Belted Galloway Management Practical
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Cattle Dry Matter Intake
On average, cattle consume 2-3% of their body weight in dry matter per day.
Pasture Rest Periods
Rest periods allow time for the grass to regrow. If over 50% of leaves are removed, it can be detrimental to the pasture.
Minimum Grass Height
The minimum grass height that should be left in a pasture after cattle have moved to a fresh pasture is 4 inches.
Continuous Grazing
Cattle are maintained on one pasture for an unlimited time.
Rotational Grazing
Cattle are moved at intervals through different pastures to allow for periods of grazing and periods of forage rest.
Managed Intensive Grazing
A high-density of cattle is moved frequently through multiple pastures to maximize forage use.
Daily Forage Requirement Formula
The formula used to calculate a herd's Daily Forage Requirement while on pasture is 1.4%.
Pasture Yield Calculation
For every inch of forage height above 2-inches, the following Dry Matter is available per acre.
Pasture Size Calculation
(weight x %DMI x #cattle & Grazing period)/ ((DM/acre) x (% Utilization))
Plant Density (punds of DM/acre/inch)
low --> 150-200
medium --> 200-250
high --> 250-300
Parasite Management
To avoid parasites & larvae from being consumed, a low, medium, and high grazing management approach is recommended.
Where did the Belted Galloway breed originate?
Galloway Providence, Southwest
