WCU Funds Nursing 100 Week 4 Assessment 3 Notes + Crutches, Canes, & Walkers
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Crutch Adjustment
Adjusting crutches based on patient's height and hand grip. they can be adjusted from the top or the bottom
All weight should be on
the hand grips, not on axillae(armpit)
Hand grips should be even with the
top of the hip line
when the patient uses the handgrips, the elbow should be
Elbow should be bent at 30 degrees when using handgrips
before a patient starts ambulating with crutches, they must be wearing a
Gait Belt
Tripod Position
Starting position for walking with crutches, looks like a triangle
2 Point Gait
Move right crutch and left foot together, then left crutch and right foot together
4 Point Gait
Move right crutch, then left foot, then left crutch, then right foot
3 Point Gait
Move both crutches and injured leg together, then move non-injured leg
Swing-To Gait
Move both crutches, then swing both legs to placement of crutches
Swing-Through Gait
Move both crutches, then swing both legs forward past placement of crutches
Which leg is used when going down the stairs with crutches or canes
Good Leg
Which leg is used when going DOWN stairs with crutches or canes
Bag leg
Remember, Good leg=up, bad leg=down
the good leg goes first when going UP stairs followed by the bad leg
The bad leg goes first when going DOWN the stairs, followed by the good leg
How to Go Up Stairs with Crutches
Good leg goes up on step followed by crutches, then bad leg goes up step
How to Go Down Stairs with Crutches
Move crutches on step, followed by bad leg, then move good leg down on step
How to sit down with crutches?
Backing up to chair, feeling chair with good leg, using crutches for support, bending good leg while sitting down
How to stand up with crutches
Using crutches for support, pushing up on non-injured side, standing up
How to Adjust a Cane
Most canes are adjusted from the bottom
Two ways to know if a cane fits a patients
1. Top of cane even with Great Trochanter(prominence of the Femur)
2. top of the cane should be even with the wrist crease closest to hand
What degree should the patients elbow be at when holding a cane?
Elbow should be flexed at a 15-30 degree angle when holding a cane
Should the patient be wearing a gait belt when practicing with a cane?
Patient should wear gait belt when practicing with a cane
Where should the patient hold their cane? Where should the nurse stand next to the patient?
Nurse stands on weak side, patient holds cane on strong side
Approximately how many inches should the cane be held from the side of the foot?
Cane should be held approximately 4 inches from side of foot
How would a patient ambulate with a cane?
Move cane with weak side forward, then move strong side forward
How does a patient go up and down stairs with a cane?
Going up and down stairs using a cane
Going Up Stairs with Cane
Hold cane on good/strong side, move good leg up onto step, put weight on cane, then move cane and bad leg up onto step
Going Down Stairs with Cane
Move cane down on step with bad leg, then move good leg down onto step
Sitting Down with Cane
Backing up to chair, feeling chair with back of legs, using cane for support, bending weak leg while sitting down
Standing Up from chair with Cane
Placing cane on strong side, leaning forward, pushing up on armrest, standing up
How to adjust a walker?
Adjust walker at the bottom, each leg adjusted separately
Walker needs to be adjust before patient use
What are the two ways to know if a walker fits the patient?
1. have the patient hold the walker handgrips with both hands and there should be a 15-30 degree bend in elbows
2 the patients wrists are even with the handgrips
Patient should wear what before they use a walker? and which side should the nurse stand on?
Patient should wear gait belt and nurse stands on weak side
Walker Starting Position
Back tips of walker match up with middle of foot
How to ambulate with a walker?
Lift walker and move forward, move weak side, then move strong side
Sitting Down with Walker
Backing up to chair, extending weak leg, feeling for chair armrest, sitting down
Standing Up from chair with Walker
Leaning forward, extending weak leg, pushing up on armrest, standing up
Human Senses
Sight, smell, hearing, taste, and touch
Sensory Alterations
Inability to see, smell, hear, taste, or feel
Sensory Deficits
Difficulty with one or more main senses
Sensory Deprivation
Lack of ability to receive sensory stimulus perception
Sensory Overload
Receiving stimuli beyond ability to process
Cataracts
Cloudy area on eye lens caused by proteins breaking down and clumping together, causing cloudy and blurry vision, difficulty seeing at night, double vision, faded and yellowing colors
Diabetic Retinopathy
Affects blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision loss and complete blindness, can cause glaucoma
What Increases risk for cataracts and diabetic retinopathy?
