BISC 202 Gene regulation and lac operon (W12-13)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
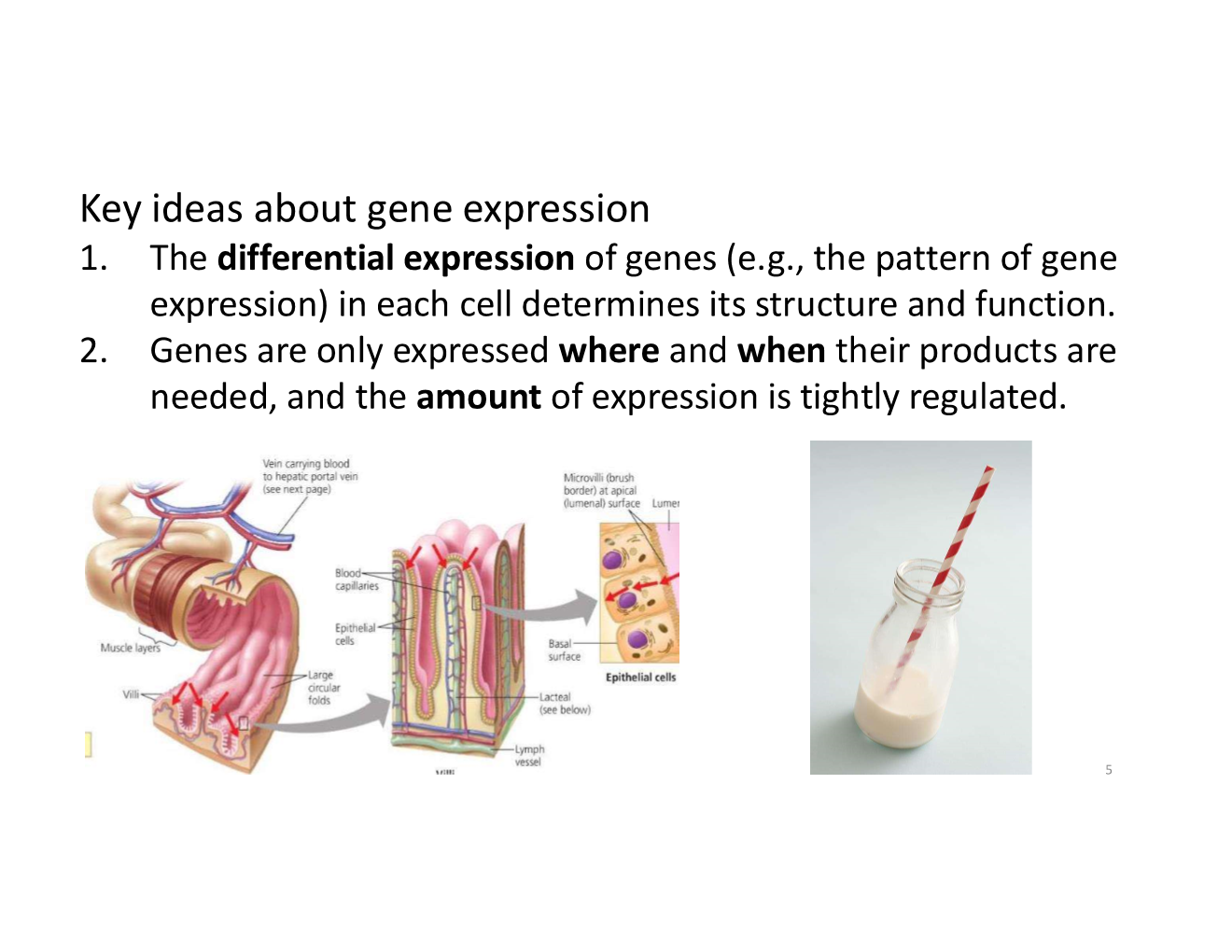
key ideas about gene expression
what is gene regulation about?
how we express a gene or not
how we make a protein or not
why is it important to study gene regulation?

D. All of the above
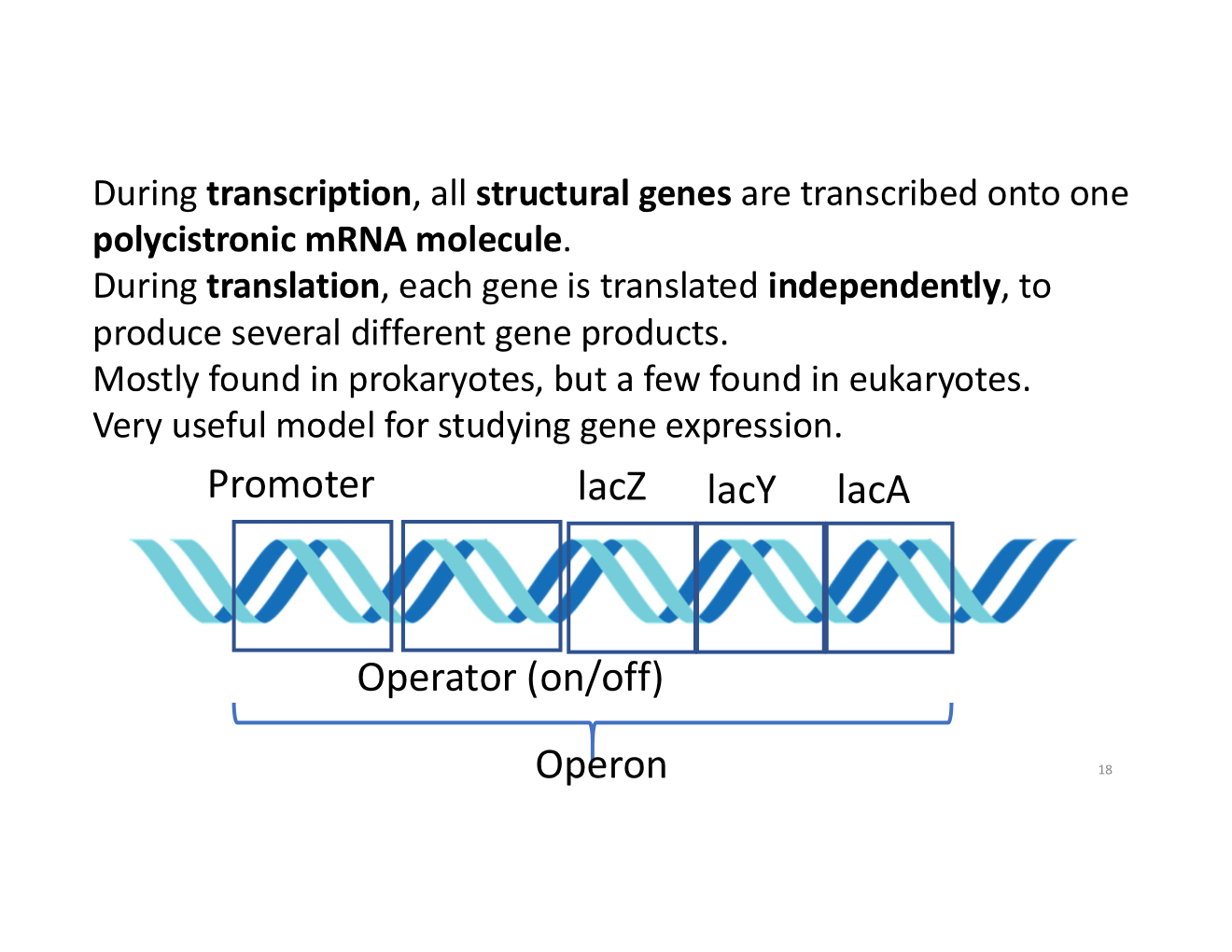
operon
a cluster of structural genes that are co-ordinately regulated by a single promoter region
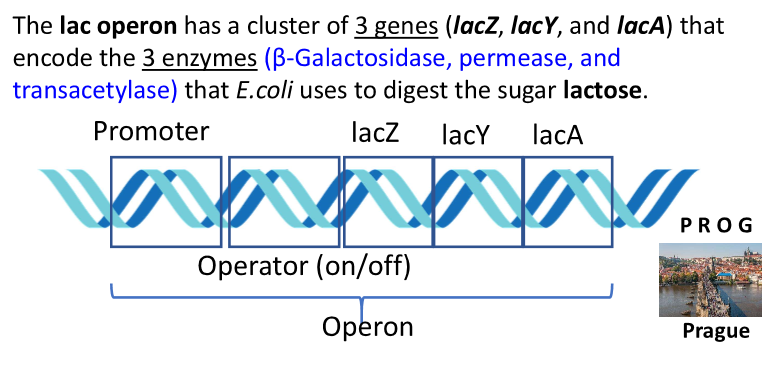
the lac operon
what happens to structural genes during transcription and translation
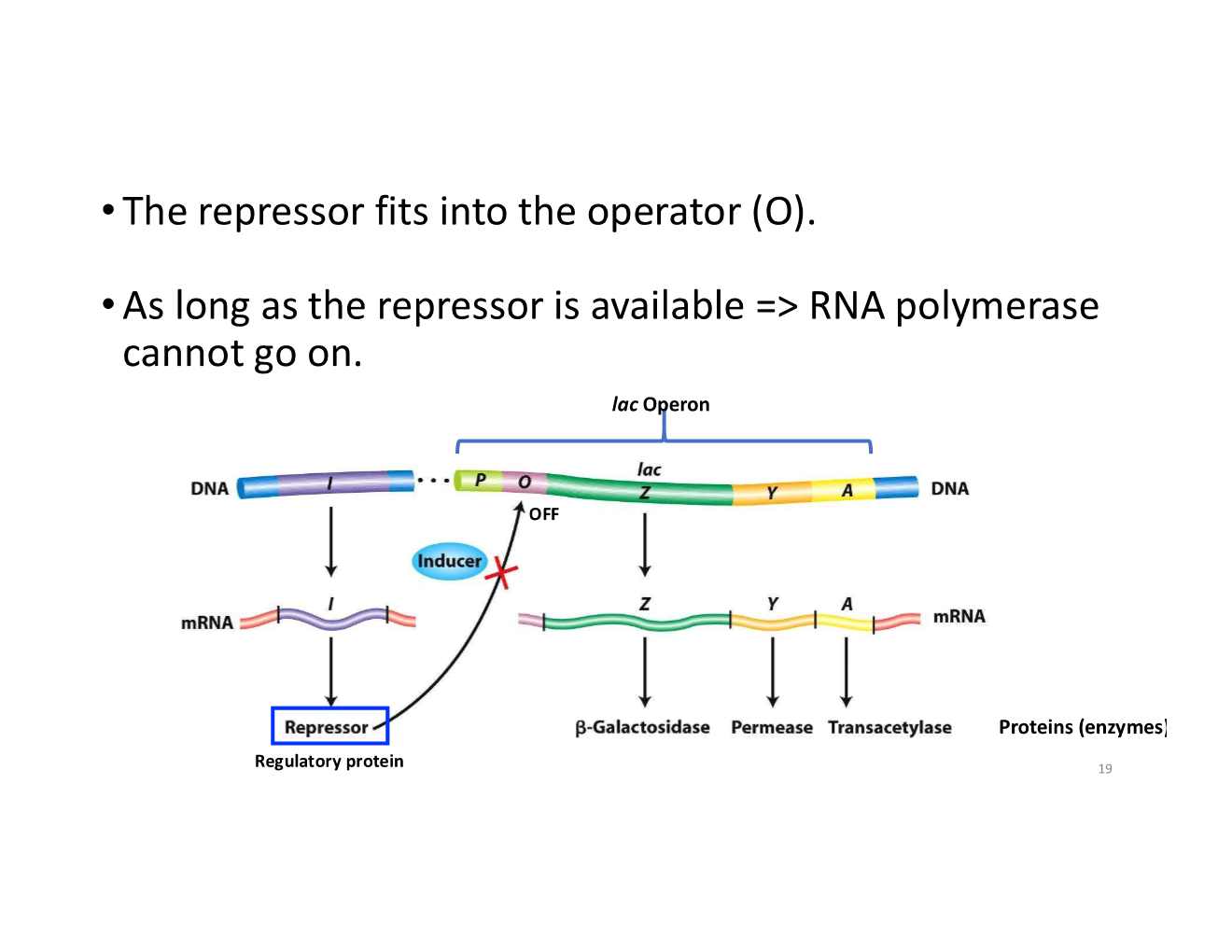
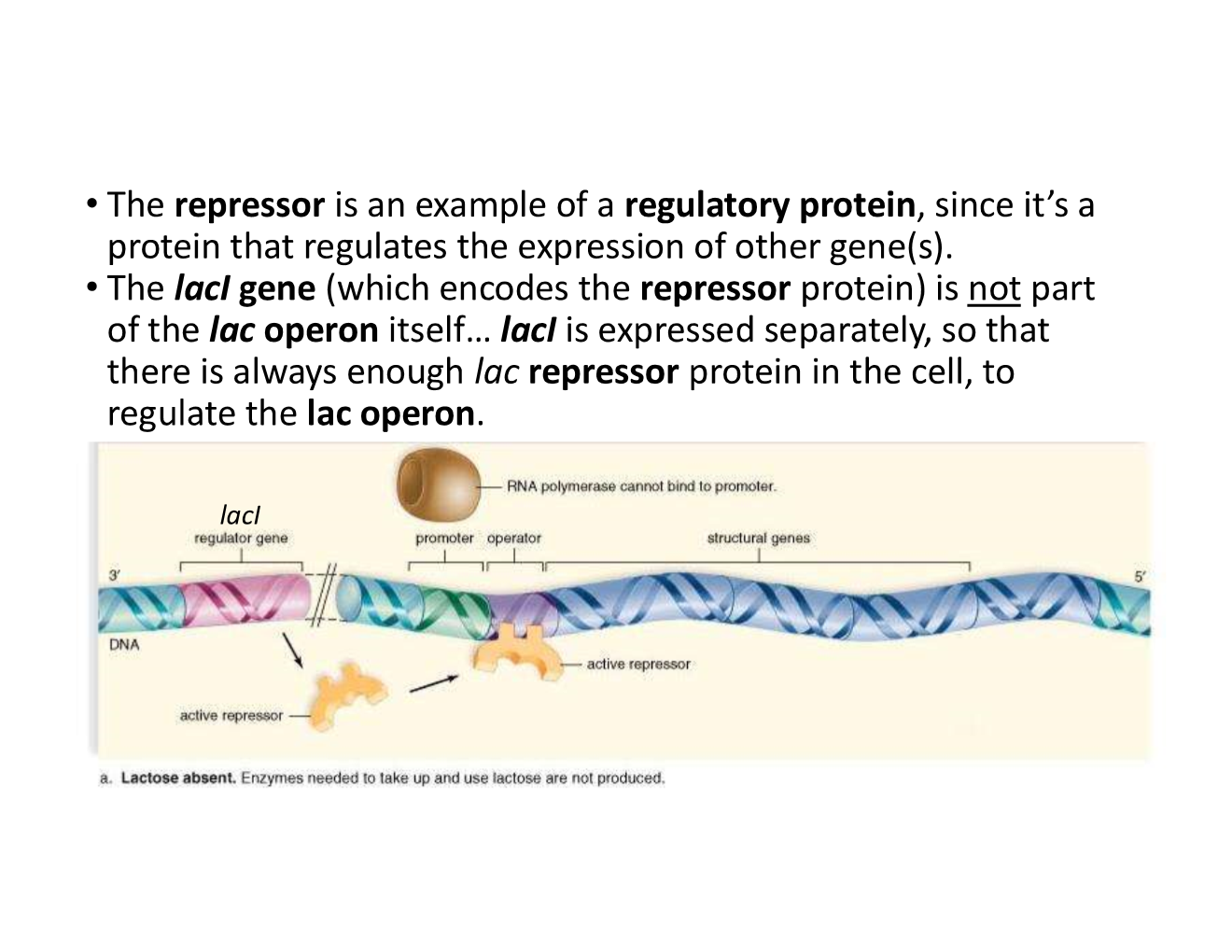
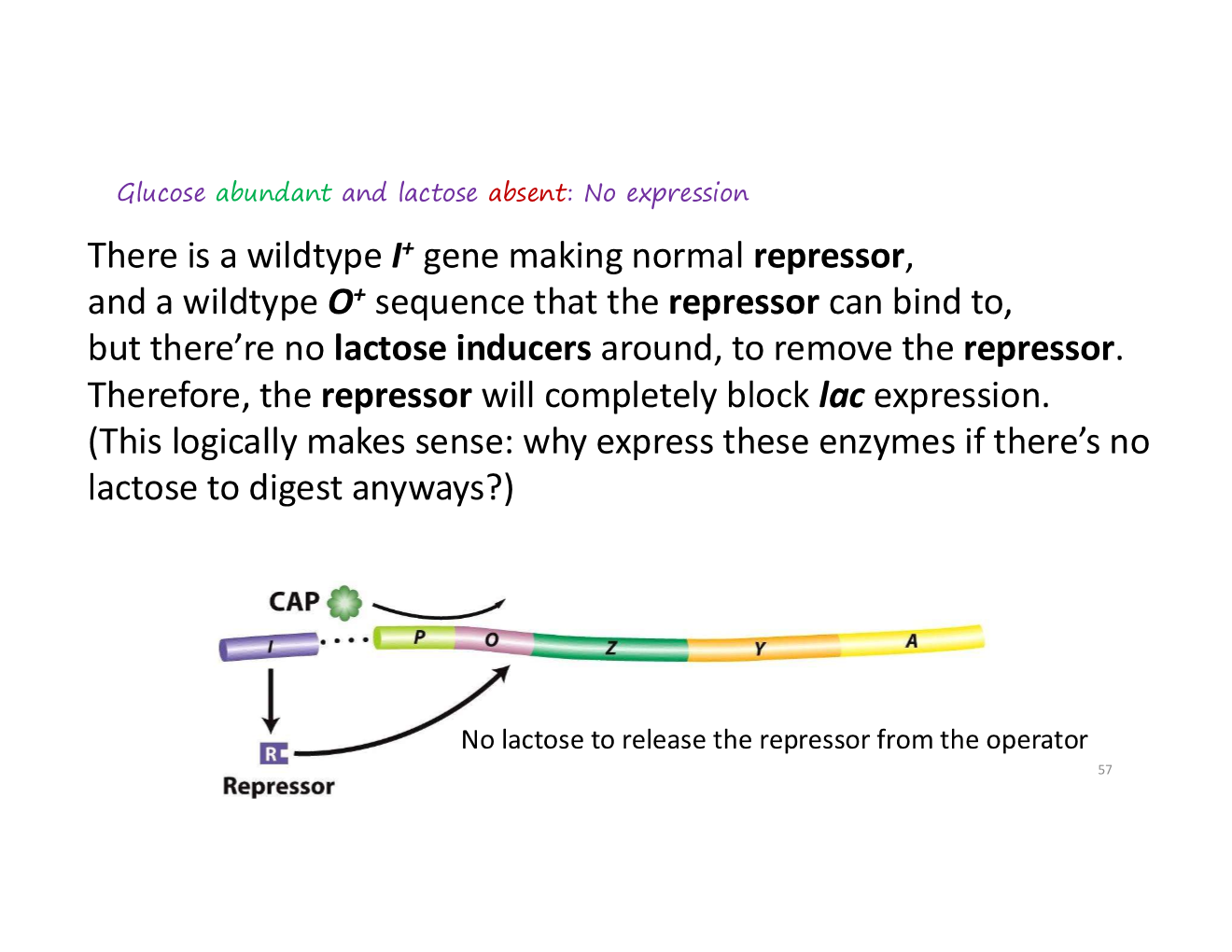
repressor
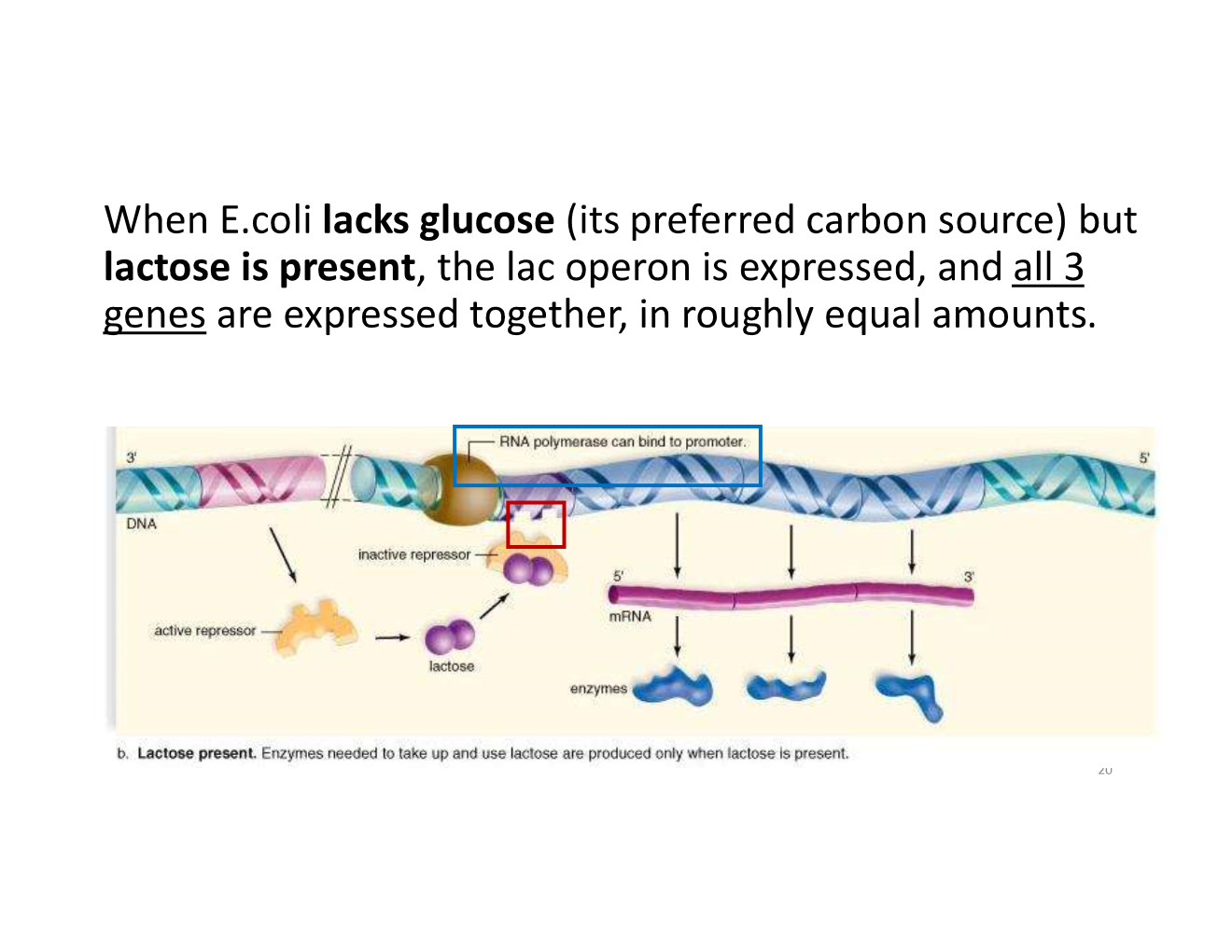
when is the lac operon expressed?
when is the lac operon not expressed?