Scotland
The Belted Galloway breed is a cross of what two breeds?
Galloway Cattle and Dutch Belted
What does polled mean?
Cattle that are naturally horn-less
What are the three color options of Beltie coat?
Dun, red, or black
To be registered in the Belted Galloway Society Herd Book, cattle must be genertically acceptable and properly marked. What are the proper markings?
Heifers + Cows: Solid color w/ continuous uninterrupted white belt around the midsection, no extraneous white except under dew claws
Bulls: Must be solid colored w/ a continuous uninterrupted white belt around midsection, no white anywhere else
What are the purposes of the appendix for the Belted Galloway Society
to increase the # of registered Belties and to allow for genetic improvement
Markings: Incomplete Belt
M1

Markings: No Belt
M2
Markings: White above dew claw
M3
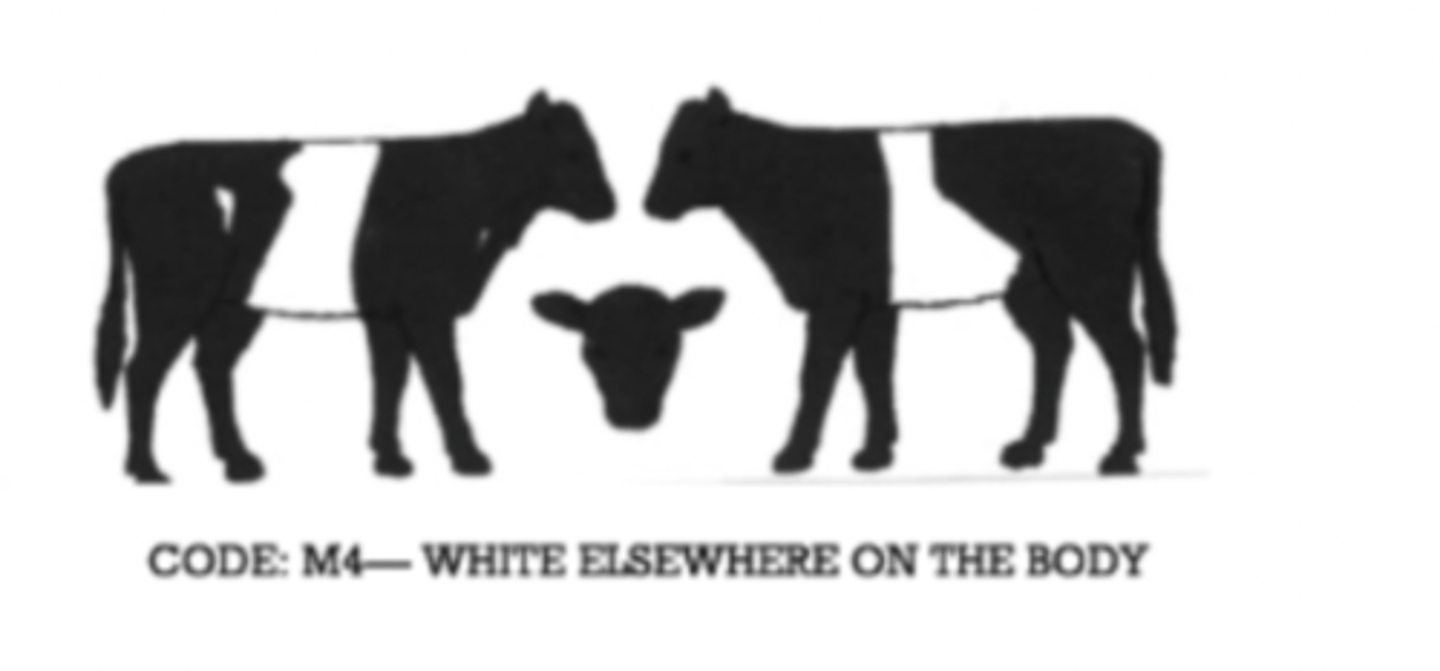
Markings: White elsewhere on the body
M4

Top causes of injuries to farm workers
#1: Machinery
#2: Animals
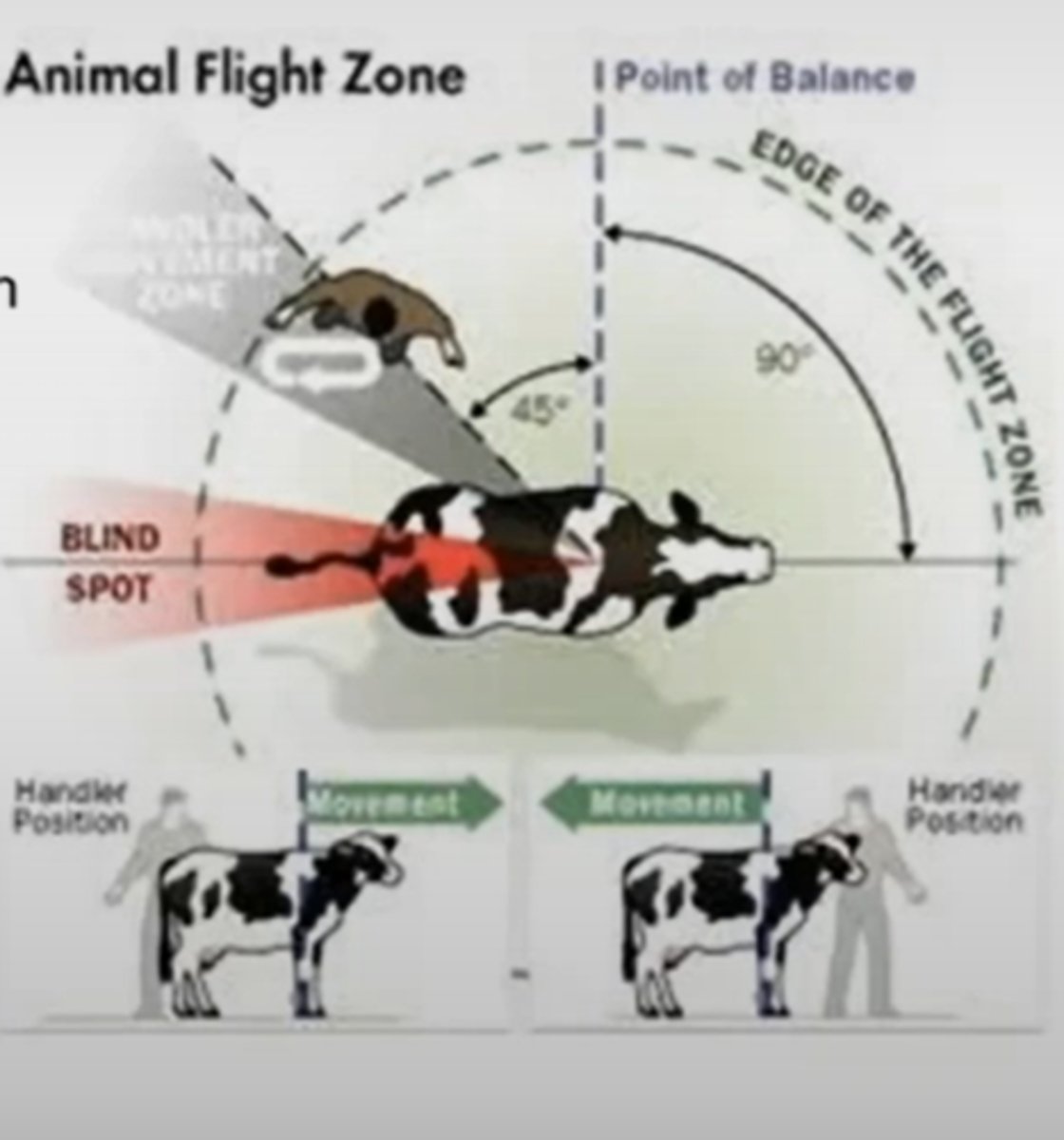
T/F: Cattle have wide panoramic vision, but poor depth perception
True
To move cattle from one location to another...
1. Make sure the pathway between the locations is free of distractions
2. get the boss cow moving in the desired direction
3. walk in a zig-zag pattern behind the herds point of balance at the edge of the dlight zone
How can you use the flight zone and point of balance to moce a cow on pasture forward?
