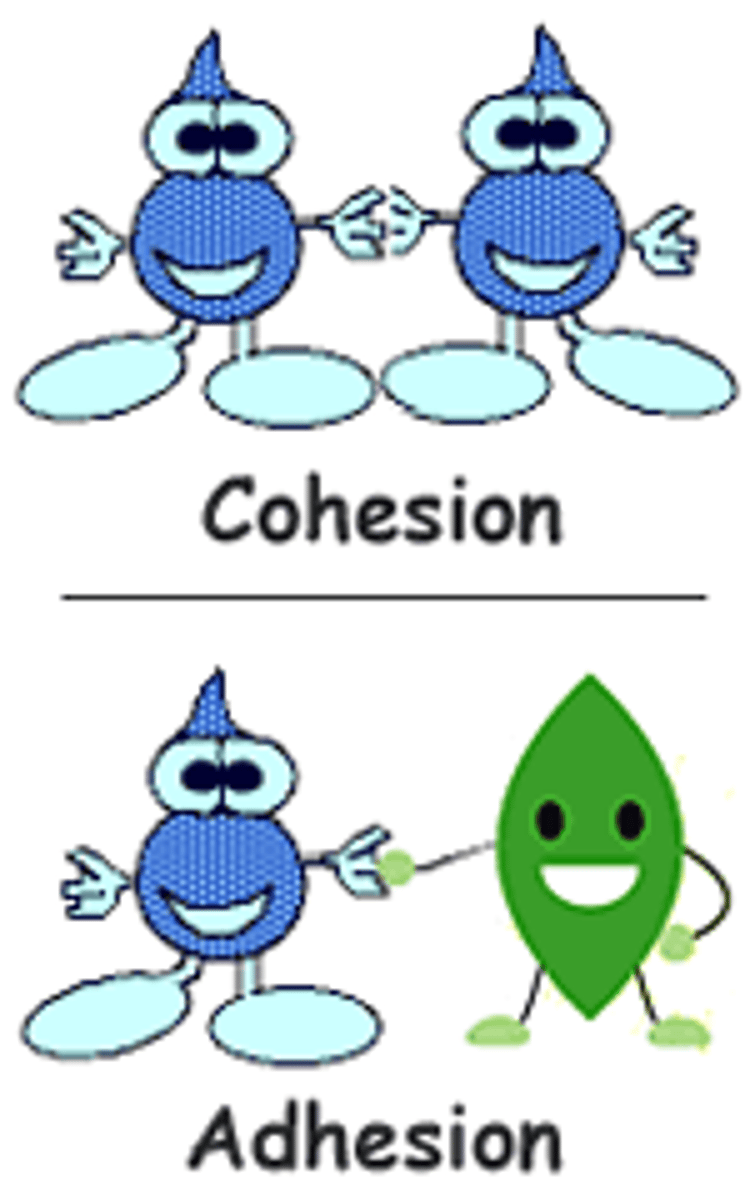
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances (water and another substance)
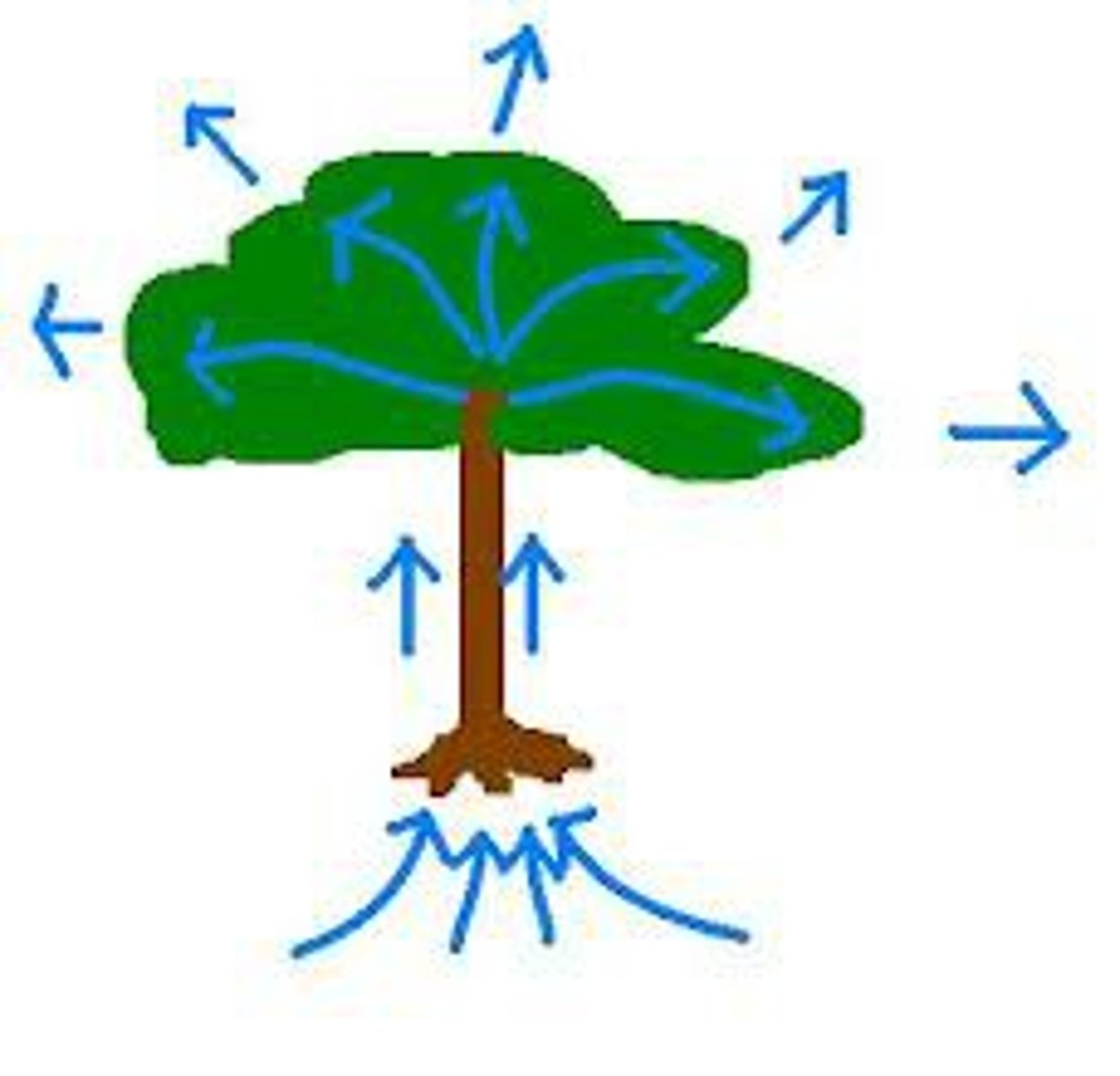
Capillary Action
tendency of water to rise in a thin tube against the force of gravity, and due of the cohesion and adhesion forces of attraction.
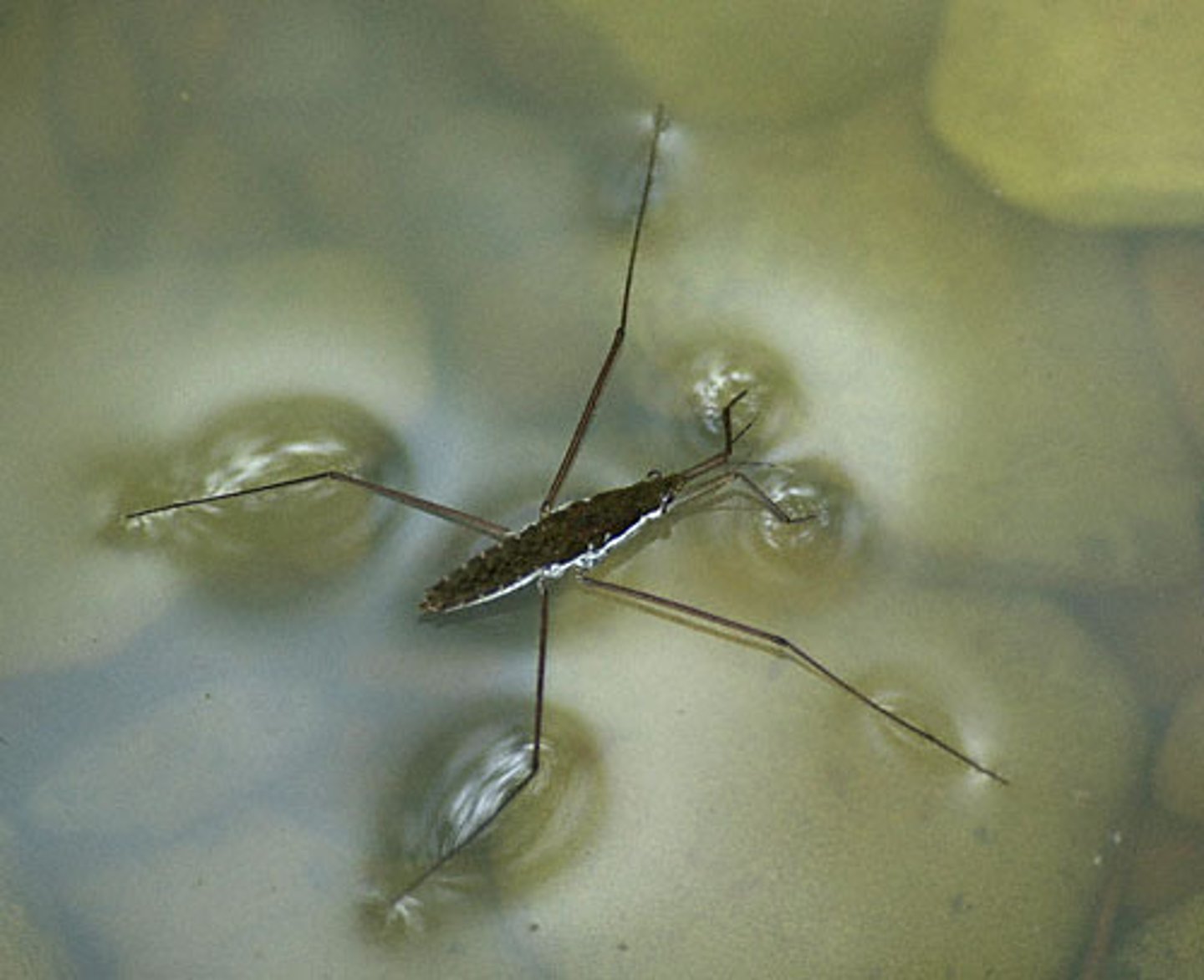
Surface Tension
An invisible film at the surface of water that allows objects to walk. This is caused by the cohesive forces.