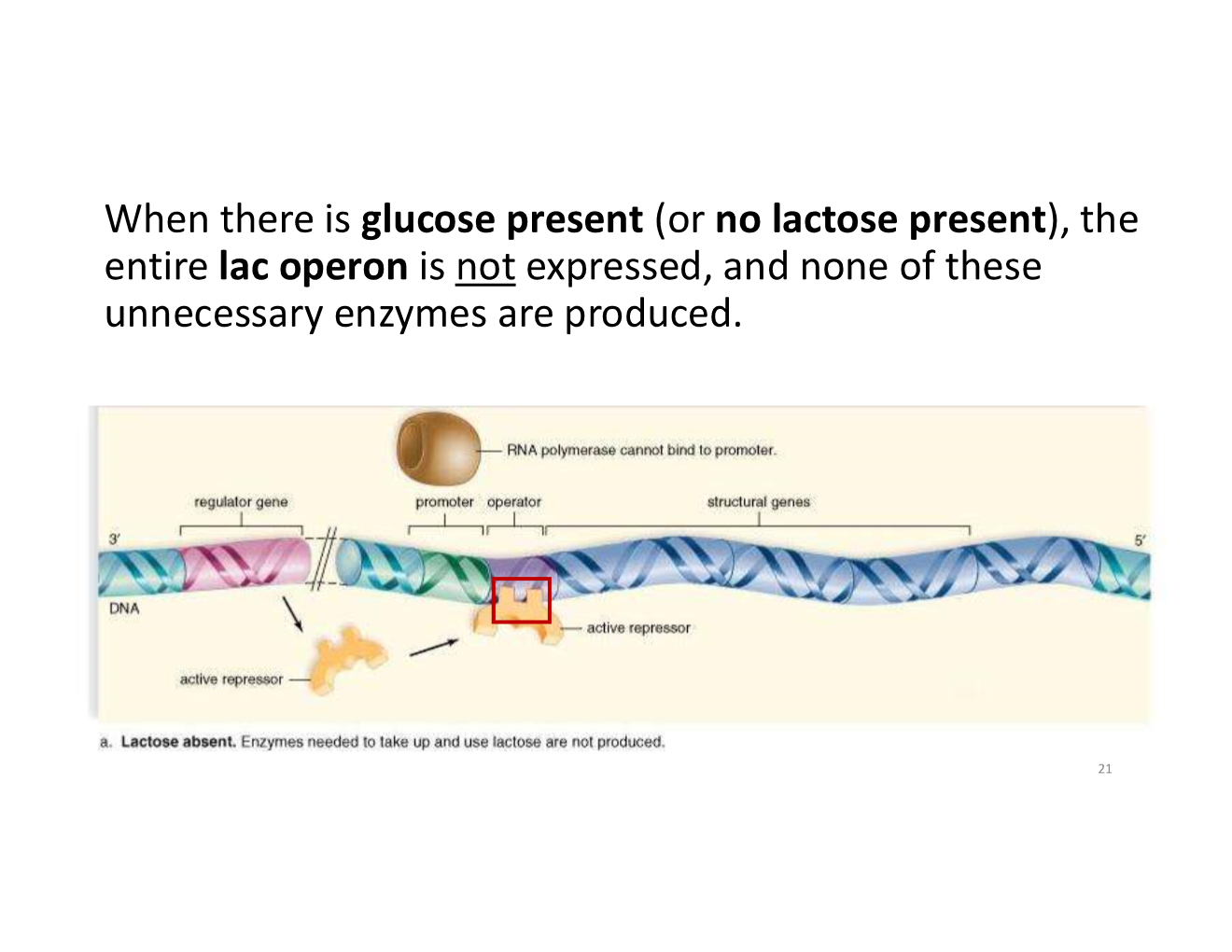
no lactose present
non-induced lac operon
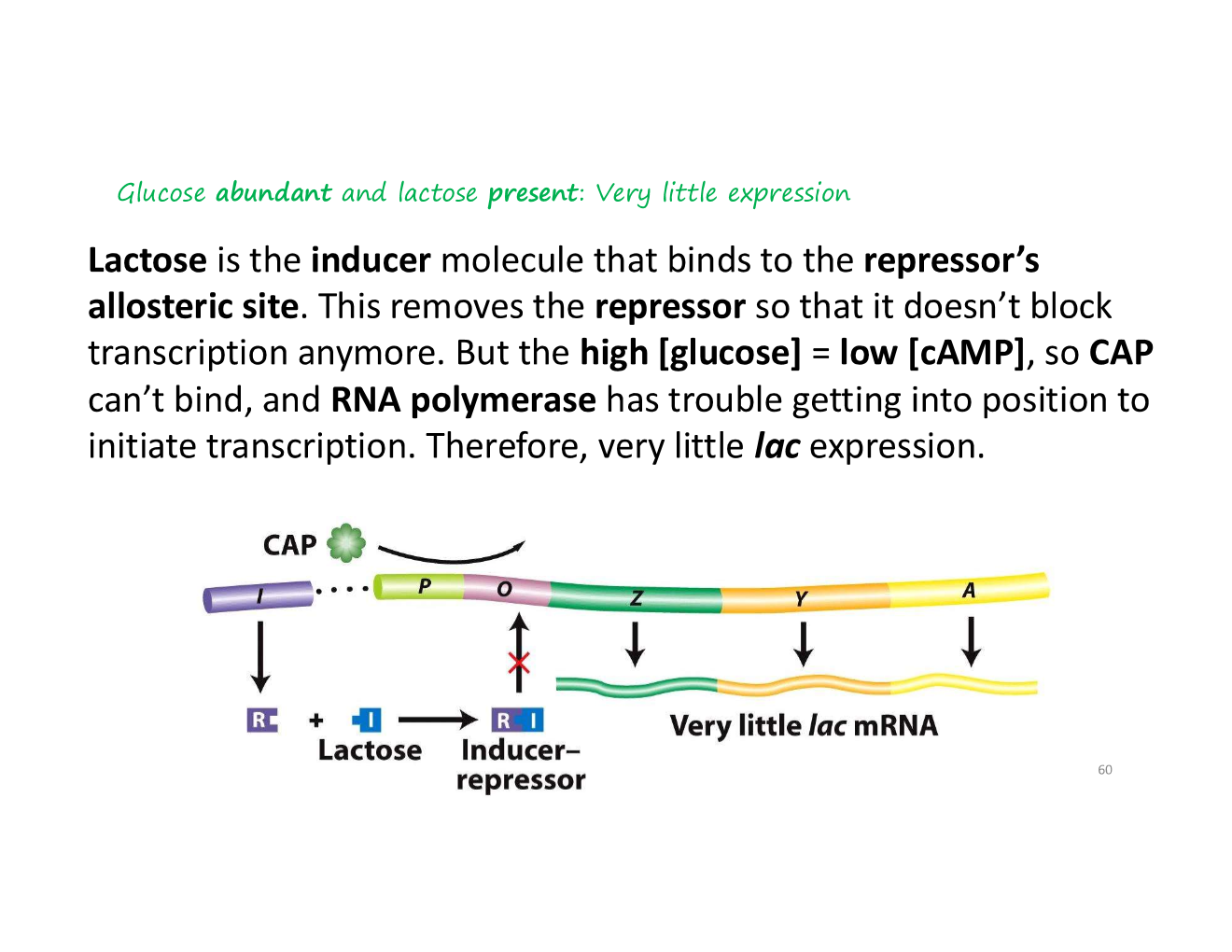
lactose present
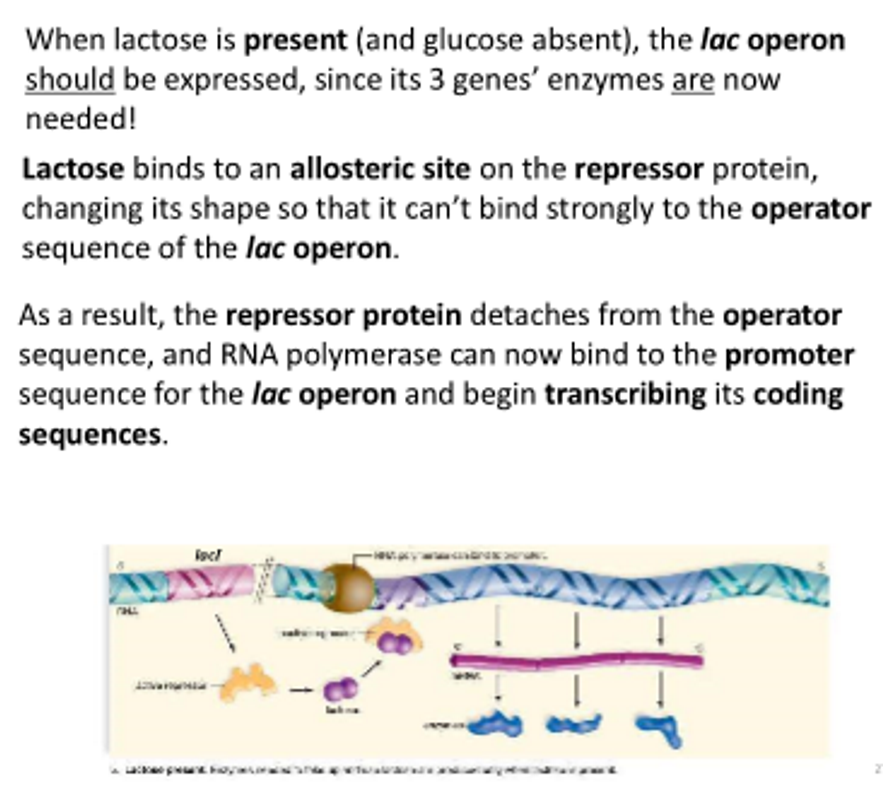
inducer
An inducer is a molecule that induces the expression of an operon. Lactose is a classic example.
how does an inducer work?
Inducers are a type of allosteric effector. They bind to an allosteric site on a protein (like a repressor), which changes the protein's shape and affects its function
inducible system
A system where the expression of a gene can be turned on (induced) by adding a specific molecule, such as an inducer. This usually involves the inducer preventing a repressor from blocking transcription.
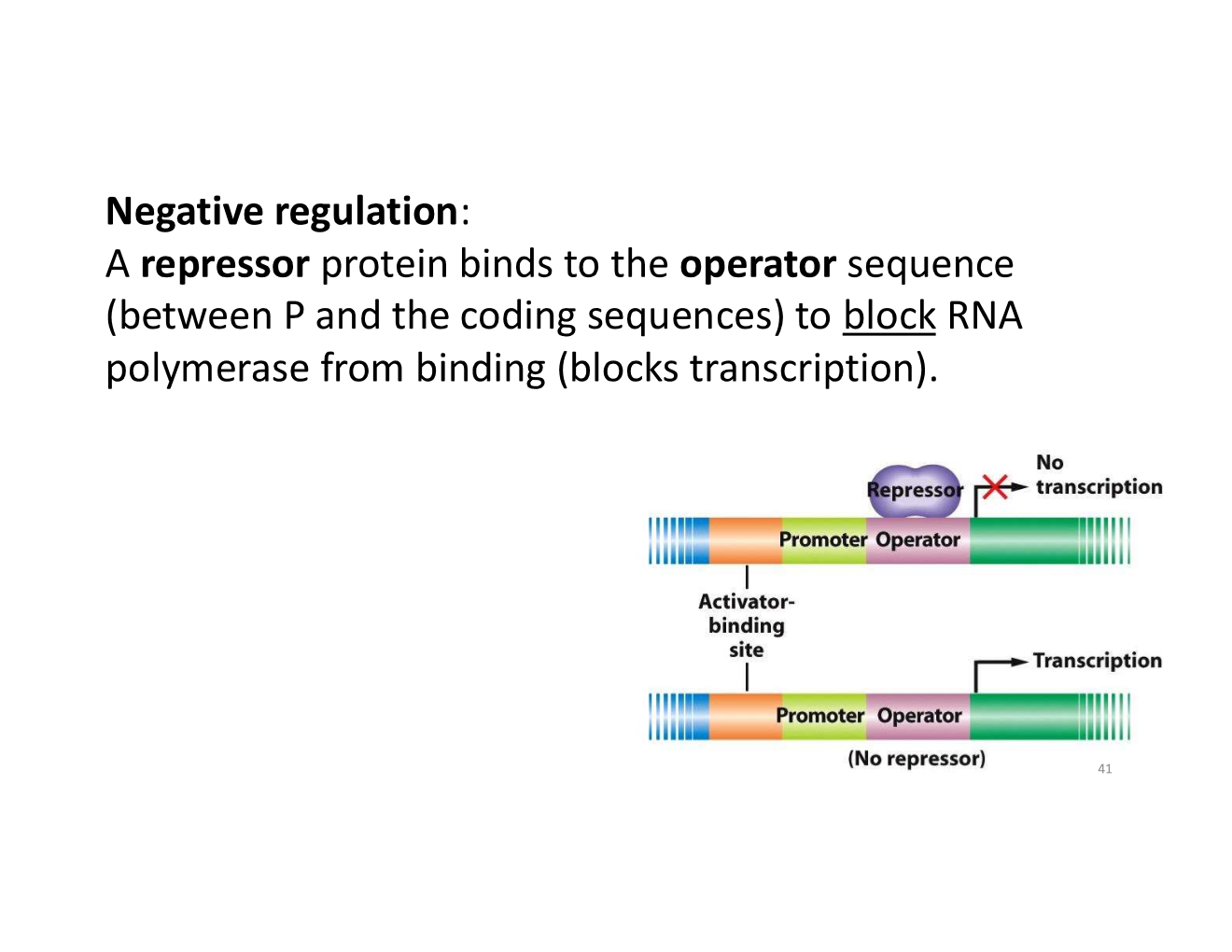
negative regulation
in negative regulation, binding of the regulatory molecule decreases transcription
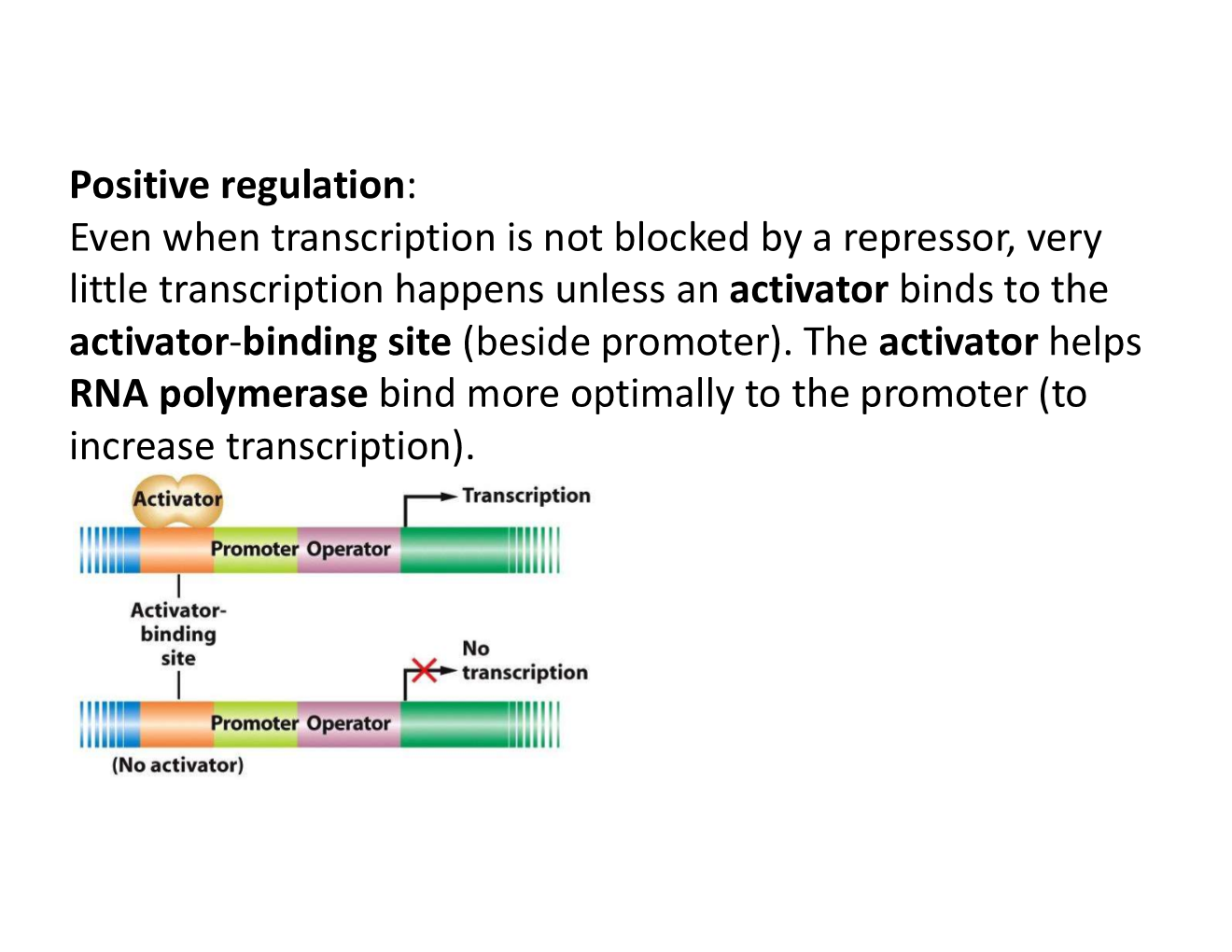
positive regulation
in positive regulation, binding of the regulatory molecule increases transcription
transcriptional regulation
The process of controlling gene expression by regulating the transcription of genes, which is the first step in creating a protein from a gene.
what must bacterial cells need to be able to do?
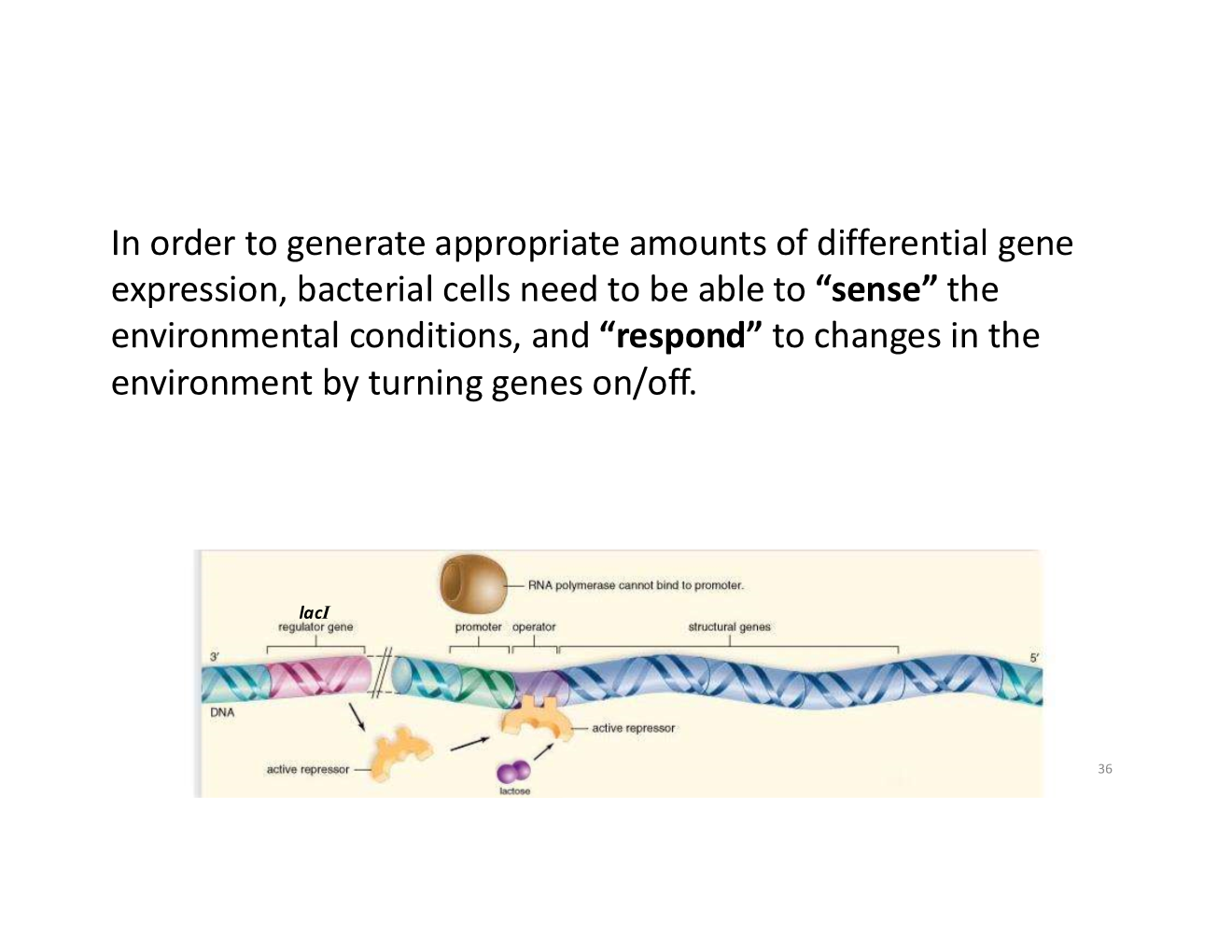
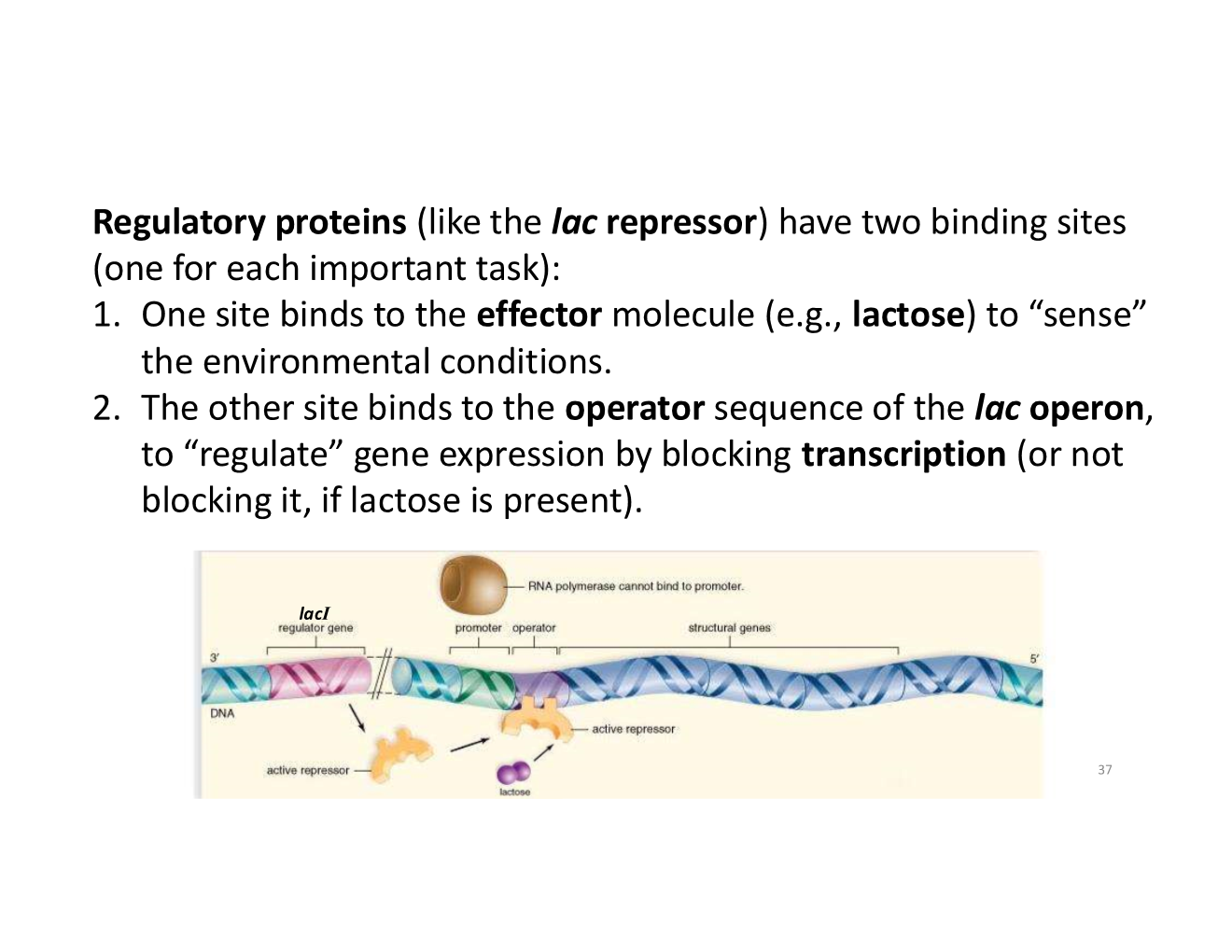
regulatory proteins binding sites
what is helpful when studying the regulation of a gene/operon?
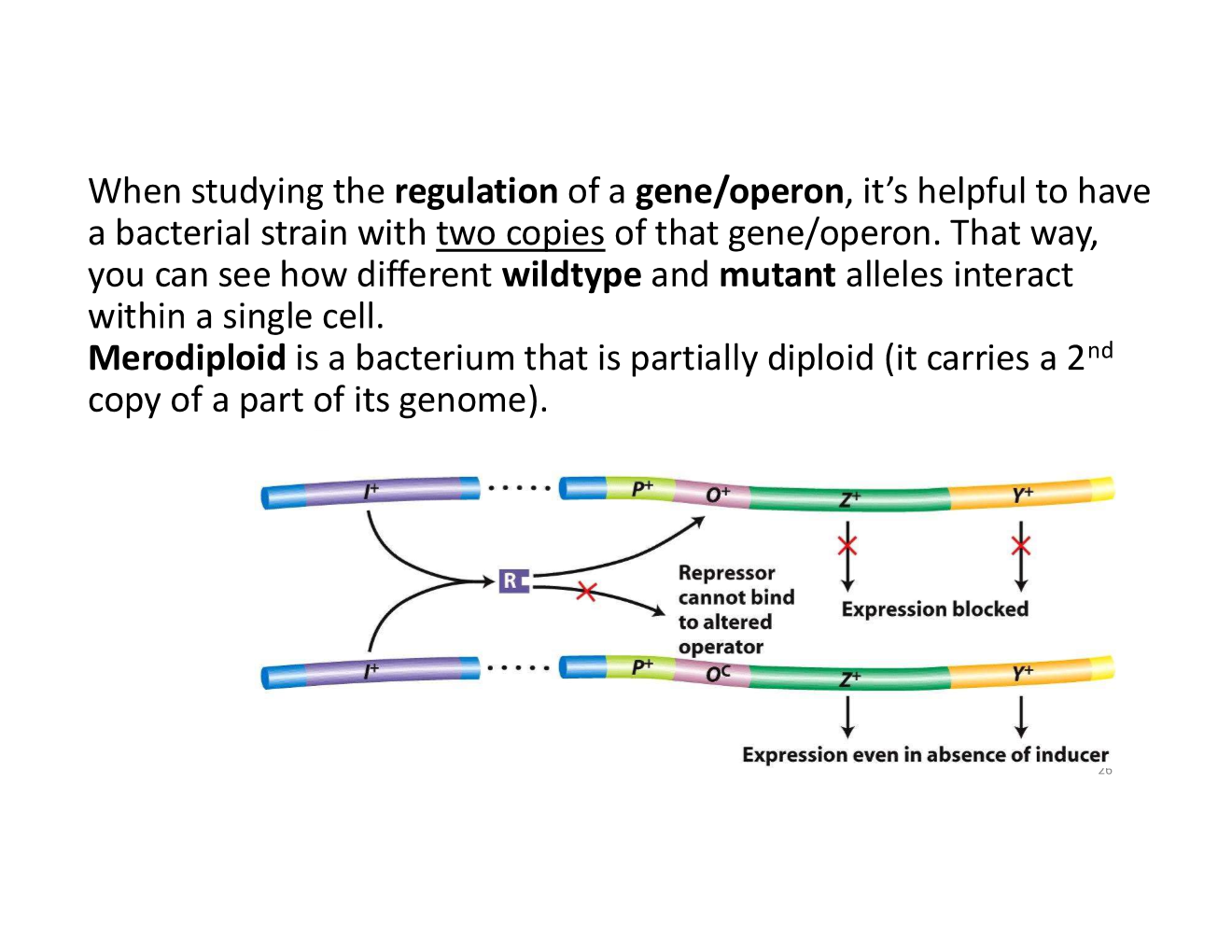
what is merodiploid?
a bacterium that is partially diploid (it carries a 2nd copy of a part of its genome)
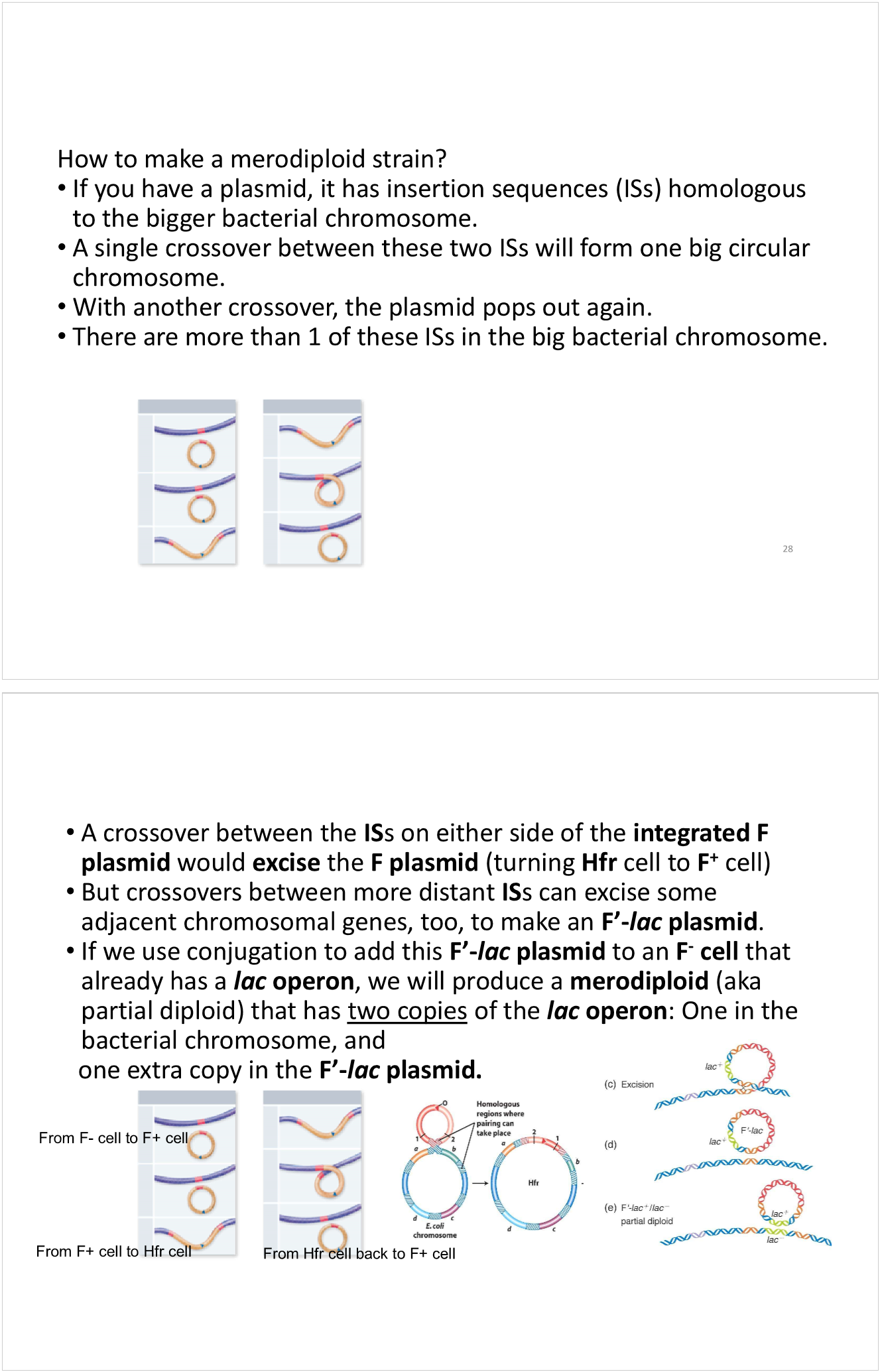
how do you make a merodiploid strain?