Curved gates, be steady, calm, quiet, move at an angle behind them and enter the flight zone
How to stop cattle from walking?
Leave flight zone
How can you use the flight zone and point of blance to move a cow on pasture backward?
Enter the flight zone at the front of the point of balance
Signs of stress or aggression
1. Excessive tail whipping
2. defecates + urinates frequently
3. rigid tense psture
4. Head tossing
5. Vocalizing
Types of restraint
1. headlock
2. squeeze shute
3. halter
4. show shute
What side do you stand on when leading a steer
left side
when turning a cow, what way should u turn
clockwise
Pull and release method pf halter training
apply pressure on a halter ina. forward motion to get a calf to walk. As soon as the calf takes a step, release pressure o provide positive reinforcement for cooperation.
Why should a halter be tied to a fence post when a calf is misbehaving?
Stronger than us, objective is for them to pull and realize they cannot win
How can you settle a distressed cow?
1. Brush/ scratch --> reward
2. Tie up --> punish/train
Breed class vs. showmanship class
breed class: jusged on the animals conformation comapred to other cattle of te same breed and age (based on breed standard)
showmanship: judged on handlers ability to fir and show an animal as well as the handlers knowledge of the animal
Traits judged for market steers
Muscling, finish, structural correctness, growth capacity, balance, frame size
Muscling
Desirable appearance: wide base, heavy muscling, trim middle
Finish
good, even fat distribution, rounded topline
Structural correctness
straight topline, level hooks and pins
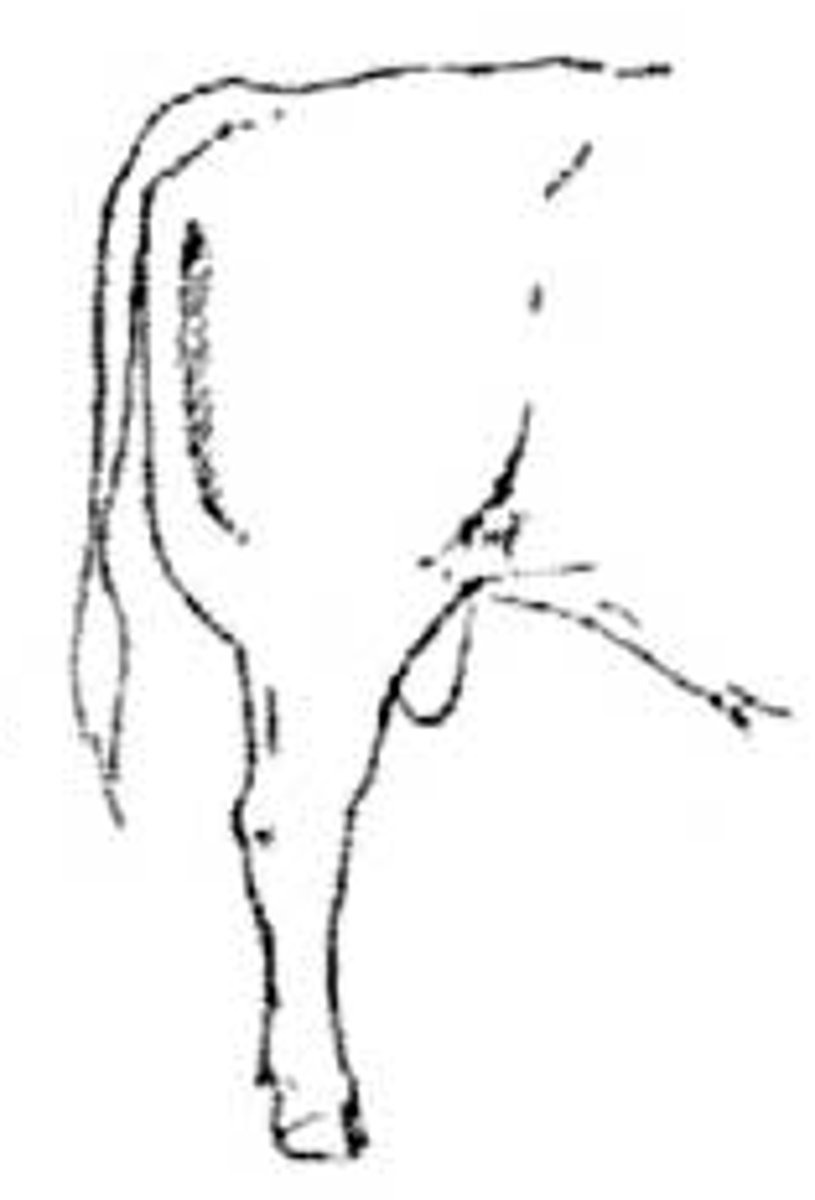
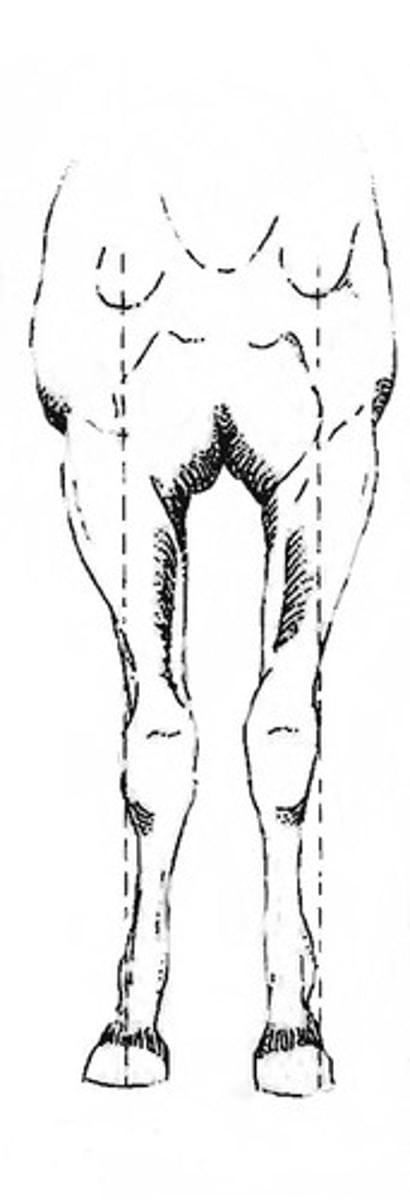
Post legged
hock hyper extension
sickle hocked
hock too flexed
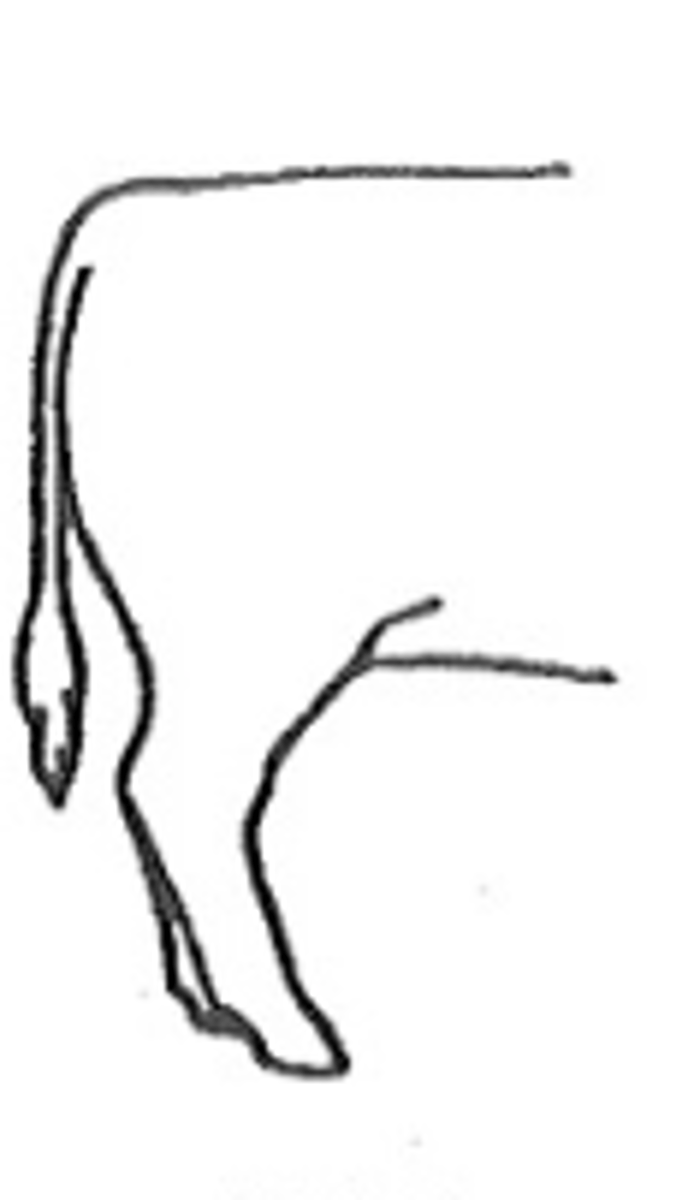

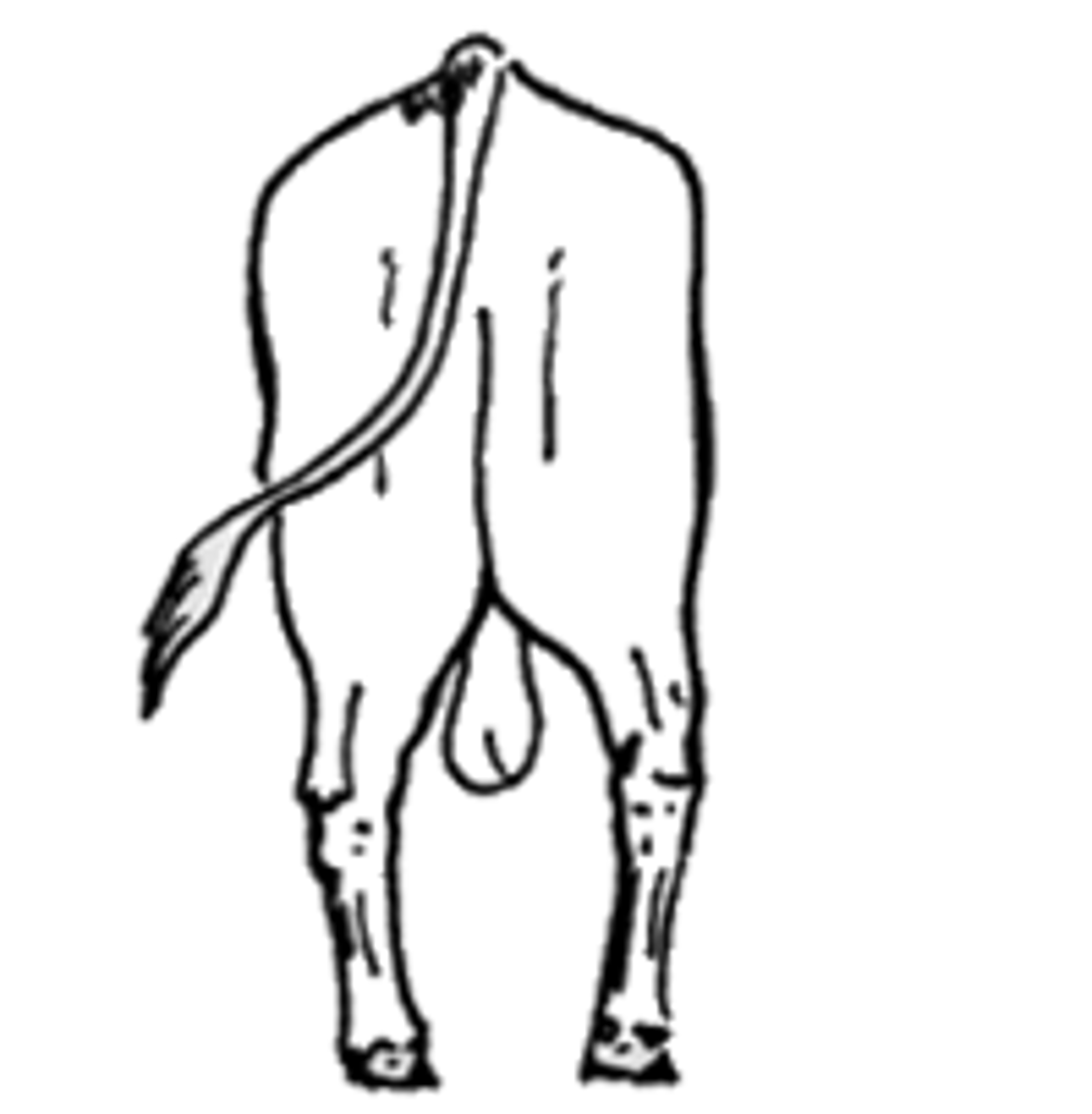
Bow legged
hocks tuned out, toes turned in
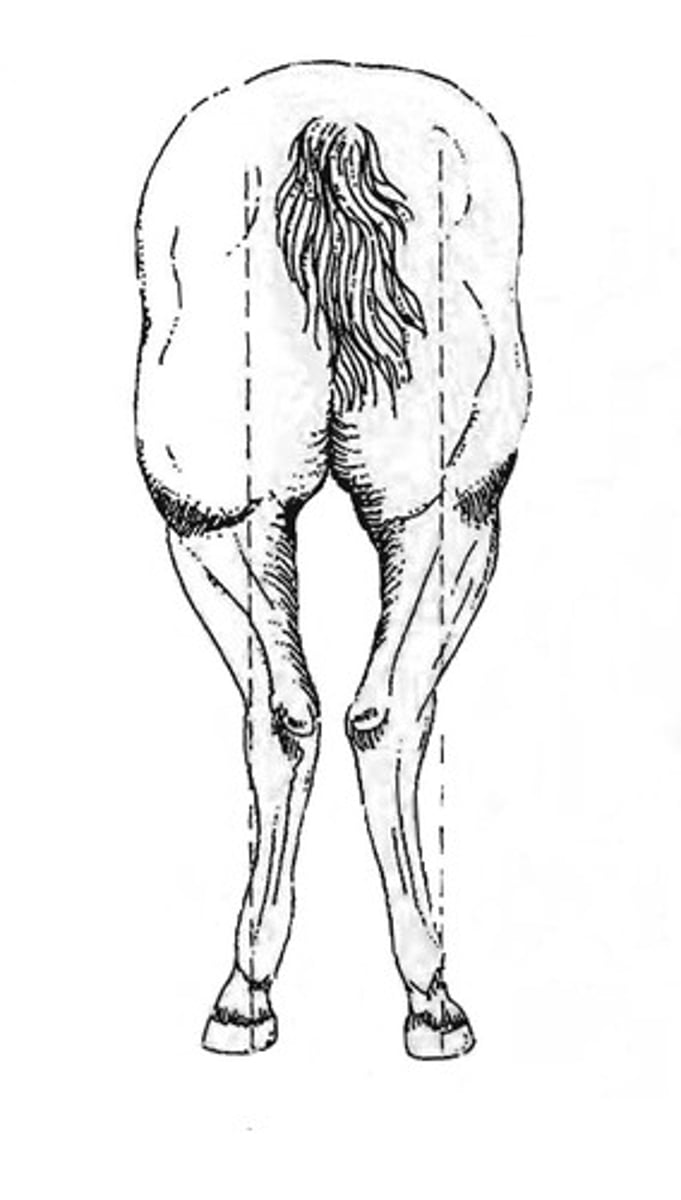
Cow hocked
Hocks close together, feet wide apart
Knock kneed
carpus turned in, toes out
Growth capacity
wide chest, long bodied, uniform in depth
Balance
Uniform body depth
Frame size
Medium (1200-1400lbs)
When walking in a show ring, lead and show stick in which hands?
lead --> right
show stick --> left
Side to side show position
even weight bearing in all limbs, square under body, head high, cattle line up side by side
