Biomedical Electrodes and Sensors
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Electrodes
should be made of metals which resist corrosion and oxidation
Pt, Au, Ag
Type of electrodes
Superficial (disc / cup) electrodes
Needle electrodes
Micro-electrodes
Superficial (disc / cup) electrodes (10)
ECG (Electrocardiography):
Ag/AgCl disposable surface electrodes
record electrical activity of the heart
EMG (Electromyography):
Ag or Pt discs
measure muscle electrical activity
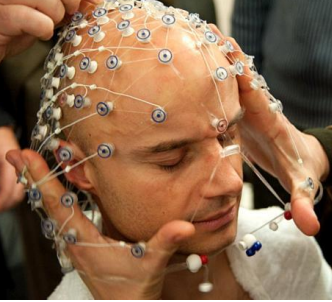
EEG (Electroencephalography):
Pt cup electrodes
glued to the scalp
an electrolyte gel is injected into the electrode cup for better conductivity
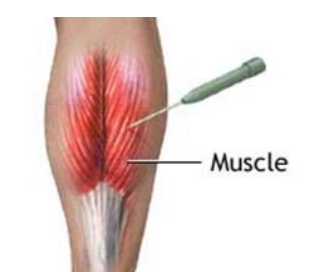
Needle electrodes (2)
Invasive electrodes used to record biovoltages from a small area of tissue
fx.: individual nerves and muscle fibers
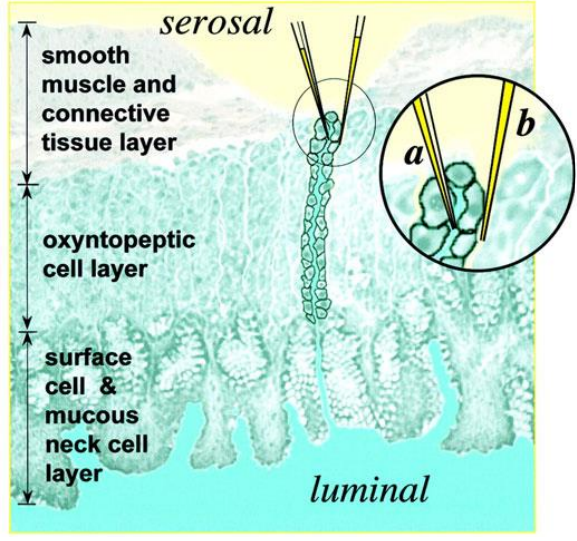
Micro-electrodes (3)
Used for biovoltages from individual cells
It is a glass capillary with an open end filled with an electrolyte of standard concentration
tip diameter: <0.5 μm
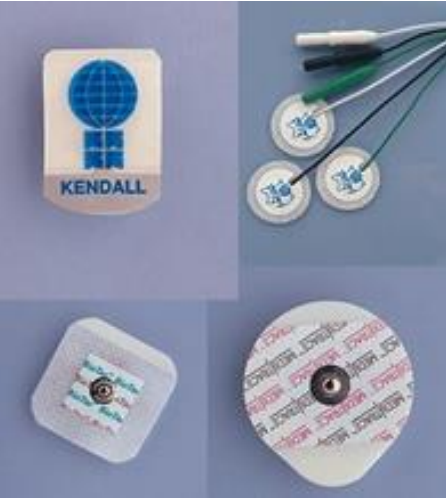
Superficial ECG Electrodes (photo)