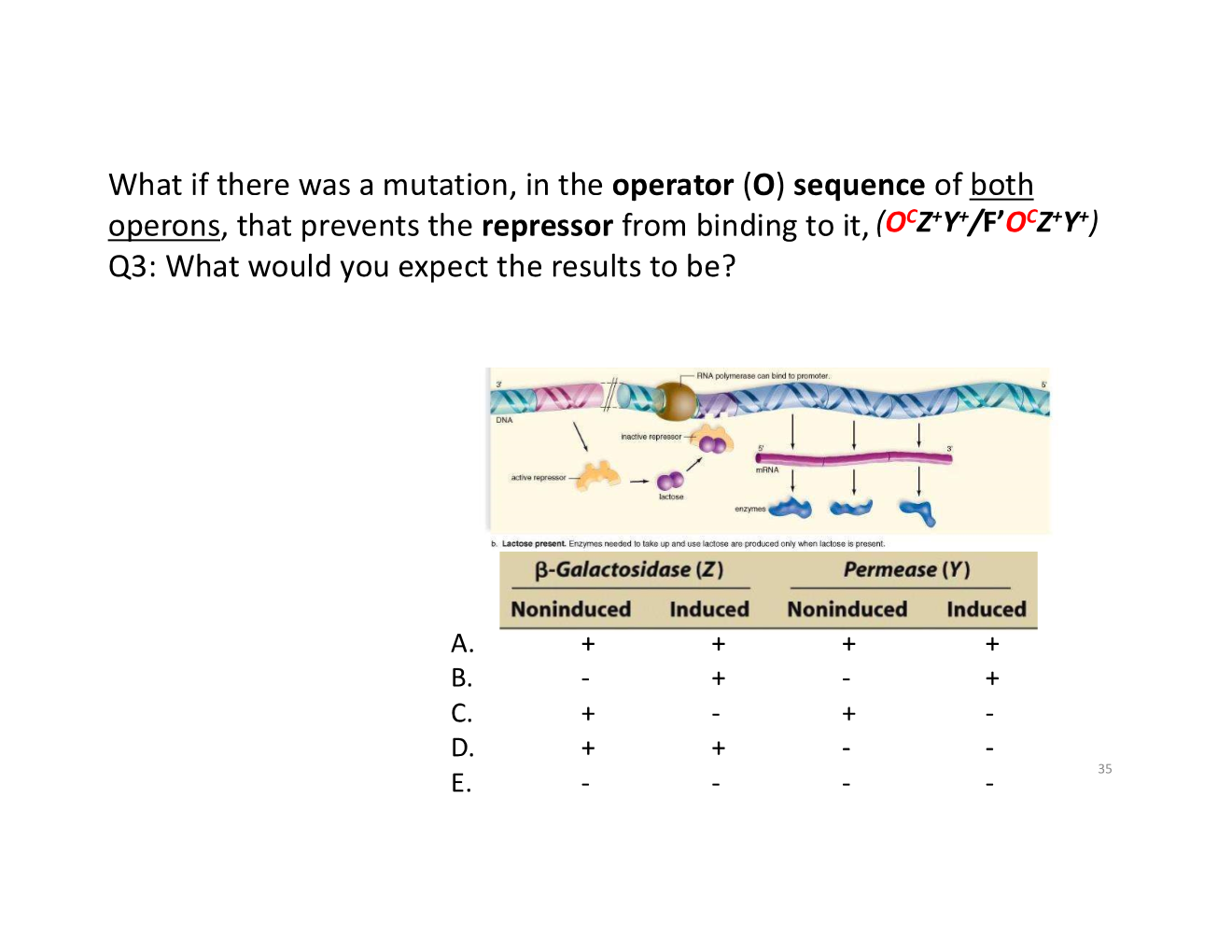
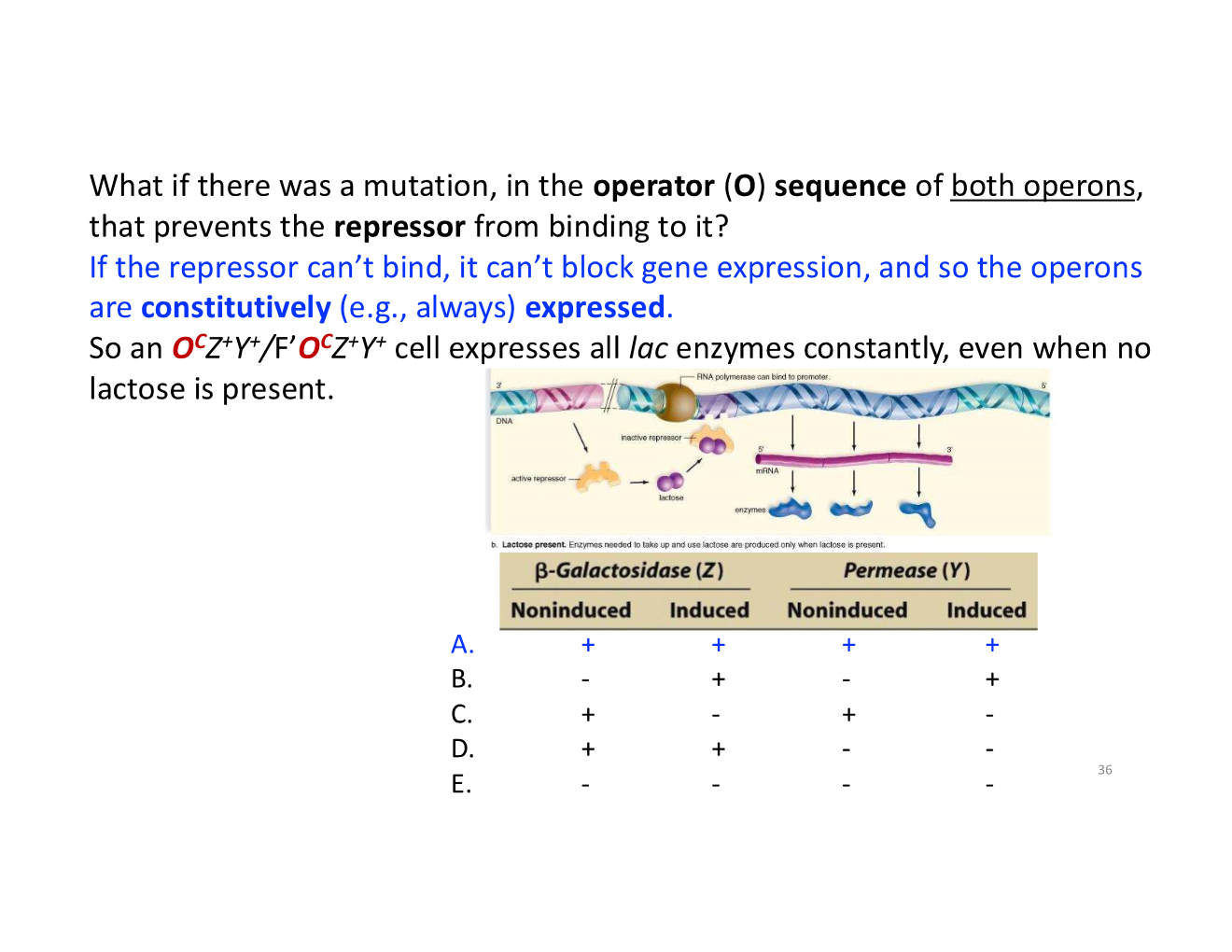
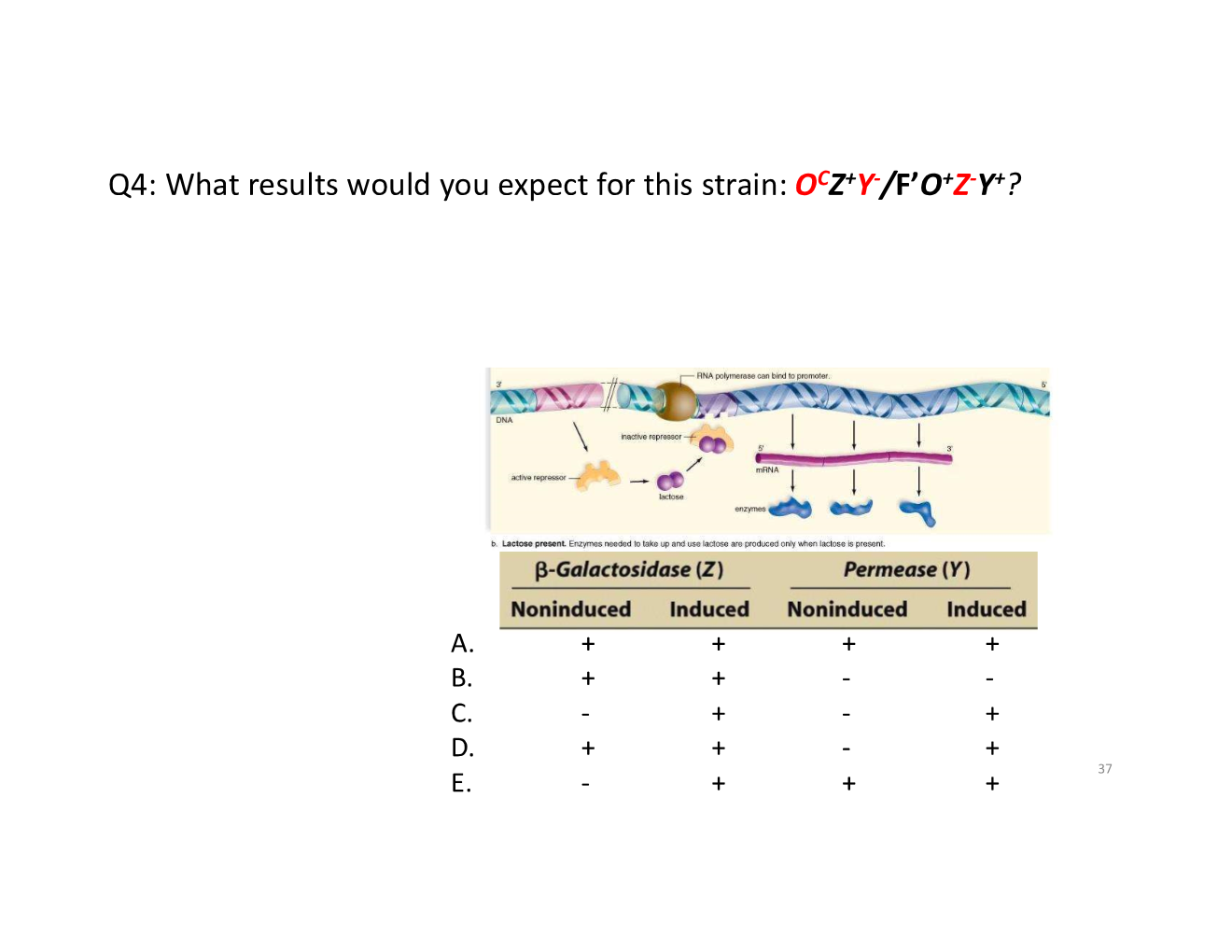
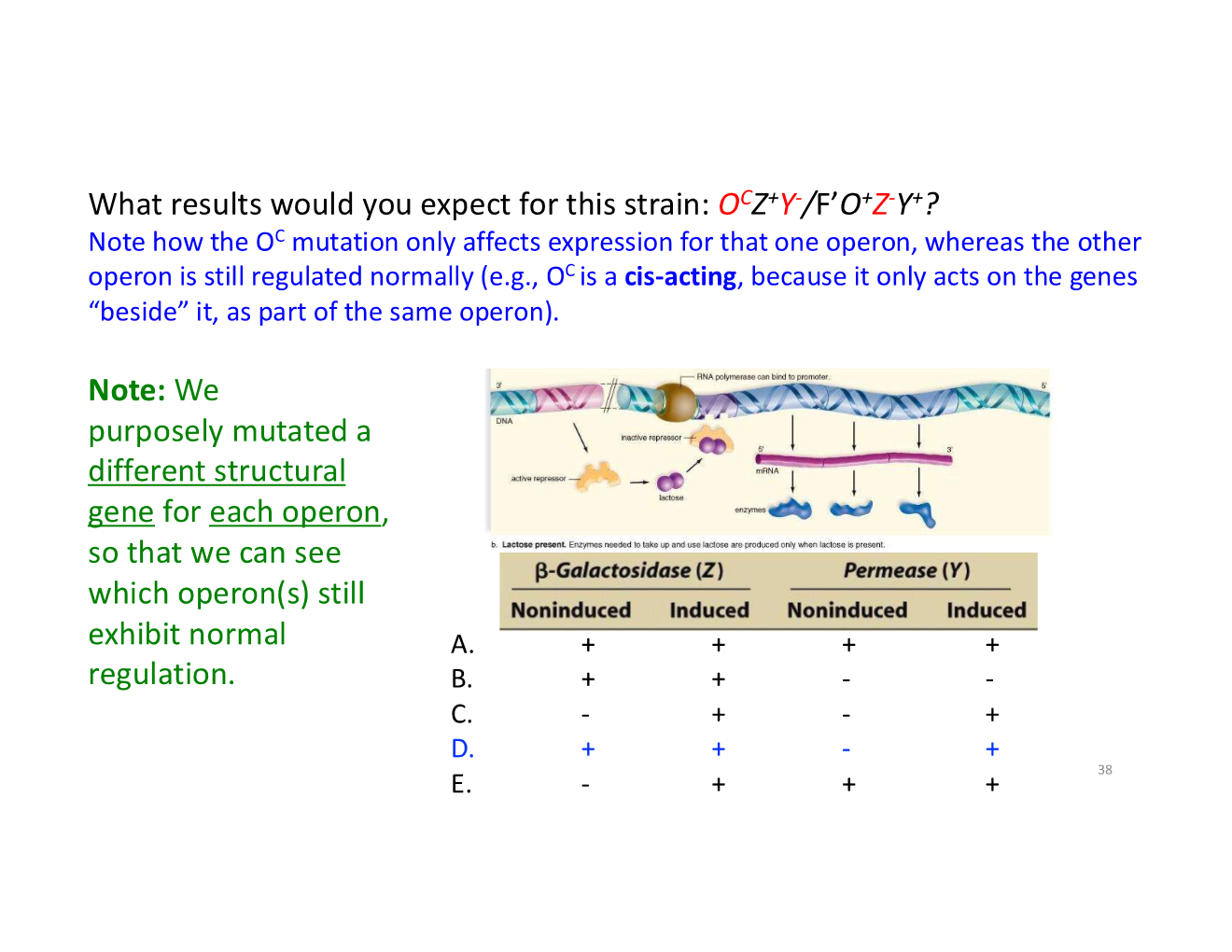
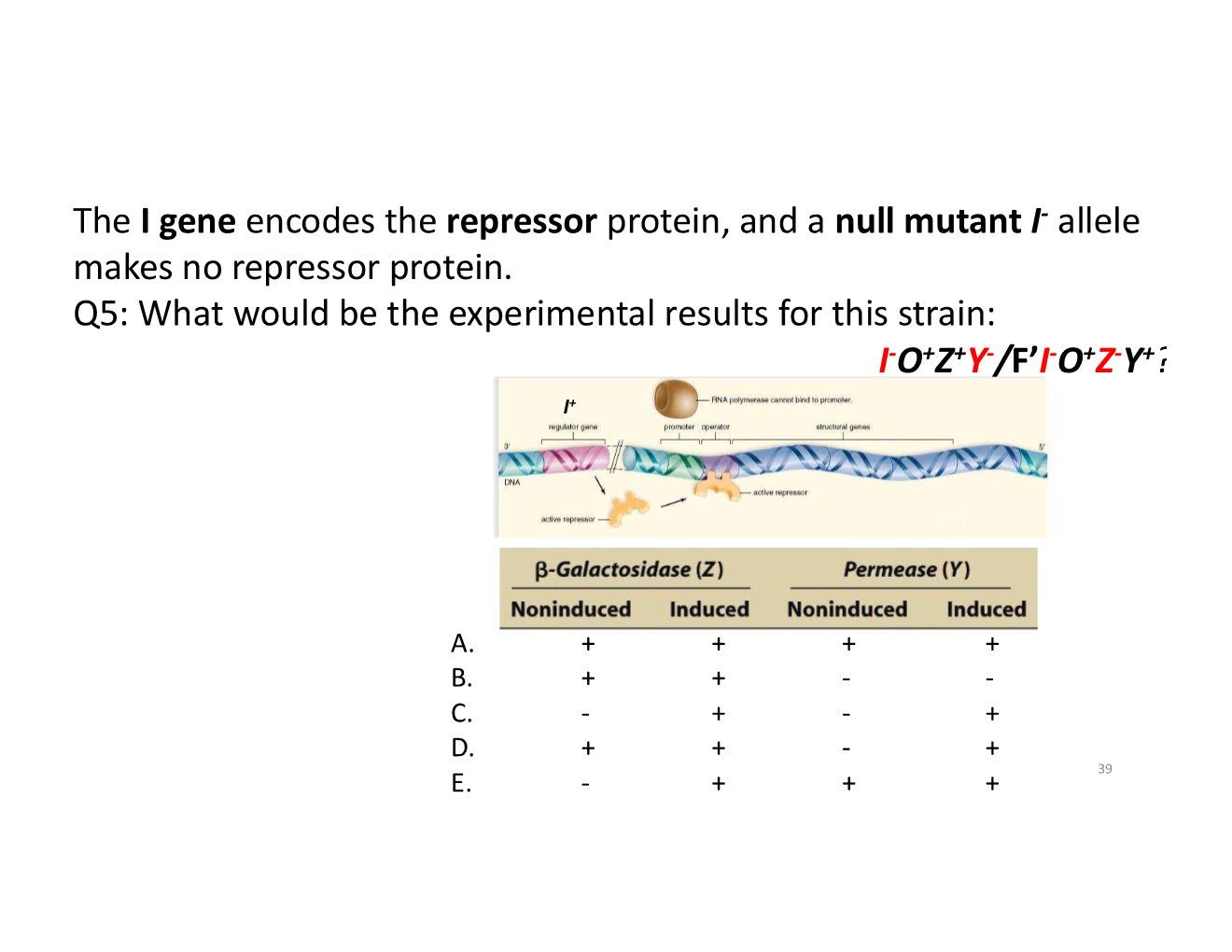
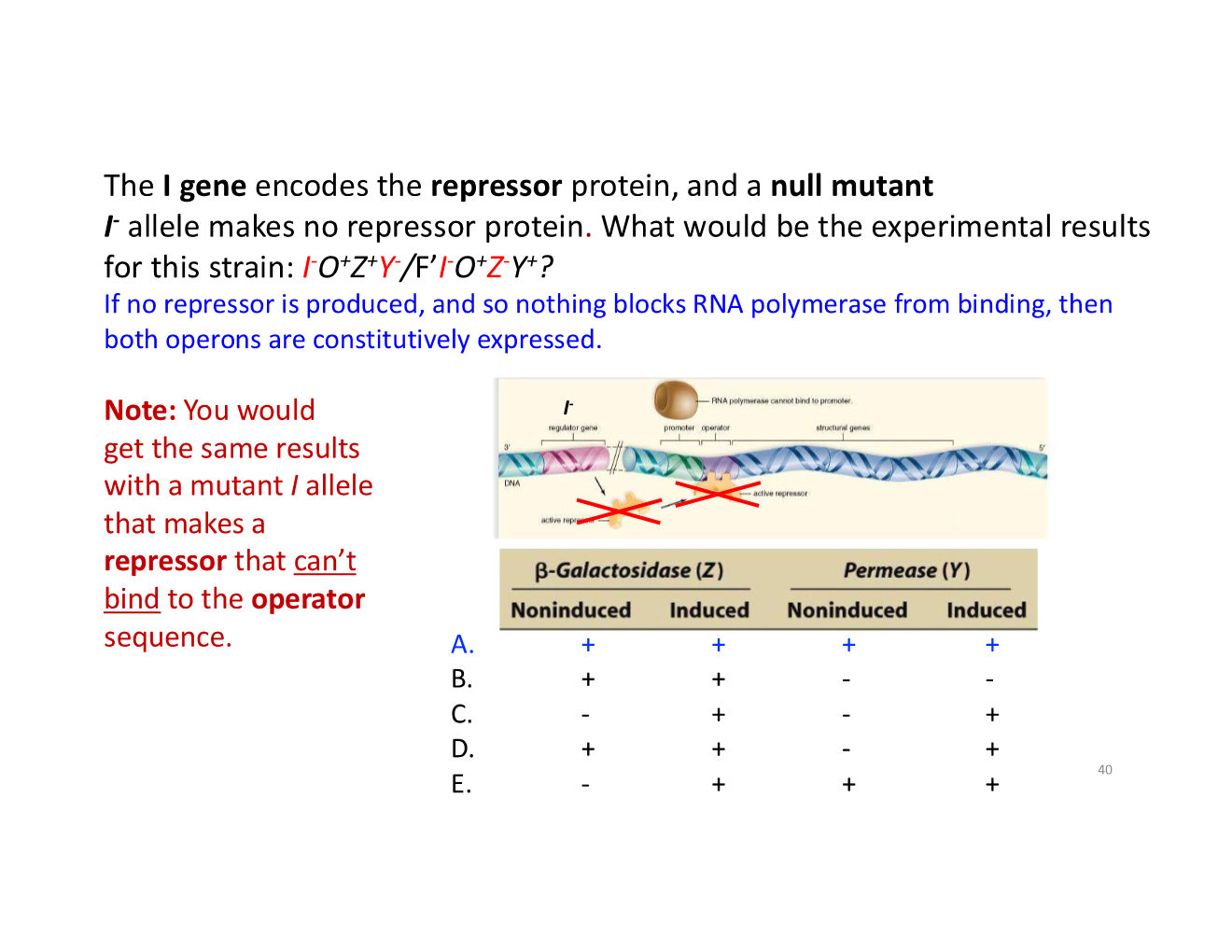
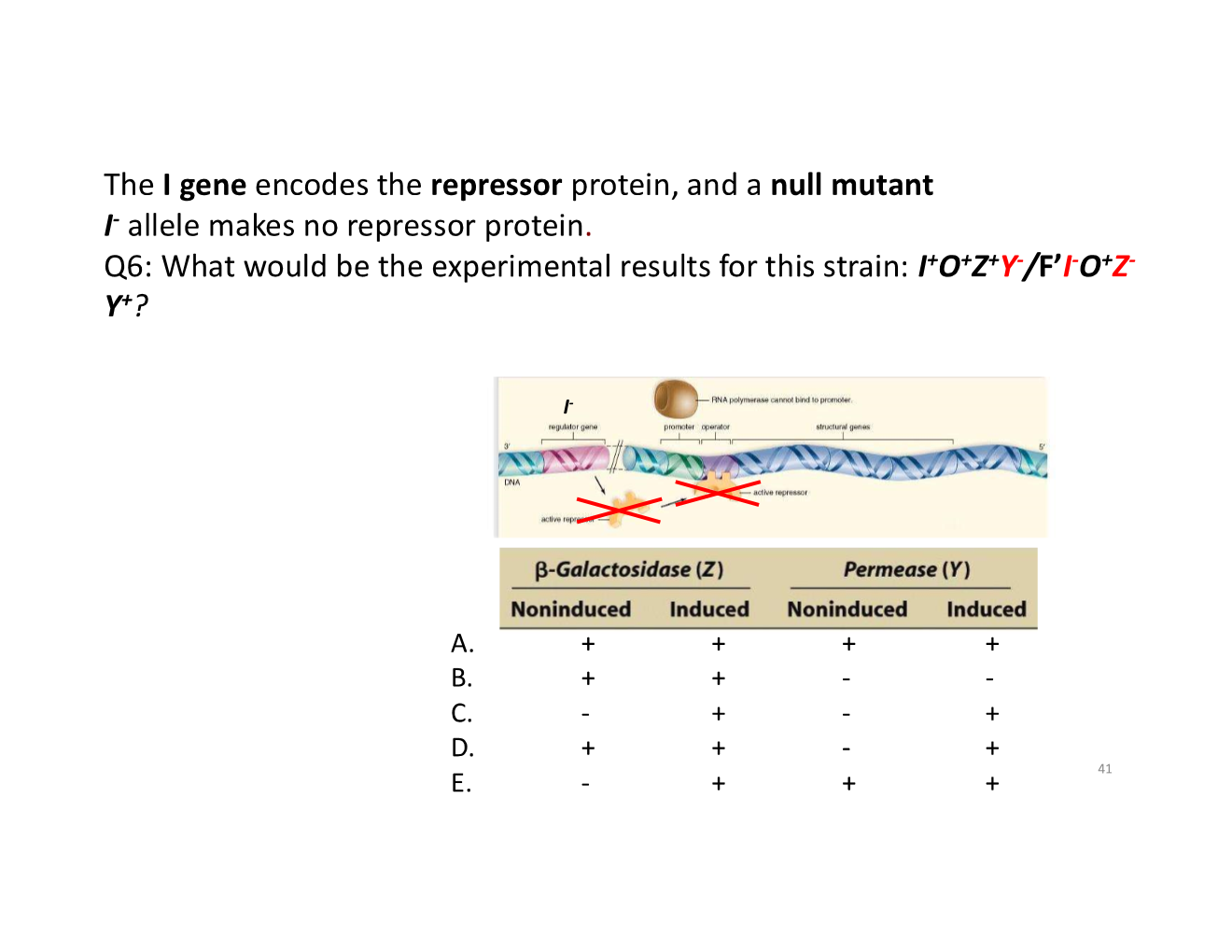
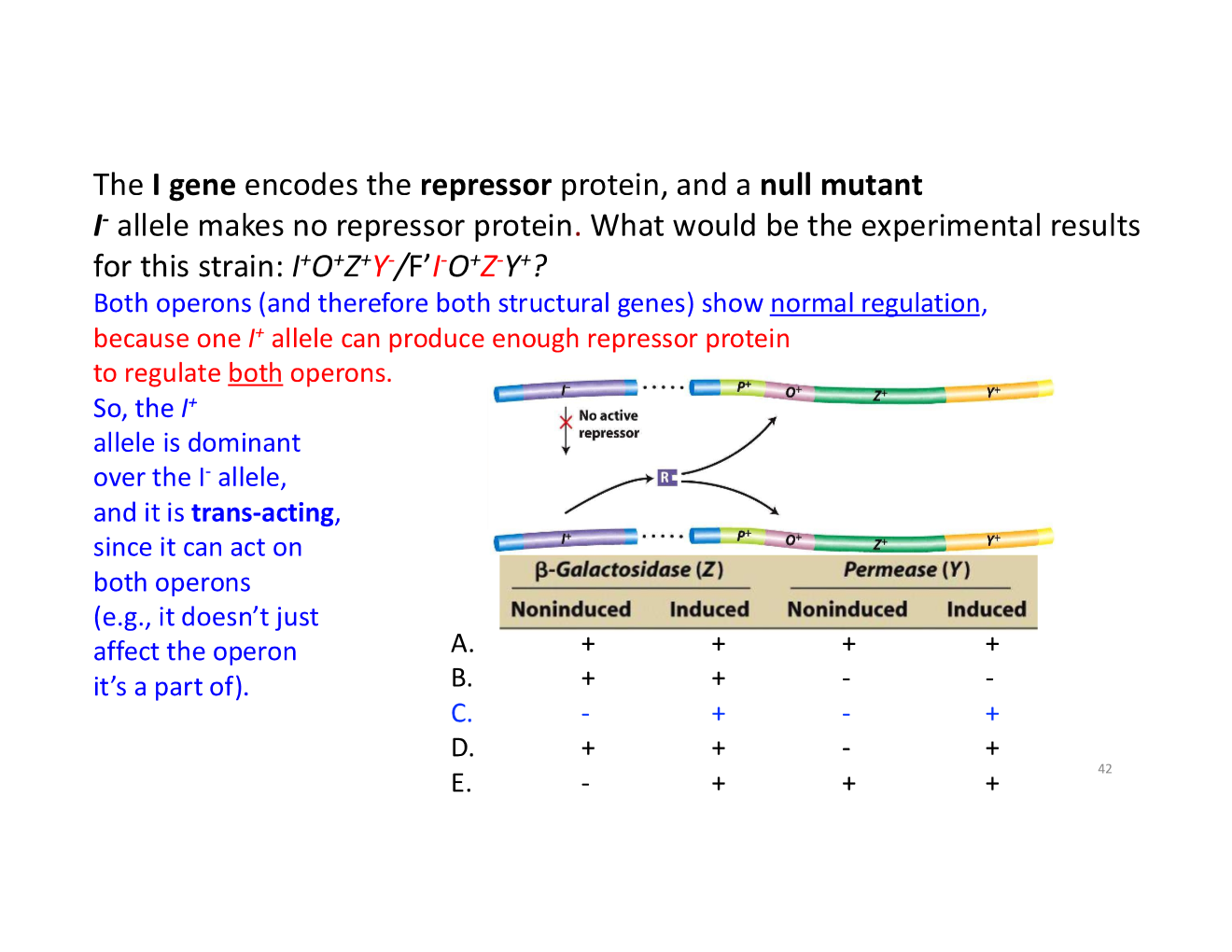
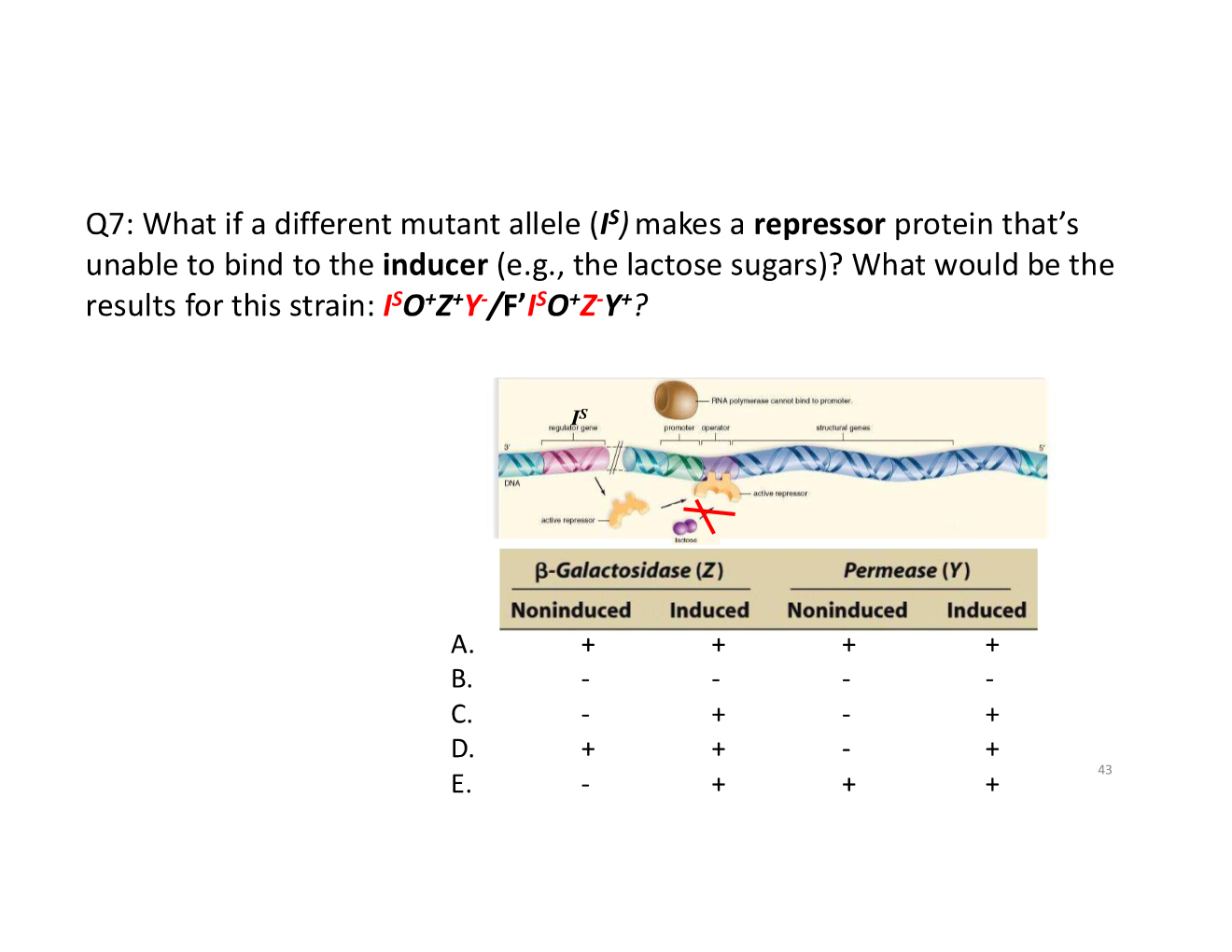
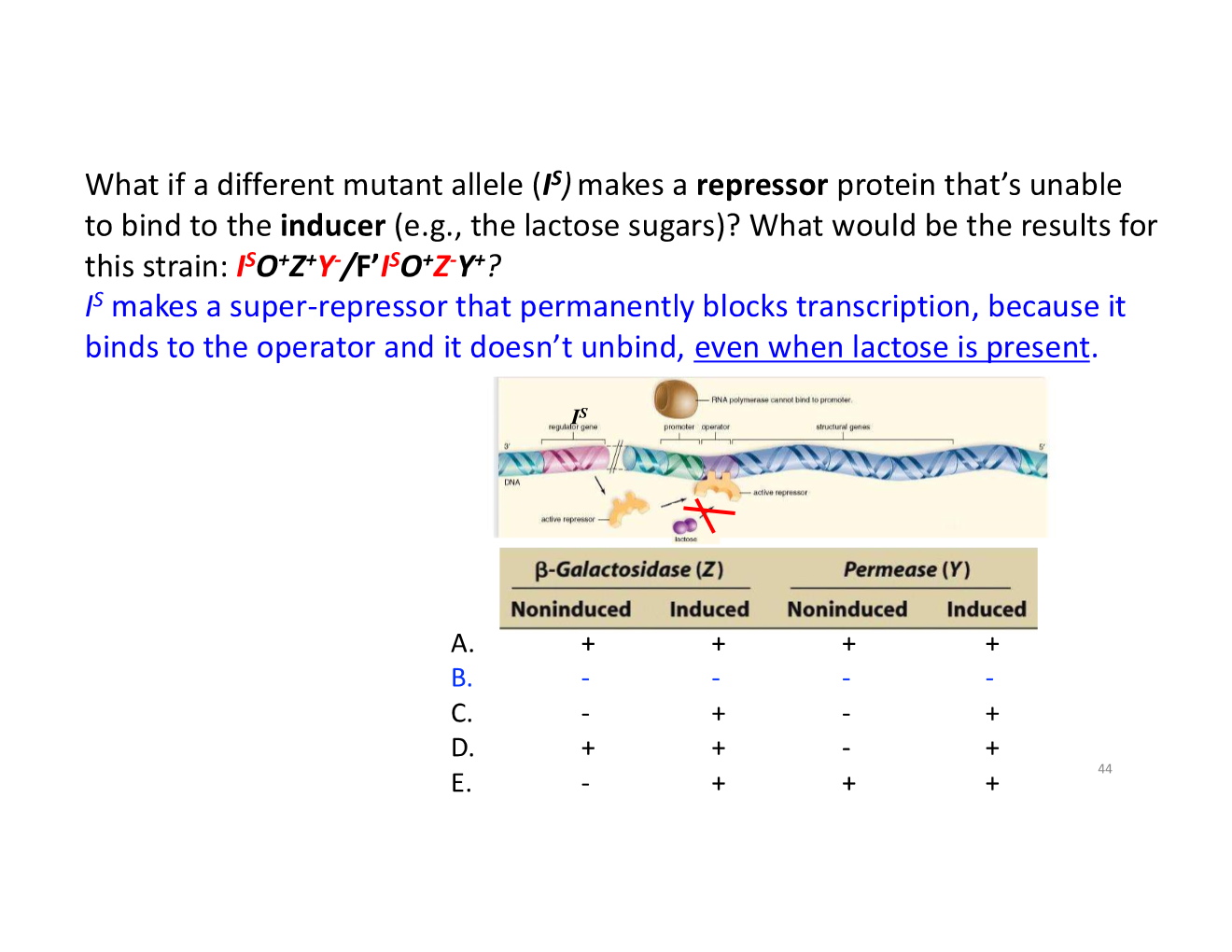