Head to tail show position
Stagger hind legs w/ right leg further back, front feet square under shoulders, head up, nose to butt
How many lbs of beef were consumed per capita in the U.S. in 2024
58 lbs
Which country is the worlds largest beed producer and consumer
USA
Goal output for Cow-Calf producers
1 healthy weanling per mom, per year @ 400-750lbs by 6-10 months
Typical diet of Cow-calf farms
Pasture --> less expensive, supplement hay, haulage or silage in winter
Creep feed on Cow-calf farm
allows only babies to eat, creep feed increases weaning weight by 20-80 lbs but 3-20lbs of grain are required for every lb of added weight
Percent Calf Crop formula
(# calves born/#of cows in breeding herd) x 100
goal: 95%
Weaning percent formula
(# of calves weaned/#of cows in breeding herd) x 100
goal: 85%
What can impact weaning weight?
1. breed
2. genetics
3. moms BCS
4. age
5. feed
6. health
Break-even point
annual cow cost/lb calf weaned
Goal output for stockers
600-900 lbs @12-18m, gain 1-2.25 lbs/day
Typical diet on Stocker Operations
forage, roughage, grass, hay, crop residue, silage, haylage
goal output for Feedlots
1000-1450 @18-24 months
Typical diet on Feedlots
high energy --> concentrates, corn, oats, some forage, gain 3 lbs/day fed over 3-6 months
BCS using 6 parts of the body
1. Brisket, ribs, back, tailhead, pins, hooks
Distinguish between BCS 5 and 6
If there are the last 2 ribs visible than its a 5, if no ribs are visible its a 6 or above
Distinguish between BCS 7 an 8
Still able to see some of the hooks/pins --> 7
pins and hooks complelty covered --> 8
fat deposits on the both sides of tailhead --> 8
Freezer beef
Purchasing beef in bulk from a farmer typically frozen
Whole share of beef
400 lbs
freezer space --> 40 cuft
Half a share of beef
200 lbs
freezer space --> 20 cuft
1/4 share of beef
100 lbs
freezer space --> 10 cuft
1/8 share of beef
50 lbs
freezer space --> 5 cuft
Fed cattle weight sent for processing
Steer/heifer --> 1000-1450 lbs
cull cow/bull --> 1200-2000 lbs
Cut sheet
tells a butcher what the consumers specifications for breakdown and packaging of a carcass
Legal precautions for cattle slaughtered under 30 months of age
must have all specified risk materials (SRM) removed at slaughter and bone in cuts are not permitted
Why are bone in cuts of beef permitted from cattle under 30 months of age?
