Wavelength
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
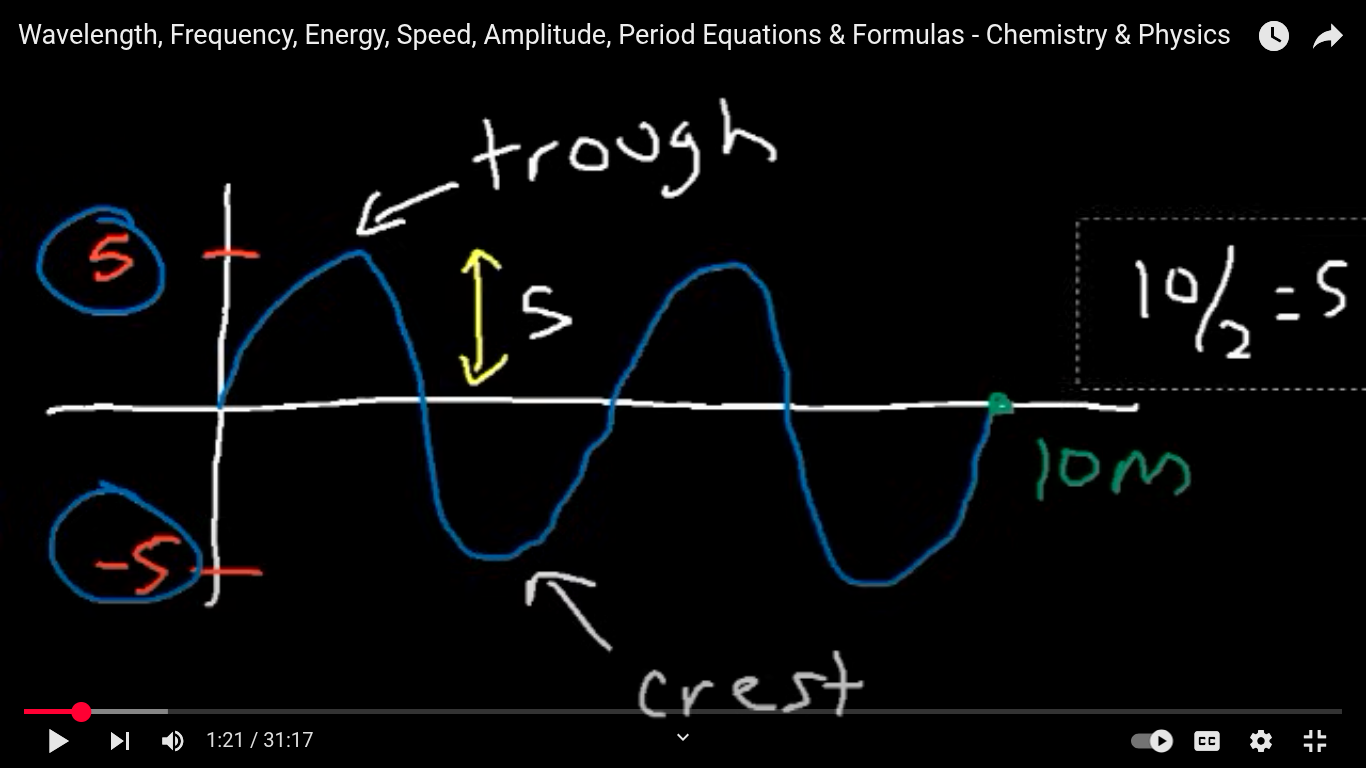
Troughs
The lowest points of a wave, its the vertical height between the wave and the resting point
Crest
The highest points of a wave, representing the maximum vertical height between above the resting point.
Amplitude
The distance from the resting point to the crest or trough of a wave, indicating the wave's energy.
Amplitude stays the same regardless of the wavelength.