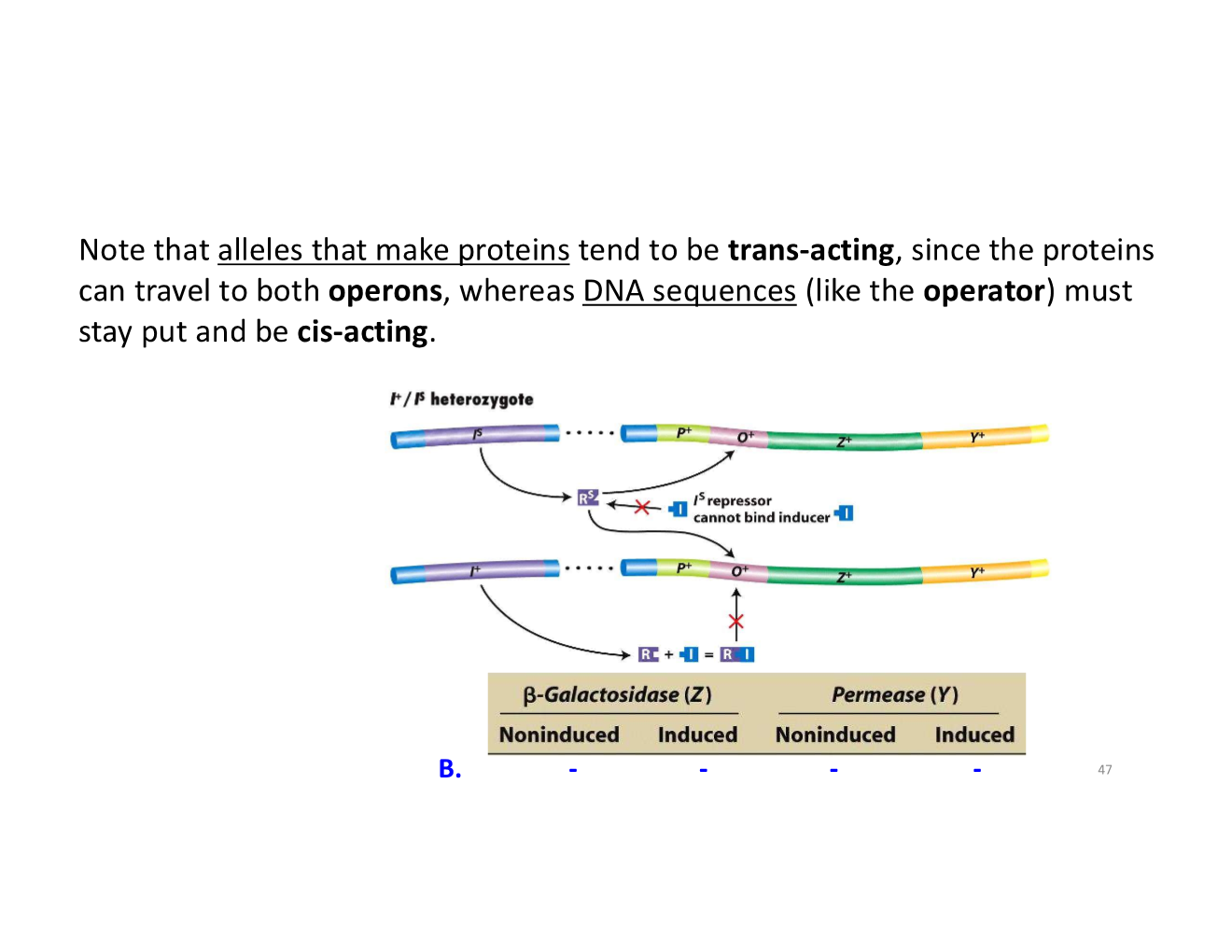
trans-acting vs cis-acting
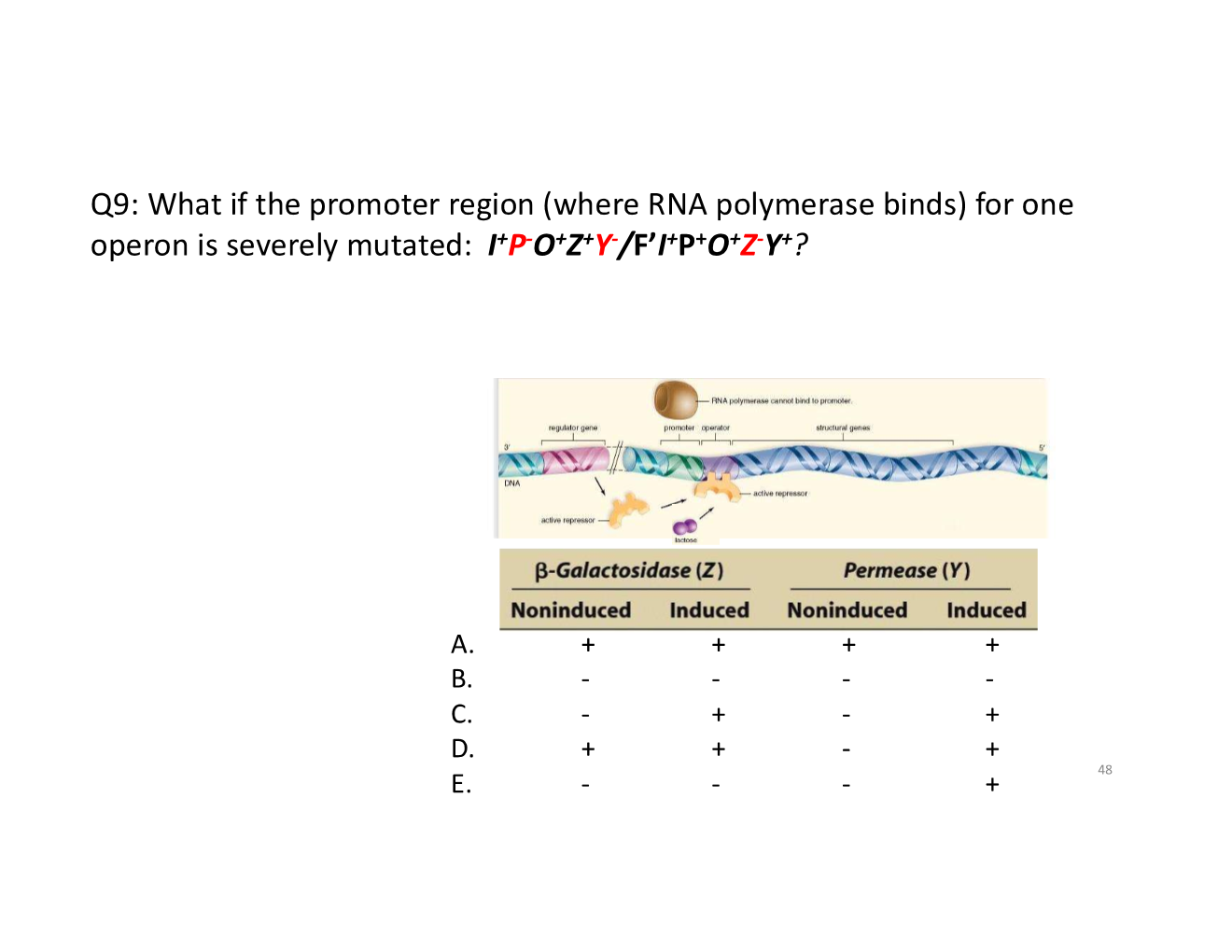
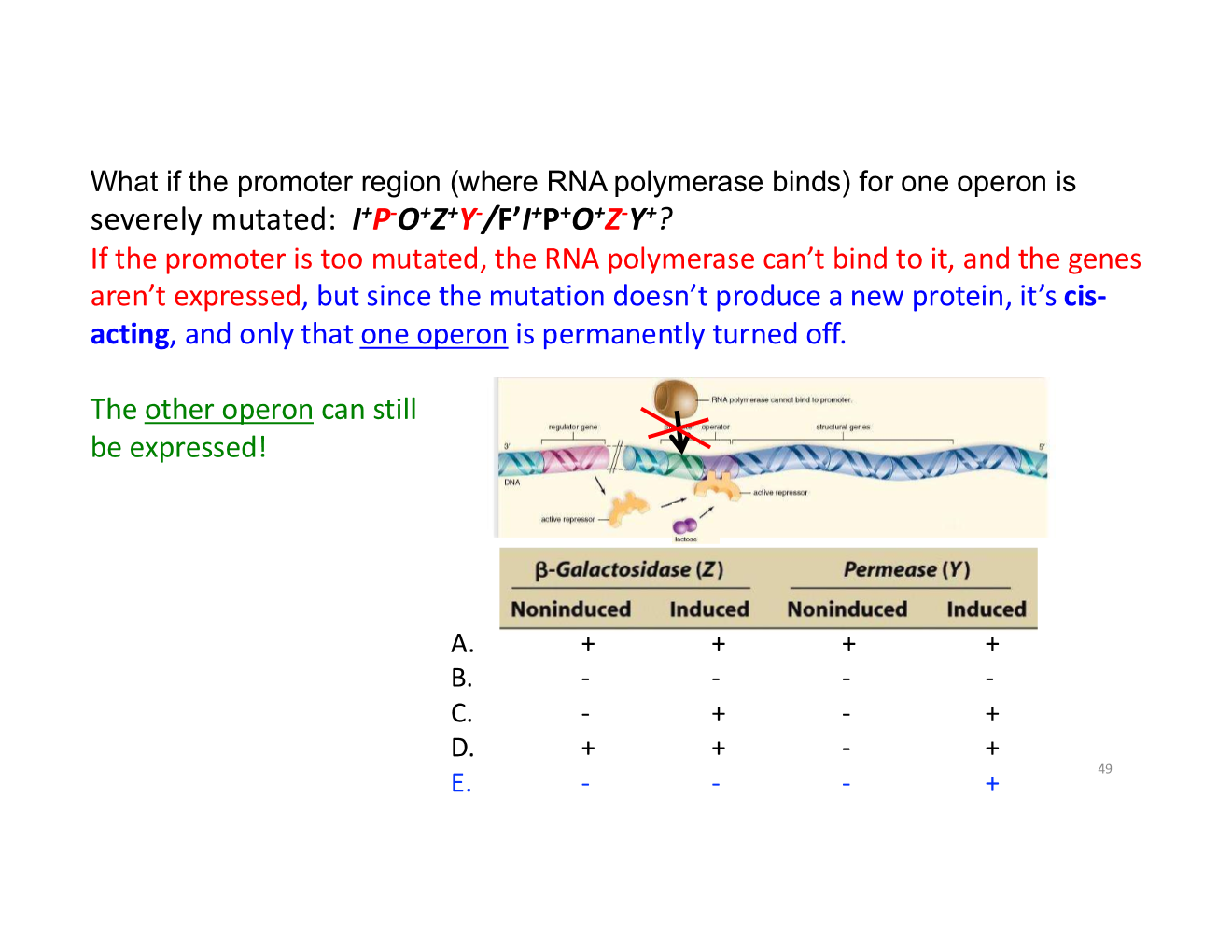

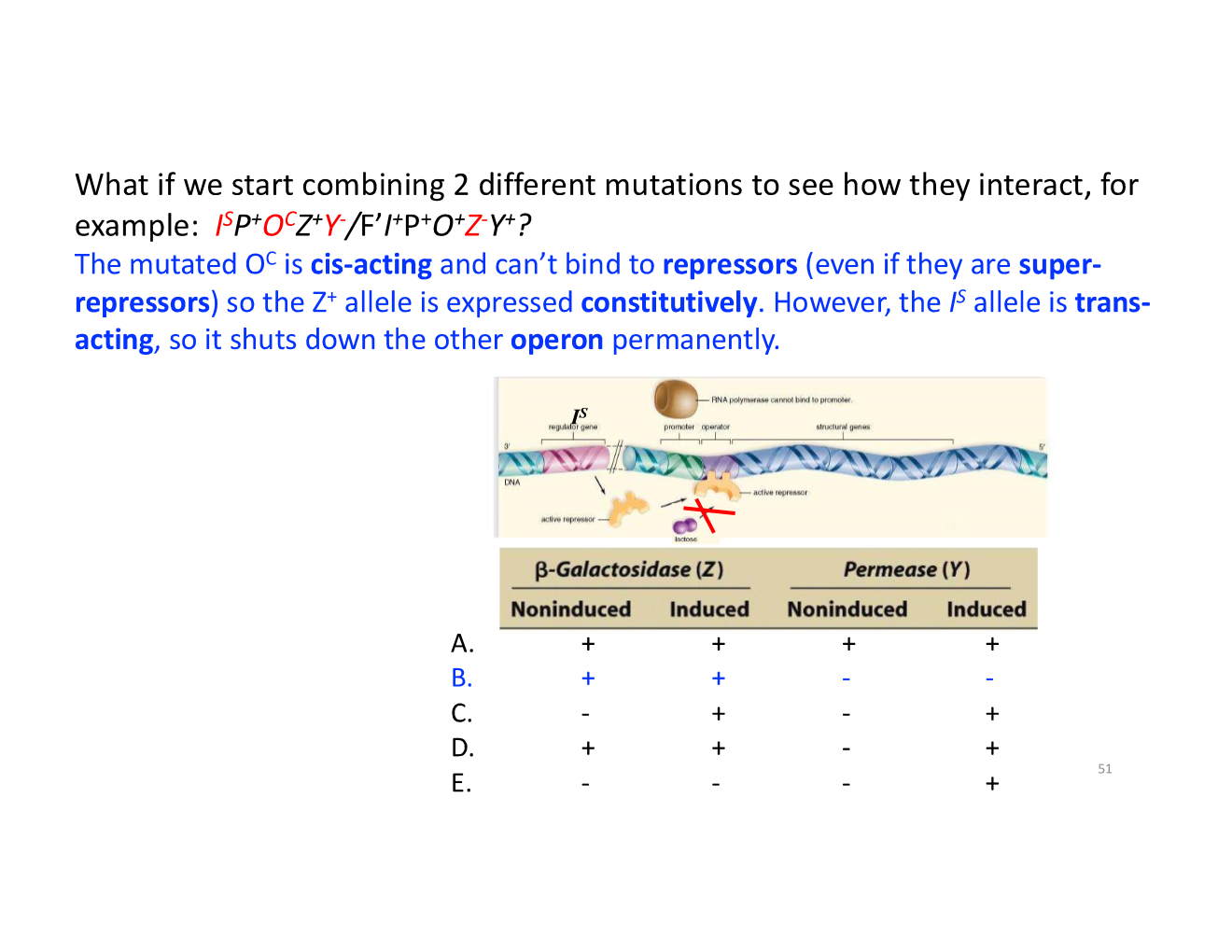

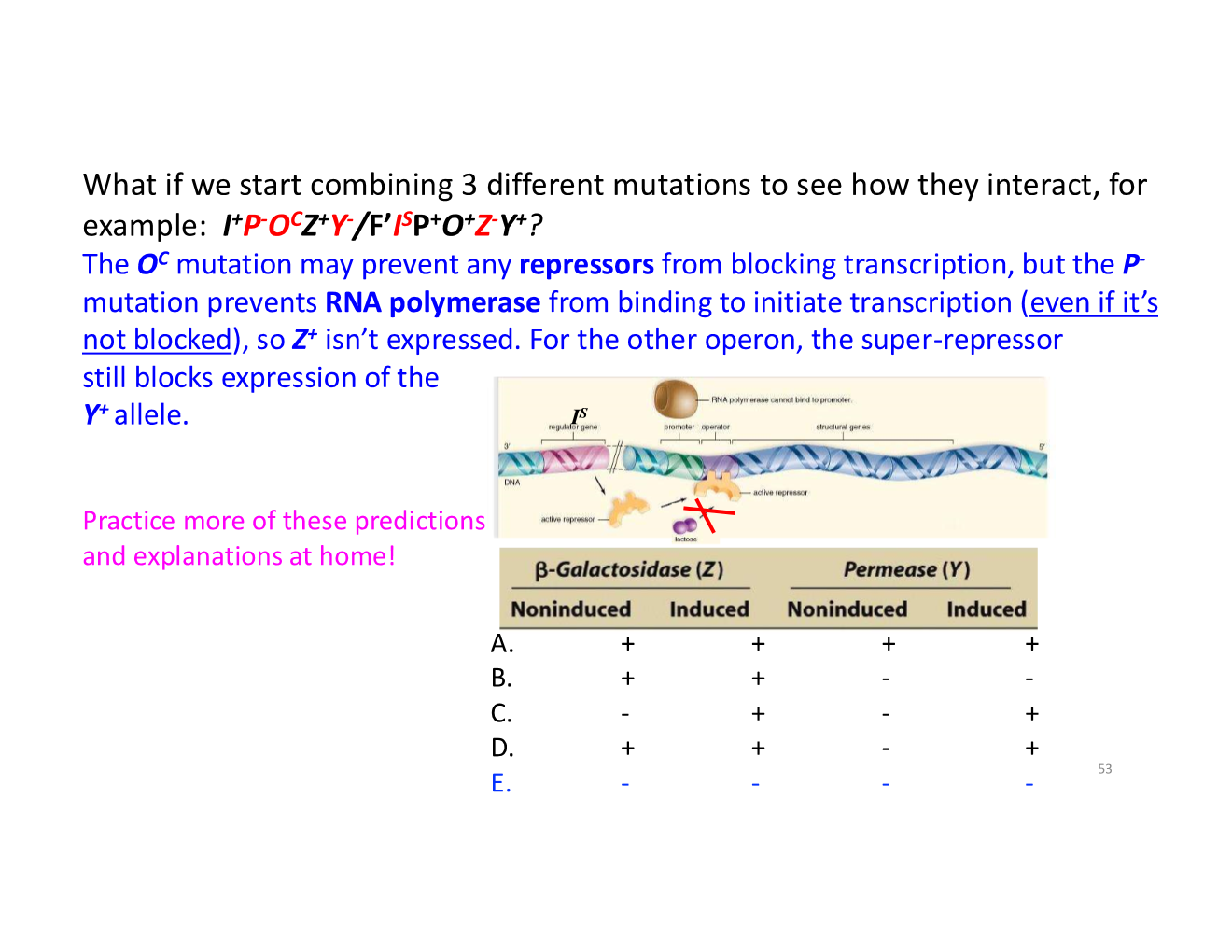
gene regulation/lac operon key concepts

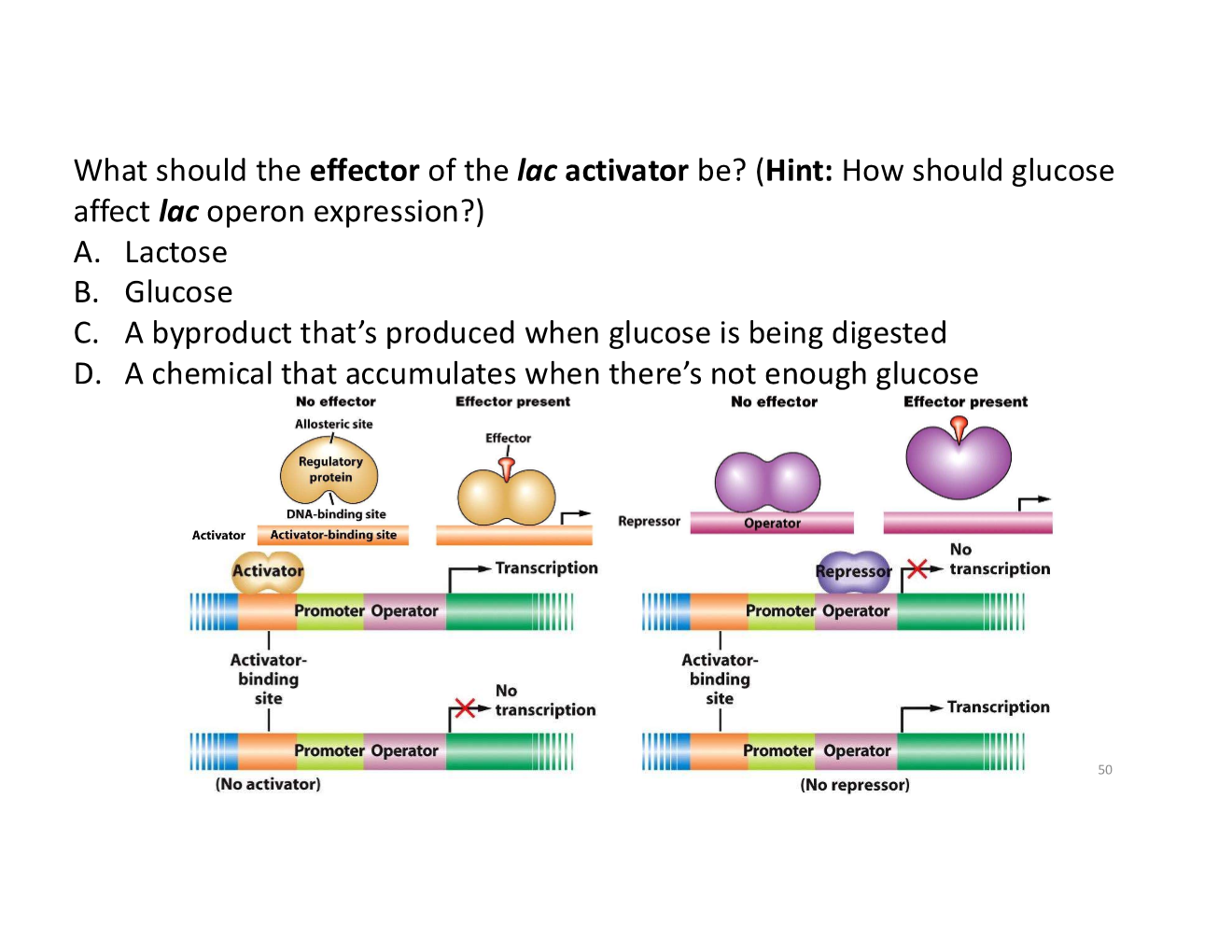
what effect should the absence of glucose have on lac operons when lactose is present?