Younger animals are at lower risk of BSE due to its long incubation period
Dressing percentage
(hot carcass weight/live weight) x 100
ideal = grain-fed 60-63% grass-fed = 56-58%
Carcass-cutting yield
(lbs of meat/hot carcass weight) x 100
ideal = 55-70%
2 main factors that dtermine the USDA Quality Grade for beef
1. physciological age/maturity of a carcass
2. marbling in the ribeye between the 12th and 13th rib
Maturity Age Ranges and USDA Quality Grades
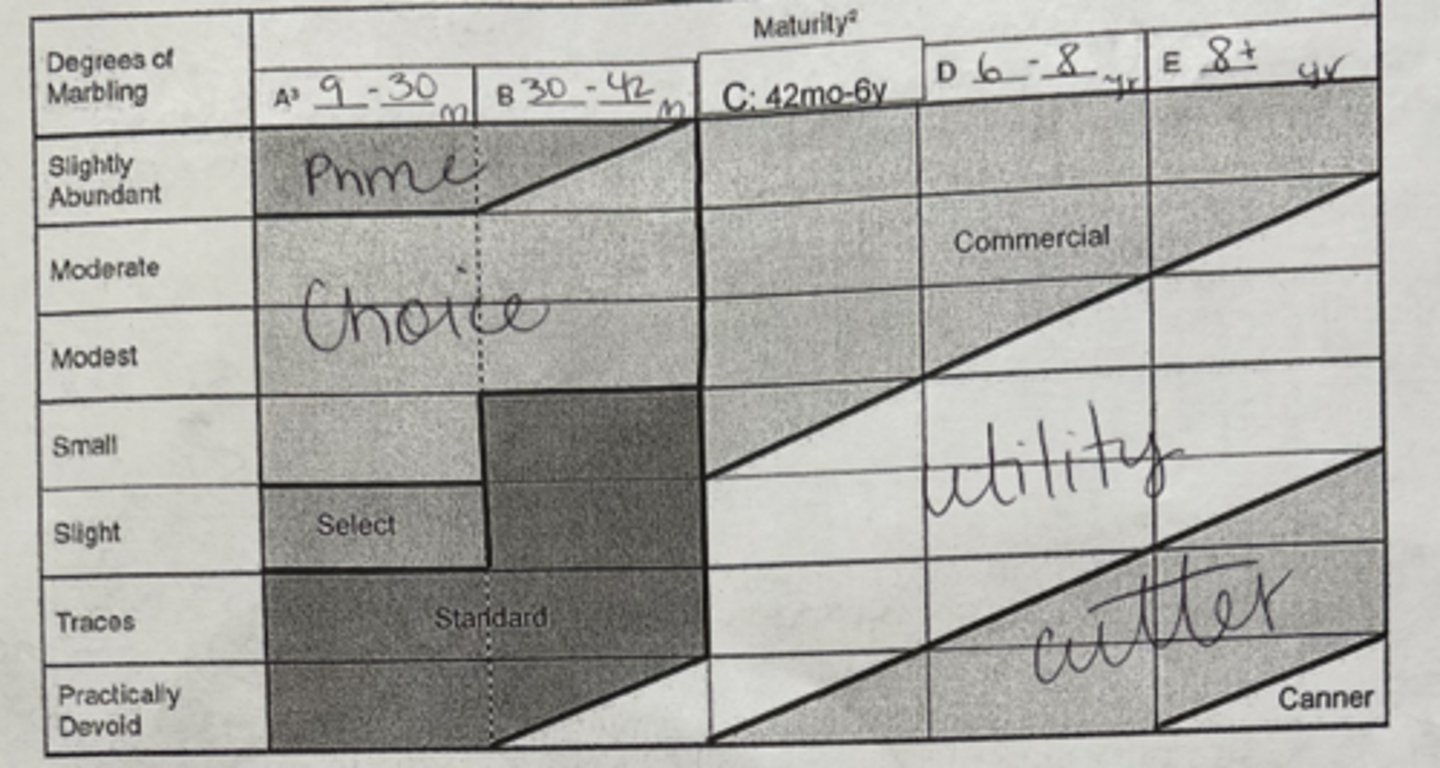
% of fed cattle quality grades 2024
Prime --> 10.3%
Choice --> 73.7%
Select --> 12.3%
Other --> 3.2%
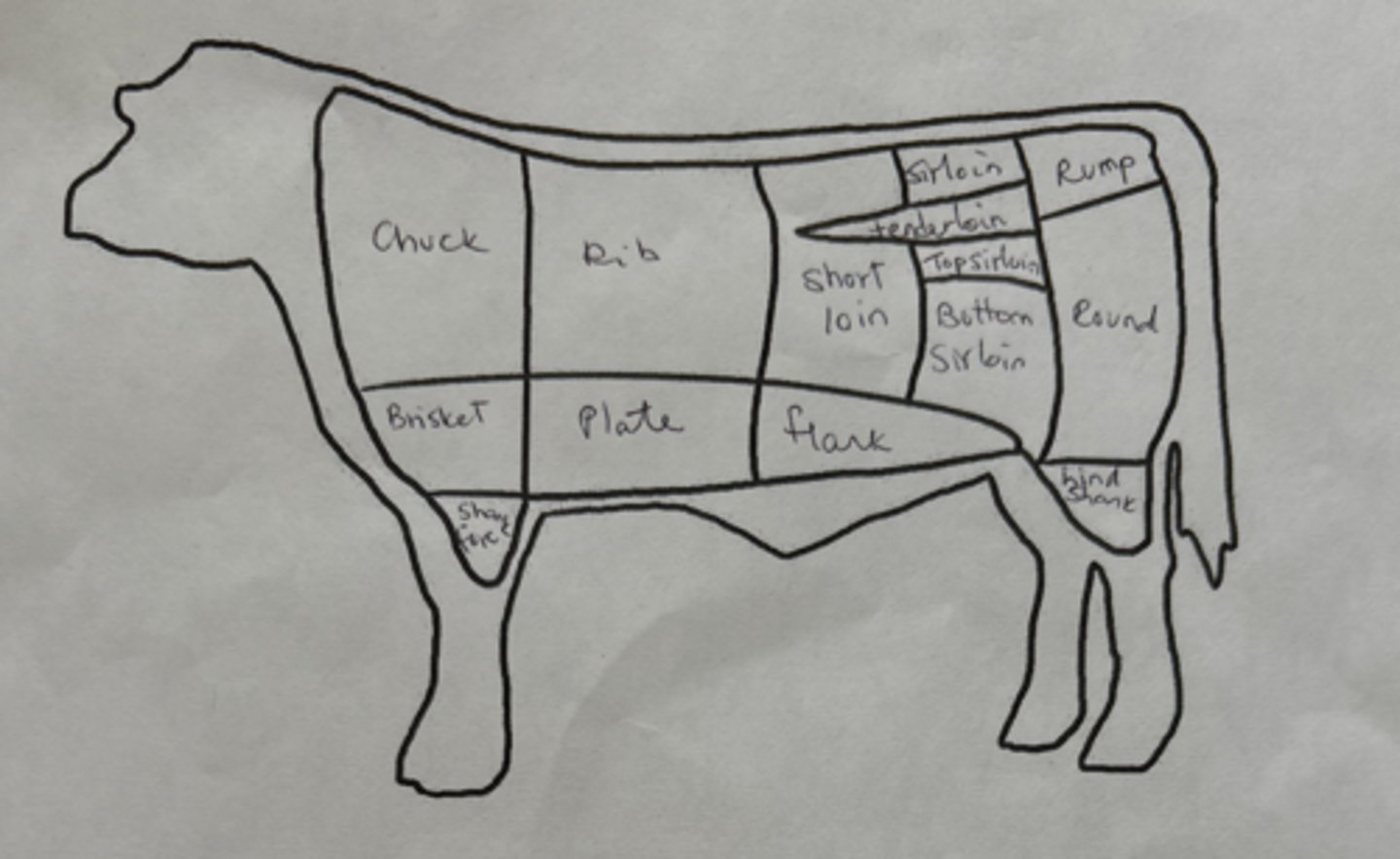
Cuts of beef
What percent of a cows body weight do they eat in dry matter a day
2-3%
Hay wastage
soiled w manure or urine or just not eaten
Rate of hay wastage on beef farms
6-20%
Vaccinating Pre-breeding
prevent infertility, early embryonic loss, and abortions
vaccnating pre-caving
boost cows immunity and production of antibodies in colostrum to pass to calves and maximize passive transfer of immunity
vaccinating pre-weaning + booster
boost calves active immunity after maternal antibodies drop and before weaning stress
vx pre-transfer to new production phase or post transfer
if vx history is unknown
Why might a farmer give an IN vx