Hydrophilic
A substance that likes water. Having an affinity (love) for water; usually polar molecules.
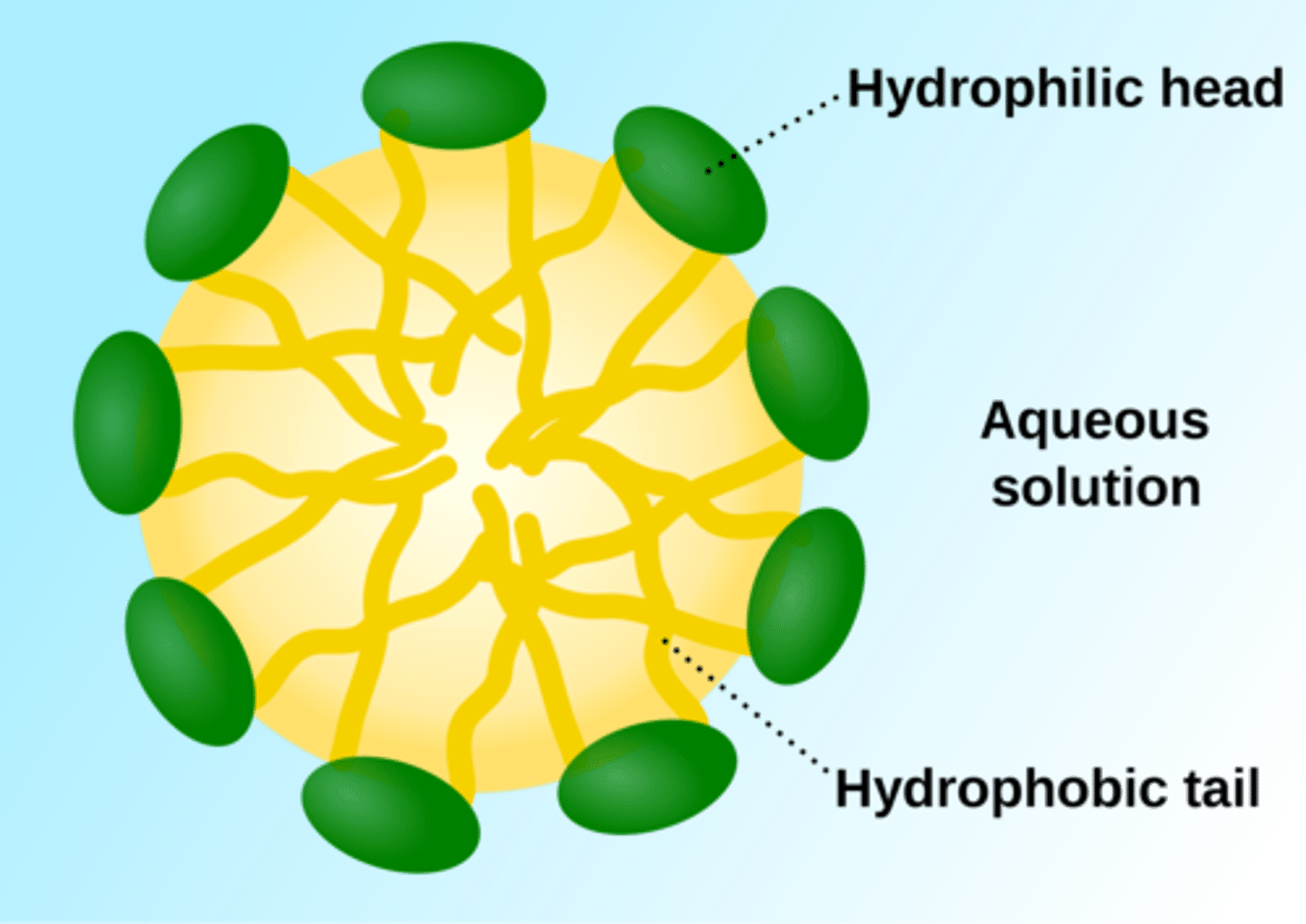
Hydrophobic
A substance that water hates water (it is repealed by water); usually non-polar molecules, like oil.
Expansion upon freezing
hydrogen bonds in ice are more "ordered and spaced out" making ice larger and LESS DENSE