lac operon expression should be promoted, with an activator
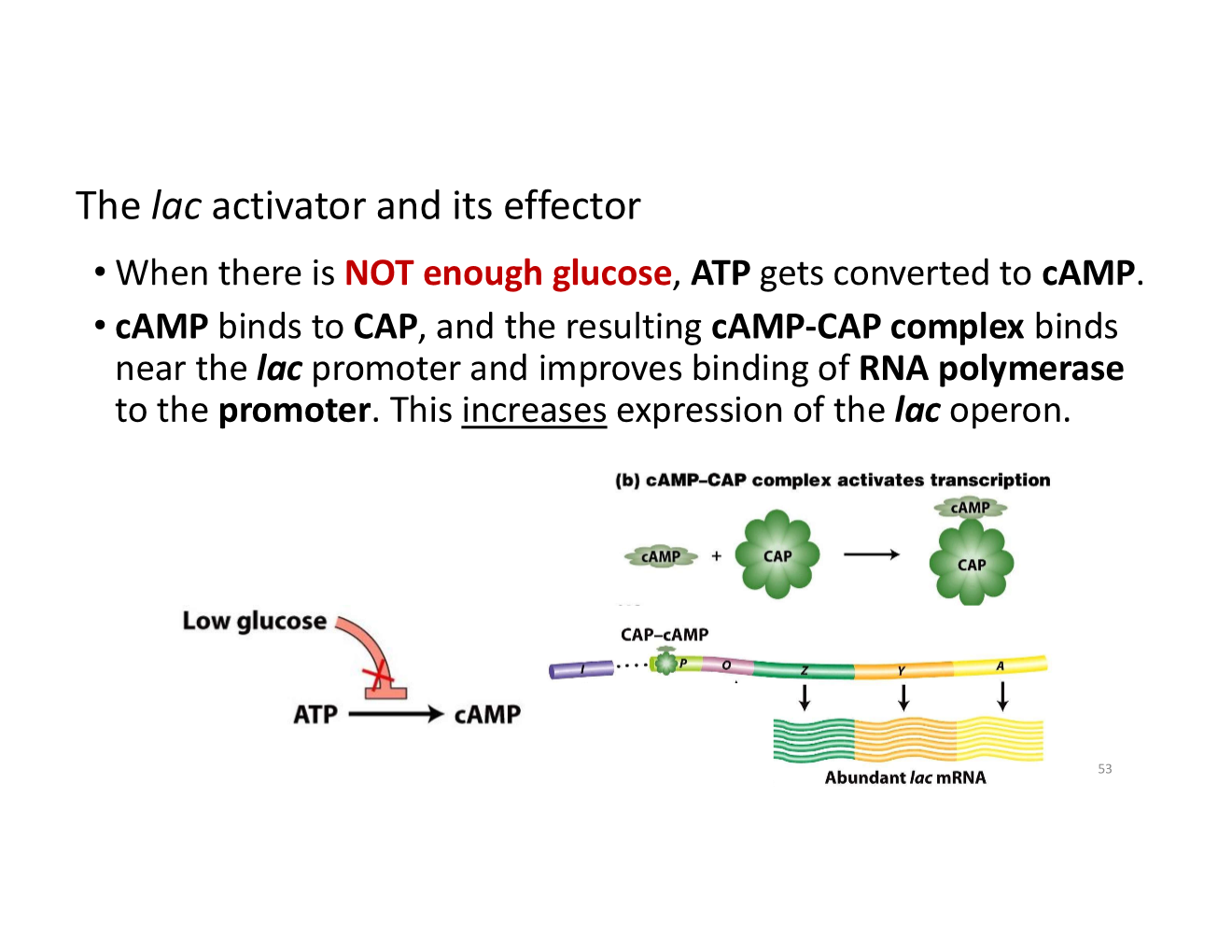
what happens when there is not enough glucose?
cells need more lac enzymes to use the available lactose as a carbon and energy source instead
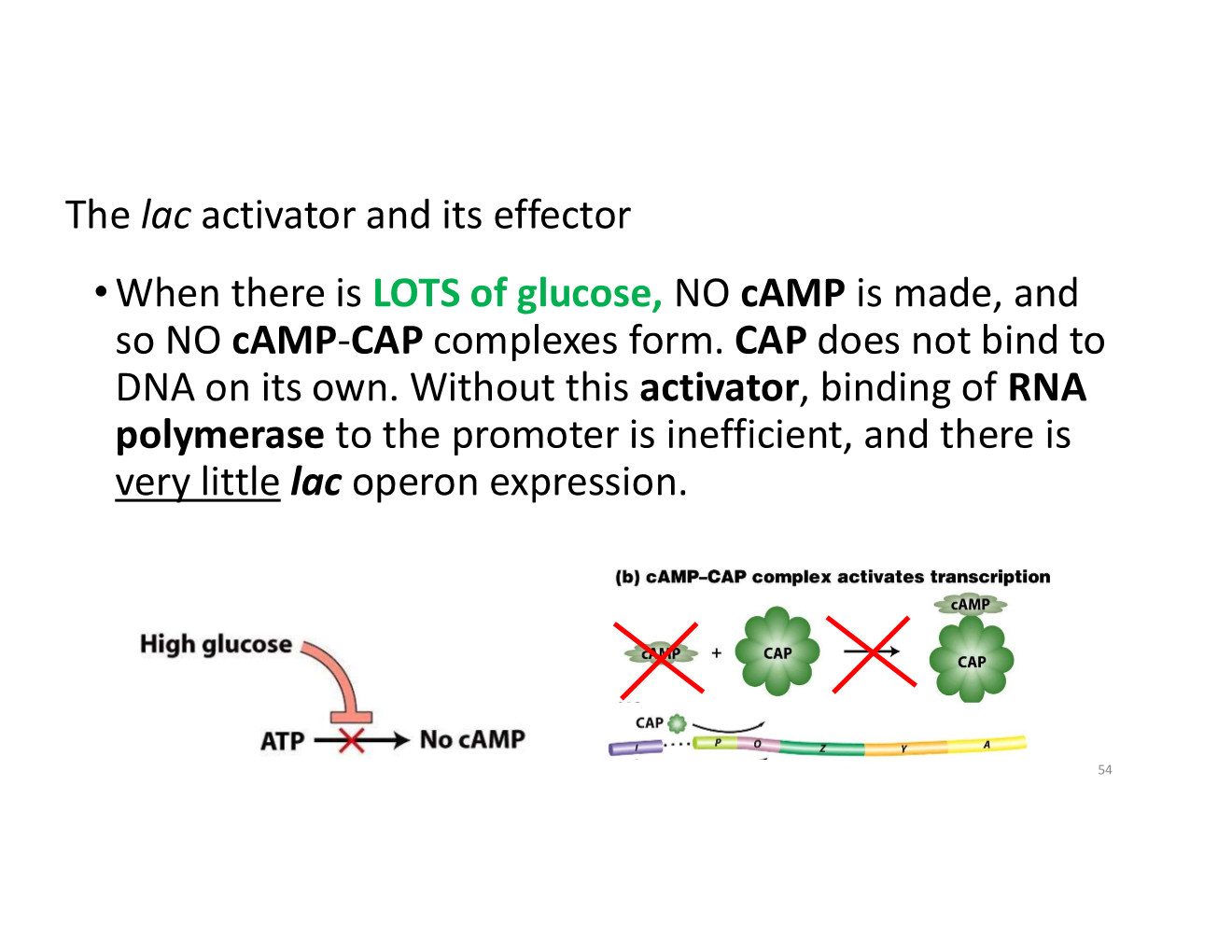
what happens when glucose is abundant?
there is much less expression of the lac operon
ultimate
digesting lactose takes more time/energy than digesting glucose
proximate
the activator protein is not bound to the lac operon
activators and repressors
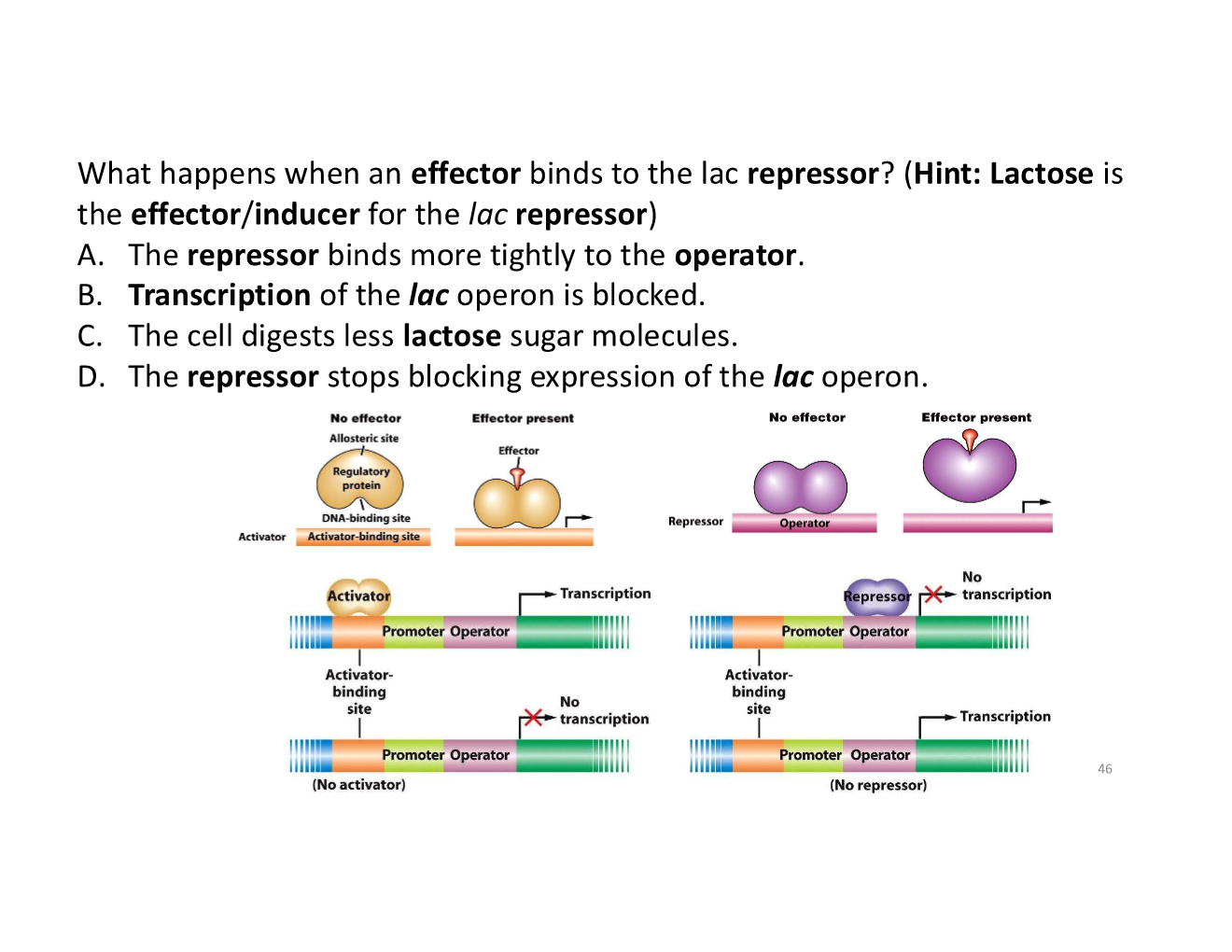
D. the repressor stops blocking expression of the lac operon
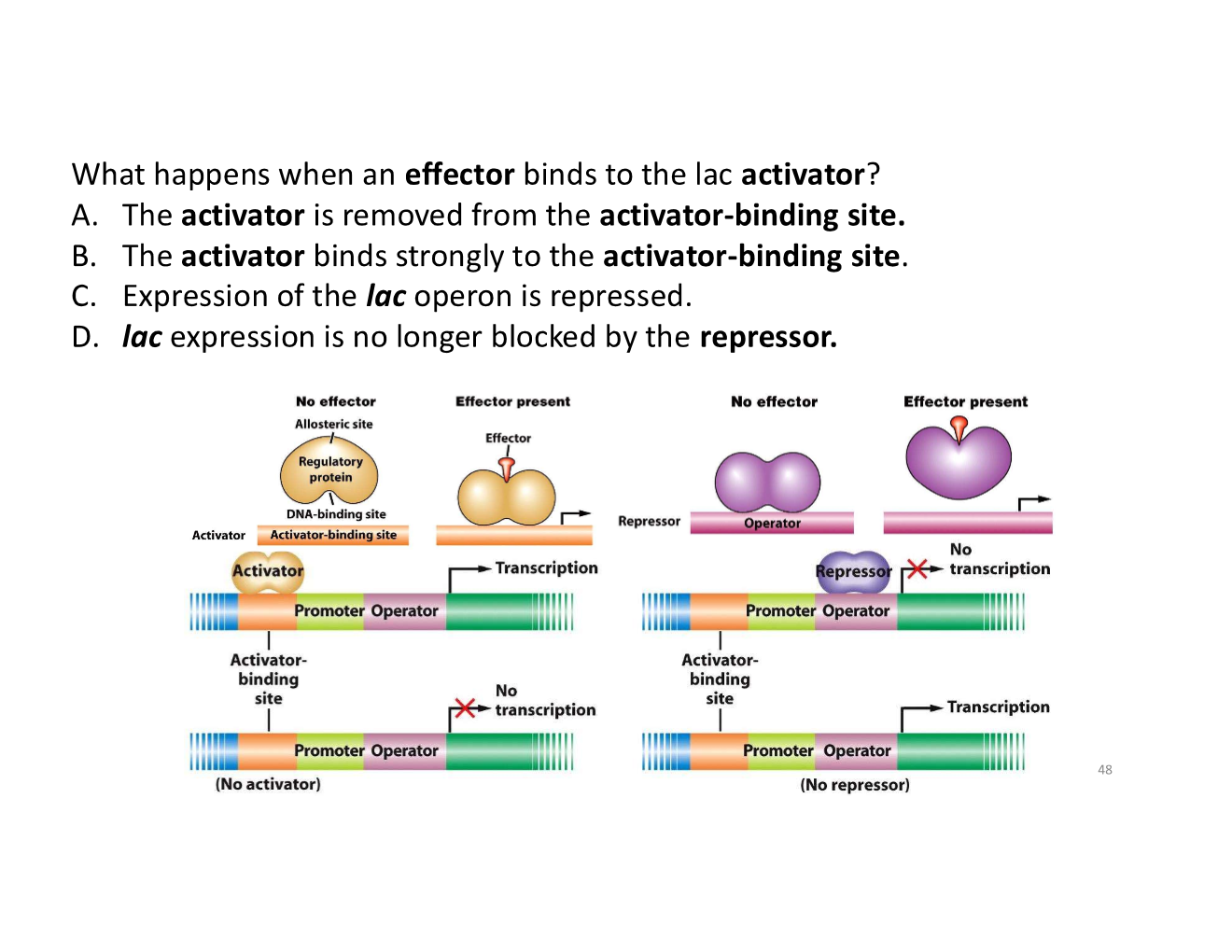
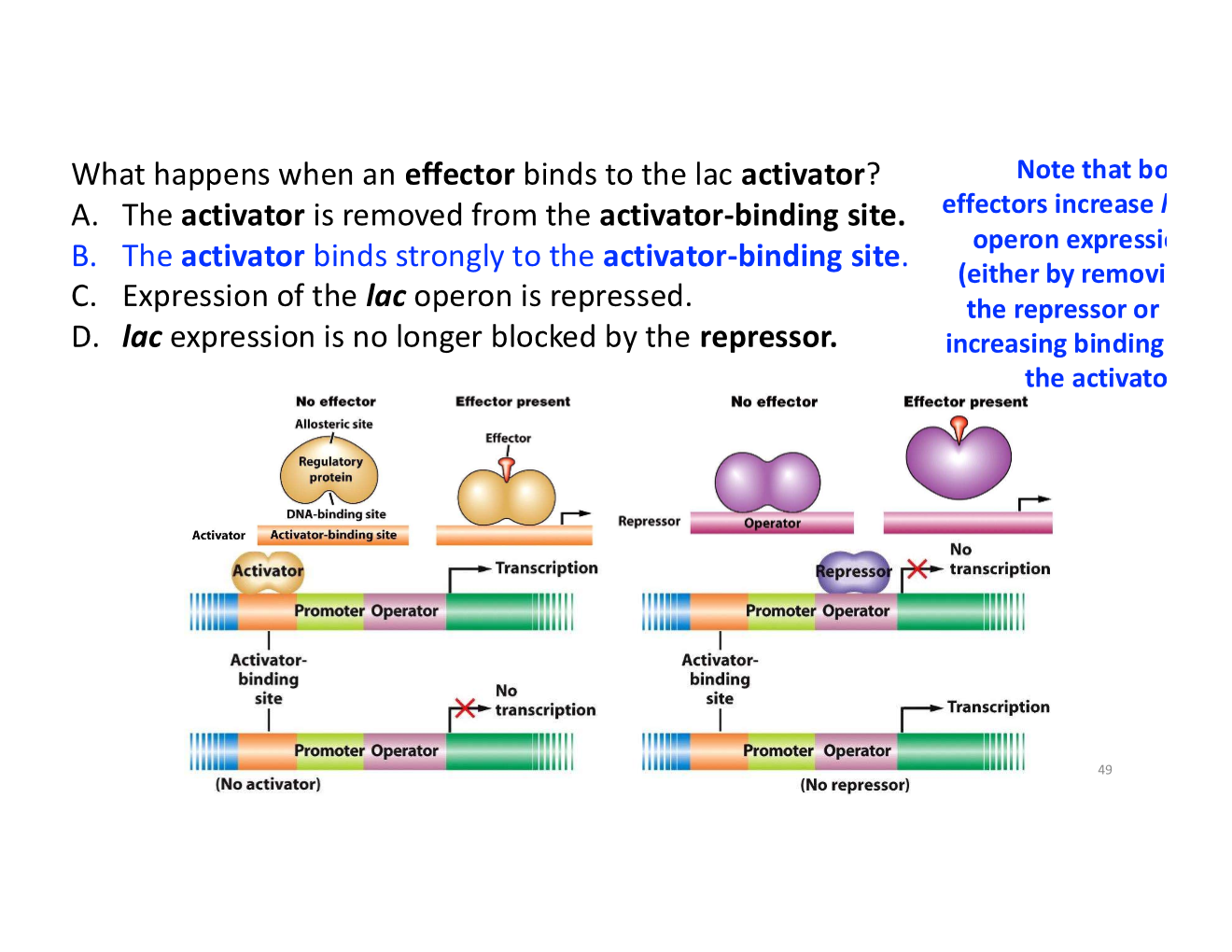
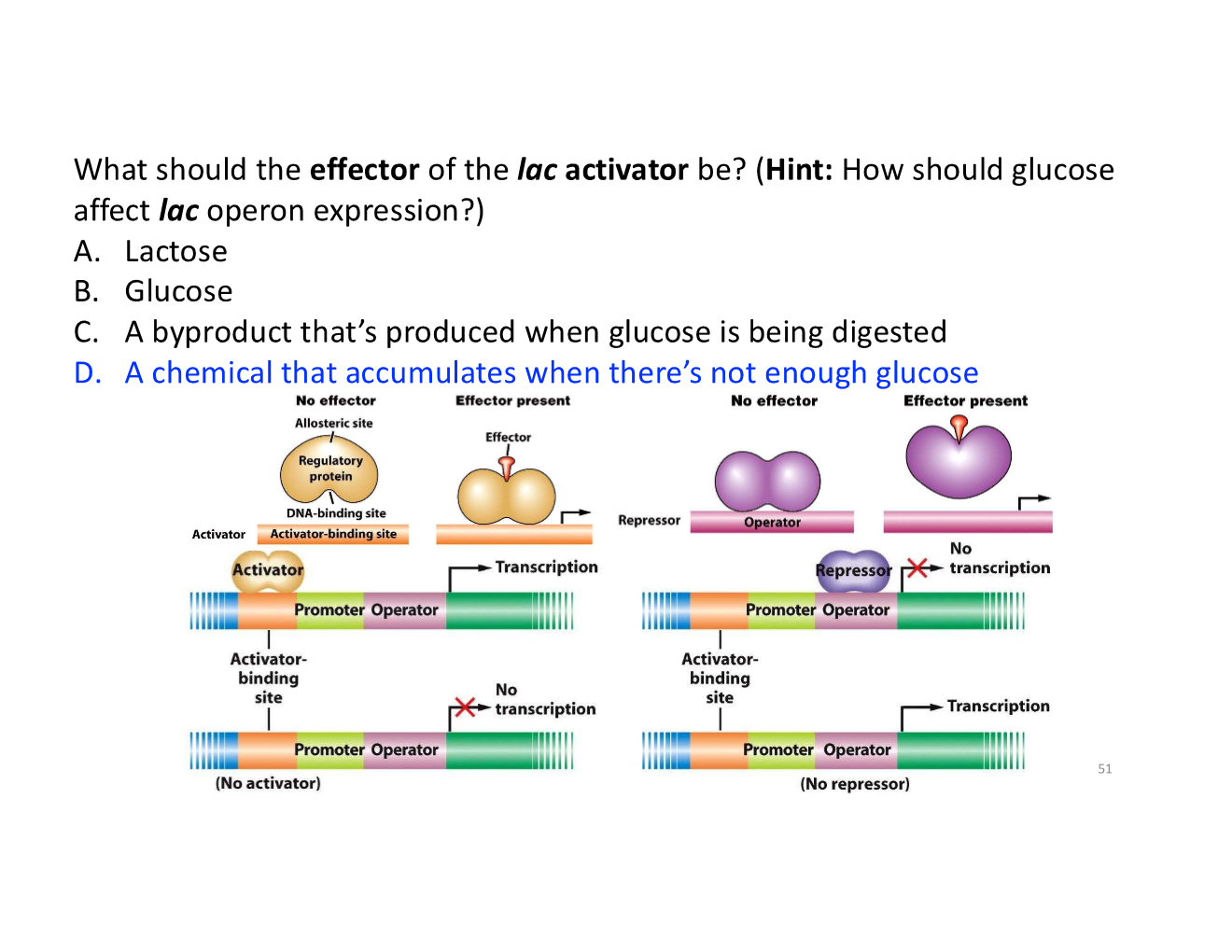
