Chapter 17: Working capital management – inventory control
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the main objective of inventory management?

What are the key costs of holding high inventory levels?

What are the risks and costs of holding too little inventory?

What are the key objectives and terms in good inventory management?

What is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and how is it calculated? What is assumed?

What costs does EOQ aim to balance and how are holding costs calculated?
What are the two main costs EOQ aims to balance?
Why is average inventory assumed to be x/2 in EOQ?
What kind of relationship exists between order quantity and total holding costs?
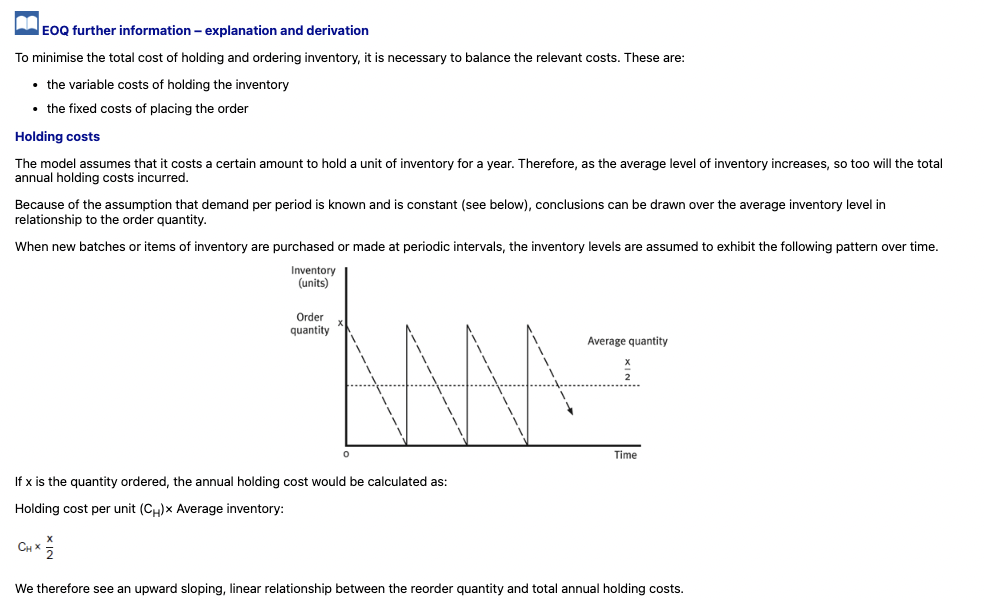
How are ordering costs calculated in the EOQ model?
What happens to ordering costs as order quantity increases?
What is the relationship between total holding and ordering costs in EOQ?
What is the economic order quantity (EOQ)?

When considering quantity discounts, should you automatically increase the order size above EOQ?
What are the 5 steps for evaluating quantity discounts?

What are the main criticisms of the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model?

What are two common inventory management systems?
How does the periodic review system work?
In a periodic review system, how is the reorder quantity determined?
Example – If weekly demand = 80 units, next review in 6 weeks, 3-week lead time, buffer = 35 units, and current stock = 250 units, how many units should be ordered?
What is slow-moving inventory and why is it important to monitor?
What actions can be taken to manage slow-moving inventory?
What is the 80/20 rule in inventory management?
What is Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management?
What are the main aims of JIT systems?
How does JIT differ from traditional inventory management?

What is the core principle behind Just-in-Time (JIT) systems?
What are some examples of waste that JIT systems aim to eliminate?
How does JIT reduce work-in-progress (WIP)?
How do suppliers support JIT processes?
How does JIT reduce finished goods inventory?
What is the impact of JIT on the manufacturing plant’s layout?
What are the key outcomes of implementing JIT concepts?
What type of supplier relationship does JIT require?
What purchasing and forecasting advantages does JIT offer?
What are some logistics implications of JIT?

What are the three main inventory control systems?
How does a Reorder Level (ROL) system work?
What is a practical example of a ROL system?
What assumptions must hold for a ROL system to work well?
What is a periodic review system and how does it differ from a ROL system?
What are mixed inventory systems?
What is the formula for calculating the Reorder Level (ROL) when demand and lead time are known?

How is the ROL calculated when demand or lead time is uncertain?
What is buffer stock and why is it used?
How is buffer stock calculated?
What factors influence the optimum level of buffer stock?

What are inventory warning levels used for?
How is the maximum inventory level calculated?
When does the maximum inventory level typically occur?
How is the minimum inventory level calculated?