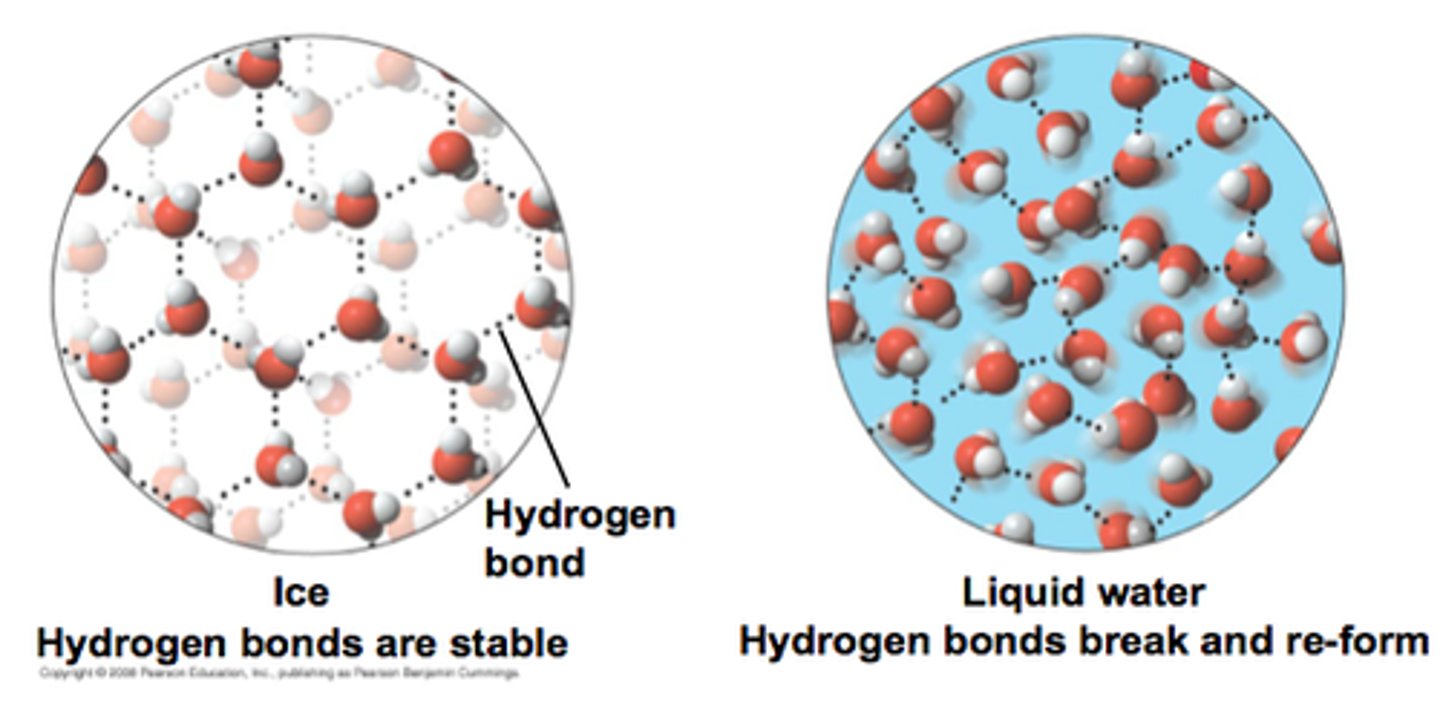
High Specific Heat of Water
It takes a lot of energy to heat up water, which allows for a stable environment; due to hydrogen bonding

Polar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
Elements in carbohydrates
CHO
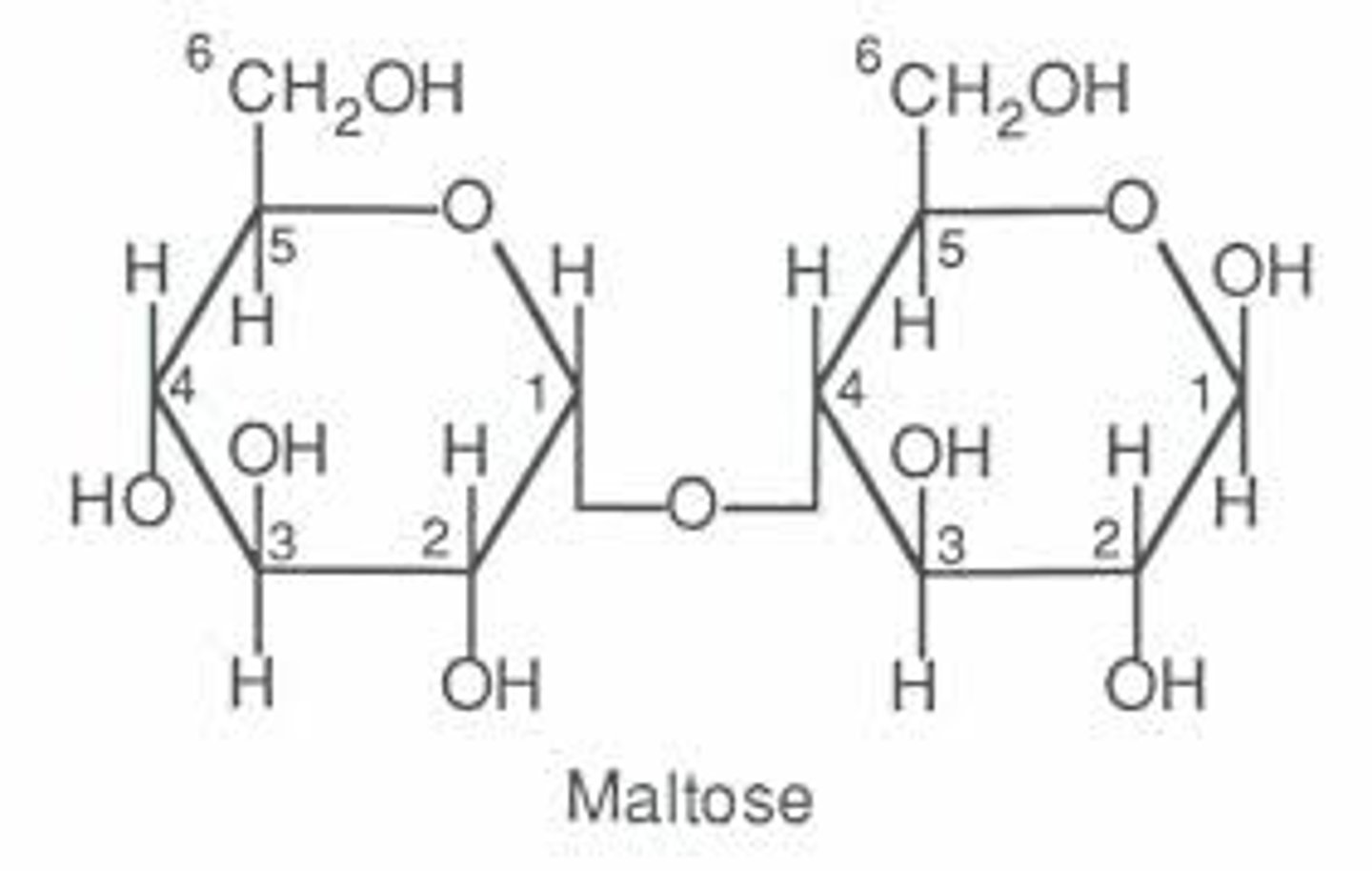
Carbohydrate monomers
monosaccharide