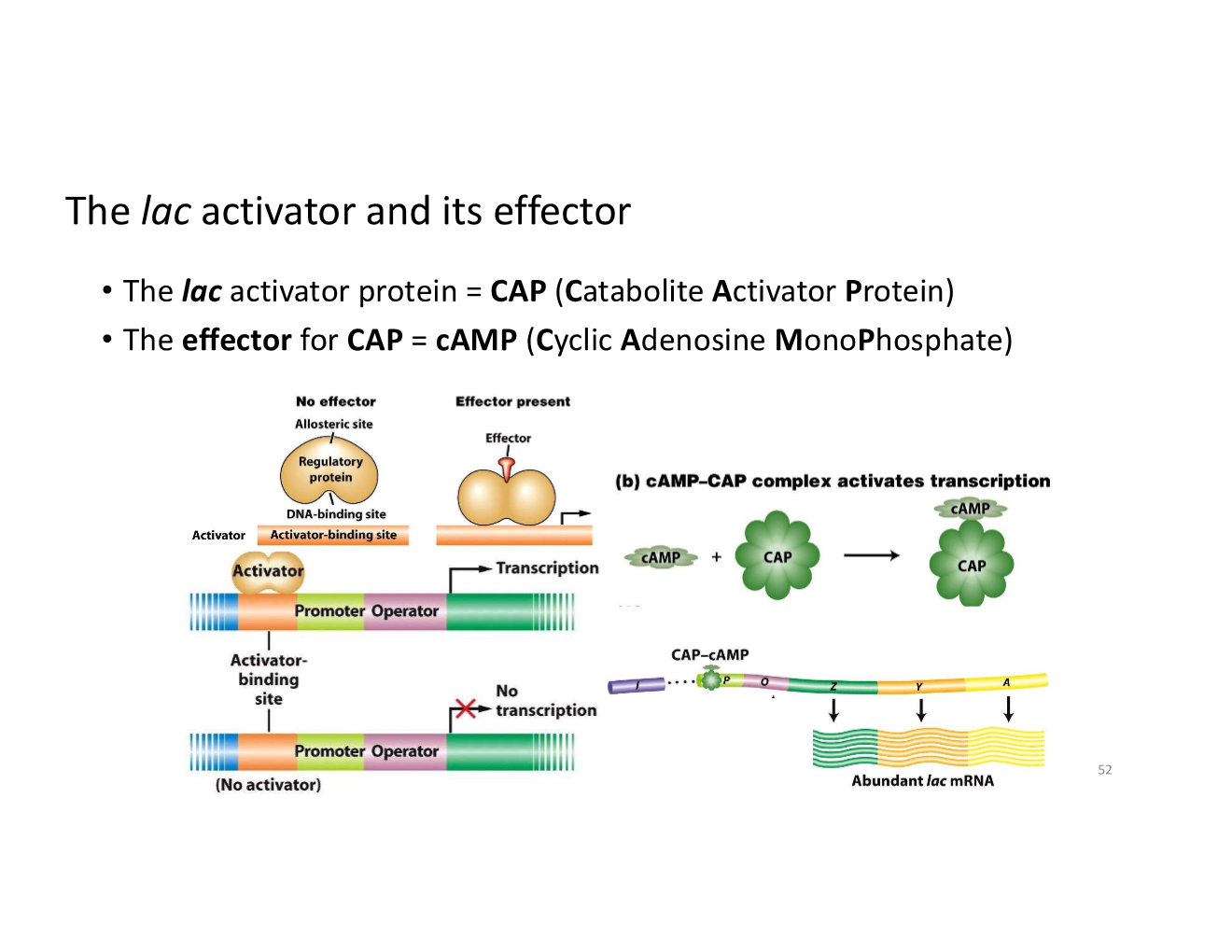
the lac activator and its effector
the lac activator and its effector when there’s not enough glucose
the lac activator and its effector when there’s lots of glucose

A. no expression

B. Very little expression


ara operon
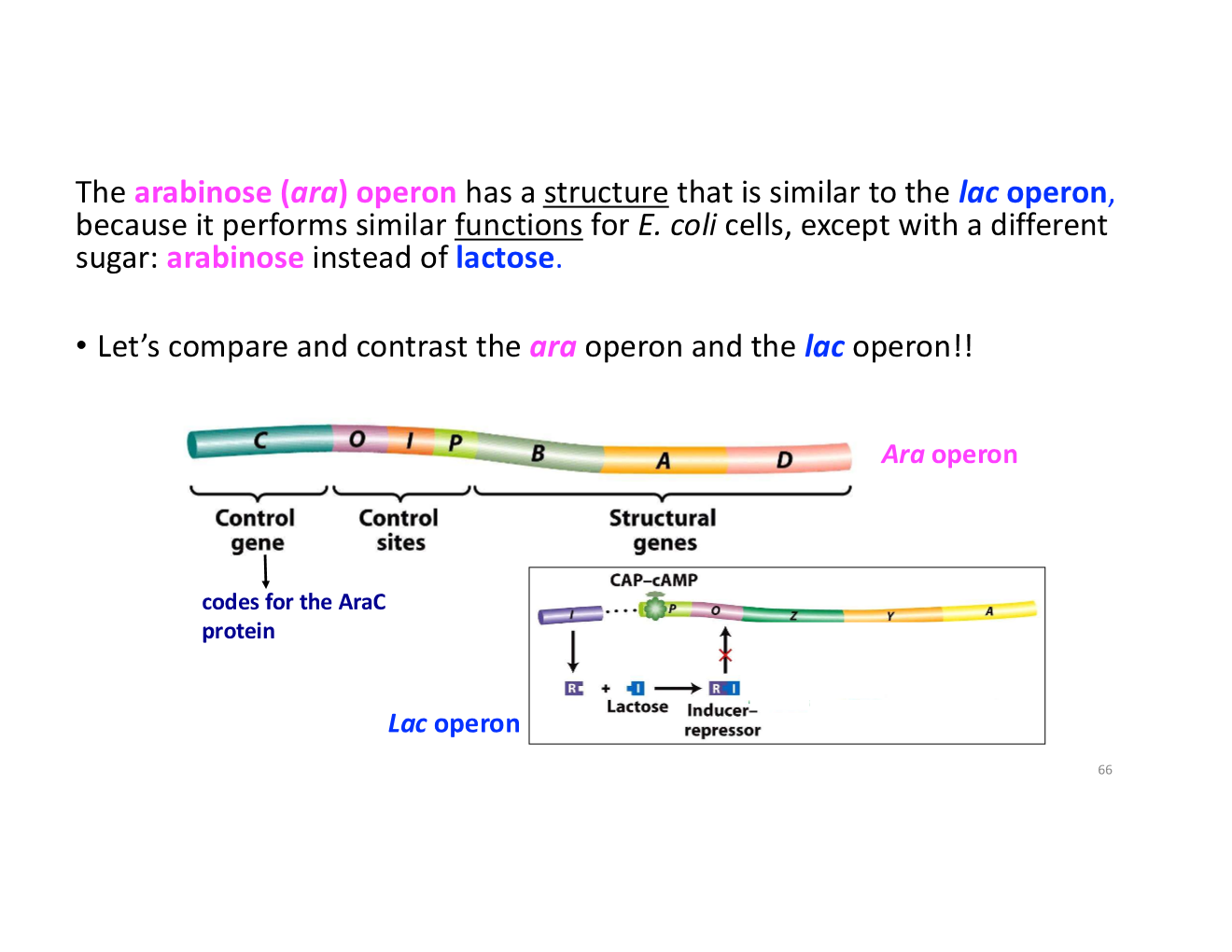
ara operon vs lac operon
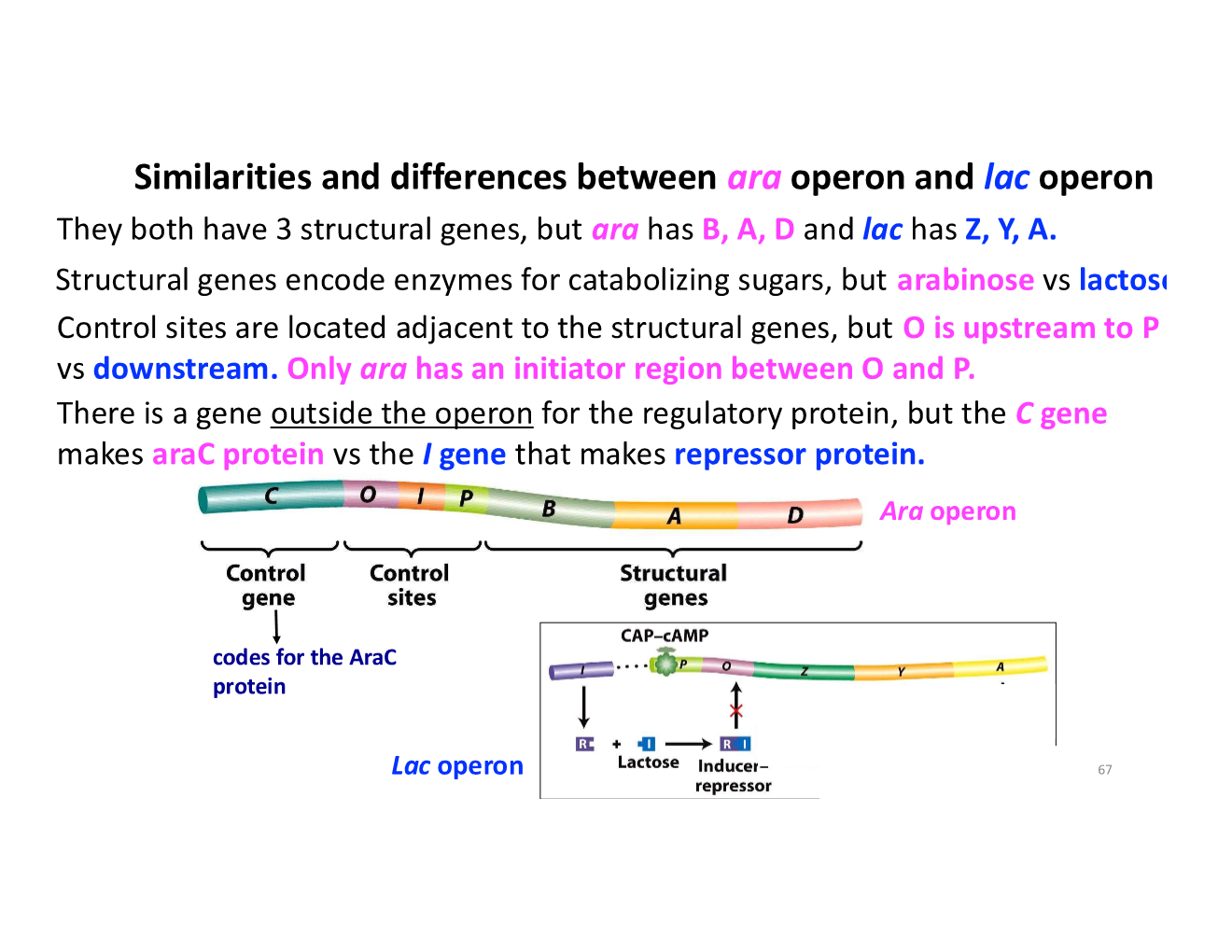
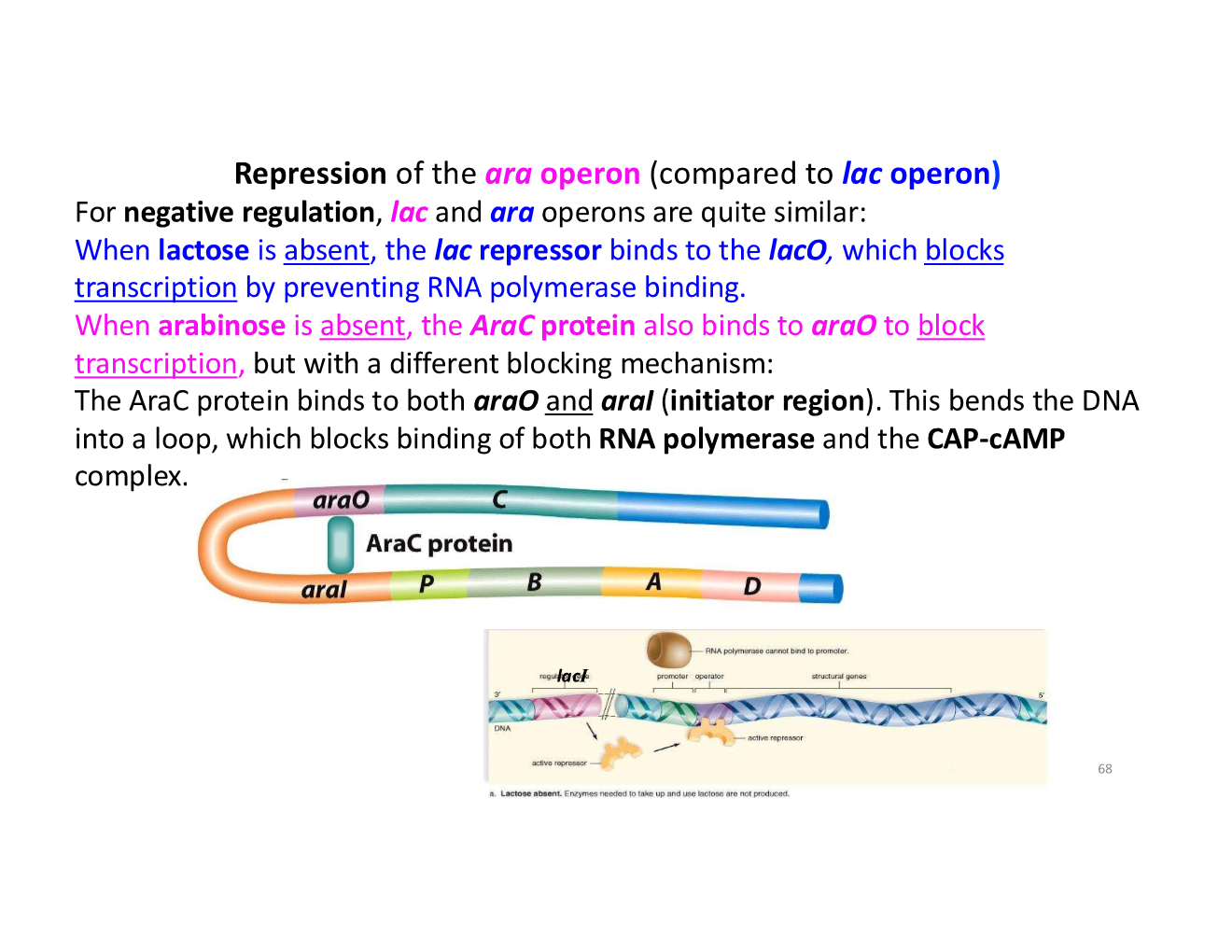
repression of the ara operon vs lac operon
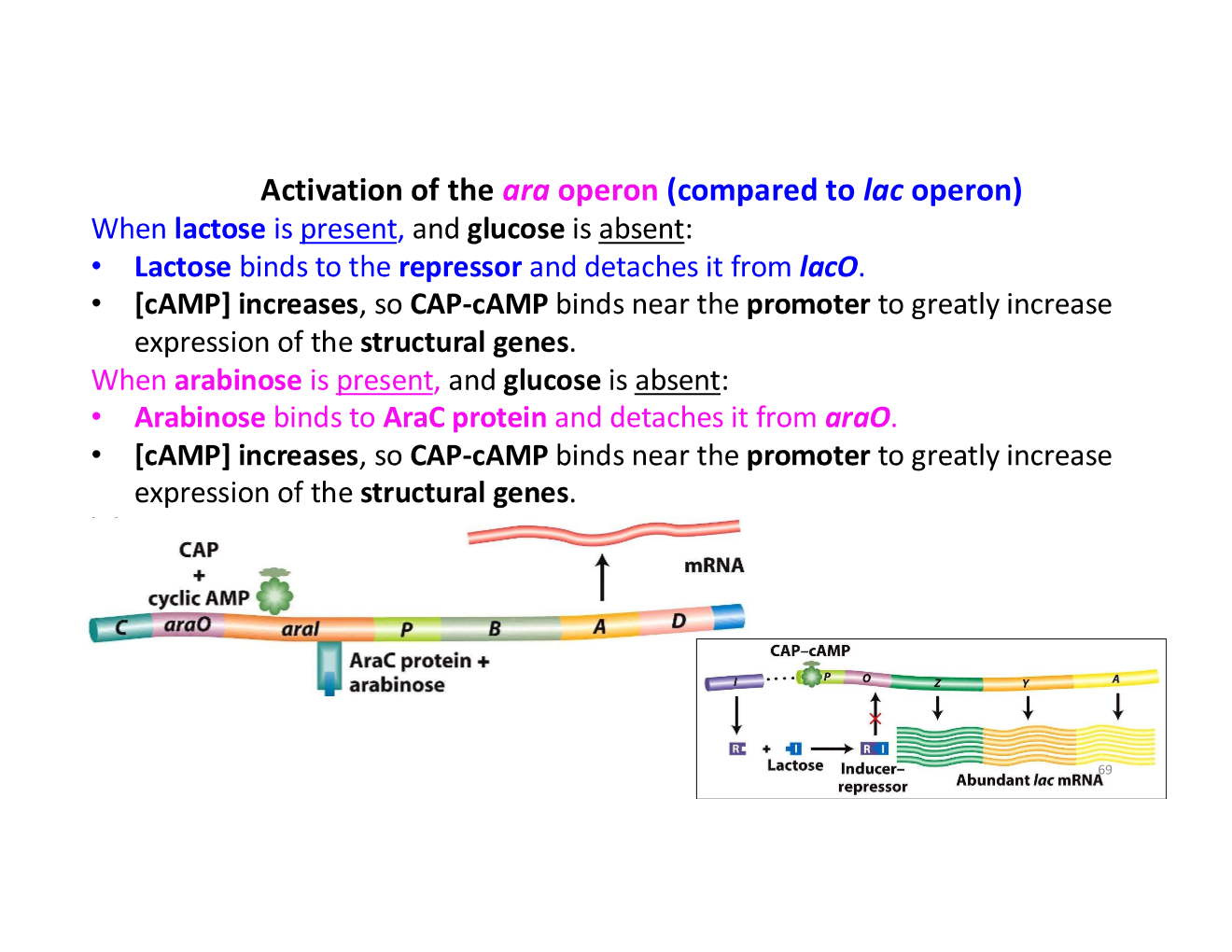
activation of the ara operon vs lac operon
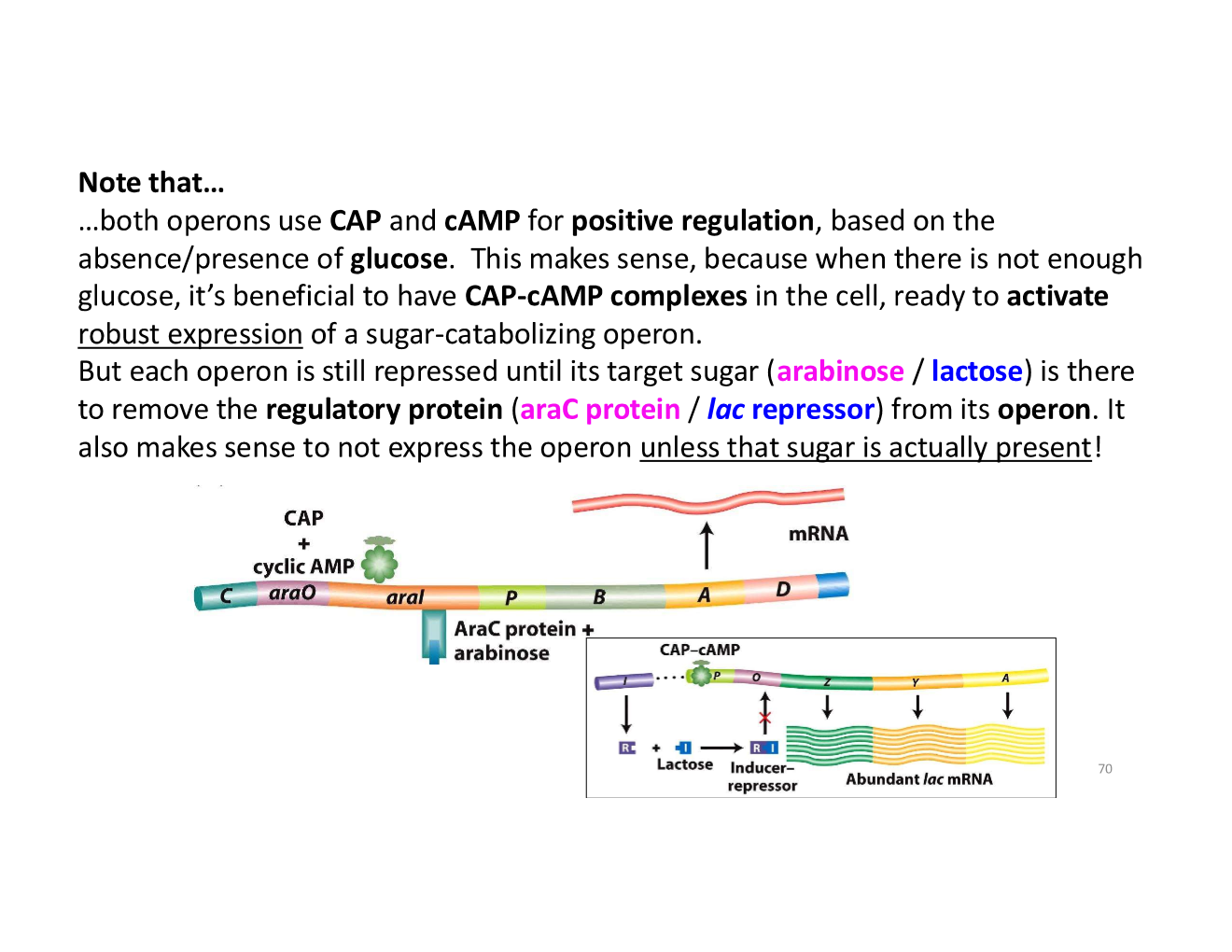
why does it make sense that both the ara operon and lac operon use CAP and cAMP for positive regulation?
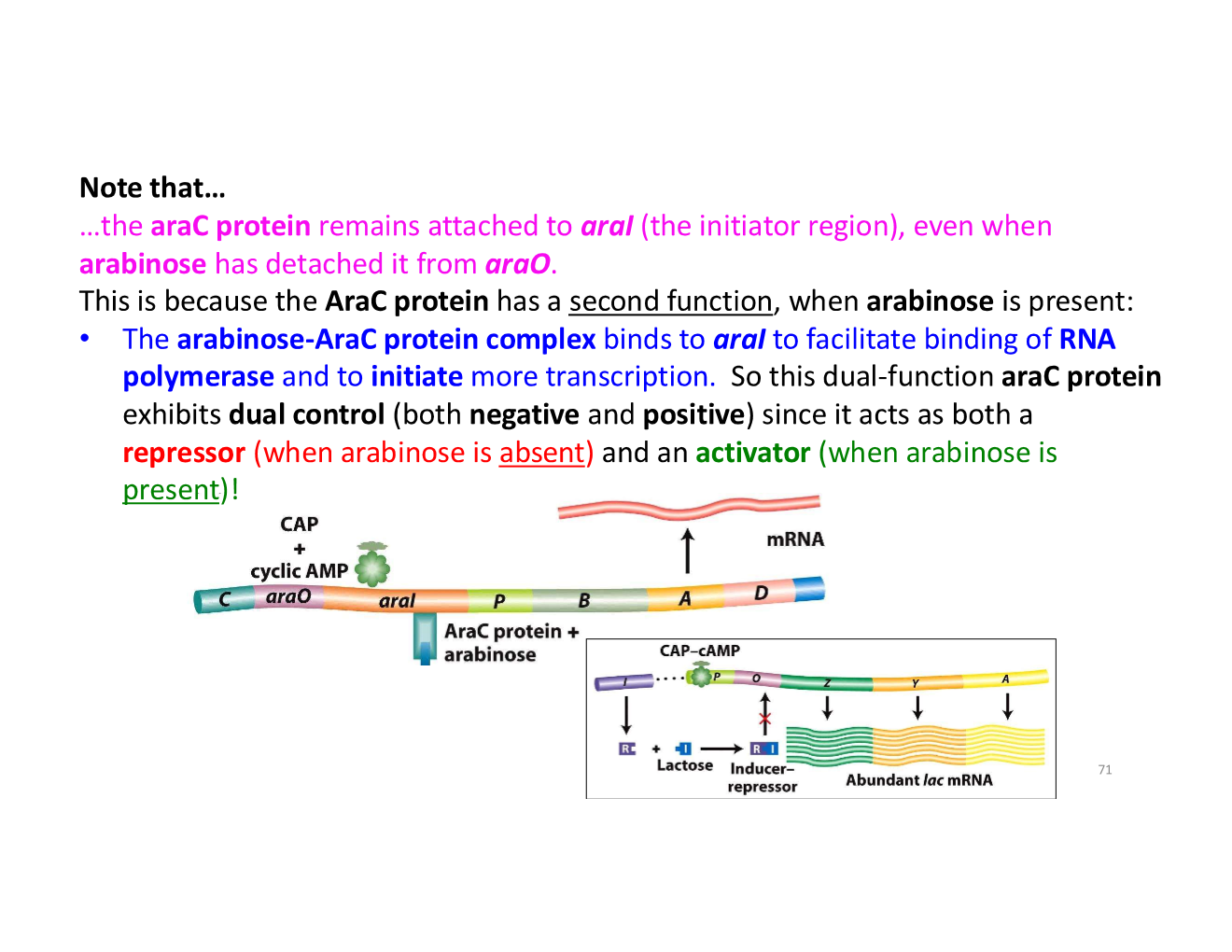
why does the AraC protein remain attached to aral?