Superficial EEG electrodes (photo)
Contact Voltage Problems in Superficial Electrodes
Electrodes can generate unwanted "contact voltages" when in contact with the body
Due to electrochemical reactions with skin fluids, sweat, and humidity
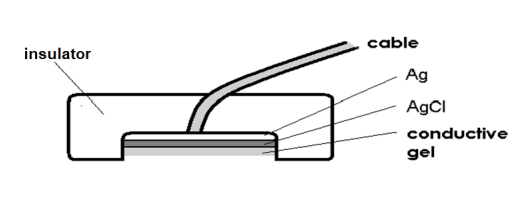
Polarisable electrodes
Produce variable contact voltage that changes over time
Create an uncontrolled variable bias, making them unsuitable for accurate measurements
Non-polarisable electrodes
Generate a constant contact voltage, providing a measurable and consistent bias
Suitable for accurate measurements as the bias can be accounted for
Ag-AgCl electrode is used
Sensors Research Goal
To create sensors that can measure every variable in the human body, enhancing diagnostic and monitoring capabilities
Sensors design (3)
need to be protected from body fluids
designed to avoid insertion biases
Act of measurement should not alter the value of the quantity being measured, ensuring reliability and accuracy in data collection
Main Sensor Categories (7)
Mechanical variables
force, pressure, velocity
Temperature
Electromagnetic radiation
all ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum
Chemical and biochemical concentrations
Others: biomagnetism, gas-flow
Force (and Pressure) Sensors most common type based on
Piezoelectric Crystals - voltage produced across certain crystals when force/pressure is applied

Force (and Pressure) Sensors used in (4)
balances
pressure measurement devices
force-platforms
ultrasound imaging devices
Force (and Pressure) Sensors Pressure monitoring (5)
intravascular