Function of carbohydrates
Quick energy, short-term energy storage
Function of lipids
Long-term energy storage, insulation, cell membranes (phospholipids)
Elements in lipids
CHO
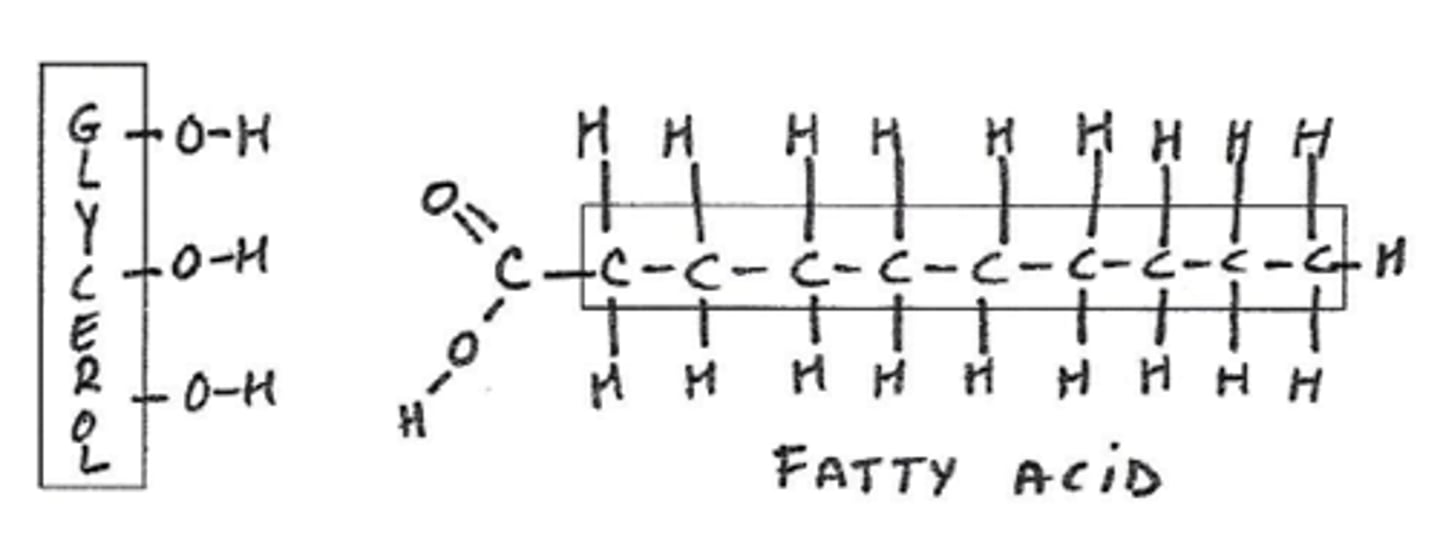
Lipids building blocks
glycerol and fatty acid tails
Elements in nucleic acids
CHONP
Function of proteins
Structure, enzymes, immunne defense (antibodies)