Smoking
Sleep
Essential for health and healing, inadequate sleep affects almost every system in the body, can lead to chronic health problems like depression, heart disease, hypertension, and diabetes
Circadian Rhythm
Internal process that controls sleep-wake cycle, occurs every 24 hours, regulates biological clock and sleep-wake patterns, synchronized with environmental cues like light and temperature
Sleep-Wake Homeostasis
Assists body in remembering to sleep after a given time; regulates level of sleep based on sleep deprivation; affected by factors like lighting, medications, caffeine, sleep environment, and stress
Stages of Sleep: Stage 1
Wake/lightest stage of sleep, transition from wakefulness to sleep, easily aroused, relaxed but aware of surroundings, normal breathing and skeletal muscle tone, lasts 1-5 minutes, 5% of total sleep cycle
Stages of Sleep: Stage 2
Deeper sleep, difficult to awaken, decreased heart rate and body temperature, first cycle lasts 25 minutes and becomes longer with each cycle, consumes 50% of total sleep cycle, number of cycles increase with aging
Stages of Sleep: Stage 3
Mental cloudiness if awoken in this stage, immune system strengthens, muscles, tissues, and bones repair and regenerate, number of cycles decline with aging, can last up to 40 minutes
Stages of Sleep: Stage 4
Includes REM (dreaming stage), irregular and erratic breathing, elevated heart rate, begins 90 minutes after falling asleep, initial cycle lasts 10 minutes and becomes longer throughout the night, can last up to 1 hour
Recommended Hours of Sleep for Newborns,
14-17 hours
Recommended Hours of Sleep INFANTS
12-15 hours
Recommended hours of sleep TODDLERS
11-14 hours
Recommended Hours of Sleep for Preschool, School-Age Children, and Adolescents
10-13 hours,
Recommended Hours of Sleep School-Age Children
9-11 hours,
Recommended Hours of Sleep: ADOLESCENTS
8-10 hours
Recommended Hours of Sleep for Young Adults
7-9 hours
Recommended Hours of Sleep for Middle Adults
7-9 hours,
Recommended Hours of Sleep for Older Adults
7-8 hours
Sleep Deprivation
Occurs when client does not meet body's biological sleep requirements, affects cognitive function, judgment, response time, can trigger seizure disorders, migraines, and tension headaches
Sleep Disorders: Insomnia
Ongoing inability to sleep despite opportunity to do so
Sleep Disorders: Apnea
Absence of inspiratory airflow for at least 10 seconds
Sleep Disorders: Hypopnea
Decrease in oxygen saturation lasting 10 seconds or longer
Sleep Disorders: Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Recurrent episodes of upper airway collapse and obstruction while sleeping, combined with waking from sleep
Sleep Disorders: Narcolepsy
Chronic sleep condition characterized by sudden sleepiness and sudden periods of sleep
Sleep Disorders: Hypersomnia
Excessive daytime fatigue without improvement after more sleep
Sleep Disorders: Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS)
Uncontrollable urge to move legs during sleep
Promoting Sleep: Avoid Stimulants
Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine 4-6 hours before bedtime
Promoting Sleep: Remove Light and Noise
Create a dark and quiet sleep environment
Promoting Sleep: Bedtime Routine
Establish a routine like taking a warm shower or bath
Promoting Sleep: Room Conditions
Keep room dark, quiet, and at a comfortable, cold temperature
Promoting Sleep: Bedtime Habits
Go to bed only when tired, if no sleep in 20 minutes, go to another room and engage in relaxing activities
Promoting Sleep: Consistent Sleep Schedule
Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day
Promoting Sleep: Nap Guidelines
Keep naps short and before 3 p.m.