urodynamic
intracranial
intra-uterine
intra-ocular
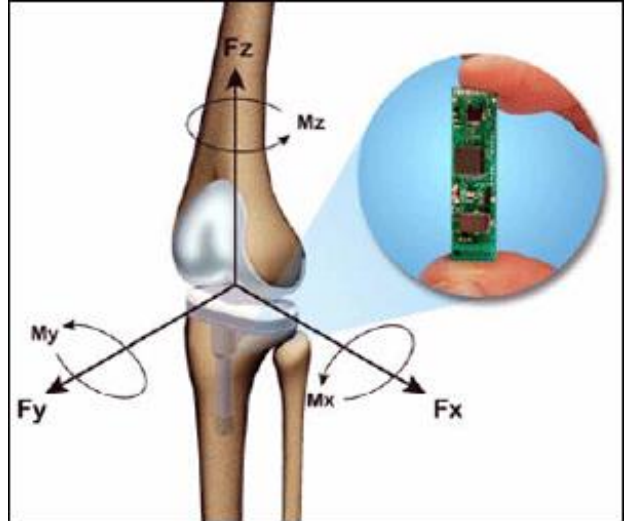
Micro force Sensors
implanted in knee joint and provide ongoing information on forces and torques in joint
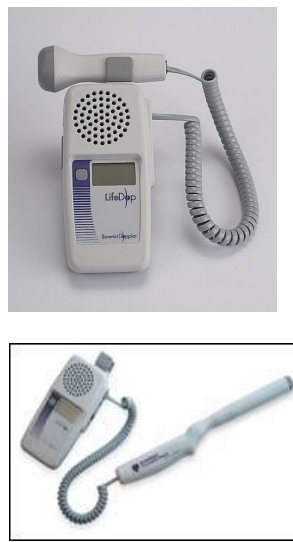
Velocity Sensors general
Based on the Doppler Effect
change in the frequency of reflected sound waves from a moving object is proportional to the velocity of the object
Used for vascular measurements
fx.: EchoHeart
EchoHeart
first transvaginal audio Doppler probe
It is intended as an economical and convenient method to determine fetal viability in very early stages of pregnancy
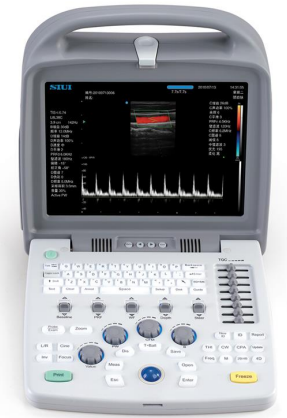
Velocity Sensors device
Red-orange colour: blood moving in one direction
Blue colour: blood moving in opposite direction (towards or away from sensor)
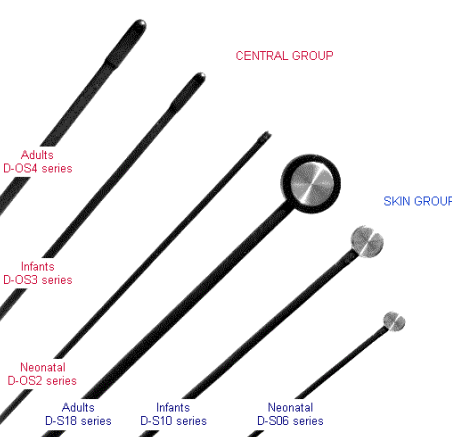
Temperature sensors
devices used to measure temperature in various environments and applications
used for central (nasopharynx - oesophagus - rectal) and skin temperature measurement
Temperature Sensors types
Semiconductors temperature sensors
Resistance wire temperature sensors
Lead zirconate titanate capacitors
Thermocouples
Semiconductors temperature sensors
change in electrical conductivity of semiconductor with temperature
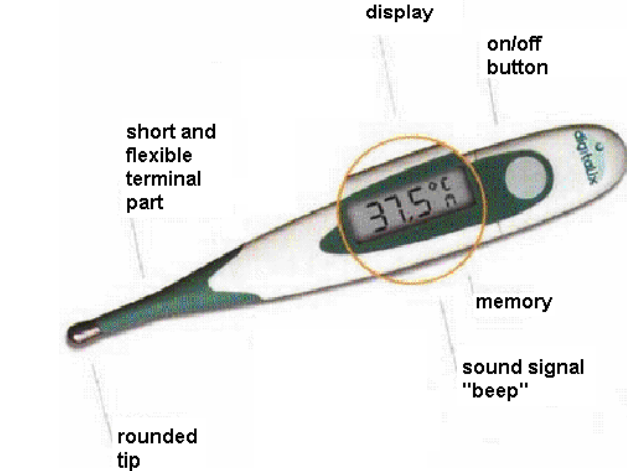
Resistance wire temperature sensors
change in resistance of wire with temperature
Lead zirconate titanate capacitors
change of capacitance of capacitor with temperature
Thermocouples
voltage produced at a junction of two dissimilar metals varies with temperature