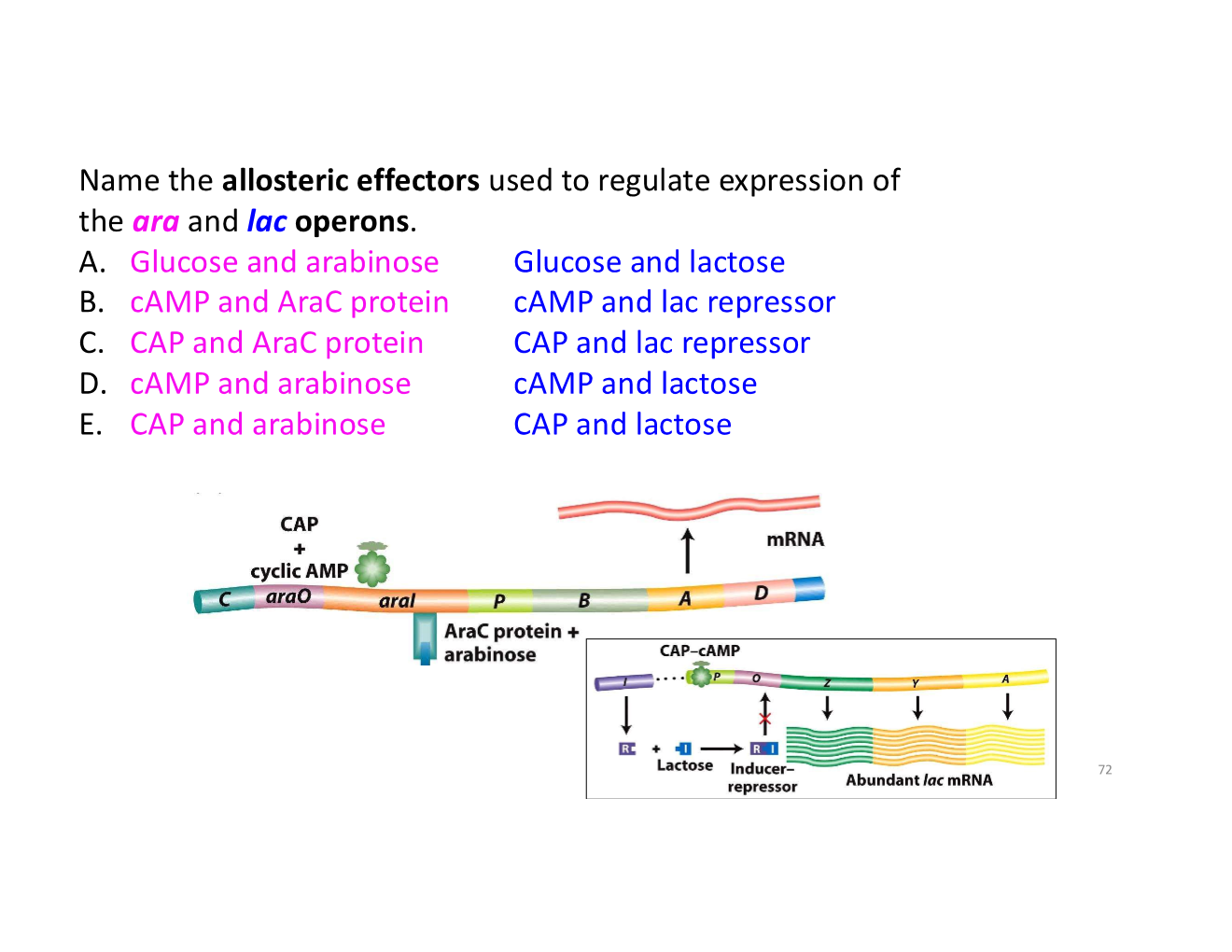
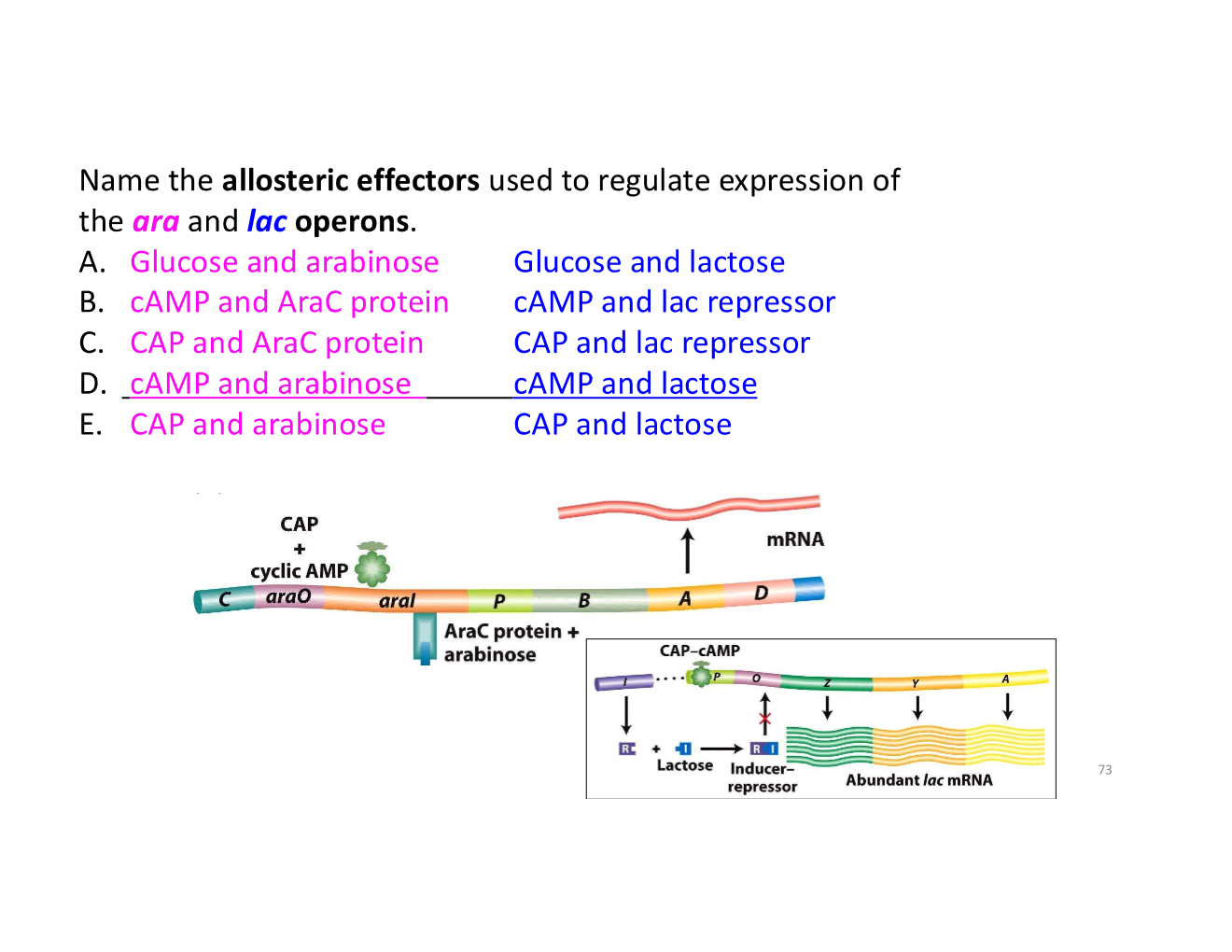
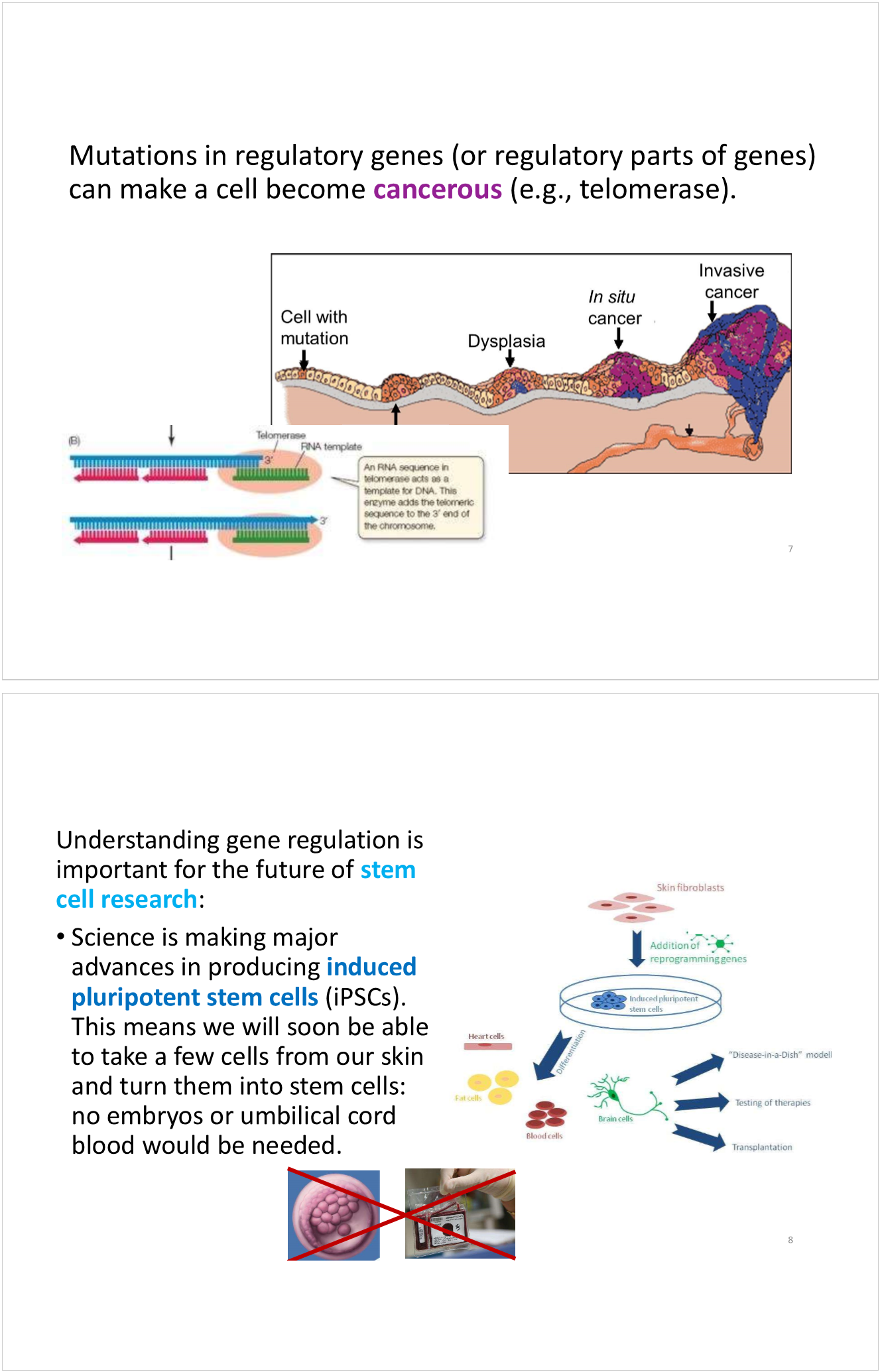
coordinated control of gene expression with operons
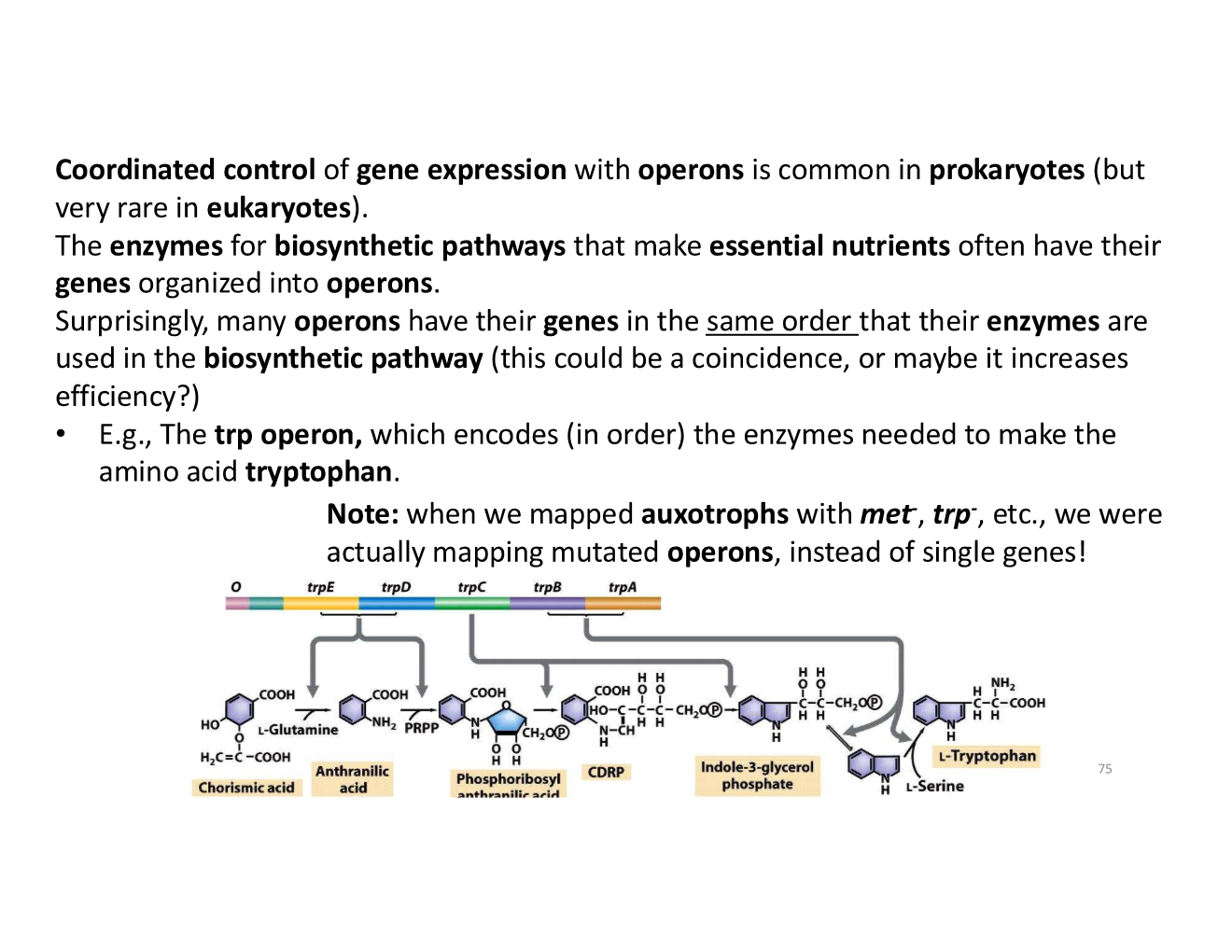
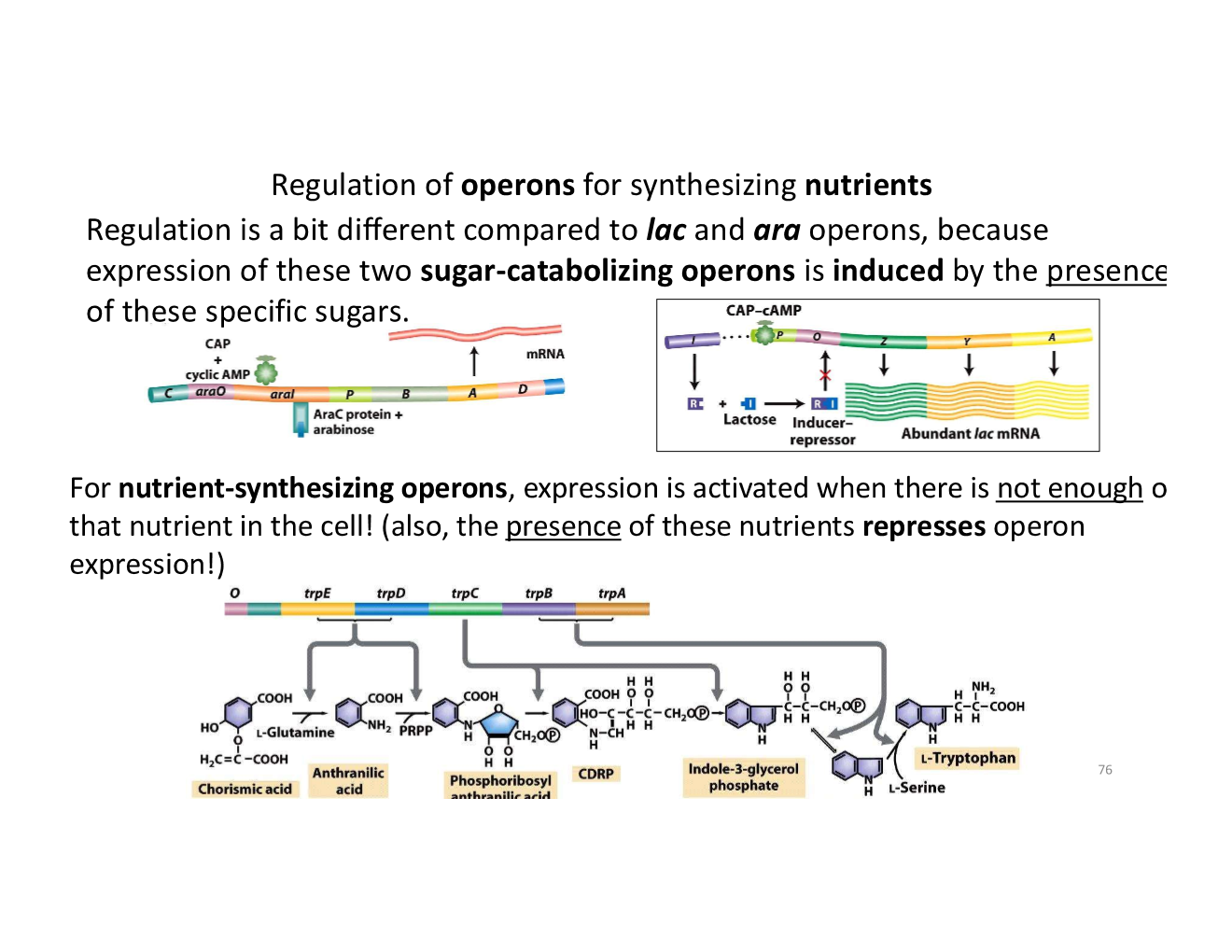
regulation of operons for synthesizing nutrients
what are the two mechanisms for regulation of the trp operon?
repression and attenuation
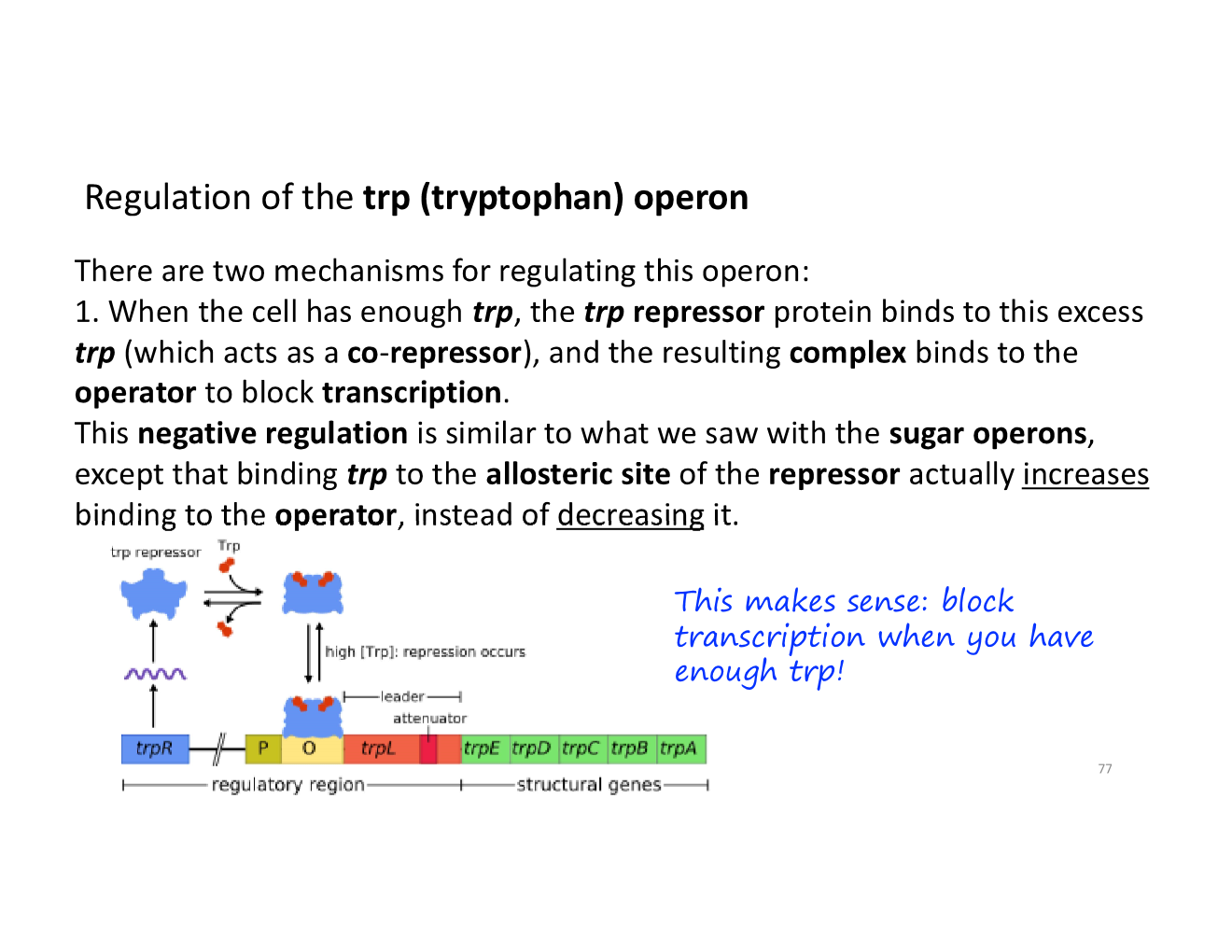
regulation of the trp operon with repression
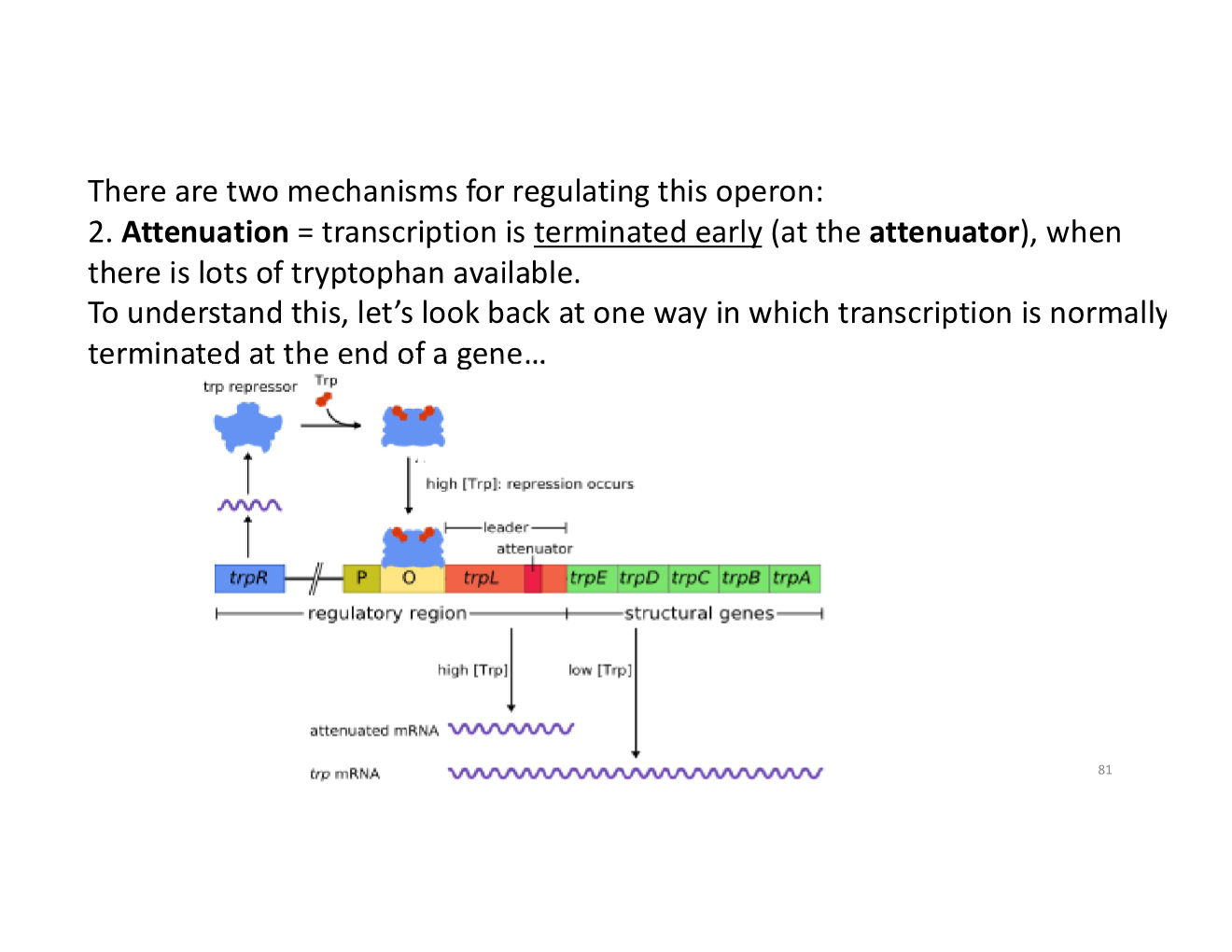
regulation of the trp operon with attenuation
what kind of control is the trp repressor an example of?
a repressible system (something in the environment can repress gene expression)
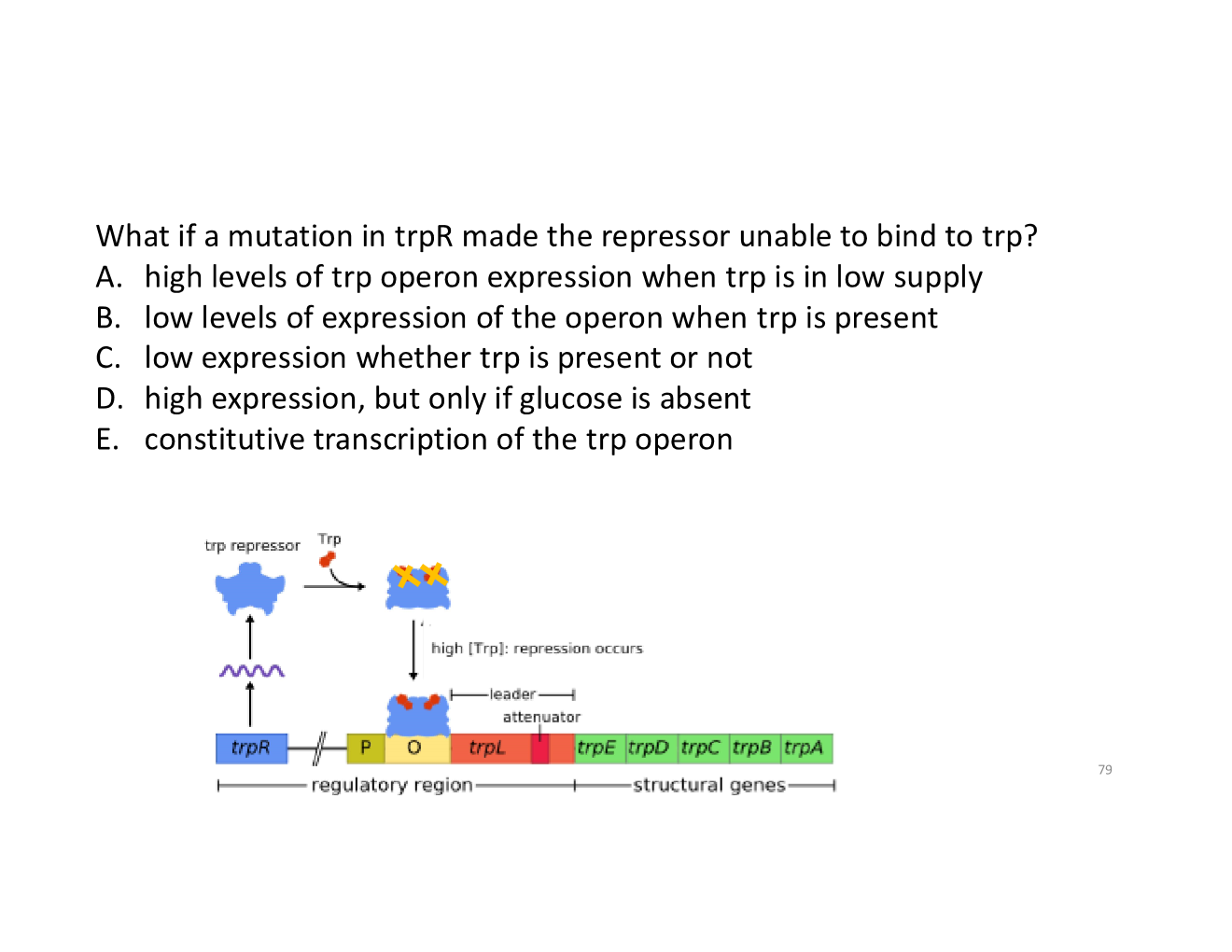
E. constitutive transcription of the trp operon
how does termination mechanism of transcription relate to trp operons?