Promoting Sleep: Exercise Timing
Complete exercise at least three hours before bedtime
Promoting Sleep: Bedroom Environment
Remove work items and televisions from the bedroom, use the bedroom only for sleep and sexual activity
Joint Movements: Abduction
Lateral movement away from the midline
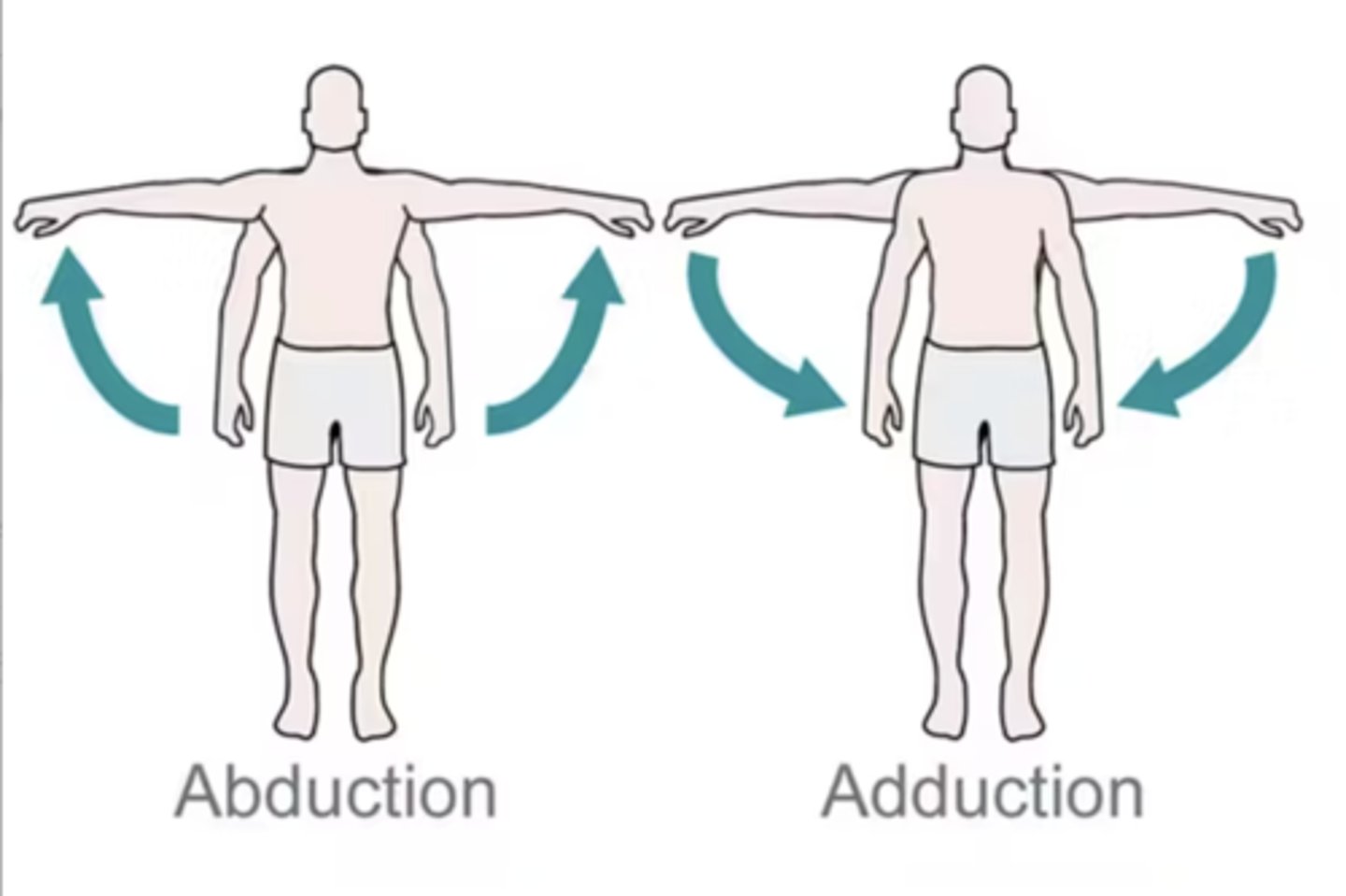
Joint Movements: Adduction
Lateral movement towards the midline

Joint Movements: Circumduction
Circular movement

Joint Movements: Flexion