IR / Visible / UV Sensors definition
detect and respond to light in different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, including infrared (IR), visible light, and ultraviolet (UV) wavelengths
fx.: Tympanic (ear) Thermometer
Types of Light Sensors (6)
Semiconductor based
Photoresistors (Photoconductors)
Photodiodes
Phototransistors
Image Sensors (CMOS, CCD)
Photomultiplier Tubes (PMTs) - detect low light
Photodiodes (photo)

Photomultiplier tubes (photo)

Image Sensor (photo + example)
in digital cameras 20 Megapixel camera means 20 million light sensors
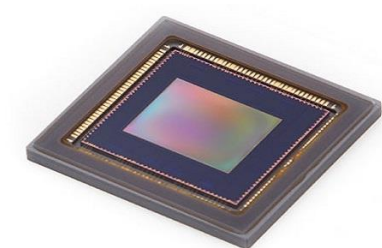
Semiconductor Tympanic (ear) Thermometer
based on the measurement of infra-red radiation emitted from the ear drum
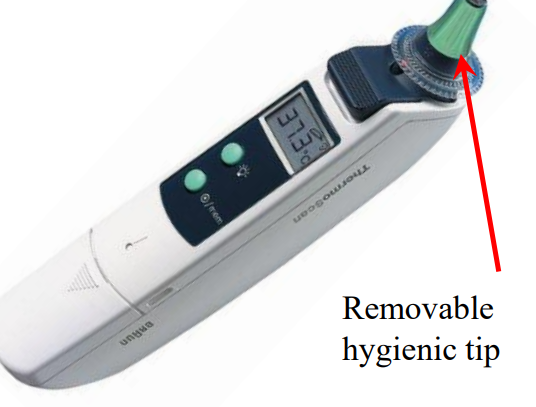
Photodiode arrays
components of spectrophotometers
Measure concentrations of metabolically important substances in body fluids
blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine and amniotic fluid
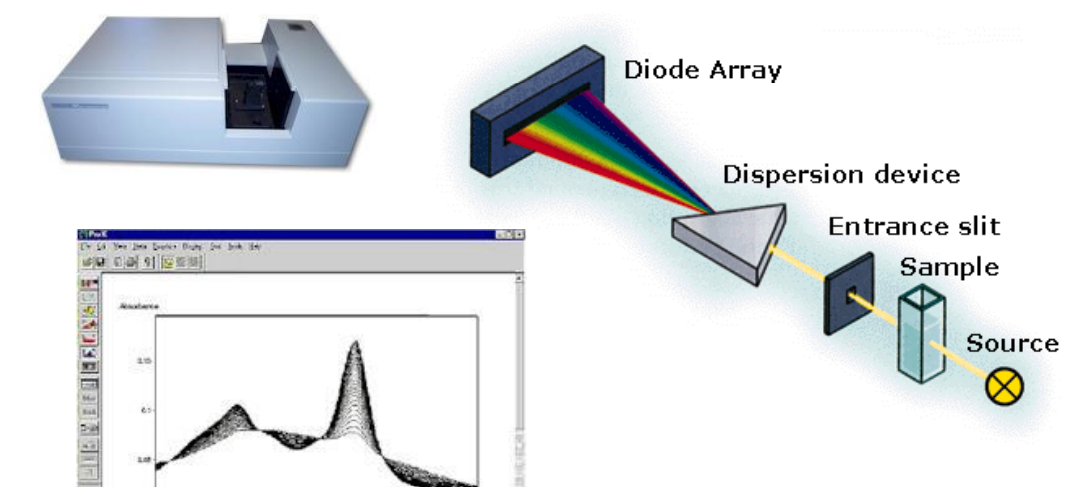
Substances that can be quantitatively analyzed of Photodiode Arrays (lot so choose some to know)
hemoglobin, erythrocytes, hematocrit, amylase, bilirubin, cholesterol, glucose, urea, creatinine, lipase, triglyceride, albumin, alcohol, ammonia, copper, magnesium, lactate, calcium, iron, magnesium, aluminium, sodium carbonate, carbon monoxide and even certain enzymes
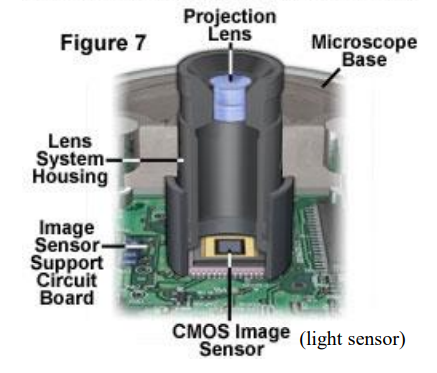
CMOS Image Sensor Projection Lens (photo)
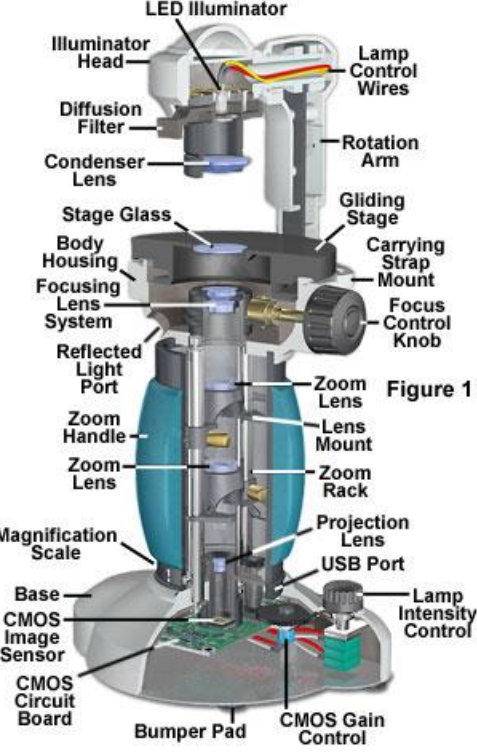
Digital Microscopes (photo)
Pulse Oximeter (2)
part of – in vivo spectrophotometry
Measures the oxygen saturation of a patient's blood