Elements in proteins
CHONS
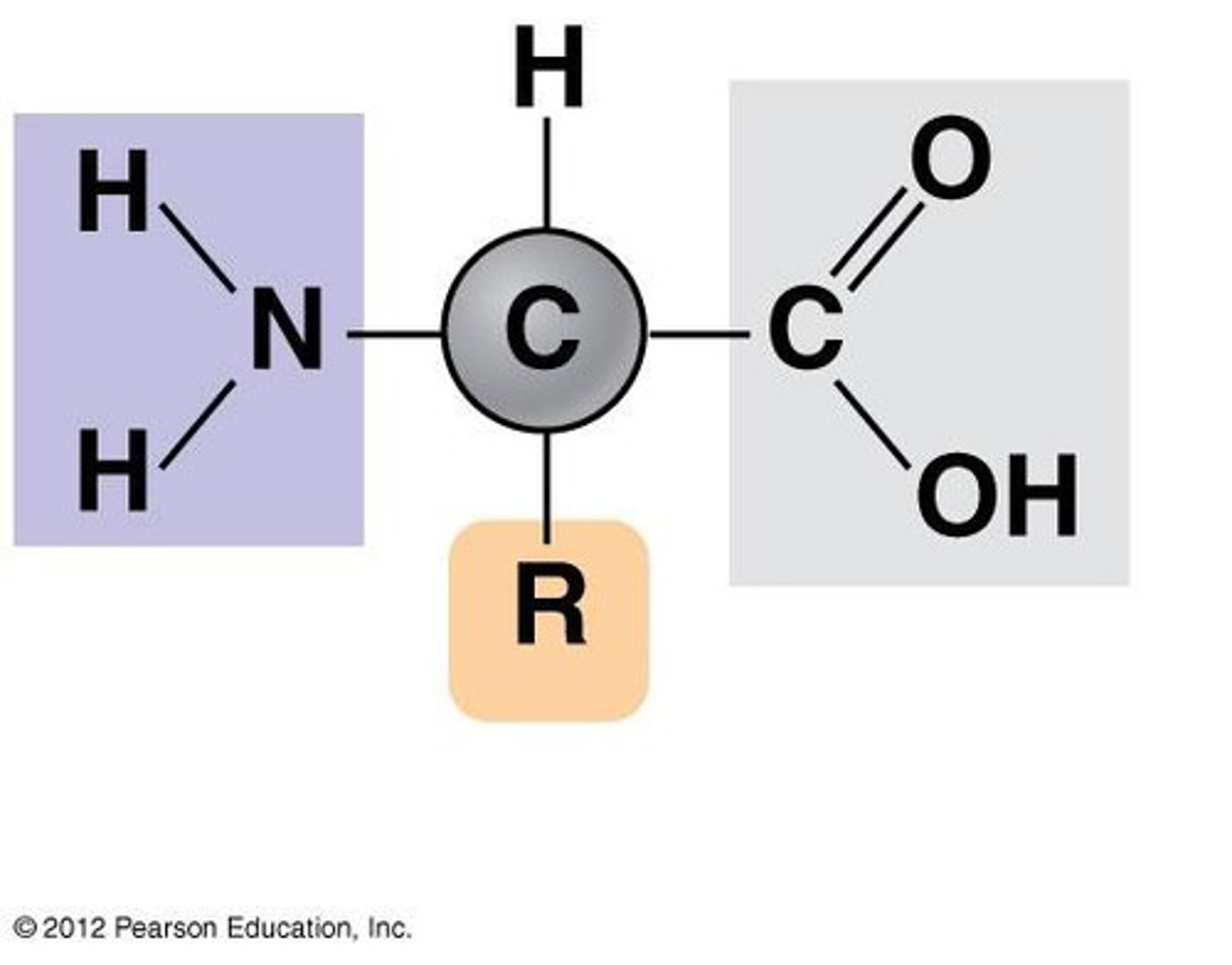
Protein monomer
amino acids
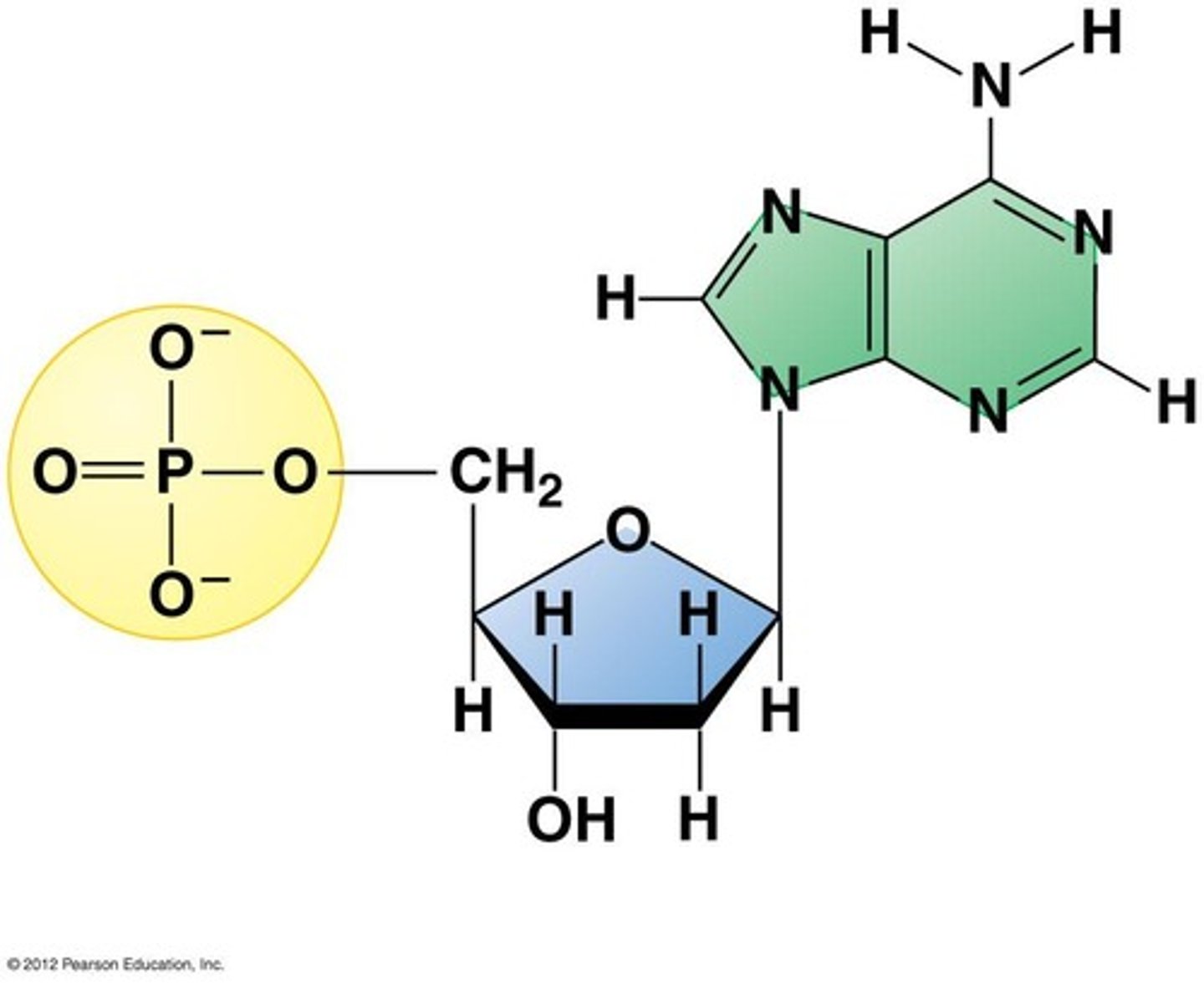
Nucleic acid monomer
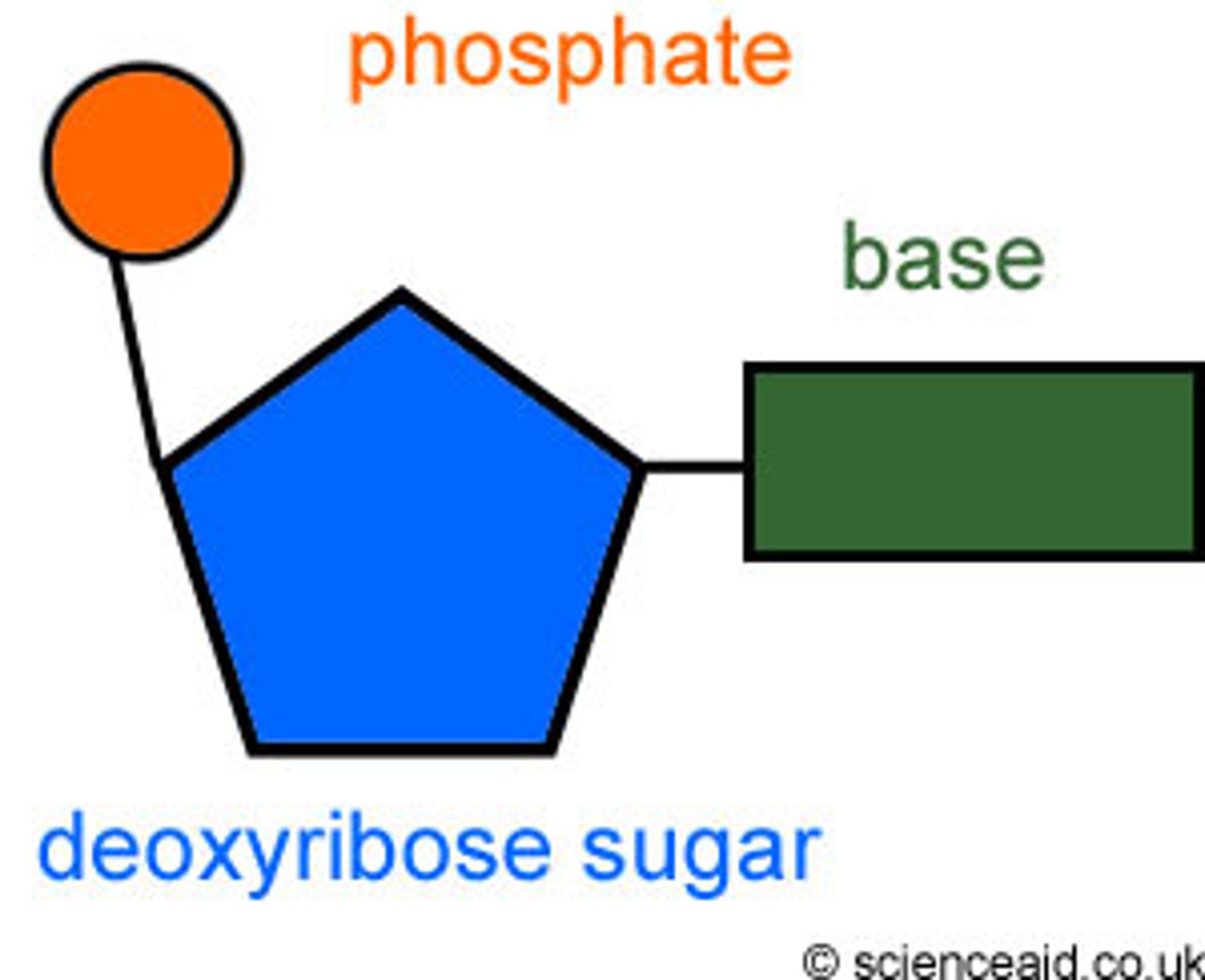
Nucleotides (sugar + phosphate + nitrogen base)
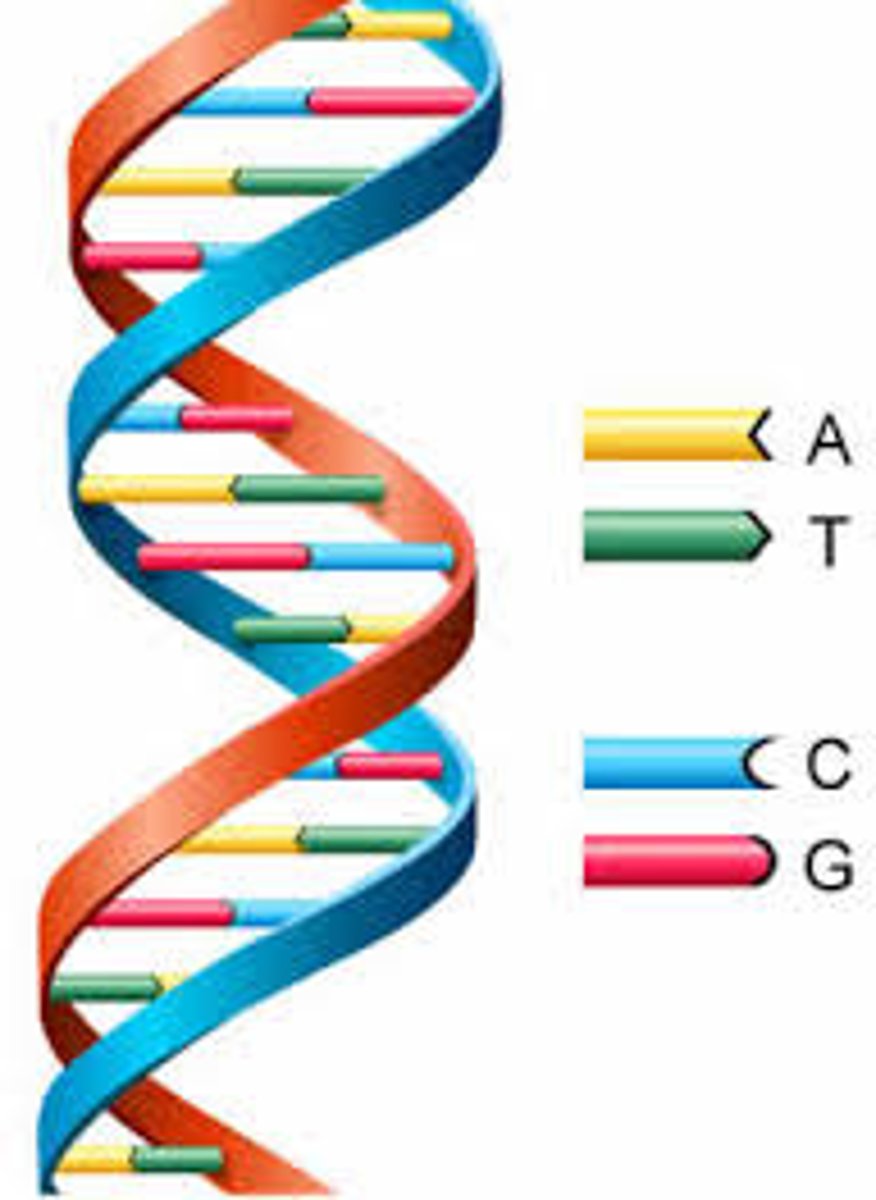
Function of nucleic acids
Stores genetic information (DNA, RNA)
Polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
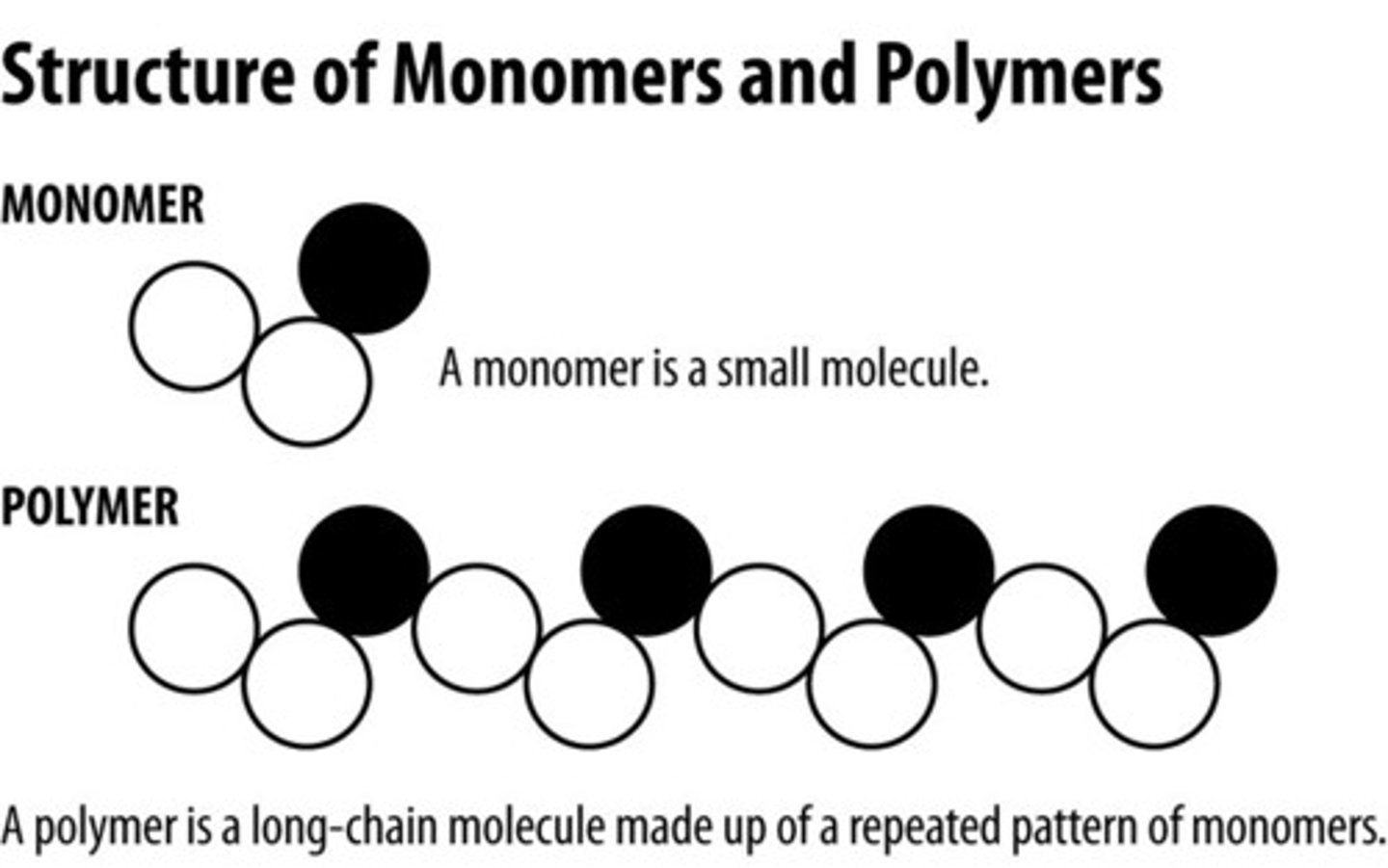
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
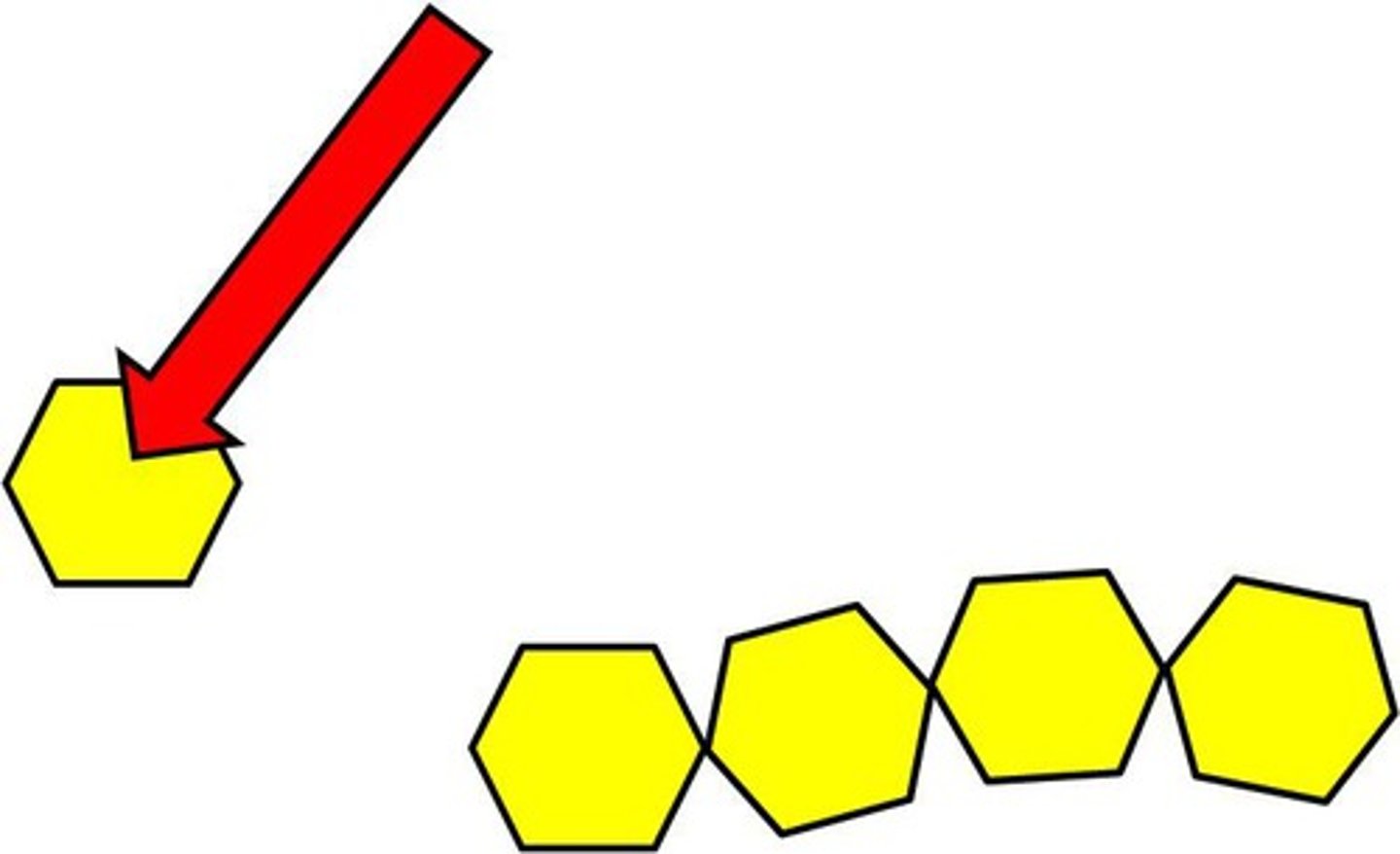
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.

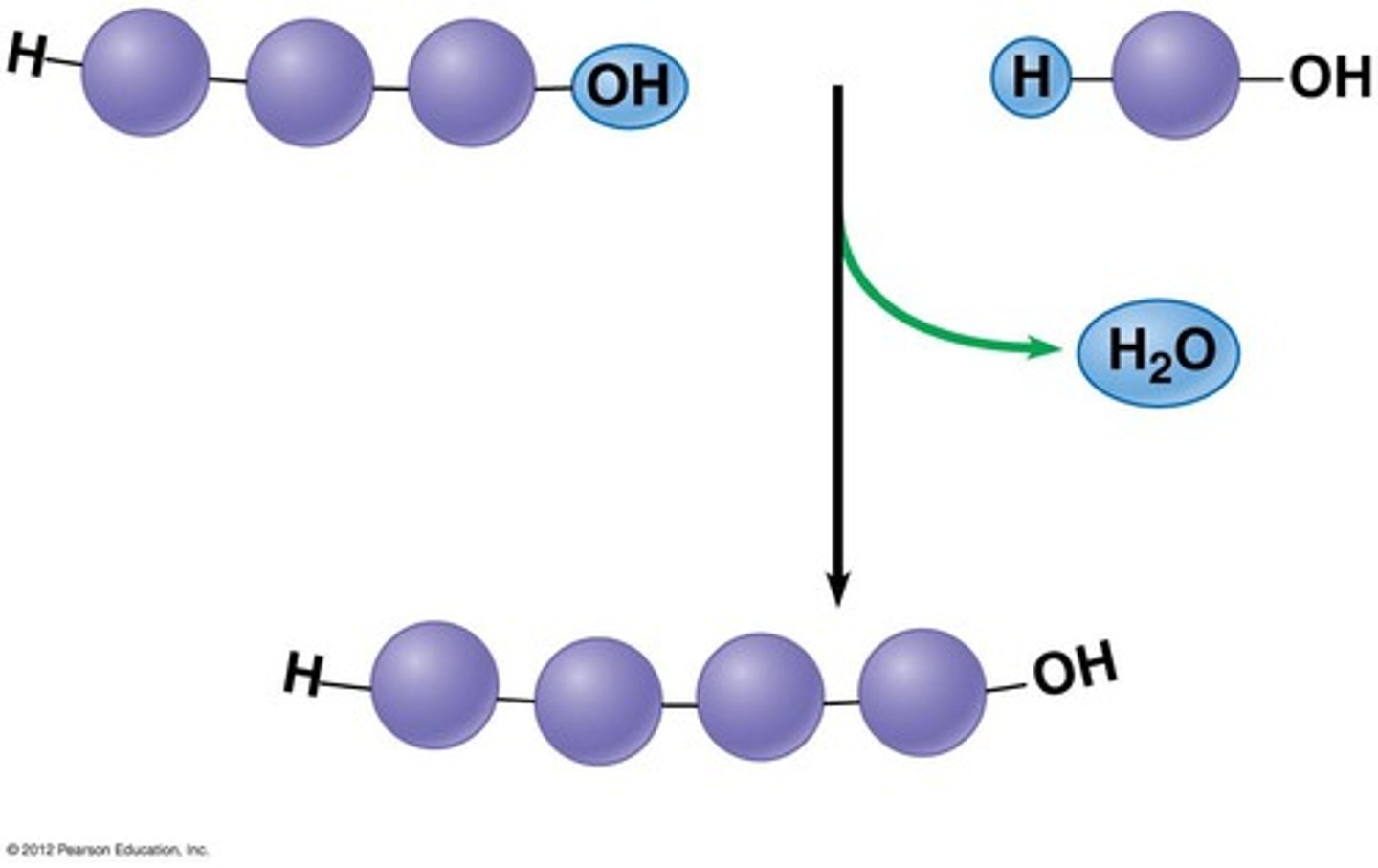
Dehydration Synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