Decreasing the angle of a joint
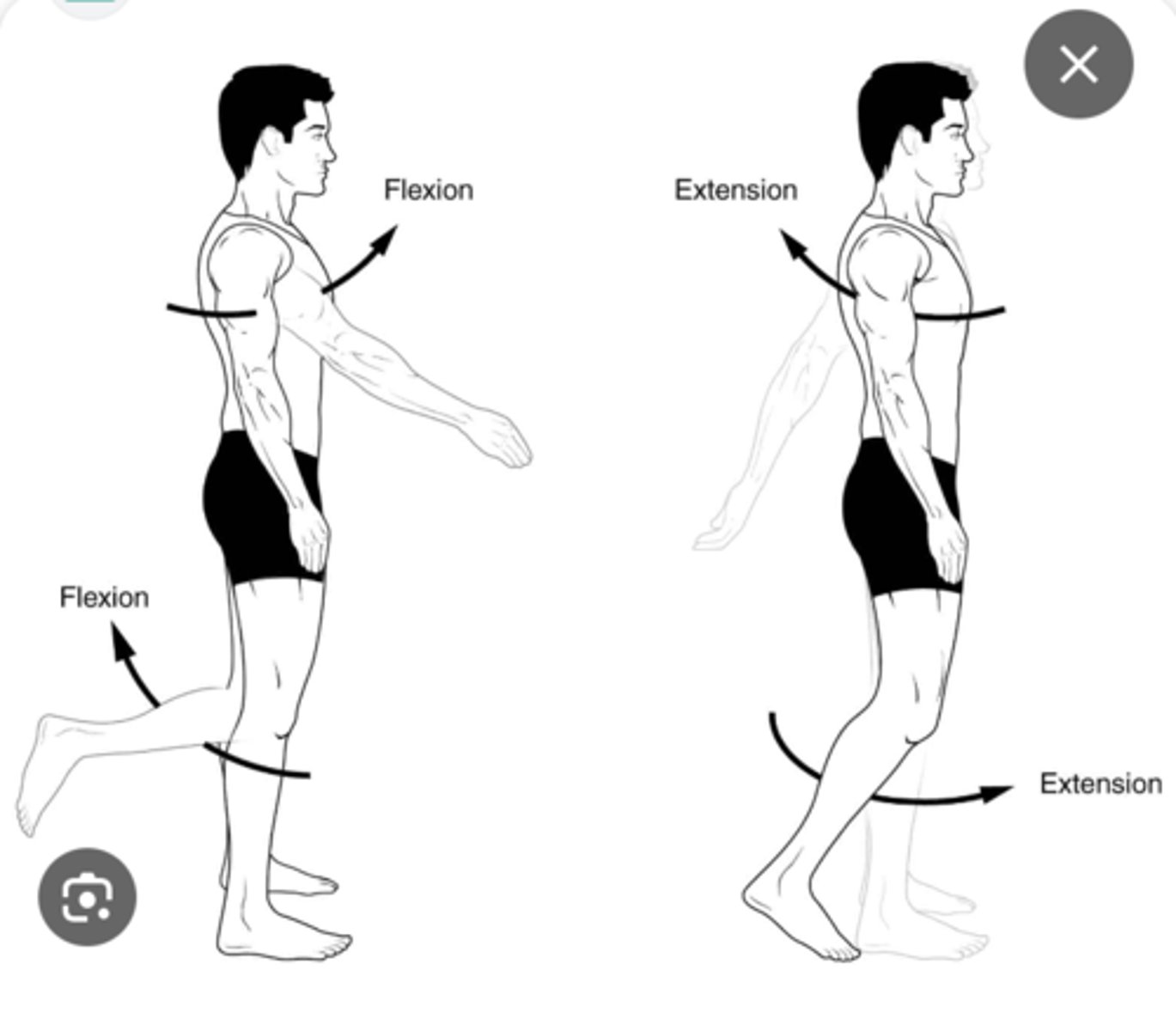
Joint Movements: Extension
Increasing the angle of a joint

Joint Movements: Hyperextension
Flexion of a joint beyond its normal limits
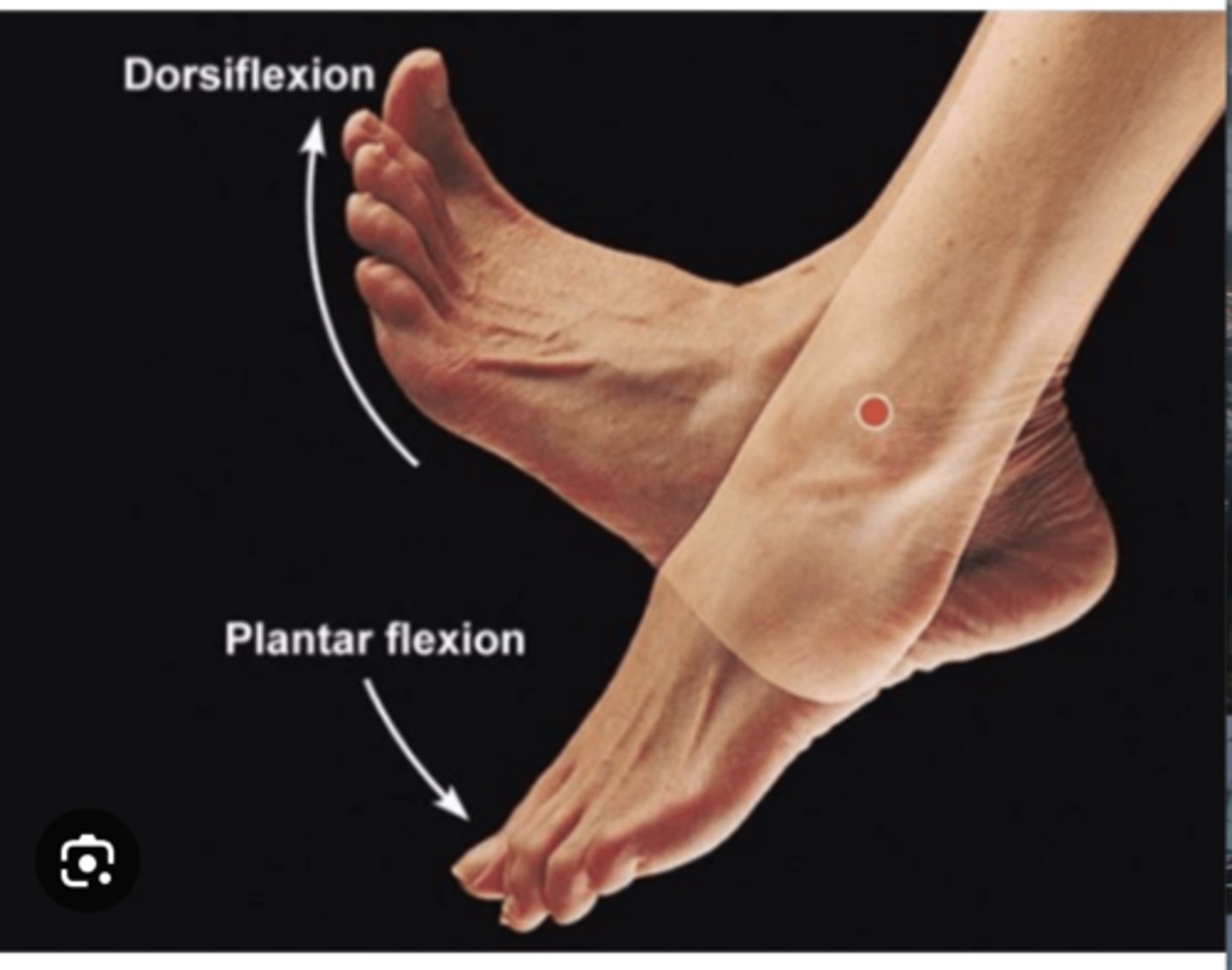
Joint Movements: Dorsiflexion
Flexion at the ankle, lifting the foot upwards
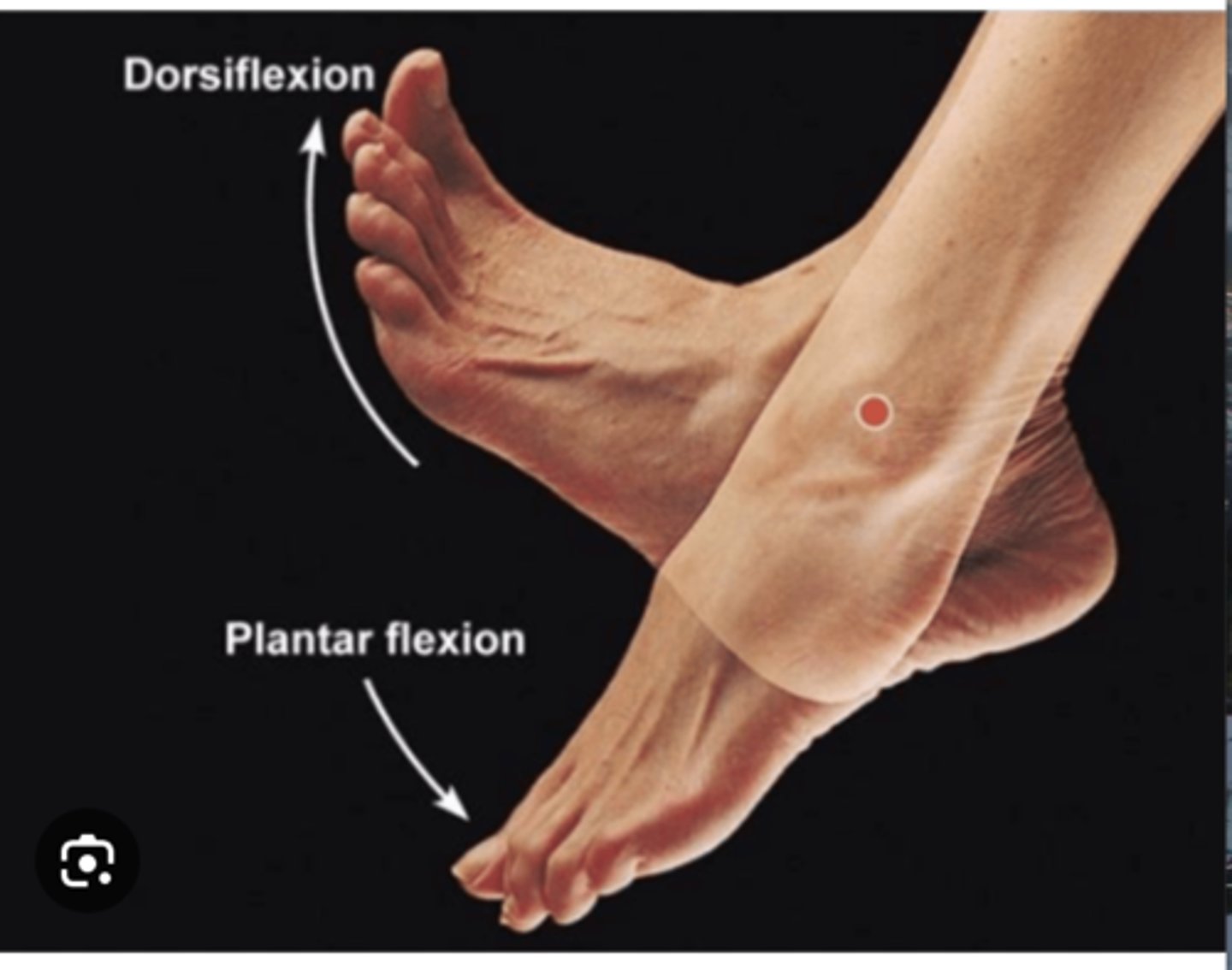
Joint Movements: Plantar Flexion
Flexion at the ankle, pointing the foot downwards
Joint Movements: Rotation