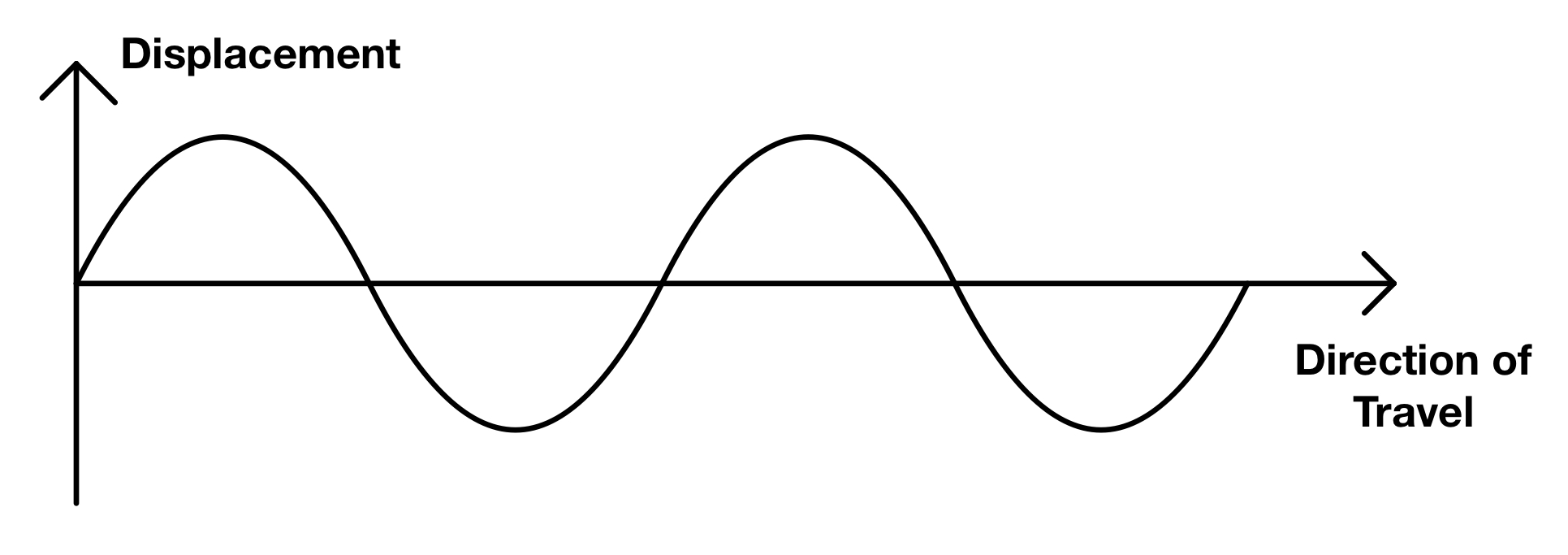
Transverse Waves
Waves in which the particle displacement is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, such as light waves.
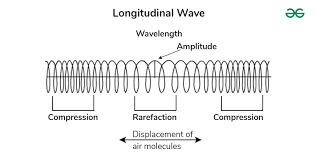
Longitudinal Waves
Waves in which the particle displacement is parallel to the direction of wave propagation, such as sound waves.
Frequency
The number of cycles that occur in one second
More compressed →higher frequency
Less compressed → lower frequency
10 Hz → 10 cycles / per second
1 / T
Period
How many seconds it takes for one waves to pass
time / # cycles
Interference
The phenomenon that occurs when two or more waves overlap and combine to form a new wave pattern.
Constructive interference
happens when two waves both align at their crests or troughs, this means they’re both in phase
Destructive interference
happens when waves meet at a crest and the other at the trough in a phase
Propagation
The way in which a wave travels through a medium or space, characterized by its speed and direction.
Wavelength
The distance a wave travels before it repeats itself ( the distance b/t two identical points on two crests of troughs)
distance (m) / number of cycles x 2
Concave Wall
Makes the wave converge
Convex Wall
Makes the wave diverge
Reflection
Waves hit a barrier and reflect back out changing its direction
Frequency stays the same
Refraction
occurs when the direction of the wave changes (go through)
Diffraction
occurs when the waves pass through an open barrier that allows them to bend around the barrier - Changes direction & shape
Changes the speed