Key Components and Functionality of Pulse Oximeter (5)
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Red LED: Emits light at a wavelength of 660 nm.
Infrared LED: Emits light at wavelengths of 905 nm, 910 nm, or 940 nm.
Photodiode
A sensor that detects the amount of light that passes through the patient's tissue
Pulse Oximeter Light Absorption and process (5)
Oxyhemoglobin (oxygenated hemoglobin)
absorbs more infrared light
Deoxyhemoglobin (deoxygenated hemoglobin)
absorbs more red light
The device calculates the ratio of oxyhemoglobin to deoxyhemoglobin
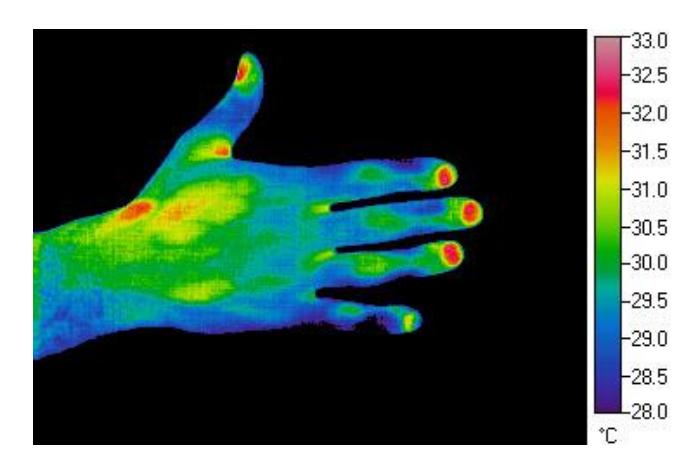
Infra Red Sensors (IR camera) (2)
Temperature measurement at a distance
Colour-scale coded temperature map
X / gamma Sensors types (8)
Semiconductor-Based Sensors
Silicon Sensors
Germanium Sensors
Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CdZnTe) and Amorphous Selenium (aSe)
Gas-Filled Sensors
Geiger-Muller Tube
Ionization Chamber
Proportional Counter
Thermoluminescence (TL) and Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) Crystals
Silicon Sensors
Measure individual X-ray photon energy
Germanium Sensors
Measure individual gamma photon energy
Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CdZnTe) and Amorphous Selenium (aSe)
Measure X/gamma energy fluence rate (energy per unit area per unit time)
Geiger-Muller Tube
Functions primarily as a detector rather than a sensor, providing simple count rates of radiation events
Ionization Chamber
Measures the total energy fluence (energy per unit area) from ionizing radiation
Proportional Counter
Measures the energy of individual alpha, beta, and gamma particles, providing detailed information about the radiation type and energy
Thermoluminescence (TL) and Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) Crystals (2)
LiF : Mg : Ti
Measure total energy absorbed over a specific period
TL personal dosemeters (photo)

Radioactivity contamination monitors (photo)

Patient dose measurement meters (photo)

RF Sensors (antennas) (2)
MRI system coil (generate/recieve signals)
MRI antennas measure RF coming from the human body

Chemical and Biochemical Sensors
specialized devices designed to detect and measure specific chemicals or biological substances in a sample
Chemical and Biochemical Sensors types
Ion-Selective Sensors
Gas Sensors
Biomolecular Sensors
Ion-Selective Sensors (2)
Detect specific ions
fx.: pH sensors for hydrogen ions
Measure ion concentration through selective membrane interaction
Gas Sensors (2)
Measure gas levels like O₂, CO₂, and NH₃
Important in medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring
Biomolecular Sensors (2)
Detect biomolecules such as proteins and cancer biomarkers
Significant in early disease detection and personalized treatment
Biomagnetic sensors (3)
based on the Hall effect
A semiconductor with current in a magnetic field generates a voltage perpendicular to the current direction
proportional to the magnetic field's strength