Circular movement around an axis
Joint Movements: Internal Rotation
Rotation towards the body
Joint Movements: External Rotation
Rotation away from the body
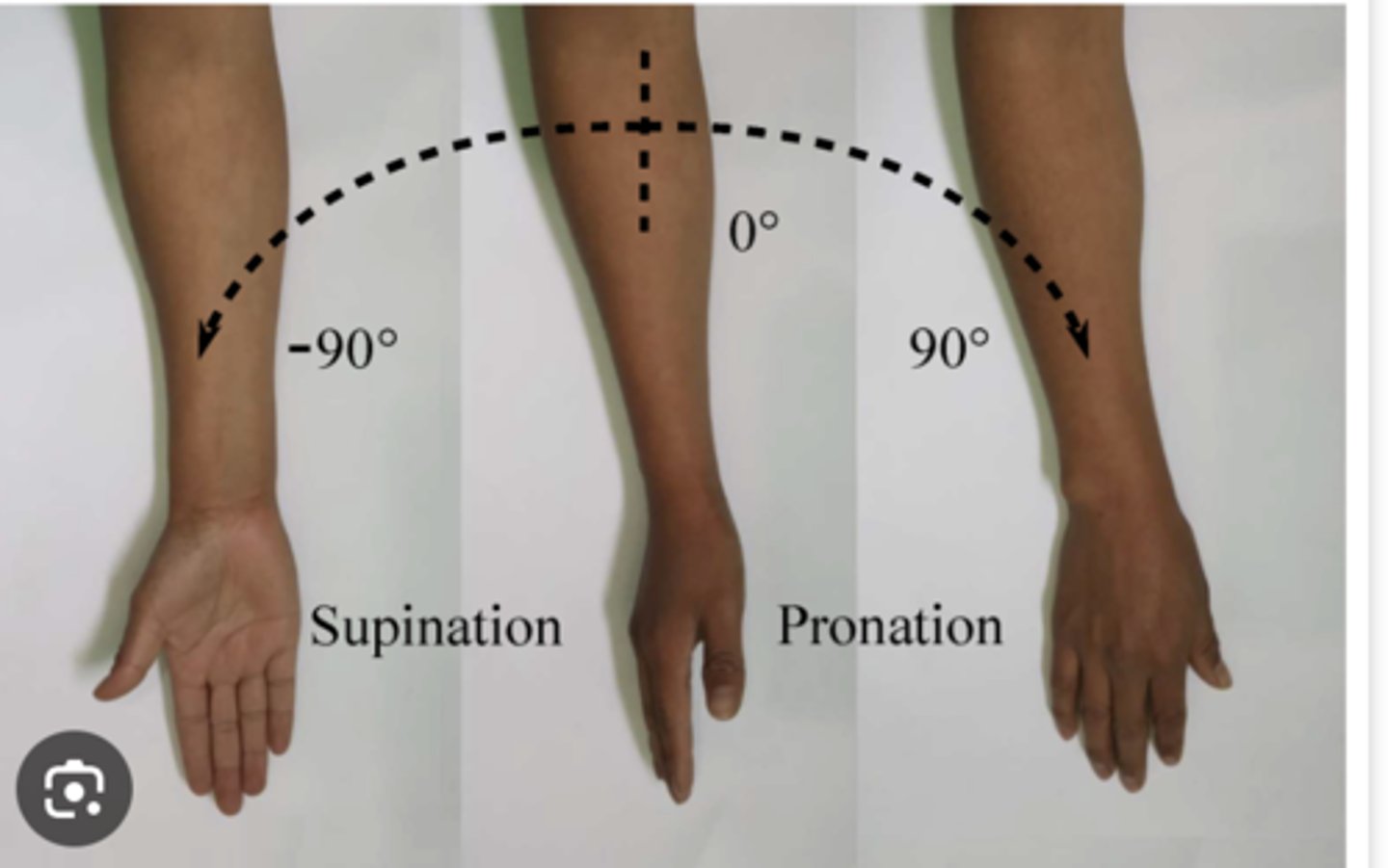
Joint Movements: Supination
Rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces up (supine position)
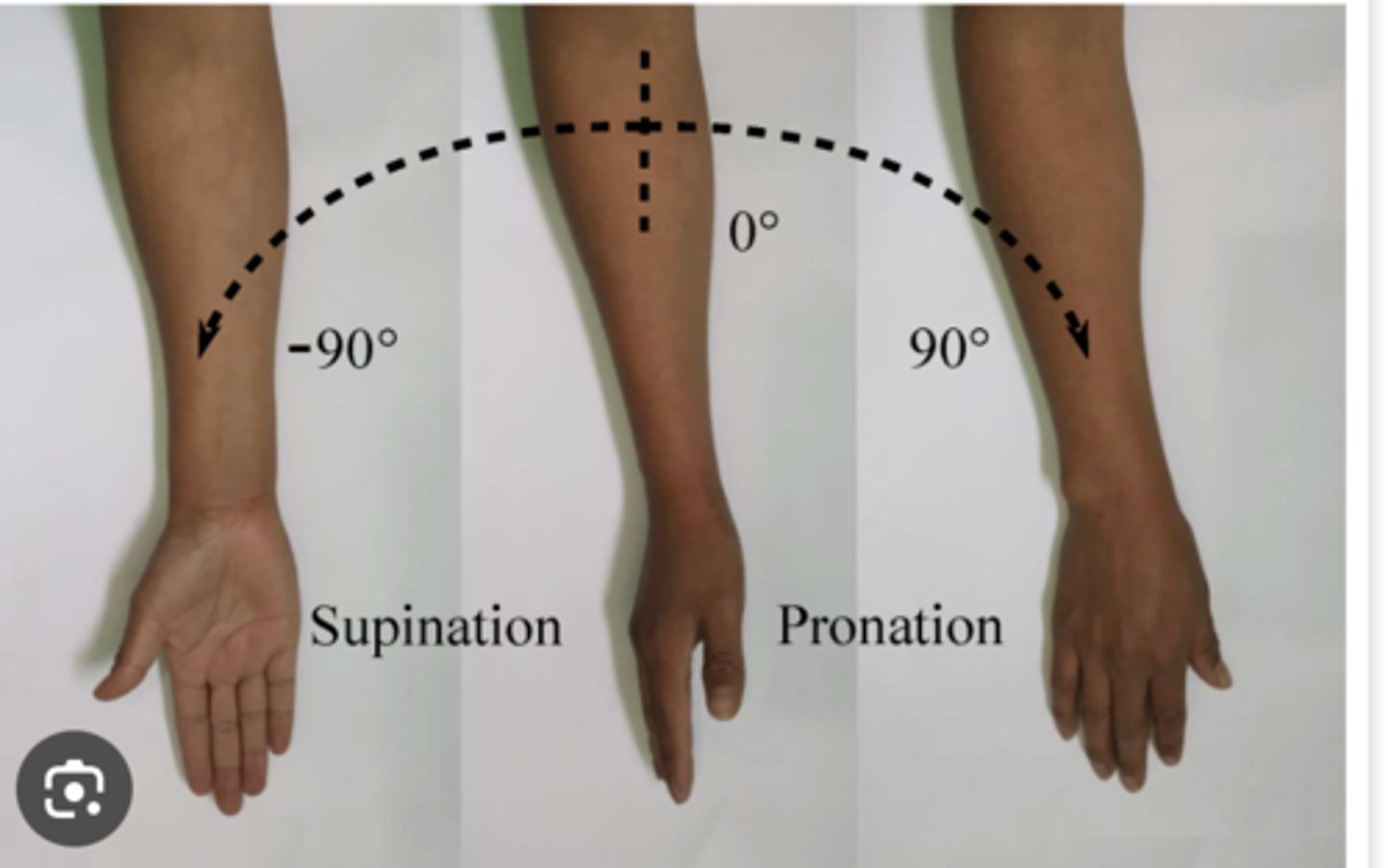
Joint Movements: Pronation
Rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces down (prone position)
Joint Movements: Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