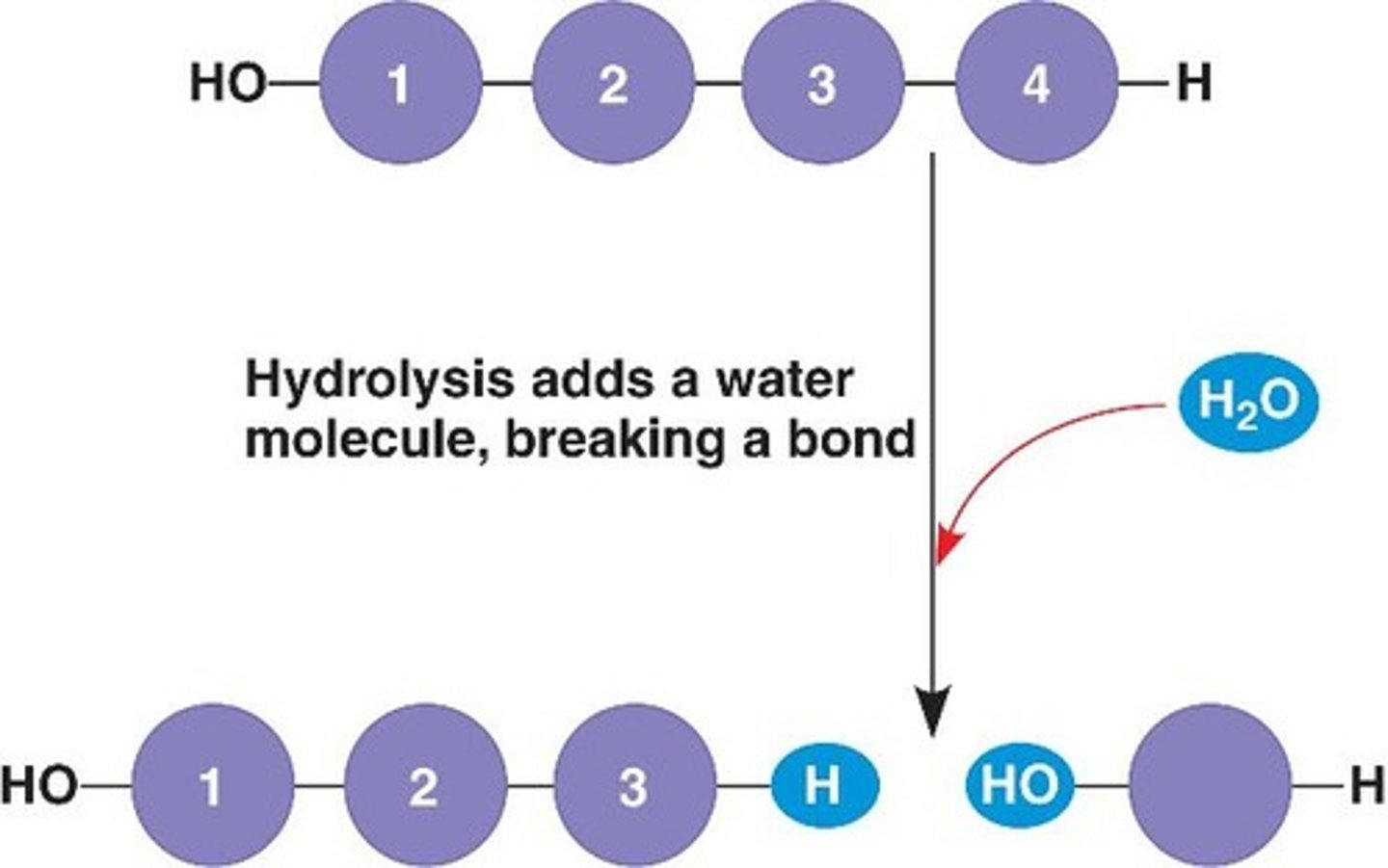
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
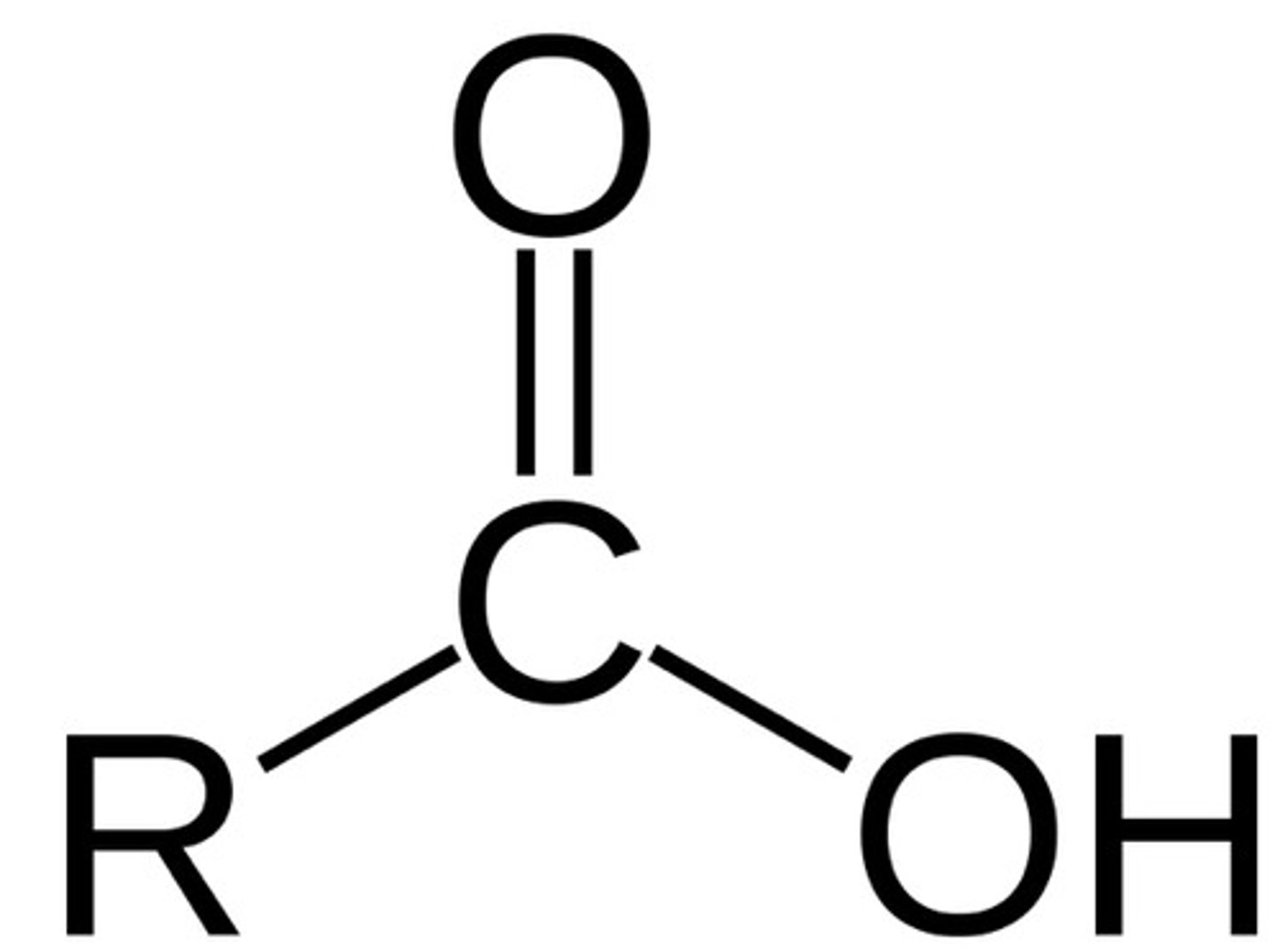
Carboxyl Group
A functional group consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. (acidic)
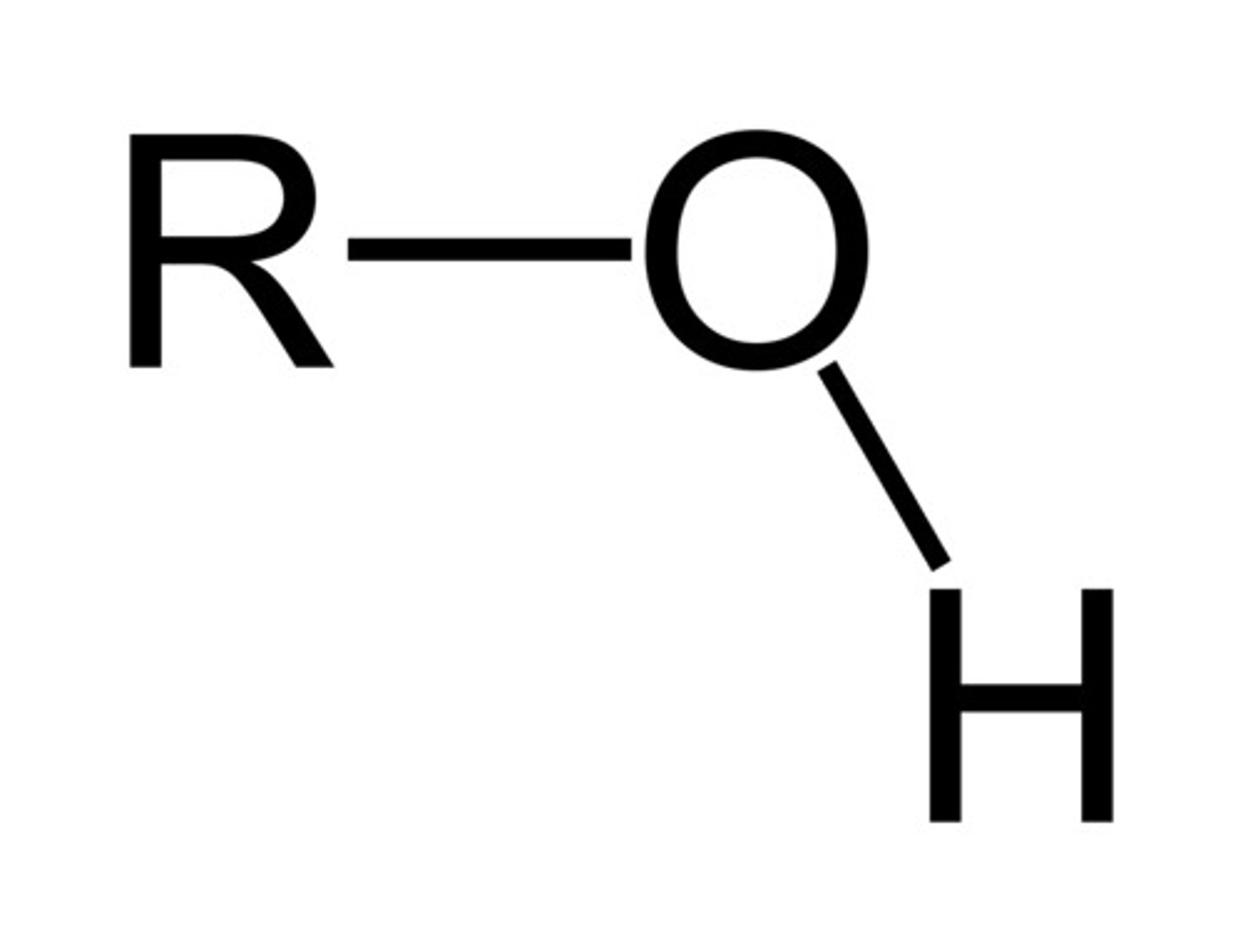
Hydroxyl Group
A chemical group consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom.
