Gi system drugs
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
GI tract
small and large intestine
pharynx
oral cavity
stomach
rectal and anal canal
oesophagus
Accessory organs
teeth
tongue
salivary glands
liver
pancreas
gall bladder
Antacids
neutralise stomach acid and provide relief from heartburn and indigestion
Antacids eg
Aluminium hydroxide
Calciym carbonate
Magnesium hydroxide
Aluminium hydoxide mechanism of action

Aluminium hydoxide indications

Aluminium hydoxide side effects

Aluminium hydoxide nursing responsibilities

Aluminium hydoxide health teaching

calcium carbonate mechanism of action

calcium carbonate indications

calcium carbonate side effects

calcium carbonate nursing responsibilities

calcium carbonate health teaching

Magnesium hydroxide mechanism of action
used as a laxitive
The suspension of magnesium hydroxide is ingested and enters the stomach. According to the amount ingested, the magnesium hydroxide will either act as an antacid or a laxative.
Magnesium hydroxide indications
As an antacid, it is used for the temporary relief of heartburn, upset stomach, sour stomach or acid indigestion.
As a laxative, it is used for the relief of occasional constipation by promoting bowel movements
Magnesium hydroxide side effects
drowsiness or flushing (warmth, redness or tingly feeling).
Daily use of magnesium hydroxide can result in fluid and electrolyte disturbances.
Excessive use of the laxative effects of magnesium hydroxide may result in abdominal cramping, nausea and/or diarrhea.
Magnesium hydroxide nursing responsibilities
monitor bowel movements
Magnesium hydroxide health teaching
hydration
diet
H2 receptor antagonists
a class of medications that reduce stomach acid production by blocking the H2 histamine receptors in the stomach lining
H2 receptor antagonists eg
Famotidine,cimetidine,ranitidine
Famotidine mechanism of action

Famotidine indications

Famotidine side effects

Famotidine nursing responsibilities

Famotidine health teaching

cimetidine mechanism of action

cimetidine indications

cimetidine side effects

cimetidine nursing responsibilities

cimetidine health teaching

ranitidine mechanism of action
Ranitidine is a medicine that reduces the amount of acid your stomach makes.
ranitidine indications
it was used for indigestion, heartburn and acid reflux, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD – this is when you keep getting acid reflux), and to prevent and treat stomach ulcers.
ranitidine side effects
Constipation; diarrhoea; dizziness; fatigue; headache; myalgia; skin reactions.
ranitidine nursing responsibilities
monitor hydration food levels
ranitidine health teaching
medication use
drug interactions
PPI
a type of medication that reduces stomach acid production
PPIS eg
Omeprazole
Lansoprazole
Esomeprazole
Omeprazole mechanism of action

Omeprazole indications

Omeprazole side effects

Omeprazole nursing responsibilities

Omeprazole health teaching

Lansoprazole mechanism of action

Lansoprazole indications

Lansoprazole side effects

Lansoprazole nursing responsibilities

Lansoprazole health teaching

Esomeprazole mechanism of action
the usual dose to treat:
heartburn and acid reflux is 20mg a day
gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Esomeprazole indications
to treat conditions where there is too much acid in the stomach
Esomeprazole side effects
Headaches. Make sure you rest and drink plenty of fluids. ...
Feeling sick. Try taking esomeprazole with or after a meal or snack. ...
Being sick. Take, small, frequent sips of water to avoid dehydration. ...
Diarrhoea. ...
Constipation. ...
Stomach pain. ...
Farting (flatulence)
Esomeprazole nursing responsibilites
monitor fluids
bowels
Esomeprazole health teaching
monitor on drug dosage
interactions
timing
Antiemetics
help prevent and treat nausea and vomiting.
Antiemetics eg
Ondansetron,metoclopramide,prochlorperaxine
Ondansetron mechanism of action

Ondansetron indications
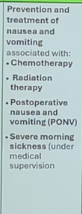
Ondansetron side effects

Ondansetron nursing responsibilities

Ondansetron health teaching

metoclopramide mechanism of action

metoclopramide indications
metoclopramide side effects

metoclopramide nursing responsibility

metoclopramide health teaching

prochlorperaxine mechanism of action
prochlorperazine mainly blocks D2 dopamine receptors in the brain. It can also block histaminergic, cholinergic, and noradrenergic receptors.
prochlorperaxine indications
to treat nervous, emotional, and mental conditions (eg, schizophrenia) and non-psychotic anxiety. It is also used to control severe nausea and vomiting.
prochlorperaxine side effects
Feeling sleepy or drowsy. Do not drive, cycle or use tools or machinery. ...
Blurred vision. Do not drive, cycle or use tools or machinery while this is happening. ...
Dry mouth. Try chewing sugar-free gum or sucking sugar-free sweets.
Headaches. ...
Stuffy nose.
prochlorperaxine nursing responsibilities
Monitor BP (sitting, standing, lying down), ECG, pulse, and respiratory rate before and frequently during the period of dosage adjustment. May cause Q-wave and T-wave changes in ECG. ...
Assess for falls risk. ...
Antiemetic: Assess patient for nausea and vomiting before and 30–60 min after administration.
prochlorperaxine health teaching
medication use
side effects
avoid alcohol
drug interactions
Laxatives
relief constipation and promote bowel movement
Laxatives eg
Lactulose,senna,bisacodyl
Lactulose mechanism of action

Lactulose indications

Lactulose side effects

Lactulose nursing responsibilities

Lactulose health teaching

senna mechanism of action

senna indications

senna side effects

senna nursing responsibility

senna health teaching

bisacodyl mechanism of action
This type of medicine can help you empty your bowels if you have difficulty pooing (constipation).
Bisacodyl is also used in hospitals to help you empty your bowels before surgery or some examinations or treatments. Your hospital will explain how to use it.
bisacodyl indications
treat constipation
bisacodyl side effects
Feeling sick (nausea) Try taking bisacodyl with some food. ...
Diarrhoea. Stop taking bisacodyl and drink plenty of fluids, such as water or squash. ...
Stomach pain or cramps. Reduce your dose of bisacodyl or stop taking it until these side effects go away.
bisacodyl nursing responsibilities
May lead to hypokalemia. • May cause abdominal pain and cramps
monitor assessment
adminstration
bisacodyl health teaching
monitor diet
monitor stool
drug interactions
anti diarrhoea med
loperamide
Loperamide mechanism

Loperamide indications

Loperamide side effects

Loperamide nursing responsibility

Loperamide health teacing