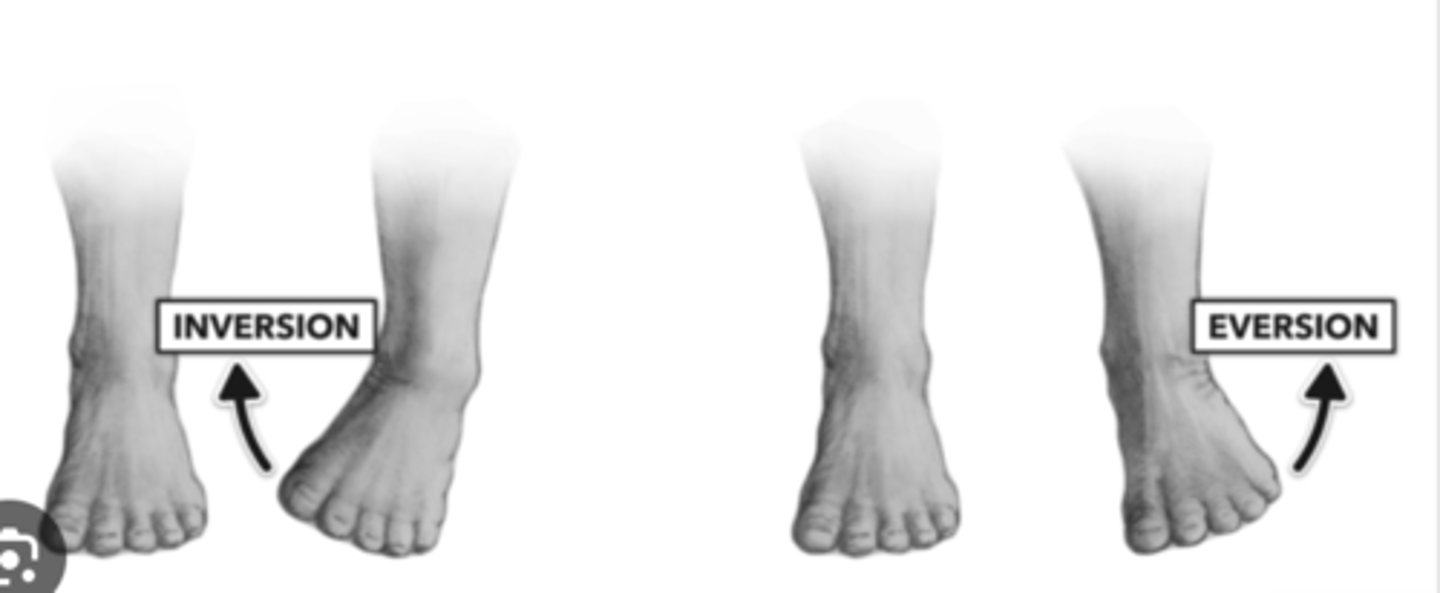
Joint Movements: Eversion
Turning the sole of the foot outward

Three Types of Muscles: Skeletal
Works with tendons and bones to move the body, voluntary control
Three Types of Muscles: Cardiac
Forms the bulk of the heart, produces contractions that create a heartbeat, involuntary control
Three Types of Muscles: Smooth/Visceral
Forms walls of hollow organs and blood vessels, involuntary control
Factors Influencing Mobility
-Developmental considerations
-Physical health
-Muscular, Skeletal, or Nervous System Problems
-Problems Involving Other Body Systems
-Mental health
-Lifestyle
-Attitude and values
-Fatigue and stress
-External factors
Effects of Immobility
Cardiovascular System
Respiratory System
GI System
Urinary system
Musculoskeletal System
Metabolic System
Integument System
Psychological Well-Being
Variables Leading to Back Injury in Health Care Workers
Uncoordinated lifts
Manual Lifting and transferring of patients without assistive devices
Lifting when fatigued or after recent back injury recovery
Repetitive movements such as lifting, transferring, and repositioning patients
Standing for long periods of time
Transferring patients
Repetitive tasks
Transferring/repositioning uncooperative or confused patients
Proper Body Mechanics
Using proper body movement in daily activities, preventing and correcting posture problems, enhancing coordination and endurance