- young calves when maternal antibodies might inerfere w/ a vx administered SQ or IM
- cattle just arriving at a new segment of the beef production cycle to boost local or mucosal immunity
IM and SQ dos and donts
Admsinister in neck msucling, avoiding trachea, give in hind (rump)
Needle Gauge
diameter of needle, smaller the # --> larger diameter
Needle gauge for IM/SQ for cattle
16-18 (we use 20)
Typical range of weights and age for beef calves at weaning in the U.S.
400-750 lbs by 6-10 months of age (180-300 days)
Method of weaning: Total separation
abrupt phycial seperation of cows and claves, leads to high illness risk
Method of weaning: Fenceline weaning
cow calf pairs separated by phyical barrier but maintian visual and auditory, and nose to nose contact
Method of weaning: quiet weaning
nose flip is inserted to prevent nursing while maintining contact w mom, least risk of illness
Purpose of a 205-day Adjusted Weaning Weights
to be able to compare calves weaning weights at 205 days to make a scale of averages to compare mom productivity
205-day Adjusted WW
= ((adjusted WW-adjusted BW)/age of calf at weaning) x 205 days + ajusted BW
Calf sex Ajustment WW
= 205-day Adjusted WW + 60 lb (of heifer) or + 0 lb (if bull/steer)
Goal market weight and age
1000-1450 lbs @18-24 months