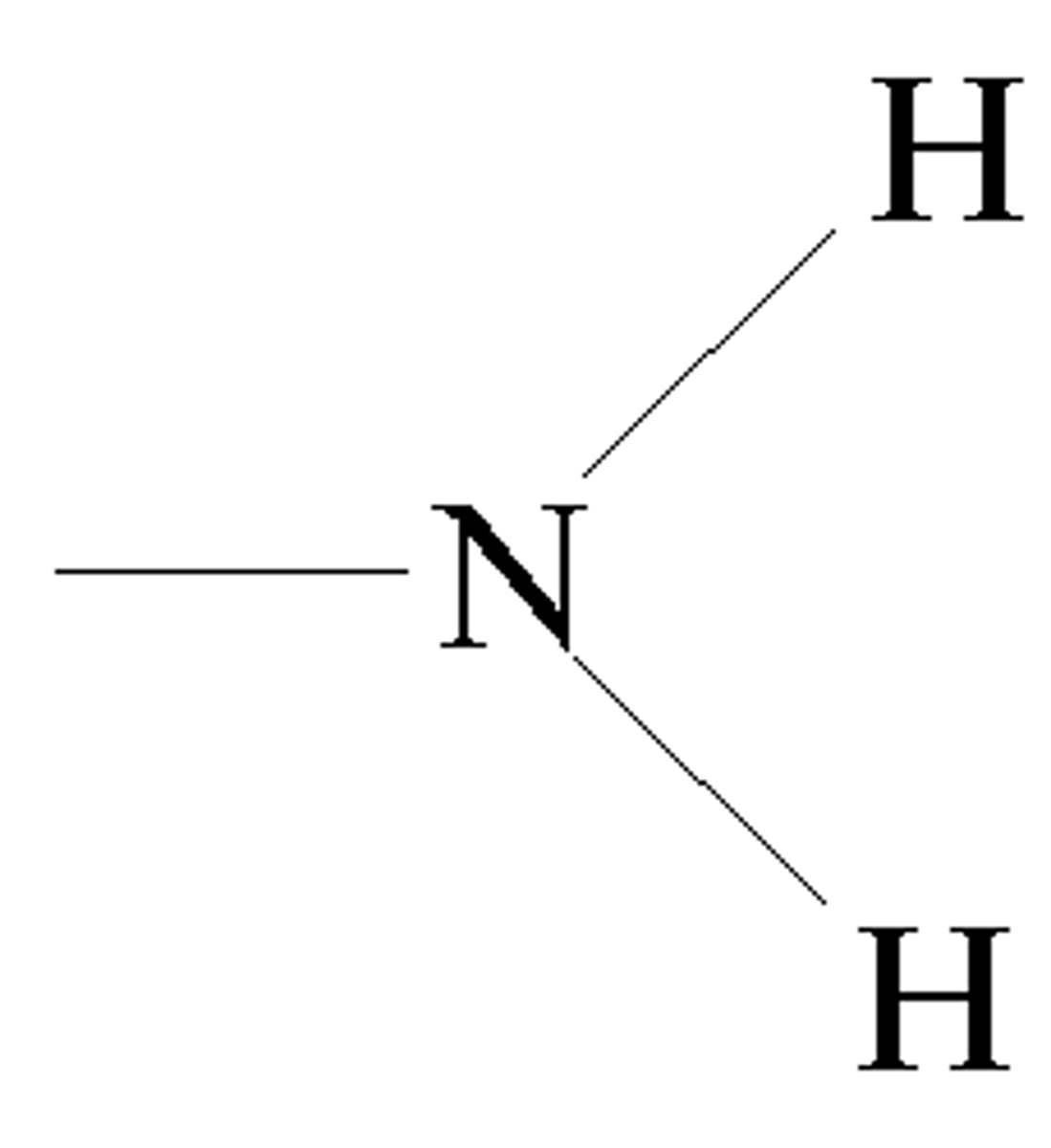
Amino Group
A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms (basic)
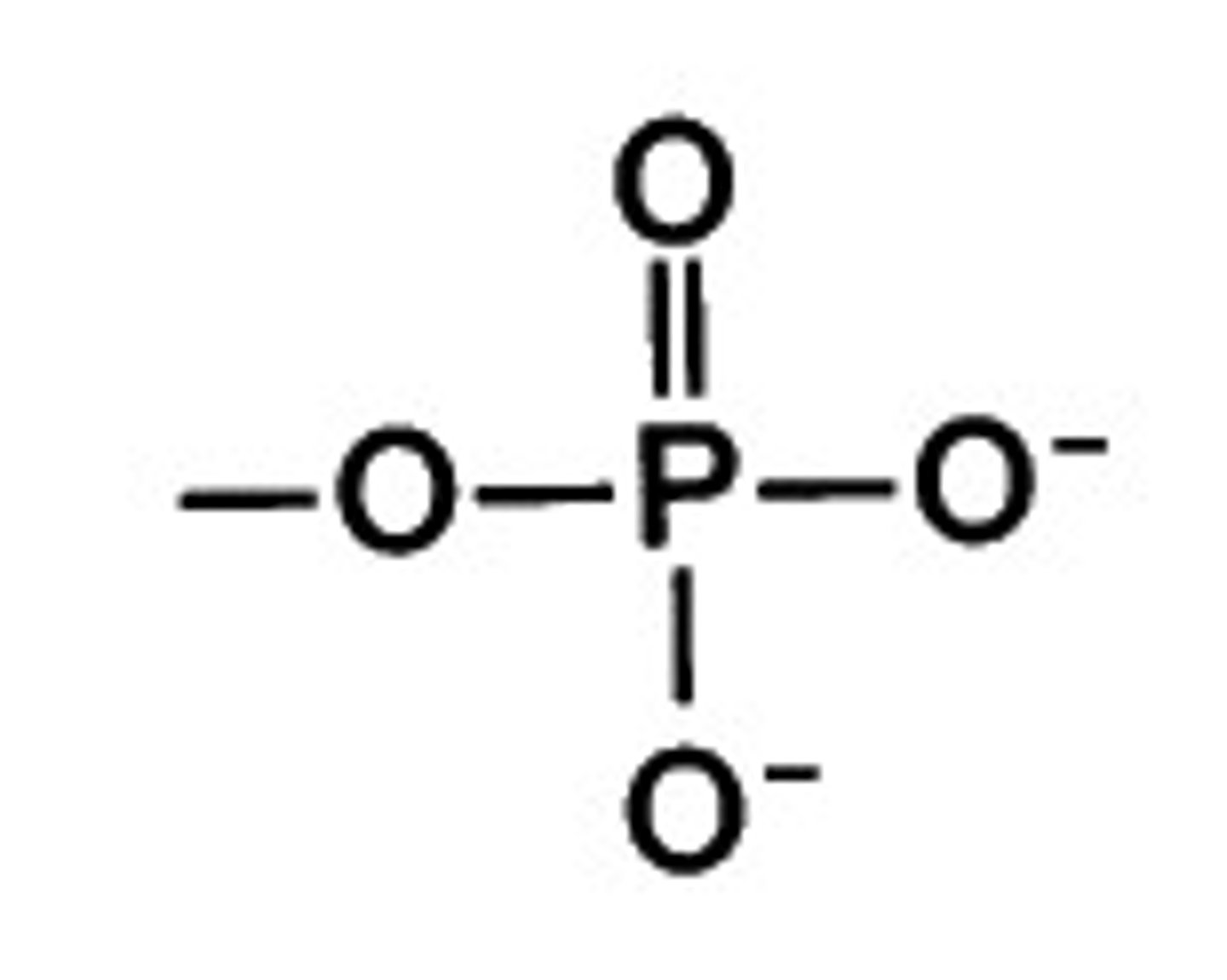
Phosphate Group
A functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base