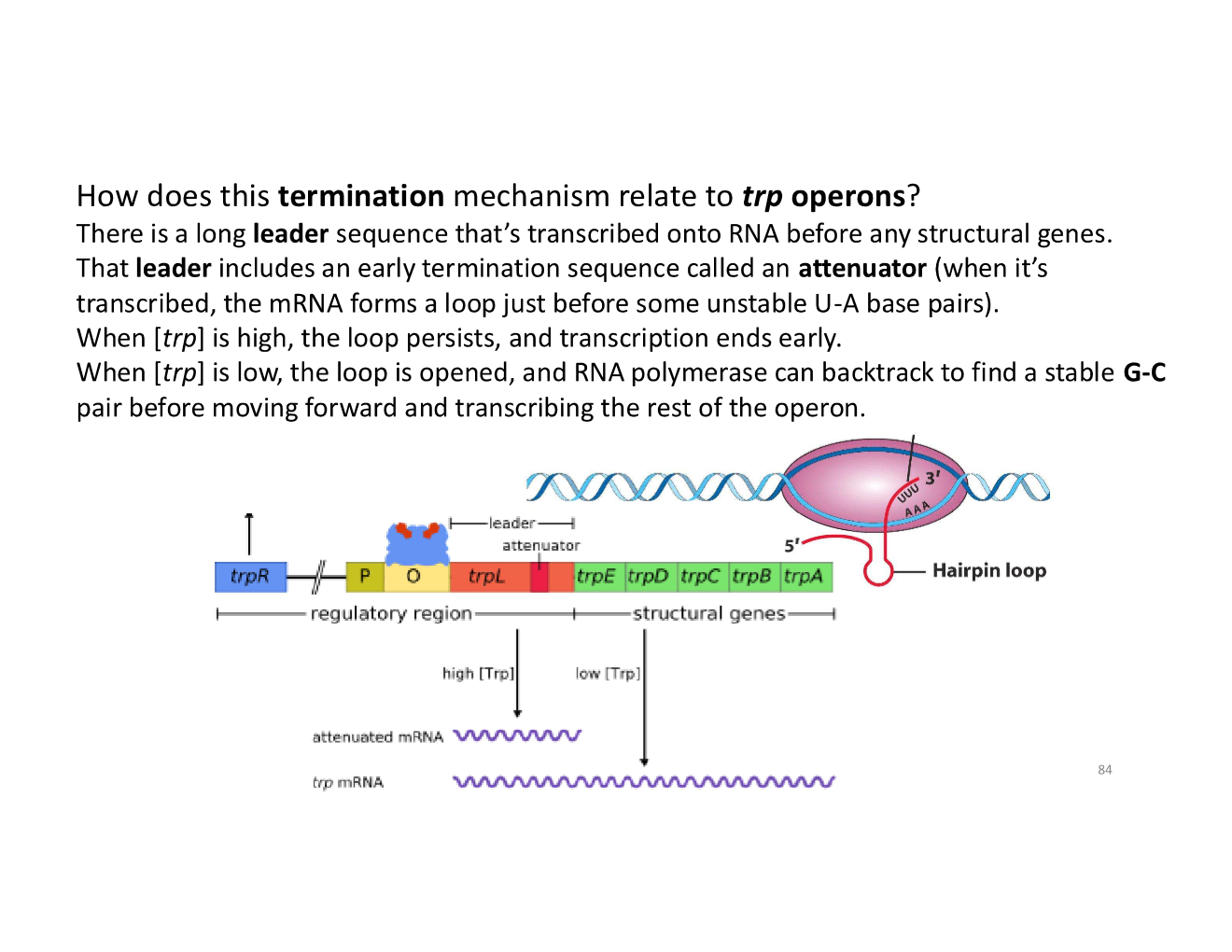
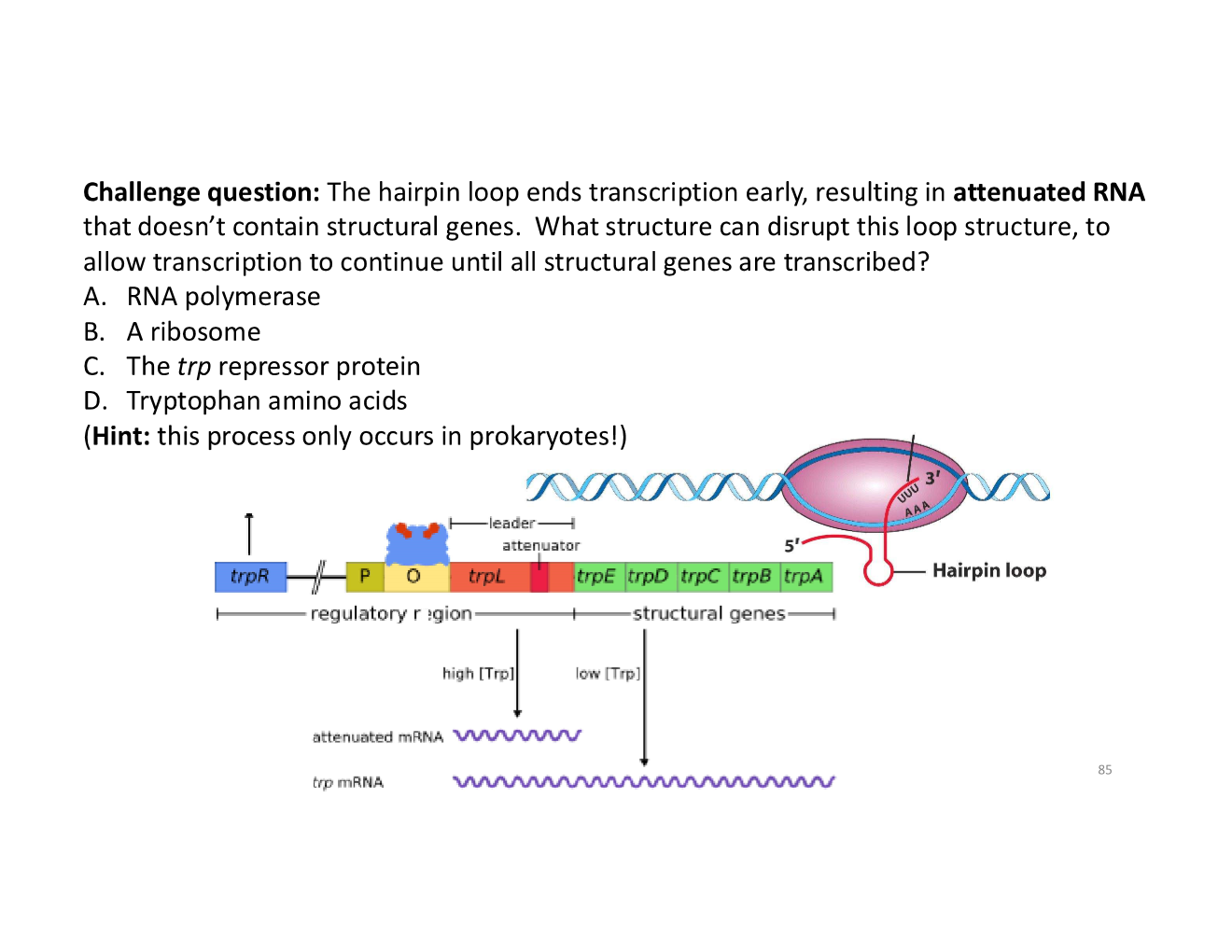
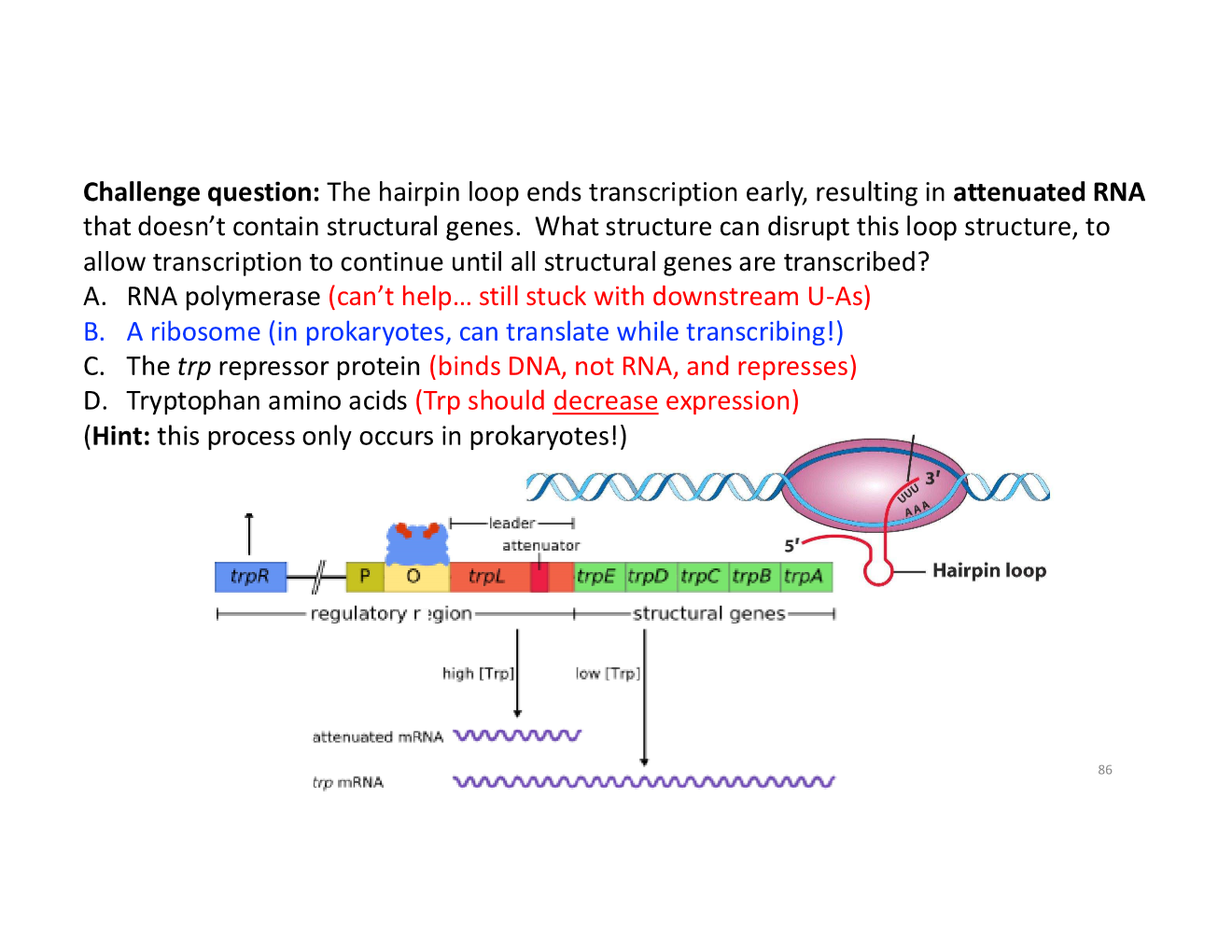
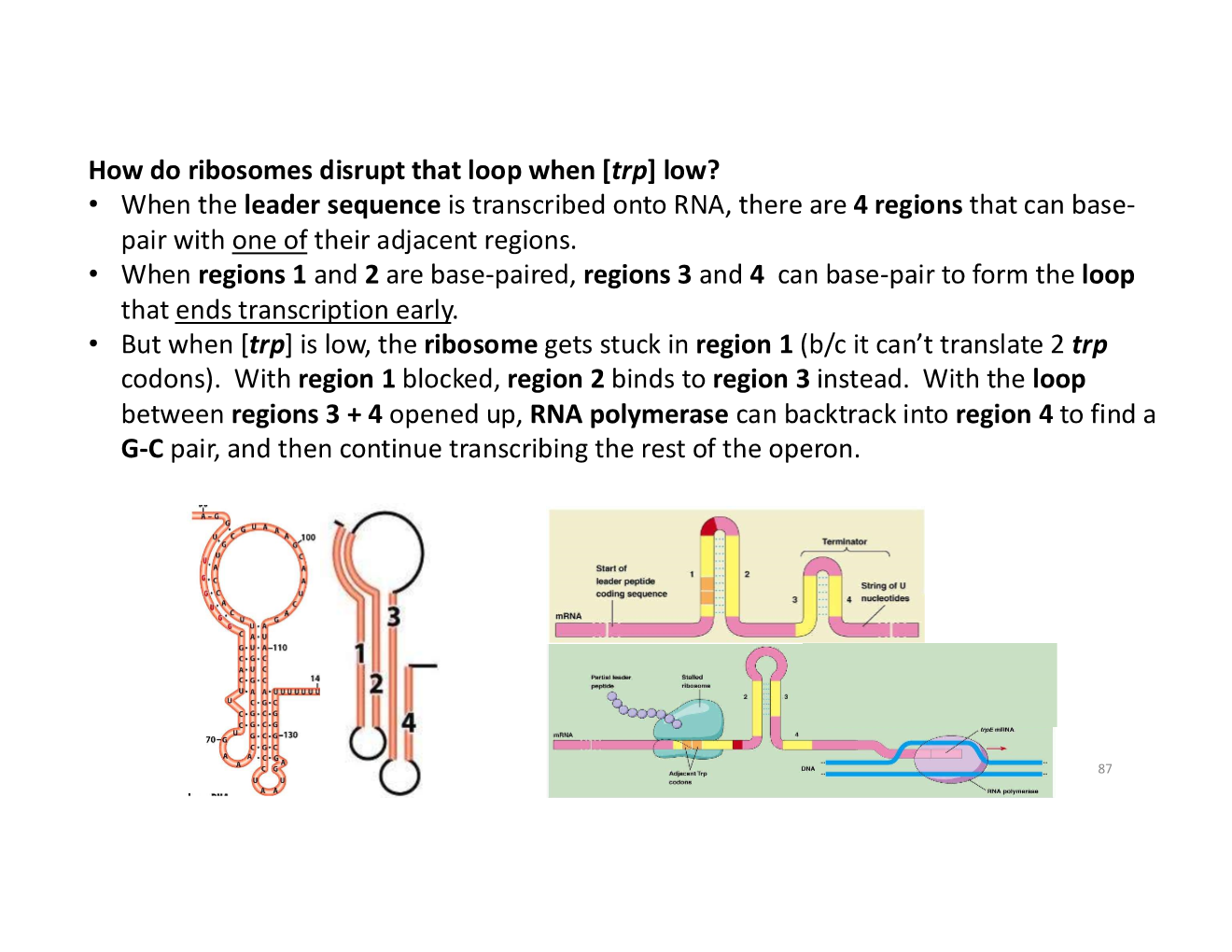
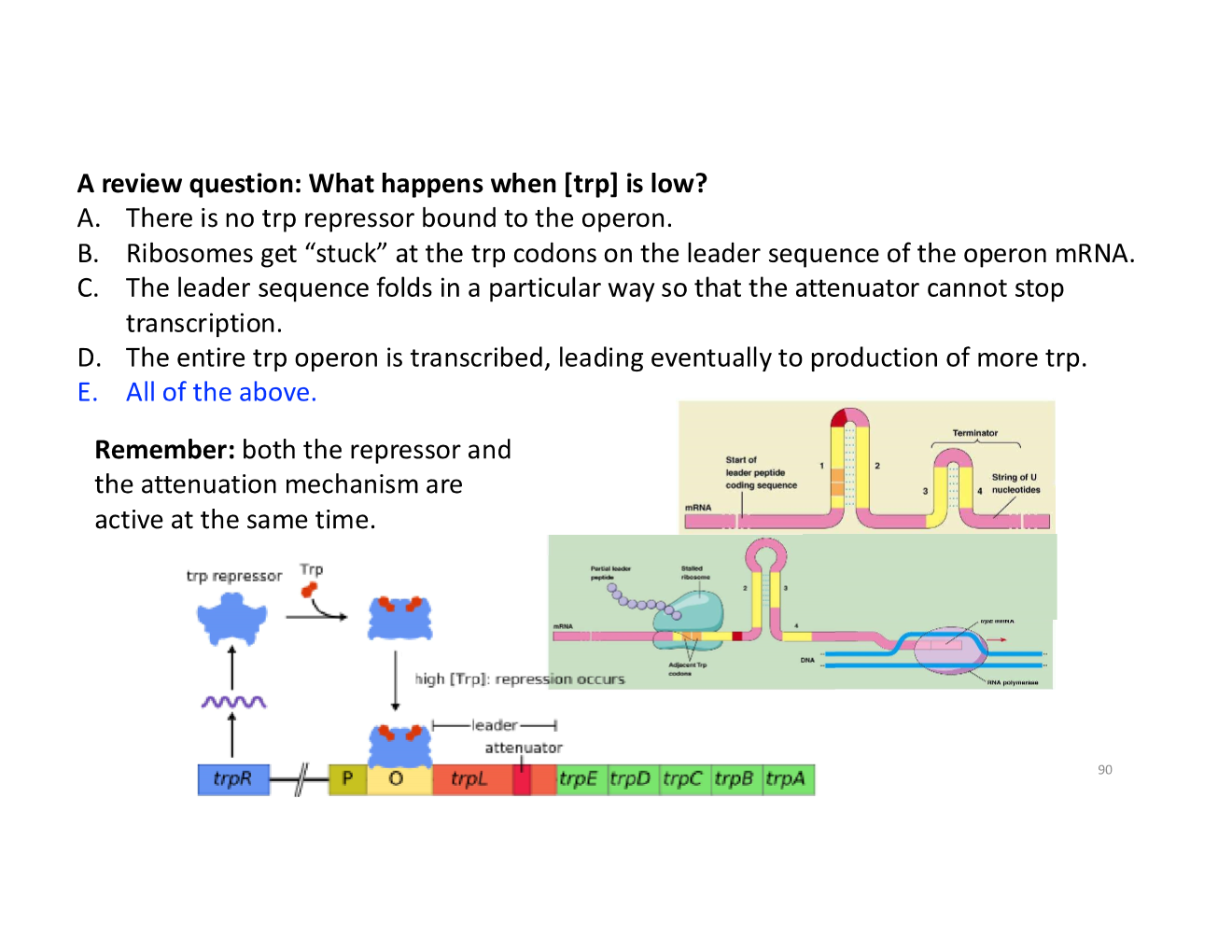
how do ribosomes disrupt the hairpin loop when [trp] low?
what happens when [trp] is high?
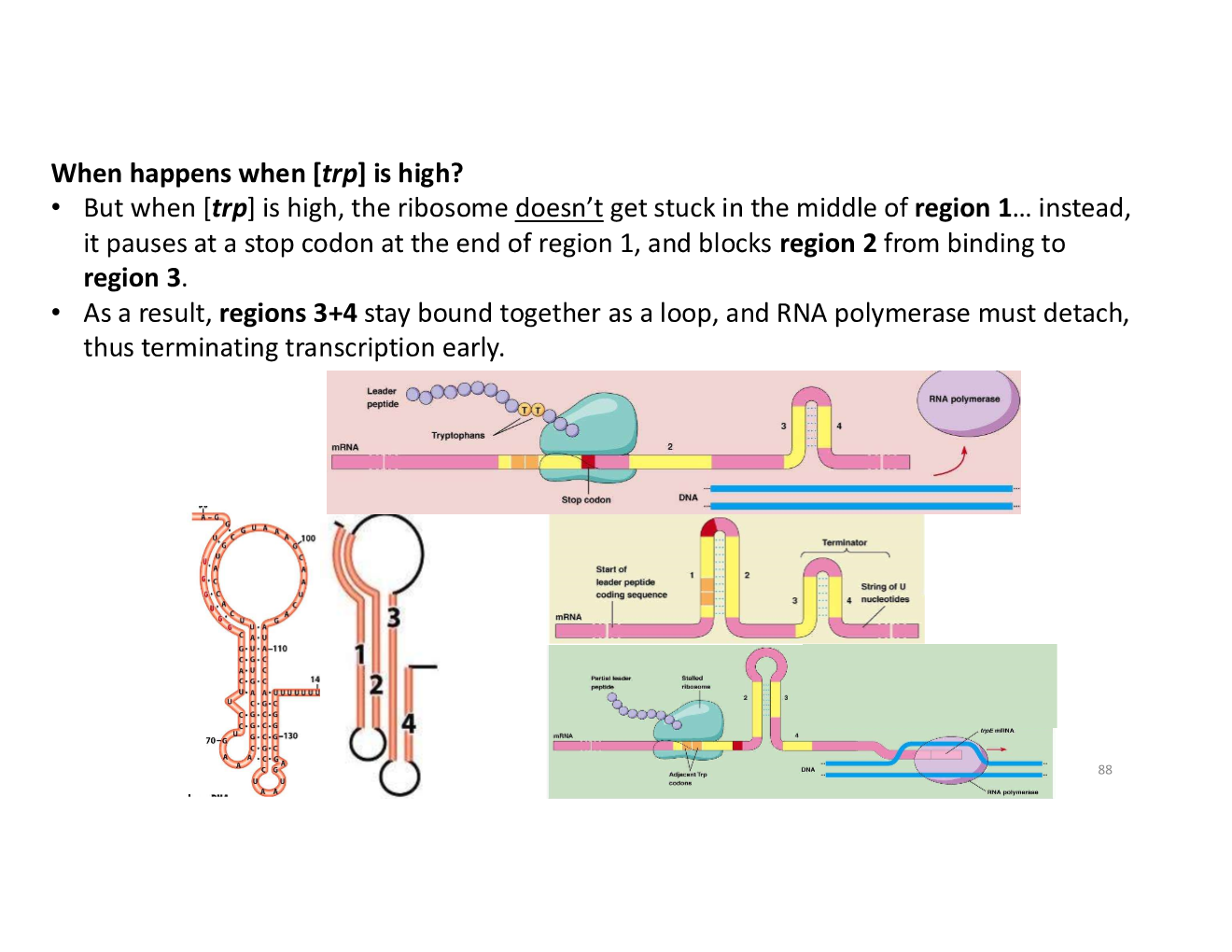
what happens when [trp] is low?
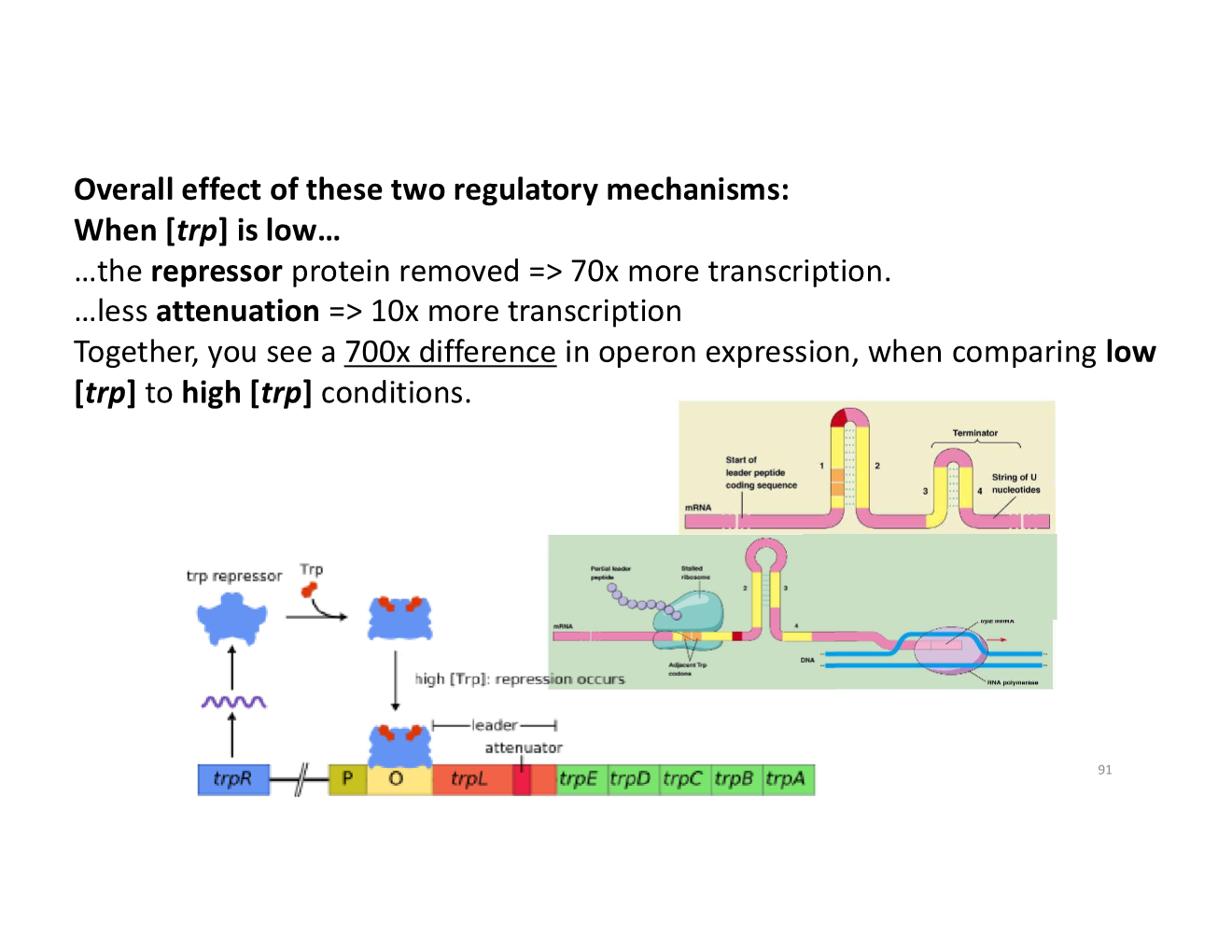
what is the overall effect of the two regulatory mechanisms?
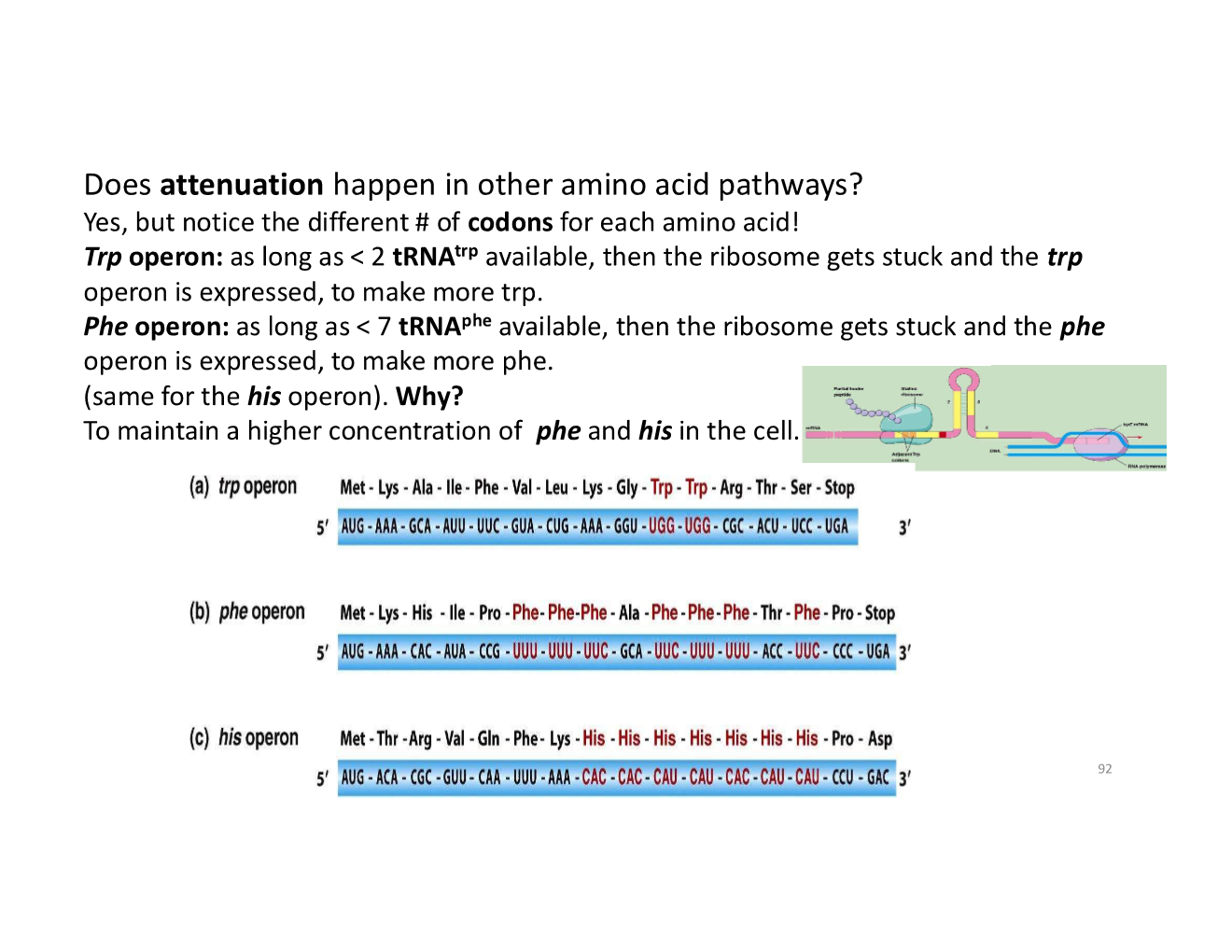
does attenuation happen in other amino acid pathways?